RNA Helicase DDX3 Interacts with the Capsid Protein of Hepatitis E Virus and Plays a Vital Role in the Viral Replication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Plasmids
2.3. Transfection
2.4. Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
2.5. DDX3 Depletion
2.6. BioID Assay
2.7. Electroporation
2.8. Luciferase Reporter Assay and Cell Viability Assay
2.9. Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) and Western Blotting
2.10. Reverse Transcription and Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.11. Computational Analysis of Protein–Protein Interaction
2.12. Protein Network Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. BioID and Mass Spectrometry Analysis
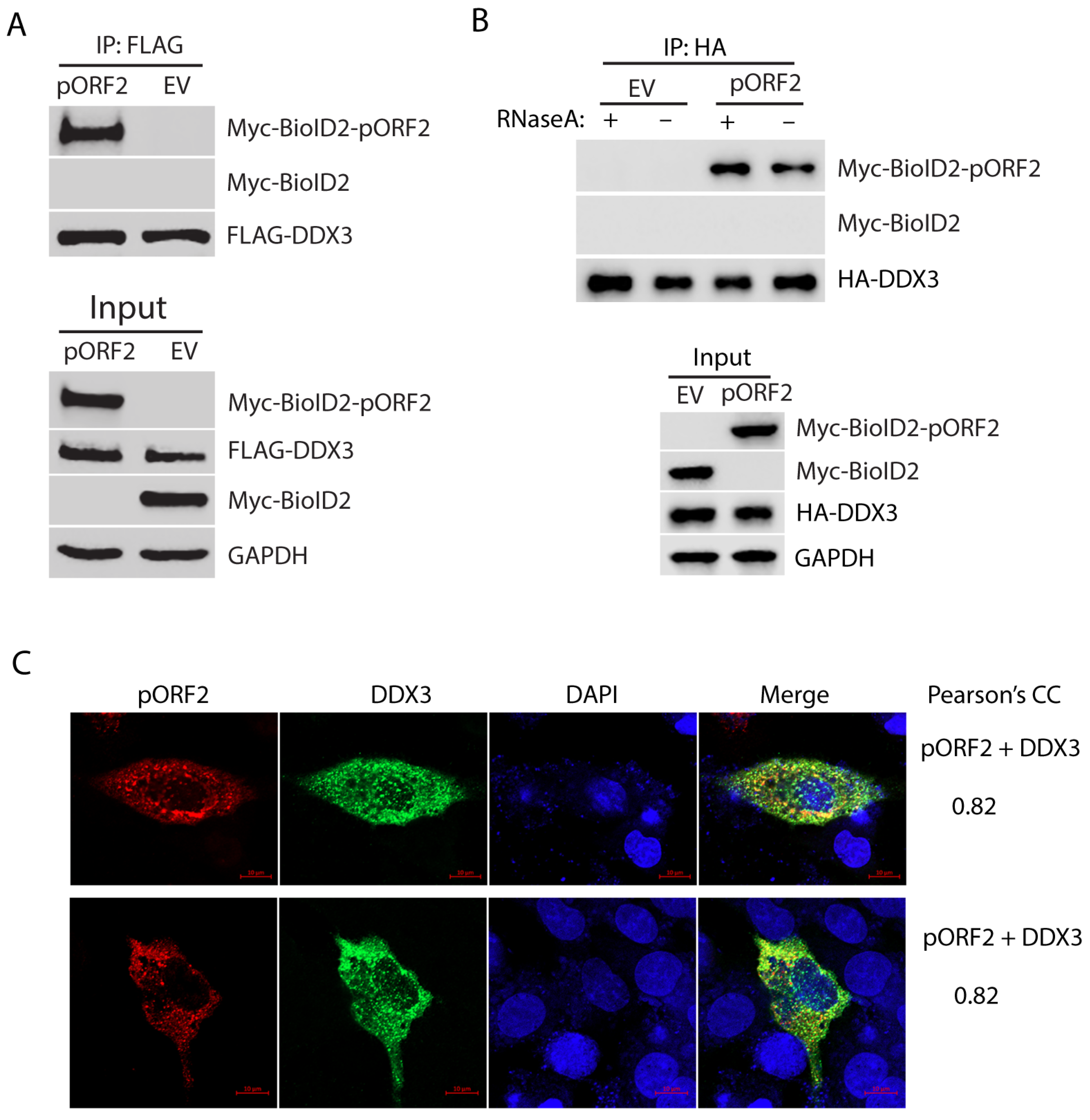
3.2. The Capsid Protein Interacts with DDX3 Independent of RNA Association
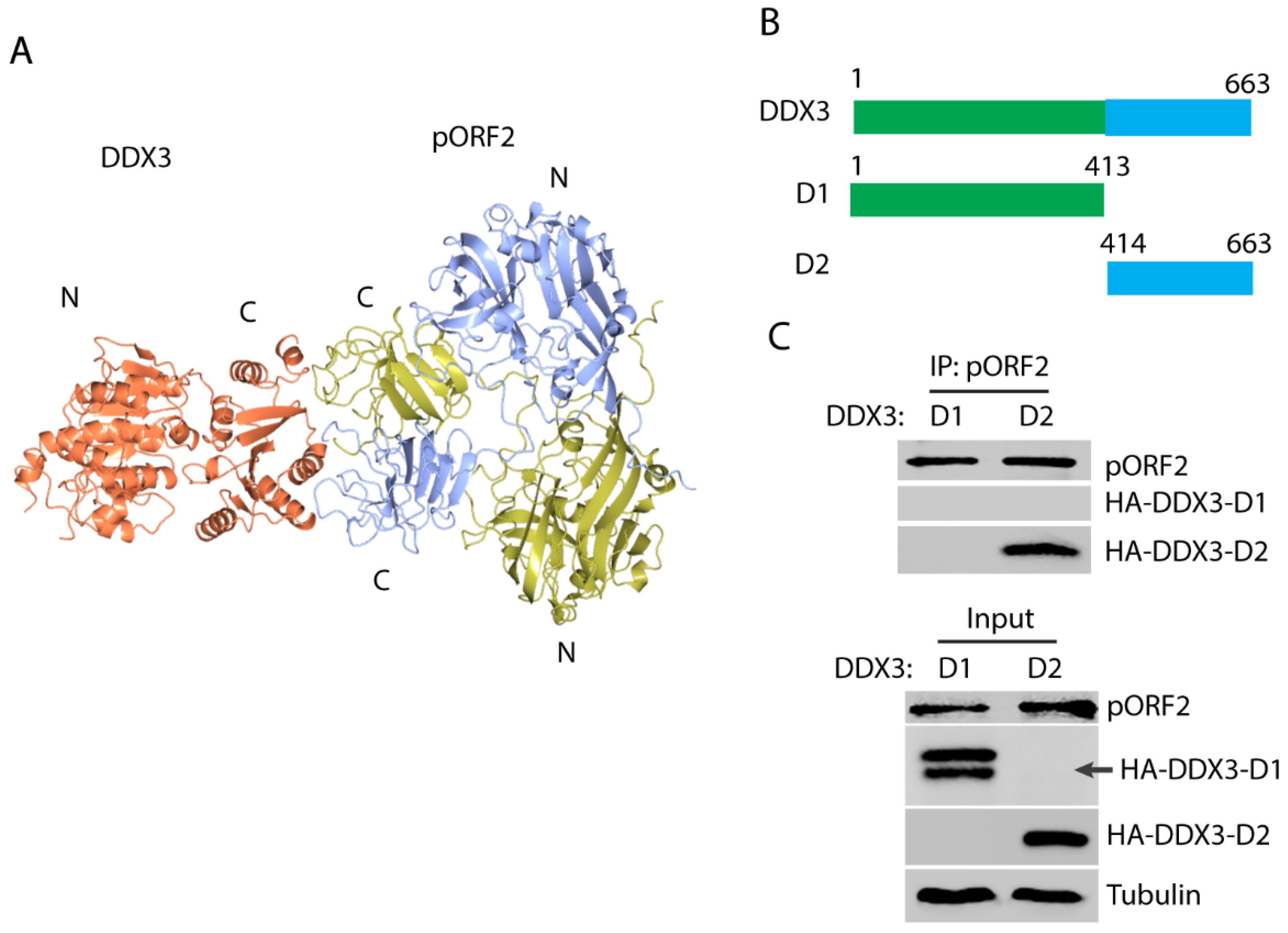
3.3. HEV Capsid Protein Interacts with the C-Terminal Region of DDX3
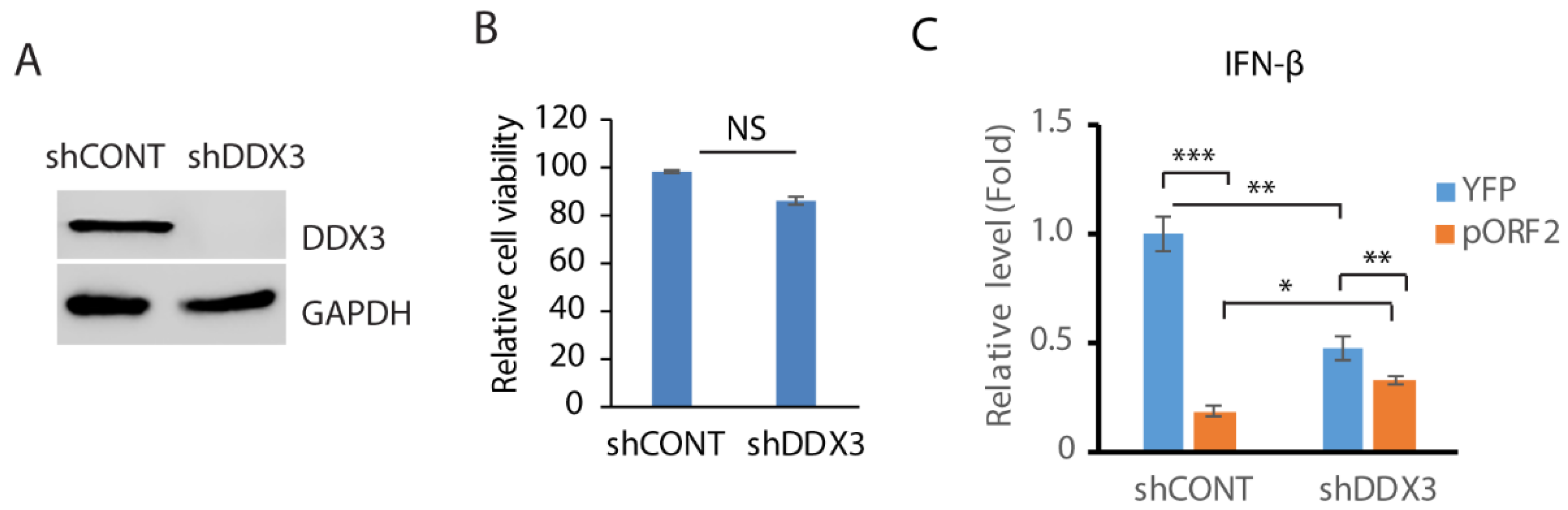
3.4. Depletion of DDX3 Impedes the IFN-β Induction
3.5. DDX3 Depletion Reduces the Replication of HEV
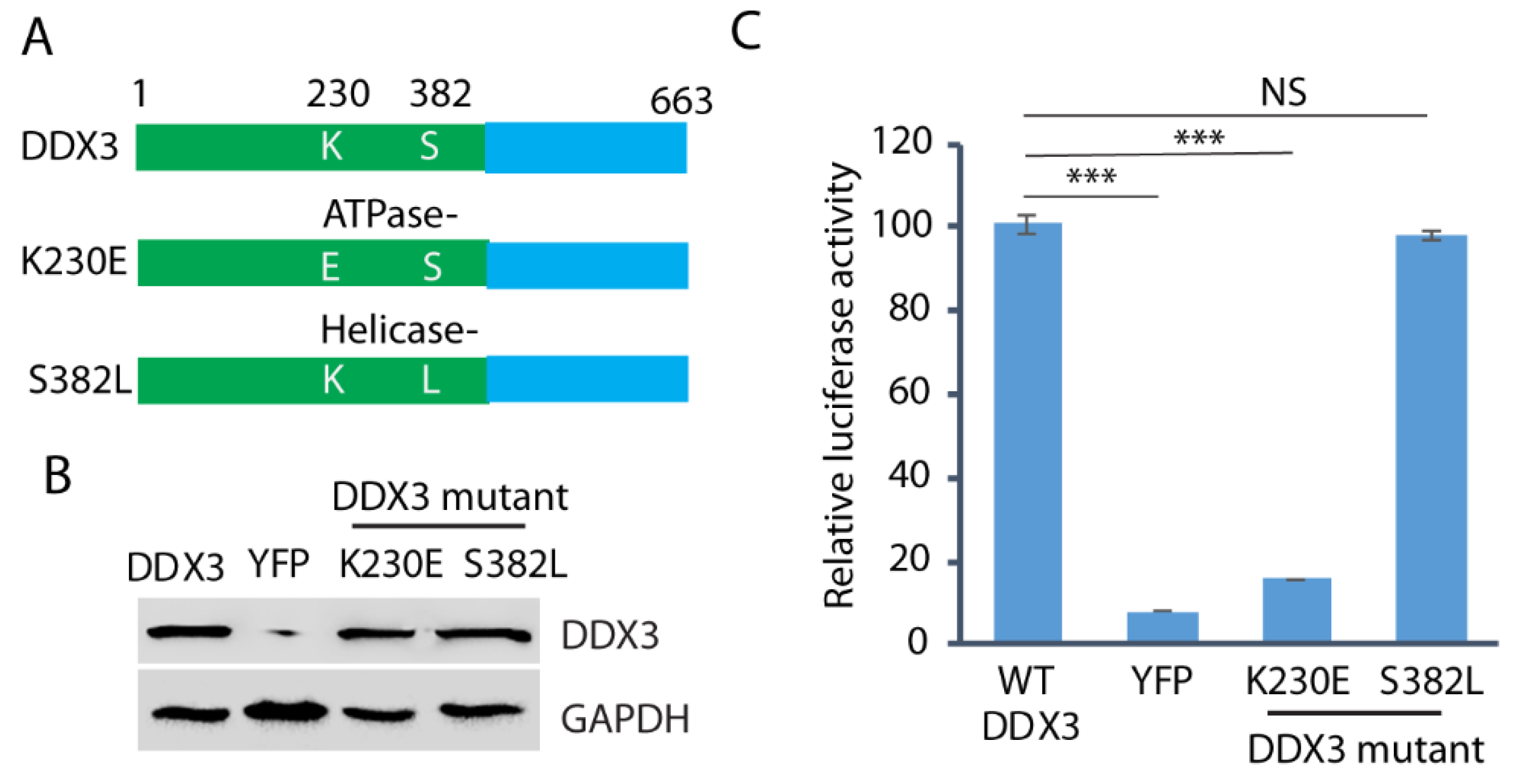
3.6. The ATPase Motif of DDX3 Is Required for HEV Replication
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singleton, M.R.; Dillingham, M.S.; Wigley, D.B. Structure and mechanism of helicases and nucleic acid translocases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordin, O.; Banroques, J.; Tanner, N.K.; Linder, P. The DEAD-box protein family of RNA helicases. Gene 2006, 367, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, V.; Maga, G. From the magic bullet to the magic target: Exploiting the diverse roles of DDX3X in viral infections and tumorigenesis. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 1357–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, M.; Baran, M.; Bowie, A.G. Viral targeting of DEAD box protein 3 reveals its role in TBK1/IKKepsilon-mediated IRF activation. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szappanos, D.; Tschismarov, R.; Perlot, T.; Westermayer, S.; Fischer, K.; Platanitis, E.; Kallinger, F.; Novatchkova, M.; Lassnig, C.; Muller, M.; et al. The RNA helicase DDX3X is an essential mediator of innate antimicrobial immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.H.; Chen, C.M.; Lee, Y.W.; You, L.R. DNA Damage, Liver Injury, and Tumorigenesis: Consequences of DDX3X Loss. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, T.; Endo, T.; Isotani, A.; Ogawa, M.; Ikawa, M. An azoospermic factor gene, Ddx3y and its paralog, Ddx3x are dispensable in germ cells for male fertility. J. Reprod. Dev. 2019, 65, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.G.; Park, S.H.; Song, K. Gene structure of the human DDX3 and chromosome mapping of its related sequences. Mol. Cells 2001, 12, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresta, C.; Ferlin, A.; Moro, E. Deletion and expression analysis of AZFa genes on the human Y chromosome revealed a major role for DBY in male infertility. Human. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedavalli, V.S.; Neuveut, C.; Chi, Y.H.; Kleiman, L.; Jeang, K.T. Requirement of DDX3 DEAD box RNA helicase for HIV-1 Rev-RRE export function. Cell 2004, 119, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiumi, H.; Sakai, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T. DEAD/H BOX 3 (DDX3) helicase binds the RIG-I adaptor IPS-1 to up-regulate IFN-beta-inducing potential. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taschuk, F.; Cherry, S. DEAD-Box Helicases: Sensors, Regulators, and Effectors for Antiviral Defense. Viruses 2020, 12, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariumi, Y.; Kuroki, M.; Abe, K.; Dansako, H.; Ikeda, M.; Wakita, T.; Kato, N. DDX3 DEAD-box RNA helicase is required for hepatitis C virus RNA replication. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13922–13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, M.E.; Zorzetto-Fernandes, A.L.; Radoshitzky, S.; Chi, X.; Dallari, S.; Marooki, N.; Leger, P.; Foscaldi, S.; Harjono, V.; Sharma, S.; et al. DDX3 suppresses type I interferons and favors viral replication during Arenavirus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulasi Raman, S.N.; Liu, G.; Pyo, H.M.; Cui, Y.C.; Xu, F.; Ayalew, L.E.; Tikoo, S.K.; Zhou, Y. DDX3 Interacts with Influenza A Virus NS1 and NP Proteins and Exerts Antiviral Function through Regulation of Stress Granule Formation. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3661–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kim, S.; Ryu, W.S. DDX3 DEAD-Box RNA helicase inhibits hepatitis B virus reverse transcription by incorporation into nucleocapsids. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5815–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, S. Molecular biology and pathogenesis of hepatitis E virus. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 1999, 1999, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Hepatitis E virus. In Fields Virology, 4th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2001; Volume 2, pp. 3051–3061. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Gracia, M.T.; Suay-Garcia, B.; Mateos-Lindemann, M.L. Hepatitis E and pregnancy: Current state. Rev. Med. Virol. 2017, 27, e1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachish, T.; Erez, O.; Daudi, N.; Shouval, D.; Schwartz, E. Acute hepatitis E virus in pregnant women in Israel and in other industrialized countries. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 73, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, M.A.; Drexler, J.F.; Meng, X.J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; de Souza, W.M.; Ulrich, R.G.; Smith, D.B. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Hepeviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Simmonds, P.; Members of The International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses Study Group; Jameel, S.; Emerson, S.U.; Harrison, T.J.; Meng, X.J.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Purdy, M.A. Consensus proposals for classification of the family Hepeviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, Y.J. Advances in Hepatitis E Virus Biology and Pathogenesis. Viruses 2021, 13, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.; Teng, J.L.L.; Chiu, T.H.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Hepatitis E Virus Genotypes and Evolution: Emergence of Camel Hepatitis E Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.H.; Tan, B.H.; Teo, E.C.; Lim, S.G.; Dan, Y.Y.; Wee, A.; Aw, P.P.; Zhu, Y.; Hibberd, M.L.; Tan, C.K.; et al. Chronic Infection with Camelid Hepatitis E Virus in a Liver Transplant Recipient Who Regularly Consumes Camel Meat and Milk. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 355–357.e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.C.; Bai, H.; Yoshizaki, S.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Doan, Y.H.; Takahashi, K.; Mishiro, S.; Takeda, N.; Wakita, T. Genotype 5 Hepatitis E Virus Produced by a Reverse Genetics System Has the Potential for Zoonotic Infection. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yang, Y.; Nan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.J. The Capsid Protein of Hepatitis E Virus Inhibits Interferon Induction via Its N-terminal Arginine-Rich Motif. Viruses 2019, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Gastaminza, P.; Cheng, G.; Kapadia, S.; Kato, T.; Burton, D.R.; Wieland, S.F.; Uprichard, S.L.; Wakita, T.; Chisari, F.V. Robust hepatitis C virus infection in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9294–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Faulk, K.; Mather, K.; Torian, U.; Engle, R.E.; Emerson, S.U. Adaptation of a genotype 3 hepatitis E virus to efficient growth in cell culture depends on an inserted human gene segment acquired by recombination. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5697–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.I.; Jensen, S.C.; Noble, K.A.; Kc, B.; Roux, K.H.; Motamedchaboki, K.; Roux, K.J. An improved smaller biotin ligase for BioID proximity labeling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, R.; Yu, Y.; Kannan, H.; Fredericksen, B.; Zhang, Y.J. Enhancement of interferon induction by ORF3 product of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8696–8705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schopp, I.M.; Amaya Ramirez, C.C.; Debeljak, J.; Kreibich, E.; Skribbe, M.; Wild, K.; Bethune, J. Split-BioID a conditional proteomics approach to monitor the composition of spatiotemporally defined protein complexes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roux, K.J.; Kim, D.I.; Burke, B.; May, D.G. BioID: A Screen for Protein-Protein Interactions. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2018, 91, 19.23.11–19.23.15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, A.; Wilm, M.; Vorm, O.; Mann, M. Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eng, J.K.; McCormack, A.L.; Yates, J.R. An approach to correlate tandem mass spectral data of peptides with amino acid sequences in a protein database. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 1994, 5, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellacheruvu, D.; Wright, Z.; Couzens, A.L.; Lambert, J.P.; St-Denis, N.A.; Li, T.; Miteva, Y.V.; Hauri, S.; Sardiu, M.E.; Low, T.Y.; et al. The CRAPome: A contaminant repository for affinity purification-mass spectrometry data. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Khattar, S.K.; Fredericksen, B.; Zhang, Y.J. Hepatitis E virus inhibits type I interferon induction by ORF1 products. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11924–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Wang, R.; Shen, M.; Faaberg, K.S.; Samal, S.K.; Zhang, Y.J. Induction of type I interferons by a novel porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus isolate. Virology 2012, 432, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, R.; Yang, S.; Ma, Z.; Lin, S.; Nan, Y.; Li, Q.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Y.J. Karyopherin Alpha 6 Is Required for Replication of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus and Zika Virus. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics 2016, 54, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Mori, Y.; Miyazaki, N.; Cheng, R.H.; Yoshimura, M.; Unno, H.; Shima, R.; Moriishi, K.; Tsukihara, T.; Li, T.C.; et al. Biological and immunological characteristics of hepatitis E virus-like particles based on the crystal structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12986–12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.W.; Beran, B.; Bi, C.; Bluhm, W.F.; Dimitropoulos, D.; Goodsell, D.S.; Prlic, A.; Quesada, M.; Quinn, G.B.; Westbrook, J.D.; et al. The RCSB Protein Data Bank: Redesigned web site and web services. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D392–D401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floor, S.N.; Condon, K.J.; Sharma, D.; Jankowsky, E.; Doudna, J.A. Autoinhibitory Interdomain Interactions and Subfamily-specific Extensions Redefine the Catalytic Core of the Human DEAD-box Protein DDX3. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 2412–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, B.G.; Wiehe, K.; Hwang, H.; Kim, B.H.; Vreven, T.; Weng, Z. ZDOCK server: Interactive docking prediction of protein-protein complexes and symmetric multimers. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1771–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiumi, H.; Ikeda, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Watanabe, A.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Kato, N.; Shimotohno, K.; Seya, T. Hepatitis C virus core protein abrogates the DDX3 function that enhances IPS-1-mediated IFN-beta induction. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.; Torian, U.; Nguyen, H.; Emerson, S.U. A bicistronic subgenomic mRNA encodes both the ORF2 and ORF3 proteins of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5919–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Rifo, R.; Rubilar, P.S.; Limousin, T.; de Breyne, S.; Decimo, D.; Ohlmann, T. DEAD-box protein DDX3 associates with eIF4F to promote translation of selected mRNAs. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 3745–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissler, R.; Golbik, R.P.; Behrens, S.E. The DEAD-box helicase DDX3 supports the assembly of functional 80S ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 4998–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogbom, M.; Collins, R.; van den Berg, S.; Jenvert, R.M.; Karlberg, T.; Kotenyova, T.; Flores, A.; Karlsson Hedestam, G.B.; Schiavone, L.H. Crystal structure of conserved domains 1 and 2 of the human DEAD-box helicase DDX3X in complex with the mononucleotide AMP. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epling, L.B.; Grace, C.R.; Lowe, B.R.; Partridge, J.F.; Enemark, E.J. Cancer-associated mutants of RNA helicase DDX3X are defective in RNA-stimulated ATP hydrolysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 1779–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Putnam, A.; Jankowsky, E. ATP hydrolysis is required for DEAD-box protein recycling but not for duplex unwinding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20209–20214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Potratz, J.P.; Tijerina, P.; Del Campo, M.; Lambowitz, A.M.; Russell, R. DEAD-box proteins can completely separate an RNA duplex using a single ATP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20203–20208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guu, T.S.; Liu, Z.; Ye, Q.; Mata, D.A.; Li, K.; Yin, C.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Y.J. Structure of the hepatitis E virus-like particle suggests mechanisms for virus assembly and receptor binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12992–12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owsianka, A.M.; Patel, A.H. Hepatitis C virus core protein interacts with a human DEAD box protein DDX3. Virology 1999, 257, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, A.G.; Dalrymple, D.; Boulant, S.; McGivern, D.R.; Clayton, R.F.; Scott, M.J.; Adair, R.; Graham, S.; Owsianka, A.M.; Targett-Adams, P.; et al. Requirement of cellular DDX3 for hepatitis C virus replication is unrelated to its interaction with the viral core protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ge, L.L.; Li, P.P.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.J.; Sun, M.X.; Huang, L.; Shen, Z.Q.; Hu, X.C.; Ishag, H.; et al. Cellular DDX3 regulates Japanese encephalitis virus replication by interacting with viral un-translated regions. Virology 2014, 449, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primer a | Sequence (5′ to 3′) b | Target |
|---|---|---|
| KH2F4 | GCTCGAGTGCCCTAGGGTTGTTCTGCTGCTGTTC | Kernow ORF2 |
| KH2R4 | ACGTCTCGAATTCTTAAGACTCCCGGGTTTTGCCTACCTCCG | Kernow ORF2 |
| DDX3-F1 | CGAATTCAGTCATGTGGCAGTGGAAAAT | DDX3 |
| DDX3-R1 | ACTCGAGTCAGTTACCCCACCAGTCAAC | DDX3 |
| DDX3-D1-F1 | TGAATTCGCCACCATGAGTCATGTGGCAGTGGA | DDX3 D1 |
| DDX3-D1-R1 | GCTCGAGTTCAGAGGTAGAGCCAACTCT | DDX3 D1 |
| DDX3-D2-F2 | TGAATTCGCCACCATGGCTGTAGGAAGAGTTGGCTC | DDX3 D2 |
| DDX3-D2-R2 | GCTCGAGGTTACCCCACCAGTCAACC | DDX3 D2 |
| shDDX3-F1 | GATCCGGAGTGATTACGATGGCATTGTTCAAGAGACAATGCCATCGTAATCACTCCTTTTTTG | DDX3 |
| shDDX3-R1 | AATTCAAAAAAGGAGTGATTACGATGGCATTGTCTCTTGAACAATGCCATCGTAATCACTCCG | DDX3 |
| DDX3-K230E-F1 | TGTGCCCAAACAGGGTCTGGAGAGACTGCAGCATTTCTGTTGCCC | DDX3 K230E |
| DDX3-K230E-R1 | GGGCAACAGAAATGCTGCAGTCTCTCCAGACCCTGTTTGGGCACA | DDX3 K230E |
| DDX3-S382L-F1 | TTCCTTAGGAAAAGTAGCCAAAAACATCATAGTGTGGCG | DDX3 S382L |
| DDX3-S382L-R1 | CGCCACACTATGATGTTTAGTGCTACTTTTCCTAAGGAA | DDX3 S382L |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Sallapalli, B.T.; Chang, P.; He, J.; Coyaud, E.; Pierce, B.G.; Zhang, Y.-J. RNA Helicase DDX3 Interacts with the Capsid Protein of Hepatitis E Virus and Plays a Vital Role in the Viral Replication. Pathogens 2025, 14, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020177
Lin S, Sallapalli BT, Chang P, He J, Coyaud E, Pierce BG, Zhang Y-J. RNA Helicase DDX3 Interacts with the Capsid Protein of Hepatitis E Virus and Plays a Vital Role in the Viral Replication. Pathogens. 2025; 14(2):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020177
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shaoli, Bhargava Teja Sallapalli, Peixi Chang, Jia He, Etienne Coyaud, Brian G. Pierce, and Yan-Jin Zhang. 2025. "RNA Helicase DDX3 Interacts with the Capsid Protein of Hepatitis E Virus and Plays a Vital Role in the Viral Replication" Pathogens 14, no. 2: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020177
APA StyleLin, S., Sallapalli, B. T., Chang, P., He, J., Coyaud, E., Pierce, B. G., & Zhang, Y.-J. (2025). RNA Helicase DDX3 Interacts with the Capsid Protein of Hepatitis E Virus and Plays a Vital Role in the Viral Replication. Pathogens, 14(2), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14020177







