Mouse Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Comprising Host-Virus Immunologic Interactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Animal model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Human | Natural target of infection | |
| Chimpanzee | An immunocompetent host fully susceptible to HBV infection, similar to human infection (including cccDNA) | Ethical constraints, large size, high costs, transient infection |
| Tupaia | Susceptible to HBV infection, similar to human infection (including cccDNA) | Relatively large size, not easily available, outbred animals, transient infection |
| Mouse | Small, inbred animals, genetically and immunologically well-known | No-infection |
| Transgenic mouse | convenient, inbred animals, immunological experiment with adoptive transfer | No-infection, immune tolerance |
| Transfected mouse by hydrodynamic injection | Analysis of mutant strains, immunocompetent | No-infection, transient gene expression, |
| Transfected mouse by adeno-associated virus | High replication levels, analysis of mutant strains, immunocompetent, relatively long-time gene-expression | No-infection, transient gene expression, possible vector-driven interferences |
| Human liver-chimeric mouse | Susceptible to HBV infection (including cccDNA), capable to use clinical specimen, assessment of efficacy of anti-HBV agents | high costs, immunocompromised, Transient infection (but relatively long infection) |
2. Mouse Models
2.1. HBV-Transgenic Mouse Models
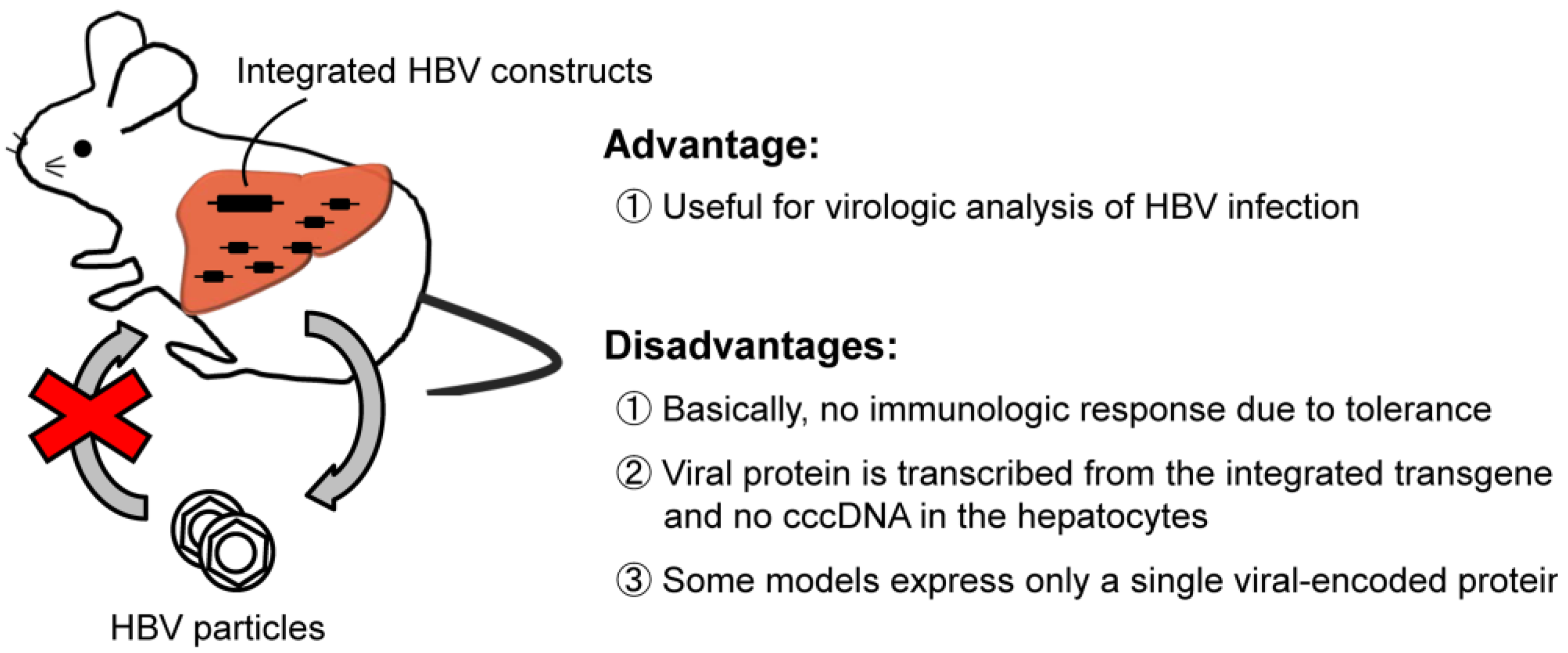
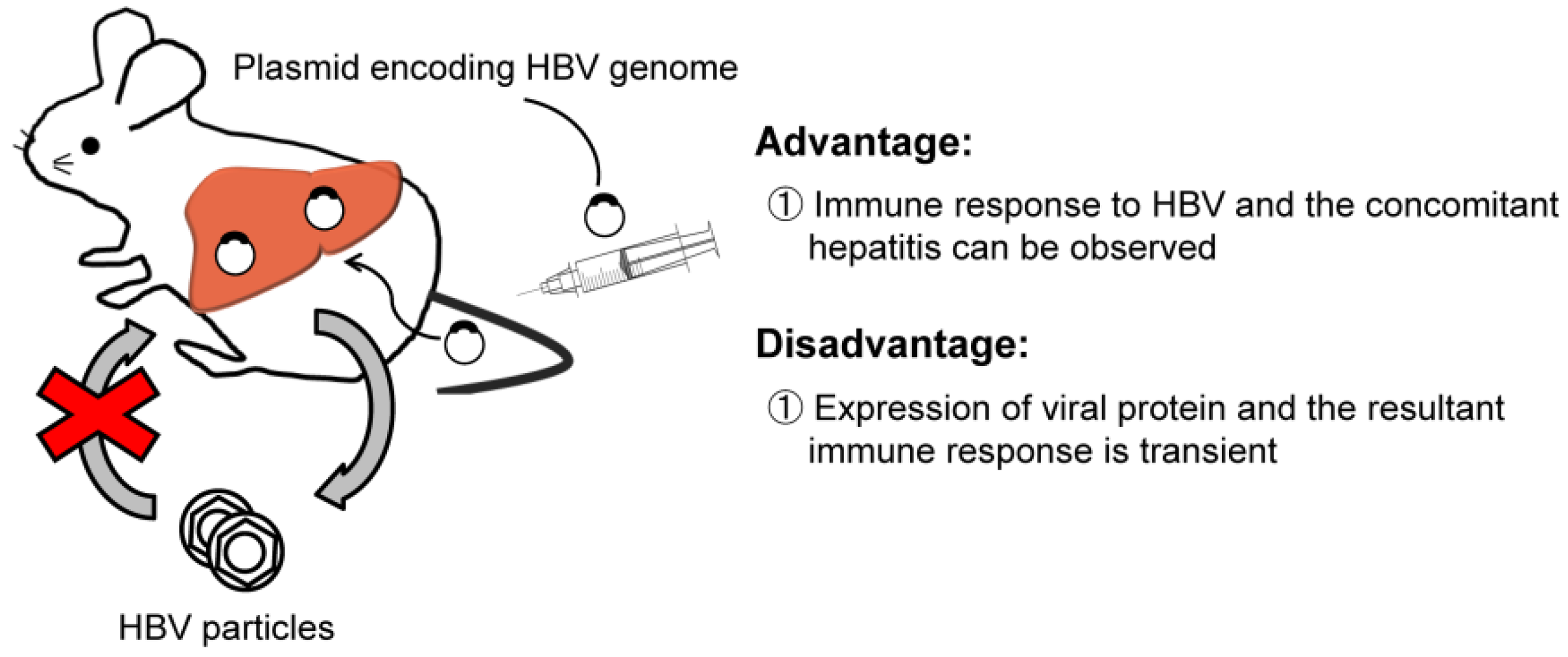
2.2. HBV Transfection by Hydrodynamic Injection
2.3. HBV Transfection by Adeno-Associated Virus
2.4. Chimeric Mouse Models of HBV Infection

2.5. Genetically Humanized Mice
2.6. Humanized Mice with Human Immune System and Liver Tissues
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, W.M. Hepatitis B virus infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1733–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.L.; Ratziu, V.; Yuen, M.F.; Poynard, T. Viral hepatitis B. Lancet 2003, 362, 2089–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganem, D.; Prince, A.M. Hepatitis B virus infection--natural history and clinical consequences. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandri, M.; Volz, T.K.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Petersen, J. Animal models for the study of HBV replication and its variants. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 34 Suppl 1, S54–S62. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, E.; Keist, R.; Niederost, B.; Pult, I.; Blum, H.E. Hepatitis B virus infection of tupaia hepatocytes in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology 1996, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, L.F.; Chisari, F.V.; McGrath, P.P.; Dalgard, D.W.; Kirschstein, R.L.; Almeida, J.D.; Edington, T.S.; Sharp, D.G.; Peterson, M.R. Transmission of type B viral hepatitis to chimpanzees. J. Infect. Dis. 1973, 127, 648–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, F.V.; Pinkert, C.A.; Milich, D.R.; Filippi, P.; McLachlan, A.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L. A transgenic mouse model of the chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier state. Science 1985, 230, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Chisari, F.V.; Filippi, P.; McLachlan, A.; Milich, D.R.; Riggs, M.; Lee, S.; Palmiter, R.D.; Pinkert, C.A.; Brinster, R.L. Expression of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide inhibits hepatitis B surface antigen secretion in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 1986, 60, 880–887. [Google Scholar]
- Gilles, P.N.; Fey, G.; Chisari, F.V. Tumor necrosis factor alpha negatively regulates hepatitis B virus gene expression in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 3955–3960. [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Martinez, V.; Loh, Y.T.; Rogler, C.E.; Chisari, F.V. Hepatitis B virus nucleocapsid particles do not cross the hepatocyte nuclear membrane in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 5469–5475. [Google Scholar]
- Milich, D.R.; Jones, J.E.; Hughes, J.L.; Maruyama, T.; Price, J.; Melhado, I.; Jirik, F. Extrathymic expression of the intracellular hepatitis B core antigen results in T cell tolerance in transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 455–466. [Google Scholar]
- Milich, D.R.; Jones, J.E.; Hughes, J.L.; Price, J.; Raney, A.K.; McLachlan, A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6599–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.M.; Koike, K.; Saito, I.; Miyamura, T.; Jay, G. HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature 1991, 351, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, K.; Moriya, K.; Iino, S.; Yotsuyanagi, H.; Endo, Y.; Miyamura, T.; Kurokawa, K. High-level expression of hepatitis B virus HBx gene and hepatocarcinogenesis in transgenic mice. Hepatology 1994, 19, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, K.; Miyazaki, J.; Hino, O.; Tomita, N.; Chisaka, O.; Matsubara, K.; Yamamura, K. Expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Matzke, B.; Schaller, H.; Chisari, F.V. High-level hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 6158–6169. [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Rochford, R.; Chung, J.; Shapiro, M.; Purcell, R.; Chisari, F.V. Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection. Science 1999, 284, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Ishikawa, T.; Hobbs, M.V.; Matzke, B.; Schreiber, R.; Chisari, F.V. Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity 1996, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Steiger, C.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Cd8(+) T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitia, G.; Isogawa, M.; Kakimi, K.; Wieland, S.F.; Chisari, F.V.; Guidotti, L.G. Depletion of neutrophils blocks the recruitment of antigen-nonspecific cells into the liver without affecting the antiviral activity of hepatitis B virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13717–13722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitia, G.; Isogawa, M.; Iannacone, M.; Campbell, I.L.; Chisari, F.V.; Guidotti, L.G. MMPs are required for recruitment of antigen-nonspecific mononuclear cells into the liver by CTLs. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 113, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitia, G.; Iannacone, M.; Aiolfi, R.; Isogawa, M.; van Rooijen, N.; Scozzesi, C.; Bianchi, M.E.; von Andrian, U.H.; Chisari, F.V.; Guidotti, L.G. Kupffer cells hasten resolution of liver immunopathology in mouse models of viral hepatitis. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakimi, K.; Lane, T.E.; Wieland, S.; Asensio, V.C.; Campbell, I.L.; Chisari, F.V.; Guidotti, L.G. Blocking chemokine responsive to gamma-2/interferon (IFN)-gamma inducible protein and monokine induced by IFN-gamma activity in vivo reduces the pathogenetic but not the antiviral potential of hepatitis B virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannacone, M.; Sitia, G.; Isogawa, M.; Marchese, P.; Castro, M.G.; Lowenstein, P.R.; Chisari, F.V.; Ruggeri, Z.M.; Guidotti, L.G. Platelets mediate cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced liver damage. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannacone, M.; Sitia, G.; Ruggeri, Z.M.; Guidotti, L.G. HBV pathogenesis in animal models: Recent advances on the role of platelets. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClary, H.; Koch, R.; Chisari, F.V.; Guidotti, L.G. Relative sensitivity of hepatitis B virus and other hepatotropic viruses to the antiviral effects of cytokines. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakimi, K.; Guidotti, L.G.; Koezuka, Y.; Chisari, F.V. Natural killer T cell activation inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, O.; Schlemmer, K.H.; Hartmann, E.; Hagelschuer, I.; Paessens, A.; Graef, E.; Deres, K.; Goldmann, S.; Niewoehner, U.; Stoltefuss, J.; et al. Inhibition of human hepatitis B virus (HBV) by a novel non-nucleosidic compound in a transgenic mouse model. Antiviral Res. 2002, 54, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julander, J.G.; Sidwell, R.W.; Morrey, J.D. Characterizing antiviral activity of adefovir dipivoxil in transgenic mice expressing hepatitis B virus. Antiviral Res. 2002, 55, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julander, J.G.; Colonno, R.J.; Sidwell, R.W.; Morrey, J.D. Characterization of antiviral activity of entecavir in transgenic mice expressing hepatitis B virus. Antiviral Res. 2003, 59, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaffrey, A.P.; Nakai, H.; Pandey, K.; Huang, Z.; Salazar, F.H.; Xu, H.; Wieland, S.F.; Marion, P.L.; Kay, M.A. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus in mice by RNA interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Bock, C.T.; Wedemeyer, H.; Wustefeld, T.; Locarnini, S.; Dienes, H.P.; Kubicka, S.; Manns, M.P.; Trautwein, C. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication in vivo by nucleoside analogues and siRNA. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, G.; Poeck, H.; Lucifora, J.; Baschuk, N.; Esser, K.; Esposito, I.; Hartmann, G.; Protzer, U. 5' triphosphorylated small interfering RNAs control replication of hepatitis B virus and induce an interferon response in human liver cells and mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levrero, M.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Belloni, L.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M. Control of cccDNA function in hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucifora, J.; Xia, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Zhang, K.; Stadler, D.; Cheng, X.; Sprinzl, M.F.; Koppensteiner, H.; Makowska, Z.; Volz, T.; et al. Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA. Science 2014, 343, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Publicover, J.; Goodsell, A.; Nishimura, S.; Vilarinho, S.; Wang, Z.E.; Avanesyan, L.; Spolski, R.; Leonard, W.J.; Cooper, S.; Baron, J.L. IL-21 is pivotal in determining age-dependent effectiveness of immune responses in a mouse model of human hepatitis B. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Publicover, J.; Gaggar, A.; Nishimura, S.; Van Horn, C.M.; Goodsell, A.; Muench, M.O.; Reinhardt, R.L.; van Rooijen, N.; Wakil, A.E.; Peters, M.; et al. Age-dependent hepatic lymphoid organization directs successful immunity to hepatitis B. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 3728–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.L.; Althage, A.; Chung, J.; Chisari, F.V. Hydrodynamic injection of viral DNA: A mouse model of acute hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13825–13830. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.R.; Wu, H.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S. An immunocompetent mouse model for the tolerance of human chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17862–17867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.L.; Althage, A.; Chung, J.; Maier, H.; Wieland, S.; Isogawa, M.; Chisari, F.V. Immune effectors required for hepatitis B virus clearance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 798–802. [Google Scholar]
- Rehermann, B. Pathogenesis of chronic viral hepatitis: Differential roles of T cells and NK cells. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dion, S.; Bourgine, M.; Godon, O.; Levillayer, F.; Michel, M.L. Adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer leads to persistent hepatitis B virus replication in mice expressing HLA-A2 and HLA-DR1 molecules. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5554–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, L.; Zhu, D.; Peng, H.; Su, L.; Fu, Y.X.; Zhang, L. A mouse model for HBV immunotolerance and immunotherapy. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilan, E.; Burakova, T.; Dagan, S.; Nussbaum, O.; Lubin, I.; Eren, R.; Ben-Moshe, O.; Arazi, J.; Berr, S.; Neville, L.; et al. The hepatitis B virus-trimera mouse: A model for human HBV infection and evaluation of anti-HBV therapeutic agents. Hepatology 1999, 29, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, J.L.; Sandgren, E.P.; Degen, J.L.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L. Neonatal bleeding in transgenic mice expressing urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Cell 1990, 62, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.A.; Sandgren, E.P.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L. Complete reconstitution of mouse liver with xenogeneic hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4942–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandri, M.; Burda, M.R.; Torok, E.; Pollok, J.M.; Iwanska, A.; Sommer, G.; Rogiers, X.; Rogler, C.E.; Gupta, S.; Will, H.; et al. Repopulation of mouse liver with human hepatocytes and in vivo infection with hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 2001, 33, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, D.F.; Schiller, D.E.; Elliott, J.F.; Douglas, D.N.; Hao, C.; Rinfret, A.; Addison, W.R.; Fischer, K.P.; Churchill, T.A.; Lakey, J.R.; et al. Hepatitis C virus replication in mice with chimeric human livers. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateno, C.; Yoshizane, Y.; Saito, N.; Kataoka, M.; Utoh, R.; Yamasaki, C.; Tachibana, A.; Soeno, Y.; Asahina, K.; Hino, H.; et al. Near completely humanized liver in mice shows human-type metabolic responses to drugs. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezillon, N.M.; DaSilva, L.; L'Hote, D.; Bernex, F.; Piquet, J.; Binart, N.; Morosan, S.; Kremsdorf, D. Rescue of fertility in homozygous mice for the urokinase plasminogen activator transgene by the transplantation of mouse hepatocytes. Cell Transplant. 2008, 17, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, H.; Paulk, N.; Ranade, A.; Dorrell, C.; Al-Dhalimy, M.; Ellis, E.; Strom, S.; Kay, M.A.; Finegold, M.; Grompe, M. Robust expansion of human hepatocytes in Fah-/-/Rag2-/-/Il2rg-/- mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissig, K.D.; Wieland, S.F.; Tran, P.; Isogawa, M.; Le, T.T.; Chisari, F.V.; Verma, I.M. Human liver chimeric mice provide a model for hepatitis B and C virus infection and treatment. J. Clin. Invest. 2010, 120, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuge, M.; Hiraga, N.; Takaishi, H.; Noguchi, C.; Oga, H.; Imamura, M.; Takahashi, S.; Iwao, E.; Fujimoto, Y.; Ochi, H.; et al. Infection of human hepatocyte chimeric mouse with genetically engineered hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuleman, P.; Libbrecht, L.; De Vos, R.; de Hemptinne, B.; Gevaert, K.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Roskams, T.; Leroux-Roels, G. Morphological and biochemical characterization of a human liver in a uPA-SCID mouse chimera. Hepatology 2005, 41, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Kato, T.; Orito, E.; Ito, K.; Acharya, S.K.; Gish, R.G.; Kramvis, A.; Shimada, T.; Izumi, N.; et al. Influence of hepatitis B virus genotypes on the intra- and extracellular expression of viral DNA and antigens. Hepatology 2006, 44, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandri, M.; Burda, M.R.; Zuckerman, D.M.; Wursthorn, K.; Matschl, U.; Pollok, J.M.; Rogiers, X.; Gocht, A.; Kock, J.; Blum, H.E.; et al. Chronic infection with hepatitis B viruses and antiviral drug evaluation in uPA mice after liver repopulation with tupaia hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.; Dandri, M.; Mier, W.; Lutgehetmann, M.; Volz, T.; von Weizsacker, F.; Haberkorn, U.; Fischer, L.; Pollok, J.M.; Erbes, B.; et al. Prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in vivo by entry inhibitors derived from the large envelope protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsuji, H.; Noguchi, C.; Hiraga, N.; Mori, N.; Tsuge, M.; Imamura, M.; Takahashi, S.; Iwao, E.; Fujimoto, Y.; Ochi, H.; et al. Emergence of a novel lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B virus variant with a substitution outside the YMDD motif. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 3867–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, L.; Allweiss, L.; Guerrieri, F.; Pediconi, N.; Volz, T.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M.; Levrero, M. IFN-alpha inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploss, A.; Evans, M.J.; Gaysinskaya, V.A.; Panis, M.; You, H.; de Jong, Y.P.; Rice, C.M. Human occludin is a hepatitis C virus entry factor required for infection of mouse cells. Nature 2009, 457, 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, M.; Horwitz, J.A.; Robbins, J.B.; Barry, W.T.; Feng, Q.; Mu, K.; Jones, C.T.; Schoggins, J.W.; Catanese, M.T.; Burton, D.R.; et al. A genetically humanized mouse model for hepatitis C virus infection. Nature 2011, 474, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, M.; Horwitz, J.A.; Donovan, B.M.; Labitt, R.N.; Budell, W.C.; Friling, T.; Vogt, A.; Catanese, M.T.; Satoh, T.; Kawai, T.; et al. Completion of the entire hepatitis C virus life cycle in genetically humanized mice. Nature 2013, 501, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkongolo, S.; Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Kaufman, C.; Lindner, T.; Esser-Nobis, K.; Lohmann, V.; Mier, W.; Mehrle, S.; Urban, S. Cyclosporin a inhibits hepatitis B and hepatitis D virus entry by cyclophilin-independent interference with the NTCP receptor. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Watashi, K.; Tsukuda, S.; Aly, H.H.; Fukasawa, M.; Fujimoto, A.; Suzuki, R.; Aizaki, H.; Ito, T.; Koiwai, O.; et al. Evaluation and identification of hepatitis B virus entry inhibitors using HepG2 cells overexpressing a membrane transporter NTCP. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watashi, K.; Urban, S.; Li, W.; Wakita, T. NTCP and beyond: Opening the door to unveil hepatitis B virus entry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 2892–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhuang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Xia, N.; et al. HBV life cycle is restricted in mouse hepatocytes expressing human NTCP. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washburn, M.L.; Bility, M.T.; Zhang, L.; Kovalev, G.I.; Buntzman, A.; Frelinger, J.A.; Barry, W.; Ploss, A.; Rice, C.M.; Su, L. A humanized mouse model to study hepatitis C virus infection, immune response, and liver disease. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, B.S.; Alter, H.J.; Visnich, S. A “new” antigen in leukemia sera. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1965, 191, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Inuzuka, T.; Takahashi, K.; Chiba, T.; Marusawa, H. Mouse Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Comprising Host-Virus Immunologic Interactions. Pathogens 2014, 3, 377-389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3020377
Inuzuka T, Takahashi K, Chiba T, Marusawa H. Mouse Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Comprising Host-Virus Immunologic Interactions. Pathogens. 2014; 3(2):377-389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3020377
Chicago/Turabian StyleInuzuka, Tadashi, Ken Takahashi, Tsutomu Chiba, and Hiroyuki Marusawa. 2014. "Mouse Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Comprising Host-Virus Immunologic Interactions" Pathogens 3, no. 2: 377-389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3020377
APA StyleInuzuka, T., Takahashi, K., Chiba, T., & Marusawa, H. (2014). Mouse Models of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Comprising Host-Virus Immunologic Interactions. Pathogens, 3(2), 377-389. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens3020377





