The Experimental Infections of the Human Isolate of Strongyloides Stercoralis in a Rodent Model (The Mongolian Gerbil, Meriones Unguiculatus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Immunosuppressed Gerbils Were Susceptible to the Human Isolate of S. stercoralis
2.2. The Human Isolate of S. stercoralis Life Cycle Could Be Maintained by Gerbil-to-Gerbil Transfer
3. Discussion
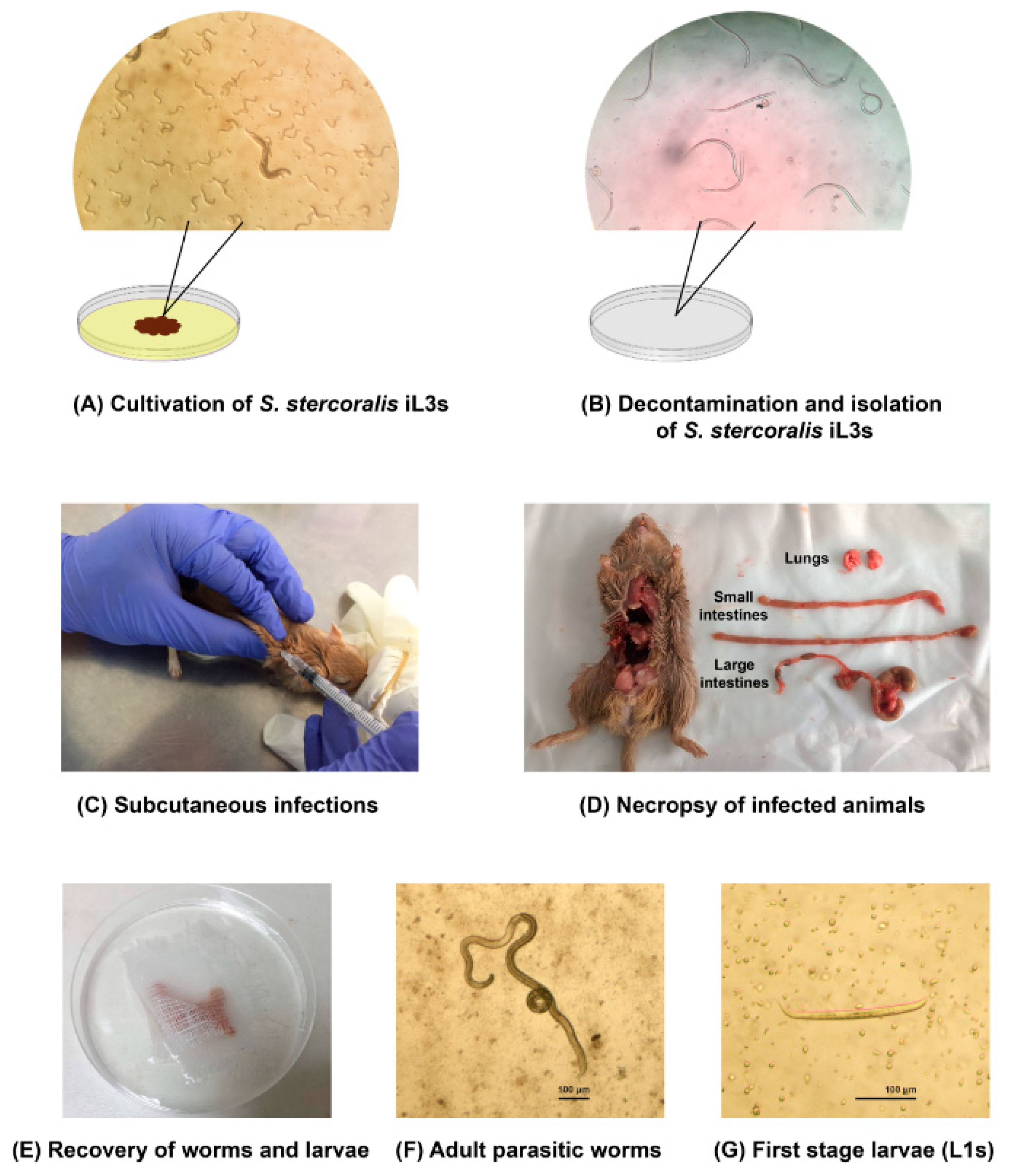
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Immunosuppression of Animals
4.3. The Human Isolate of S. stercoralis Infective Stage (iL3s)
4.4. Experimental Infections
4.5. Coproparasitological Examination
4.6. Necropsy and Recovery of S. stercoralis
4.7. Statistics Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krolewiecki, A.J.; Lammie, P.; Jacobson, J.; Gabrielli, A.F.; Levecke, B.; Socias, E.; Arias, L.M.; Sosa, N.; Abraham, D.; Cimino, R.; et al. A public health response against Strongyloides stercoralis: Time to look at soil-transmitted helminthiasis in full. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schar, F.; Trostdorf, U.; Giardina, F.; Khieu, V.; Muth, S.; Marti, H.; Vounatsou, P.; Odermatt, P. Strongyloides stercoralis: Global Distribution and Risk Factors. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisoffi, Z.; Buonfrate, D.; Montresor, A.; Requena-Mendez, A.; Munoz, J.; Krolewiecki, A.J.; Gotuzzo, E.; Mena, M.A.; Chiodini, P.L.; Anselmi, M.; et al. Strongyloides stercoralis: A plea for action. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farthin, M.; Albonico, M.; Bisoffi, Z.; Buonfrate, D.; Katelaris, P.; Kelly, P.; Savioli, L.; Le Mair, A. Management of Strongyloidiasis. Available online: http://www.webcitation.org/75si8tJzH (accessed on 2 February 2019).
- Beknazarova, M.; Whiley, H.; Judd, J.A.; Shield, J.; Page, W.; Miller, A.; Whittaker, M.; Ross, K. Argument for Inclusion of Strongyloidiasis in the Australian National Notifiable Disease List. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, G.V.; Beeching, N.J.; Khoo, S.; Bailey, J.W.; Partridge, S.; Blundell, J.W.; Luksza, A.R. A British Second World War veteran with disseminated strongyloidiasis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 98, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendki, V.; Fenaux, P.; Durand, R.; Thellier, M.; Bouchaud, O. Strongyloidiasis in man 75 years after initial exposure. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 931–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, L.A.; Terashima, A.; Canales, M.; Gotuzzo, E. Update on strongyloidiasis in the immunocompromised host. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2011, 13, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonfrate, D.; Requena-Mendez, A.; Angheben, A.; Munoz, J.; Gobbi, F.; Van Den Ende, J.; Bisoffi, Z. Severe strongyloidiasis: A systematic review of case reports. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, D.S.; Yoon, Y.K.; Sohn, J.W.; Kim, M.J. Donor-Derived Strongyloidiasis Infection in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: A Review and Pooled Analysis. Transplant. Proc. 2016, 48, 2442–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez Guillamet, L.J.; Saul, Z.; Miljkovich, G.; Vilchez, G.A.; Mendonca, N.; Gourineni, V.; Lillo, N.; Pinto, M.; Baig, A.; Gangcuangco, L.M. Strongyloides Stercoralis Infection Among Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)-Infected Patients in the United States of America: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Am. J. Case Rep. 2017, 18, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myint, A.; Chapman, C.; Almira-Suarez, I.; Mehta, N. Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome in an immunocompetent host resulting in bandemia and death. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, F.L.Y.; Kennedy, B.; Nelson, R. Fatal Strongyloides hyperinfection syndrome in an immunocompetent adult with review of the literature. Intern. Med. J. 2018, 48, 872–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grove, D.I.; Northern, C. Infection and immunity in dogs infected with a human strain of Strongyloides stercoralis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1982, 76, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genta, R.M.; Harper, J.S., 3rd; Gam, A.A.; London, W.I.; Neva, F.A. Experimental disseminated strongyloidiasis in Erythrocebus patas. II. Immunology. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1984, 33, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, J.S.; Genta, R.M.; Gam, A.; London, W.T.; Neva, F.A. Experimental disseminated strongyloidiasis in Erythrocebus patas. I. Pathology. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1984, 33, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schad, G.A.; Hellman, M.E.; Muncey, D.W. Strongyloides stercoralis: Hyperinfection in immunosuppressed dogs. Exp. Parasitol. 1984, 57, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, K.E.; Neva, F.A.; Gam, A.A.; Cicmanec, J.; London, W.T.; Phillips, J.M.; Metcalfe, D.D. The immune response to nematode parasites: Modulation of mast cell numbers and function during Strongyloides stercoralis infections in nonhuman primates. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1988, 38, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandground, J.H. Some studies on susceptibility, resistance, and acquired immunity to infection with Strongyloides stercoralis (Nematoda) in dogs and cats. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1928, 8, 507–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, D.L.; Davey, D.G. Observations on a natural infection with Strongyloides in the dog. J. Parasitol. 1939, 25, 117–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galliard, H. Pathogenesis of Strongyloides. Helminthol. Abstr. 1967, 36, 247–260. [Google Scholar]
- Dawkins, H.J.; Grove, D.I. Attempts to establish infections with Strongyloides stercoralis in mice and other laboratory animals. J. Helminthol. 1982, 56, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotman, H.L.; Yutanawiboonchai, W.; Brigandi, R.A.; Leon, O.; Nolan, T.J.; Schad, G.A.; Abraham, D. Strongyloides stercoralis: Complete life cycle in SCID mice. Exp. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, J.B.; Shao, H.; Massey, H.C.; Li, X. Transgenesis in Strongyloides and related parasitic nematodes: Historical perspectives, current functional genomic applications and progress towards gene disruption and editing. Parasitology 2017, 144, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breloer, M.; Abraham, D. Strongyloides infection in rodents: Immune response and immune regulation. Parasitology 2017, 144, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viney, M.; Kikuchi, T. Strongyloides ratti and S. venezuelensis—Rodent models of Strongyloides infection. Parasitology 2017, 144, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, T.J.; Megyeri, Z.; Bhopale, V.M.; Schad, G.A. Strongyloides stercoralis: The first rodent model for uncomplicated and hyperinfective strongyloidiasis, the Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus). J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 168, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Massey, H.C., Jr.; Nolan, T.J.; Schad, G.A.; Kraus, K.; Sundaram, M.; Lok, J.B. Successful transgenesis of the parasitic nematode Strongyloides stercoralis requires endogenous non-coding control elements. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junio, A.B.; Li, X.; Massey, H.C., Jr.; Nolan, T.J.; Todd Lamitina, S.; Sundaram, M.V.; Lok, J.B. Strongyloides stercoralis: Cell- and tissue-specific transgene expression and co-transformation with vector constructs incorporating a common multifunctional 3′ UTR. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 118, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarqi, M.M.; Stoltzfus, J.D.; Pilgrim, A.A.; Nolan, T.J.; Wang, Z.; Kliewer, S.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Lok, J.B. Regulation of Life Cycle Checkpoints and Developmental Activation of Infective Larvae in Strongyloides stercoralis by Dafachronic Acid. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mati, V.L.; Raso, P.; de Melo, A.L. Strongyloides stercoralis infection in marmosets: Replication of complicated and uncomplicated human disease and parasite biology. Parasit Vectors 2014, 7, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerlin, R.L.; Nolan, T.J.; Schad, G.A. Strongyloides stercoralis: Histopathology of uncomplicated and hyperinfective strongyloidiasis in the Mongolian gerbil, a rodent model for human strongyloidiasis [corrected]. Int. J. Parasitol. 1995, 25, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithithaworn, P.; Fujimaki, Y.; Mitsui, Y.; Prasanthong, R.; Yutanawiboonchai, W.; Aoki, Y. Efficacy of ivermectin against Strongyloides stercoralis infection in jirds (Meriones unguiculatus). Exp. Parasitol. 1998, 89, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, T.J.; Bhopale, V.M.; Rotman, H.L.; Abraham, D.; Schad, G.A. Strongyloides stercoralis: High worm population density leads to autoinfection in the jird (Meriones unguiculatus). Exp. Parasitol. 2002, 100, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croker, C.; Reporter, R.; Redelings, M.; Mascola, L. Strongyloidiasis-related deaths in the United States, 1991–2006. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genta, R.M. Strongyloides stercoralis: Loss of ability to disseminate after repeated passage in laboratory beagles. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1989, 83, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neefs, J.M.; Van de Peer, Y.; De Rijk, P.; Chapelle, S.; De Wachter, R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 3025–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, S.; Gam, A.A.; Neva, F.A. Molecular differences between several species of Strongyloides and comparison of selected isolates of S. stercoralis using a polymerase chain reaction-linked restriction fragment length polymorphism approach. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 56, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Hayashida, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Sato, H. Hyper-variable regions in 18S rDNA of Strongyloides spp. as markers for species-specific diagnosis. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 104, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Sato, H.; Fujita, S.; Nguema, P.P.; Nobusue, K.; Miyagi, K.; Kooriyama, T.; Takenoshita, Y.; Noda, S.; Sato, A.; et al. Molecular identification of the causative agent of human strongyloidiasis acquired in Tanzania: Dispersal and diversity of Strongyloides spp. and their hosts. Parasitol. Int. 2010, 59, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schar, F.; Guo, L.; Streit, A.; Khieu, V.; Muth, S.; Marti, H.; Odermatt, P. Strongyloides stercoralis genotypes in humans in Cambodia. Parasitol. Int. 2014, 63, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagayasu, E.; Aung, M.; Hortiwakul, T.; Hino, A.; Tanaka, T.; Higashiarakawa, M.; Olia, A.; Taniguchi, T.; Win, S.M.T.; Ohashi, I.; et al. A possible origin population of pathogenic intestinal nematodes, Strongyloides stercoralis, unveiled by molecular phylogeny. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, K.; Kasuya, S.; Khamboonruang, C.; Sukhavat, K.; Ieda, M.; Takatsuka, N.; Kita, K.; Ohtomo, H. A modified agar plate method for detection of Strongyloides stercoralis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1991, 45, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Source of iL3s | Group | No. | Gender | Dose of iL3s | Dose of MPA | Direct Smear | Agar Plate | Recovered Adult Parasitic Worms | Recovered L1s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | 1 | 1 | Male | 1000 | 2 mg | − | + | 4 | NF |
| 2 | − | + | 2 | NF | |||||
| 3 | − | − | NF | NF | |||||
| 4 | − | − | NF | NF | |||||
| 5 | − | − | NF | NF | |||||
| 6 | Female | 1000 | 2 mg | Death | |||||
| 7 | Death | ||||||||
| 2 | 8 | Male | 10,000 | 2 mg | + | +++ | 188 | 22,000 | |
| 9 | + | ++ | 22 | 4800 | |||||
| 10 | + | ++ | 55 | 3500 | |||||
| 11 | + | +++ | ND * | ND * | |||||
| 12 | Female | 10,000 | 2 mg | − | − | NF | NF | ||
| 13 | − | − | NF | NF | |||||
| Gerbil | 3 | 14 | Male | 4000 | 1 mg | − | + | 7 | 66 |
| 15 | − | + | 2 | 500 | |||||
| 4 | 16 | Male | 5000 | 1 mg | − | + | 20 | 110 | |
| 17 | − | + | 2 | 140 | |||||
| 5 | 18 | Male | 10,000 | 1 mg | + | ++ | 1 | ND ** | |
| 19 | + | ++ | 55 | ND ** | |||||
| 6 | 20 | Male | 3000 | 2 mg | + | ++ | 20 | 110 | |
| 21 | − | − | NF | NF | |||||
| 7 | 22 | Male | 5000 | 2 mg | Death | ||||
| 23 | Death | ||||||||
| 8 | 24 | Male | 10,000 | 2 mg | + | +++ | 143 | 20,000 | |
| 25 | + | +++ | 97 | 5000 | |||||
| 26 | + | +++ | ND * | ND * | |||||
| 27 | Female | 10,000 | 2 mg | − | ++ | 2 | NF | ||
| 28 | − | ++ | 44 | 2000 | |||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charuchaibovorn, S.; Sanprasert, V.; Nuchprayoon, S. The Experimental Infections of the Human Isolate of Strongyloides Stercoralis in a Rodent Model (The Mongolian Gerbil, Meriones Unguiculatus). Pathogens 2019, 8, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8010021
Charuchaibovorn S, Sanprasert V, Nuchprayoon S. The Experimental Infections of the Human Isolate of Strongyloides Stercoralis in a Rodent Model (The Mongolian Gerbil, Meriones Unguiculatus). Pathogens. 2019; 8(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharuchaibovorn, Sarit, Vivornpun Sanprasert, and Surang Nuchprayoon. 2019. "The Experimental Infections of the Human Isolate of Strongyloides Stercoralis in a Rodent Model (The Mongolian Gerbil, Meriones Unguiculatus)" Pathogens 8, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8010021
APA StyleCharuchaibovorn, S., Sanprasert, V., & Nuchprayoon, S. (2019). The Experimental Infections of the Human Isolate of Strongyloides Stercoralis in a Rodent Model (The Mongolian Gerbil, Meriones Unguiculatus). Pathogens, 8(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8010021




