Antiparasitic Activity of Chalepensin and Graveoline Isolated from Ruta chalepensis L.: In Vitro Evaluation Against Strongyloides venezuelensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
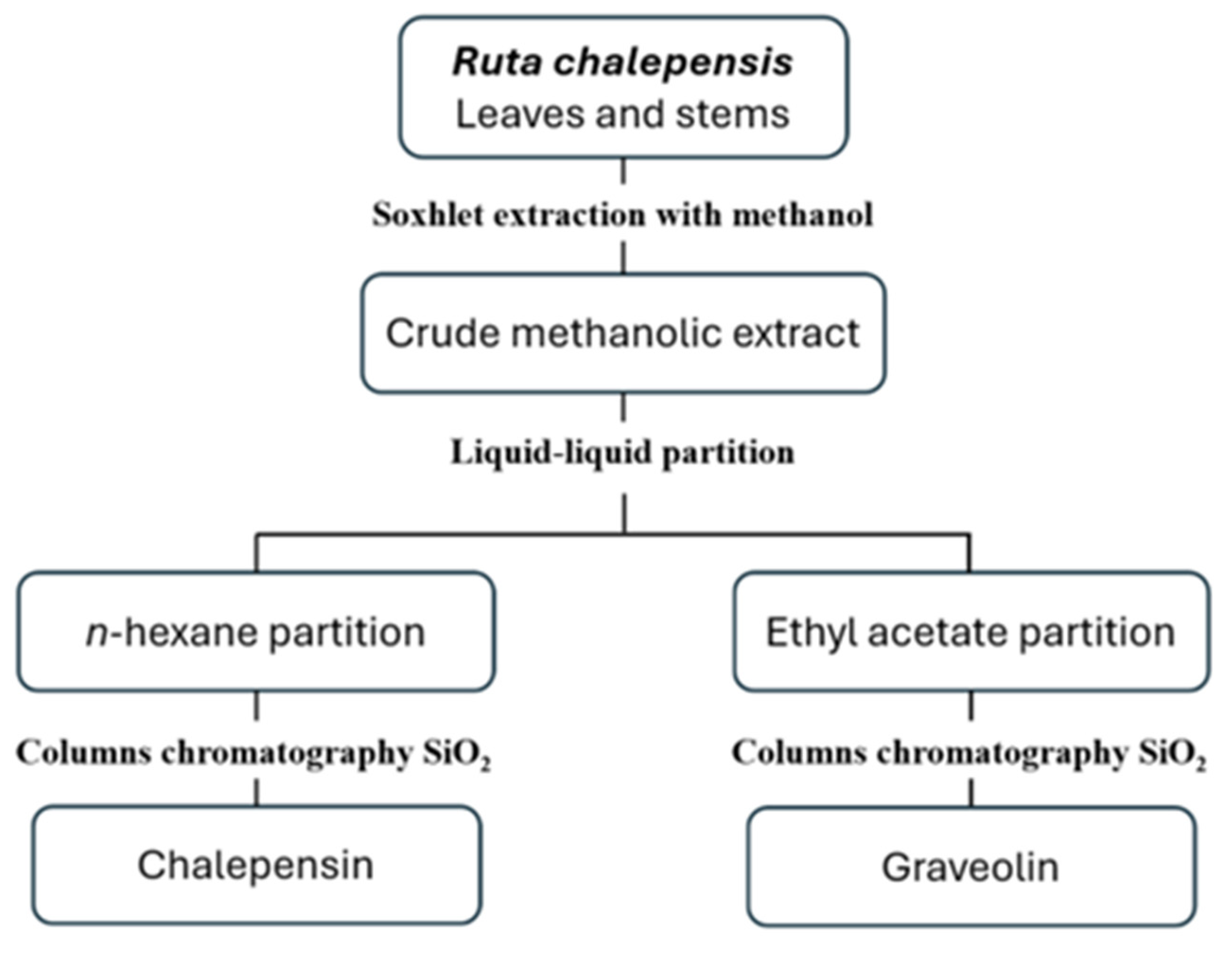
2.1. Plant Material and Isolation of Compounds
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Nematocidal Activity of Compounds Against Strongyloides venezuelensis
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) on Parthenogenetic Females of Strongyloides venezuelensis
2.5. Cytotoxic Activity of Compounds in Vero Cells
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
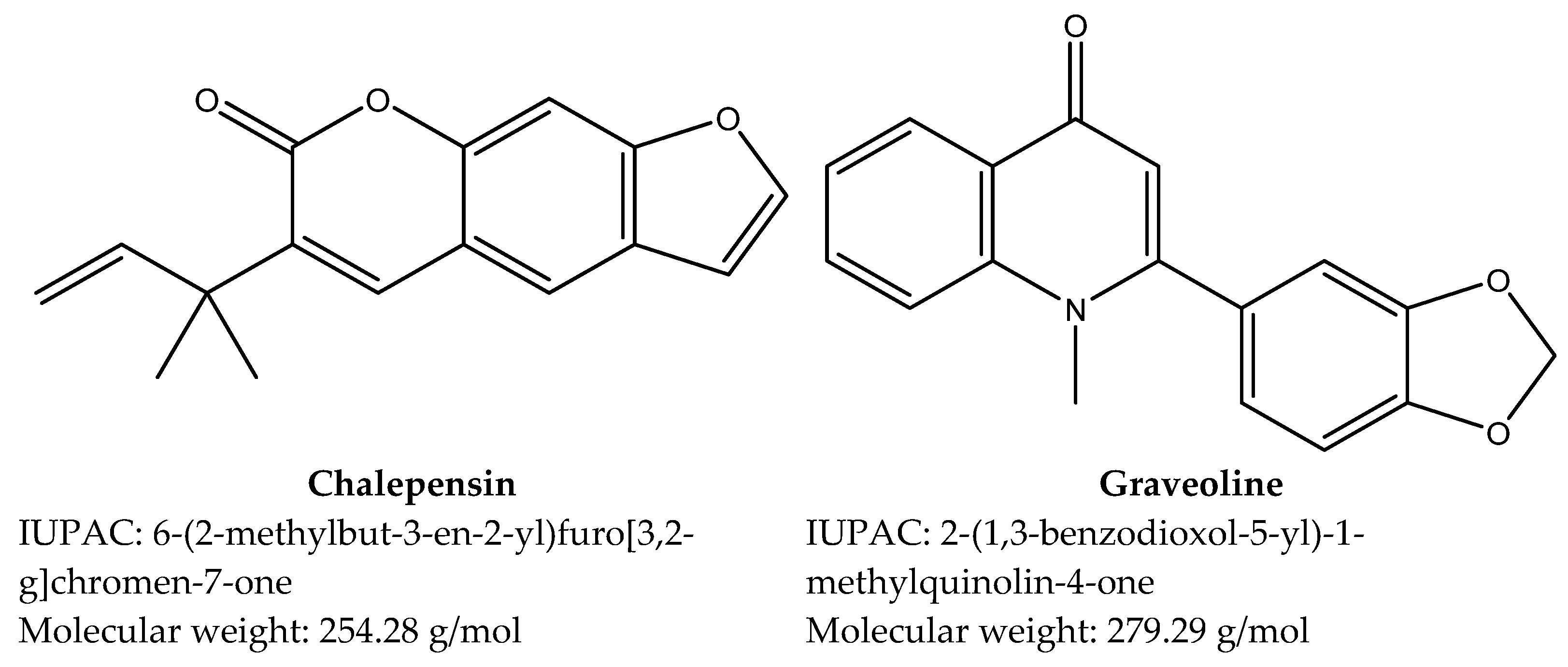
3.1. Compounds Isolated from Ruta chalepensis
3.2. In Vitro Toxicity Against Vero Cells and Nematocidal Activity of Compounds Against Strongyloides venezuelensis L3
3.3. In Vitro Nematocidal Activity of Compounds in Strongyloides venezuelensis Adults
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nag, V.L.; Kalita, J.M. Epidemiology of Parasitic Infections. In Textbook of Parasitic Zoonoses; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Eslahi, A.V.; Hashemipour, S.; Olfatifar, M.; Houshmand, E.; Hajialilo, E.; Mahmoudi, R.; Badri, M.; Ketzis, J.K. Global Prevalence and Epidemiology of Strongyloides stercoralis in Dogs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Parasit. Vectors 2022, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslahi, A.V.; Badri, M.; Nahavandi, K.H.; Houshmand, E.; Dalvand, S.; Riahi, S.M.; Johkool, M.G.; Asadi, N.; Hoseini Ahangari, S.A.; Taghipour, A.; et al. Prevalence of Strongyloidiasis in the General Population of the World: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pathog. Glob. Health 2021, 115, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonfrate, D.; Bisanzio, D.; Giorli, G.; Odermatt, P.; Fürst, T.; Greenaway, C.; French, M.; Reithinger, R.; Gobbi, F.; Montresor, A.; et al. The Global Prevalence of Strongyloides stercoralis Infection. Pathogens 2020, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luvira, V.; Siripoon, T.; Phiboonbanakit, D.; Somsri, K.; Watthanakulpanich, D.; Dekumyoy, P. Strongyloides stercoralis: A Neglected but Fatal Parasite. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 7, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanam, L.S.K.; Basavraj, G.K.; Papireddy, C.K.R. Strongyloides stercoralis Hyper Infection Syndrome. Indian J. Surg. 2021, 83, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.Y.; Aggarwal, S.; Carrig, M.; Azeem, A.; Nguyen, A.; Devries, S.; Destache, C.; Nguyen, T.; Velagapudi, M. Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in Humans: A Narrative Review of the Most Neglected Parasitic Disease. Cureus 2023, 15, e46908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.A.; Utzinger, J.; Muhi, S.; Becker, S.L.; Keiser, J.; Khieu, V.; Gray, D.J. Strongyloidiasis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2024, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.M.; Ozdemir, C.; Reza, N. Strongyloides stercoralis Infection in the UK: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Published Cases. Clin. Med. 2024, 24, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez-Camacho, C.; Pérez-Molina, J.A.; Buonfrate, D.; Rodari, P.; Gotuzzo, E.; Luengo, B.; Plana, M.N. Ivermectin vs Moxidectin for Treating Strongyloides stercoralis Infection: A Systematic Review. Parasitology 2025, 151, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czeresnia, J.M.; Weiss, L.M. Strongyloides stercoralis. Lung 2022, 200, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamesipour, F.; Kheyri, P.; Shojaat, S.; Chelgerdi Dehkordi, B.; Basirpour, B.; Afzal, S.S.; Hejazi, S.H. A Review of the Effect of Medicinal Plant on Helminthic Infections. Infect. Dis. Herb. Med. 2021, 2, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, S.; Armson, A.; Lymbery, A.J.; Zahedi, A.; Ash, A. Medicinal Plants as a Source of Antiparasitics: An Overview of Experimental Studies. Pathog. Glob. Health 2023, 117, 535–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Garza, N.E.; Gomez-Flores, R.; Quintanilla-Licea, R.; Elizondo-Luévano, J.H.; Romo-Sáenz, C.I.; Marín, M.; Sánchez-Montejo, J.; Muro, A.; Peláez, R.; López-Abán, J. In Vitro Anthelmintic Effect of Mexican Plant Extracts and Partitions Against Trichinella spiralis and Strongyloides venezuelensis. Plants 2024, 13, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, A.T.; Ferreira, S.; Duarte, A.P. Genus Ruta: A Natural Source of High Value Products with Biological and Pharmacological Properties. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 260, 113076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla-Licea, R.; Mata-Cárdenas, B.; Vargas-Villarreal, J.; Bazaldúa-Rodríguez, A.; Kavimngeles-Hernández, I.; Garza-González, J.; Hernández-García, M. Antiprotozoal Activity against Entamoeba histolytica of Plants Used in Northeast Mexican Traditional Medicine. Bioactive Compounds from Lippia graveolens and Ruta chalepensis. Molecules 2014, 19, 21044–21065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessalegn Asmelashe, G.; Abdelwuhab, M.; Asrie, A.B. In Vivo Antiplasmodial Activity Evaluation of the Leaves of Ruta chalepensis L. (Rutaceae) against Plasmodium berghei. Discov. Phytomedicine 2017, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntalli, N.G.; Manconi, F.; Leonti, M.; Maxia, A.; Caboni, P. Aliphatic Ketones from Ruta chalepensis (Rutaceae) Induce Paralysis on Root Knot Nematodes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7098–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortu, E.; Sanna, G.; Scala, A.; Pulina, G.; Caboni, P.; Battacone, G. In Vitro Anthelmintic Activity of Active Compounds of the Fringed Rue Ruta chalepensis against Dairy Ewe Gastrointestinal Nematodes. J. Helminthol. 2017, 91, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasso-Díaz, G.; Torres-Hernández, G.; Zamilpa, A.; Becerril-Pérez, C.M.; Ramírez-Bribiesca, J.E.; Hernández-Mendo, O.; Sánchez-Arroyo, H.; Olmedo-Juárez, A.; González-Cortazar, M.; Mendoza-De Gives, P. Ruta chalepensis Full Extract and Organic Phases Exhibit Nematocidal Activity against Haemonchus contortus Eggs and Infective Larvae (L3). Helminthologia 2022, 59, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, P.J.; Shnawa, B.H.; Hamad, S.M.; Hamad, B.S.; Ahmed, M.H. The Efficiency of Fabricated Ag/ZnO Nanocomposite Using Ruta chalepensis L. Leaf Extract as a Potent Protoscolicidal and Anti-Hydatid Cysts Agent. J. Biomater. Appl. 2023, 38, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaldúa-Rodríguez, A.F.; Quintanilla-Licea, R.; Verde-Star, M.J.; Hernández-García, M.E.; Vargas-Villarreal, J.; Garza-González, J.N. Furanocoumarins from Ruta chalepensis with Amebicide Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elizondo-Luévano, J.H.; Rodríguez-Garza, N.E.; Bazaldúa-Rodríguez, A.F.; Romo-Sáenz, C.I.; Tamez-Guerra, P.; Verde-Star, M.J.; Gomez-Flores, R.; Quintanilla-Licea, R. Cytotoxic, Anti-Hemolytic, and Antioxidant Activities of Ruta chalepensis L. (Rutaceae) Extract, Fractions, and Isolated Compounds. Plants 2023, 12, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla-Licea, R.; Mata-Cárdenas, B.; Vargas-Villarreal, J.; Bazaldúa-Rodríguez, A.; Verde-Star, M. Antiprotozoal Activity against Entamoeba histolytica of Furocoumarins Isolated from Ruta chalepensis. Planta Med. 2016, 81, S1–S381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, Y.; Palomares-Rius, J.E.; Hino, A.; Afrin, T.; Mondal, S.I.; Nakatake, A.; Maruyama, H.; Kikuchi, T. Secretome Analysis of Strongyloides venezuelensis Parasitic Stages Reveals That Soluble and Insoluble Proteins Are Involved in Its Parasitism. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, M.; Sánchez-Montejo, J.; Ramos, S.; Muro, A.; López-Abán, J.; Peláez, R. Deciphering Chemical Rules for Drug Penetration into Strongyloides. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, K.A.; El-Neketi, M.; Lahloub, M.-F.; Elbermawi, A. Nanoemulsions of Jasminum humile L. and Jasminum grandiflorum L. Essential Oils: An Approach to Enhance Their Cytotoxic and Antiviral Effects. Molecules 2022, 27, 3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Majmaie, S.; Nahar, L.; Rahman, M.M.; Nath, S.; Saha, P.; Talukdar, A.D.; Sharples, G.P.; Sarker, S.D. Anti-MRSA Constituents from Ruta chalepensis (Rutaceae) Grown in Iraq, and In Silico Studies on Two of Most Active Compounds, Chalepensin and 6-Hydroxy-Rutin 3′,7-Dimethyl Ether. Molecules 2021, 26, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juneja, K.; Beuerle, T.; Sircar, D. Enhanced Accumulation of Biologically Active Coumarin and Furanocoumarins in Callus Culture and Field-grown Plants of Ruta chalepensis Through LED Light-treatment. Photochem. Photobiol. 2022, 98, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, L.; Al-Majmaie, S.; Al-Groshi, A.; Rasul, A.; Sarker, S.D. Chalepin and Chalepensin: Occurrence, Biosynthesis and Therapeutic Potential. Molecules 2021, 26, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Mu, C.; Wang, B.; Jin, J. Graveoline Analogs Exhibiting Selective Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity as Potential Lead Compounds for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2016, 21, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satou, T.; Koga, M.; Matsuhashi, R.; Koike, K.; Tada, I.; Nikaido, T. Assay of Nematocidal Activity of Isoquinoline Alkaloids Using Third-Stage Larvae of Strongyloides ratti and S. venezuelensis. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 104, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos-Rocha, T.J.; Cavalcanti, M.G.D.S.; Veras, D.L.; Feitosa, A.P.S.; Gonçalves, G.G.A.; Portela-Junior, N.C.; Lúcio, A.S.S.C.; Silva, A.L.D.; Padilha, R.J.R.; Marques, M.O.M.; et al. Ultrastructural Changes in Schistosoma mansoni Male Worms After In Vitro Incubation with the Essential Oil of Mentha x villosa Huds. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. 2016, 58, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, C.M.B.L.; Freitas, F.I.d.S.; Morais, L.C.S.L.d.; Cavalcanti, M.G.d.S.; Silva, L.F.d.; Padilha, R.J.R.; Barbosa, C.G.S.; Santos, F.A.B.d.; Alves, L.C.; Diniz, M.d.F.F.M. Ultrastructural Study on the Morphological Changes to Male Worms of Schistosoma mansoni after in Vitro Exposure to Allicin. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2011, 44, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertão, H.G.; da Silva, R.A.R.; Padilha, R.J.R.; de Azevedo Albuquerque, M.C.P.; Rádis-Baptista, G. Ultrastructural Analysis of Miltefosine-Induced Surface Membrane Damage in Adult Schistosoma mansoni BH Strain Worms. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 110, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.J.; Robertson, A.P.; Choudhary, S. Ivermectin: An Anthelmintic, an Insecticide, and Much More. Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.M.; Timson, D.J. The Mechanism of Action of Praziquantel: Can New Drugs Exploit Similar Mechanisms? Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 676–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | Vero Cells IC50 (µM) | S. venezuelensis L3 LC50 (µM) | SI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | |||
| Chalepensin | 3365.9 ± 58.3 | 5.7 ± 1.2 a,* | 3.9 ± 1.3 a,* | 3.4 ± 0.9 a,* | 990.0 |
| Graveoline | 640.3 ± 26.4 | 28.3 ± 6.7 b | 25.9 ± 5.9 b | 24.4 ± 5.8 b | 26.2 |
| Ivermectin | ND | 2.1± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 1.5 ± 0.3 | ND |
| ANOVA | - | F(2,23) = 36.59 p = 0.0004 | F(2,23) = 45.46 p = 0.0002 | F(2,23) = 42.08 p = 0.0003 | - |
| Dunnett’s comparison to ivermectin | - | a p = 0.4878 b p = 0.0004 | a p = 0.6464 b p = 0.0003 | a p = 0.7294 b p = 0.0003 | - |
| Compound | LC50 in µM | SI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | ||
| Chalepensin | 17.3 ± 3.1 | 17.1 ± 2.9 | 16.8 ± 2.4 | 200.4 |
| Graveoline | 27.8 ± 4.8 | 26.9 ± 5.1 | 26.5 ± 3.2 | 24.2 |
| t-test | p = 0.0334 | p = 0.0444 | p = 0.0137 | - |
| Compound | Concentration µM | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Chalepensin | 30.0 | All dead |
| 15.0 | Most affected and some dead | |
| 7.5 | Slightly affected | |
| 3.8 | Slightly affected | |
| 1.9 | Healthy | |
| Graveoline | 60.0 | All dead |
| 30.0 | Most dead and some affected | |
| 15.0 | Slightly affected | |
| 7.5 | Healthy | |
| 3.8 | Healthy | |
| Ivermectin | 10.0 | Slightly affected |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Garza, N.E.; Marín, M.; Sánchez-Montejo, J.; Elizondo-Luévano, J.H.; Bazaldúa-Rodríguez, A.F.; Quintanilla-Licea, R.; Romo-Sáenz, C.I.; Peláez, R.; Muro, A.; López-Abán, J. Antiparasitic Activity of Chalepensin and Graveoline Isolated from Ruta chalepensis L.: In Vitro Evaluation Against Strongyloides venezuelensis. Pathogens 2025, 14, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050419
Rodríguez-Garza NE, Marín M, Sánchez-Montejo J, Elizondo-Luévano JH, Bazaldúa-Rodríguez AF, Quintanilla-Licea R, Romo-Sáenz CI, Peláez R, Muro A, López-Abán J. Antiparasitic Activity of Chalepensin and Graveoline Isolated from Ruta chalepensis L.: In Vitro Evaluation Against Strongyloides venezuelensis. Pathogens. 2025; 14(5):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050419
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Garza, Nancy E., Miguel Marín, Javier Sánchez-Montejo, Joel H. Elizondo-Luévano, Aldo F. Bazaldúa-Rodríguez, Ramiro Quintanilla-Licea, César I. Romo-Sáenz, Rafael Peláez, Antonio Muro, and Julio López-Abán. 2025. "Antiparasitic Activity of Chalepensin and Graveoline Isolated from Ruta chalepensis L.: In Vitro Evaluation Against Strongyloides venezuelensis" Pathogens 14, no. 5: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050419
APA StyleRodríguez-Garza, N. E., Marín, M., Sánchez-Montejo, J., Elizondo-Luévano, J. H., Bazaldúa-Rodríguez, A. F., Quintanilla-Licea, R., Romo-Sáenz, C. I., Peláez, R., Muro, A., & López-Abán, J. (2025). Antiparasitic Activity of Chalepensin and Graveoline Isolated from Ruta chalepensis L.: In Vitro Evaluation Against Strongyloides venezuelensis. Pathogens, 14(5), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050419







