Evaluation of the Zoonotic Potential of Transmissible Mink Encephalopathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Transmission of Cattle-Adapted TME in Experimental Models
| Dose | Cattle TME | Raccoon TME | L-BSE | c-BSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | 40 (38 / 2) | |||
| 40 mg | 23 (19.5 / 3.5) | 18 (11.5 / 6.5) | ||
| 25 mg | 26 (21.5 / 4.5) | |||
| 2.5 mg | 25 (20 / 5) | |||
| 0.5 mg | 57 (55 / 2) 93 (85 / 8) |
2.2. Transmission of other cattle prion strains

2.3. Comparative Pathologies of the Diseases Induced by the Different Cattle Prions


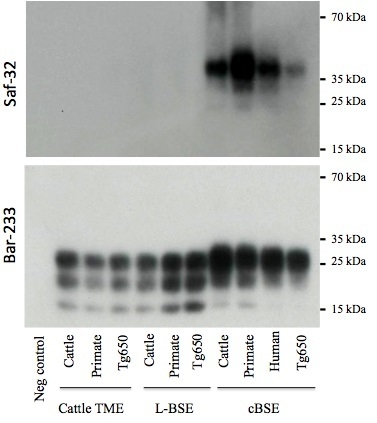
2.3. PrPres Detection: Strain Discrimination by Proteinase K Sensitivity and Antibody Reactivity


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Ethics Statement
3.2. Experimental Animals
3.3. Experimental Inoculations
3.4. Neuropathology and Immunohistochemistry
3.4. PrPres Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Liberski, P.P.; Sikorska, B.; Guiroy, D.; Bessen, R.A. Transmissible mink encephalopathy - review of the etiology of a rare prion disease. Folia Neuropathol. 2009, 47, 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, R.F.; Bessen, R.A.; Lehmann, S.; Hartsough, G.R. Epidemiological and experimental studies on a new incident of transmissible mink encephalopathy. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72(Pt 3), 589–594. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, R.F.; Hadlow, W.J. Transmissible mink encephalopathy. Rev. Sci. Tech. 1992, 11, 539–550. [Google Scholar]
- Harrington, R.D.; Baszler, T.V.; O'Rourke, K.I.; Schneider, D.A.; Spraker, T.R.; Liggitt, H.D.; Knowles, D.P. A species barrier limits transmission of chronic wasting disease to mink (mustela vison). J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1086–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.M.; Hadlow, W.J.; Huff, T.P.; Wells, G.A.; Dawson, M.; Marsh, R.F.; Gorham, J.R. Experimental infection of mink with bovine spongiform encephalopathy. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75(Pt 9), 2151–2155. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, R.F.; Bessen, R.A. Epidemiologic and experimental studies on transmissible mink encephalopathy. Dev. Biol. Stand. 1993, 80, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hamir, A.N.; Kunkle, R.A.; Miller, J.M.; Bartz, J.C.; Richt, J.A. First and second cattle passage of transmissible mink encephalopathy by intracerebral inoculation. Vet. Pathol. 2006, 43, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, T.; Bencsik, A.; Biacabe, A.G.; Morignat, E.; Bessen, R.A. Phenotypic similarity of transmissible mink encephalopathy in cattle and l-type bovine spongiform encephalopathy in a mouse model. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, S.; Baron, T. Strain-specific barriers against bovine prions in hamsters. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1906–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalone, C.; Zanusso, G.; Acutis, P.; Ferrari, S.; Capucci, L.; Tagliavini, F.; Monaco, S.; Caramelli, M. Identification of a second bovine amyloidotic spongiform encephalopathy: Molecular similarities with sporadic creutzfeldt-jakob disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3065–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capobianco, R.; Casalone, C.; Suardi, S.; Mangieri, M.; Miccolo, C.; Limido, L.; Catania, M.; Rossi, G.; Di Fede, G.; Giaccone, G.; et al. Conversion of the base prion strain into the bse strain: The origin of bse? PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, T.; Vulin, J.; Biacabe, A.G.; Lakhdar, L.; Verchere, J.; Torres, J.M.; Bencsik, A. Emergence of classical bse strain properties during serial passages of h-bse in wild-type mice. PLoS One 2011, 6, e15839. [Google Scholar]
- Will, R.G.; Ironside, J.W.; Zeidler, M.; Cousens, S.N.; Estibeiro, K.; Alperovitch, A.; Poser, S.; Pocchiari, M.; Hofman, A.; Smith, P.G. A new variant of creutzfeldt-jakob disease in the uk. Lancet 1996, 347, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasmezas, C.I.; Deslys, J.P.; Demaimay, R.; Adjou, K.T.; Lamoury, F.; Dormont, D.; Robain, O.; Ironside, J.; Hauw, J.J. Bse transmission to macaques. Nature 1996, 381, 743–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, M.E.; Will, R.G.; Ironside, J.W.; McConnell, I.; Drummond, D.; Suttie, A.; McCardle, L.; Chree, A.; Hope, J.; Birkett, C.; et al. Transmissions to mice indicate that 'new variant' cjd is caused by the bse agent. Nature 1997, 389, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Gibbs, C.J., Jr.; Rodgers-Johnson, P.; Asher, D.M.; Sulima, M.P.; Bacote, A.; Goldfarb, L.G.; Gajdusek, D.C. Human spongiform encephalopathy: The national institutes of health series of 300 cases of experimentally transmitted disease. Ann. Neurol. 1994, 35, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasmezas, C.I.; Comoy, E.; Hawkins, S.; Herzog, C.; Mouthon, F.; Konold, T.; Auvre, F.; Correia, E.; Lescoutra-Etchegaray, N.; Sales, N.; et al. Risk of oral infection with bovine spongiform encephalopathy agent in primates. Lancet 2005, 365, 781–783. [Google Scholar]
- Yutzy, B.; Holznagel, E.; Coulibaly, C.; Stuke, A.; Hahmann, U.; Deslys, J.P.; Hunsmann, G.; Lower, J. Time-course studies of 14-3-3 protein isoforms in cerebrospinal fluid and brain of primates after oral or intracerebral infection with bovine spongiform encephalopathy agent. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 3469–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasemann, S.; Neumann, M.; Geissen, M.; Bodemer, W.; Kaup, F.J.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Morel, N.; Aguzzi, A.; Glatzel, M. Preclinical deposition of pathological prion protein in muscle of experimentally infected primates. PLoS One 2010, 5, e13906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ono, F.; Terao, K.; Tase, N.; Hiyaoka, A.; Ohyama, A.; Tezuka, Y.; Wada, N.; Kurosawa, A.; Sato, Y.; Tobiume, M.; et al. Experimental transmission of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (bse) to cynomolgus macaques, a non-human primate. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 64, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Comoy, E.E.; Casalone, C.; Lescoutra-Etchegaray, N.; Zanusso, G.; Freire, S.; Marce, D.; Auvre, F.; Ruchoux, M.M.; Ferrari, S.; Monaco, S.; et al. Atypical bse (base) transmitted from asymptomatic aging cattle to a primate. PLoS One 2008, 3, e3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, F.; Tase, N.; Kurosawa, A.; Hiyaoka, A.; Ohyama, A.; Tezuka, Y.; Wada, N.; Sato, Y.; Tobiume, M.; Hagiwara, K.; et al. Atypical l-type bovine spongiform encephalopathy (l-bse) transmission to cynomolgus macaques, a non-human primate. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 64, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Beringue, V.; Le Dur, A.; Tixador, P.; Reine, F.; Lepourry, L.; Perret-Liaudet, A.; Haik, S.; Vilotte, J.L.; Fontes, M.; Laude, H. Prominent and persistent extraneural infection in human prp transgenic mice infected with variant cjd. PLoS One 2008, 3, e1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beringue, V.; Herzog, L.; Reine, F.; Le Dur, A.; Casalone, C.; Vilotte, J.L.; Laude, H. Transmission of atypical bovine prions to mice transgenic for human prion protein. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1898–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Zheng, M.; Casalone, C.; Qing, L.; Huang, S.; Chakraborty, B.; Wang, P.; Chen, F.; Cali, I.; Corona, C.; et al. Evaluation of the human transmission risk of an atypical bovine spongiform encephalopathy prion strain. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 3697–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Plinston, C.; Hunter, N.; Casalone, C.; Corona, C.; Tagliavini, F.; Suardi, S.; Ruggerone, M.; Moda, F.; Graziano, S.; et al. Chronic wasting disease and atypical forms of bovine spongiform encephalopathy and scrapie are not transmissible to mice expressing wild-type levels of human prion protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchi, P.; Giese, A.; Capellari, S.; Brown, P.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Windl, O.; Zerr, I.; Budka, H.; Kopp, N.; Piccardo, P.; et al. Classification of sporadic creutzfeldt-jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, S.; Bencsik, A.; Morignat, E.; Mestre-Frances, N.; Perret-Liaudet, A.; Baron, T. Differentiation of prions from l-type bse versus sporadic creutzfeldt-jakob disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 2028–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, J.; Gutierrez Adan, A.; Brun, A.; Pintado, B.; Ramirez, M.A.; Parra, B.; Doyle, D.; Rogers, M.; Salguero, F.J.; Sanchez, C.; et al. Early detection of prpres in bse-infected bovine prp transgenic mice. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamir, A.N.; Miller, J.M.; O'Rourke, K.I.; Bartz, J.C.; Stack, M.J.; Chaplin, M.J. Transmission of transmissible mink encephalopathy to raccoons (procyon lotor) by intracerebral inoculation. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2004, 16, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Comoy, E.E.; Mikol, J.; Ruchoux, M.-M.; Durand, V.; Luccantoni-Freire, S.; Dehen, C.; Correia, E.; Casalone, C.; Richt, J.A.; Greenlee, J.J.; et al. Evaluation of the Zoonotic Potential of Transmissible Mink Encephalopathy. Pathogens 2013, 2, 520-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030520
Comoy EE, Mikol J, Ruchoux M-M, Durand V, Luccantoni-Freire S, Dehen C, Correia E, Casalone C, Richt JA, Greenlee JJ, et al. Evaluation of the Zoonotic Potential of Transmissible Mink Encephalopathy. Pathogens. 2013; 2(3):520-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030520
Chicago/Turabian StyleComoy, Emmanuel E., Jacqueline Mikol, Marie-Madeleine Ruchoux, Valérie Durand, Sophie Luccantoni-Freire, Capucine Dehen, Evelyne Correia, Cristina Casalone, Juergen A. Richt, Justin J. Greenlee, and et al. 2013. "Evaluation of the Zoonotic Potential of Transmissible Mink Encephalopathy" Pathogens 2, no. 3: 520-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030520
APA StyleComoy, E. E., Mikol, J., Ruchoux, M.-M., Durand, V., Luccantoni-Freire, S., Dehen, C., Correia, E., Casalone, C., Richt, J. A., Greenlee, J. J., Torres, J. M., Brown, P., & Deslys, J.-P. (2013). Evaluation of the Zoonotic Potential of Transmissible Mink Encephalopathy. Pathogens, 2(3), 520-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens2030520