Kuru: A Journey Back in Time from Papua New Guinea to the Neanderthals’ Extinction
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Background and Ethnographic Setting


3. Cannibalism

4. Kuru Etiology – the Insight into A Novel Class of Pathogens
“I’ve been impressed with the overall resemblance of kuru, and an obscure degenerative disorder of sheep called scrapie […] The lesions in the goat seem to be remarkably like those described for kuru. […] All this suggests to me that an experimental approach similar to that adopted for scrapie might prove to be extremely fruitful in the case of kuru. […] because I’ve been greatly impressed by the intriguing implication, I’ve submitted a letter to The Lancet.”

5. Epidemiology of Kuru – A Strong Support of the Cannibalism Theory
6. Transmission Experiments
- 1. Early stage (I)
- a)
- prodromal period characterized by earliest alterations in behavior; animals became inactive, sometimes “extremely dirty” and submissive. “Vicious and aggressive animals became passive and withdrew from competition with their normal cagemates, allowing smaller chimpanzees to tease and take food from them”[..] periods of sullen apathy were often interrupted by outbursts of furious screaming”,
- b)
- Period of minimal disabilities characterized by minor motor dysfunction; animals did not want to go outside cages, “to run or to climb”, they were slow and fell with forced movements; the movements were “like [..]in slow-motion cinema”.
- 2. Intermediate stage (II)The onset of this stage was characterized by difficulties exhibited when a chimp tried to rise from a supine position; gait became ataxic but animals still could sit. The gait of chimpanzees is quadrupedal – “knuckle walking” where animals placed hands on the ground not with palms but with knuckles and this pattern is preserved but the gait itself is grossly ataxic and dysmetric. Truncal titubation, so characteristic for human kuru, is present since stage II. Passive muscle tone is increased and flexion contractures may develop if an animal lives long enough. Severe coarse tremor is seen, choreiform movements are observed and the negligence develops. Difficulties in seeing, lateral nystagmus and intermittent left strabismus was seen. “Babinsky” sign was occasionally observed.
- 3. Late stage (III)Characterized by severe neurological deficits: they could not rise by themselves from a supine position, they could not sit but placed themselves in one position, and decubitus ulcers were common. They eat inedible objects. A severe startled response comprising flexion of all extremities accompanied by violent coarse trembling of all limbs was a characteristic finding.


| Species | Incubation period (months) |
|---|---|
| Goat (Capra hircus) | (104)+ |
| Guinea pig (Cavia porcellus) | (27) |
| Opossum (Didelphis marsupialis) | (22+) |
| Domestic cat (Felis domesticus) | (59) |
| Gerbil (meriones unguiculatus) | (24)+ |
| Hamster (Mesocricetus auratus) | (28) |
| Mous (Mus musculus) | 22.5 |
| Ferret (Mustela putorius) | 18 – 70.5 |
| Mink (Mustela vision) | 45 |
| Sheep (Ovis aries) | (63)+ |
| Species | Incubation period (months) |
|---|---|
| Apes | |
| Chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) | 10–82 |
| Gibbon (Hylobates lar) | + (10) |
| New World Monkeys | |
| Capuchin (Cebus albifrons) | 10 – 92 |
| Capuchin (Cebus paella) | 11–71 |
| Spider (Ateles geofffroyi) | 10–85.5 |
| Moramoset (Saguinus sp) | 1176 |
| Wolly (Lagothrix lagotricha) | 33 |
| Old World Monkeys | |
| African Green (Cercopithecus aethiops) | 18 |
| Baboon (Papio anubis) | (130) |
| Bonnet (Macaca radiate) | 19–27 |
| Bushbaby (Galago senegalensis) | (120) |
| Cynomolgus macaque (Macaca fascicularis) | 16 |
| Patas (Erythrocebus patas patas) | (136) |
| Pigtailed macaque (Macaca nemestrina) | 70 |
| Rgesus (Macaca mulatta) | 15–102 |
| Sooty mangabey (Cercocebus atys) | +(2) |
| Talapoin (Cecopithecus talapoin) | (1+) |
7. Clinical Manifestations
“I was still very young when I saw [kuru] and even after we treated it there was no help. Everyone was falling apart. [Kuru victims] were aware there was no cure and that they would die. It wasn’t just one person that this sickness came to – there were about three in a house line and then after they died there would be another three. It was…ongoing…there were many deaths. Once a [person]…was affected by kuru [their] family would think that the clan had poisoned [them] and they would start…shooting at each other and that made it worse. It was chaos ! (Taurubi) .[113]



8. Neuropathology









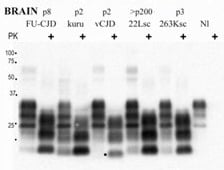
9. Genetics and Molecular Biology of Kuru


10. Conclusions and Speculations
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Asher, D.M.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Sulima, M.P.; Bacote, A.; Amyx, H.; Gajdusek, D.C. Transmission of Human Spongiform Encephalopathies to Experimental Animals: Comparison of Chimpanzee and Squirrel Monkey. In Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies – Impact on Animal and Human Health; Brown, P., Ed.; Developments of Biological Standardization, Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 1993; Volume 80, pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, D.M. Kuru: Memories of the NIH years. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2008, 363, 3618–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Kuru: An appraisal of five years of investigation. Eugen. Q. 1962, 9, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Gajdusek, D.C. Infection as the etiology of spongiform encephalopathy (Creutzfeldt-jakob disease). Science 1969, 165, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Hornabrook, R.W. Kuru. Papua New Guinea Med. J. 1975, 4, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Hornabrook, R.W. Kuru and clinical neurology. In Slow Transmissible Diseases of the Nervous System; Prusiner, S.B., Hadlow, W.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; pp. 37–66. [Google Scholar]
- Liberski, P.P.; Brown, P. Kuru − fifty years later. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2007, 41, 548–556. [Google Scholar]
- Liberski, P.P.; Brown, P. Kuru: A half-opened window onto the landscape of neurodegenerative diseases. Folia Neuropathol. 2004, 42 Suppl A, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liberski, P.P.; Brown, P. Kuru: Its ramifications after fifty years. Exp. Gerontol. 2009, 44, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberski, P.P.; Brown, P. Prion Disease: From Ritualistic Endocannibalism to Cellular Endocannibalism – From Kuru to Autophagy. In Aging and Age-Related Disease: The Basics; Karasek, M., Ed.; Nova Science Publisher, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 373–420. [Google Scholar]
- Liberski, P.P.; Gajdusek, D.C. Kuru: Fourty years later, a historical note. Brain Pathol. 1997, 7, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Zigas, V. Clinical, pathological and epidemiological study of an acute progressive degenerative disease of the central nervous system among natives of the Eastern Highlands of New Papua. Am. J. Med. 1959, 26, 442–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Zigas, V. Studies of kuru. I. The ethnologic setting of kuru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 80–91. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Alpers, M. Transmission and passage of experimental kuru to chimpanzees. Science 1967, 155, 212–214. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr. Transmission of two subacute spongiform encephalopathies of man (kuru and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease) to New World monkeys. Nature 1971, 230, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J.; Alpers, M. Experimental transmission of a kuru-like syndrome to chimpanzees. Nature 1966, 209, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Rogers, N.G.; Basnight, M.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Alpers , M.P. Transmission experiments with kuru in chimpanzees and the isolation of latent viruses from the explanted tissues of affected animals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1969, 162, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Zigas, V. Degenerative disease of the central nervous system in New Guinea. The endemic occurrence of “kuru” in the native population. N. Engl. J. Med. 1957, 257, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Asher, D.M.; Alpers, M.P.; Beck, E.; Daniel, P.M.; Matthews, W.B. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (spongiform encephalopathy): Transmission to chimpanzee. Science 1968, 161, 388–389. [Google Scholar]
- Jaskolski, M.; Liberski, P.P. Kurt Wüthrich – co-winner of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, 2002. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2002, 62, 288–289. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Kuru and its contribution to medicine. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3697–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyreuther, K.; Masters, C.L. βA4-Amyloid Domain is Essential for Axonal Sorting of APP: Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease. In Proceedings of Abstracts of the satellite meeting “Brain Tumors and Alzheimer’s Disease, From Neuropathology to Molecular Biology”, Bali, Indonesia, 3–5 September 1997.
- Gajdusek, D.C. Infectious Amyloids: Subacute Spongiform Encephalopathies as Transmissible Cerebral Amyloidosis. In Fields Virology, 3rd Ed.; Fields, B.N., Knippe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Eds.; Lippincott-Raven Publ: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996; pp. 2851–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Molecular Casting of Infectious Amyloids, Inorganic and Organic Replication: Nucleation, Conformational Change and Self-Assembly. In Self-Assembling Peptide Systems in Biology, Medicine and Engineering; Aggeli, A., Boden, N., Zhang, S., Eds.; Springer: New York, 2001; pp. 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ashe, K.H.; Aguzzi, A. Prions, prionoids and pathogenic proteins in Alzheimer disease. Prion 2013, 7, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Alpers, M.P.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr. Kuru: Epidemiological and Virological Studies of Unique New Guinean Disease with Wide Significance to General Medicine. In Essays on Kuru; Hornabrook, R.W., Ed.; E.W. Classey Ltd.: Faringdon, Berks, UK, 1976; pp. 125–145. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Alpers, M.P. Genetic studies in relation to kuru. I. Cultural, historical, and demographic background. Am. J. Hum. Gen. 1972, 24, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Alpers, M.P. Kuru in childhood: Disappearance of the disease in the younger age group. 7th Annual Meeting of American Pediatric Society. J. Pediatr. 1966, 69, 886–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Farquhar, J. (Eds.) Kuru. Early Letters and Field-Notes from the Collection of D. Carleton Gajdusek; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981.
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J. Unconventional Viruses Causing the Spongiform Virus Encephalopathies. A Fruitless Search for the Coat and Core. In Viruses and Environment; Kurstak, E., Maramosch, K., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Reid, H.L. Studies of kuru. IV: The kuru pattern in Moke, a representative Fore village. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 628–638. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Early images of kuru and the people of Okapa. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3636–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Kuru in the New Guinea Highlands. In Tropical Neurology; Spillane, J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1973; pp. 376–383. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Le kuru. In Colloque sur les Viruses lents, a Talloires, France, Organize le 17 Septembre 1978; pp. 25–57, Collection Foundation Merieux, 1979.
- Gajdusek, D.C. Observations on the Early History of Kuru Investigation. In Slow Transmissible Diseases of the Nervous System; Prusiner, S.B., Hadlow, W.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 1, pp. 7–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Slow virus infections of the nervous system. N. Engl. J. Med. 1967, 276, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Unconventional Viruses and the Origin and Disappearance of Kuru. In Les Prix Nobel en 1976; Nobel Fdn PA Norstedt & Soner: Stockholm, Sweden, 1977; pp. 167–216. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Unconventional viruses and the origin and disappearance of kuru. Science 1977, 197, 943–960. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Urgent Opportunistic Observations: The study of Changing, Transient and Disappearing Phenomena of Medical Interst in Disrupted Primitive Human Communities. In Health and Disease in Tribal Societies; CIBA Foundation Symposium, Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1977; pp. 69–102. [Google Scholar]
- Zigas, V.; Gajdusek, D.C. Kuru. Clinical study of a new syndrome resembling paralysis agitans in natives of the eastern Highlands of Australian New Guinea. Med. J. Aust. 1959, 44, 745–754. [Google Scholar]
- Zigas, V.; Gajdusek, D.C. Kuru. Clinical, pathological and epidemiological study of a recently discovered acute progressive degenerative disease of the central nervous system reaching “epidemic” proportions among natives of the Eastern Highlands of New Guinea. Papua New Guinea Med. J. 1959, 3, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mathews, J.D. The changing face of kuru: A personal perspective. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3679–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.D. The epidemiology of kuru. Papua New Guinea Med. J. 1967, 10, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum, S. Cannibalism, kuru and anthropology. Folia Neuropathol. 2009, 47, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum, S. Kuru Sorcery. Disease and Danger in the New Guinea Highlands, 2nd Ed. ed; Paradigm Publishers: Colorado, CO, USA, 2013; p. 224. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.H.; Rhodes, F.A.; Robson, H.N. A possible genetic basis for kuru. Am. J. Hum. Gen. 1959, 11, 169–187. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.H.; Rhodes, F.A.; Robson, H.N. Observations on kuru. I. A possible genetic basis. Australas Ann. Med. 1958, 7, 269–275. [Google Scholar]
- Glasse, R.; Lindenbaum, S. Fieldwork in the South Fore: The Process of Ethnographic Inquiry. In Prion Diseases of Humans and Animals; Prusiner, S.B., Collinge, J., Powell, J., Anderton, B., Eds.; Ellis Horwood: New York, London, Toronto, Sydney, Singapore, 1993; pp. 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum, S. Understanding kuru: The contribution of anthropology and medicine. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3715–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenbaum, S. Images of Catastrophe: The Making of an Epidemic. In The Political Economy of AIDS; Singer, M., Ed.; Baywood Publ Co Inc.: Amityville, New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 33–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum, S. Kuru, prions, and human affairs. Ann. Rev. Antrop. 2001, 30, 363–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenbaum, S. Thinking about cannibalism. Ann. Rev. Antrop. 2004, 33, 475–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.D.; Glasse, R.M.; Lindenbaum, S. Kuru and cannibalism. Lancet 1968, 2, 449–452. [Google Scholar]
- Glasse, R. Cannibalism in the Kuru region of New Guinea. Trans. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1967, 29, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arens, W. The Man-Eating Myth: Anthropology and Anthropophagy: Anthropology and Anthropophagy; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Zigas, V. Origin of Investigations on Slow Virus Infections in Man. In Slow Transmissible Diseases of the Nervous System; Prusiner, S.B., Hadlow, W.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 1, pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, L.; Gajdusek, D.C. Nutrition in the kuru region. II. A nutritional evaluation of tradition Fore diet in Moke village in 1957. Acta Trop. 1969, 26, 331–345. [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson, E.R.; Gajdusek, D.C. Nutrition in the kuru region. I. Gardening, Food handling, and diet of the Fore people. Acta Trop. 1969, 26, 281–330. [Google Scholar]
- Sorenson, E.R.; Gajdusek, D.C. The study of child growth and development in primitive cultures. A research archive for ethnopediatric film investigations of styles in the patterning of the nervous system. Pediatrics 1966, 37, 149–243. [Google Scholar]
- Curtain, C.C.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Zigas, V. Studies on kuru. II. Serum proteins in natives from the kuru region of New Guinea. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 92–109. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchin, D.; Bearn, A.G.; Alpers, M.P.; Gajdusek, D.C. Genetic studies in relation to kuru. III. Distribution of the inherited serum group-specific protein (Gc) phenotypes in New Guineans: An association of kuru and the Gc Ab phenotype. Am. J. Hum. Gen. 1972, 24, S72–S85. [Google Scholar]
- Mbaginta’o, I.G. Medical practices and funeral ceremony of the Dunkwi Anga. J. Soc. Océanistes 1976, 32, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plato, C.C.; Gajdusek, D.C. Genetic studies in relation to kuru. IV. Dermatoglyphics of the Fore and Anga populations of the Eastern Highlands of New Guinea. Am. J. Hum. Gen. 1972, 24, S86–S93. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, R.T.; Gajdusek, D.C. Blood Group Genetical Studies on Kuru-Afflicted Natives of the Eastern Highlands of New Guimea, and Comparison with Unaffected Neighboring Tribes in Papua New Guinea. In Proceedings of the 8th Congress of International Society of Blood Transfusions, Tokyo, Japan, 12–15 September 1960; pp. 255–259.
- Simmons, R.T.; Graydon, J.J.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Alpers, M.P.; Hornabrook, R.W. Genetic studies in relation to kuru. II. Blood-group genetic patterns and populations of the eastern Highlands of New Guinea. Am. J. Hum. Gen. 1972, 24, S39–S71. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, R.T.; Graydon, J.J.; Zigas, V.; Baker, V.; Larkin, L.; Gajdusek, D.C. Studies on kuru. V. A blood group genetical survey of the kuru region and other parts of Papua New Guinea. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 639–664. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, R.T.; Graydon, J.J.; Zigas, V.; Baker, V.; Larkin, L.; Gajdusek, D.C. Studies on kuru. VI. Blood groups in kuru. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 665–668. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesenfeld, S.L.; Gajdusek, D.C. Genetic studies in relation to kuru. VI. Evaluation of increased liability to kuru in Gc, Ab-Ab indyviduals. Am. J. Hum. Gen. 1975, 27, 498–504. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Kuru and Scrapie. In Prion Diseases of Humans and Animals; Prusiner, S.B., Collinge, J., Powell, J., Anderton, B., Eds.; Ellis Horwood: New York, London, Toronto, Sydney, Singapore, 1993; pp. 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hadlow, W.J. Kuru likened to scrapie: The story remembered. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadlow, W.J. Neuropathology and the scrapie-kuru connection. Brain Pathol. 1995, 5, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadlow, W.J. Scrapie and kuru. Lancet 1959, 2, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadlow, W.J. The Scrapie-Kuru Connection: Recollections of How it Came About. In Prion Diseases of Humans and Animals; Prusiner, S.B., Collinge, J., Powell, J., Anderton, B., Eds.; Ellis Horwood: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Collinge, C.J.; Whitfield, J.; McKintosch, E.; Frosh, A.; Mead, S.; Hill, A.F.; Brandner, S.; Thomas, D.; Alpers, M.P. A clinical study of kuru patients with long incubation periods at the end of the epidemic in Papua New Guinea. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3725–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besnoit, C. La tremblante ou nevrite peripherique enzootique du mouton. Rev Vet (Tolouse) 1899, 24, 265–277. [Google Scholar]
- M'Gowan, J.P. Investigation into the disease of sheep called “scrapie” (Traberkrankheit, La tremblante). With especial reference to its association with Sarcosporidiosis; William Blackwood and Sons: Edinburgh, Scotland, 1914. [Google Scholar]
- Innes, J.R.M.; Saunders, L.Z. Comparative Neuropathology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1962; p. 839. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb, L.G.; Cervenakova, L.; Gajdusek, D.C. Genetic studies in relation to kuru: An overview. Curr. Mol. Med. 2004, 4, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnik, I. Significance of vacuolated neurones in the medulla of sheep infected with scrapie. Nature 1957, 180, 393–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnik, I. Vacuolated neurons in sheep affected with scrapie. Nature 1957, 179, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J. Attempts to demonstrate a transmissible agent in kuru, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and other sub-acute and chronic system degenerations of man. Nature 1964, 204, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrell, R.W.; Lomas, D.A. Conformational disease. Lancet 1997, 350, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Transmissible and nontransmissible dementias: Distinction between primary cause and pathogenetic mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease and aging. Mount. Sinai J. Med. 1988, 55, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Gajdusek, D.C. Attempts to Demonstrate A Transmissible Agent in Kuru, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, and Other Subacute and Chronic Progressive Nervous System Degenerations of Man. In Slow, Latent, and Temperate Virus Infections; Gajdusek, D.C., Gibbs, C.J., Jr., Alpers, M., Eds.; NINDB Monograph No. 2. US Department of Heath, Education, and Welfare: Washington D.C., USA, 1965; pp. 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Alpers, M.P.; Gajdusek, D.C. Changing pattern of kuru: Epidemiological changes in the period of increasing contact of the Fore people with western civilization. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1965, 14, 852–879. [Google Scholar]
- Alpers, M.P. Epidemiology and Ecology of Kuru. In Slow Transmissible Diseases of the Nervous System; Prusiner, S.B., Hadlow, W.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 1, pp. 67–90. [Google Scholar]
- Alpers, M.P. The epidemiology of kuru: Monitoring the epidemic from its peak to the end. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3707–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Kuru in Childhood: Implications for the Problem of Whether Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy Affects Humans. In Transmissible Subacute Spongiform Encephalopathies: Prion Diseases; Court, L., Dodet, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb, L.G. Kuru: The old epidemic in a new mirror. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Zigas, V.; Baker, J. Studies on kuru. III. Patterns of kuru incidence: Demographic and geographic epidemiological analysis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1961, 10, 99–627. [Google Scholar]
- Mathews, J.D. A transmission model for kuru. Lancet 1967, 1, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.D. Kuru as An Epidemic Disease. In Essays on kuru; Hornabrook, R.W., Ed.; Papua New Guinea Institute of Medical Research, Monographs no 3: Faringdon, Berkshire, UK, 1976; pp. 83–104. [Google Scholar]
- Alpers, M.P. Some tributes to research colleagues and other contributors to our knowledge about kuru. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3614–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klitzman, R.L.; Alpers, M.P.; Gajdusek, D.C. The natural incubation period of kuru and the episodes of transmission in three clusters of patients. Neuroepidemiology 1984, 3, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervenakova, L.; Goldfarb, L.G.; Garruto, R.; Lee, H.S.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Brown, P. Phenotype-genotype studies in kuru: Implications for new variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13239–13241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Gibbs, C.J.; Rodgers-Johnson, P.; Asher, D.; Sulima, M.P.; Bacote, A.; Goldfarb, L.G.; Gajdusek, D.C. Human spongiform encephalopathy: The National Institutes of Health series of 300 cases of experimentally transmitted disease. Ann. Neurol. 1994, 35, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Amyx, H.L.; Bacote, A.; Masters, C.L.; Gajdusek, D.C. Oral transmission of kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, and scrapie to nonhuman primates. J. Infect. Dis. 1980, 142, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Amyx, H. Strain Variation in the Viruses of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease and Kuru. In Slow Transmissible Diseases of the Nervous System; Prusiner, S.B., Hadlow, W.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 1, pp. 87–110. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Gajdusek, D.C. Transmission and Characterization of the Agents of Spongiform Virus Encephalopathies: Kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease, Scrapie and Mink Encephalopathy. Res. Publ. Assoc. Res. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 1971, 49, 383–410. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, C.J. Spongiform Encephalopathies – Slow, Latent, and Temperate Virus Infections – in Retrospect. In Prion Diseases of Humans and Animals; Prusiner, S.B., Collinge, J., Powell, J., Anderon, B., Eds.; Ellis Horwood: New York, London, Toronto, Sydney, Singapore, 1993; pp. 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Liberski, P.P. Wirusy powolne układu nerwowego człowieka i zwierząt. Część I. Kuru. (Slow viruses of the nervous system of man and animals. part I. Kuru). Post. Hig. Med. Dośw. 1981, 35, 471–493. [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr. Transmission of kuru from man to Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatto) 8.1/2 years after inoculation. Nature 1972, 240, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.A.; Wolfe, L.G.; Deinhardt, F.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J. Transmission of kuru and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease to Marmoset monkeys. Intervirology 1974, 2, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Masters, C.L.; Alpers, M.P.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Kakulas, B.A. Experimental kuru in the gibbon and Sooty mangabey and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the pigtailed macaque. J. Med. Primatol. 1976, 5, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, E.; Daniel, P.M. Kuru and Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease: Neuropathological Lesions and Their Significance. In Slow Transmissible Diseases of the Nervous System; Prusiner, S.B., Hadlow, W.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 1, pp. 253–270. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, E.; Daniel, P.M.; Alpers, M.P.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr. Neuropathological Comparisons of Experimental Kuru in Chimpanzees with Human Kuru. With a Note on Its Relation to Scrapie and Spongiform Encephalopathy. Locarno, Switzerland, 31 May —3 June 1967; Burdzy, K., Kallos, P., Eds.; Additamentum to Arch Allergy and Appl Immunol: Basel, Karger, Switzerland, 1969; Volume 36, pp. 553–562. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, E.; Daniel, P.M.; Alpers, M.P.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr. Experimental kuru in chimpanzees. A pathological report. Lancet 1966, 2, 1056–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, E.; Daniel, P.M.; Asher, M.P.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr. Experimental kuru in chimpanzees. A neuropathological study. Brain 1973, 96, 441–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, E.; Daniel, P.M.; Gajdusek, D.C. A Comparison between the Neuropathological Changes in Kuru and Scrapie, System Degeneration. In Proceedings of the VIth International Congress Neuropathological, Zurich, Switzerland, 31 August – 3 September 1965; pp. 213–218.
- Beck, E.; Daniel, P.M. Kuru and Scrapie Compared: Are They Examples of System Degeneration? In Slow, Latent, and Temperate Virus Infections; Gajdusek, D.C., Gibbs, C.J., Jr., Alpers, M.P., Eds.; US Dept Health, Education, Welfare: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; pp. 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, E.; Daniel, P.M. Prion Diseases from A Neuropathologist’s Perspective. In Prion Diseases of Humans and Animals; Prusiner, S.B., Collinge, J., Powell, J., Anderton, B., Eds.; Ellis Horwood: New York, London, Toronto, Sydney, Singapore, 1993; pp. 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, E.; Bak, J.; Christ, J.F.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Hassler, R. Experimental kuru in the Spider monkey. Histopathological and Ultrastructural studies of the brain during early stages of incubation. Brain 1975, 98, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, A. The promised medicine: Fore reflections on the scientific investigation of kuru. Oceania 2006, 76, 186–202. [Google Scholar]
- Alpers, M.P. Kuru: Age and Duration Studies. Mimeographed; Departament of Medicine, University of Adelaide: Adelaide, Australia, 1964; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Alpers, M.P. Kuru: Implications of Its Transmissibility for the Interpretation of Its Changing Epidemiologic Pattern. In The Central Nervous System; Bailey, O.T., Smith, D.E., Eds.; International Academy of Pathology Monograph No. 9. Williams & Wilkins Comp: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1968; pp. 234–250. [Google Scholar]
- Beasley, A. Frontier journals. Fore experiences on the kuru patrols. Oceania 2009, 79, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, A. Frontier Science: The Early Investigation of Kuru in Papua New Guinea. In Challenging Science: Issues in New Zealand; Dew, K., Fitzgerald, R., Eds.; Dunmore Press: Palmerston North, New Zealand, 2004; pp. 146–166. [Google Scholar]
- Beasley, A. Kuru truths: Obtaining Fore narratives. Field Methods 2006, 18, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, A. Richard Hornabrook’s first impressions of kuru and Okapa. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3626–3627. [Google Scholar]
- Collinge, C.J.; Whitfield, J.; McKintosch, E.; Beck, J.; Mead, S.; Thomas, D.; Alpers, M.P. Kuru in the 21st century – an acquired human prion disease with very long incubation periods. Lancet 2006, 367, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinge, J. Lessons of kuru research: Background to recent studies with some personal reflections. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdusek, D.C.; Sorenson, E.R.; Meyer, J. A comprehensive cinema record of disappearing kuru. Brain 1970, 93, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Alpers, M.P. Kuru with incubation periods exceeding two decades. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, M.P. Kuru: A Clinical Study; Mimeographed; Dept. Medicine, University of Adelaide: Adelaide, Australia, 1964; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Klatzo, I.; Gajusek, D.C.; Zigas, V. Evaluation of Pathological Findings in Twelve Cases of Kuru. In Encephalitides; van Boagert, L., Radermecker, J., Hozay, J., Lowenthal, A., Eds.; Elsevier Publ. Comp.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1959; pp. 172–190. [Google Scholar]
- Klatzo, I.; Gajusek, D.C. Pathology of kuru. Lab. Invest. 1959, 8, 799–847. [Google Scholar]
- Biernat, W.; Liberski, P.P.; Guiroy, D.C.; Yanagihara, R.; Gajdusek, D.C. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunohistochemistry in astrocytes in experimental Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and in human kuru, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome. Neurodegeneration 1995, 4, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, M.; Robertson, E.G. Observations on kuru. III: Pathological features in five cases. Australas Ann. Med. 1959, 8, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kakulas, B.A.; Lecours, A.-R.; Gajdusek, D.C. Further observations on the pathology of kuru. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1967, 26, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardo, P.; Safar, J.; Ceroni, M.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J. Immunohistochemical localization of prion protein in spongiform encephalopathies and normal brain tissue. Neurology 1990, 40, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrimgeour, E.M.; Masters, C.L.; Alpers, M.P.; Kaven, J.; Gajdusek, D.C. A clinico-pathological study of case of kuru. J. Neurol. Sci. 1983, 59, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrimgeou, E.M. Some recollections about kuru in a patient at Rabaul in 1978, and subsequent experiences with prion diseases. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3663–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorska, B.; Liberski, P.P.; Sobów, T.; Budka, H.; Ironside, J.W. Ultrastructural study of florid plaques in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: A comparison with amyloid plaques in kuru, sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2009, 35, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitelberger, F. Eigenartige familiar-hereditare Krankheit des Zetralnervensystems in einer niederosterreichischen Sippe. Wien Klein Wochen 1962, 74, 687–691. [Google Scholar]
- Neuman, M.A.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Zigas, V. Neuropathologic findings in exotic neurologic disorder among natives of the Highlands of New Guinea. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1964, 23, 486–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, C.L.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease virus isolations from the Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome. With an analysis of the various forms of amyloid plaque deposition in the virus induced spongiform encephalopathies. Brain 1981, 104, 559–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberski, P.P.; Sikorska, B.; Lindenbaum, S.; Goldfarb, L.G.; McLean, C.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Brown, P. Kuru: Genes, cannibals and neuropathology. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 71, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainfellner, J.; Liberski, P.P.; Guiroy, D.C.; Cervénaková, L.; Brown, P.; Gajdusek , D.C.; Budka, H. Pathology and immunohistochemistry of a kuru brain. Brain Pathol. 1997, 7, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, C.A. The neuropathology of kuru and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3685–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, C.A.; Ironside, J.W.; Alpers, M.P.; Brown, P.W.; Cervenakova, L.; Anderson, R.M.; Masters, C.L. Comparative neuropathology of kuru with the new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Evidence for strain of agent predominating over genotype of host. Brain Pathol. 1998, 8, 428–437. [Google Scholar]
- Peat, A.; Field, E.J. An unusual structure in kuru brain. Acta Neuropathol. (Berl) 1970, 15, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberski, P.P. The occurrence of cytoplasmic lamellar bodies in scrapie infected and normal hamster brains. Neuropatol. Pol. 1988, 26, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Liberski, P.P.; Yanagihara, R.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Gajdusek, D.C. Re-evaluation of experimental Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Serial studies of the Fujisaki strain of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease virus in mice. Brain 1990, 113, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, P.W.; Earle, K.M.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Gajdusek, D.C. Experimental kuru encephalopathy in chimpanzees and spider monkey. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1969, 28, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodbrand, I.A.; Ironside, J.W.; Nicolson, D.; Bell, J.E. Prion protein accumulations in the spinal cords of patients with sporadic and growth hormone-associated Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 183, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, S.; Whitfield, J.; Boone, K.; Puva, A.; O’Malley, C.; Linehan, J.M.; Joiner, S.; Scaravilli, F.; Calder, I.; Alpers, M.P.; et al. Central and peripheral pathology of kuru: Pathological analysis of a recent case and comparison with other forms of human prion diseases. Phil. Trans. R. S. 2008, 363, 3755–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinge, J.; Sidle, K.C.L.; Meads, J.; Ironside, J.W.; Hill, A.F. Molecular analysis of prion strain variation and the etiology of “new variant” CJD. Nature 1996, 383, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchi, P.; Castellani, R.; Capellari, S.; Ghetti, B.; Young, K.; Chen, S.G.; Farlow, M.; Dickson, D.W.; Sima, A.A.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Molecular basis of phenotypic variability in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 39, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Brown, P.; Cervenakova, L.; Garruto, R.; Alpers, M.P.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Goldafrb, L.G. Increased susceptibility to kuru of carriers of the PRNP 129 Methionine/Methionine genotype. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, S.; Poulter, M.; Uphill, J.; Beck, J.; Whitfield, J.; Webb, T.E.F.; Campbell, T.; Adamson, G.; Deriziotis, P.; Tabrizi, S.J.; et al. Genetic risk factors for variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, S.; Stumpf, M.P.; Whitfield, J.; Beck, J.A.; Poulter, M.; Campbell, T.; Uphill, J.B.; Goldstein, D.; Alpers, M.; Fisher, E.M.; et al. Balancing selection at the prion protein gene consistent with prehistoric kurulike epidemics. Science 2003, 300, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, S.; Whitfield, J.; Poulter, M.; Shah, P.; Uphill, J.; Beck, J.; Campbell, T.; al-Dujaly, H.; Hummerich, H.; Alpers, M.P.; et al. Genetic susceptibility, evolution and the kuru epdemic. Phil. Trans. R. S. 2008, 363, 3741–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, S. Prion disease genetics. Eur. J. Human Genet. 2006, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantos, B.; Bhata, K.; Doey, L.J.; al-Sarraj, S.; Doshi, R.; Beck, J.; Collinge, J. Is the neuropathology of new variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and kuru similar? Lancet 1997, 350, 187–188. [Google Scholar]
- Aguzzi, A.; Heikenwalder, M. Prion diseases: Cannibals and garbage piles. Nature 2003, 423, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookfield, J.F. Human evolution: A legacy of cannibalism in our genes? Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, R592–R593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, S.; Whitfield, J.; Poulter, M.; Shah, P.; Uphill, J.; Campbell, T.; al-Dujaily, H.; Hummerich, H.; Beck, J.; Mein, C.A.; et al. A novel protective prion protein variant that colocalizes with kuru exposure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2056–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, S.; Uphill, J.; Beck, J.; Poulter, M.; Campbell, T.; Lowe, J.; Adamson, G.; Hummerich, H.; Klopp, N.; Rückert, I.M.; et al. Genome-wide association study in multiple human prion diseases suggests genetic risk factors additional to PRNP. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlar, R.A.; Leonard, B.L.; Billman, B.R.; Lambert, P.M.; Marlar, J.E. Biochemical evidence of cannibalism at a prehistoric Puebloan site in southwestern Colorado. Nature 2000, 407, 25–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riel-Salvatore, J. Mad Neanderthal disease? Some comments on A potential role for Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies in Neanderthal extinction. Med. Hyp. 2008, 71, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underdown, S. A potential role for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in Neanderthal extinction. Med. Hyp. 2008, 71, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth, J.D.F.; Joiner, S.; Linehan, J.M.; Asante, E.A.; Brandner, S.; Collinge, J. The origin of the prion agent of kuru: Molecular and biological strain typing. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2008, 363, 3747–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth, J.D.F.; Joiner, S.; Linehan, J.M.; Desbruslais, M.; Fox, K.; Cooper, S.; Cronier, S.; Asante, E.A.; Mead, S.; Brandner, S.; et al. Kuru prions and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prions have equivalent transmission properties in transgenic and wild-type mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 105, 3885–3890. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, A.F.; Desbruslais, M.; Joiner, S.; Sidle, K.L.C.; Gowland, I.; Collinge, J.; Doey, L.J.; Lantos, P. The same prion strain causes vCJD and BSE. Nature 1997, 389, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchi, P.; Cescatti, M.; Notari, S.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Capellari, S.; Giese, A.; Zou, W.Q.; Kretzschmar, H.; Ghetti, B.; Brown, P. Agent strain variation in human prion disease: Insights from a molecular and pathological review of the National Institutes of Health series of experimentally transmitted disease. Brain 2010, 133, 3030–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchi, P; Saverioni, D. Molecular pathology, classification, and diagnosis of sporadic human prion disease variants. Folia Neuropathol 2012, 50, 20–45. [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis, L.; Chakrabarty, T.; Miyazawa, K.; Nduom, N.A.; Emmerling, K. The kuru infectious agent is a unique geographic isolate distinct from Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and scrapie agents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13529–13534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Liberski, P.P. Kuru: A Journey Back in Time from Papua New Guinea to the Neanderthals’ Extinction. Pathogens 2013, 2, 472-505. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030472
Liberski PP. Kuru: A Journey Back in Time from Papua New Guinea to the Neanderthals’ Extinction. Pathogens. 2013; 2(3):472-505. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030472
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiberski, Pawel P. 2013. "Kuru: A Journey Back in Time from Papua New Guinea to the Neanderthals’ Extinction" Pathogens 2, no. 3: 472-505. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030472
APA StyleLiberski, P. P. (2013). Kuru: A Journey Back in Time from Papua New Guinea to the Neanderthals’ Extinction. Pathogens, 2(3), 472-505. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030472