Reshaping Our Knowledge: Advancements in Understanding the Immune Response to Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus’ Generalities
2.1. Molecular Structure and Function
2.2. HRSV Entry into the Host Cell
3. Epidemiology
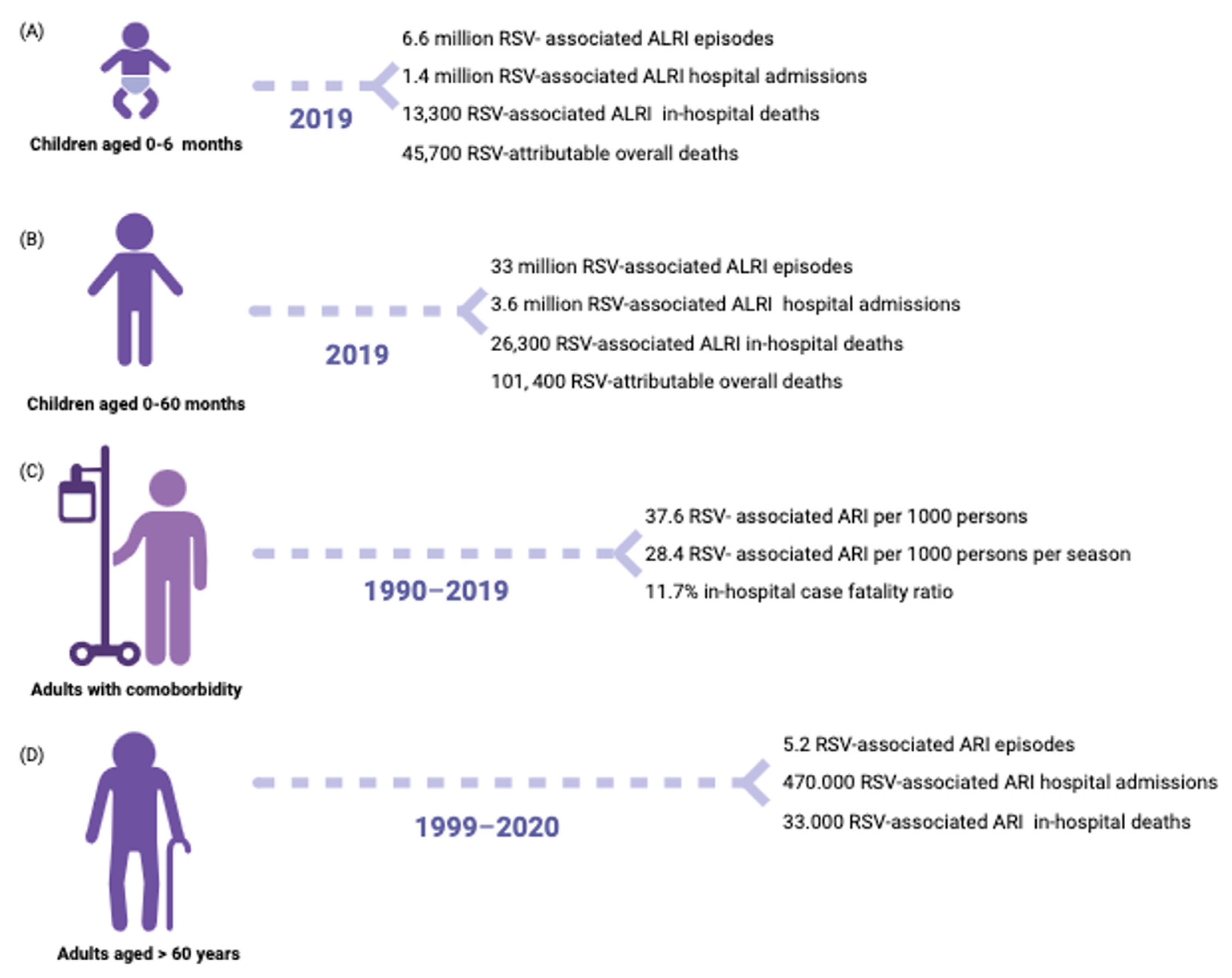
3.1. Host and Environmental Factors
3.1.1. Infants
3.1.2. People Living with Primary or Secondary Immunodeficiency
3.1.3. Elders
3.2. Viral Factors
3.3. RSV and SARS-CoV-2
4. Immune Response
4.1. Innate Immune Response
4.1.1. Dendritic Cells
4.1.2. Neutrophils
4.1.3. Eosinophils
4.1.4. Monocytes and Macrophages
4.1.5. NK Cells
4.2. Adaptive Immune Response
4.2.1. CD4 Lymphocytes
4.2.2. CD8 Lymphocytes
4.2.3. Humoral Immune Response
4.2.4. Immunological Memory
5. RSV Prevention Strategies
5.1. Monoclonal Antibodies
5.2. Vaccines
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Florin, T.A.; Plint, A.C.; Zorc, J.J. Viral bronchiolitis. Lancet 2017, 389, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohmwald, K.; Espinoza, J.; Rey-Jurado, E.; Gómez, R.; González, P.; Bueno, S.; Riedel, C.; Kalergis, A. Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus: Infection and Pathology. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 37, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, H.; Nokes, D.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Dherani, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Singleton, R.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Roca, A.; Wright, P.F.; Bruce, N.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Blau, D.M.; Caballero, M.T.; Feikin, D.R.; Gill, C.J.; Madhi, S.A.; Omer, S.B.; Simões, E.A.F.; Campbell, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in children younger than 5 years in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 2047–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.S. Protecting the Family to Protect the Child: Vaccination Strategy Guided by RSV Transmission Dynamics. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 1679–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhdari, P.; Brosio, F.; Malaventura, C.; Stefanati, A.; Orsi, A.; Icardi, G.; Gabutti, G. Human respiratory syncytial virus and hospitalization in young children in Italy. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2015 LRI Collaborators Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory tract infections in 195 countries: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 1133–1161. [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Vennard, S.; Jasiewicz, F.; Brogden, R.; Nair, H.; RESCEU Investigators; Nair, H.; Campbell, H.; Shi, T.; Li, Y.; et al. Disease Burden Estimates of Respiratory Syncytial Virus related Acute Respiratory Infections in Adults With Comorbidity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226 (Suppl. S1), S17–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savic, M.; Penders, Y.; Shi, T.; Branche, A.; Pirçon, J. Respiratory syncytial virus disease burden in adults aged 60 years and older in high-income countries: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2023, 17, e13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee on Infectious Diseases and Bronchiolitis Guidelines Committee; Brady, M.T.; Byington, C.L.; Davies, H.D.; Edwards, K.M.; Jackson, M.A.; Maldonado, Y.A.; Murray, D.L.; Orenstein, W.A.; Rathore, M.H.; et al. Updated Guidance for Palivizumab Prophylaxis Among Infants and Young Children at Increased Risk of Hospitalization for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Pediatrics 2014, 134, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/beyfortus#authorisation-details-section (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- Hammitt, L.L.; Dagan, R.; Yuan, Y.; Baca Cots, M.; Bosheva, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Muller, W.J.; Zar, H.J.; Brooks, D.; Grenham, A.; et al. Nirsevimab for Prevention of RSV in Healthy Late-Preterm and Term Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, E.A.F.; Madhi, S.A.; Muller, W.J.; Atanasova, V.; Bosheva, M.; Cabañas, F.; Baca Cots, M.; Domachowske, J.B.; Garcia-Garcia, M.L.; Grantina, I.; et al. Efficacy of nirsevimab against respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infections in preterm and term infants, and pharmacokinetic extrapolation to infants with congenital heart disease and chronic lung disease: A pooled analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2023, 7, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruigrok, R.W.; Crépin, T. Nucleoproteins of Negative Strand RNA Viruses; RNA Binding, Oligomerisation and Binding to Polymerase Co-Factor. Viruses 2010, 2, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawar, R.G.; Duquerroy, S.; Vonrhein, C.; Varela, P.F.; Damier-Piolle, L.; Castagné, N.; MacLellan, K.; Bedouelle, H.; Bricogne, G.; Bhella, D.; et al. Crystal Structure of a Nucleocapsid-Like Nucleoprotein-RNA Complex of Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Science 2009, 326, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowton, V.M.; McGivern, D.R.; Fearns, R. Unravelling the complexities of respiratory syncytial virus RNA synthesis. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 1805–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.E.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, H.K. Contribution of Dendritic Cells in Protective Immunity against Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Viruses 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermingham, A.; Collins, P.L. The M2-2 protein of human respiratory syncytial virus is a regulatory factor involved in the balance between RNA replication and transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11259–11264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero, J.A.; Mas, V.; McLellan, J.S. Structural, antigenic and immunogenic features of respiratory syncytial virus glycoproteins relevant for vaccine development. Vaccine 2017, 35, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukreyev, A.; Yang, L.; Fricke, J.; Cheng, L.; Ward, J.M.; Murphy, B.R.; Collins, P.L. The secreted form of respiratory syncytial virus G glycoprotein helps the virus evade antibody-mediated restriction of replication by acting as an antigen decoy and through effects on Fc receptor-bearing leukocytes. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 12191–12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mart Nez, I.; Vald, S.O.; Delfraro, A.; Arbiza, J.; Russi, J.; Melero, J.A. Evolutionary pattern of the G glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial viruses from antigenic group B: The use of alternative termination codons and lineage diversification. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandini, S.; Biagi, C.; Lanari, M. Respiratory Syncytial Virus: The Influence of Serotype and Genotype Variability on Clinical Course of Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyari, F.; Marchant, D.; Moraes, T.J.; Duan, W.; Mastrangelo, P.; Hegele, R.G. Identification of nucleolin as a cellular receptor for human respiratory syncytial virus. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.-W.; Tan, E.; Lin, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Tan, G.M.-Y.; Vararattanavech, A.; Yeo, C.Y.; Soon, C.H.; Soong, T.W.; et al. The small hydrophobic protein of the human respiratory syncytial virus forms pentameric ion channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 24671–24689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornhill, E.M.; Verhoeven, D. Respiratory Syncytial Virus’s Non-structural Proteins: Masters of Interference. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Liao, H.; Hu, Y.; Luo, K.; Hu, S.; Zhu, H. Innate Immune Evasion by Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 865592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Drunen Littel-van Den Hurk, S.; Watkiss, E.R. Pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.L.; Graham, B.S. Viral and host factors in human respiratory syncytial virus pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2040–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, T.; Gibbs, J.D.; Örvell, C.; Imani, F. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein Induces Lung Epithelial Cell Cycle Arrest through a p53 Dependent Pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildyal, R.; Ho, A.; Dias, M.; Soegiyono, L.; Bardin, P.G.; Tran, K.C.; Teng, M.N.; Jans, D.A. The Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein Possesses a Crm1-Mediated Nuclear Export Mechanism. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5353–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Tran, K.C.; Teng, M.N.; Heesom, K.J.; Matthews, D.A.; Barr, J.N.; Hiscox, J.A. The Interactome of the Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus NS1 Protein Highlights Multiple Effects on Host Cell Biology. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7777–7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Le Nouen, C.; Luongo, C.; Buchholz, U.J.; Collins, P.L.; Bukreyev, A. Nonstructural Proteins 1 and 2 of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Suppress Maturation of Human Dendritic Cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8780–8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, C.D.; Unger, S.A.; Walton, M.; Schwarze, J. The Human Immune Response to Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 481–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Hillyer, P.; Le Nouën, C.; Buchholz, U.J.; Rabin, R.L.; Collins, P.L.; Bukreyev, A. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Interferon Antagonist NS1 Protein Suppresses and Skews the Human T Lymphocyte Response. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battles, M.B.; McLellan, J.S. Respiratory syncytial virus entry and how to block it. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, R.; Ward, M.; Bright, H.; Priest, R.; Foster, M.R.; Hurle, M.; Blair, E.; Bird, M. Isolation and characterisation of potential respiratory syncytial virus receptor(s) on epithelial cells. Microbes Infect. 2003, 5, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Xu, L.; Xie, Z. Receptors for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection and Host Factors Regulating the Life Cycle of Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 858629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.M.; McNally, B.A.; Ioannidis, I.; Flano, E.; Teng, M.N.; Oomens, A.G.; Walsh, E.E.; Peeples, M.E. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Uses CX3CR1 as a Receptor on Primary Human Airway Epithelial Cultures. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Todd, S.O.; Meng, J.; Barnum, T.R.; Chirkova, T.; Haynes, L.M.; Jadhao, S.J.; Tripp, R.A.; Oomens, A.G.; Moore, M.L.; et al. Mutating the CX3C Motif in the G Protein Should Make a Live Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccine Safer and More Effective. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02059-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirkova, T.; Lin, S.; Oomens, A.G.P.; Gaston, K.A.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Meng, J.; Stobart, C.C.; Cotton, C.U.; Hartert, T.V.; Moore, M.L.; et al. CX3CR1 is an important surface molecule for respiratory syncytial virus infection in human airway epithelial cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2543–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, D.; Singhera, G.K.; Utokaparch, S.; Hackett, T.L.; Boyd, J.H.; Luo, Z.; Si, X.; Dorscheid, D.R.; McManus, B.M.; Hegele, R.G. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is a determinant of respiratory virus entry and tropism. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11359–11373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiki, H.; Watanabe, T.; Suganuma, M. Cell-surface nucleolin acts as a central mediator for carcinogenic, anti-carcinogenic, and disease-related ligands. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, P.; Hegele, R.G. RSV fusion: Time for a new model. Viruses 2013, 5, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, C.; Madhi, S.A. Review and Update of Active and Passive Immunization Against Respiratory Syncytial Virus. BioDrugs Clin. Immunother. Biopharm. Gene Ther. 2023, 37, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoes, E.A. Respiratory syncytial virus infection. Lancet 1999, 354, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutsaya, A.; Teros-Jaakkola, T.; Kakkola, L.; Toivonen, L.; Peltola, V.; Waris, M.; Julkunen, I. Prospective clinical and serological follow-up in early childhood reveals a high rate of subclinical RSV infection and a relatively high reinfection rate within the first 3 years of life. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 1622–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glezen, W.P.; Taber, L.H.; Frank, A.L.; Kasel, J.A. Risk of primary infection and reinfection with respiratory syncytial virus. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1960 1986, 140, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Riccio, M.; Spreeuwenberg, P.; Osei-Yeboah, R.; Johannesen, C.K.; Fernandez, L.V.; Teirlinck, A.C.; Wang, X.; Heikkinen, T.; Bangert, M.; Caini, S.; et al. Burden of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in the European Union: Estimation of RSV-associated hospitalizations in children under 5 years. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, jiad188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, J. Genetic susceptibility to RSV disease. In Respiratory Syncytial Virus; Cane, P.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 14, pp. 115–140. [Google Scholar]
- Córdova-Dávalos, L.E.; Hernández-Mercado, A.; Barrón-García, C.B.; Rojas-Martínez, A.; Jiménez, M.; Salinas, E.; Cervantes-García, D. Impact of genetic polymorphisms related to innate immune response on respiratory syncytial virus infection in children. Virus Genes 2022, 58, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, C.; Resch, B.; Simões, E.A.F. Risk factors for severe respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infection. Open Microbiol. J. 2011, 5, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Tsutsumi, H.; Matsuda, K.; Nagai, K.; Ogra, P.L.; Chiba, S. Effect of maternal antibody on IgA antibody response in nasopharyngeal secretion in infants and children during primary respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75, 2115–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, J.E.; Firestone, C.-Y.; Murphy, B.R. Passively Acquired Antibodies Suppress Humoral But Not Cell-Mediated Immunity in Mice Immunized with Live Attenuated Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccines. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3910–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyes, J.; Cohen, C.; Pretorius, M.; Groome, M.; von Gottberg, A.; Wolter, N.; Walaza, S.; Haffejee, S.; Chhagan, M.; Naby, F.; et al. Epidemiology of respiratory syncytial virus-associated acute lower respiratory tract infection hospitalizations among HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected South African children, 2010–2011. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208 (Suppl. S3), S217–S226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhi, S.A.; Venter, M.; Madhi, A.; Petersen, M.K.; Klugman, K.P. Differing manifestations of respiratory syncytial virus-associated severe lower respiratory tract infections in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected and uninfected children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2001, 20, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, J.N.; Chemaly, R.F. Management of RSV infections in adult recipients of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2011, 117, 2755–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.P.; Ghantoji, S.S.; Mulanovich, V.E.; Ariza-Heredia, E.J.; Chemaly, R.F. Management of respiratory viral infections in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients. Am. J. Blood Res. 2012, 2, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watson, A.; Wilkinson, T.M.A. Respiratory viral infections in the elderly. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2021, 15, 175346662199505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVincenzo, J.P.; Wilkinson, T.; Vaishnaw, A.; Cehelsky, J.; Meyers, R.; Nochur, S.; Harrison, L.; Meeking, P.; Mann, A.; Moane, E.; et al. Viral load drives disease in humans experimentally infected with respiratory syncytial virus. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Saleeby, C.M.; Bush, A.J.; Harrison, L.M.; Aitken, J.A.; Devincenzo, J.P. Respiratory syncytial virus load, viral dynamics, and disease severity in previously healthy naturally infected children. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.L.; Melero, J.A. Progress in understanding and controlling respiratory syncytial virus: Still crazy after all these years. Virus Res. 2011, 162, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.-C.; Lin, K.-P.; Wang, L.-A.; Yeh, T.-K.; Liu, P.-Y. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection: A Narrative Review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Raya, B.; Viñeta Paramo, M.; Reicherz, F.; Lavoie, P.M. Why has the epidemiology of RSV changed during the COVID-19 pandemic? eClinicalMedicine 2023, 61, 102089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Hartog, G.; Van Kasteren, P.B.; Schepp, R.M.; Teirlinck, A.C.; Van Der Klis, F.R.M.; Van Binnendijk, R.S. Decline of RSV-specific antibodies during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reicherz, F.; Xu, R.Y.; Abu-Raya, B.; Majdoubi, A.; Michalski, C.; Golding, L.; Stojic, A.; Vineta, M.; Granoski, M.; Cieslak, Z.; et al. Waning Immunity Against Respiratory Syncytial Virus During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226, 2064–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.; Ashman, M.; Taha, M.-K.; Varon, E.; Angoulvant, F.; Levy, C.; Rybak, A.; Ouldali, N.; Guiso, N.; Grimprel, E. Pediatric Infectious Disease Group (GPIP) position paper on the immune debt of the COVID-19 pandemic in childhood, how can we fill the immunity gap? Infect. Dis. Now 2021, 51, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dee, K.; Schultz, V.; Haney, J.; Bissett, L.A.; Magill, C.; Murcia, P.R. Influenza A and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Trigger a Cellular Response That Blocks Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Virus 2 Infection in the Respiratory Tract. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 227, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phetsouphanh, C.; Darley, D.R.; Wilson, D.B.; Howe, A.; Munier, C.M.L.; Patel, S.K.; Juno, J.A.; Burrell, L.M.; Kent, S.J.; Dore, G.J.; et al. Immunological dysfunction persists for 8 months following initial mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Files, J.K.; Boppana, S.; Perez, M.D.; Sarkar, S.; Lowman, K.E.; Qin, K.; Sterrett, S.; Carlin, E.; Bansal, A.; Sabbaj, S.; et al. Sustained cellular immune dysregulation in individuals recovering from SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e140491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukens, M.V.; Van De Pol, A.C.; Coenjaerts, F.E.J.; Jansen, N.J.G.; Kamp, V.M.; Kimpen, J.L.L.; Rossen, J.W.A.; Ulfman, L.H.; Tacke, C.E.A.; Viveen, M.C.; et al. A Systemic Neutrophil Response Precedes Robust CD8 + T-Cell Activation during Natural Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Infants. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monick, M.M.; Yarovinsky, T.O.; Powers, L.S.; Butler, N.S.; Carter, A.B.; Gudmundsson, G.; Hunninghake, G.W. Respiratory syncytial virus up-regulates TLR4 and sensitizes airway epithelial cells to endotoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 53035–53044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagro, A.; Tominac, M.; Krsulović-Hresić, V.; Baće, A.; Matić, M.; Drazenović, V.; Mlinarić-Galinović, G.; Kosor, E.; Gotovac, K.; Bolanca, I.; et al. Increased Toll-like receptor 4 expression in infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 135, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberle, H.A.; Takizawa, R.; Casola, A.; Brasier, A.R.; Dieterich, H.-J.; Van Rooijen, N.; Gatalica, Z.; Garofalo, R.P. Respiratory syncytial virus-induced activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in the lung involves alveolar macrophages and toll-like receptor 4-dependent pathways. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murawski, M.R.; Bowen, G.N.; Cerny, A.M.; Anderson, L.J.; Haynes, L.M.; Tripp, R.A.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Finberg, R.W. Respiratory syncytial virus activates innate immunity through Toll-like receptor 2. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Oh, D.S.; Jung, H.E.; Chang, J.; Lee, H.K. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Contribute to the Production of IFN-β via TLR7-MyD88-Dependent Pathway and CTL Priming during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Viruses 2019, 11, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandini, S.; Bottau, P.; Faldella, G.; Lanari, M. Immunological, Viral, Environmental, and Individual Factors Modulating Lung Immune Response to Respiratory Syncytial Virus. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 875723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenbarth, S.C. Dendritic cell subsets in T cell programming: Location dictates function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, G.; He, S.; Li, E. RSV Infection in Neonatal Mice Induces Pulmonary Eosinophilia Responsible for Asthmatic Reaction. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 817113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.M.; Bonville, C.A.; Rosenberg, H.F.; Domachowske, J.B. Respiratory Syncytical Virus–induced Chemokine Expression in the Lower Airways: Eosinophil Recruitment and Degranulation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimova-Yaneva, D.; Russell, D.; Main, M.; Brooker, R.J.; Helms, P.J. Eosinophil activation and cysteinyl leukotriene production in infants with respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Clin. Htmlent Glyphamp Asciiamp Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, J.S. Eosinophil cationic protein and chemokines in nasopharyngeal secretions of infants with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) bronchiolitis and non-RSV bronchiolitis. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2007, 22, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Hosoya, M.; Kanno, H.; Suzuki, H. Serum regulated upon activation, normal T cell expressed and presumably secreted concentrations and eosinophils in respiratory syncytial virus infection. Pediatr. Int. 2006, 48, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, J.P.; Hussain, I.R.; Warner, J.A.; Johnston, S.L.; Warner, J.O. Type 1 and Type 2 Cytokine Imbalance in Acute Respiratory Syncytial Virus Bronchiolitis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, M.F.E.; Bloxham, D.M.; White, D.K.; Ross-Russell, R.I.; Tasker, R.T.C.; O’Donnell, D.R. Lymphocyte apoptosis in acute respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 137, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Kim, C.W.; Oh, D.S.; Jung, H.E.; Lee, H.K. Monocytes Contribute to IFN-β Production via the MyD88-Dependent Pathway and Cytotoxic T-Cell Responses against Mucosal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Immune Netw. 2021, 21, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midulla, F.; Villani, A.; Panuska, J.R.; Dab, I.; Kolls, J.K.; Merolla, R.; Ronchetti, R. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Lung Infection in Infants: Immunoregulatory Role of Infected Alveolar Macrophages. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 168, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, P.; Zhao, D. Alveolar macrophages and airway hyperresponsiveness associated with respiratory syncytial virus infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jans, J.; Unger, W.W.J.; Vissers, M.; Ahout, I.M.L.; Schreurs, I.; Wickenhagen, A.; De Groot, R.; De Jonge, M.I.; Ferwerda, G. Siglec-1 inhibits RSV-induced interferon gamma production by adult T cells in contrast to newborn T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhu, H.; Sun, R.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Natural Killer Cells Are Involved in Acute Lung Immune Injury Caused by Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.S.; Bunton, L.A.; Wright, P.F.; Karzon, D.T. Role of T lymphocyte subsets in the pathogenesis of primary infection and rechallenge with respiratory syncytial virus in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, C.; Pickles, R.J.; Yao, W.; Liao, B.; Boone, A.; Choi, M.; Battaglia, D.M.; Askin, F.B.; Whitmire, J.K.; Silvestri, G.; et al. Human T cells efficiently control RSV infection. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e168110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregoning, J.S.; Schwarze, J. Respiratory Viral Infections in Infants: Causes, Clinical Symptoms, Virology, and Immunology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 74–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayanni, P.G.; Koukoulias, K.; Kuvalekar, M.; Watanabe, A.; Velazquez, Y.; Ramos, C.A.; Leen, A.M.; Vasileiou, S. T cell immune profiling of respiratory syncytial virus for the development of a targeted immunotherapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, bjh.18933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, M.F.E.; Bloxham, D.M.; Cowburn, A.S.; O’Donnell, D.R. Changes in helper lymphocyte chemokine receptor expression and elevation of IP-10 during acute respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants: Respiratory syncytial virus and reduced Th1. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 22, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, C.T.; Elson, C.O.; Fouser, L.A.; Kolls, J.K. The Th17 Pathway and Inflammatory Diseases of the Intestines, Lungs, and Skin. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2013, 8, 477–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinley, J.; Thwaites, R.; Brebner, W.; Greenan-Barrett, L.; Aerssens, J.; Öner, D.; Bont, L.; Wildenbeest, J.; Martinón-Torres, F.; Nair, H.; et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Animal Studies Investigating the Relationship Between Serum Antibody, T Lymphocytes, and Respiratory Syncytial Virus Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226, S117–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystrom, J.; Al-Adhoubi, N.; Al-Bogami, M.; Jawad, A.; Mageed, R. Th17 Lymphocytes in Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Viruses 2013, 5, 777–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Li, N.; He, Y.; Feng, J.; Mei, Z.; Du, Y.; Jie, Z. Th17/Treg cell imbalance plays an important role in respiratory syncytial virus infection compromising asthma tolerance in mice. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 156, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nomura, T.; Ono, M. Regulatory T Cells and Immune Tolerance. Cell 2008, 133, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, R.B.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Varga, S.M. Foxp3+ CD4 Regulatory T Cells Limit Pulmonary Immunopathology by Modulating the CD8 T Cell Response during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2382–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bem, R.A.; Bos, A.P.; Bots, M.; Wolbink, A.M.; Van Ham, S.M.; Medema, J.P.; Lutter, R.; Van Woensel, J.B.M. Activation of the Granzyme Pathway in Children With Severe Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 63, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weerd, W.; Twilhaar, W.N.; Kimpen, J.L. T Cell Subset Analysis in Peripheral Blood of Children with RSV Bronchiolitis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 30, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, M.; Peeters, V.; Alliet, P.; Gillis, P.; Kortleven, J.; Magerman, K.; Rummens, J.L. Peripheral blood T and B lymphocyte subpopulations in infants with acute respiratory syncytial virus brochiolitis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 1997, 8, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, P.S.; Fonceca, A.M.; Howarth, D.; Correia, J.B.; Slupsky, J.R.; Trinick, R.E.; Al Turaiki, W.; Smyth, R.L.; Flanagan, B.F. Respiratory syncytial virus infection of airway epithelial cells, in vivo and in vitro, supports pulmonary antibody responses by inducing expression of the B cell differentiation factor BAFF. Thorax 2013, 68, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sande, C.J.; Mutunga, M.N.; Medley, G.F.; Cane, P.A.; Nokes, D.J. Group- and Genotype-Specific Neutralizing Antibody Responses Against Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Infants and Young Children With Severe Pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiborst, J.; Ogra, P.L. Mucosal immunity and viral infections. Ann. Med. 2001, 33, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, H.; Matsuda, K.; Yamazaki, H.; Ogra, P.L.; Chiba, S. Different kinetics of antibody responses between IgA and IgG classes in nasopharyngeal secretion in infants and children during primary respiratory syncytial virus infection. Pediatr. Int. 1995, 37, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, M.S.; Jozwik, A.; Makris, S.; Dunning, J.; Paras, A.; DeVincenzo, J.P.; De Haan, C.A.M.; Wrammert, J.; Openshaw, P.J.M.; Chiu, C. Impaired Antibody-mediated Protection and Defective IgA B-Cell Memory in Experimental Infection of Adults with Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascough, S.; Dayananda, P.; Kalyan, M.; Kuong, S.U.; Gardener, Z.; Bergstrom, E.; Paterson, S.; Kar, S.; Avadhan, V.; Thwaites, R.; et al. Divergent age-related humoral correlates of protection against respiratory syncytial virus infection in older and young adults: A pilot, controlled, human infection challenge model. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2022, 3, e405–e416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee Chung, H.; Jang, Y.Y. High Serum IgE Level in the Children with Acute Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection Is Associated with Severe Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, AB110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsey, A.R.; Singh, H.K.; Walsh, E.E. Serum antibody decay in adults following natural respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 1493–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunck, B.N.; Aideyan, L.; Ye, X.; Avadhanula, V.; Ferlic-Stark, L.; Zechiedrich, L.; Gilbert, B.E.; Piedra, P.A. A prospective surveillance study on the kinetics of the humoral immune response to the respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein in adults in Houston, Texas. Vaccine 2021, 39, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunck, B.N.; Angelo, L.S.; Henke, D.; Avadhanula, V.; Cusick, M.; Ferlic-Stark, L.; Zechiedrich, L.; Gilbert, B.E.; Piedra, P.A. Adult Memory T Cell Responses to the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Protein During a Single RSV Season (2018–2019). Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 823652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Liu, Y.; Weinstein, J.S.; Craft, J.; Kaech, S.M. An Interleukin-21- Interleukin-10-STAT3 Pathway Is Critical for Functional Maturation of Memory CD8+ T Cells. Immunity 2011, 35, 792–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, K.H.; Becker, A.; Franceschina, C.; De Freitas, D.D.N.; Lape, I.; Da Cunha, M.D.; Leitão, L.; Rigo, M.M.; Pinto, L.A.; Stein, R.T.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus reduces STAT3 phosphorylation in human memory CD8 T cells stimulated with IL-21. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirkova, T.; Rosas-Salazar, C.; Gebretsadik, T.; Jadhao, S.J.; Chappell, J.D.; Peebles, R.S.; Dupont, W.D.; Newcomb, D.C.; Berdnikovs, S.; Gergen, P.J.; et al. Effect of Infant RSV Infection on Memory T Cell Responses at Age 2–3 Years. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 826666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malloy, A.M.W.; Lu, Z.; Kehl, M.; Pena DaMata, J.; Lau-Kilby, A.W.; Turfkruyer, M. Increased innate immune activation induces protective RSV-specific lung-resident memory T cells in neonatal mice. Mucosal Immunol. 2023, S1933021923000478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varese, A.; Nakawesi, J.; Farias, A.; Kirsebom, F.C.M.; Paulsen, M.; Nuriev, R.; Johansson, C. Type I interferons and MAVS signaling are necessary for tissue resident memory CD8+ T cell responses to RSV infection. PLOS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PATH. RSV Vaccine and mAb Snapshot. Available online: https://media.path.org/documents/RSV-snapshot_02JUN2023_clinical-stage_dBtD8W3.pdf?_gl=1*1td33gz*_gcl_au*MTU2NjcxNzUzNC4xNjg2OTk5NTk4*_ga*MTY0NzQ5MjA1Ni4xNjg2OTk5NTk4*_ga_YBSE7ZKDQM*MTY4Njk5OTU5OC4xLjAuMTY4Njk5OTU5OC42MC4wLjA (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- Garegnani, L.; Styrmisdóttir, L.; Roson Rodriguez, P.; Escobar Liquitay, C.M.; Esteban, I.; Franco, J.V. Palivizumab for preventing severe respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andabaka, T.; Nickerson, J.W.; Rojas-Reyes, M.X.; Rueda, J.D.; Bacic Vrca, V.; Barsic, B. Monoclonal antibody for reducing the risk of respiratory syncytial virus infection in children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 8, 2243–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keam, S.J. Nirsevimab: First Approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domachowske, J.B.; Khan, A.A.; Esser, M.T.; Jensen, K.; Takas, T.; Villafana, T.; Dubovsky, F.; Griffin, M.P. Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of MEDI8897, an Extended Half-life Single-dose Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prefusion F-targeting Monoclonal Antibody Administered as a Single Dose to Healthy Preterm Infants. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2018, 37, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA AREXVY Approval. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/167806/download (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- FDA ABRYSVO Approval. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/168890/download (accessed on 9 July 2023).
- Papi, A.; Ison, M.G.; Langley, J.M.; Lee, D.-G.; Leroux-Roels, I.; Martinon-Torres, F.; Schwarz, T.F.; Van Zyl-Smit, R.N.; Campora, L.; Dezutter, N.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prefusion F Protein Vaccine in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, E.E.; Pérez Marc, G.; Zareba, A.M.; Falsey, A.R.; Jiang, Q.; Patton, M.; Polack, F.P.; Llapur, C.; Doreski, P.A.; Ilangovan, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of a Bivalent RSV Prefusion F Vaccine in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampmann, B.; Madhi, S.A.; Munjal, I.; Simões, E.A.F.; Pahud, B.A.; Llapur, C.; Baker, J.; Pérez Marc, G.; Radley, D.; Shittu, E.; et al. Bivalent Prefusion F Vaccine in Pregnancy to Prevent RSV Illness in Infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Virulence Factor | Protein Type | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| N | Capsid protein | Protecting viral RNA from nuclease, regulating viral RNA transcription and replication [14,15] |
| P | Polymerase cofactor phosphoprotein | Regulating viral RNA transcription and replication [14,15] |
| L | RNA dependent RNA polymerase | Mediating viral RNA transcription and replication [15,16] |
| MM2-1 | Matrix protein | Regulating viral RNA transcription as elongation factor, mediating virions assembly [17,18] |
| M2-2 | Matrix protein | Inhibiting viral RNA transcription, assuring balance between viral transcription and replication [17,18] |
| G | Membrane glycoprotein | Mediating adhesion to host cells’ membrane and antibody neutralization (as secretory form) [19,20,21] |
| F | Membrane glycoprotein | Mediating entry in the host cells [22,23] |
| SH | Small hydrophobic membrane protein | Increasing the membrane’s permeability in the host cells, inhibiting infected cells’ apoptosis [24,25,26,27,28] |
| M | Phosphorylated matrix protein | Mediating virion assembly, increasing virus replication trough host cell transcription inhibition and cell cycle arrest in G1 phase [29,30] |
| NS1, NS2 | Non-structural proteins | Inhibiting IFNI/III production, dendritic cells activation, T-cell response and, infected cells’ apoptosis [31,32] |
| Receptor | Viral Protein Ligand | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| CXCR3 | Protein G | Virus adhesion, Th2 response, IFN I production inhibition [36,37,38,39,40] |
| HSPGs | Protein G and F | Virus adhesion [36,37] |
| Nucleolin | Protein F | Virus internalization [23,42,43] |
| TLR4 | Protein F | Endocytosis pathway activation [36,37,41] |
| ICAM-1 | Protein F | Virus adhesion, neutrophils and eosinophils adhesion to the airway epithelium [36,37] |
| IGFR1 | Protein F | Virus internalization [36,37] |
| EGFR | Protein F | Endocytosis pathway activation, epithelial cells fusion (syncytia) and mucus secretion [36,37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Attaianese, F.; Guiducci, S.; Trapani, S.; Barbati, F.; Lodi, L.; Indolfi, G.; Azzari, C.; Ricci, S. Reshaping Our Knowledge: Advancements in Understanding the Immune Response to Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091118
Attaianese F, Guiducci S, Trapani S, Barbati F, Lodi L, Indolfi G, Azzari C, Ricci S. Reshaping Our Knowledge: Advancements in Understanding the Immune Response to Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Pathogens. 2023; 12(9):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091118
Chicago/Turabian StyleAttaianese, Federica, Sara Guiducci, Sandra Trapani, Federica Barbati, Lorenzo Lodi, Giuseppe Indolfi, Chiara Azzari, and Silvia Ricci. 2023. "Reshaping Our Knowledge: Advancements in Understanding the Immune Response to Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus" Pathogens 12, no. 9: 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091118
APA StyleAttaianese, F., Guiducci, S., Trapani, S., Barbati, F., Lodi, L., Indolfi, G., Azzari, C., & Ricci, S. (2023). Reshaping Our Knowledge: Advancements in Understanding the Immune Response to Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus. Pathogens, 12(9), 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens12091118






