Hepatitis B Virus Molecular Epidemiology, Host-Virus Interaction, Coinfection, and Laboratory Diagnosis in the MENA Region: An Update
Abstract
:1. Introduction
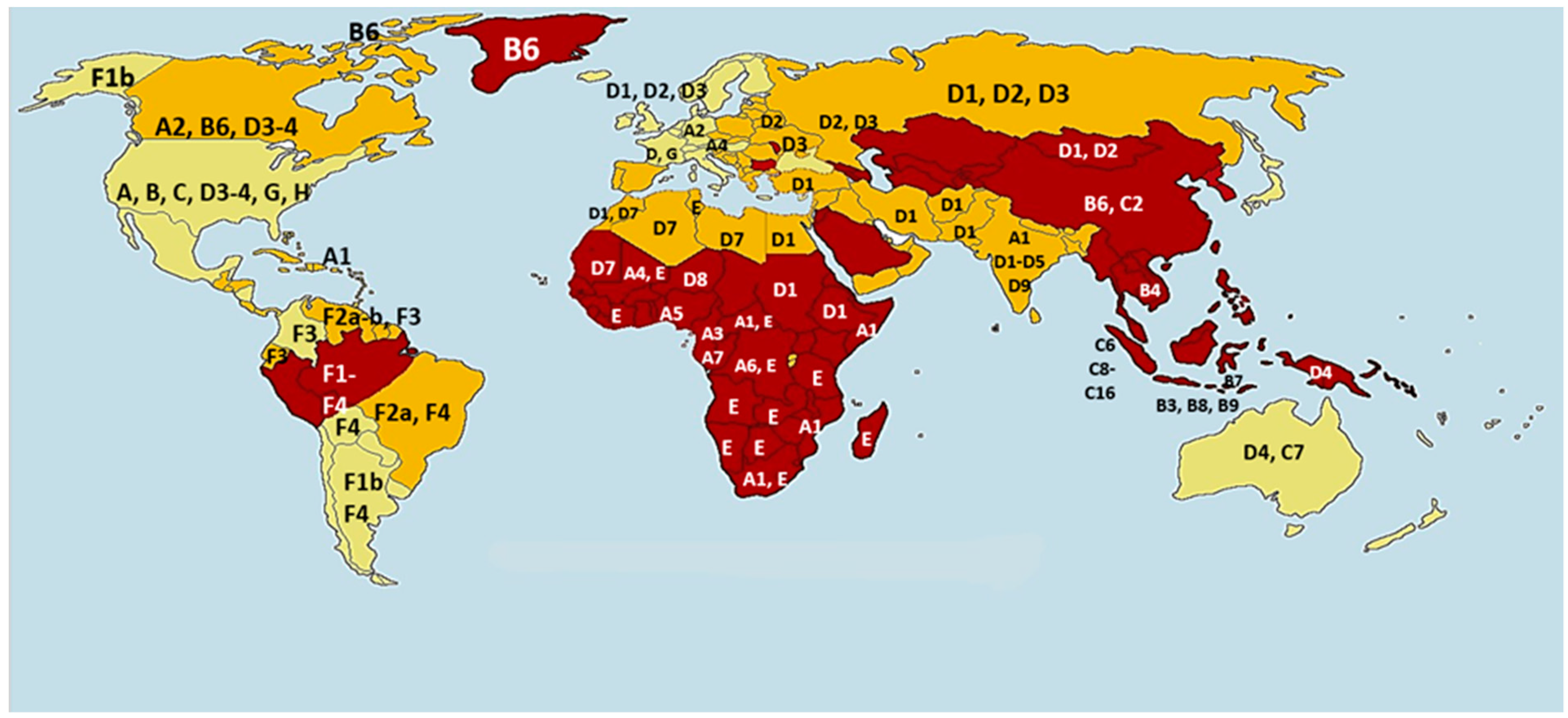
2. HBV Genotype Distribution and Clinical Relevance
3. HBV Pathogenesis Associated with Host-Virus Interactions
3.1. Host Factors: Genetic Variations
3.2. Viral Factors
3.2.1. Viral Precore (HBeAg) and Core (HBcAg) Mutations
3.2.2. Viral PreS/S (HBsAg) Mutations
3.2.3. Viral X Gene (HBxAg) Mutations
4. HBV Coinfections
4.1. HCV/HBV Coinfections
4.2. HIV/HBV Coinfections
4.3. TTV/HBV Coinfections
4.4. HEV/HBV Coinfection
4.5. HPgV/HBV Coinfection
5. Laboratory Diagnosis of HBV
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| cccDNA | Covalently closed circular DNA |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| ddPCR | Droplet digital PCR |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association studies |
| HBc | Hepatitis B core protein |
| HBcAg | Hepatitis B core antigen |
| HBeAg | Hepatitis B e antigen |
| HBeAb | Hepatitis B e antibody |
| HBsAg | Hepatitis B surface antigen |
| HBsAb | Hepatitis B surface antibody |
| HBV | Hepatitis B Virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C Virus |
| HEV | Hepatitis E Virus |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency Virus |
| HPgV (GBV-C/HGV) | Human Pegivirus (GB virus C/Hepatitis G virus) |
| IgM | Immunoglobulin M |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| MENA | Middle East and North Africa |
| OBI | Occult hepatitis B virus infection |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PD-1 | programmed death-1 |
| Th1 | T-helper 1 cells |
| Th2 | T-helper 2 cells |
| TLR | Toll-like receptors |
| TTV | Torque Teno Virus |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Majdalawieh, A.F.; Nasrallah, G.K. Seroprevalence and incidence of hepatitis E virus among blood donors: A review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2017, 27, e1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Hepatitis B. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/bfaq.htm#overview (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Shen, T.; Yan, X.-M. Hepatitis B virus genetic mutations and evolution in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis B. Available online: www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Gasim, G.I. Hepatitis B virus in the Arab world: Where do we stand? Arab J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 14, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igde, F.; Taskin, H.; Igde, M.; Yazici, Z.; Atilla, A. Where we are in the fight against Hepatitis B Infection; Trends in Hepatitis B virus seroprevalence in Black Sea Region of Turkey. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2018, 21, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Erden, S.; Büyüköztürk, S.; Calangu, S.; Yilmaz, G.; Palanduz, S.; Badur, S. A study of serological markers of hepatitis B and C viruses in Istanbul, Turkey. Med. Princ. Pract. 2003, 12, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatekin, G.; Kilinç, M.; Oksuz, B.G.; Igde, M. Hepatitis B seroprevalence in children and women and the impact of the hepatitis B vaccination program in the Black Sea Region of Turkey. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2013, 7, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öner, S.; Yapici, G.; Şaşmaz, C.T.; Kurt, A.Ö.; Buğdayci, R. Hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV, and VDRL seroprevalence of blood donors in Mersin, Turkey. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 41, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Kangin, M.; Turhanoglu, M.; Gulsun, S.; Cakabay, B. Seroprevalence of hepatitis B and C among children in endemic areas of Turkey. Hepat. Mon. 2010, 10, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Merat, S.; Rezvan, H.; Nouraie, M.; Jamali, J.; Assari, S.; Abolghasemi, H.; Radmard, A.-R.; Zaer-Rezaii, H.; Zeid-Abadi-Nejhad, M.; Hosseini, M.-R. The prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen and anti-hepatitis B core antibody in Iran: A population-based study. Arch. Iran. Med. 2009, 12, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, S.; Moghadami, M.; Lankarani, K.; Alborzi, A.; Mahbudi, A. The efficacy of hepatitis B vaccination among school age children in Southern Iran. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2010, 12, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Fathimoghaddam, F.; Hedayati-Moghaddam, M.R.; Bidkhori, H.R.; Ahmadi, S.; Sima, H.R. The prevalence of hepatitis B antigen-positivity in the general population of Mashhad, Iran. Hepat. Mon. 2011, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aghamohamad, A.; Montazeri, M.; Akbari, M. Prevalence of hepatitis B and hepatitis C in blood donors at Semnan province from 2008 to 2011. Koomesh 2014, 15, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Bozorgi, S.H.; Ramezani, H.; Nooranipour, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Baghernejad, A.; Mostajeri, A.; Kargar-Fard, H.; Sadri, M.; Alavian, S.M. Risk factors of viral hepatitis: Yet to explore. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2012, 47, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadali, F.; Aliheidari, S.; Mirrezaie, S.; Hajibeigi, B. Changes In Frequency Of Hbv, Hcv, Hiv And Syphlis Infections Which Removed From Blood Supply In Tehran Blood Donations 2005: P-279-: P-2792010: P-279. Vox Sang. 2013, 105, 162. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, H.; Bile, K.; Jooma, R.; Alam, S.; Afrid, H. Prevalence of hepatitis B and C viral infections in Pakistan: Findings of a national survey appealing for effective prevention and control measures. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2010, 16, S15–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, N.S.; Sheikh, A.S.; Sheikh, A.A.; Yahya, S. Sero-prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection in Balochistan Province of Pakistan. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Saudi Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2011, 17, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaullah, S.; Khan, S.; Khan, J. Trend of transfusion transmitted infections frequency in blood donors: Provide a road map for its prevention and control. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, M.A.; Malik, J.R.; Ashraf, M.Z. Seropositivity of Hepatitis B and C in Blood Donors at CMH Lahore, Pakistan. In Proceedings of the 2014 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC 2014), Sendai, Japan, 4–7 November 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zaheer, H.; Saeed, U.; Waheed, Y.; Karimi, S.; Waheed, U. Prevalence and trends of hepatitis B, hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency viruses among blood donors in Islamabad, Pakistan 2005–2013. J. Blood Disord. Transfus. 2014, 5, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Tanju, I.A.; Levent, F.; Sezer, R.G.; Cekmez, F. Hepatitis B, hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus seropositivity among children in kabul, afghanistan: A cross-sectional study. Hepat. Mon. 2014, 14, e16154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumaidi, K.; Al-Jawabreh, A. Prevalence of occult HBV among hemodialysis patients in two districts in the northern part of the West Bank, Palestine. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 1694–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, K.; Awad, R.; Tebi, A.J.; Queder, A.; Laaser, U. Prevalence and risk factors of HBsAg in Gaza: Implications for prevention and control. J. Infect. 2002, 44, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astal, Z.; Dhair, M. Serologic evaluation for hepatitis B and C among healthcare workers in Southern Gaza Strip (Palestine). Iug J. Nat. Stud. 2015, 12, 153–164. [Google Scholar]
- Souan, L.; Tout, F.; Siag, M.; Sughayer, M.A. Seroprevalence rates of transfusion-transmitted infections among blood donors in Jordan. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani-Hakime, N.; Musharrafieh, U.; Samaha, H.; Almawi, W.Y. Prevalence of antibodies against hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus among blood donors in Lebanon, 1997–2003. Am. J. Infect. Control 2006, 34, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, T.; Raja‘a, Y.; Bahaj, S.; Al-Shami, A.; Lu, M.; Roggendorf, M.; Tong, C. Hepatitis B virus carrier rate, prevalence and susceptibility and impact of immunization program among households in the city of Taiz, Yemen. Vaccine 2012, 30, 5564–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alodini, A.Q. Prevalence of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infections among blood donors at Al-Thawra Hospital Sana’a City-Yemen. Yemeni J. Med. Sci. 2012, 6, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Murad, E.A.; Babiker, S.M.; Gasim, G.I.; Rayis, D.A.; Adam, I. Epidemiology of hepatitis B and hepatitis C virus infections in pregnant women in Sana’a, Yemen. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2013, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarky, A.; Akram, W.; Al-Naaimi, A.; Omer, A. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis B and C in Iraq: A national survey 2005–2006. Zanco J. Med. Sci. 2013, 17, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al–Juboury, A.W.; AL-ASSADI, M.K.; Ali, A.M. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis B and C among blood donors in Babylon Governorate-Iraq. Med. J. Babylon 2010, 7, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Ataallah, T.M.; Hanan, K.A.; Maysoun, K.S.; Sadoon, A.A. Prevalence of hepatitis B and C among blood donors attending the National Blood Transfusion Center in Baghdad, Iraq from 2006–2009. Saudi Med. J. 2011, 32, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Fawzi, Z.; Al Hilali, A.; Al Malki, A.; Al Matawa, H.; Yousef, B.; Ali Bin Ali, A.; Al Mansour, S. Survey of hepatitis markers among donors in the State of Qatar. Qatar Med. J. 2007, 16, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Awaidy, S.; Abu-Elyazeed, R.; Al Hosani, H.; Al Mulla, A.; Al Busaiedy, S.; Al Amiry, A.; Farah, Z.; Al Marrie, A.; Bock, H.L.; Al-Shaar, I. Sero-epidemiology of hepatitis B infection in pregnant women in Oman, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates. J. Infect. 2006, 52, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Humayed, S.; El-Mekki, A.; Mahfouz, A. Hepatitis B virus infection in Aseer Region, south-western Saudi Arabia: A call for an immediate action against a preventable disease. Public Health 2017, 146, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshayea, A.I.; Eid, G.E.; El-Hazmi, M.M.; Alhetheel, A.F. Prevalence and characterization of occult hepatitis B infection among blood donors in central Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2016, 37, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMutairi, H.H.; AlAhmari, M.M.; Al-Zahran, B.H.; Abbas, I.S.; Al Ghamdi, J.S.; Rajaa, Y.A.; Sallam, T.A. Prevalence of serological markers and nucleic acid for blood-borne viral infections in blood donors in Al-Baha, Saudi Arabia. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, S.M. Prevalence of hepatitis B and C in donated blood from the jazan region of saudi arabia. Malays. J. Med. Sci. MJMS 2013, 20, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- El Beltagy, K.E.; Al Balawi, I.A.; Almuneef, M.; Memish, Z.A. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus markers among blood donors in a tertiary hospital in Tabuk, northwestern Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 12, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qadi, A.A.; Tamim, H.; Ameen, G.; Bu-Ali, A.; Al-Arrayed, S.; Fawaz, N.A.; Almawi, W.Y. Hepatitis B and hepatitis C virus prevalence among dialysis patients in Bahrain and Saudi Arabia: A survey by serologic and molecular methods. Am. J. Infect. Control 2004, 32, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, R.; Sanad, N.; Al-Shemmari, S.; Siddique, I.; Chowdhury, R.I.; Al-Hamdan, S.; Al-Bashir, A. Prevalence of viral markers among first-time Arab blood donors in Kuwait. Transfusion 2005, 45, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habil, F.E.; Mahdi, W.K.; Abdelwahab, S.F.; Abdel-Hamid, M. Hepatitis B virus genotype D predominates HBsAg-positive egyptian blood donors and is mainly associated with a negative HBeAg serostatus. Intervirology 2013, 56, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, E. Blood donor recruitment strategies and their impact on blood safety in Egypt. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2014, 50, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, A.; Horn, J.; Mikolajczyk, R.T.; Krause, G.; Ott, J.J. Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.; Hamad, T. Hepatitis B virus Seroprevalence among children with cancer in Sudan. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baha, W.; Foullous, A.; Dersi, N.; They-they, T.P.; Nourichafi, N.; Oukkache, B.; Lazar, F.; Benjelloun, S.; Ennaji, M.M.; Elmalki, A. Prevalence and risk factors of hepatitis B and C virus infections among the general population and blood donors in Morocco. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzouki, A.-N.; Smeo, M.-N.; Sammud, M.; Elahmer, O.; Daw, M.; Furarah, A.; Abudher, A.; Mohamed, M. Prevalence of hepatitis B and C virus infections and their related risk factors in Libya: A national seroepidemiological survey. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2013, 19, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Magrahe, H.; Furarah, A.R.; El-Figih, K.; El-Urshfany, S.; Ghenghesh, K.S. Maternal and neonatal seroprevalence of Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in Tripoli, Libya. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2010, 4, 168–170. [Google Scholar]
- Qirbi, N.; Hall, A. Epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection in the Middle East. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2001, 7, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Alavian, S.M.; Haghbin, H. Relative importance of hepatitis B and C viruses in hepatocellular carcinoma in EMRO countries and the middle east: A systematic review. Hepat. Mon. 2016, 16, e35106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, K.I.; Al-Azawi, S.H.; Chandra, P.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Knuth, A. Status of hepatocellular carcinoma in Gulf region. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 2, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Goyal, M.; Wu, C.H.; Wu, G.Y. The Molecular and Structural Basis of HBV-resistance to Nucleos (t) ide Analogs. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2014, 2, 202–211. [Google Scholar]
- Buti, M.; Rodriguez-Frias, F.; Jardi, R.; Esteban, R. Hepatitis B virus genome variability and disease progression: The impact of pre-core mutants and HBV genotypes. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 34, S79–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, K.M.; Lauring, A.S. Complexities of viral mutation rates. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01031-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunbul, M. Hepatitis B virus genotypes: Global distribution and clinical importance. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramvis, A.; Kew, M. Relationship of genotypes of hepatitis B virus to mutations, disease progression and response to antiviral therapy. J. Viral Hepat. 2005, 12, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozzi, V.; Shen, F.; Chen, J.; Colledge, D.; Jackson, K.; Locarnini, S.; Yuan, Z.; Revill, P.A. In vitro studies identify a low replication phenotype for hepatitis B virus genotype H generally associated with occult HBV and less severe liver disease. Virology 2018, 519, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Al-Jarallah, B.M.; Sanai, F.M.; Hersi, A.S.; Al-Swat, K.; Azzam, N.A.; Al-Dukhayil, M.; Al-Maarik, A.; Al-Faleh, F.Z. Hepatitis B genotypes: Relation to clinical outcome in patients with chronic hepatitis B in Saudi Arabia. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2006, 12, 7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mowafy, M.; Elgaml, A.; El-Mesery, M.; Elegezy, M. Molecular analysis of Hepatitis B virus sub-genotypes and incidence of preS1/preS2 region mutations in HBV-infected Egyptian patients from Mansoura. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, Z.N.A. An overview of occult hepatitis B virus infection. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2011, 17, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamjoom, G.A.; El-Daly, M.M.; Azhar, E.I.; Fallatah, H.I.; Akbar, H.O.; Babatin, M.; Alghamdi, A.S.; Dgdgi, M.I.; Hamid, M.A.; Qari, Y.A.; et al. Prevalence and molecular characterization of hepatitis D virus in Saudi Arabia: A single-center study. Saudi. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 176. [Google Scholar]
- Elbahrawy, A.; Alaboudy, A.; El Moghazy, W.; Elwassief, A.; Alashker, A.; Abdallah, A.M. Occult hepatitis B virus infection in Egypt. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodeh, M.M.; Mosavat, A.; Valizadeh, N.; Zadeh, A.M.; Boskabadi, A.; Mashkani, B.; Sima, H.; Rafatpanah, H. Genotype characteristic and phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis B virus in northeast-Iran. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 59, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Baqlani, S.A.; Sy, B.T.; Ratsch, B.A.; Al Naamani, K.; Al Awaidy, S.; Busaidy, S.A.; Pauli, G.; Bock, C.T. Molecular epidemiology and genotyping of hepatitis B virus of HBsAg-positive patients in Oman. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnabi, Z.; Saleh, N.; Baraghithi, S.; Glebe, D.; Azzeh, M. Subgenotypes and mutations in the s and polymerase genes of hepatitis B virus carriers in the West Bank, palestine. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaghloub, R.; Elbahrawy, A.; Didamony, G.E.; Elwassief, A.; Saied Mohammad, A.-G.; Alashker, A.; Zedan, H.; Abdallah, A.M.; Hemidah, M.H.; Elmestikawy, A.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Genotype E Infection among Egyptian Health Care Workers. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 2017, 5, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucifora, J.; Protzer, U. Attacking hepatitis B virus cccDNA–The holy grail to hepatitis B cure. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S41–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, R.B.; Roberts, L.R. The role of hepatitis B virus integrations in the pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 760–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, B.J.; Alward, W.L.; Hall, D.B.; Heyward, W.L.; Bender, T.R.; Francis, D.P.; Maynard, J.E. Acute hepatitis B virus infection: Relation of age to the clinical expression of disease and subsequent development of the carrier state. J. Infect. Dis. 1985, 151, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coursaget, P.; Yvonnet, B.; Chotard, J.; Vincelot, P.; Sarr, M.; Diouf, C.; Chiron, J.; Diop-Mar, I. Age-and sex-related study of hepatitis B virus chronic carrier state in infants from an endemic area (Senegal). J. Med. Virol. 1987, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghaier, I.; Zidi, S.; Mouelhi, L.; Ghazoueni, E.; Brochot, E.; Almawi, W.Y.; Loueslati, B.Y. TLR3 and TLR4 SNP variants in the liver disease resulting from hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 76, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chihab, H.; Zaidane, I.; Elhabazi, A.; Jadid, F.-Z.; El Fihri, R.; Elmessaoudi-Idrissi, M.; Chair, M.; Badre, W.; Tahiri, M.; Pineau, P. Toll-like receptor 9 polymorphisms and Hepatitis B virus clearance in Moroccan chronic carriers. Gene 2019, 687, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talaat, R.M.; Abdelkhalek, M.S.; El-Maadawy, E.A.; Abdel-Mageed, W.S.; El-Shenawy, S.Z.; Osman, M.A. Association of TNF-Alpha gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to hepatitis B virus infection in Egyptians. Hum. Immunol. 2017, 78, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, R.M.; Dondeti, M.F.; El-Shenawy, S.Z.; Khamiss, O.A. Transforming growth factor-β1 gene polymorphism (T29C) in Egyptian patients with Hepatitis B virus infection: A preliminary study. Hepat. Res. Treat. 2013, 2013, 293274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghaier, I.; Zidi, S.; Mouelhi, L.; Dabbech, R.; Ghazouani, E.; Brochot, E.; Stayoussef, M.; Yacoubi-Loueslati, B. The relationship between TNF alpha gene polymorphisms (−238/−308), TNF RII VNTR (p75) and outcomes of hepatitis B virus infection in Tunisian population. Gene 2015, 568, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihab, H.; Jadid, F.Z.; Foka, P.; Zaidane, I.; El Fihry, R.; Georgopoulou, U.; Marchio, A.; Elhabazi, A.; Chair, M.; Pineau, P. Programmed cell death-1 3′-untranslated region polymorphism is associated with spontaneous clearance of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 1730–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Al-Anazi, M.R.; Abdo, A.A.; Sanai, F.M.; Al-Hamoudi, W.; Alswat, K.A.; Al-Ashgar, H.I.; Khalaf, N.Z.; Eldali, A.M.; Viswan, N.A. Association between HLA variations and chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Saudi Arabian patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e80445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, A.; Khalak, H.G.; Alkuraya, F.S.; Al-hamoudy, W.; Alswat, K.; Al Balwi, M.A.; Al AbdulKareem, I.; Sanai, F.M.; Abdo, A.A. Genome-wide association study of chronic hepatitis B virus infection reveals a novel candidate risk allele on 11q22. 3. J. Med. Genet. 2013, 50, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Al-Anazi, M.R.; Nazir, N.; Wani, K.; Abdo, A.A.; Sanai, F.M.; Khan, M.Q.; Al-Ashgar, H.I.; Albenmousa, A.; Al-hamoudi, W.K. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in micro RNA s with susceptibility to hepatitis B virus infection and HBV-related liver complications: A study in a Saudi Arabian population. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akcay, I.M.; Katrinli, S.; Ozdil, K.; Doganay, G.D.; Doganay, L. Host genetic factors affecting hepatitis B infection outcomes: Insights from genome-wide association studies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Li, J.; Wands, J.R.; Wen, Y.-M. Hepatitis B virus genetic variants: Biological properties and clinical implications. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2013, 2, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.T.; Billaud, J.-N.; Sällberg, M.; Guidotti, L.G.; Chisari, F.V.; Jones, J.; Hughes, J.; Milich, D.R. A function of the hepatitis B virus precore protein is to regulate the immune response to the core antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14913–14918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, S.; Li, J.; Vitvitski, L.; Trépo, C. Active hepatitis B virus replication in the presence of anti-HBe is associated with viral variants containing an inactive pre-C region. Virology 1990, 176, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, P.J.; Korba, B.E.; Miller, R.H.; Jacob, J.R.; Baldwin, B.H.; Hornbuckle, W.E.; Purcell, R.H.; Tennant, B.C.; Gerin, J.L. Effects of age and viral determinants on chronicity as an outcome of experimental woodchuck hepatitis virus infection. Hepatology 2000, 31, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yotsumoto, S.; Kojima, M.; Shoji, I.; Yamamoto, K.; Okamoto, H.; Mishiro, S. Fulminant hepatitis related to transmission of hepatitis B variants with precore mutations between spouses. Hepatology 1992, 16, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayari, R.; Lakhoua-Gorgi, Y.; Bouslama, L.; Safar, I.; Kchouk, F.H.; Aouadi, H.; Jendoubi-Ayed, S.; Najjar, T.; Ayed, K.; Abdallah, T.B. Investigation of DNA sequence in the Basal core promoter, precore, and core regions of hepatitis B virus from Tunisia shows a shift in genotype prevalence. Hepat. Mon. 2012, 12, e6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinot-Peignoux, M.; Lapalus, M.; Laouénan, C.; Lada, O.; Netto-Cardoso, A.C.F.; Boyer, N.; Ripault, M.P.; Carvalho-Filho, R.; Asselah, T.; Marcellin, P. Prediction of disease reactivation in asymptomatic hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B patients using baseline serum measurements of HBsAg and HBV-DNA. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayed, K.; Gorgi, Y.; Ayed-Jendoubi, S.; Aouadi, H.; Sfar, I.; Najjar, T.; Abdallah, T.B. Hepatitis B virus genotypes and precore/core-promoter mutations in Tunisian patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Infect. 2007, 54, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaresi, M.; Elkoush, A.; Alshehhi, H.; Alzaabi, A.; Islam, A. Hepatitis B virus genotypes and precore and core mutants in UAE patients. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Al-Anazi, M.R.; Nazir, N.; Abdo, A.A.; Sanai, F.M.; Al-Hamoudi, W.K.; Alswat, K.A.; Al-Ashgar, H.I.; Khan, M.Q.; Albenmousa, A. The correlation between hepatitis B virus precore/core mutations and the progression of severe liver disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Tsuda, F.; Akahane, Y.; Sugai, Y.; Yoshiba, M.; Moriyama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Miyakawa, Y.; Mayumi, M. Hepatitis B virus with mutations in the core promoter for an e antigen-negative phenotype in carriers with antibody to e antigen. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 8102–8110. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, A.; Kawai, S.; Kwei, K.; Gewaily, D.; Hutter, A.; Tong, D.R.; Li, J.; Wands, J.R.; Tong, S. Chimeric constructs between two hepatitis B virus genomes confirm transcriptional impact of core promoter mutations and reveal multiple effects of core gene mutations. Virology 2009, 387, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabarczyk, P.; Garmiri, P.; Liszewski, G.; Doucet, D.; Sulkowska, E.; Brojer, E.; Allain, J.P.; Polish Blood Transfusion Centres Viral Study Group. Molecular and serological characterization of hepatitis B virus genotype A and D infected blood donors in Poland. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B: The virus and disease. Hepatology 2009, 49, S13–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churin, Y.; Roderfeld, M.; Roeb, E. Hepatitis B virus large surface protein: Function and fame. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2015, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Boltjes, A.; Groothuismink, Z.M.; van Oord, G.W.; Janssen, H.L.; Woltman, A.M.; Boonstra, A. Monocytes from chronic HBV patients react in vitro to HBsAg and TLR by producing cytokines irrespective of stage of disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Pei, R.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Bucchi, A.; Sowa, J.P.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D. Hepatitis B virus suppresses toll-like receptor–mediated innate immune responses in murine parenchymal and nonparenchymal liver cells. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, A.J.; Haniffa, M.; Kennedy, P.T.; Ho, Z.Z.; Boni, C.; Shin, A.; Banu, N.; Chia, A.; Lim, S.G.; Ferrari, C. Mobilizing monocytes to cross-present circulating viral antigen in chronic infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3766–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.-H.; Changchien, C.-S.; Lee, C.-M.; Hung, C.-H.; Hu, T.-H.; Wang, J.-H.; Wang, J.-C.; Lu, S.-N. Combined mutations in pre-s/surface and core promoter/precore regions of hepatitis B virus increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: A case-control study. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.-H.; Su, I.-J.; Wang, H.-C.; Tsai, J.-H.; Huang, Y.-J.; Chang, W.-W.; Lai, M.-D.; Lei, H.-Y.; Huang, W. Hepatitis B virus pre-S2 mutant surface antigen induces degradation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 through c-Jun activation domain-binding protein 1. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.F.; Liu, C.J.; Jow, G.M.; Chen, P.J.; Kao, J.H.; Chen, D.S. High prevalence and mapping of pre-S deletion in hepatitis B virus carriers with progressive liver diseases. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1153–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkady, A.; Iijima, S.; Aboulfotuh, S.; Ali, E.M.; Sayed, D.; Abdel-Aziz, N.M.; Ali, A.M.; Murakami, S.; Isogawa, M.; Tanaka, Y. Characteristics of escape mutations from occult hepatitis B virus infected patients with hematological malignancies in South Egypt. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeid, W.M.A.; Ramadan, D.I.; Shemis, M.A. Prevalence of mutations within major hydrophilic region of hepatitis B virus and their correlation with genotypes among chronically infected patients in Egypt. Arab J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 17, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qudari, A.Y.; Amer, H.M.; Abdo, A.A.; Hussain, Z.; Al-Hamoudi, W.; Alswat, K.; Almajhdi, F.N. Surface gene variants of hepatitis B Virus in Saudi Patients. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Saudi Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2016, 22, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Chaouch, H.; Taffon, S.; Villano, U.; Equestre, M.; Bruni, R.; Belhadj, M.; Hannachi, N.; Aouni, M.; Letaief, A.; Ciccaglione, A.R. Naturally occurring surface antigen variants of hepatitis B virus in Tunisian patients. Intervirology 2016, 59, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, G.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Huang, L.-M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, J.-C.; Hsu, C.-T.; Yang, S.-S.; Wu, C.-C. Detection of the hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) antigen and anti-HBx antibodies in cases of human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5598–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Bouchard, M.J. The hepatitis B virus X protein elevates cytosolic calcium signals by modulating mitochondrial calcium uptake. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Lian, Z.; Wallet, S.; Feitelson, M.A. The hepatitis B x antigen effector, URG7, blocks tumour necrosis factor α-mediated apoptosis by activation of phosphoinositol 3-kinase and β-catenin. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 3275–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchard, M.J.; Puro, R.J.; Wang, L.; Schneider, R.J. Activation and inhibition of cellular calcium and tyrosine kinase signaling pathways identify targets of the HBx protein involved in hepatitis B virus replication. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 7713–7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.-F.; Lau, S.H.; Hu, L.; Xie, D.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.-C.; Fung, J.; Bai, X. COOH-terminal truncated HBV X protein plays key role in hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5061–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Al-Anazi, M.R.; Nazir, N.; Ghai, R.; Abdo, A.A.; Sanai, F.M.; Al-Hamoudi, W.K.; Alswat, K.A.; Al-Ashgar, H.I.; Khan, M.Q. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) X gene mutations and their association with liver disease progression in HBV-infected patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 105115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Anazi, M.R.; Nazir, N.; Colak, D.; Al-Ahdal, M.N.; Al-Qahtani, A.A. Deletion and Functional Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein: Evidence for an Effect on Cell Cycle Regulators. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zayadi, A.R.; Abe, K.; Selim, O.; Naito, H.; Hess, G.; Ahdy, A. Prevalence of GBV-C/hepatitis G virus viraemia among blood donors, health care personnel, chronic non-B non-C hepatitis, chronic hepatitis C and hemodialysis patients in Egypt. J. Virol. Methods 1999, 80, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Manzoor, S.; Waheed, Y.; Tariq, H.; Hanif, K. Phylogenetic analysis of Torque Teno Virus genome from Pakistani isolate and incidence of co-infection among HBV/HCV infected patients. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, A.J.; Turkova, A.; Cunnington, A.J. When do coinfections matter? Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Inigo, E.; Bartolome, J.; Ortiz-Movilla, N.; Platero, C.; Lopez-Alcorocho, J.M.; Pardo, M.; Castillo, I.; Carreno, V. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV) can coinfect the same hepatocyte in the liver of patients with chronic HCV and occult HBV infection. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15578–15581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbenson, M.; Thomas, D.L. Occult hepatitis B. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potthoff, A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Boecher, W.O.; Berg, T.; Zeuzem, S.; Arnold, J.; Spengler, U.; Gruengreiff, K.; Kaeser, T.; Schuchmann, M.; et al. The HEP-NET B/C co-infection trial: A prospective multicenter study to investigate the efficacy of pegylated interferon-alpha2b and ribavirin in patients with HBV/HCV co-infection. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, R.; Ishimura, N.; Niigaki, M.; Hamamoto, S.; Satoh, S.; Tanaka, S.; Kushiyama, Y.; Uchida, Y.; Ihihara, S.; Akagi, S.; et al. Serologically silent hepatitis B virus coinfection in patients with hepatitis C virus-associated chronic liver disease: Clinical and virological significance. J. Med. Virol. 1999, 58, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, T.L.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Waggoner, J.G.; Banks, S.M.; Hoofnagle, J.H. The significance of antibody to hepatitis C virus in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 1991, 14, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaramonte, M.; Stroffolini, T.; Vian, A.; Stazi, M.A.; Floreani, A.; Lorenzoni, U.; Lobello, S.; Farinati, F.; Naccarato, R. Rate of incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with compensated viral cirrhosis. Cancer 1999, 85, 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donato, F.; Boffetta, P.; Puoti, M. A meta-analysis of epidemiological studies on the combined effect of hepatitis B and C virus infections in causing hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 75, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thio, C.L. Hepatitis B and human immunodeficiency virus coinfection. Hepatology 2009, 49, S138–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Gilany, A.H.; El-Fedawy, S. Bloodborne infections among student voluntary blood donors in Mansoura University, Egypt. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2006, 12, 742–748. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mughales, J.A. Co-infection assessment in HBV, HCV, and HIV patients in Western Saudi Arabia. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 1545–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, I.; Gungor, S.; Sener, A.G.; Yurtsever, S.G. The prevalence of HBV, HCV and HIV infections among blood donors in Izmir, Turkey. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 26, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, C.L.; Seaberg, E.C.; Skolasky, R., Jr.; Phair, J.; Visscher, B.; Munoz, A.; Thomas, D.L.; Multicenter, A.C.S. HIV-1, hepatitis B virus, and risk of liver-related mortality in the Multicenter Cohort Study (MACS). Lancet 2002, 360, 1921–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.; Christian, B.; Fabian, E.; Macha, I.; Gawile, C.; Mpangala, S.; Ulenga, N.; Thio, C.L.; Ammerman, L.R.; Mugusi, F.; et al. Brief Report: HIV/HBV Coinfection is a Significant Risk Factor for Liver Fibrosis in Tanzanian HIV-Infected Adults. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2017, 76, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourtis, A.P.; Bulterys, M.; Hu, D.J.; Jamieson, D.J. HIV-HBV coinfection—A global challenge. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1749–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkan, A.; Ozdarendeli, A.; Bulut, Y.; Saral, Y.; Ozden, M.; Kelestimur, N.; Toraman, Z.A. Prevalence and genotypic distribution of hepatitis GB-C/HG and TT viruses in blood donors, mentally retarded children and four groups of patients in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 58, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- AbuOdeh, R.; Al-Mawlawi, N.; Al-Qahtani, A.A.; Bohol, M.F.; Al-Ahdal, M.N.; Hasan, H.A.; AbuOdeh, L.; Nasrallah, G.K. Detection and genotyping of torque teno virus (TTV) in healthy blood donors and patients infected with HBV or HCV in Qatar. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mozaini, M.A.; Al-Ahdal, M.N.; Kessie, G.; Dela Cruz, D.M.; Rezeig, M.A.; Al-Shammary, F.J. Molecular epidemiology and genotyping of TT virus isolated from Saudi blood donors and hepatitis patients. Ann. Saudi Med. 2006, 26, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafez, M.M.; Shaarawy, S.M.; Hassan, A.A.; Salim, R.F.; Abd El Salam, F.M.; Ali, A.E. Prevalence of transfusion transmitted virus (TTV) genotypes among HCC patients in Qaluobia governorate. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasirga, E.; Sanlidag, T.; Akcali, S.; Keskin, S.; Aktas, E.; Karakoc, Z.; Helvaci, M.; Sozen, G.; Kuzu, M. Clinical significance of TT virus infection in children with chronic hepatitis B. Pediatr. Int. 2005, 47, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuOdeh, R.O.; Al-Absi, E.; Ali, N.H.; Khalili, M.; Al-Mawlawi, N.; Hadwan, T.A.; Althani, A.A.; Nasrallah, G.K. Detection and phylogenetic analysis of human pegivirus (GBV-C) among blood donors and patients infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) in Qatar. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki Mel, S.; Salama, O.S.; Mansour, F.A.; Hossein, S. Hepatitis E virus coinfection with hepatotropic viruses in Egyptian children. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2008, 41, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taremi, M.; Khoshbaten, M.; Gachkar, L.; EhsaniArdakani, M.; Zali, M. Hepatitis E virus infection in hemodialysis patients: A seroepidemiological survey in Iran. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis E. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e (accessed on 1 January 2019).
- Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Majdalawieh, A.F.; Mesleh, A.G.; Abdalla, O.M.; Nasrallah, G.K. Laboratory challenges in the diagnosis of hepatitis E virus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kheradpezhouh, M.; Taremi, M.; Gachkar, L.; Aghabozorgi, S.; Khoshbaten, M. Presence and significance of transfusion-transmitted virus infection in Iranian patients on maintenance hemodialysis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2007, 40, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hoan, N.X.; Tong, H.V.; Hecht, N.; Sy, B.T.; Marcinek, P.; Meyer, C.G.; Song, L.H.; Toan, N.L.; Kurreck, J.; Kremsner, P.G.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus Superinfection and Clinical Progression in Hepatitis B Patients. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 2080–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alhetheel, A.; El-Hazmi, M.M. Hepatitis G virus in Saudi blood donors and chronic hepatitis B and C patients. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdani, L.; Ravanshad, M.; Khanlari, Z.; Dawood Mousavi Nasab, S.; Ali Ahmadi, N.; Imanzad, M. Prevalence of GBV-C among Iranian HBV positive patients using PCR-RFLP technique. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2013, 6, S70–S76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fiordalisi, G.; Zanella, I.; Mantero, G.; Bettinardi, A.; Stellini, R.; Paraninfo, G.; Cadeo, G.; Primi, D. High prevalence of GB virus C infection in a group of Italian patients with hepatitis of unknown etiology. J. Infect. Dis. 1996, 174, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiba, M.; Okamoto, H.; Mishiro, S. Detection of the GBV-C hepatitis virus genome in serum from patients with fulminant hepatitis of unknown aetiology. Lancet 1995, 346, 1131–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskus, T.; Radkowski, M.; Wang, L.F.; Vargas, H.; Rakela, J. Lack of evidence for hepatitis G virus replication in the livers of patients coinfected with hepatitis C and G viruses. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 7804–7806. [Google Scholar]
- Alter, H.J. G-pers creepers, where’d you get those papers? A reassessment of the literature on the hepatitis G virus. Transfusion 1997, 37, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.F.; Dai, C.Y.; Chuang, W.L.; Lin, W.Y.; Lin, Z.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Hsieh, M.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Tsai, J.F.; Chang, W.Y.; et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of HGV/GBV-C infection in patients with chronic hepatitis B or C. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 59, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kao, J.H.; Chen, P.J.; Lai, M.Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, D.S. Effects of GB virus-C/hepatitis G virus on hepatitis B and C viremia in multiple hepatitis virus infections. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köse, Ş.; Dal, T. Laboratory Diagnosis of HBV. In Viral Hepatitis: Chronic Hepatitis B; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mühlbacher, A.; Weber, B.; Bürgisser, P.; Eiras, A.; Cabrera, J.; Louisirirotchanakul, S.; Tiller, F.-W.; Kim, H.-S.; Helden, J.V.; Bossi, V. Multicenter study of a new fully automated HBsAg screening assay with enhanced sensitivity for the detection of HBV mutants. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 197, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawi, F.B.; Robertson, P.W.; LePage, A.K.; Jayamaha, J.; Baleriola, C.; Rawlinson, W.D. The reliability of HBV core antibody in serological screening for hepatitis B virus. Pathology 2013, 45, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, S.; Nandi, S.; Biswas, S.; Sadhukhan, S.K.; Saha, M.K. Performance and diagnostic usefulness of commercially available enzyme linked immunosorbent assay and rapid kits for detection of HIV, HBV and HCV in India. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacher, B.; Moriconi, F.; Bowden, S.; Hammond, R.; Louisirirotchanakul, S.; Phisalprapa, P.; Tanwandee, T.; Wursthorn, K.; Brunetto, M.R.; Wedemeyer, H. Multicenter evaluation of the Elecsys HBsAg II quant assay. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, M.; Yamashita, N.; Kagita, M.; Asari, S.; Iwatani, Y.; Tsuchida, T.; Iinuma, K.; Mushahwar, I.K. Quantitation of hepatitis B surface antigen by an automated chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 115, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Country | Sample Size | Prevalence (%) | Diagnostic Assay Used | Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turkey | 101,648 | 4 | Elecysys HBsAg II ELISA (Roche Diagnostics, Germany) | 2018 | [6] |
| 1404 | 6.6 | micro-ELISA method | 2003 | [7] | |
| 12,010 | 3.8 | ELISA | 2013 | [8] | |
| 30,716 | 2.2 | - | 2011 | [9] | |
| 10,391 | 8.1 | ELISA E170 (Roche, Germany) | 2010 | [10] | |
| Iran | 6583 | 2.6 | Enzygnost HBsAg 5.0 kit (Dade Behring, Germany) | 2009 | [11] |
| 708 | 0.28 | Radim kit (KHB31WB) through immunoenzymometric assay | 2010 | [12] | |
| 284 | 0.35 | ELISA using the EIAgen HBsAg Kit | 2011 | [13] | |
| 124,704 | 0.24 | ELISA | 2014 | [14] | |
| 20,591 | 0.23 | The DIASORIN (Italy) kits | 2012 | [15] | |
| 2,026,628 | 0.38 | Third generation ELISA kits | 2014 | [16] | |
| Pakistan | 7000 | 2.5 | ELISA Abbott Determine (TM) | 2010 | [17] |
| 11,900 | 9.8 | Immunochromatography technique-based kit commercially (Determine-Abbott USA). | 2011 | [18] | |
| 127,828 | 2.68 | BEST 2000 ELISA (Biokit, Spain) | 2012 | [19] | |
| 2155 | 1.34 | - | 2013 | [20] | |
| 160,376 | 2.35 | Fourth generation ELISA kits (Bio-kit) | 2014 | [21] | |
| Afghanistan | 330 | 3.6 | Fast cassette kits | 2014 | [22] |
| Palestine | 146 | 8.2 | ELISA | 2014 | [23] |
| 17,060 | 3.8 | Abbot EIA | 2002 | [24] | |
| 399 | 2.8 | ELISA | 2004 | [25] | |
| Jordan | 62,933 | 0.52 | Murex HBsAg Version 3 ELISA kit (DiaSorin S.p.A., Dartford, UK) or BioRad Monalisa HBsAg sandwich ELISA kit (Bio-Rad, Marnesla Coquette, France). | 2016 | [26] |
| Lebanon | 16,084 | 0.92 | Hepanostika HBsAg Uni-Form II, a sandwich ELISA (Biomerieux, Marcy l’Etoile, France) | 2006 | [27] |
| Yemen | 521 | 16.9 | Monolisa enzyme immune assays (BIO-RAD, France) | 2012 | [28] |
| 3000 | 2.1 | ELISA | 2014 | [29] | |
| 400 | 10.8 | Fourth generation ELISA | 2013 | [30] | |
| Iraq | 9610 | 1.6 | ELISA | 2013 | [31] |
| 23,336 | 0.73 | ELISA | 2010 | [32] | |
| 495,648 | 0.66 | ELISA | 2011 | [33] | |
| Qatar | 78,428 | 0.9 | - | 2007 | [34] |
| 495 | 1.0 | ELISA (Axsym, Abbott Laboratories) | 2006 | [35] | |
| Oman | 604 | 7.1 | |||
| UAE | 595 | 1.5 | |||
| Saudi Arabia | 10,234 | 5.9 | Fourth generation ELISA | 2017 | [36] |
| 8501 | 0.7 | chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassays (ARCHITECT® HBsAg, ARCHITECT®) | 2016 | [37] | |
| 2807 | 0.8 | ELISA (BioRad, Marnes–la-Coquette, France) | 2016 | [38] | |
| 29,949 | 3.8 | ELISA (Siemens-BEPIII, Dade Behring, Marburg, Germany) | 2013 | [39] | |
| 3192 | 3 | EIA (Abbott Laboratories, Chicago, IL, USA) | 2008 | [40] | |
| 2330 | 11.8 | PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis | 2004 | [41] | |
| Bahrain | 7714 | 3.7 | EIA/ELISA, and reconfirmed by PCR | 2004 | [41] |
| Kuwait | 12,798 | 1.92 | -Chemiluminescent immunoassays -Neutralization confirmatory assay (Auszyme monoclonal, Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL) | 2005 | [42] |
| Egypt | 12,000 | 1.98 | ELISA | 2013 | [43] |
| 308,762 | 1.22 | Enzygnost HBsAg 6.0 | 2014 | [44] | |
| Sudan | 5965 | 9.76 | - | 2015 | [45] |
| 178 | 21.3 | ELISA | 2016 | [46] | |
| 404 | 11 | Enzygnost HBsAg; 5.0 EIA | 2011 | ||
| Morocco | 23,578 | 1.81 | Murex HBsAg Version 3 | 2013 | [47] |
| Libya | 65,761 | 2.2 | Third generation microparticle EIA (Axsym) | 2013 | [48] |
| 1500 | 1.5 | ELISA | 2010 | [49] |
| Company name | Coating | Biomarker detected | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Sample size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elecsys® HBsAg II assay | Anti-HBsAg | HBsAg | 100% | 99.97% | 9084 | [152] |
| Architect | - | HBcAb | 79.90% | 98% | 260 | [153] |
| - | HBsAg and HBcAb | 100% | 90% | |||
| Elecsys | - | HBcAb | 78.90% | 90.20% | ||
| Hepalisa | Direct sandwich ELISA, microwell plates coated with Anti- HBsAg | HBsAg | 100% | 100% | 100 | [154] |
| Microscreen HBsAg | Microwell plates coated with Anti- HBsAg | 100% | 97.8% | |||
| ERBA LISA HEPATITIS B | Sandwich ELISA, microwell plates coated with Anti- HBsAg | 100% | 100% | |||
| HEPACARD | Immunochromatographic assay, membrane coated with Anti-HBsAg | HBsAg | 100% | 100% | 100 | [154] |
| Crystal HBsAg | ||||||
| SD BIOLINE HBsAg |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Taleb, S.A.; Zaied, R.E.; Fahad, S.M.; Smatti, M.K.; Rizeq, B.R.; Al Thani, A.A.; Yassine, H.M.; Nasrallah, G.K. Hepatitis B Virus Molecular Epidemiology, Host-Virus Interaction, Coinfection, and Laboratory Diagnosis in the MENA Region: An Update. Pathogens 2019, 8, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8020063
Al-Sadeq DW, Taleb SA, Zaied RE, Fahad SM, Smatti MK, Rizeq BR, Al Thani AA, Yassine HM, Nasrallah GK. Hepatitis B Virus Molecular Epidemiology, Host-Virus Interaction, Coinfection, and Laboratory Diagnosis in the MENA Region: An Update. Pathogens. 2019; 8(2):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8020063
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Sadeq, Duaa W., Sara A. Taleb, Roan E. Zaied, Sara M. Fahad, Maria K. Smatti, Balsam R. Rizeq, Asmaa A. Al Thani, Hadi M. Yassine, and Gheyath K. Nasrallah. 2019. "Hepatitis B Virus Molecular Epidemiology, Host-Virus Interaction, Coinfection, and Laboratory Diagnosis in the MENA Region: An Update" Pathogens 8, no. 2: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8020063
APA StyleAl-Sadeq, D. W., Taleb, S. A., Zaied, R. E., Fahad, S. M., Smatti, M. K., Rizeq, B. R., Al Thani, A. A., Yassine, H. M., & Nasrallah, G. K. (2019). Hepatitis B Virus Molecular Epidemiology, Host-Virus Interaction, Coinfection, and Laboratory Diagnosis in the MENA Region: An Update. Pathogens, 8(2), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8020063






