Antimicrobial Resistance and Risk Factors of Canine Bacterial Skin Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample and Isolates Collection
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. Retrospective Analysis of Risk Factors for MRSP Infection
2.4. Whole Genome Sequencing of S. pseudintermedius and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis of aacA-aphD Expression
3. Results
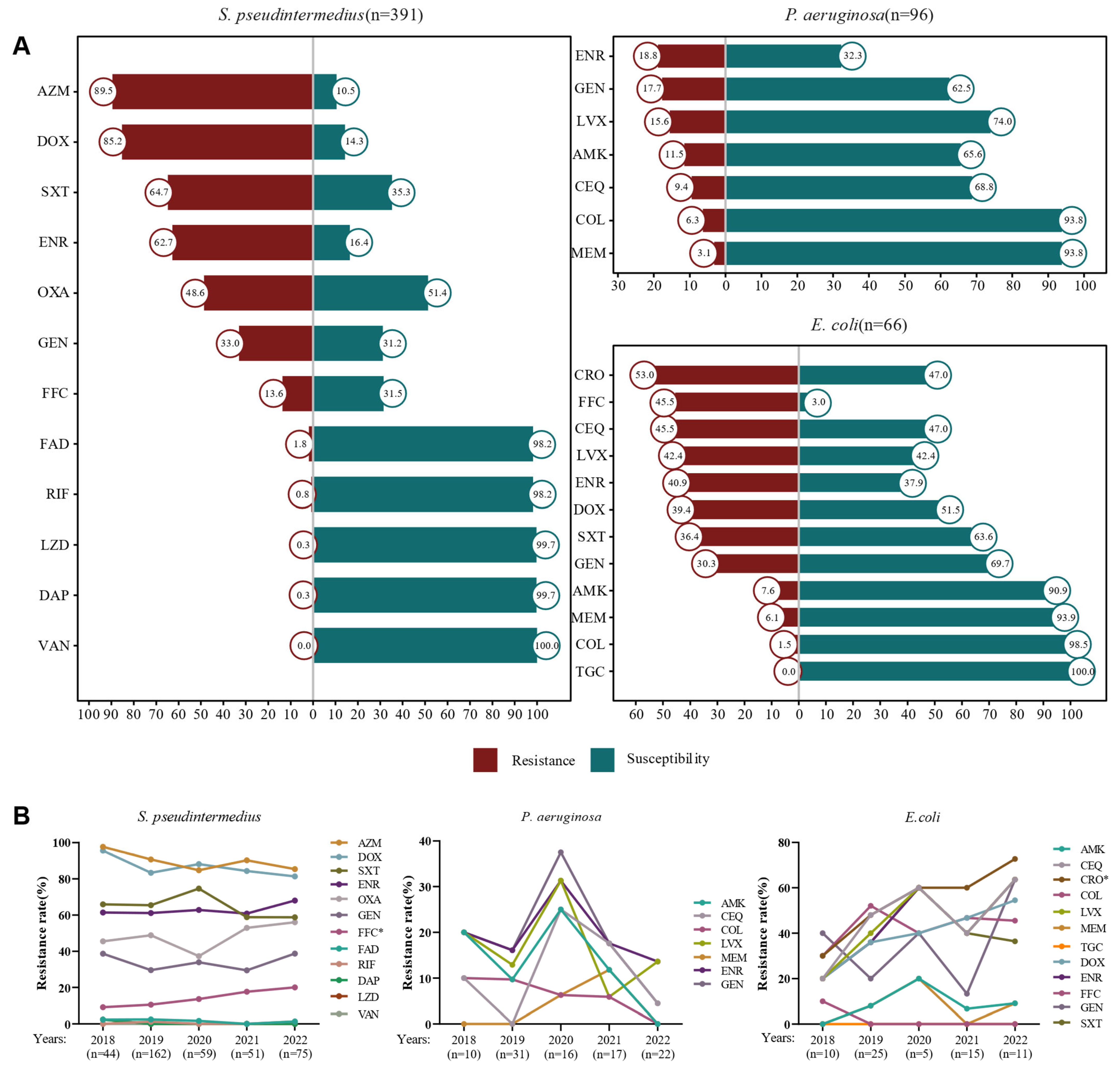
3.1. Isolation of Bacterial Strains and Antimicrobial Resistance Analysis
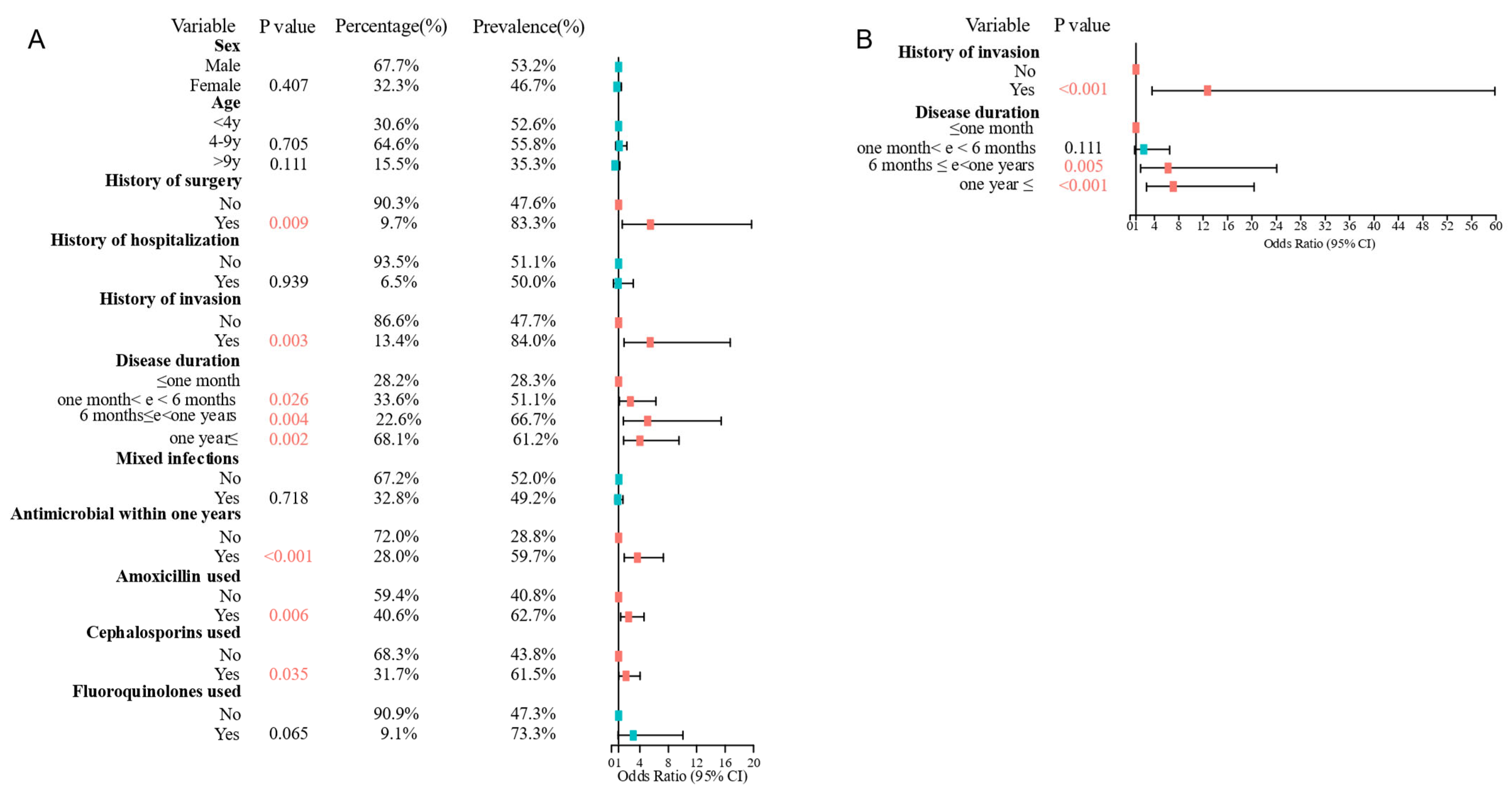
3.2. Retrospective Analysis of Canine Bacterial Skin Infection Cases
3.3. Risk Factors for MRSP Infections Were History of Invasion and Disease Duration
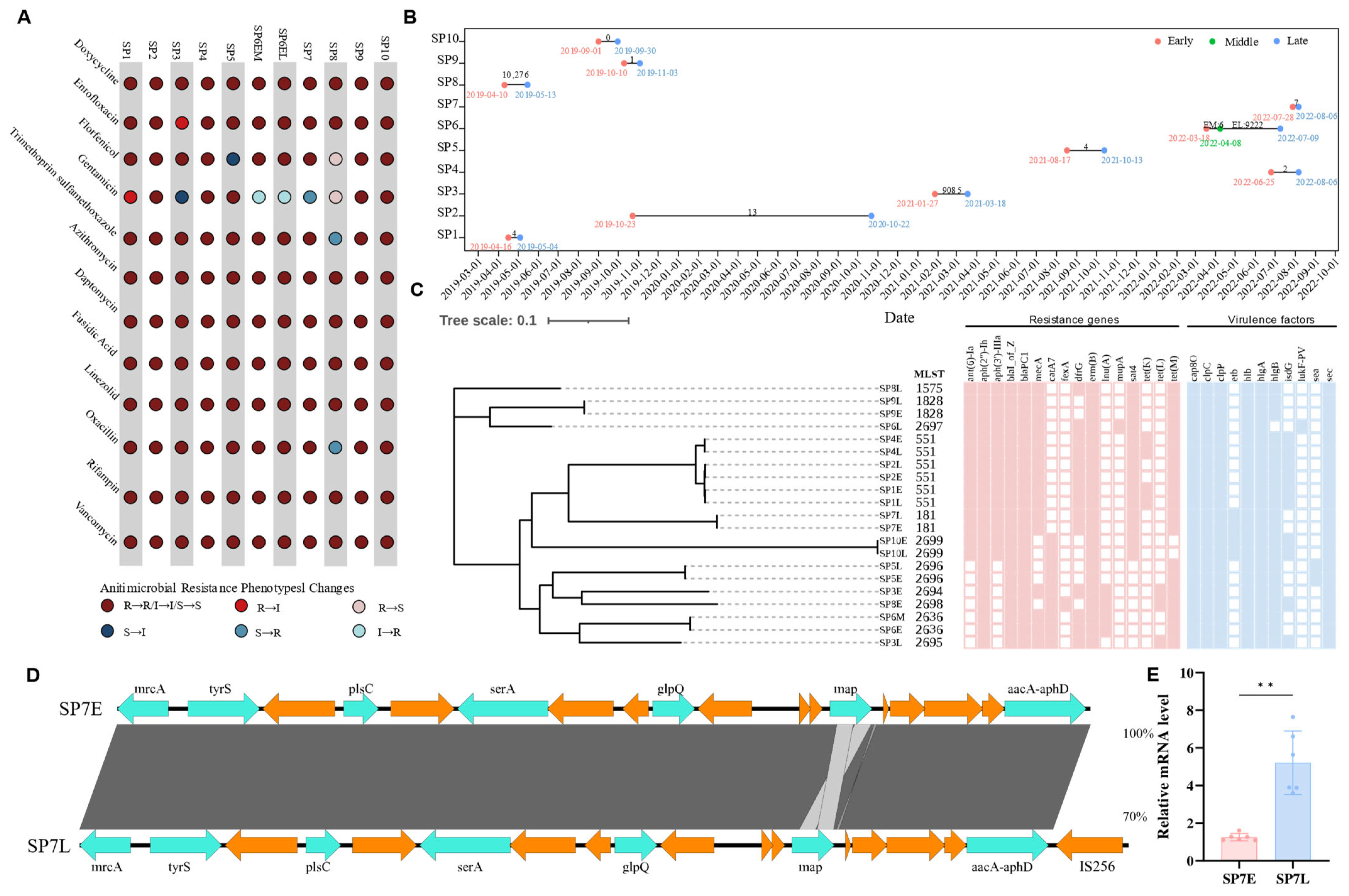
3.4. Genomic and Phenotypic Insights into Antimicrobial Resistance in S. pseudintermedius
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eyerich, S.; Eyerich, K.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Biedermann, T. Cutaneous Barriers and Skin Immunity: Differentiating A Connected Network. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, C.; de Jong, A.; Moyaert, H.; El Garch, F.; Janes, R.; Klein, U.; Morrissey, I.; Thiry, J.; Youala, M. Antimicrobial susceptibility monitoring of dermatological bacterial pathogens isolated from diseased dogs and cats across Europe (ComPath results). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escher, M.; Vanni, M.; Intorre, L.; Caprioli, A.; Tognetti, R.; Scavia, G. Use of antimicrobials in companion animal practice: A retrospective study in a veterinary teaching hospital in Italy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler, A.; Lloyd, D.H. What has changed in canine pyoderma? A narrative review. Vet. J. 2018, 235, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, S.A.; Helbig, K.J. The Complex Diseases of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Canines: Where to Next? Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattab, J.; Mosca, F.; Di Francesco, C.E.; Aste, G.; Marruchella, G.; Guardiani, P.; Tiscar, P.G. Occurrence, antimicrobial susceptibility, and pathogenic factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in canine clinical samples. Vet. World 2021, 14, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Belas, A.; Franco, A.; Aboim, C.; Gama, L.T.; Pomba, C. Increase in antimicrobial resistance and emergence of major international high-risk clonal lineages in dogs and cats with urinary tract infection: 16 year retrospective study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardabassi, L.; Schwarz, S.; Lloyd, D.H. Pet animals as reservoirs of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompilio, A.; De Nicola, S.; Crocetta, V.; Guarnieri, S.; Savini, V.; Carretto, E.; Di Bonaventura, G. New insights in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius pathogenicity: Antibiotic-resistant biofilm formation by a human wound-associated strain. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Robb, A.R.; Wright, E.D.; Foster, A.M.E.; Walker, R.; Malone, C. Skin infection caused by a novel strain of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in a Siberian husky dog owner. JMM Case Rep. 2017, 4, e005087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventrella, G.; Moodley, A.; Grandolfo, E.; Parisi, A.; Corrente, M.; Buonavoglia, D.; Guardabassi, L. Frequency, antimicrobial susceptibility and clonal distribution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in canine clinical samples submitted to a veterinary diagnostic laboratory in Italy: A 3-year retrospective investigation. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 211, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weese, J.S.; van Duijkeren, E. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in veterinary medicine. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullahi, I.N.; Zarazaga, M.; Campaña-Burguet, A.; Eguizábal, P.; Lozano, C.; Torres, C. Nasal Staphylococcus aureus and S. pseudintermedius carriage in healthy dogs and cats: A systematic review of their antibiotic resistance, virulence and genetic lineages of zoonotic relevance. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 3368–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-H.; Ma, Y.-C.; Shia, W.-Y.; Hsieh, Y.-L.; Wang, C.-M. Risk Factors for Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus Species Isolated from Dogs with Superficial Pyoderma and Their Owners. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saputra, S.; Jordan, D.; Worthing, K.A.; Norris, J.M.; Wong, H.S.; Abraham, R.; Trott, R.J.; Abraham, S. Antimicrobial resistance in coagulase-positive staphylococci isolated from companion animals in Australia: A one year study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e176379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chen, S.; Lyu, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Dang, X.; An, Q.; Song, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Gong, X.; et al. China antimicrobial resistance surveillance network for pets (CARPet), 2018 to 2021. One Health Adv. 2023, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically (M07), 11th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals, 5th ed.; CLSI supplement VET01S; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; CLSI supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar]
- Treangen, T.J.; Ondov, B.D.; Koren, S.; Phillippy, A.M. The Harvest suite for rapid core-genome alignment and visualization of thousands of intraspecific microbial genomes. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 524. [Google Scholar]
- Inouye, M.; Dashnow, H.; Raven, L.A.; Schultz, M.B.; Pope, B.J.; Tomita, T.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. SRST2: Rapid genomic surveillance for public health and hospital microbiology labs. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Haft, D.H.; Prasad, A.B.; Slotta, D.J.; Tolstoy, I.; Tyson, G.H.; Zhao, S.; Hsu, C.-H.; McDermott, P.F.; et al. Validating the AMRFinder Tool and Resistance Gene Database by Using Antimicrobial Resistance Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in a Collection of Isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00483-19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis--10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar]
- Deatherage, D.E.; Barrick, J.E. Identification of mutations in laboratory-evolved microbes from next-generation sequencing data using breseq. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1151, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dinkova, V.; Rusenova, N. A Retrospective Study (2019–2023) on the Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Isolates from Canine Clinical Samples Submitted to the University Veterinary Hospital in Stara Zagora, Bulgaria. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocera, F.P.; Ambrosio, M.; Fiorito, F.; Cortese, L.; De Martino, L. On Gram-Positive- and Gram-Negative-Bacteria-Associated Canine and Feline Skin Infections: A 4-Year Retrospective Study of the University Veterinary Microbiology Diagnostic Laboratory of Naples, Italy. Animals 2021, 11, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, A.; Youala, M.; El Garch, F.; Simjee, S.; Rose, M.; Morrissey, I.; Moyaert, H. Antimicrobial susceptibility monitoring of canine and feline skin and ear pathogens isolated from European veterinary clinics: Results of the ComPath Surveillance programme. Vet. Dermatol. 2020, 31, 431-e114. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, V.; Zhelev, G.; Marutsov, P.; Koev, K.; Georgieva, S.; Toneva, I.; Urumova, V. Microbiological and antibacterial resistance profile in canine otitis externa-a comparative analysis. Bulg. J. Vet. Med. 2019, 22, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, C.; Thiry, D.; Taminiau, B.; Daube, G.; Fontaine, J. External Ear Canal Evaluation in Dogs with Chronic Suppurative Otitis Externa: Comparison of Direct Cytology, Bacterial Culture and 16S Amplicon Profiling. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, A.; Lloyd, D.H.; Weese, J.S.; Blondeau, J.M.; Boothe, D.; Breitschwerdt, E.; Guardabassi, L.; Papich, M.G.; Rankin, S.; Turnidge, J.D.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and antimicrobial therapy of canine superficial bacterial folliculitis (Antimicrobial Guidelines Working Group of the International Society for Companion Animal Infectious Diseases). Vet. Dermatol. 2014, 25, 163-e43. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Chung, T.; Hwang, C. Clonal distribution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates from skin infection of dogs in Korea. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 210, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Viegas, F.M.; Santana, J.A.; Silva, B.A.; Xavier, R.G.C.; Bonisson, C.T.; Câmara, J.L.S.; Rennó, M.C.; Cunha, J.L.R.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Lobato, F.C.F.; et al. Occurrence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus spp. in diseased dogs in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e269422. [Google Scholar]
- Duim, B.; Verstappen, K.M.; Broens, E.M.; Laarhoven, L.M.; van Duijkeren, E.; Hordijk, J.; de Heus, P.; Spaninks, M.; Timmerman, A.J.; Wagenaar, J.A. Changes in the Population of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and Dissemination of Antimicrobial-Resistant Phenotypes in the Netherlands. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Morais, C.; Costa, S.S.; Leal, M.; Ramos, B.; Andrade, M.; Ferreira, C.; Abrantes, P.; Pomba, C.; Couto, I. Genetic diversity and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius associated with skin and soft-tissue infections in companion animals in Lisbon, Portugal. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1167834. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.F.; McEwan, N.A. Staphylococcal and micrococcal adherence to canine and feline corneocytes: Quantification using a simple adhesion assay. Vet. Dermatol. 2007, 18, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Nocera, F.P.; Pizzano, F.; Masullo, A.; Cortese, L.; De Martino, L. Antimicrobial Resistant Staphylococcus Species Colonization in Dogs, Their Owners, and Veterinary Staff of the Veterinary Teaching Hospital of Naples, Italy. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehner, G.; Linek, M.; Bond, R.; Lloyd, D.H.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Thom, N.; Straube, I.; Verheyen, K.; Loeffler, A. Case-control risk factor study of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (MRSP) infection in dogs and cats in Germany. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Song, L.; Wang, B.; Shang, J.; Yue, X.; Qu, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; et al. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance among Escherichia coli from chicken and swine, China, 2008–2015. Vet Microbiol 2017, 203, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q. Research on the veterinary antimicrobial use and characteristics of antimicrobial resistance among Escherichia coli from pigs/chickens in China. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University College of Veterinary Medicine, Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Heyvaert, L.; Treier, A.; Zurfluh, K.; Cernela, N.; Biggel, M.; Stephan, R. High occurrence of Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, and Vagococcus lutrae harbouring oxazolidinone resistance genes in raw meat-based diets for companion animals-a public health issue, Switzerland, September 2018 to May 2020. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200496. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S. Antimicrobial Resistance Detection and Analysis of Enterobacteriaceae bacteria from Food Sources of Dogs and Cats. Master’s Thesis, China Agricultural University College of Veterinary Medicine, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Fan, R.; Wang, Y.; Lei, L.; Feßler, A.T.; Wang, Z.; Wu, C.; Schwarz, S.; Wang, Y. Analysis of combined resistance to oxazolidinones and phenicols among bacteria from dogs fed with raw meat/vegetables and the respective food items. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15500. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Plésiat, P.; Nikaido, H. The challenge of efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 337–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arais, L.R.; Barbosa, A.V.; Carvalho, C.A.; Cerqueira, A.M. Antimicrobial resistance, integron carriage, and gyrA and gyrB mutations in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from dogs with otitis externa and pyoderma in Brazil. Vet. Dermatol. 2016, 27, 113-e31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dégi, J.; Moțco, O.; Dégi, D.M.; Suici, T.; Mareș, M.; Imre, K.; Cristina, R.T. Antibiotic Susceptibility Profile of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Canine Isolates from a Multicentric Study in Romania. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y. Investigatin on Antibiotics Resistance and Molecular Characteristics of Clinical Escherichia coli isolates from Dogs and Cats in Beijing. Ph.D. Thesis, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- QYResearch. China Pets Anti-Infective Drugs Market Status and Forecast. 2021–2027; QYResearch: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Li, T.; Cheng, M.; Sun, H.; Cui, M.; Zhang, C.; Xu, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, C. Current status and trends in antimicrobial use in food animals in China, 2018–2020. One Health Adv. 2023, 1, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Key, F.M.; Khadka, V.D.; Romo-González, C.; Blake, K.J.; Deng, L.; Lynn, T.C.; Lee, J.C.; Chiu, I.M.; García-Romero, M.T.; Lieberman, T.D. On-person adaptive evolution of Staphylococcus aureus during treatment for atopic dermatitis. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 593–603. [Google Scholar]
- Fazakerley, J.; Williams, N.; Carter, S.; McEwan, N.; Nuttall, T. Heterogeneity of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates from atopic and healthy dogs. Vet. Dermatol. 2010, 21, 578–585. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, T. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of Two Oxacillin-Resistant and mecA-Positive Strains of Staphylococcus haemolyticus Isolated from Ear Swab Samples of Patients with Otitis Media. Infect. Ddrug Resist. 2024, 17, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Casagrande Proietti, P.; Bietta, A.; Coletti, M.; Marenzoni, M.L.; Scorza, A.V.; Passamonti, F. Insertion sequence IS256 in canine pyoderma isolates of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius associated with antibiotic resistance. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 157, 376–382. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, S.; Nsofor, C.A.; Thitiananpakorn, K.; Tan, X.-E.; Aiba, Y.; Takenouchi, R.; Kiga, K.; Sasahara, T.; Miyanaga, K.; Veeranarayanan, S.; et al. Metabolic remodeling by RNA polymerase gene mutations is associated with reduced β-lactam susceptibility in oxacillin-susceptible MRSA. mBio 2024, 15, e33924. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Lei, H.; Liang, H.; Li, X.; Li, B. The development of variation-based rifampicin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus deciphered through genomic and transcriptomic study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130112. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.A.; Lamers, M.H. Novel Antibiotics Targeting Bacterial Replicative DNA Polymerases. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanborough, T.; Ho, N.A.T.; Bulloch, E.M.M.; Bashiri, G.; Dawes, S.S.; Akazong, E.W.; Titterington, J.; Allison, T.M.; Jiao, W.; Johnston, J.M. Allosteric inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus MenD by 1,4-dihydroxy naphthoic acid: A feedback inhibition mechanism of the menaquinone biosynthesis pathway. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2023, 378, 20220035. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, V.M.; Deringer, J.R.; Callantine, S.D.; Deobald, C.F.; Berger, P.H.; Kapur, V.; Stauffacher, C.V.; Bohach, G.A. Characterization of the canine type C enterotoxin produced by Staphylococcus intermedius pyoderma isolates. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 2346–2352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, I.M.; de Moraes Assumpção, Y.; Paletta, A.C.C.; Antunes, M.; da Silva, I.T.; Jaeger, L.H.; Ferreira, R.F.; de Oliveira Ferreira, E.; de Araújo Penna, B. Investigation on biofilm composition and virulence traits of S. pseudintermedius isolated from infected and colonized dogs. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 2923–2936. [Google Scholar]
- Springer, M.T.; Singh, V.K.; Cheung, A.L.; Donegan, N.P.; Chamberlain, N.R. Effect of clpP and clpC deletion on persister cell number in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 848–857. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Chen, S.; Ma, S.; Jiao, Y.; Hong, H.; Wang, S.; Huang, W.; An, Q.; Song, Y.; Dang, X.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance and Risk Factors of Canine Bacterial Skin Infections. Pathogens 2025, 14, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040309
Wang Q, Chen S, Ma S, Jiao Y, Hong H, Wang S, Huang W, An Q, Song Y, Dang X, et al. Antimicrobial Resistance and Risk Factors of Canine Bacterial Skin Infections. Pathogens. 2025; 14(4):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040309
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qian, Siyu Chen, Shizhen Ma, Ying Jiao, Huiyi Hong, Siying Wang, Wei Huang, Qi An, Yu Song, Xukun Dang, and et al. 2025. "Antimicrobial Resistance and Risk Factors of Canine Bacterial Skin Infections" Pathogens 14, no. 4: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040309
APA StyleWang, Q., Chen, S., Ma, S., Jiao, Y., Hong, H., Wang, S., Huang, W., An, Q., Song, Y., Dang, X., Zhang, G., Ding, H., Wang, Y., Xia, Z., Wang, L., & Lyu, Y. (2025). Antimicrobial Resistance and Risk Factors of Canine Bacterial Skin Infections. Pathogens, 14(4), 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14040309




