Experimental Infection of Ferrets with Bartonella henselae: In Search of a Novel Animal Model for Zoonotic Bartonellosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
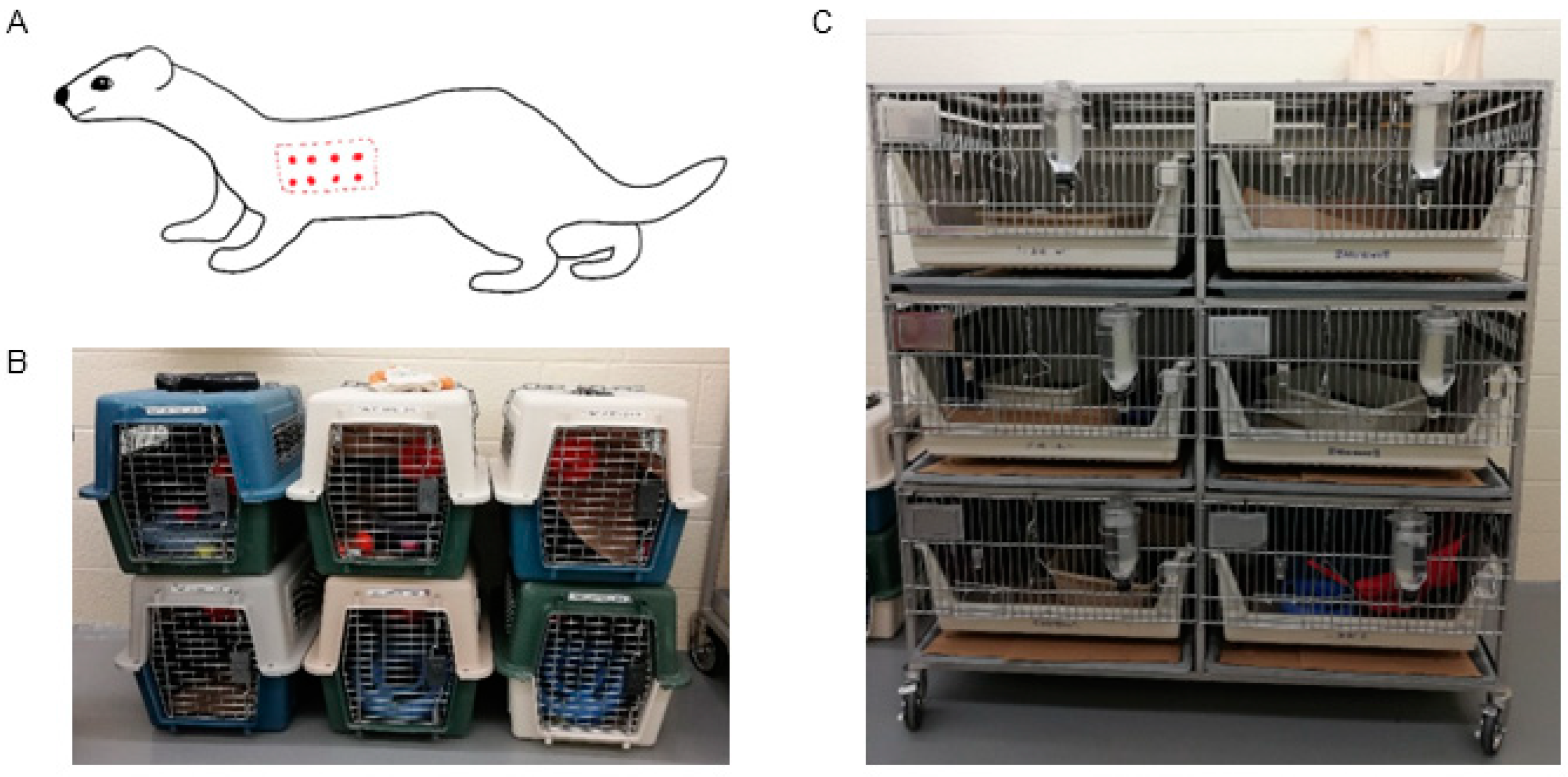
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Housing and Husbandry
2.3. Ethical Statement
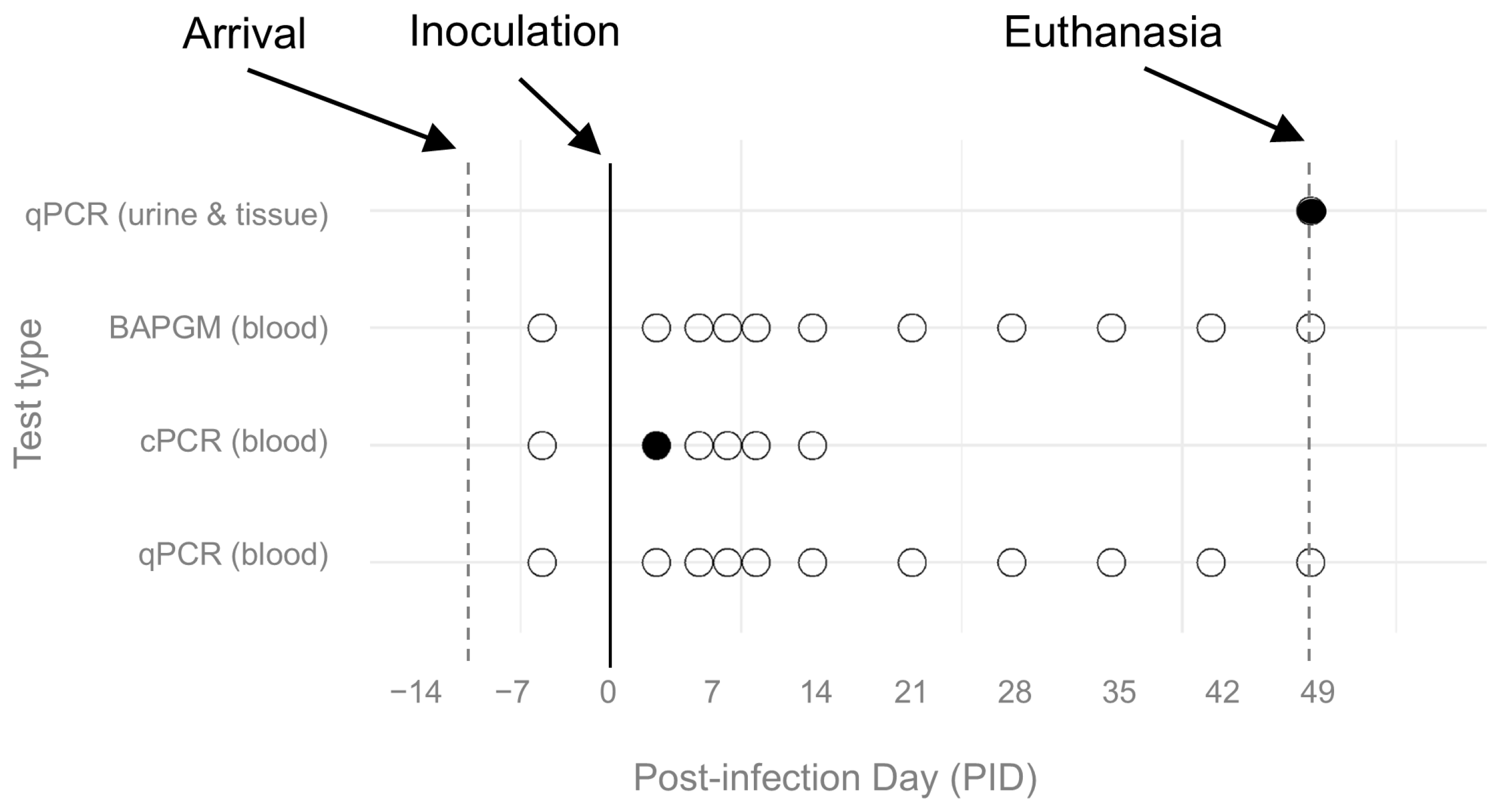
2.4. Study Design
2.5. Inoculum and Animal Procedures
2.6. Humane Endpoints
2.7. Diagnostic Procedures
2.8. Experimental Outcomes
2.9. Statistical Methods
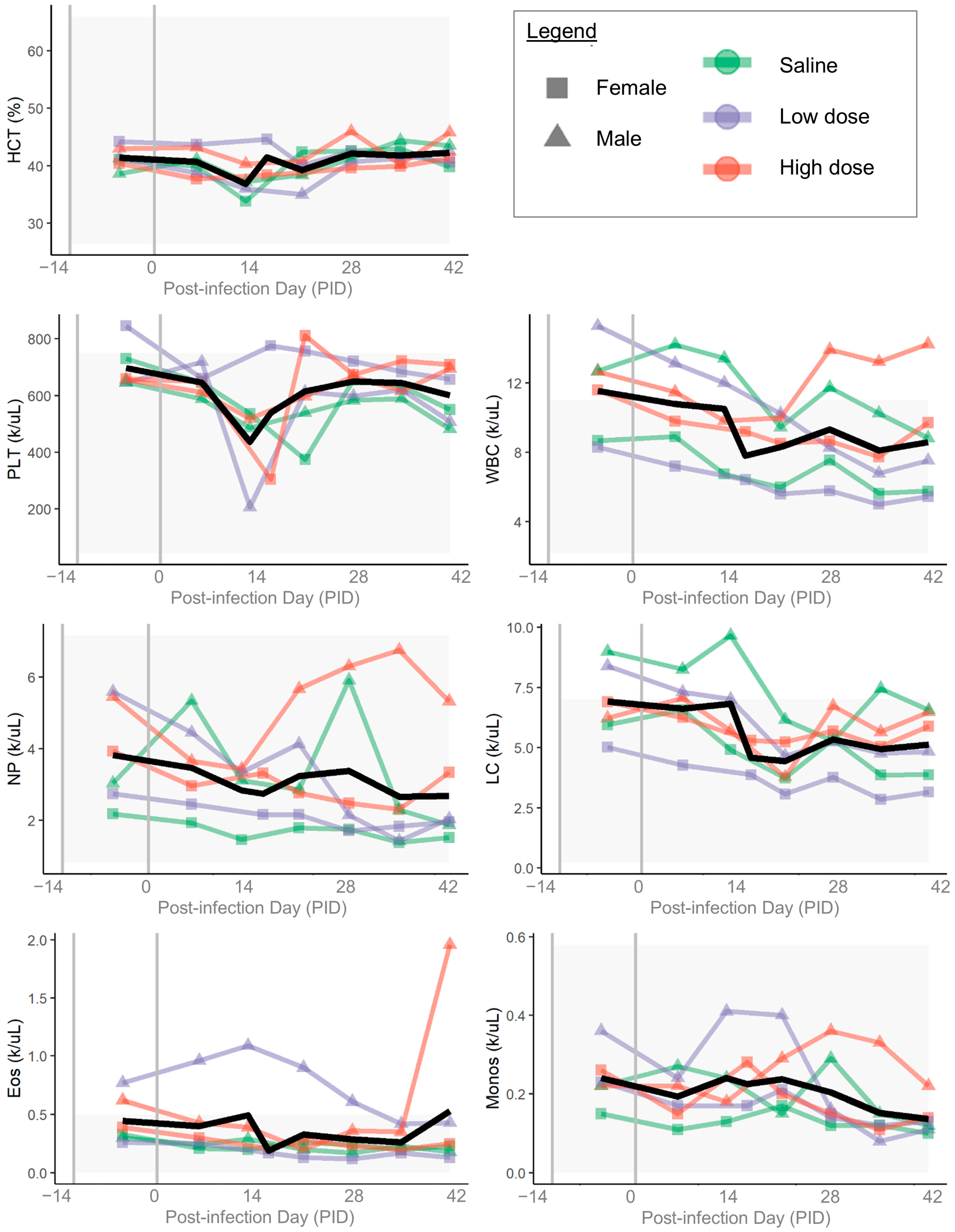
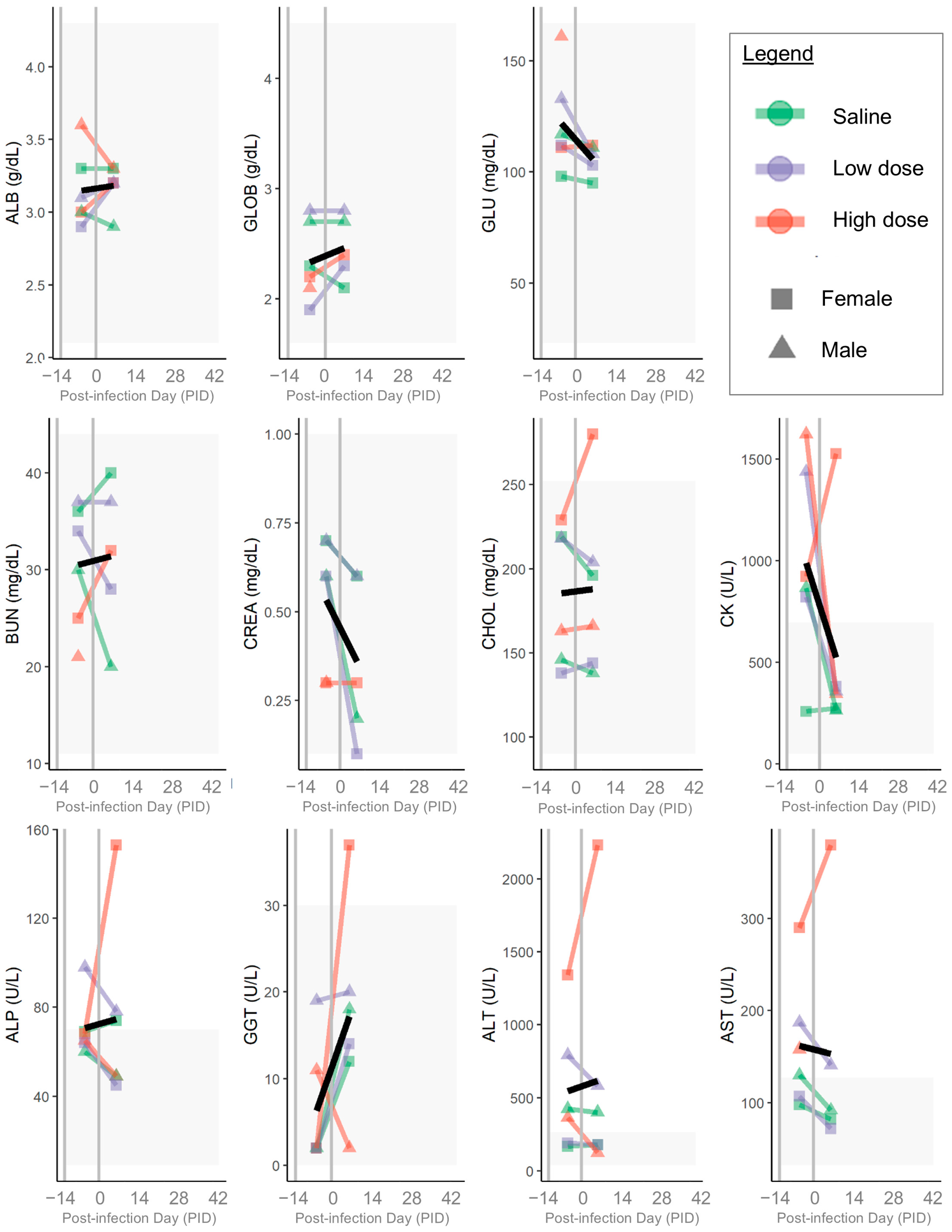
3. Results
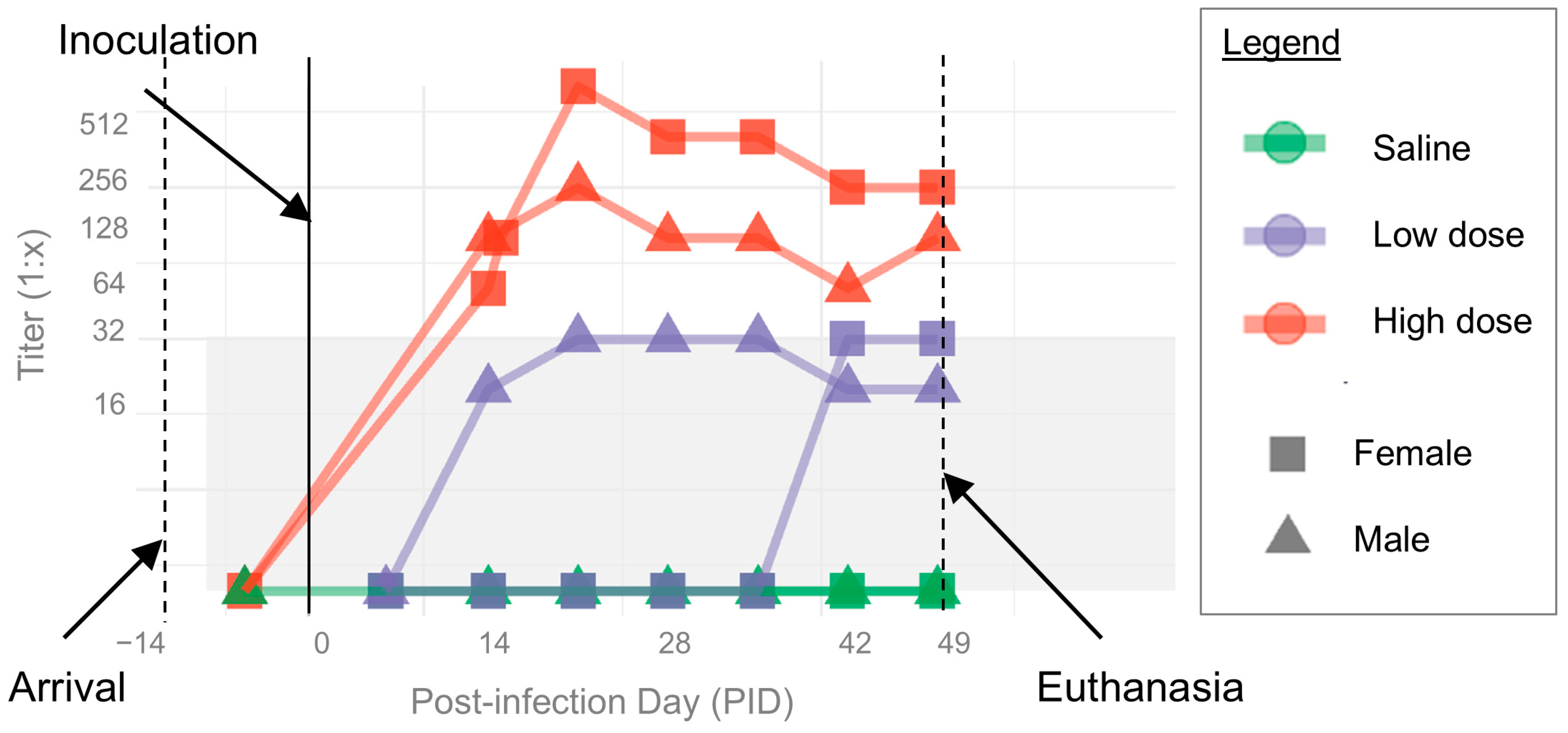
3.1. B. henselae Infection
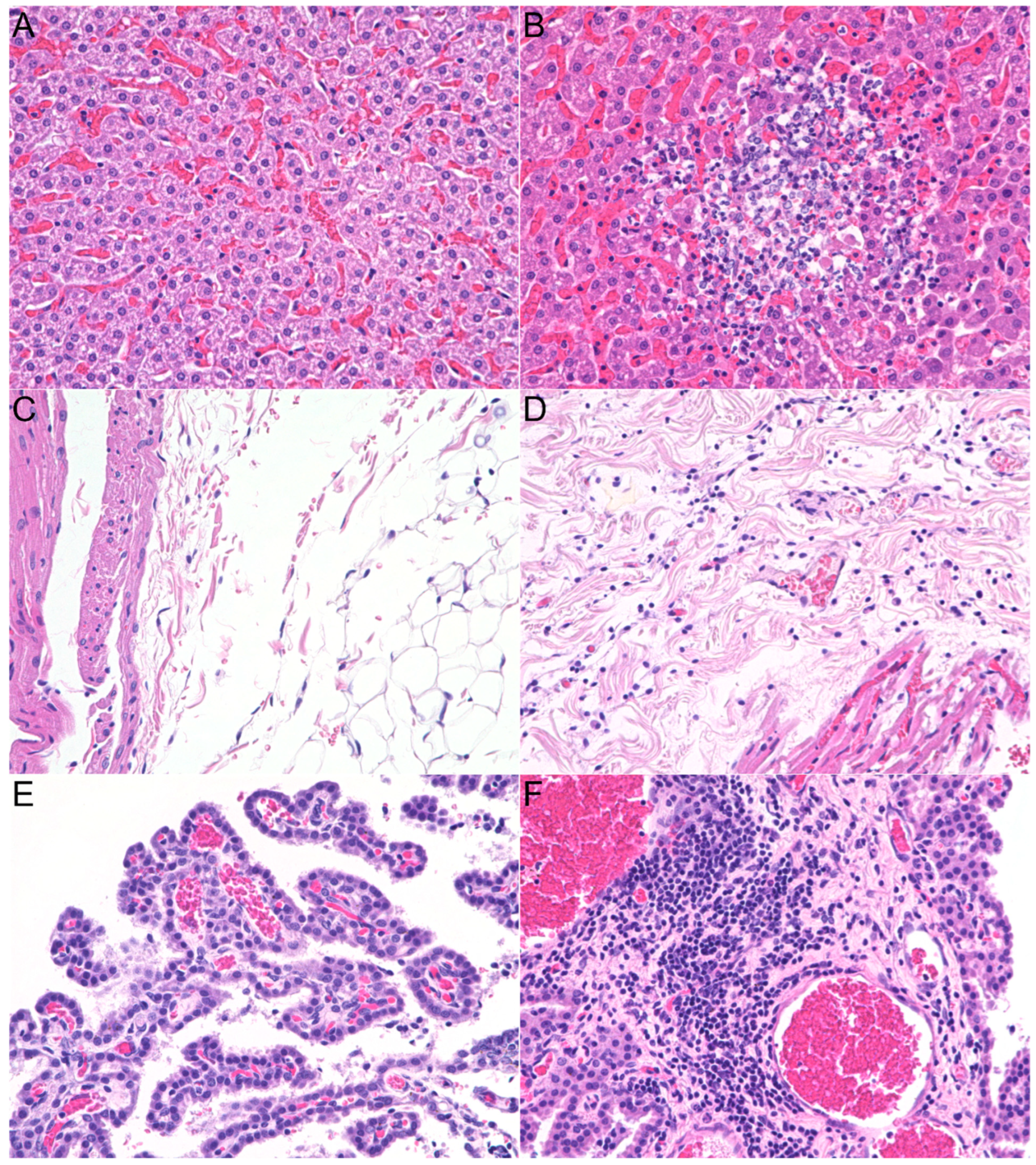
3.2. Histopathologic Lesions
3.3. Clinical Disease
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheslock, M.A.; Embers, M.E. Human Bartonellosis: An Underappreciated Public Health Problem? Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2019, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, D.W.; Rassoulian-Barrett, S.L.; Hoogestraat, D.R.; Salipante, S.J.; SenGupta, D.; Dietrich, E.A.; Cookson, B.T.; Marx, G.E.; Lieberman, J.A. Bartonella spp. Infections Identified by Molecular Methods, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taber, R.; Pankowski, A.; Ludwig, A.L.; Jensen, M.; Magsamen, V.; Lashnits, E. Bartonellosis in Dogs and Cats, an Update. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2022, 52, 1163–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regier, Y.; O’rourke, F.; Kempf, V.A. Bartonella spp.—A chance to establish One Health concepts in veterinary and human medicine. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qurollo, B. Feline Vector-Borne Diseases in North America. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2019, 49, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzuti, M.; Bailey, P.; Derrick, C.; Albrecht, B.; Carr, A.L.; Covington, E.W.; Deri, C.R.; Green, S.B.; Hayes, J.; Hobbs, A.L.; et al. Epidemiology and treatment of invasive Bar-tonella spp. infections in the United States. Infection 2024, 52, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okaro, U.; Addisu, A.; Casanas, B.; Anderson, B. Bartonella Species, an Emerging Cause of Blood-Culture-Negative Endocarditis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 709–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edouard, S.; Nabet, C.; Lepidi, H.; Fournier, P.-E.; Raoult, D. Bartonella, a common cause of endocarditis: A report on 106 cases and review. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, R.; Curtis, S.; Schilling, W.H.; James, P.R. Blood culture negative endocarditis in the modern era of 16S rRNA sequencing. Clin. Med. 2020, 20, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allizond, V.; Costa, C.; Sidoti, F.; Scutera, S.; Bianco, G.; Sparti, R.; Banche, G.; Dalmasso, P.; Cuffini, A.M.; Cavallo, R.; et al. Serological and molecular detection of Bartonella henselae in specimens from patients with suspected cat scratch disease in Italy: A comparative study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.A.; Moore, A.R.; Perea, A.E.; Mead, P.S. Cat scratch disease: U.S. clinicians’ experience and knowledge. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.A.; Saha, S.; Mead, P.S. Cat-Scratch Disease in the United States, 2005–2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canneti, B.; Cabo-López, I.; Puy-Núñez, A.; García García, J.C.; Cores, F.J.; Trigo, M.; Suárez-Gil, A.P.; Rodriguez-Regal, A. Neurological presentations of Bartonella henselae infection. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Danesh-Meyer, H.V.; Bhatti, M.T. Neuroretinitis: A comprehensive review on aetiologies, clinical manifestations, and treatment options. Eye 2025, 39, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurja, S.; Stroe, A.Z.; Pundiche, M.B.; Docu Axelerad, S.; Mateescu, G.; Micu, A.O.; Popescu, R.; Oltean, A.; Docu Axelerad, A. The Clinical Profile of Cat-Scratch Disease’s Neu-ro-Ophthalmological Effects. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iralu, J.; Bai, Y.; Crook, L.; Tempest, B.; Simpson, G.; McKenzie, T.; Koster, F. Rodent-associated Bartonella febrile illness, southwestern United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.M.; Perez-Tanoira, R.; Martin-Martin, I.; Prieto-Perez, L.; Tefasmariam, A.; Tiziano, G.; Escudero, R.; Gil-Zamorano, J.; Gil-Gil, H.; Gorgolas, M.; et al. Arthropod-Borne Bacteria Cause Nonmalarial Fever in Rural Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study in 394 Patients. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoy, M.; Bai, Y.; Sheff, K.; Morway, C.; Baggett, H.; Maloney, S.A.; Boonmar, S.; Bhengsri, S.; Dowell, S.F.; Sitdhirasdr, A.; et al. Identification of Bartonella infections in febrile human patients from Thailand and their potential animal reservoirs. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.L.; Idris, N.; Tay, S.T. Serological review of Bartonella henselae and Bartonella quintana infection among Malaysian pa-tients with unknown causes of febrile illnesses. Trop. Biomed. 2022, 39, 328–331. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, J.C.; Robveille, C.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Neurobartonelloses: Emerging from obscurity! Parasites Vectors 2024, 17, 416. [Google Scholar]
- Nawrocki, C.C.; Max, R.J.; Marzec, N.S.; Nelson, C.A. Atypical manifestations of cat-scratch disease, United States, 2005–2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beydon, M.; Rodriguez, C.; Karras, A.; Cez, A.; Rafat, C.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Fain, O.; Philipponnet, C.; Puéchal, X.; Dossier, A.; et al. Bartonella and Coxiella infections presenting as systemic vasculitis: Case series and review of literature. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamekhi Amiri, F. Bartonellosis in Chronic Kidney Disease: An Unrecognized and Unsuspected Diagnosis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2017, 21, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingos Grilo, R.; Madureira, M.; Reis Melo, A.; Tavares, M. Cat-scratch disease: A rare cause of osteomyelitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2024, 17, e257341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guptill, L.; Slater, L.N.; Wu, C.C.; Lin, T.L.; Glickman, L.T.; Welch, D.F.; Tobolski, J.; HogenEsch, H. Evidence of reproductive failure and lack of perinatal transmission of Bartonella henselae in experimentally infected cats. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 65, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guptill, L.; Slater, L.; Wu, C.; Lin, T.; Glickman, L.T.; Welch, D.F.; HogenEsch, H. Experimental infection of young specific pathogen-free cats with Bartonella henselae. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foil, L.; Andress, E.; Freeland, R.L.; Roy, A.F.; Rutledge, R.; Triche, P.C.; O’Reilly, K.L. Experimental Infection of Domestic Cats with Bar-tonella henselae by Inoculation of Ctenocephalides fells (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) Feces. J. Med. Entomol. 1998, 35, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Hew, C.M.; Weber, D.K.; Lee, W.I. Experimental infection of specific pathogen free (SPF) cats with two different strains of Bartonella henselae type I: A comparative study. Vet. Res. 2002, 33, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Stuckey, M.J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G.; Henn, J.B.; Koehler, J.E.; Chang, C.-C. Experimental infection of cats with Afipia felis and various Bartonella species or subspecies. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappin, M.R.; Davis, W.L.; Hawley, J.R.; Brewer, M.; Morris, A.; Stanneck, D. A flea and tick collar containing 10% imidacloprid and 4.5% flumethrin prevents flea transmission of Bartonella henselae in cats. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficociello, J.; Bradbury, C.; Morris, A.; Lappin, M. Detection of Bartonella henselae IgM in Serum of Experimentally Infected and Naturally Exposed Cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 1264–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, C.A.; Lappin, M.R. Evaluation of topical application of 10% imidacloprid–1% moxidectin to prevent Bartonella henselae transmission from cat fleas. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2010, 236, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, R.C.; Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Floyd-Hawkins, K.A.; Kikuchi, Y.; Koehler, J.E.; Pedersen, N.C. Experimental and natural infection with Bartonella henselae in domestic cats. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1997, 20, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Floyd-Hawkins, K.; Chi, B.; Yamamoto, K.; Roberts-Wilson, J.; Gurfield, A.N.; Abbott, R.C.; Pedersen, N.C.; Koehler, J.E. Experimental Transmission of Bar-tonella henselae by the Cat Flea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1952–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanutto, M.D.S.; Mamizuka, E.M.; Raiz-Júnior, R.; Lima, T.M.; Diogo, C.L.; Okay, T.S.; Hagiwara, M.K. Experimental infection and horizontal transmission of Bartonella henselae in domestic cats. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2001, 43, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guptill, L.; Slater, L.; Wu, C.-C.; Glickman, L.T.; Lin, T.-L.; Welch, D.F.; Crippen, J.T.; HogenEsch, H. Immune response of neonatal specific pathogen-free cats to experimental infection with Bartonella henselae. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1999, 71, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, C.E.; Mcdermott, M.; Jameson, P.H.; Atkins, C.L.; Marks, A.M. Bartonella henselae infection in cats: Evaluation during pri-mary infection, treatment, and rechallenge infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 1682–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordick, D.L.; Brown, T.T.; Shin, K.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Clinical and pathologic evaluation of chronic Bartonella henselae or Bar-tonella clarridgeiae infection in cats. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1536–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordick, D.L.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Relapsing bacteremia after blood transmission of Bartonella henselae to cats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1997, 58, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koesling, J.; Aebischer, T.; Falch, C.; Schulein, R.; Dehio, C. Cutting Edge: Antibody-Mediated Cessation of Hemotropic Infection by the Intraerythrocytic Mouse Pathogen Bartonella grahamii. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.K.; Le Rhun, D.; Lecuelle, B.; Le Naour, E.; Vayssier-Taussat, M. Role of the spleen in Bartonella spp. infection. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 64, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siewert, L.K.; Fromm, K.; Dehio, C.; Pinschewer, D.D. Cutting Edge: Redundant Roles for MHC Class II-, CD1d-, and MR1-restricted T Cells in Clearing Bartonella Infection. J. Immunol. 2024, 213, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromm, K.; Boegli, A.; Ortelli, M.; Wagner, A.; Bohn, E.; Malmsheimer, S.; Wagner, S.; Dehio, C. Bartonella taylorii: A Model Organism for Studying Bartonella Infection in vitro and in vivo. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 913434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida, A.R.; Vieira-Damiani, G.; da Silva, M.N.; Lania, B.G.; Soares, T.C.B.; Drummond, M.R.; Lins, K.d.A.; Ericson, M.E.; Gupta, K.; Velho, P.E.N. Bartonella henselae Infection in Sickle Cell Disease Mice Is Associated with Hyperalgesia. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.N.; Vieira-Damiani, G.; Ericson, M.E.; Gupta, K.; de Almeida, A.R.; Drummond, M.R.; Soares, T.C.B.; Lania, B.G.; Gilioli, R.; Velho, P.E.N.F. Acute and Late Bartonella henselae Murine Model Infection. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.N.; Vieira-Damiani, G.; Ericson, M.E.; Gupta, K.; Gilioli, R.; de Almeida, A.R.; Drummond, M.R.; Lania, B.G.; Lins, K.d.A.; Soares, T.C.B.; et al. Bartonella henselae transmission by blood transfusion in mice. Transfusion 2016, 56, 1556–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karem, K.L.; Dubois, K.A.; McGill, S.L.; Regnery, R.L. Characterization of Bartonella henselae-specific immunity in BALB/c mice. Immunology 1999, 97, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewert, L.K.; Dehio, C.; Pinschewer, D.D. Adaptive immune defense prevents Bartonella persistence upon trans-placental transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.; Cha, B.J.; Amin, J.; Smith, L.K.; Anderson, B. Zebrafish Embryo Model of Bartonella henselae Infection. Zebrafish 2014, 11, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drut, A.; Bublot, I.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Chabanne, L.; Vayssier-Taussat, M.; Cadoré, J.-L. Comparative microbiological features of Bartonella henselae infection in a dog with fever of unknown origin and granulomatous lymphadenitis. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 203, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, S.C.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Washabau, R.J.; Matise, I.; Maggi, R.G.; Duncan, A.W. Detection of Bartonella henselae DNA in two dogs with pyogranulomatous lymphadenitis. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2007, 230, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, T.N.; Washabau, R.J.; Goldschmidt, M.H.; Cullen, J.M.; Rogala, A.R.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Detection of Bartonella henselae and Bartonella clarridgeiae DNA in hepatic specimens from two dogs with hepatic disease. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 222, 47–51+35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohad, D.G.; Morick, D.; Avidor, B.; Harrus, S. Molecular detection of Bartonella henselae and Bartonella koehlerae from aortic valves of Boxer dogs with infective endocarditis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 141, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.D.; Sellon, R.K.; Tucker, R.L.; Wills, T.B.; Simonsen, A.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bilateral mandibular pyogranulomatous lymphadenitis and pulmonary nodules in a dog with Bartonella henselae bacteremia. Can. Vet. J. 2014, 55, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mexas, A.M.; Hancock, S.I.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Bartonella henselae and Bartonella elizabethae as Potential Canine Pathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4670–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomel, B.B.; Ermel, R.W.; Kasten, R.W.; Henn, J.B.; Fleischman, D.A.; Chang, C.-C. Experimental infection of dogs with various Bartonella species or subspecies isolated from their natural reservoir. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, N.; Cherry, N.A.; Linder, K.E.; Pierce, E.; Sontakke, N.; Hegarty, B.C.; Bradley, J.M.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Experimental infection of dogs with Bartonella henselae and Bartonella vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 156, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-I.; Kim, S.-G.; Kim, S.-M.; Kim, E.-H.; Park, S.-J.; Yu, K.-M.; Chang, J.-H.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, S.; Casel, M.A.B.; et al. Infection and Rapid Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in Ferrets. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belser, J.A.; Eckert, A.M.; Huynh, T.; Gary, J.M.; Ritter, J.M.; Tumpey, T.M.; Maines, T.R. A Guide for the Use of the Ferret Model for Influenza Virus Infection. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Layton, D.; Wheatley, A.K.; Kent, S.J. Improving immunological insights into the ferret model of human viral infec-tious disease. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2019, 13, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurdson, C.; Mathiason, C.; Perrott, M.; Eliason, G.; Spraker, T.; Glatzel, M.; Manco, G.; Bartz, J.; Miller, M.; Hoover, E. Experimental Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) in the Ferret. J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 138, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludlow, M.; Rennick, L.J.; Nambulli, S.; de Swart, R.L.; Duprex, W.P. Using the ferret model to study morbillivirus entry, spread, transmission and cross-species infection. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 4, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fontoura Budaszewski, R.; von Messling, V. Morbillivirus experimental animal models: Measles virus pathogenesis in-sights from canine distemper virus. Viruses 2016, 8, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillet, S.; Svitek, N.; von Messling, V. Ferrets as a model for morbillivirus pathogenesis, complications, and vaccines. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 330, 73–87. [Google Scholar]
- McCallan, L.; Corbett, D.; Andersen, P.L.; Aagaard, C.; McMurray, D.; Thompson, S.; Strain, S.; McNair, J. A New Experimental Infection Model in Fer-rets Based on Aerosolised Mycobacterium bovis. Vet. Med. Int. 2011, 2011, 981410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, R.D.; Ludlow, M.; de Jong, A.; Rennick, L.J.; Verburgh, R.J.; van Amerongen, G.; van Riel, D.; van Run, P.R.W.A.; Herfst, S.; Kuiken, T.; et al. Delineating morbillivirus entry, dis-semination and airborne transmission by studying in vivo competition of multicolor canine distemper viruses in ferrets. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramod, R.K.; Atul, P.K.; Pandey, M.; Anbazhagan, S.; Mhaske, S.T.; Barathidasan, R. Care, management, and use of ferrets in bio-medical research. Lab. Anim. Res. 2024, 40, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, S.E.; Chomel, B.B.; Gill, V.A.; Doroff, A.M.; Miller, M.A.; Burek-Huntington, K.A.; Kasten, R.W.; Byrne, B.A.; Goldstein, T.; Mazet, J.A. Bartonella spp. exposure in northern and southern sea otters in Alaska and California. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, S.E.; Chomel, B.B.; Gill, V.A.; Kasten, R.W.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Byrne, B.A.; Burek-Huntington, K.A.; Miller, M.A.; Goldstein, T.; et al. Novel Bartonella infection in northern and southern sea otters (Enhydra lutris kenyoni and Enhydra lutris nereis). Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 170, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadurai, S.K.; Birkenheuer, A.J.; Blanton, H.L.; Maggi, R.G.; Belfiore, N.; Marr, H.S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Stoskopf, M.K. Prevalence of selected vector-borne organisms and identification of Bartonella species DNA in North American river otters (Lontra canadensis). J. Wildl. Dis. 2010, 46, 947–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Millán, J.; Proboste, T.; de Mera, I.G.F.; Chirife, A.D.; de la Fuente, J.; Altet, L. Molecular detection of vector-borne pathogens in wild and domestic carnivores and their ticks at the human–wildlife interface. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 284–290. [Google Scholar]
- Sepúlveda-García, P.; Raffo, E.; Medina-Vogel, G.; Muñoz, F.; Muñoz, P.; Alabí, A.; Navarrete-Talloni, M.J.; Gonçalves, L.R.; de Mello, V.V.C.; Machado, R.Z.; et al. Molecular survey of Bartonella spp. and haemoplasmas in American minks (Neovison vison). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2094–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.H.; Girard, Y.A.; Gilardi, K.; Hernandez, Y.; Poppenga, R.; Chomel, B.B.; Foley, J.E.; Johnson, C.K. Pathogen and rodenticide exposure in Amer-ican badgers (Taxidea taxus) in California. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrikagoitia, X.; Gil, H.; García-Esteban, C.; Anda, P.; Juste, R.A.; Barral, M. Presence of Bartonella Species in Wild Carnivores of Northern Spain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana-Rios, J.; Verdaguer-Diaz, J.I.; Opazo, G.; Leong, B.C.; Zett, C.; Smith, R.T.; Freund, K.B. Not cat-scratch disease: Bartonella henselae neuroretinitis associated with non-feline pet mammals. IDCases 2020, 22, e00978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Chomel, B.; Kasten, R.; Chang, C.; Tseggai, T.; Decker, P.; Mackowiak, M.; Floyd-Hawkins, K.; Pedersen, N. Homologous protection but lack of heterologous-protection by various species and types of Bartonella in specific pathogen-free cats. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 65, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, P.; Sevala, S.; Balakrishnan, N.; Marr, H.; Wilson, J.; Maggi, R.; Birkenheuer, A.; Lappin, M.; Chomel, B.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Validation of Bartonella henselae Western Immunob-lotting for Serodiagnosis of Bartonelloses in Dogs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01335-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Species360 Zoological Information Management System. ZIMS Expected Test Results for Mustela Putorius Furo. Available online: http://zims.species360.org (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Oteo, J.A.; Maggi, R.; Portillo, A.; Bradley, J.; García-Álvarez, L.; San-Martín, M.; Roura, X.; Breitschwerdt, E. Prevalence of Bartonella spp. by culture, PCR and serology, in veterinary personnel from Spain. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portillo, A.; Maggi, R.; Oteo, J.A.; Bradley, J.; García-Álvarez, L.; San-Martín, M.; Roura, X.; Breitschwerdt, E. Bartonella spp. Prevalence (Serology, Culture, and PCR) in Sanitary Workers in La Rioja Spain. Pathogens 2020, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanat, M.; Maggi, R.G.; Linder, K.E.; Horton, S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Cross-contamination in the Molecular Detection of Bartonella from Paraffin-embedded Tissues. Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.W.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. A combined approach for the enhanced detection and isolation of Bartonella species in dog blood samples: Pre-enrichment liquid culture followed by PCR and subculture onto agar plates. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 69, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, R.G.; Birkenheuer, A.J.; Hegarty, B.C.; Bradley, J.M.; Levy, M.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Comparison of serological and molecular panels for diagnosis of vector-borne diseases in dogs. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaro, U.; George, S.; Anderson, B. What is in a cat scratch? Growth of Bartonella henselae in a biofilm. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, A.; Dehio, C. Intruders below the radar: Molecular pathogenesis of Bartonella spp. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 42–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmer, E.M.; Lavengood, K.; Miller, M.; Rodgers, J.; Fenster, S.D. Evaluating the Impacts of Coinfection on Immune System Function of the Deer Mouse (Peromyscus Maniculatus) Using Sin Nombre Virus and Bartonella as Model Pathogen Systems. J. Wildl. Dis. 2018, 54, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanık-Yüksek, S.; Gülhan, B.; Hürmüzlü, S.; Özkaya-Parlakay, A.; Güneş, A.; Oğuz-Erdoğan, A.S.; Tezer, H. Challenges of the treatment of pediatric hepatosplenic bartonellosis: Case report and literature review. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2022, 16, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massei, F.; Gori, L.; Macchia, P.; Maggiore, G. The Expanded Spectrum of Bartonellosis in Children. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 19, 691–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisoy, E.S.; Correa, A.G.; Wagner, M.L.; Kaplan, S.L. Hepatosplenic cat-scratch disease in children: Selected clinical features and treatment. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 28, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderHeyden, T.R.; Yong, S.L.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Maggi, R.G.; Mihalik, A.R.; Parada, J.P.; Fimmel, C.J. Granulomatous hepatitis due to Bartonella henselae infection in an immunocompetent patient. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laham, F.R.; Kaplan, S.L. Hepatosplenic cat-scratch fever. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroescu, R.F.; Chisavu, F.; Steflea, R.M.; Doros, G.; Bizerea-Moga, T.-O.; Vulcanescu, D.D.; Marti, T.D.; Boru, C.; Avram, C.R.; Gafencu, M. A Retrospective Analysis of Systemic Bartonella henselae Infection in Children. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, T.E.; Koehler, J.E. Granulomatous hepatitis and necrotizing splenitis due to Bartonella henselae in a patient with cancer: Case report and review of hepatosplenic manifestations of Bartonella infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khonde, P.; Byrnes, K. The Brief Case: Granulomatous hepatitis in an immunocompromised patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2023, 61, e0189222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamps, L.W.; Scott, M.A. Cat-scratch disease: Historic, clinical, and pathologic perspectives. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 121 (Suppl_1), S71–S80. [Google Scholar]
- García, J.C.; Núñez, M.J.; Castro, B.; Fernández, J.M.; Portillo, A.; Oteo, J.A. Hepatosplenic cat scratch disease in immunocompetent adults: Report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Medicine 2014, 93, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.K.; Das, P.; Shalimar; Swatantra, G.; Chaudhry, R. Multifocal hepatic abscesses in immunocompetent patient due to Bartonella henselae: Case report with review of literature. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2019, 37, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanat, M.; Broadhurst, J.; Linder, K.E.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Identification of Bartonella henselae in 2 Cats With Pyogranulomatous Myocarditis and Diaphragmatic Myositis. Vet. Pathol. 2012, 49, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsmo, E.J.; Fenton, H.; Cleveland, C.A.; Shock, B.; Cunningham, M.; Howerth, E.W.; Yabsley, M.J. Necrotizing interstitial pneumonia and suppurative myocarditis associated with Bartonella henselae infection in three Florida pumas. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, T.; Fox, P.; Balakrishnan, N.; Ericson, M.; Hooker, V.; Breitschwerdt, E. Pyogranulomatous Pancarditis with Intramyocardial Bartonella henselae San Antonio 2 (BhSA2) in a Dog. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, J.; Johnson, J.; Scott, M.; Madhusudhan, K. Fatal Meningitis and Encephalitis Due to Bartonella henselae Bacteria. J. Forensic Sci. 2002, 47, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouch, B.; Coventry, S. A case of fatal disseminated Bartonella henselae infection (cat-scratch disease) with encephalitis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2007, 131, 1591–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, V.L., Jr.; Curi, A.L.; Pinto, A.D.; Nunes, E.P.; Teixeira, M.D.; Rozental, T.; Favacho, A.R.; Lemos, E.R.; Bóia, M.N. Cat scratch disease complicated with aseptic meningitis and neuroretinitis. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassab, I.; Isada, C.; Azar, M.M.; Sarsam, N.; Jiang, M.; Camelo-Piragua, S.; Kaul, D.; Malinis, M. Into the unknown: Diagnosing mysterious brain lesions. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2022, 24, e13829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, K.D.; Drummond, M.R.; Velho, P.E. Cutaneous manifestations of bartonellosis. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2019, 94, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashnits, E.; Neupane, P.; Maggi, R.G.; Linder, K.E.; Bradley, J.M.; Balakrishnan, N.; Southern, B.L.; McKeon, G.P.; Chandrashekar, R.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Detection of Bartonella spp. in dogs after infection with Rickettsia rickettsii. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.S.; Martins, S.A.; Scheffer, F.R.; Maekawa, A.S.; Silva, R.D.; Araújo, G.R.; Velho, P.E.; Drummond, M.R. Investigation of natural infection of BALB C mice by Bartonella henselae. Braz. J. Infect Dis. 2024, 29, 104483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Alhaskawi, A.; Zou, X.; Zhou, H.; Ezzi, S.H.A.; Kota, V.G.; Abdulla, M.H.A.H.; Olga, A.; Abdalbary, S.A.; Lu, H. Post-COVID reactivation of latent Bartonella henselae infection: A case report and literature review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, A.; Corvilain, E.; Ghelfenstein-Ferreira, T.; Camelena, F.; Meignin, V.; Berçot, B.; Le Goff, J.; Salmona, M. Unmasking Bartonella henselae infection in the shadows of long COVID thanks to clinical metagenomics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2024, 43, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, J.C.; Maggi, R.G.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Viability and Desiccation Resistance of Bartonella henselae in Biological and Non-Biological Fluids: Evidence for Pathogen Environmental Stability. Pathogens 2023, 12, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Hew, C.M.; Weber, D.K.; Lee, W.I.; Koehler, J.E.; Pedersen, N.C. Infection and re-infection of domestic cats with various Bartonella species or types: B. henselae type I is protective against heterologous challenge with B. henselae type II. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 92, 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Rust, M.K. The Biology and Ecology of Cat Fleas and Advancements in Their Pest Management: A Review. Insects 2017, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappin, M.R.; Fitzgerald, R. Pradofloxacin for Treatment of Bartonella henselae in Experimentally Inoculated Cats. Pathogens 2024, 13, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrett, C.O.; Sebbane, F.; Adamovicz, J.J.; Andrews, G.P.; Hinnebusch, B.J. Flea-Borne Transmission Model To Evaluate Vaccine Efficacy against Naturally Acquired Bubonic Plague. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2052–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M.J.; Jacobs, D.E.; Mencke, N. Establishment of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis felis) on the ferret (Mustela putorius furo) and its control with imidacloprid. Med. Vet. Èntomol. 2001, 15, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lashnits, E.; Robveille, C.; Neupane, P.; Richardson, T.; Linder, K.; McKeon, G.; Maggi, R.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Experimental Infection of Ferrets with Bartonella henselae: In Search of a Novel Animal Model for Zoonotic Bartonellosis. Pathogens 2025, 14, 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050421
Lashnits E, Robveille C, Neupane P, Richardson T, Linder K, McKeon G, Maggi R, Breitschwerdt EB. Experimental Infection of Ferrets with Bartonella henselae: In Search of a Novel Animal Model for Zoonotic Bartonellosis. Pathogens. 2025; 14(5):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050421
Chicago/Turabian StyleLashnits, Erin, Cynthia Robveille, Pradeep Neupane, Toni Richardson, Keith Linder, Gabriel McKeon, Ricardo Maggi, and Edward B. Breitschwerdt. 2025. "Experimental Infection of Ferrets with Bartonella henselae: In Search of a Novel Animal Model for Zoonotic Bartonellosis" Pathogens 14, no. 5: 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050421
APA StyleLashnits, E., Robveille, C., Neupane, P., Richardson, T., Linder, K., McKeon, G., Maggi, R., & Breitschwerdt, E. B. (2025). Experimental Infection of Ferrets with Bartonella henselae: In Search of a Novel Animal Model for Zoonotic Bartonellosis. Pathogens, 14(5), 421. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050421







