Emergence of Tigecycline-Nonsusceptible Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with Metallo-β-Lactamase and Transferable Ceftazidime-Avibactam Resistance in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Identification of K. pneumoniae Clinical Isolates
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Nanopore Sequencing
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR and Mutation Analysis
2.6. Efflux Pump Inhibition Test
2.7. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.8. Conjugation and Plasmid Analysis
3. Results
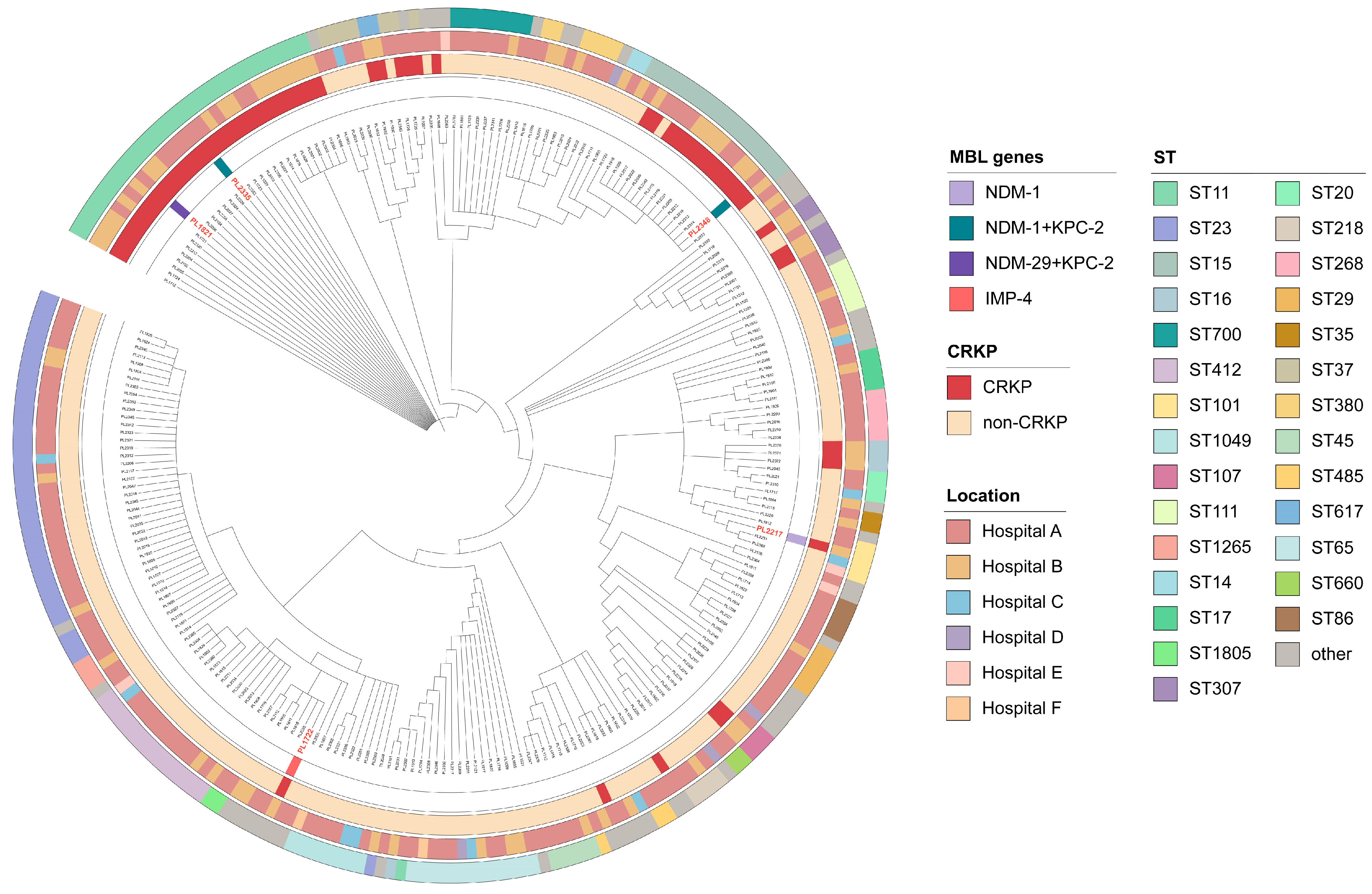
3.1. Prevalence and Clinical Characterization of Isolates
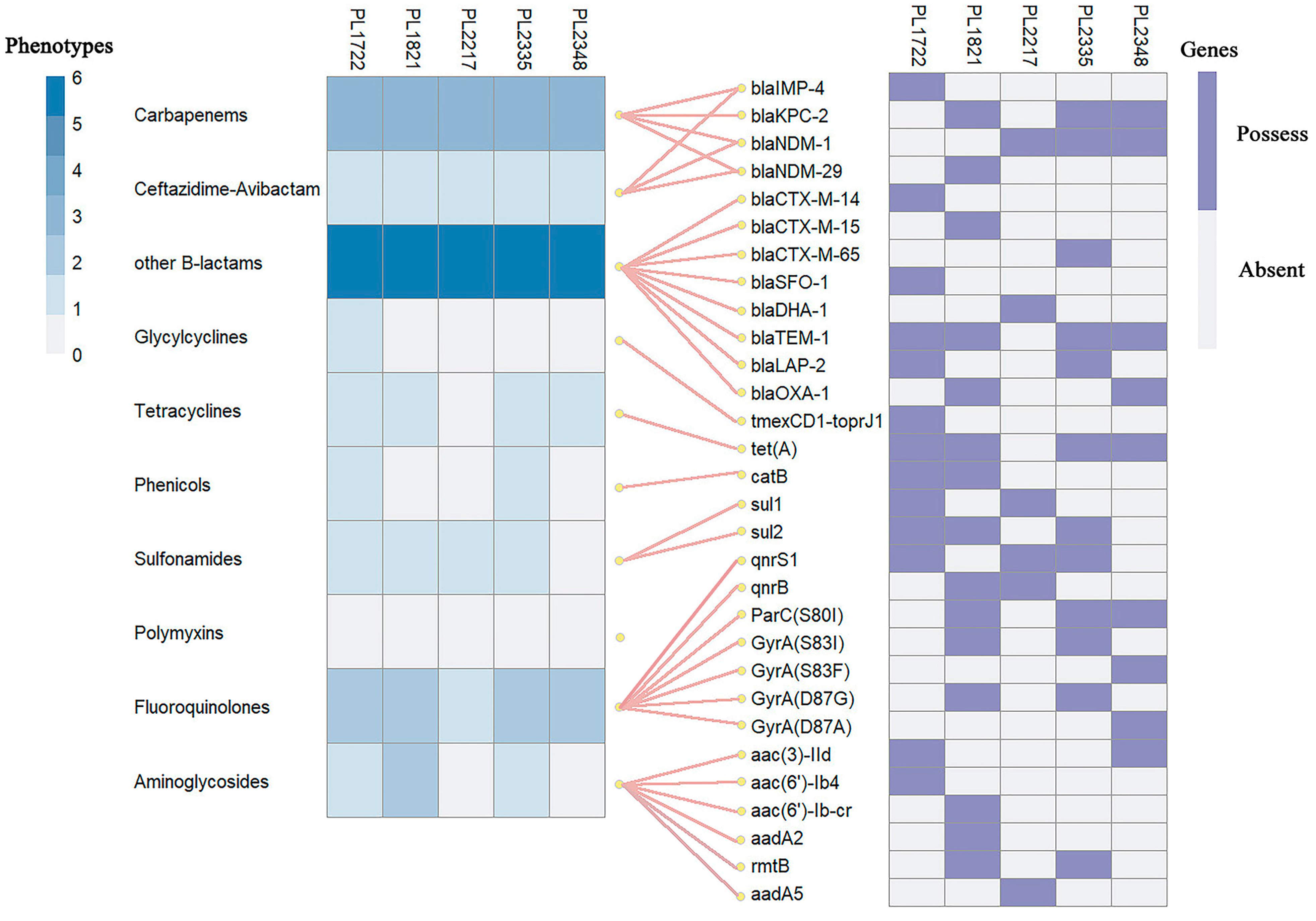
3.2. Resistance Profiles and Associated Determinants
3.3. Expression and Mutation Analysis of Tigecycline Resistance-Related Genes
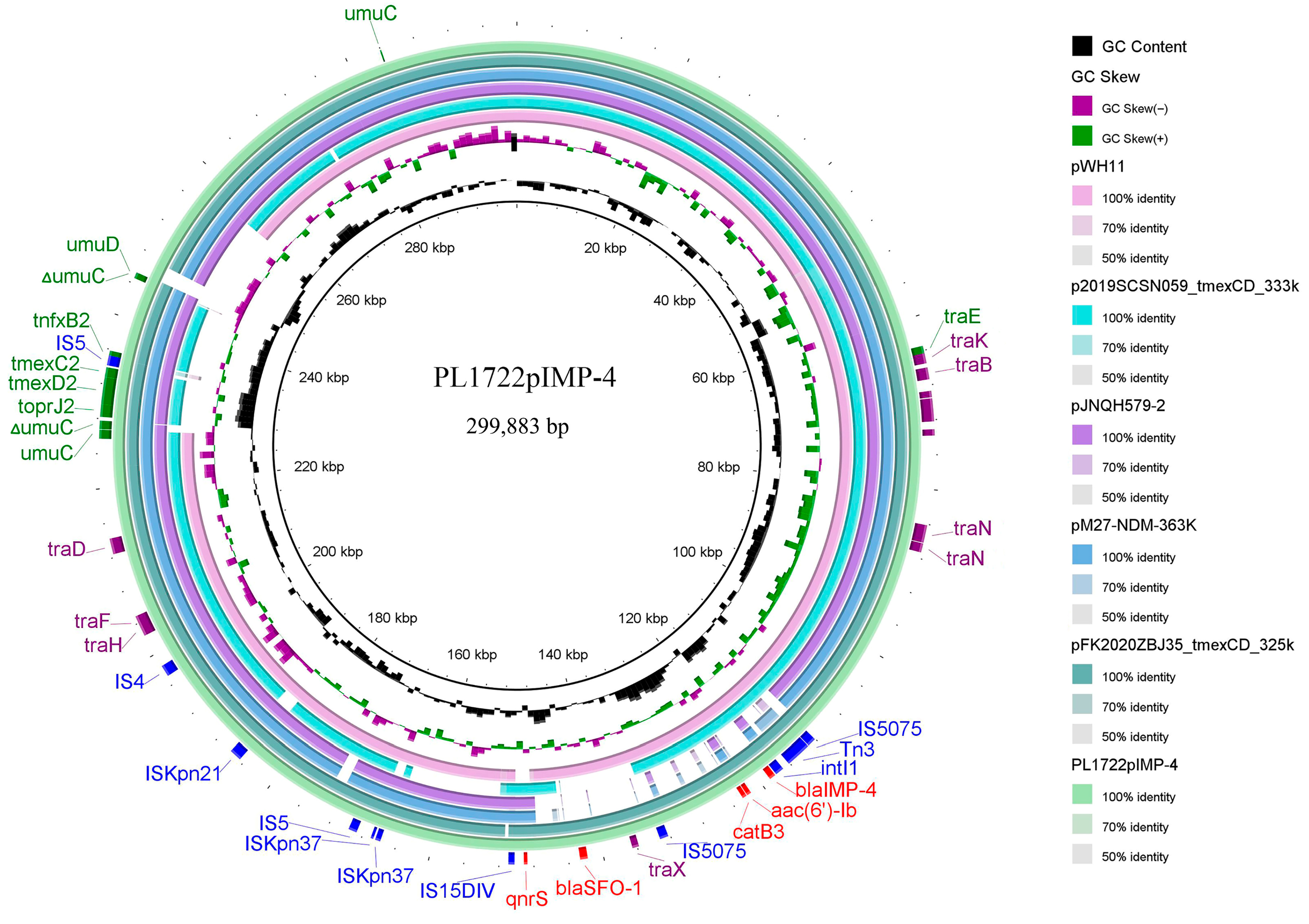
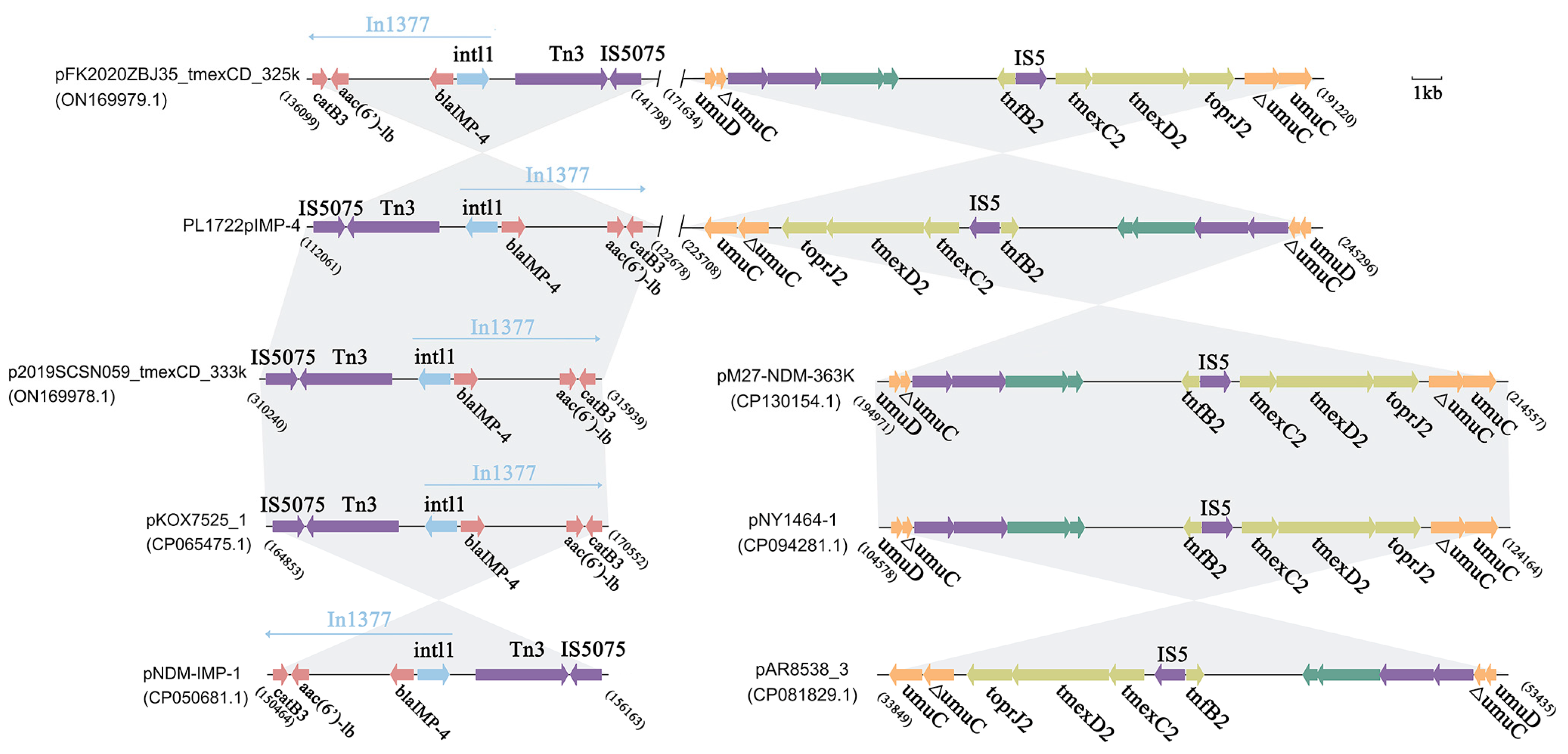
3.4. Structural Analysis of blaIMP-4, tmexCD2-toprJ2 Coexistence Plasmid
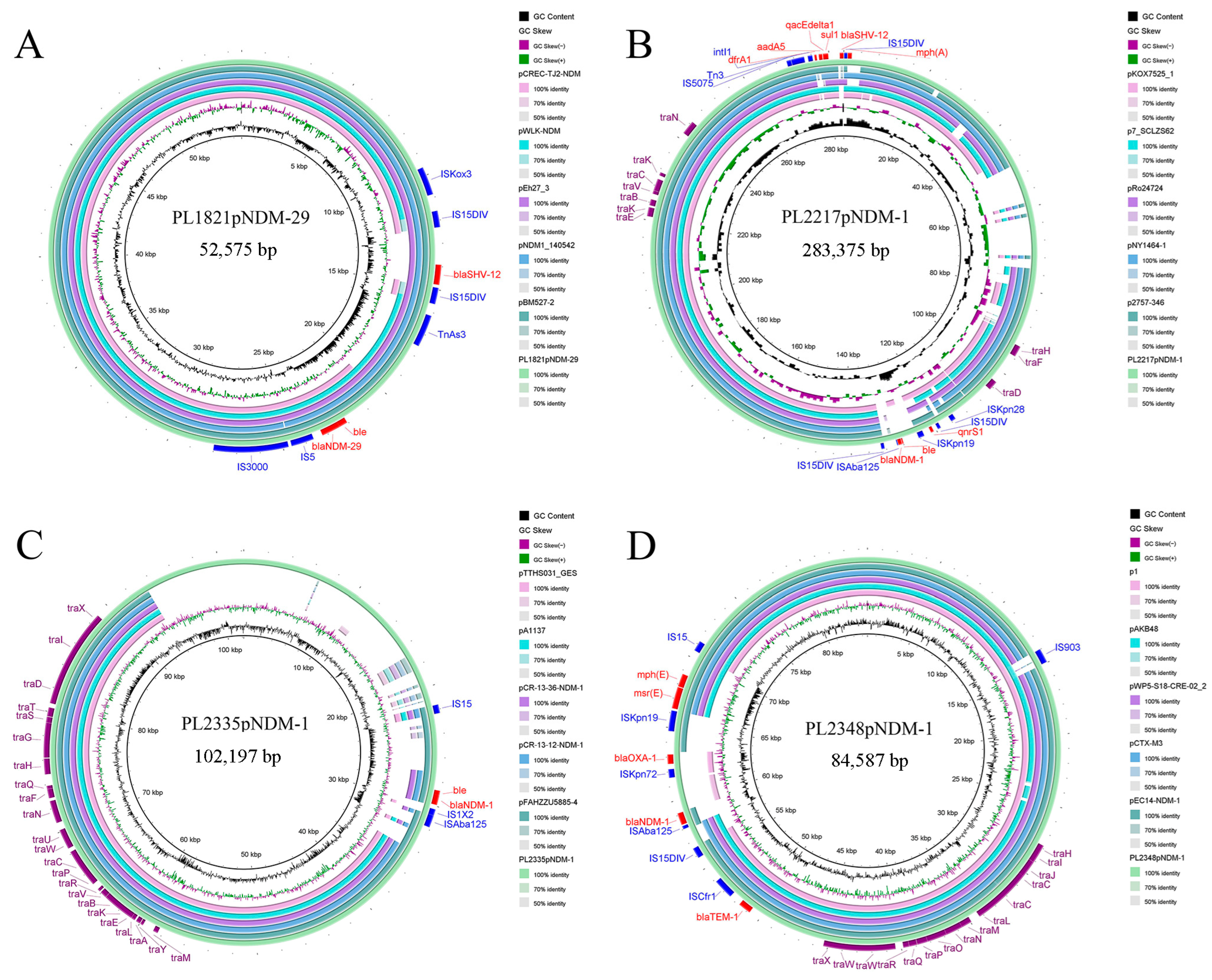
3.5. Genomic Characterization and Comparative Genomic Analysis of Plasmids Carrying blaNDM-1 and blaNDM-29
3.6. Transferable CZA Resistance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, R.M.; Bachman, M.A. Colonization, Infection, and the Accessory Genome of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240093461 (accessed on 22 July 2024).
- Zhang, R.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H.; Chan, E.W.; Li, J.; Fang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liao, K.; Chen, S. Nationwide Surveillance of Clinical Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) Strains in China. eBioMedicine 2017, 19, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Wang, M.; Zhu, D.; Wang, F. CHINET efforts to control antimicrobial resistance in China. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 21, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgul, F.; Bozkurt, I.; Sunbul, M.; Esen, S.; Leblebicioglu, H. Risk factors and mortality in the Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection: Case control study. Pathog. Glob. Health 2016, 110, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Price, L.S.; Poirel, L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Schwaber, M.J.; Daikos, G.L.; Cormican, M.; Cornaglia, G.; Garau, J.; Gniadkowski, M.; Hayden, M.K.; et al. Clinical epidemiology of the global expansion of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemases. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaber, M.J.; Lev, B.; Israeli, A.; Solter, E.; Smollan, G.; Rubinovitch, B.; Shalit, I.; Carmeli, Y.; Israel Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Working Group. Containment of a country-wide outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Israeli hospitals via a nationally implemented intervention. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Sharma, L.; Dela Cruz, C.S.; Zhang, D. Clinical Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Control Strategies of Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 750662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shi, Q.; Hu, H.; Hong, B.; Wu, X.; Du, X.; Akova, M.; Yu, Y. Emergence of ceftazidime/avibactam resistance in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in China. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 124.e1–124.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Cai, Y. Resistance to ceftazidime–avibactam and underlying mechanisms. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, B.; Machuca, I.; Pascual, A. Treatment of Infections Caused by Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase-, AmpC-, and Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00079-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sader, H.S.; Farrell, D.J.; Flamm, R.K.; Jones, R.N. Variation in Potency and Spectrum of Tigecycline Activity against Bacterial Strains from U.S. Medical Centers since Its Approval for Clinical Use (2006 to 2012). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.-D.; Berhin, C.; Bogaerts, P.; Glupczynski, Y. In vitro susceptibility of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae clinical isolates to tigecycline. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2696–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Duin, D.; Cober, E.; Richter, S.S.; Perez, F.; Cline, M.; Kaye, K.S.; Kalayjian, R.C.; Salata, R.A.; Evans, S.; Fowler, V.G.; et al. Tigecycline Therapy for Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (CRKP) Bacteriuria Leads to Tigecycline Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O1117–O1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Shi, Q.; Fu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, Y.; Du, X. Tigecycline resistance caused by rpsJ evolution in a 59-year-old male patient infected with KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae during tigecycline treatment. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 66, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, W.E.; Rybak, M.J. Tigecycline: First of a New Class of Antimicrobial Agents. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2006, 26, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialek-Davenet, S.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Guyot, K.; Mayer, N.; Tournebize, R.; Brisse, S.; Leflon-Guibout, V.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.-H. Differential contribution of AcrAB and OqxAB efflux pumps to multidrug resistance and virulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Wan, M.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Yang, Q.; Partridge, S.R.; Wang, Y.; Zong, Z.; Doi, Y.; Shen, J.; et al. Emergence of a Plasmid-Encoded Resistance-Nodulation-Division Efflux Pump Conferring Resistance to Multiple Drugs, Including Tigecycline, in Klebsiella pneumoniae. mBio 2020, 11, e02930-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Z.; Gao, X.; Yang, Q.-W.; Lv, L.-C.; Wan, M.; Yang, J.; Cai, Z.-P.; Liu, J.-H. A Novel Transferable Resistance-Nodulation-Division Pump Gene Cluster, tmexCD2-toprJ2, Confers Tigecycline Resistance in Raoultella ornithinolytica. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e02229-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xu, G.; Nan-Meng; Li, G.-L.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Mei, C.-Y.; Jiao, X.; Wang, J. Emergence of carbapenem- and tigecycline-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST617. J. Glob. Antimicrob Resist. 2022, 29, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Meng, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Jiao, X.; Wang, J. Distribution and Spread of the Mobilized RND Efflux Pump Gene Cluster tmexCD-toprJ in Klebsiella pneumoniae from Different Sources. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0536422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Peng, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Exploring tet(X)-bearing tigecycline-resistant bacteria of swine farming environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmat Ullah, S.; Irum, S.; Mahnoor, I.; Ismatullah, H.; Mumtaz, M.; Andleeb, S.; Rahman, A.; Jamal, M. Exploring the resistome, virulome, and mobilome of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates: Deciphering the molecular basis of carbapenem resistance. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, T.; Hu, J.; Song, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. Five-year change of prevalence and risk factors for infection and mortality of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infection in a tertiary hospital in north China. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, G.; Lin, M.; Chen, Y.; He, R.; Galvão, K.N.; El-Gawad El-Sayed Ahmed, M.A.; Roberts, A.P.; Wu, Y.; et al. Molecular characterization of carbapenem-resistant and virulent plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae from patients with bloodstream infections in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewardson, A.J.; Marimuthu, K.; Sengupta, S.; Allignol, A.; El-Bouseary, M.; Carvalho, M.J.; Hassan, B.; Delgado-Ramirez, M.A.; Arora, A.; Bagga, R.; et al. Effect of carbapenem resistance on outcomes of bloodstream infection caused by Enterobacteriaceae in low-income and middle-income countries (PANORAMA): A multinational prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, D.; Kordevani, R.; Keller, N.; Tal, I.; Marzel, A.; Gal-Mor, O.; Maor, Y.; Rahav, G. Outcome of carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Sun, Q.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, K.; Chan, E.W.-C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaber, M.J.; Carmeli, Y. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: A potential threat. JAMA 2008, 300, 2911–2913. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Sun, L.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Liu, X. Risk Factors and Mortality of Elderly Patients with Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 6767–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, C.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, H.; Cao, J.; Chen, S.; Lv, H.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Q.; Sun, L.; et al. Prevalence, risk factors and molecular epidemiology of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in patients from Zhejiang, China, 2008–2018. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, T.; He, X.; Shao, J.; Wu, C.; Mao, W.; Jia, H.; He, F.; Kong, Y.; Wu, J.; et al. Global Phylogeography and Genomic Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant blaOXA-232–Carrying Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 15 Lineage. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 29, 2246–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, H.; Yang, X.; Ye, L.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, J.; Chan, E.W.-C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Global genomic profiling of Klebsiella pneumoniae: A spatio-temporal population structure analysis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; Peng, K.; Chen, Q.; Hou, X.; Huang, W.; Lv, H.; Yang, X.; Lei, G.; Li, R. Coexistence of tmexCD-toprJ, blaNDM-1, and blaIMP-4 in One Plasmid Carried by Clinical Klebsiella spp. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00549-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yi, Y.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Jing, H.; Zhu, B.; Liu, C.H. Structural Diversity of Class 1 Integrons and Their Associated Gene Cassettes in Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from a Hospital in China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-W.; Lin, Y.-T.; Yang, T.-C.; Wang, F.-D. Risk Factors, Outcomes, and Mechanisms of Tigecycline-Nonsusceptible Klebsiella pneumoniae Bacteremia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 7357–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, E.-J.; Oh, Y.; Jeong, S.H. Development of Tigecycline Resistance in Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 147 via AcrAB Overproduction Mediated by Replacement of the ramA Promoter. Ann. Lab. Med. 2020, 40, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckman, M.; Petersen, P.J.; Projan, S.J. Mutations in the interdomain loop region of the tetA(A) tetracycline resistance gene increase efflux of minocycline and glycylcyclines. Microb. Drug Resist. 2000, 6, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Xu, Z.; Lv, L.; Chen, S.; Hong, M.; Liu, J.-H. Promoter regulatory mode evolution enhances the high multidrug resistance of tmexCD1-toprJ1. mBio 2024, 15, e00218-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, Q.; Su, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, C. Persistent ciprofloxacin exposure induced the transformation of Klebsiella pneumoniae small colony variant into mucous phenotype. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1259296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, T.; Peng, K.; Peng, J.; Liu, X.; Xia, Z.; Chi, L.; Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; et al. Conjugative plasmids facilitate the transmission of tmexCD2-toprJ2 among carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-L.; Lai, C.-C.; Tsai, Y.-W.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. High ceftazidime-avibactam resistance among carbapenem-resistant Enterobacter species: Data from the Antimicrobial Testing Leadership and Surveillance (ATLAS) programme, 2014–2021. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, Q.; Jin, L.; Wang, H. The transferability and evolution of NDM-1 and KPC-2 co-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae from clinical settings. eBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boralli, C.M.D.S.; Paganini, J.A.; Meneses, R.S.; Mata, C.P.S.M.D.; Leite, E.M.M.; Schürch, A.C.; Paganelli, F.L.; Willems, R.J.L.; Camargo, I.L.B.C. Characterization of blaKPC-2 and blaNDM-1 Plasmids of a K. pneumoniae ST11 Outbreak Clone. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, B.; Wang, G.; Long, H.; Zhou, Y. Whole genome sequence of blaNDM and blaKPC co-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate KSH203 with capsular serotype K25 belonging to ST11 from China. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 20, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Li, Q.; Zhang, F.; Ding, M.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y. Characterisation of blaNDM-5 and blaKPC-2 co-occurrence in K64-ST11 carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 27, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Primer | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| ramA | ramA-F | ACGATTTCCGCTCAGGTGATT |
| ramA-R | CAATACGCAGCGGTTGATGC | |
| ramR | ramR-F | CAGCTGGCACATTTCGTTGA |
| ramR-R | GCTATATCGACTGGGGCGTG | |
| rarA | rarA-F | TGCGGCCAGAAAATTTAGCG |
| rarA-R | TTACCGCTGAGATCCGTTCG | |
| soxS | soxS-F soxS-R | GCATCACGGTACGGAACATC AGTCGCCAGAAAGTCAGGATAC |
| acrA | acrA-F | TTTGTTCTGATGGCGCGTTG |
| acrA-R | CCAGGTCACTGCTTCTCAGG | |
| acrB | acrB-F | GATCATCGGCACCACGGTAT |
| acrB-R | ACAGCGACGGGATAAACAGG | |
| oqxA | oqxA-F | GGTGCTGGTGAAGTCGATCA |
| oqxA-R | CAATGTATCCCGAGACGCGA | |
| oqxB | oqxB-F | CAACTACGCCACGCTGAAAG |
| oqxB-R | GGACGTTTTGCTCCTGCATC | |
| tolC | tolC-F | TTTACCGCGCCAGGGTTATC |
| tolC-R | CAGCAGGAAAATGCGCTCAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni, Y.; Peng, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Qian, H. Emergence of Tigecycline-Nonsusceptible Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with Metallo-β-Lactamase and Transferable Ceftazidime-Avibactam Resistance in China. Pathogens 2025, 14, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030253
Ni Y, Peng J, Xu Y, Zhu L, Wang X, Jin H, Qian H. Emergence of Tigecycline-Nonsusceptible Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with Metallo-β-Lactamase and Transferable Ceftazidime-Avibactam Resistance in China. Pathogens. 2025; 14(3):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030253
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi, Yajuan, Jiefu Peng, Yawen Xu, Liguo Zhu, Xiao Wang, Hui Jin, and Huimin Qian. 2025. "Emergence of Tigecycline-Nonsusceptible Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with Metallo-β-Lactamase and Transferable Ceftazidime-Avibactam Resistance in China" Pathogens 14, no. 3: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030253
APA StyleNi, Y., Peng, J., Xu, Y., Zhu, L., Wang, X., Jin, H., & Qian, H. (2025). Emergence of Tigecycline-Nonsusceptible Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with Metallo-β-Lactamase and Transferable Ceftazidime-Avibactam Resistance in China. Pathogens, 14(3), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14030253






