Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild European and American Mink (Mustela lutreola and Neogale vison) from Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
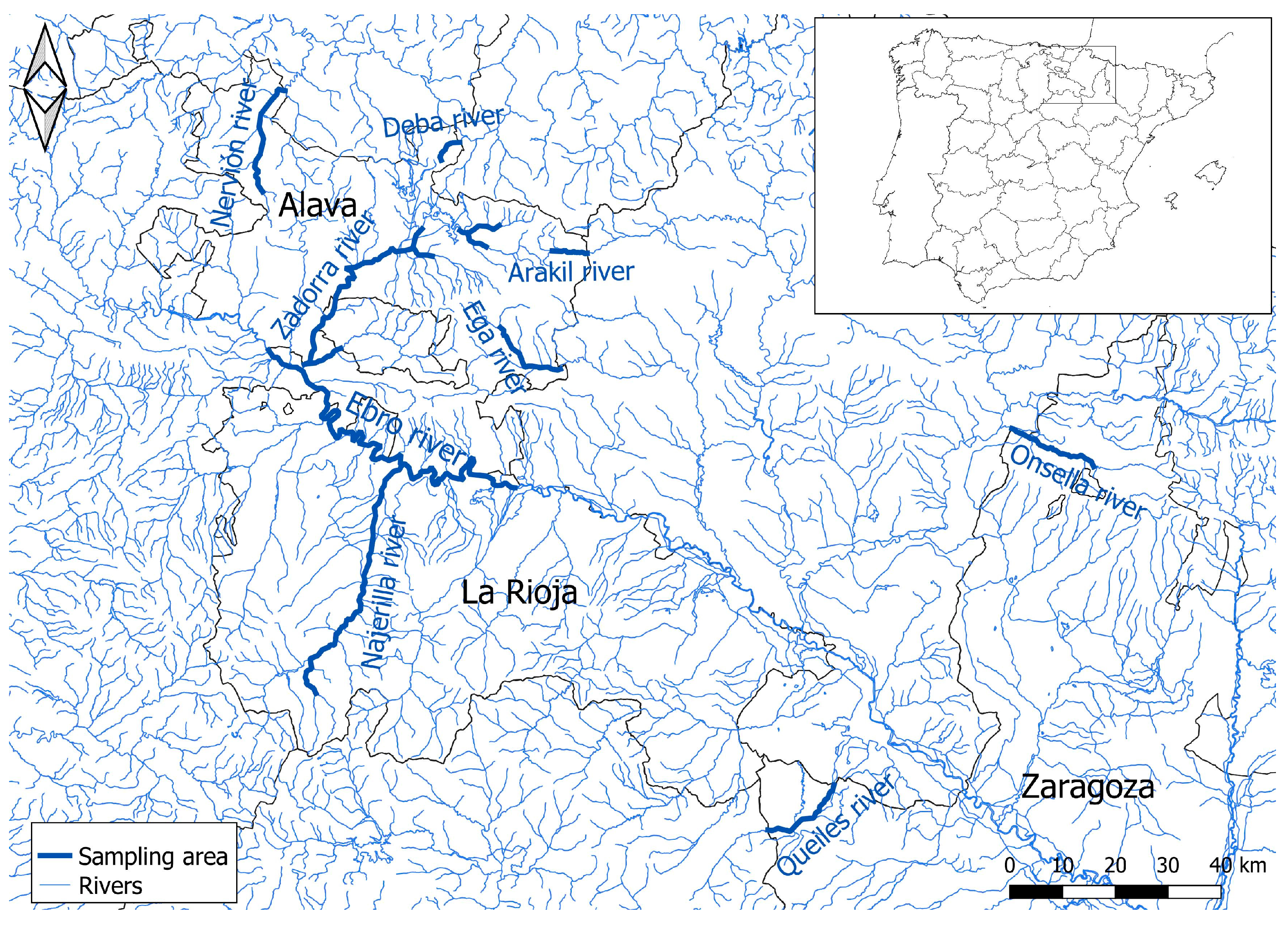
2.1. Animals
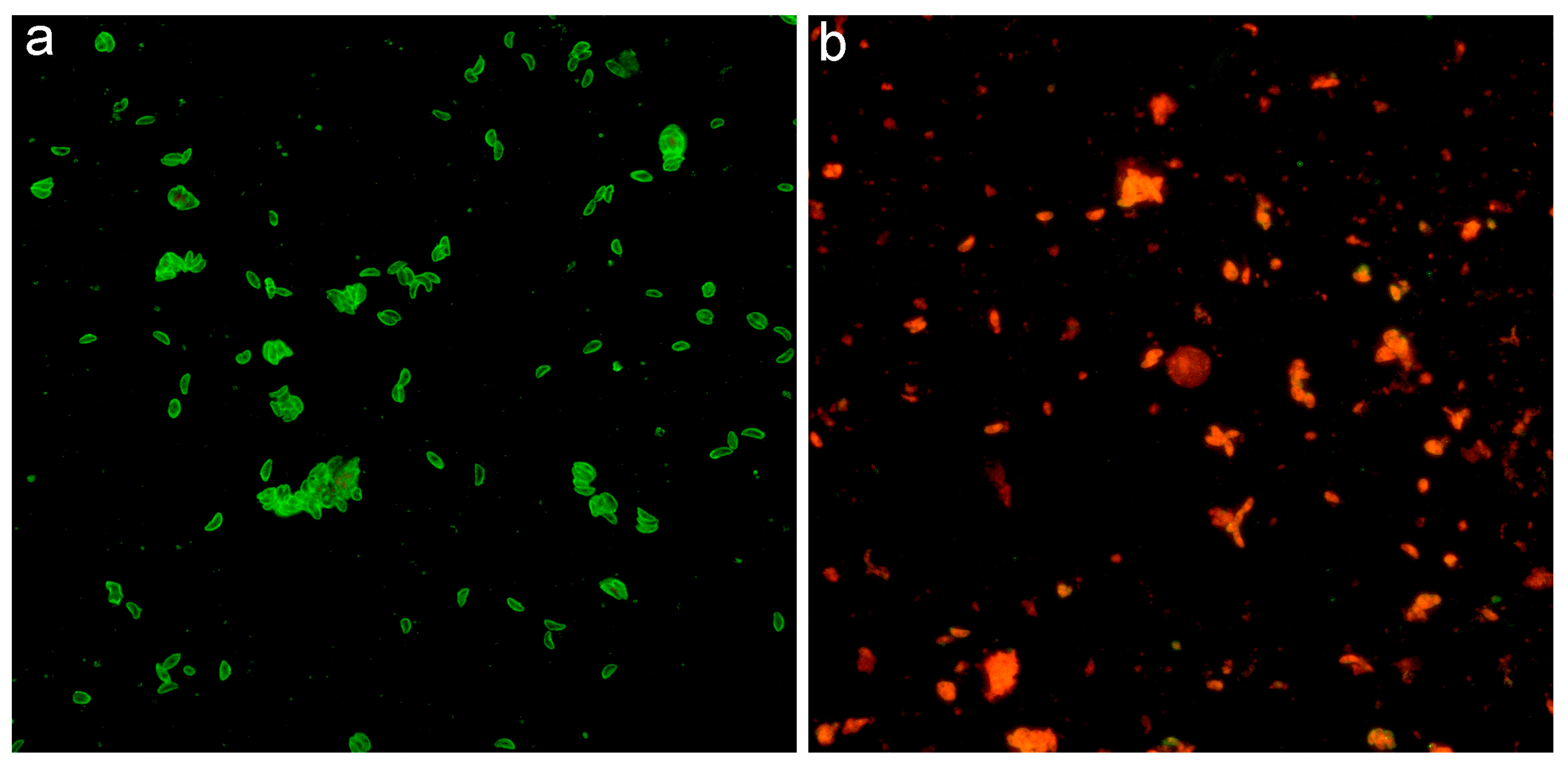
2.2. Serological Technique
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IFAT | Indirect fluorescent antibody test |
| FIEB | Research in ethology and biodiversity |
| MAT | Modified agglutination test |
| IFI | Indirect immunofluorescent test |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| WOAH | World Organization for Animal Health |
References
- Hill, D.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii: Transmission, diagnosis and prevention. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2002, 8, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, R.K. An outbreak of toxoplasmosis in farmed mink (Mustela vison). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2001, 13, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, Y.L.; Fitzgerald, S.D.; Sikarske, J.G.; Murphy, A.; Grosjean, N.; Kiupel, M. Toxoplasmosis in a Free-ranging Mink. J Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, F.; Shang, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Q. A comparative study of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence in mink using a modified agglutination test, a Western blot, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2015, 27, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka, J.; Karamon, J.; Wójcik-Fatla, A.; Dutkiewicz, J.; Bilska-Zając, E.; Zając, V.; Piotrowska, W.; Cencek, T. Toxoplasma gondii infection in selected species of free-living animals in Poland. Ann. Agric. Env. Med. 2019, 26, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Murata, F.H.A.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Yang, Y.R.; Su, C. All about toxoplasmosis in cats: Last decade. Vet Parasitol. 2020, 283, 109145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, R.; Cabezón, O.; Millán, J.; Pabón, M.; Arnal, M.C.; Luco, D.F.; Gortázar, C.; Dubey, J.P.; Almeria, S. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in wild carnivores from Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 148, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miró, G.; Montoya, A.; Jiménez, S.; Frisuelos, C.; Mateo, M.; Fuentes, I. Prevalence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii and intestinal parasities in stray, farm and household cats in Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Elmore, S.A.; Jones, J.L.; Conrad, P.A.; Patton, S.; Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii: Epidemiology, feline clinical aspects, and prevention. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, M.; Cabezón, O.; Dubey, J.P.; Almería, S.; Ribas, M.P.; Escobar, L.E.; Ramos, B.; Medina-Vogel, G. Toxoplasma gondii infection in wild mustelids and cats across an urban-rural gradient. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.S.; Frenkel, J.K. Prevalence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in wild mammals of Missouri and East Central Kansas: Biologic and ecologic considerations of transmisión. J. Wildl. Dis. 1995, 31, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejlíček, K.; Literák, I.; Nezval, J. Toxoplasmosis in wild mammals from the Czech Republic. J. Wildl. Dis. 1997, 33, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, R.N.; Cook, T.G. A congenital Toxoplasma-like disease in ferrets (Mustela putorious furo). N. Z. Vet. J. 1986, 34, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turčeková, L.; Hurníková, Z.; Spišák, F.; Miterpáková, M.; Chovancová, B. Toxoplasma gondii in protected wildlife in the Tatra National Park (TANAP), Slovakia. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2014, 21, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, L.V. Bacterial and parasitic diseases of ferrets. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2009, 12, 531–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smielewska-Los, E.; Turniak, W. Toxoplasma gondii infection in Polish farmed mink. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 122, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridham, T.J.; Belcher, J. Toxoplasmosis in mink. Can. J.Comp. Med. Vet. Sci. 1958, 22, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Akdesir, E.; Origgi, F.C.; Wimmershoff, J.; Frey, J.; Frey, C.F.; Ryser-Degiorgis, M.P. Causes of mortality and morbidity in free-ranging mustelids in Switzerland: Necropsy data from over 50 years of general health surveillance. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remes, N.; Kärssin, A.; Must, K.; Tagel, M.; Lassen, B.; Jokelainen, P. Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence in free-ranging moose (Alces alces) hunted for human consumption in Estonia: Indicator host species for environmental Toxoplasma gondii oocyst contamination. Vet Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2018, 11, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulpo, D.L.; Headley, S.A.; Biazzono, L.; da Cunha, I.A.L.; Igarashi, M.; de Barros, L.D.; Taroda, A.; Cardim, S.T.; Bogado, A.L.G.; Navarro, I.T.; et al. Oocyst shedding in cats vaccinated by the nasal and rectal routes with crude rhoptry proteins of Toxoplasma gondii. Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 131, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardaudov, A. Study on the toxoplasmosis among wild animals. Exp. Pathol. Parasitol. 2003, 6, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Maran, T.; Skumatov, D.; Gomez, A.; Põdra, M.; Abramov, A.V.; Dinets, V. Mustela lutreola. IUCN Red List. Threat Species. 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/307907972_Mustela_lutreola (accessed on 29 March 2025).
- Matas Méndez, P.; Fuentes Corripio, I.; Montoya Matute, A.; Bailo Barroso, B.; Grande Gómez, R.; Apruzzese Rubio, A.; Ponce Gordo, F.; Mateo Barrientos, M. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in endangered wild felines (Felis silvestris and Lynx pardinus) in Spain. Animals 2023, 13, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osten-Sacken, N.; Pikalo, J.; Steinbach, P.; Heddergott, M. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Antibodies and Risk Factors in Two Sympatric Invasive Carnivores (Procyon lotor and Nyctereutes procyonoides) from Zgorzelec County, Poland. Pathogens 2024, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Põdra, M.; Gómez, A. Rapid expansion of the American mink poses a serious threat to the European mink in Spain. Mammalia 2018, 82, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WOAH: World Organisation for Animal Health. Toxoplasmosis. 2017. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/esp/Health_standards/tahm/3.10.08_Toxoplasmosis.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Villanueva-Saz, S.; Basurco, A.; Martín, V.; Fernández, A.; Loste, A.; Verde, M.T. Comparison of a qualitative immunochromatographic test with two quantitative serological assays for the detection of antibodies to Leishmania infantum in dogs. Acta Vet. Scand. 2019, 61, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva-Saz, S.; Giner, J.; Verde, M.; Yzuel, A.; González, A.; Lacasta, D.; Marteles, D.; Fernández, A. Prevalence of microfilariae, antigen and antibodies of feline dirofilariosis infection (Dirofilaria immitis) in the Zaragoza metropolitan area, Spain. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2021, 23, 100541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, J.; Basurco, A.; Alcover, M.M.; Riera, C.; Fisa, R.; López, R.A.; Juan-salles, C.; Verde, M.T.; Fernández, A.; Yzuel, A.; et al. First report on natural infection with Leishmania infantum in a domestic ferret (Mustela putorius furo) in Spain. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 19, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Saz, S.; Giner, J.; Palomar, A.M.; Gómez, M.A.; Põdra, M.; Aranda, M.d.C.; Jiménez, M.d.l.Á.; Lizarraga, P.; Hernández, R.; Portillo, A.; et al. No Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Wild Mink (Mustela lutreola and Neogale vison) from Northern Spain during the First Two Years of Pandemic. Animals 2022, 12, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Saz, S.; Giner, J.; Tobajas, A.P.; Pérez, M.D.; González-Ramírez, A.M.; Macías-León, J.; González, A.; Verde, M.; Yzuel, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R.; et al. Serological evidence of SARS-CoV-2 and co-infections in stray cats in Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrells, A.; Bartley, P.M.; Zimmer, I.A.; Roy, S.; Kitchener, A.C.; Meredith, A.; Wright, S.E.; Innes, E.A.; Katzer, F. Evidence of the three main clonal Toxoplasma gondii lineages from wild mammalian carnivores in the UK. Parasitology 2013, 140, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, M.P.; Almería, S.; Fernández-Aguilar, X.; De Pedro, G.; Lizarraga, P.; Alarcia-Alejos, O.; Molina-López, R.; Obón, E.; Gholipour, H.; Temiño, C.; et al. Tracking Toxoplasma gondii in freshwater ecosystems: Interaction with the invasive American mink (Neogale vison) in Spain. Parasitol Res 2018, 117, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millán, J.; Cabezón, O.; Pabón, M.; Dubey, J.P.; Almería, S. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in feral cats (Felis silvestris catus) in Majorca, Balearic Islands, Spain. Vet. Parasitol 2009, 165, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepúlveda, M.A.; Muñoz-Zanzi, C.; Rosenfeld, C.; Jara, R.; Pelican, K.M.; Hill, D. Toxoplasma gondii in feral American mink at the Maullín River, Chile. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 175, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlers, A.; Mitchell, M.; Dubey, J.; Schooley, R.; Heske, E. Risk factors for Toxoplasma gondii exposure in semiaquatic mammals in a freshwater ecosystem. J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heddergott, M.; Pikalo, J.; Müller, F.; Osten-Sacken, N.; Steinbach, P. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild American Mink (Neogale vison): The First Serological Study in Germany and Poland. Pathogens 2024, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, M.E.; Pagh, S.; Stensgaard, A.S.; Chriel, M.; Petersen, H.H. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Cryptosporidium in Feral and Farmed American Mink (Neogale vison) in Denmark. Acta Parasitol. 2021, 66, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, J.D.S.; Dunstone, N. Sex-related differences in the diet of the mink Mustela vison. Ecography 1985, 8, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Tao, L.F.; Xu, L.X.; Yan, R.F.; Song, X.; Li, X. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in shellfish and fish in parts of China. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 200, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas-López, A.; Álvarez-García, G.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Cantos-Barreda, A.; Ibáñez-López, F.J.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cerón, J.J.; Martínez-Carrasco, C. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the serological diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection highlight the lack of a One Health integrative research. Res. Vet. Sci. 2023, 155, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas-López, A.; Cantos-Barreda, A.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Martínez-Carrasco, C.; Ibáñez-López, F.J.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cerón, J.J.; Álvarez-García, G. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the validation of serological methods for detecting anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in humans and animals. Vet. Parasitol. 2024, 328, 110173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lappin, M.R.; Thulliez, P. Long-term antibody responses of cats fed Toxoplasma gondii tissue cysts. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouatbi, M.; Amairia, S.; Amdouni, Y.; Boussaadoun, M.A.; Ayadi, O.; Al-Hosary, A.A.T.; Rekik, M.; Ben Abdallah, R.; Aoun, K.; Darghouth, M.A.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in North Africa: A review. Parasite 2019, 26, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Parker, S.; Al-Adhami, B.; Bachand, N.; Jenkins, E. Comparison of tissues (heart vs. brain) and serological tests (MAT, ELISA and IFAT) for detection of Toxoplasma gondii in naturally infected wolverines (Gulo gulo) from the Yukon, Canada. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Saz, S.; Martínez, M.; Giner, J.; Pérez, M.D.; Tobajas, A.P.; Yzuel, A.; Verde, M.T.; Lacasta, D.; Fernández, A.; Marteles, D.; et al. Evaluation of an immunochromatographic serologic test to detect the presence of anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in cats. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2023, 52, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Saz, S.; Giner, J.; Marteles, D.; Verde, M.; Yzuel, A.; Riera, C.; Fisa, R.; Alcover, M.; Fernández, A. Leishmaniosis caused by Leishmania infantum in ferrets: Update review. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2021, 15, 100229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, R.; Williams, E.S.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii in captive black-footed ferrets (Mustela nigripes), 1992–1998: Clinical signs, serology, pathology, and prevention. J. Wildl. Dis. 2003, 39, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, P.; Dietz, H.H.; Uttenthal, A.; Hansen, M. Sero-prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Danish farmed mink (Mustela vison S.). Vet. Parasitol. 1994, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwab, E.K.; Zhu, X.Q.; Majumdar, D.; Pena, H.F.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. Geographical patterns of Toxoplasma gondii genetic diversity revealed by multilocus PCR-RFLP genotyping. Parasitology 2014, 141, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.D.; Bräunig, P.; Machado, D.W.N.; Cargnelutti, J.F.; Silva Júnior, J.V.J.; Sangioni, L.A.; Vogel, F.S.F. Genotyping of human isolates from human toxoplasmosis outbreak: Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism and Sanger Sequencing. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2025, 56, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joeres, M.; Cardron, G.; Passebosc-Faure, K.; Plault, N.; Fernández-Escobar, M.; Hamilton, C.M.; O’Brien-Anderson, L.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Galal, L.; Luttermann, C.; et al. A ring trial to harmonize Toxoplasma gondii microsatellite typing: Comparative analysis of results and recommendations for optimization. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 42, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.M.; Xie, Y.T.; Xu, Z.S.; Chen, H.; Hide, G.; Yang, T.B.; Shen, J.L.; Lai, D.H.; Lun, Z.R. Genetic analyses of Chinese isolates of Toxoplasma gondii reveal a new genotype with high virulence to murine hosts. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 241, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajzenberg, D.; Collinet, F.; Mercier, A.; Vignoles, P.; Dardé, M.L. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii isolates with 15 microsatellite markers in a single multiplex PCR assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4641–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajzenberg, D.; Bañuls, A.L.; Tibayrenc, M.; Dardé, M.L. Microsatellite analysis of Toxoplasma gondii shows considerable polymorphism structured into two main clonal groups. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galal, L.; Hamidović, A.; Dardé, M.L.; Mercier, M. Diversity of Toxoplasma gondii strains at the global level and its determinants. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Shwab, E.K.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Dubey, J.P. Moving towards an integrated approach to molecular detection and identification of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 2010, 137, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vada, R.; Illanas, S.; Acevedo, P.; Adriaens, T.; Apollonio, M.; Belova, O.; Blanco-Aguiar, J.A.; Csányi, S.; Body, G.; Fernández-De-Mera, I.G.; et al. Feral American mink Neogale vison continues to expand its European range: Time to harmonise population monitoring and coordinate control. Mammal. Rev. 2023, 53, 158–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lebrero, M.E.; Villora, J.; Gómez, M.A.; Podra, M.; Aranda, M.d.C.; Villanueva-Saz, S.; Fernández, A.; Lizarraga, P.; Quilez, P.; Gómez, Á.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild European and American Mink (Mustela lutreola and Neogale vison) from Spain. Pathogens 2025, 14, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050427
Lebrero ME, Villora J, Gómez MA, Podra M, Aranda MdC, Villanueva-Saz S, Fernández A, Lizarraga P, Quilez P, Gómez Á, et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild European and American Mink (Mustela lutreola and Neogale vison) from Spain. Pathogens. 2025; 14(5):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050427
Chicago/Turabian StyleLebrero, María Eugenia, José Villora, María Asunción Gómez, Madis Podra, María del Carmen Aranda, Sergio Villanueva-Saz, Antonio Fernández, Patricia Lizarraga, Pablo Quilez, Álex Gómez, and et al. 2025. "Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild European and American Mink (Mustela lutreola and Neogale vison) from Spain" Pathogens 14, no. 5: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050427
APA StyleLebrero, M. E., Villora, J., Gómez, M. A., Podra, M., Aranda, M. d. C., Villanueva-Saz, S., Fernández, A., Lizarraga, P., Quilez, P., Gómez, Á., & Marteles, D. (2025). Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild European and American Mink (Mustela lutreola and Neogale vison) from Spain. Pathogens, 14(5), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14050427







