Deciphering the Longevity and Levels of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Children: A Year-Long Study Highlighting Clinical Phenotypes and Age-Related Variations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study
- Patients visiting the hospital with fever or respiratory symptoms.
- Asymptomatic patients attending pre-surgical screenings, admitted for non-SARS-CoV-2-related symptoms, or screened due to contact with a symptomatic case.
- Admitted patients with fever and/or respiratory symptoms.
- Admitted patients showing symptoms compatible with MIS-C.
2.2. Variables
2.3. Laboratory
2.4. Statistics
2.5. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Antibody Levels One Year after Confirmed Infection and Association with Epidemiological and Clinical Variables
3.3. Clinical Outcomes
3.4. Other Serological Results Obtained during the First Year
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehta, N.S.; Mytton, O.T.; Mullins, E.W.S.; Fowler, T.A.; Falconer, C.L.; Murphy, O.B.; Langenberg, C.; Jayatunga, W.J.P.; Eddy, D.H.; Nguyen-Van-Tam, J.S. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): What do we know about children? A systematic review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anna, B.; Corrinna, F.; Karpenko, J.; Grygiel, B. SARS-CoV-2 infection in the context of Kawasaki disease and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2023, 212, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justo Arevalo, S.; Castillo-Chávez, A.; Uribe Calampa, C.S.; Zapata Sifuentes, D.; Huallpa, C.J.; Landa Bianchi, G.; Garavito-Salini Casas, R.; Quiñones Aguilar, M.; Pineda Chavarría, R. What do we know about the function of SARS-CoV-2 proteins? Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1249607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokhrel, S.; Kraemer, B.R.; Burkholz, S.; Mochly-Rosen, D. Natural variants in SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein pinpoint structural and functional hotspots with implications for prophylaxis and therapeutic strategies. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, J. The SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Role in Viral Structure, Biological Functions, and a Potential Target for Drug or Vaccine Mitigation. Viruses 2021, 13, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, W.N.; Tan, C.W.; Foo, R.; Kang, A.E.Z.; Peng, Y.; Sivalingam, V.; Tiu, C.; Ong, X.M.; Zhu, F.; Young, B.E.; et al. Serological differentiation between COVID-19 and SARS infections. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Lam, E.C.; Astudillo, M.G.; Yang, D.; Miller, T.E.; Feldman, J.; Hauser, B.M.; Caradonna, T.M.; Clayton, K.L.; Nitido, A.D.; et al. COVID-19-neutralizing antibodies predict disease severity and survival. Cell 2021, 184, 476–488.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, E.C.; Dejenie, T.A. Protective roles and protective mechanisms of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 infection and their potential clinical implications. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1055457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölfel, R.; Corman, V.M.; Guggemos, W.; Seilmaier, M.; Zange, S.; Müller, M.A.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Vollmar, P.; Rothe, C.; et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 2020, 581, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, S.L.; Kaufman, H.W.; Meyer, W.A.; Bush, C.; Cohen, O.; Cronin, K.; Kabelac, C.; Leonard, S.; Anderson, S.; Petkov, V.; et al. Risk of and duration of protection from SARS-CoV-2 reinfection assessed with real-world data. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavaro, D.F.; Laghetti, P.; Milano, E.; Brindicci, G.; Volpe, A.; Lagioia, A.; Saracino, A.; Monno, L. Anti-spike S1 receptor-binding domain antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 persist several months after infection regardless of disease severity. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 3158–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolotin, S.; Tran, V.; Osman, S.; Brown, K.A.; Buchan, S.A.; Joh, E.; Deeks, S.L.; Allen, V.G. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Survey Estimates Are Affected by Anti-Nucleocapsid Antibody Decline. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdoubi, A.; Michalski, C.; O’Connell, S.E.; Dada, S.; Narpala, S.; Gelinas, J.; Mehta, D.; Cheung, C.; Winkler, D.F.; Basappa, M.; et al. A majority of uninfected adults show preexisting antibody reactivity against SARS-CoV-2. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e146316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kids Corona, Research on COVID-19. Available online: https://www.sjdhospitalbarcelona.org/en/research-innovation/research/kids-corona-research-covid-19 (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Brotons, P.; Launes, C.; Buetas, E.; Fumado, V.; Henares, D.; De Sevilla, M.F.; Redin, A.; Fuente-Soro, L.; Cuadras, D.; Mele, M.; et al. Susceptibility to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection among Children and Adults: A Seroprevalence Study of Family Households in the Barcelona Metropolitan Region, Spain. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, E970–E977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, I.; de Sevilla, M.F.; Fumado, V.; Bassat, Q.; Bonet-Carne, E.; Fortuny, C.; Garcia-Miquel, A.; Jou, C.; Adroher, C.; Melé Casas, M.; et al. Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus infection among children in summer schools applying stringent control measures in Barcelona, Spain. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mele-Casas, M.; Launes, C.; de Sevilla, M.F.; Hernandez-Garcia, M.; Pons-Tomas, G.; Bassat, Q.; Fumado, V.; Fortuny, C.; Garcia-Miquel, A.; Bonet-Carne, E.; et al. Low transmission of SARS-CoV-2 derived from children in family clusters: An observational study of family households in the Barcelona Metropolitan Area, Spain. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, A.; Fortuny, C.; Fumadó, V.; Jordan, I.; Ruiz-López, L.; González-Navarro, E.A.; Egri, N.; Esteve-Solé, A.; Luo, Y.; Vlagea, A.; et al. Acute and long-term immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in unvaccinated children and young adults with inborn errors of immunity. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1084630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callow, K.A.; Parry, H.F.; Sergeant, M.; Tyrrell, D.A.J. The time course of the immune response to experimental coronavirus infection of man. Epidemiol. Infect. 1990, 105, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.; Chan, J.F.W.; Tse, H.; Chen, H.; Lau, C.C.Y.; Cai, J.P.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Xiao, X.; To, K.K.W.; Lau, S.K.P.; et al. Cross-reactive antibodies in convalescent SARS patients’ sera against the emerging novel human coronavirus EMC (2012) by both immunofluorescent and neutralizing antibody tests. J. Infect. 2013, 67, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mioch, D.; Vanbrabant, L.; Reimerink, J.; Kuiper, S.; Lodder, E.; van den Bijllaardt, W.; Kluytmans, J.; Wissing, M.D.; Augustijn, H.; Bartels, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 antibodies persist up to 12 months after natural infection in healthy employees working in non-medical contact-intensive professions. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 126, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunay, G.A.; Barroso, M.; Woidy, M.; Danecka, M.K.; Engels, G.; Hermann, K.; Neumann, F.S.; Paul, K.; Beime, J.; Escherich, G.; et al. Long-Term Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Children. J. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 43, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, E.M.; Fabricius, D.; Class, M.; Topfstedt, F.; Lorenzetti, R.; Janowska, I.; Schmidt, F.; Staniek, J.; Zernickel, M.; Stamminger, T.; et al. High antibody levels and reduced cellular response in children up to one year after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Chiara, C.; Cantarutti, A.; Costenaro, P.; Donà, D.; Bonfante, F.; Cosma, C.; Ferrarese, M.; Cozzani, S.; Petrara, M.R.; Carmona, F.; et al. Long-term Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Children and Adults after Mild Infection. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, E2221616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulou, D.; Charakida, M.; Marmarinos, A.; Karaviti, D.; Avgeris, M.; Gourgiotis, D.; Tsolia, M.N. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Kinetics in Unvaccinated Hospitalized Children With COVID-19. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2024, 43, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chansaenroj, J.; Yorsaeng, R.; Puenpa, J.; Wanlapakorn, N.; Chirathaworn, C.; Sudhinaraset, N.; Sripramote, M.; Chalongviriyalert, P.; Jirajariyavej, S.; Kiatpanabhikul, P.; et al. Long-term persistence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein-specific and neutralizing antibodies in recovered COVID-19 patients. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flacco, M.E.; Acuti Martellucci, C.; Baccolini, V.; De Vito, C.; Renzi, E.; Villari, P.; Manzoli, L. Risk of reinfection and disease after SARS-CoV-2 primary infection: Meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panico, A.; Bagordo, F.; Nolasco, E.; Grassi, T.; Bianco, A.; Indino, F.; Taurino, F.; De Donno, A.; Lobreglio, G. Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Hospitalized Patients. Pathogens 2024, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, G.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B.; He, J.; Yin, S.; Huang, J.; Fan, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG levels in relation to disease severity of COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Qiao, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Longitudinal profiling of antibody response in patients with COVID-19 in a tertiary care hospital in Beijing, China. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 614436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalakas, M.C.; Bitzogli, K.; Alexopoulos, H. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies within IVIg preparations: Cross-reactivities with seasonal coronaviruses, natural autoimmunity, and therapeutic implications. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 627285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapp, S.A.; Abrams, J.; Lu, A.T.; Hussaini, L.; Kao, C.M.; Hunstad, D.A.; Rosenberg, R.B.; Zafferani, M.J.; Ede, K.C.; Ballan, W.; et al. Serologic and cytokine signatures in children with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome and Coronavirus disease 2019. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Le Pen, J.; Yatim, A.; Dong, B.; Aquino, Y.; Ogishi, M.; Pescarmona, R.; Talouarn, E.; Rinchai, D.; Zhang, P.; et al. Inborn errors of OAS-RNase L in SARS-CoV-2-related multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. Science 2023, 379, eabo3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotulo, G.A.; Palma, P. Understanding COVID-19 in children: Immune determinants and post-infection conditions. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 94, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). In COVID-19 Vaccines; National Institute of Child Health and Human Development: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.S.; Costa, V.; Racine-Brzostek, S.E.; Acker, K.P.; Yee, J.; Chen, Z.; Karbaschi, M.; Zuk, R.; Rand, S.; Sukhu, A.; et al. Association of age with SARS-CoV-2 antibody response. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e214302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Echevarría, A.; Sainz, T.; Falces-Romero, I.; de Felipe, B.; Escolano, L.; Alcolea, S.; Pertiñez, L.; Neth, O.; Calvo, C. Long-term persistence of anti-sars-cov-2 antibodies in a pediatric population. Pathogens 2021, 10, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tea, F.; Stella, A.O.; Aggarwal, A.; Darley, D.R.; Pilli, D.; Vitale, D.; Merheb, V.; Lee, F.X.Z.; Cunningham, P.; Walker, G.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies: Longevity, breadth, and evasion by emerging viral variants. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Valtanen, P.; Hope, C.M.; Masavuli, M.G.; Yeow, A.E.L.; Balachandran, H.; Mekonnen, Z.A.; Al-Delfi, Z.; Abayasingam, A.; Agapiou, D.; Stella, A.O.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant escapes neutralizing antibodies and T cell responses more efficiently than other variants in mild COVID-19 convalescents. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Univariate | Multivariable ⴕ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | IgG levels (AU/mL) 671 (IQR: 376-1443) | p-value | Beta coefficient (95% confidence interval) | p-value | |
| Age <2 years 2–4 5–11 >11 | 12 22 35 32 | 1569 (939–2109) 633 (381–1045) 616 (312–997) 649 (312–2176) | 0.034 * | −738 (−1487–12) n.a. n.a. n.a. | 0.054 n.a. n.a. n.a. |
| Sex Male Female | 57 45 | 670 (339–1619) 672 (415–1217) | 0.832 | n.a. n.a. | n.a. n.a. |
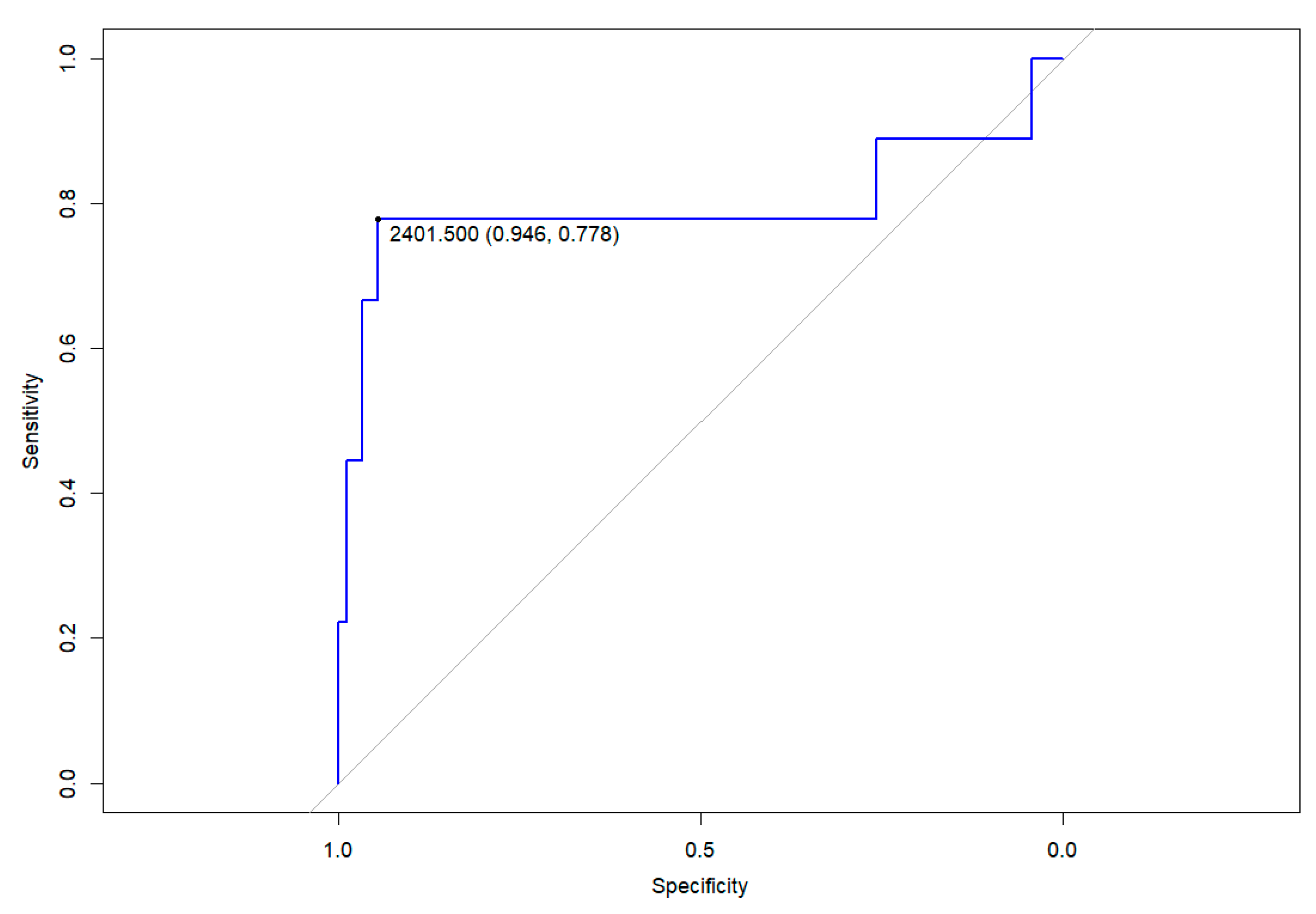
| Clinical Phenotype Asymptomatic Fever+−URTI LRTI MIS-C | 46 34 9 13 | 593 (249–1066) 640 (338–1327) 3012 (1406–6671) 601 (128–1548) | 0.042 ** 0.851 ** 0.003 ** 0.416 ** | −309 (−829–210) n.a. 3028 (2112–3945) n.a. | 0.240 n.a. <0.001 n.a. |
| Correlationsⴕⴕ | |||||
| Blood parameters at diagnosis Leucocytes Lymphocytes C-Reactive Protein protein | 25 | −0.212 −0.187 0.461 | 0.298 0.371 0.027 | n.a. n.a. n.a. | n.a. n.a. n.a. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pons-Tomàs, G.; Pino, R.; Soler-García, A.; Launes, C.; Martínez-de-Albeniz, I.; Ríos-Barnés, M.; Melé-Casas, M.; Hernández-García, M.; Monsonís, M.; Gené, A.; et al. Deciphering the Longevity and Levels of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Children: A Year-Long Study Highlighting Clinical Phenotypes and Age-Related Variations. Pathogens 2024, 13, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080622
Pons-Tomàs G, Pino R, Soler-García A, Launes C, Martínez-de-Albeniz I, Ríos-Barnés M, Melé-Casas M, Hernández-García M, Monsonís M, Gené A, et al. Deciphering the Longevity and Levels of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Children: A Year-Long Study Highlighting Clinical Phenotypes and Age-Related Variations. Pathogens. 2024; 13(8):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080622
Chicago/Turabian StylePons-Tomàs, Gemma, Rosa Pino, Aleix Soler-García, Cristian Launes, Irene Martínez-de-Albeniz, María Ríos-Barnés, Maria Melé-Casas, María Hernández-García, Manuel Monsonís, Amadeu Gené, and et al. 2024. "Deciphering the Longevity and Levels of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Children: A Year-Long Study Highlighting Clinical Phenotypes and Age-Related Variations" Pathogens 13, no. 8: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080622
APA StylePons-Tomàs, G., Pino, R., Soler-García, A., Launes, C., Martínez-de-Albeniz, I., Ríos-Barnés, M., Melé-Casas, M., Hernández-García, M., Monsonís, M., Gené, A., de-Sevilla, M.-F., García-García, J.-J., Fortuny, C., & Fumadó, V. (2024). Deciphering the Longevity and Levels of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Children: A Year-Long Study Highlighting Clinical Phenotypes and Age-Related Variations. Pathogens, 13(8), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens13080622









