Targeting HBV cccDNA Levels: Key to Achieving Complete Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
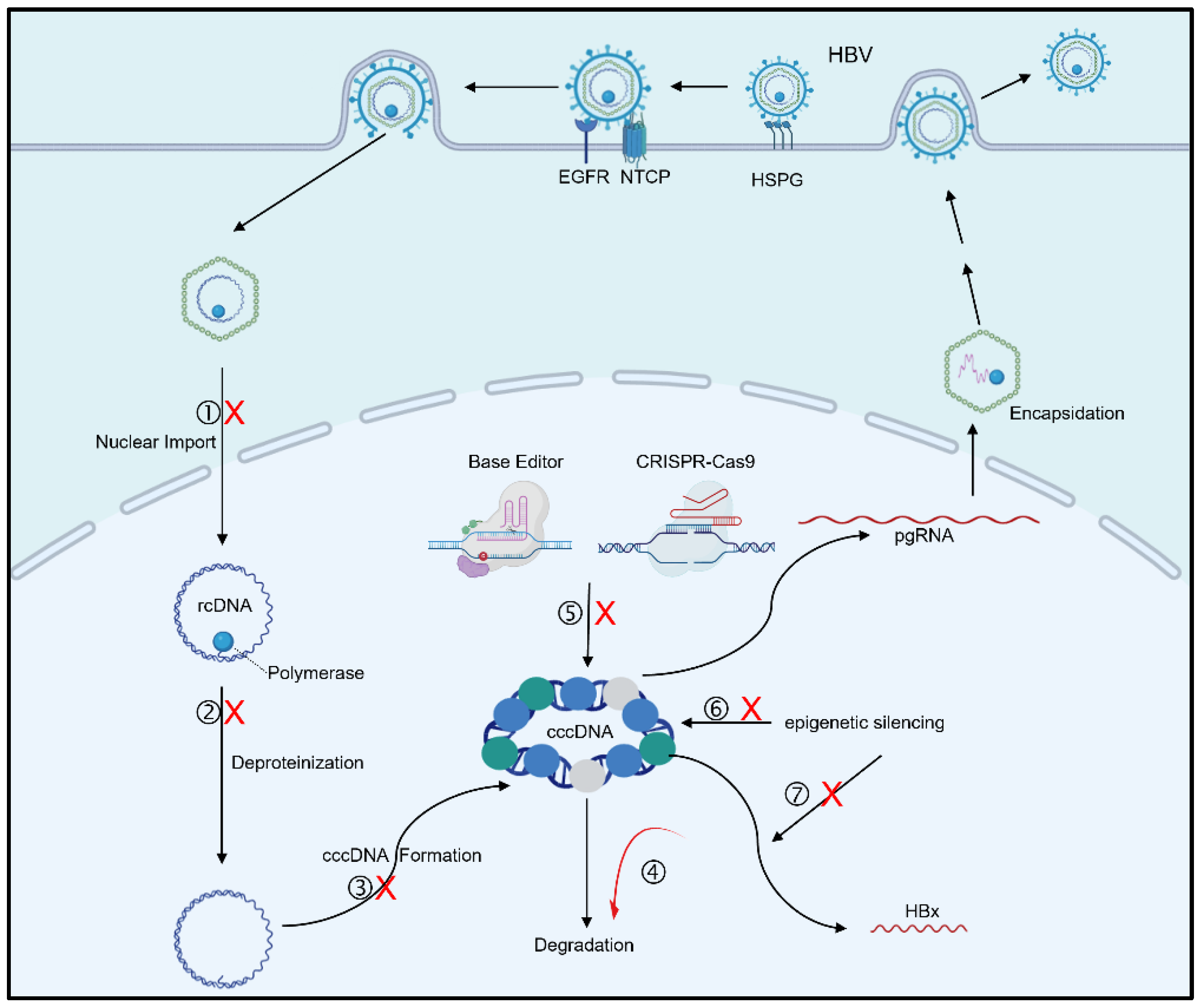
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms and Inhibitors of cccDNA Synthesis
3. Targeting cccDNA Degradation
3.1. Host Factors Target cccDNA for Degradation
3.2. Gene Editing for cccDNA
3.3. cccDNA Reducers
4. Targeting cccDNA for Transcriptional Silencing
4.1. cccDNA Epigenetic Silencing
4.2. Transcription Factors Regulating cccDNA
4.3. Targeting HBx
5. Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lanini, S.; Ustianowski, A.; Pisapia, R.; Zumla, A.; Ippolito, G. Viral Hepatitis: Etiology, Epidemiology, Transmission, Diagnostics, Treatment, and Prevention. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 1045–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, S.; Zhao, S.; Xu, X.; Poongavanam, V.; Menéndez-Arias, L.; Zhan, P.; Liu, X. Targeting hepatitis B virus cccDNA levels: Recent progress in seeking small molecule drug candidates. Drug. Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.W.; Hinman, A.R. What Is Needed to Eliminate Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus as Global Health Threats. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isorce, N.; Lucifora, J.; Zoulim, F.; Durantel, D. Immune-modulators to combat hepatitis B virus infection: From IFN-α to novel investigational immunotherapeutic strategies. Antiviral Res. 2015, 122, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gish, R.; Jia, J.D.; Locarnini, S.; Zoulim, F. Selection of chronic hepatitis B therapy with high barrier to resistance. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornberg, M.; Lok, A.S.; Terrault, N.A.; Zoulim, F. Guidance for design and endpoints of clinical trials in chronic hepatitis B—Report from the 2019 EASL-AASLD HBV Treatment Endpoints Conference. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protzer, U.; Maini, M.K.; Knolle, P.A. Living in the liver: Hepatic infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, M.; Saso, W.; Sugiyama, R.; Ishii, K.; Ohki, M.; Nagamori, S.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Ryo, A.; Yun, J.H.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor is a host-entry cofactor triggering hepatitis B virus internalization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8487–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebossé, F.; Inchauspé, A.; Locatelli, M.; Miaglia, C.; Diederichs, A.; Fresquet, J.; Chapus, F.; Hamed, K.; Testoni, B.; Zoulim, F. Quantification and epigenetic evaluation of the residual pool of hepatitis B covalently closed circular DNA in long-term nucleoside analogue-treated patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.L.; Wong, D.; Ip, P.; Kopaniszen, M.; Seto, W.K.; Fung, J.; Huang, F.Y.; Lee, B.; Cullaro, G.; Chong, C.K.; et al. Reduction of covalently closed circular DNA with long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.L.; Wong, D.K.; Wong, G.T.; Seto, W.K.; Fung, J.; Yuen, M.F. Rebound of HBV DNA after cessation of nucleos/tide analogues in chronic hepatitis B patients with undetectable covalently closed. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Seeger, C. Hepadnavirus Genome Replication and Persistence. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revill, P.A.; Tu, T.; Netter, H.J.; Yuen, L.K.W.; Locarnini, S.A.; Littlejohn, M. The evolution and clinical impact of hepatitis B virus genome diversity. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 618–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, A.; Samanta, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Barik, S.; Biswas, A. The HBV web: An insight into molecular interactomes between the hepatitis B virus and its host en route to hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandri, M.; Petersen, J. Mechanism of Hepatitis B Virus Persistence in Hepatocytes and Its Carcinogenic Potential. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62 (Suppl. S4), S281–S288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Revill, P. Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhu, L.; Yao, D.; Chen, L.; Fu, L.; Ouyang, L. Recent progress in potential anti-hepatitis B virus agents: Structural and pharmacological perspectives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 147, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, H.; Tang, L.; Wang, F.; Tolufashe, G.; Chang, J.; Guo, J.T. Mechanism of interferon alpha therapy for chronic hepatitis B and potential approaches to improve its therapeutic efficacy. Antiviral Res. 2024, 221, 105782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berraondo, P.; Di Scala, M.; Korolowicz, K.; Thampi, L.M.; Otano, I.; Suarez, L.; Fioravanti, J.; Aranda, F.; Ardaiz, N.; Yang, J.; et al. Liver-directed gene therapy of chronic hepadnavirus infection using interferon alpha tethered to apolipoprotein A-I. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.L.H.; Gane, E.; Lok, A.S.F. How to achieve functional cure of HBV: Stopping NUCs, adding interferon or new drug development? J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M.G.; Boyd, A.; Combe, E.; Testoni, B.; Zoulim, F. Covalently closed circular DNA: The ultimate therapeutic target for curing HBV infections. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Königer, C.; Wingert, I.; Marsmann, M.; Rösler, C.; Beck, J.; Nassal, M. Involvement of the host DNA-repair enzyme TDP2 in formation of the covalently closed circular DNA persistence reservoir of hepatitis B viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4244–E4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; McAllister, R.; Boregowda, R.; Sohn, J.A.; Cortes Ledesma, F.; Caldecott, K.W.; Seeger, C.; Hu, J. Does Tyrosyl DNA Phosphodiesterase-2 Play a Role in Hepatitis B Virus Genome Repair? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Yan, R.; Xu, J.Z.; Zhang, H.; Shen, S.; Mitra, B.; Marchetti, A.; Kim, E.S.; Guo, H. Characterization of the Termini of Cytoplasmic Hepatitis B Virus Deproteinated Relaxed Circular DNA. J. Virol. 2020, 95, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Sheraz, M.; McGrane, M.; Chang, J.; Guo, J.T. DNA Polymerase alpha is essential for intracellular amplification of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Gao, Z.; Xu, G.; Peng, B.; Liu, C.; Yan, H.; Yao, Q.; Sun, G.; Liu, Y.; Tang, D.; et al. DNA Polymerase κ Is a Key Cellular Factor for the Formation of Covalently Closed Circular DNA of Hepatitis B Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Q.; Yan, R.; Hu, J.; Cai, D.; Mitra, B.; Kim, E.S.; Marchetti, A.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. The role of host DNA ligases in hepadnavirus covalently closed circular DNA formation. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, K.; Que, L.; Shimadu, M.; Koura, M.; Ishihara, Y.; Wakae, K.; Nakamura, T.; Watashi, K.; Wakita, T.; Muramatsu, M. Flap endonuclease 1 is involved in cccDNA formation in the hepatitis B virus. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, K.; Liu, C.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, H.; Huang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. DNA Repair Factor Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 Is a Proviral Factor in Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA Formation. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0058522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ploss, A. Core components of DNA lagging strand synthesis machinery are essential for hepatitis B virus cccDNA formation. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis B virus cccDNA is formed through distinct repair processes of each strand. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Mills, C.; Yu, W.; Yan, R.; Aldrich, C.E.; Saputelli, J.R.; Mason, W.S.; Xu, X.; Guo, J.T.; Block, T.M.; et al. Identification of disubstituted sulfonamide compounds as specific inhibitors of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4277–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupberger, J.; Schaedler, S.; Peiran, A.; Hildt, E. Identification and characterization of a novel bipartite nuclear localization signal in the hepatitis B virus polymerase. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 8000–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Luckenbaugh, L.; Hu, H.; Yan, Z.; Gao, L.; Hu, J. Involvement of Host ATR-CHK1 Pathway in Hepatitis B Virus Covalently Closed Circular DNA Formation. mBio 2020, 11, e03423-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, M.E.; Harris, R.S.; Harki, D.A. APOBEC Enzymes as Targets for Virus and Cancer Therapy. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenglein, M.D.; Burns, M.B.; Li, M.; Lengyel, J.; Harris, R.S. APOBEC3 proteins mediate the clearance of foreign DNA from human cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Xia, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Zhang, K.; Stadler, D.; Cheng, X.; Sprinzl, M.F.; Koppensteiner, H.; Makowska, Z.; Volz, T.; et al. Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA. Science 2014, 343, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Stadler, D.; Lucifora, J.; Reisinger, F.; Webb, D.; Hösel, M.; Michler, T.; Wisskirchen, K.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, K.; et al. Interferon-γ and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Produced by T Cells Reduce the HBV Persistence Form, cccDNA, Without Cytolysis. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, D.; Kächele, M.; Jones, A.N.; Hess, J.; Urban, C.; Schneider, J.; Xia, Y.; Oswald, A.; Nebioglu, F.; Bester, R.; et al. Interferon-induced degradation of the persistent hepatitis B virus cccDNA form depends on ISG20. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e49568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledford, H.; Callaway, E. Pioneers of revolutionary CRISPR gene editing win chemistry Nobel. Nature 2020, 586, 346–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.R.; Yang, H.C.; Kuo, Y.T.; Liu, C.J.; Yang, T.Y.; Sung, K.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Shen, Y.C.; et al. The CRISPR/Cas9 System Facilitates Clearance of the Intrahepatic HBV Templates In Vivo. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, S.; Hua, L.; Liu, Y.H.; Gao, L.C.; Fu, J.; Wan, D.Y.; Dong, L.H.; Song, H.F.; Gao, X. Harnessing the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated Cas9 system to disrupt the hepatitis B virus. Gene. Ther. 2015, 22, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Qu, L.; Wang, H.; Wei, L.; Dong, Y.; Xiong, S. Targeting hepatitis B virus cccDNA by CRISPR/Cas9 nuclease efficiently inhibits viral replication. Antivir. Res. 2015, 118, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Kao, J.H.; Ching, C.; Liu, I.J.; Wang, C.C.; Tsai, C.H.; Wu, F.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, P.J.; et al. Permanent Inactivation of HBV Genomes by CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Non-cleavage Base Editing. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smekalova, E.M.; Martinez, M.G.; Combe, E.; Kumar, A.; Dejene, S.; Leboeuf, D.; Chen, C.Y.; Dorkin, J.R.; Shuang, L.S.; Kieft, S.; et al. Cytosine base editing inhibits hepatitis B virus replication and reduces HBsAg expression in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2024, 35, 102112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Khanal, S.; Cao, D.; Zhao, J.; Dang, X.; Nguyen, L.N.T.; Schank, M.; Wu, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Synthetic gRNA/Cas9 ribonucleoprotein targeting HBV DNA inhibits viral replication. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Mei, M.; Li, B.; Zhu, X.; Zu, W.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Dong, Y.; Tan, X. A non-viral CRISPR/Cas9 delivery system for therapeutically targeting HBV DNA and pcsk9 in vivo. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Li, C.; Long, Q.; Yang, Q.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. CRISPR/Cas9 delivery by NIR-responsive biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted HBV therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Mao, T.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhang, T.; Huang, H.; et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles for delivering functional Cas9/gRNA to eliminate hepatitis B virus cccDNA and integration. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2024, 13, 2284286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Tan, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, J.; Zheng, J.; Shen, H.C.; Zhang, M.; Wu, W.; et al. Discovery of Novel cccDNA Reducers toward the Cure of Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 10938–10955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, J.D.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, X.; Xiang, K.; Jiang, J.; Li, B.; Yu, Y.; Hu, H.; et al. Discovery of a first-in-class orally available HBV cccDNA inhibitor. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, D.; Chen, Y.; Cai, J.P.; Yuan, H.Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Yin, Y.; Xie, J.W.; Lin, J.M.; Luo, J.; Feng, Y.; et al. A hnRNPA2B1 agonist effectively inhibits HBV and SARS-CoV-2 omicron in vivo. Protein Cell 2023, 14, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, E.C.; Zhuo, N.Z.; Goh, Z.Y.; Bonne, I.; Malleret, B.; Ko, H.L. cccDNA-Targeted Drug Screen Reveals a Class of Antihistamines as Suppressors of HBV Genome Levels. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Jia, Z.; Tian, Y.; Yang, P.; Sun, H.; Wang, C.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; et al. HBx Protein Contributes to Liver Carcinogenesis by H3K4me3 Modification Through Stabilizing WD Repeat Domain 5 Protein. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1678–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, K.; Yao, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Pei, R.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; et al. HDAC11 restricts HBV replication through epigenetic repression of cccDNA transcription. Antivir. Res. 2019, 172, 104619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, T.; Zhu, J.; Xian, J.; Li, A.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q. miRNA-548ah promotes the replication and expression of hepatitis B virus by targeting histone deacetylase 4. Life Sci. 2019, 219, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivière, L.; Gerossier, L.; Ducroux, A.; Dion, S.; Deng, Q.; Michel, M.L.; Buendia, M.A.; Hantz, O.; Neuveut, C. HBx relieves chromatin-mediated transcriptional repression of hepatitis B viral cccDNA involving SETDB1 histone methyltransferase. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Yue, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Shen, F.; et al. PRMT5 restricts hepatitis B virus replication through epigenetic repression of covalently closed circular DNA transcription and interference with pregenomic RNA encapsidation. Hepatology 2017, 66, 398–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, Y.; Yun, H.; Zheng, W.; Geng, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X. HBx represses WDR77 to enhance HBV replication by DDB1-mediated WDR77 degradation in the liver. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8362–8378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhenda, S.; Ducroux, A.; Rivière, L.; Sobhian, B.; Ward, M.D.; Dion, S.; Hantz, O.; Protzer, U.; Michel, M.L.; Benkirane, M.; et al. Methyltransferase PRMT1 is a binding partner of HBx and a negative regulator of hepatitis B virus transcription. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4360–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.H.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Chen, W.X.; Cai, X.F.; Chen, K.; Ko, B.C.; Song, C.L.; Ran, L.K.; Li, W.Y.; et al. Sirtuin 1 regulates hepatitis B virus transcription and replication by targeting transcription factor AP-1. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.Q.; Ding, Q.Y.; Tao, N.N.; Tan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhou, Y.J.; Dong, M.L.; Cheng, S.T.; Ren, F.; et al. SIRT2 Promotes HBV Transcription and Replication by Targeting Transcription Factor p53 to Increase the Activities of HBV Enhancers and Promoters. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 836446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Remiszewski, S.; Snedeker, A.; Chiang, L.W.; Shenk, T. An allosteric inhibitor of sirtuin 2 blocks hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA establishment and its transcriptional activity. Antivir. Res. 2024, 226, 105888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.H.; Hu, J.L.; Cheng, S.T.; Yu, H.B.; Wong, V.K.W.; Law, B.Y.K.; Yang, Y.F.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.X.; et al. SIRT3 restricts hepatitis B virus transcription and replication through epigenetic regulation of covalently closed circular DNA involving suppressor of variegation 3–9 homolog 1 and SET domain containing 1A histone methyltransferases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1260–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Mertz, J.E. Distinct modes of regulation of transcription of hepatitis B virus by the nuclear receptors HNF4alpha and COUP-TF1. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2489–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, K.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, Z.; Hou, W.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X.; et al. Novel function of SART1 in HNF4α transcriptional regulation contributes to its antiviral role during HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Yeh, S.H.; Lin, W.H.; Yeh, K.H.; Yuan, Q.; Xia, N.S.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, P.J. Estrogen receptor α represses transcription of HBV genes via interaction with hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 989–998.e984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wu, J.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; He, J.; Guo, Y.; Deng, Q.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. High mobility group AT-hook 1 (HMGA1) is an important positive regulator of hepatitis B virus (HBV) that is reciprocally upregulated by HBV X protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 2157–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Feng, X.; Mao, T.; Yang, D.; Zou, J.; Zao, X.; Deng, Q.; Chen, X.; Lu, F. Yin-Yang 1 and HBx protein activate HBV transcription by mediating the spatial interaction of cccDNA minichromosome with cellular chromosome 19p13.11. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2455–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Shi, Y.; Zou, C.; Zhang, H.; Peng, H.; Wang, S.; Xia, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Cellular Id1 inhibits hepatitis B virus transcription by interacting with the novel covalently closed circular DNA-binding protein E2F4. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decorsière, A.; Mueller, H.; van Breugel, P.C.; Abdul, F.; Gerossier, L.; Beran, R.K.; Livingston, C.M.; Niu, C.; Fletcher, S.P.; Hantz, O.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein identifies the Smc5/6 complex as a host restriction factor. Nature 2016, 531, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.M.; Xu, Y.; Li, F.; Nio, K.; Reszka-Blanco, N.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Su, L. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Promotes Degradation of SMC5/6 to Enhance HBV Replication. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2846–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiba, K.; Otsuka, M.; Funato, K.; Miyakawa, Y.; Tanaka, E.; Seimiya, T.; Yamagami, M.; Tsutsumi, T.; Okushin, K.; Miyakawa, K.; et al. HBx-induced degradation of Smc5/6 complex impairs homologous recombination-mediated repair of damaged DNA. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allweiss, L.; Giersch, K.; Pirosu, A.; Volz, T.; Muench, R.C.; Beran, R.K.; Urban, S.; Javanbakht, H.; Fletcher, S.P.; Lütgehetmann, M.; et al. Therapeutic shutdown of HBV transcripts promotes reappearance of the SMC5/6 complex and silencing of the viral genome in vivo. Gut 2022, 71, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wei, L.; Xu, W. E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 restricts hepatitis B virus replication by targeting HBx for proteasomal degradation. Antivir. Res. 2021, 192, 105107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, Y.S.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Oanh, N.T.K.; Cho, M.Y.; Heo, J.; Lee, E.S.; Cho, H.; Park, Y.Y.; Cho, H. Mitochondria ubiquitin ligase, MARCH5 resolves hepatitis B virus X protein aggregates in the liver pathogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Xie, F.; Liang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Chen, Q.; et al. JMJD2D stabilises and cooperates with HBx protein to promote HBV transcription and replication. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.T.; Hu, J.L.; Ren, J.H.; Yu, H.B.; Zhong, S.; Wai Wong, V.K.; Kwan Law, B.Y.; Chen, W.X.; Xu, H.M.; Zhang, Z.Z.; et al. Dicoumarol, an NQO1 inhibitor, blocks cccDNA transcription by promoting degradation of HBx. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiba, K.; Otsuka, M.; Ohno, M.; Yamagami, M.; Kishikawa, T.; Suzuki, T.; Ishibashi, R.; Seimiya, T.; Tanaka, E.; Koike, K. Inhibition of HBV Transcription From cccDNA With Nitazoxanide by Targeting the HBx-DDB1 Interaction. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. Identification of Estradiol Benzoate as an Inhibitor of HBx Using Inducible Stably Transfected HepG2 Cells Expressing HiBiT Tagged HBx. Molecules 2022, 27, 5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Nakamoto, S.; Ao, J.; Qiang, N.; Kogure, T.; Ogawa, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Fujiwara, K.; Iwanaga, T.; Kojima, R.; et al. Antiviral Compounds Screening Targeting HBx Protein of the Hepatitis B Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Qin, J.; Sun, Y. The Ube2m-Rbx1 neddylation-Cullin-RING-Ligase proteins are essential for the maintenance of Regulatory T cell fitness. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, H.; Tang, Z.; Jin, H.; Sun, Y. Neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 suppresses growth and migration of human gastric cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, K.; Krist, D.T.; Prabu, J.R.; Hill, S.; Klügel, M.; Neumaier, L.M.; von Gronau, S.; Kleiger, G.; Schulman, B.A. NEDD8 nucleates a multivalent cullin-RING-UBE2D ubiquitin ligation assembly. Nature 2020, 578, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiba, K.; Otsuka, M.; Ohno, M.; Yamagami, M.; Kishikawa, T.; Seimiya, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, E.; Ishibashi, R.; Funato, K.; et al. Pevonedistat, a Neuronal Precursor Cell-Expressed Developmentally Down-Regulated Protein 8-Activating Enzyme Inhibitor, Is a Potent Inhibitor of Hepatitis B Virus. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1903–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Nebioglu, F.; Leuthold, M.M.; Ni, Y.; Mutz, P.; Beneke, J.; Erfle, H.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Bartenschlager, R.; Urban, S. Dual role of neddylation in transcription of hepatitis B virus RNAs from cccDNA and production of viral surface antigen. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Guo, H.; Lou, G.; Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, M. Neddylation inhibitor MLN4924 has anti-HBV activity via modulating the ERK-HNF1α-C/EBPα-HNF4α axis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Arzberger, S.; Durantel, D.; Belloni, L.; Strubin, M.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F.; Hantz, O.; Protzer, U. Hepatitis B virus X protein is essential to initiate and maintain virus replication after infection. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Chen, S.; Gong, Q.; Luo, N.; Lei, Y.; Guo, J.; He, S. Hepatitis B virus X protein modulates remodelling of minichromosomes related to hepatitis B virus replication in HepG2 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; Marchetti, A.; van de Klundert, M.; Cai, D.; Yu, X.; Mitra, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein counteracts high mobility group box 1 protein-mediated epigenetic silencing of covalently closed circular DNA. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shen, H.; Li, A.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, D.; Lu, M.; et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus (HBV) gene expression and replication by HBx gene silencing in a hydrodynamic injection mouse model with a new clone of HBV genotype B. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Ren, X.H.; Han, D.; Guan, Y.Y.; Liu, P.L.; Cheng, S.X.; Liu, H. Codelivery of HBx-siRNA and Plasmid Encoding IL-12 for Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus and Reactivation of Antiviral Immunity. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.Y.; Cheng, J.; Xing, C.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Su, R.; Wei, X.Y.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.S. Evaluation of hepatitis B viral replication and proteomic analysis of HepG2.2.15 cell line after knockdown of HBx. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2011, 10, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, P.; Zhang, C.; Han, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Z. Therapeutic recovery of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-induced hepatocyte-intrinsic immune defect reverses systemic adaptive immune tolerance. Hepatology 2013, 58, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.; Lim, Y.S.; Kim, J.B.; Jadhav, V.; Shen, L.; Bakardjiev, A.I.; Huang, S.A.; Cathcart, A.L.; Lempp, F.A.; Janas, M.M.; et al. Evaluation of RNAi therapeutics VIR-2218 and ALN-HBV for chronic hepatitis B: Results from randomized clinical trials. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petljak, M.; Dananberg, A.; Chu, K.; Bergstrom, E.N.; Striepen, J.; von Morgen, P.; Chen, Y.; Shah, H.; Sale, J.E.; Alexandrov, L.B.; et al. Mechanisms of APOBEC3 mutagenesis in human cancer cells. Nature 2022, 607, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjes, S.; Kurup, H.M.; Rieffer, A.E.; Bayarjargal, M.; Filitcheva, J.; Su, Y.; Hale, T.K.; Filichev, V.V.; Harjes, E.; Harris, R.S.; et al. Structure-guided inhibition of the cancer DNA-mutating enzyme APOBEC3A. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isozaki, H.; Sakhtemani, R.; Abbasi, A.; Nikpour, N.; Stanzione, M.; Oh, S.; Langenbucher, A.; Monroe, S.; Su, W.; Cabanos, H.F.; et al. Therapy-induced APOBEC3A drives evolution of persistent cancer cells. Nature 2023, 620, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buisson, R.; Lawrence, M.S.; Benes, C.H.; Zou, L. APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B Activities Render Cancer Cells Susceptible to ATR Inhibition. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4567–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, N.; Wong, D.; Lai, C.L.; Mak, L.Y.; Fung, J.; Ma, H.T.; Lei, M.W.; Seto, W.K.; Yuen, M.F. Effect of Antiviral Treatment on Hepatitis B Virus Integration and Hepatocyte Clonal Expansion. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, e801–e809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.Z.; Soulette, C.M.; Aggarwal, A.; Han, D.; van Buuren, N.; Wu, P.; Feierbach, B.; Lin, J.T.; Tseng, C.H.; Chen, C.Y.; et al. Effects of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate on intrahepatic viral burden and liver immune microenvironment in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2024, online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sheng, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, P.; Yang, C.; Yang, X.; et al. Removal of Integrated Hepatitis B Virus DNA Using CRISPR-Cas9. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, W.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, H. Targeting HBV cccDNA Levels: Key to Achieving Complete Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121100
He W, Zheng Z, Zhao Q, Zhang R, Zheng H. Targeting HBV cccDNA Levels: Key to Achieving Complete Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B. Pathogens. 2024; 13(12):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121100
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Wei, Zhijin Zheng, Qian Zhao, Renxia Zhang, and Hui Zheng. 2024. "Targeting HBV cccDNA Levels: Key to Achieving Complete Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B" Pathogens 13, no. 12: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121100
APA StyleHe, W., Zheng, Z., Zhao, Q., Zhang, R., & Zheng, H. (2024). Targeting HBV cccDNA Levels: Key to Achieving Complete Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B. Pathogens, 13(12), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13121100





