A Novel Strain of Orientia tsutsugamushi Detected from Chiggers (Acari: Trombiculidae) on Wild Rodents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Trapping and Sampling
2.3. Chigger Identification, Pooling, and Total DNA Extraction
2.4. PCR Assays for Screening and Detecting Orientia DNA
2.5. Nucleotide Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chigger Identification and Orientia Nucleotide Screening
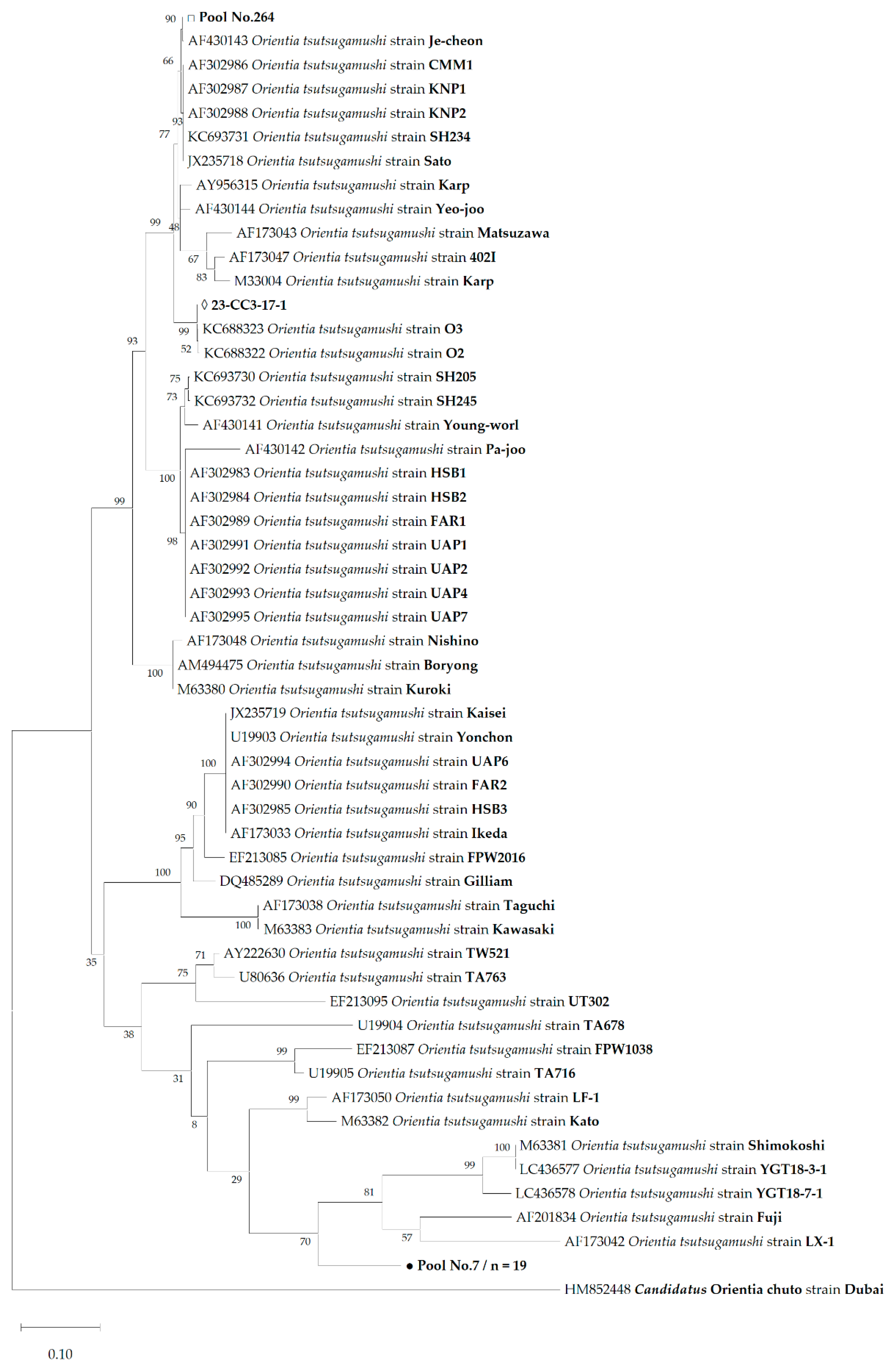
3.2. DNA Sequences of Orientia tsutsugamushi and Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luce-Fedrow, A.; Lehman, M.L.; Kelly, D.J.; Mullins, K.; Maina, A.N.; Stewart, R.L.; Ge, H.; John, H.S.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L. A review of scrub typhus (Orientia tsutsugamushi and related organisms): Then, now, and tomorrow. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, I.; Pearson, I.; Dahal, P.; Thomas, N.V.; Roberts, T.; Newton, P.N. Scrub typhus ecology: A systematic review of Orientia in vectors and hosts. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.J.; Fuerst, P.A.; Ching, W.-M.; Richards, A.L. Scrub typhus: The geographic distribution of phenotypic and genotypic variants of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48 (Suppl. 3), S203–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.J.; Richards, A.L.; Temenak, J.; Strickman, D.; Dasch, G.A. The past and present threat of rickettsial diseases to military medicine and international public health. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 34 (Suppl. 4), S145–S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.J.; Foley, D.H.; Richards, A.L. A spatiotemporal database to track human scrub typhus using the VectorMap application. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonell, A.; Lubell, Y.; Newton, P.N.; Crump, J.A.; Paris, D.H. Estimating the burden of scrub typhus: A systematic review. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Walker, D.H.; Jupiter, D.; Melby, P.C.; Arcari, C.M. A review of the global epidemiology of scrub typhus. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzard, L.; Fuller, A.; Blacksell, S.D.; Paris, D.H.; Richards, A.L.; Aukkanit, N.; Nguyen, C.; Jiang, J.; Fenwick, S.; Day, N.P. Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4404–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcells, M.E.; Rabagliati, R.; García, P.; Poggi, H.; Oddó, D.; Concha, M.; Abarca, K.; Jiang, J.; Kelly, D.J.; Richards, A.L. Endemic scrub typhus–like illness, Chile. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosson, J.F.; Galan, M.; Bard, E.; Razzauti, M.; Bernard, M.; Morand, S.; Brouat, C.; Dalecky, A.; Bâ, K.; Charbonnel, N. Detection of Orientia sp. DNA in rodents from Asia, West Africa and Europe. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masakhwe, C.; Linsuwanon, P.; Kimita, G.; Mutai, B.; Leepitakrat, S.; Yalwala, S.; Abuom, D.; Auysawasi, N.; Gilbreath, T.; Wanja, E. Identification and characterization of Orientia chuto in trombiculid chigger mites collected from wild rodents in Kenya. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01124-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarca, K.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Angulo, J.; Jiang, J.; Farris, C.M.; Richards, A.L.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Weitzel, T. Molecular description of a novel Orientia species causing scrub typhus in Chile. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Travanty, N.V.; Garshong, R.; Crossley, D.; Wasserberg, G.; Apperson, C.S.; Roe, R.M.; Ponnusamy, L. Detection of Orientia spp. Bacteria in Field-Collected Free-Living Eutrombicula Chigger Mites, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.-G.; Song, B.-G.; Kim, T.-K.; Noh, B.-E.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, W.-G.; Lee, H.I. Nationwide incidence of chigger mite populations and molecular detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi in the Republic of Korea, 2020. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumlert, R.; Chaisiri, K.; Anantatat, T.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Morand, S.; Prasartvit, A.; Makepeace, B.L.; Sungvornyothin, S.; Paris, D.H. Autofluorescence microscopy for paired-matched morphological and molecular identification of individual chigger mites (Acari: Trombiculidae), the vectors of scrub typhus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ree, H.-I. Fauna and Key to the Chigger Mites of Korea: Acarina: Trombiculidae and Leeuwenhoekiidae. Anim. Syst. Evol. Divers. 1990, 6, 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Martínez-Valdebenito, C.; Weitzel, T.; Farris, C.M.; Acosta-Jamett, G.; Abarca, K.; Richards, A.L. Development of a new genus-specific quantitative real-time PCR assay for the diagnosis of Scrub Typhus in South America. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 831045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency Disease Portal. Available online: https://dportal.kdca.go.kr/pot/is/summaryEDW.do (accessed on 6 November 2024).
- Gill, B.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.S. Surveillance for Prevalence of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Wild Rodents and Chigger Mites in Korea, 2011–2013. Public Health Wkly. Rep. 2015, 8, 572–577. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.H.; Lee, J.; Gill, B.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, D.-M.; Kim, T.-S.; Kim, Y.-S. Molecular epidemiology of Orientia tsutsugamushi from scrub typhus patients in South Korea, 2014–2015. Public Health Wkly. Rep. 2016, 9, 882–888. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Park, D.W.; Jung, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Seo, M.H.; Song, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, D.M.; Kim, C.-M. Molecular epidemiology of an Orientia tsutsugamushi gene encoding a 56-kDa type-specific antigen in chiggers, small mammals, and patients from the southwest region of Korea. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ree, H.-I.; Lee, I.-Y.; Cho, M.-K. Determination of the vector species of tsutsugamushi disease in Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 1991, 29, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ree, H.-I.; Chang, W.-H.; Kee, S.; Lee, I.-Y.; Jeon, S.-H. Detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi DNA in individual trombiculids using polymerase chain reaction in Korea. Med. Entomol. Zool. 1997, 48, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ree, H.-I.; Lee, I.-Y.; Jeon, S.-H.; Yoshida, Y. Geographical distribution of vectors and sero-strains of tsutsugamushi disease at mid-south inland of Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 1997, 35, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.I.; Shim, S.K.; Song, B.G.; Choi, E.N.; Hwang, K.J.; Park, M.Y.; Park, C.; Shin, E.-H. Detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi, the causative agent of scrub typhus, in a novel mite species, Eushoengastia koreaensis, in Korea. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Chung, J.K.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, S.J.; Ha, Y.D.; Jung, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Song, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, D.M. Seroepidemiological survey of zoonotic diseases in small mammals with PCR detection of Orientia tsutsugamushi in chiggers, Gwangju, Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2016, 54, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, I.Y.; Song, H.J.; Kim, J.; Park, H.J.; Song, D.; Jang, W.J. Geographical distribution of Orientia tsutsugamushi strains in chiggers from three provinces in Korea. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 62, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, A.; Yamamoto, N.; Koyama, S.; Makisaka, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Urabe, K.I.; Takaoka, M.; Nakazawa, K.; Urakami, H.; Fukuhara, M. Epidemiological survey of Orientia tsutsugamushi distribution in field rodents in Saitama Prefecture, Japan, and discovery of a new type. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001, 45, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, B.J.; Rosselló-Móra, R.; Busse, H.-J.; Ludwig, W.; Kämpfer, P. Notes on the characterization of prokaryote strains for taxonomic purposes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 16s Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation; Illumina: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 21.
- Elliott, I.; Thangnimitchok, N.; de Cesare, M.; Linsuwanon, P.; Paris, D.H.; Day, N.P.; Newton, P.N.; Bowden, R.; Batty, E.M. Targeted capture and sequencing of Orientia tsutsugamushi genomes from chiggers and humans. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 91, 104818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
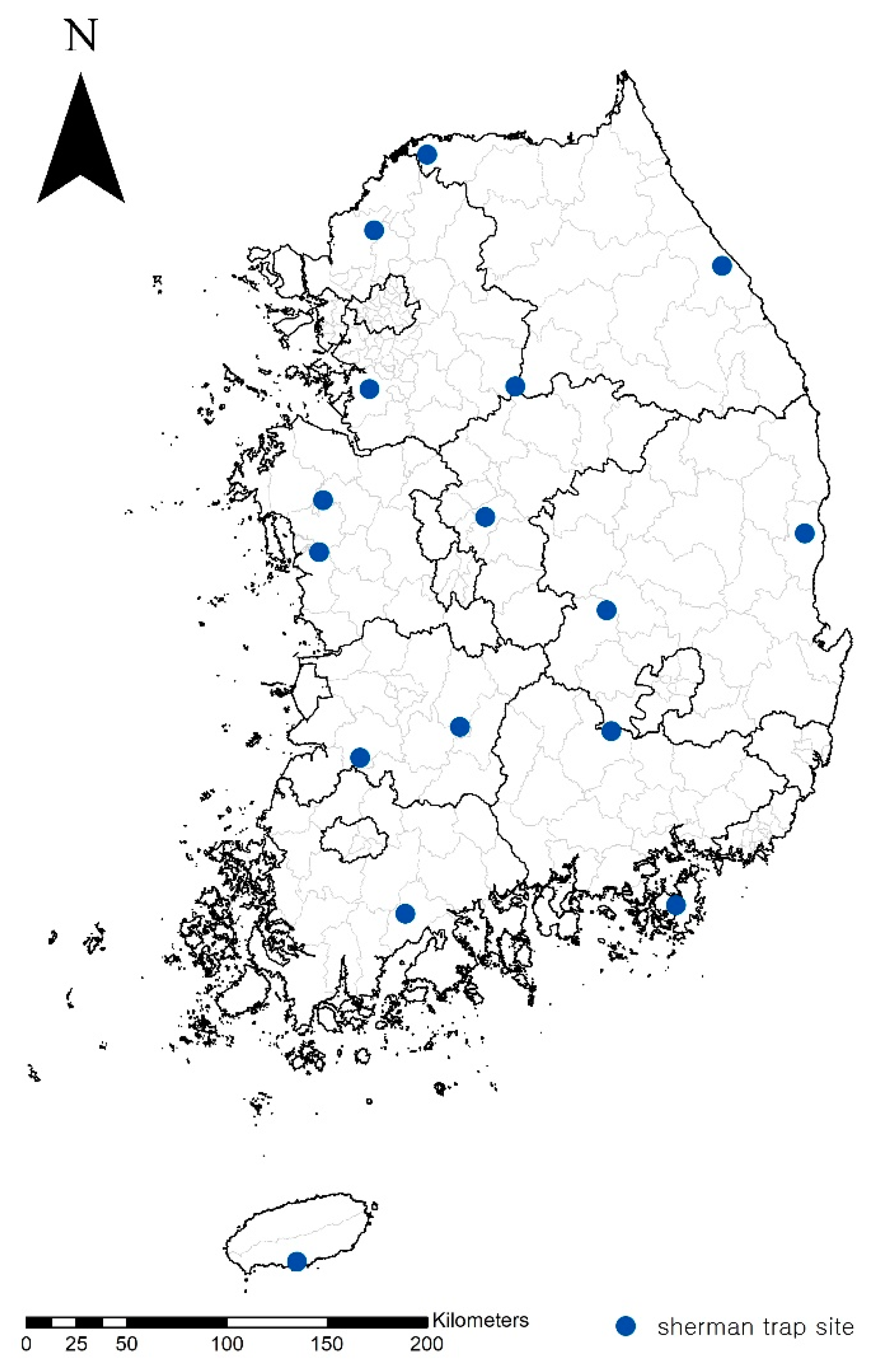

| Sample No. | Site | Rodent Species | Chigger Species | No. of Specimens/Pool |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Cheorwon | Apodemus agrarius | Leptotrimbidium pallidum | 5 |
| 144 | Paju | 10 | ||
| 162 | Paju | 10 | ||
| 264 | Yesan | 5 | ||
| 22-GW1-5 | Cheorwon | Apodemus agrarius | Unidentified | Minimum 1 to Maximum 30 |
| 22-GW1-18 | Cheorwon | |||
| 22-GW2-23 | Gangneung | |||
| 22-GW2-34 | Gangneung | |||
| 22-SD2-12 | Paju | |||
| 22-SD2-15 | Paju | |||
| 22-SD2-22 | Paju | |||
| 22-JN2-2 | Boseong | |||
| 22-JN2-22 | Boseong | |||
| 22-JN2-25 | Boseong | |||
| 22-CC1-4 | Cheongju | |||
| 23-SD2-16 | Paju | |||
| 23-SD2-18 | Paju | |||
| 23-JN2-6 | Boseong | |||
| 23-JN2-8 | Boseong | |||
| 23-JN2-23 | Boseong | |||
| 23-JN2-35 | Boseong | |||
| 23-JB-22 | Jinan | |||
| 23-JB-26 | Jinan | |||
| 23-CC3-17-1 | Yesan | |||
| 23-CC3-17-2 | Yesan |
| Target | Primer ID | Sequence (5′-3′) | Annealing Temperature | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 56-kDa tsa | Otr56_498F 1 r56_1459R 1,2 Otr56_585F 1 | AATTAGTTTAGAATGGTTACCAC TCTGTATCTGTTCGACAGATGCACTATTA GAATGTCTGCGTTGTCGTTGC | 54 °C | [12] |
| 47-kDa htrA | Otr47_145F 1 Otr47_1780R 1 Otr47_263F 2 Otr47_1133R 2 | ACAGGCCAAGATATTGGAAG AATCGCCTTTAAACTAGATTTACTTATTA GTGCTAAGAAARGATGATACTTC ACATTTAACATACCACGACGAAT | 51 °C | [11] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.I. A Novel Strain of Orientia tsutsugamushi Detected from Chiggers (Acari: Trombiculidae) on Wild Rodents. Pathogens 2025, 14, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14010029
Lee HS, Kim SY, Lee HI. A Novel Strain of Orientia tsutsugamushi Detected from Chiggers (Acari: Trombiculidae) on Wild Rodents. Pathogens. 2025; 14(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hak Seon, Seong Yoon Kim, and Hee Il Lee. 2025. "A Novel Strain of Orientia tsutsugamushi Detected from Chiggers (Acari: Trombiculidae) on Wild Rodents" Pathogens 14, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14010029
APA StyleLee, H. S., Kim, S. Y., & Lee, H. I. (2025). A Novel Strain of Orientia tsutsugamushi Detected from Chiggers (Acari: Trombiculidae) on Wild Rodents. Pathogens, 14(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14010029







