Review of Emerging Japanese Encephalitis Virus: New Aspects and Concepts about Entry into the Brain and Inter-Cellular Spreading
Abstract
1. Epidemiology of Emerging Japanese Encephalitis Virus
2. Natural Course of JEV Infection, Virus Spread in the Human Body, Diagnostics, and Anti-Viral Treatment
3. Immune Response and Vaccine
4. JEV Crossing the Blood–Brain Barrier and Brain Infection
5. Cellular Events and Cell-to-Cell Transmission of JEV
6. Summary and Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desingu, P.A.; Ray, P.K.; John, J.K.; Das, T.; Dubal, Z.B.; Rajak, K.K.; Singh, R.K.; Saikumar, G. First Complete Genome Sequence of Genotype III Japanese Encephalitis Virus Isolated from a Stillborn Piglet in India. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e01503-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Qin, Y.; Li, B.; He, Y.; Duan, Q.; Liang, J.; Chen, Z.; Su, Q.; Bi, B.; Zhao, W. Full-Length Genome Sequence of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Strain FC792, Isolated from Guangxi, China. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e01054-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, T.; Ni, H.; Beasley, D.W.C.; Ekkelenkamp, M.; Cardosa, M.J.; Barrett, A.D.T. Origin and Evolution of Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Southeast Asia. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3091–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.R.S.; Strathe, E.; Etcheverry, L.; Cohnstaedt, L.W.; McVey, D.S.; Piaggio, J.; Cernicchiaro, N. Assessment of data on vector and host competence for Japanese encephalitis virus: A systematic review of the literature. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018, 154, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samy, A.M.; Alkishe, A.A.; Thomas, S.M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Mapping the potential distributions of etiological agent, vectors, and reservoirs of Japanese Encephalitis in Asia and Australia. Acta Trop. 2018, 188, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.-B.; Xia, S.; Shi, W.-Q.; Xue, J.-B.; Li, Y.-Y.; Wu, J.-T. New strains of Japanese encephalitis virus circulating in Shanghai, China after a ten-year hiatus in local mosquito surveillance. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Fu, S.; Cao, L.; Shao, N.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Lei, W.; et al. Changing Geographic Distribution of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Genotypes, 1935–2017. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garjito, T.A.; Prihatin, M.T.; Susanti, L.; Prastowo, D.; Sa’adah, S.R.; Taviv, Y.; Satoto, T.B.T.; Waluyo, J.; Manguin, S.; Frutos, R. First evidence of the presence of genotype-1 of Japanese encephalitis virus in Culex gelidus in Indonesia. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karna, A.K.; Bowen, R.A. Experimental Evaluation of the Role of Ecologically-Relevant Hosts and Vectors in Japanese Encephalitis Virus Genotype Displacement. Viruses 2019, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon-Loriere, E.; Faye, O.; Prot, M.; Casademont, I.; Fall, G.; Fernandez-Garcia, M.D.; Diagne, M.M.; Kipela, J.-M.; Fall, I.S.; Holmes, E.C.; et al. Autochthonous Japanese Encephalitis with Yellow Fever Coinfection in Africa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1483–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preziuso, S.; Mari, S.; Mariotti, F.; Rossi, G. Detection of Japanese Encephalitis Virus in bone marrow of healthy young wild birds collected in 1997–2000 in Central Italy. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 11, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Osa, Y.; Asakawa, M. Antibodies to flaviviruses in wild ducks captured in Hokkaido, Japan: Risk assessment of invasive flaviviruses. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009, 9, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.-K.; Oh, Y.-I.; Kim, H.-R.; Lee, Y.-J.; Moon, O.-K.; Yoon, H.; Kim, B.; Lee, K.-W.; Song, J.-Y. Serosurveillance for Japanese encephalitis virus in wild birds captured in Korea. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 12, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Hwang, E.S. Changes of Epidemiological Characteristics of Japanese Encephalitis Viral Infection and Birds as a Potential Viral Transmitter in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2018, 33, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, A.; Nabeshima, T.; Inoue, S.; Agoh, M.; Morita, K. Molecular and serological epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) in a remote island of western Japan: An implication of JEV migration over the East China Sea. Trop. Med. Health 2016, 44, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Hiraoka, E.; Fujita, M.; Hijikata, N.; Ueta, M.; Takagi, K.; Konno, S.; Okuyama, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Osa, Y.; et al. Spring migration routes of mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) that winter in Japan, determined from satellite telemetry. Zool. Sci. 2008, 25, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gong, P.; Wielstra, B.; Si, Y. Southward autumn migration of waterfowl facilitates cross-continental transmission of the highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Xu, Z.; Aharon-Rotman, Y.; Yu, H.; Cao, L. First Description of Grey Heron Ardea cinerea Migration Recorded by GPS/GSM Transmitter. Ornithol. Sci. 2018, 17, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Wang, X.; Cui, G.; Pang, L.; Xu, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Li, B.; Shao, D.; et al. Possible pathogenicity of Japanese encephalitis virus in newly hatched domestic ducklings. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 227, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ke, X.; Ma, L.; Xiao, J.; et al. Comparison of genomic and amino acid sequences of eight Japanese encephalitis virus isolates from bats. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2543–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder-Smith, A.; Leong, W.Y. Importation of yellow fever into China: Assessing travel patterns. J. Travel Med. 2017, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, M.E.; García-Nicolás, O.; Brechbühl, D.; Python, S.; Zumkehr, B.; Nougairede, A.; Charrel, R.N.; Posthaus, H.; Oevermann, A.; Summerfield, A. Vector-free transmission and persistence of Japanese encephalitis virus in pigs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Wang, Q.; Cao, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wen, Y.; Huang, X.; Wen, X.; Yan, Q.; Ma, X.; Wu, R. Serological and molecular epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis virus infections in swine herds in China, 2006–2012. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 19, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.L.; Huang, Y.S.; Lyons, A.C.; Ayers, V.B.; Hettenbach, S.M.; McVey, D.S.; Burton, K.R.; Higgs, S.; Vanlandingham, D.L. North American domestic pigs are susceptible to experimental infection with Japanese encephalitis virus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, A.O., II; Chevalier, V.; Cappelle, J.; Duong, V.; Fontenille, D.; Duboz, R. How much does direct transmission between pigs contribute to Japanese Encephalitis virus circulation? A modelling approach in Cambodia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.C.; Learoyd, T.P.; Langendorf, B.J.; Logan, J.G. Japanese encephalitis: The vectors, ecology and potential for expansion. J. Travel Med. 2018, 25, S16–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Lou, Y.; Chiu, A.P.Y.; He, D. Modelling the skip-and-resurgence of Japanese encephalitis epidemics in Hong Kong. J. Theor. Biol. 2018, 454, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Palinski, R.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cao, S.; Geng, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wen, Y.; Huang, X.; Yan, Q.; et al. Aerosol and Contact Transmission Following Intranasal Infection of Mice with Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, A.M.; Elaagip, A.H.; Kenawy, M.A.; Ayres, C.F.J.; Peterson, A.T.; Soliman, D.E. Climate Change Influences on the Global Potential Distribution of the Mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus, Vector of West Nile Virus and Lymphatic Filariasis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-L.; Chang, H.-L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-T. Seasonal Patterns of Japanese Encephalitis and Associated Meteorological Factors in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Hori, K.; Kitagawa, Y.; Oikawa, Y.; Kamimura, K.; Takegami, T. An Ecological Survey of Mosquitoes and the Distribution of Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan, between 2010 and 2014. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 70, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Rehman, M.U.; Li, K.; Luo, H.; Lan, Y.; Nabi, F.; Zhang, L.; Iqbal, M.K.; Zhu, S.; Javed, M.T.; et al. Epidemiologic Survey of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection, Tibet, China, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1023–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hurk, A.F.; Ritchie, S.A.; Mackenzie, J.S. Ecology and geographical expansion of Japanese encephalitis virus. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2009, 54, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Basu, A. Japanese encephalitis-a pathological and clinical perspective. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, P.S.; Doyle, M.M.; Smart, K.M.; Young, C.C.W.; Drape, G.W.; Johnson, C.K. Predicting wildlife reservoirs and global vulnerability to zoonotic Flaviviruses. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanini, P.; Huhtamo, E.; Crobu, M.G.; Nicosia, A.M.; Servino, L.; Rivasi, F.; Allegrini, S.; Miglio, U.; Magri, A.; Minisini, R.; et al. Japanese encephalitis virus RNA detected in Culex pipiens mosquitoes in Italy. Euro Surveill. 2012, 17, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, V.C.C.; Sridhar, S.; Wong, S.-C.; Wong, S.C.Y.; Chan, J.F.W.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Chau, C.-H.; Au, T.W.K.; Hwang, Y.-Y.; Yau, C.S.W.; et al. Japanese Encephalitis Virus Transmitted Via Blood Transfusion, Hong Kong, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharucha, T.; Sengvilaipaseuth, O.; Seephonelee, M.; Vongsouvath, M.; Vongsouvath, M.; Rattanavong, S.; Piorkowski, G.; Lecuit, M.; Gorman, C.; Pommier, J.-D.; et al. Detection of Japanese Encephalitis Virus RNA in Human Throat Samples in Laos—A Pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalle, E.; Colavita, F.; Iannetta, M.; Gebremeskel Teklè, S.; Carletti, F.; Scorzolini, L.; Bordi, L.; Vincenti, D.; Castilletti, C.; Ippolito, G.; et al. Prolonged detection of dengue virus RNA in the semen of a man returning from Thailand to Italy, January 2018. Euro Surveill. 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, E.M.; Duggal, N.K.; Ritter, J.M.; Brault, A.C. Infection of epididymal epithelial cells and leukocytes drives seminal shedding of Zika virus in a mouse model. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.L.; Chong, A.C.N.; Ashbrook, A.W.; Jeng, G.; Jin, J.; Chen, H.; Tang, E.I.; Martin, L.A.; Kim, R.S.; Kenyon, R.M.; et al. Male germ cells support long-term propagation of Zika virus. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, F.A.; Torres, G.; Acevedo, J.; Fonseca, S.; Casiano, L.; de León-Rodríguez, C.M.; Santiago, G.A.; Doyle, K.; Sharp, T.M.; Alvarado, L.I.; et al. Duration of the Presence of Infectious Zika Virus in Semen and Serum. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Date, O.S.; Kim, K.S.; Manjunath, R. Infection of human amniotic and endothelial cells by Japanese encephalitis virus: Increased expression of HLA-F. Virology 2014, 471–473, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.L.; Hills, S.L.; Fischer, M.; Jacobson, J.A.; Hoke, C.H.; Hombach, J.M.; Marfin, A.A.; Solomon, T.; Tsai, T.F.; Tsu, V.D.; et al. Estimated global incidence of Japanese encephalitis: A systematic review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2011, 89, 766–774, 774A–774E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nealon, J.; Taurel, A.-F.; Yoksan, S.; Moureau, A.; Bonaparte, M.; Quang, L.C.; Capeding, M.R.; Prayitno, A.; Hadinegoro, S.R.; Chansinghakul, D.; et al. Serological Evidence of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Circulation in Asian Children From Dengue-Endemic Countries. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthakur, A.; Das, N.; Bora, B. Data from the World Health Organization (WHO) National Network Laboratory for Japanese Encephalitis. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2013, 5, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtle, L.; Solomon, T. Japanese encephalitis—The prospects for new treatments. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Deubel, V. Mice with different susceptibility to Japanese encephalitis virus infection show selective neutralizing antibody response and myeloid cell infectivity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojima, M.; Takenouchi, A.; Shimoda, H.; Kimura, N.; Maeda, K. Distinct usage of three C-type lectins by Japanese encephalitis virus: DC-SIGN, DC-SIGNR, and LSECtin. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, O.S.; Carbone, E.; Manjunath, R. Inhibition of ERK and proliferation in NK cell lines by soluble HLA-E released from Japanese encephalitis virus infected cells. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 162, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-J.; Ou, Y.-C.; Li, J.-R.; Chang, C.-Y.; Pan, H.-C.; Lai, C.-Y.; Liao, S.-L.; Raung, S.-L.; Chang, C.-J. Infection of pericytes in vitro by Japanese encephalitis virus disrupts the integrity of the endothelial barrier. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooryanarain, H.; Ayachit, V.; Gore, M. Activated CD56(+) lymphocytes (NK+NKT) mediate immunomodulatory and anti-viral effects during Japanese encephalitis virus infection of dendritic cells in-vitro. Virology 2012, 432, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hu, K.; Luo, S.; Zhang, M.; Deng, X.; Li, C.; Jin, W.; Hu, B.; He, S.; Li, M.; et al. DC-SIGN as an attachment factor mediates Japanese encephalitis virus infection of human dendritic cells via interaction with a single high-mannose residue of viral E glycoprotein. Virology 2016, 488, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Nicolás, O.; Lewandowska, M.; Ricklin, M.E.; Summerfield, A. Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells as Model to Evaluate Species Tropism of Mosquito-Borne Flaviviruses. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, M.; Lu, W.; Zhang, D.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Y. DC-SIGN promotes Japanese encephalitis virus transmission from dendritic cells to T cells via virological synapses. Virol. Sin. 2017, 32, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.-I.; Lee, Y.-M. Early Events in Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection: Viral Entry. Pathogens 2018, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.-Y.; Hsu, T.-W.; Chen, Y.-L.; Liu, S.-F.; Tsai, Y.-J.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-S.; Fan, Y.-H. Japanese encephalitis virus non-coding RNA inhibits activation of interferon by blocking nuclear translocation of interferon regulatory factor 3. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, M.; Srivastava, N.; Singh, S.K. Exploitation of microRNAs by Japanese Encephalitis virus in human microglial cells. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Kumawat, K.L.; Rastogi, M.; Basu, A.; Singh, S.K. Japanese Encephalitis Virus exploits the microRNA-432 to regulate the expression of Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling (SOCS) 5. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slonchak, A.; Khromykh, A.A. Subgenomic flaviviral RNAs: What do we know after the first decade of research. Antivir. Res. 2018, 159, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.-R.; Hua, C.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Huang, S.-H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Wan, L.; Lin, C.-W. Anti-apoptotic activity of Japanese encephalitis virus NS5 protein in human medulloblastoma cells treated with interferon-β. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2018, 51, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bacha, T.; Struchiner, C.J.; Cordeiro, M.T.; Almeida, F.C.L.; Marques, E.T.; Da Poian, A.T. 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Metabolomics of Plasma Unveils Liver Dysfunction in Dengue Patients. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7429–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-F.; Li, X.-D.; Deng, C.-L.; Dong, H.-L.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Ye, Q.; Ye, H.-Q.; Huang, X.-Y.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Zhang, B.; et al. Visualization of a neurotropic flavivirus infection in mouse reveals unique viscerotropism controlled by host type I interferon signaling. Theranostics 2017, 7, 912–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puerta-Guardo, H.; Glasner, D.R.; Espinosa, D.A.; Biering, S.B.; Patana, M.; Ratnasiri, K.; Wang, C.; Beatty, P.R.; Harris, E. Flavivirus NS1 Triggers Tissue-Specific Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction Reflecting Disease Tropism. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1598–1613.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, E.; Farooqi, J.Q.; Barr, K.L.; Prakoso, D.; Nasir, A.; Kanji, A.; Shakoor, S.; Malik, F.R.; Hasan, R.; Lednicky, J.A.; et al. Flaviviruses as a Cause of Undifferentiated Fever in Sindh Province, Pakistan: A Preliminary Report. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.W.; Goodman, C.H.; Jee, Y.; Featherstone, D.A. Differential Diagnosis of Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infections with the Inbios JE Detect™ and DEN Detect™ MAC-ELISA Kits. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, G.W.; Cho, J.E.; Ju, Y.R.; Hong, Y.-J.; Han, M.G.; Lee, W.-J.; Choi, E.Y.; Jeong, Y.E. Comparison of four serological tests for detecting antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus after vaccination in children. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2014, 5, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirikajornpan, K.; Nisalak, A.; Thaisomboonsuk, B.; Buddhari, D.; Yoon, I.-K.; Ellison, D.; Macareo, L.; Fernandez, S. Comparison of anti-DENV/JEV IgG-mAb enzyme-linked immunoabsorbent assay and hemagglutination inhibition assay. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2018, 49, 629–638. [Google Scholar]
- Bharucha, T.; Sengvilaipaseuth, O.; Vongsouvath, M.; Davong, V.; Panyanouvong, P.; Piorkowski, G.; Garson, J.A.; Newton, P.N.; de Lamballerie, X.; Dubot-Peres, A. Development of an improved RT-qPCR Assay for detection of Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) RNA including a systematic review and comprehensive comparison with published methods. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantawane, P.B.; Dhanze, H.; Ravi Kumar, G.V.P.P.S.; Grace, M.R.; Dudhe, N.C.; Bhilegaonkar, K.N. TaqMan real-time RT-PCR assay for detecting Japanese encephalitis virus in swine blood samples and mosquitoes. Anim. Biotechnol. 2018, 30, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saron, W.A.A.; Rathore, A.P.S.; Ting, L.; Ooi, E.E.; Low, J.; Abraham, S.N.; St John, A.L. Flavivirus serocomplex cross-reactive immunity is protective by activating heterologous memory CD4 T cells. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Li, F.; Nie, K.; Fu, S.H.; Zhang, W.J.; He, Y.; Lei, W.W.; Wang, Q.Y.; Liang, G.D.; Cao, Y.X.; et al. TaqMan Real-time RT-PCR Assay for Detecting and Differentiating Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sakamuru, S.; Huang, R.; Brecher, M.; Koetzner, C.A.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Qin, C.F.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Erythrosin B is a potent and broad-spectrum orthosteric inhibitor of the flavivirus NS2B-NS3 protease. Antivir. Res. 2018, 150, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Hua, C.-H.; Chuang, C.; Huang, S.-H.; Kung, S.-H.; Hour, M.-J.; Lin, C.-W. Tubacin, an HDAC6 Selective Inhibitor, Reduces the Replication of the Japanese Encephalitis Virus via the Decrease of Viral RNA Synthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topno, R.; Khan, S.A.; Chowdhury, P.; Mahanta, J. Pharmacodynamics of aminoglycosides and tetracycline derivatives against Japanese encephalitis virus. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, R.L.; Getts, D.R.; Deffrasnes, C.; van Vreden, C.; Campbell, I.L.; King, N.J.C. Inflammatory monocytes and the pathogenesis of viral encephalitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannes, N.; Summerfield, A.; Filgueira, L. Regulation of inflammation in Japanese encephalitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xiao, C.; Wang, F.; Xiang, X.; Ou, A.; Wei, J.; Li, B.; Shao, D.; Miao, D.; Zhao, F.; et al. Chemokine receptor antagonist block inflammation and therapy Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mouse model. Cytokine 2018, 110, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lixia, H.; Jun, C.; Song, H.; Fahu, Y.; Jinwen, T. Neuroprotective effect of (-)-tetrahydropalmatine in Japanese encephalitis virus strain GP-78 infected mouse model. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, P.M.; Dung, N.M.; Loan, H.T.; Kneen, R.; Wills, B.; Le Thu, T.; House, D.; White, N.J.; Farrar, J.J.; Hart, C.A.; et al. Proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in humans with Japanese encephalitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 1618–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Das, K.M.P.; Prabhudesai, K.; Deshpande, N.; Karnik, S.; Chowdhary, A.S.; Padmanabhan, U. Expression of domain III of the envelope protein from GP-78: A Japanese encephalitis virus. Virusdisease 2017, 28, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, E.; Kose, N.; Edeling, M.A.; Adhikari, J.; Sapparapu, G.; Lazarte, S.M.; Nelson, C.A.; Govero, J.; Gross, M.L.; Fremont, D.H.; et al. Mouse and Human Monoclonal Antibodies Protect against Infection by Multiple Genotypes of Japanese Encephalitis Virus. mBio 2018, 9, e00008-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunoki, M.; Kurosu, T.; Koketsu, R.K.; Takahashi, K.; Okuno, Y.; Ikuta, K. Neutralizing activities of human immunoglobulin derived from donors in Japan against mosquito-borne flaviviruses, Japanese encephalitis virus, West Nile virus, and dengue virus. Biologics 2016, 10, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, N.; Owada, T.; Matsumoto, C.; Uchida, S.; Nagai, T.; Satake, M.; Tadokoro, K. Evaluation of the protective ability of plasma from Japanese individuals against mosquito-borne viral infections. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 111, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Lei, Y.; Yang, P.; Gao, Q.; Wang, N.; Cao, L.; Yuan, S.; Huang, X.; Deng, Y.; Ma, W.; et al. Structural basis for neutralization of Japanese encephalitis virus by two potent therapeutic antibodies. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.H.; Chung, Y.J.; Ban, S.J.; Kim, E.J.; Park, Y.K.; Cho, H.W. Envelope gene sequence variation among Japanese encephalitis viruses isolated in Korea. Acta Virol. 1996, 40, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Schuh, A.J.; Guzman, H.; Tesh, R.B.; Barrett, A.D.T. Genetic diversity of Japanese encephalitis virus isolates obtained from the Indonesian archipelago between 1974 and 1987. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2013, 13, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amicizia, D.; Zangrillo, F.; Lai, P.L.; Iovine, M.; Panatto, D. Overview of Japanese encephalitis disease and its prevention. Focus on IC51 vaccine (IXIARO®). J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2018, 59, E99–E107. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, S.; Sutter, D.; Maranich, A. Tolerability of Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine in Pediatric Patients. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2017, 6, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, R.; Torresi, J. Japanese B Encephalitis: An Overview of the Disease and Use of Chimerivax-JE as a Preventative Vaccine. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2013, 2, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, N.R.; Gore, M.M. Japanese encephalitis vaccines: Immunogenicity, protective efficacy, effectiveness, and impact on the burden of disease. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeki, T.; Tajima, S.; Kyaw, A.K.; Matsumoto, F.; Miura, K.; Yamashita, A.; Yoshikawa, A.; Negishi, K.; Noguchi, Y.; Tadokoro, K.; et al. Comparison of Neutralizing Antibody Titers against Japanese Encephalitis Virus Genotype V Strain with Those against Genotype I and III Strains in the Sera of Japanese Encephalitis Patients in Japan in 2016. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 71, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandale, B.V.; Khan, S.A.; Kushwaha, K.P.; Rahman, H.; Gore, M.M. Effectiveness of Japanese encephalitis SA 14-14-2 live attenuated vaccine among Indian children: Retrospective 1:4 matched case-control study. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtle, L.; Driver, C. Risk assessment for Japanese encephalitis vaccination. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2018, 14, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.-I.; Song, B.-H.; Polejaeva, I.A.; Davies, C.J.; White, K.L.; Lee, Y.-M. Comparison of the live-attenuated Japanese encephalitis vaccine SA14-14-2 strain with its pre-attenuated virulent parent SA14 strain: Similarities and differences in vitro and in vivo. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2575–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipattanaboon, C.; Sasaki, T.; Nishimura, M.; Setthapramote, C.; Pitaksajjakul, P.; Leaungwutiwong, P.; Limkittikul, K.; Puiprom, O.; Sasayama, M.; Chaichana, P.; et al. Cross-reactivity of human monoclonal antibodies generated with peripheral blood lymphocytes from dengue patients with Japanese encephalitis virus. Biologics 2013, 7, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, T.; Masaki, H.; Takasaki, T.; Aoyama, I.; Yumisashi, T.; Yamanaka, A.; Konishi, E.; Ohnuki, Y.; Muraguchi, A.; Kishi, H. Human monoclonal antibodies against West Nile virus from Japanese encephalitis-vaccinated volunteers. Antivir. Res. 2018, 154, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, R.; Hamada, N.; Kashiwagi, T.; Imamura, Y.; Hara, K.; Nishimura, M.; Kamimura, T.; Takasaki, T.; Watanabe, H.; Koga, T. Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever in a Japanese Traveler with Pre-existing Japanese Encephalitis Virus Antibody. Trop. Med. Health 2015, 43, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Moi, M.L.; Takeshita, N.; Lim, C.-K.; Shiba, H.; Hosono, K.; Saijo, M.; Kurane, I.; Takasaki, T. Japanese encephalitis vaccine-facilitated dengue virus infection-enhancement antibody in adults. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Nicolás, O.; Ricklin, M.E.; Liniger, M.; Vielle, N.J.; Python, S.; Souque, P.; Charneau, P.; Summerfield, A. A Japanese Encephalitis Virus Vaccine Inducing Antibodies Strongly Enhancing In Vitro Infection Is Protective in Pigs. Viruses 2017, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarlinton, D. B cells still front and centre in immunology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtle, L.; Bali, T.; Buxton, G.; Chib, S.; Chan, S.; Soni, M.; Hussain, M.; Isenman, H.; Fadnis, P.; Venkataswamy, M.M.; et al. Human T cell responses to Japanese encephalitis virus in health and disease. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1331–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtle, L.; Tatullo, F.; Bali, T.; Ravi, V.; Soni, M.; Chan, S.; Chib, S.; Venkataswamy, M.M.; Fadnis, P.; Yaïch, M.; et al. Cellular Immune Responses to Live Attenuated Japanese Encephalitis (JE) Vaccine SA14-14-2 in Adults in a JE/Dengue Co-Endemic Area. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Oswal, N.; Chawla, A.S.; Agrawal, T.; Biswas, M.; Vrati, S.; Rath, S.; George, A.; Bal, V.; Medigeshi, G.R. CD8 T cells protect adult naive mice from JEV-induced morbidity via lytic function. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Counor, D.; Lu, P.; Duong, V.; Yu, Y.; Deubel, V. Protective immunity to Japanese encephalitis virus associated with anti-NS1 antibodies in a mouse model. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Saxena, K.; Mishra, S.; Kumar, A. A comprehensive analysis of predicted HLA binding peptides of JE viral proteins specific to north Indian isolates. Bioinformation 2014, 10, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, S.B.; Choi, J.Y.; Uyangaa, E.; Patil, A.M.; Hossain, F.M.A.; Hur, J.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, K.; Eo, S.K. Blockage of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase regulates Japanese encephalitis via enhancement of type I/II IFN innate and adaptive T-cell responses. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Teleki, C.; Wang, T. Memory T Cells in Flavivirus Vaccination. Vaccines (Basel) 2018, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-S.; Zhao, Q.-M.; Zuo, S.-Q.; Jia, N.; Guo, X.-F. Cytokine and chemokine responses to Japanese encephalitis live attenuated vaccine in a human population. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, e285-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gupta, N.; Hegde, P.; Lecerf, M.; Nain, M.; Kaur, M.; Kalia, M.; Vrati, S.; Bayry, J.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Kaveri, S.V. Japanese encephalitis virus expands regulatory T cells by increasing the expression of PD-L1 on dendritic cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, M.; Chen, L.; Mei, L.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Cao, S. Infection of mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells by live attenuated Japanese encephalitis virus induces cells maturation and triggers T cells activation. Vaccine 2011, 29, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais, M.; Wang, K.; Lin, X.; Qian, W.; Zhang, N.; Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Zhao, L.; Fu, Z.F.; Cui, M. TLR7 Deficiency Leads to TLR8 Compensative Regulation of Immune Response against JEV in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannes, N.; Neuhaus, V.; Scolari, B.; Kharoubi-Hess, S.; Walch, M.; Summerfield, A.; Filgueira, L. Interactions of human microglia cells with Japanese encephalitis virus. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.T.; Rathore, A.P.S.; Soundarajan, G.; St John, A.L. Japanese encephalitis virus neuropenetrance is driven by mast cell chymase. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Cao, S.; Wang, K.; Yuan, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Cui, M.; Fu, Z.F. Viral Infection of the Central Nervous System and Neuroinflammation Precede Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption during Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5602–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazielle, N.; Creidy, R.; Malcus, C.; Boucraut, J.; Ghersi-Egea, J.-F. T-Lymphocytes Traffic into the Brain across the Blood-CSF Barrier: Evidence Using a Reconstituted Choroid Plexus Epithelium. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Kalita, J.; Khan, M.Y.; Misra, U.K. Status of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in different brain regions of a rat model of Japanese encephalitis. Inflamm. Res. 2012, 61, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, U.K.; Kalita, J. Overview: Japanese encephalitis. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 91, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkari, N.B.S.; Thacker, A.K.; Barthwal, S.P.; Mishra, V.K.; Prapann, S.; Srivastava, D.; Sarkari, M. Japanese encephalitis (JE). Part I: Clinical profile of 1,282 adult acute cases of four epidemics. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Behera, S.K.; Dehury, B.; Mahapatra, N. Identification and characterization of differentially expressed genes from human microglial cell samples infected with Japanese encephalitis virus. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2017, 54, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Potokar, M.; Jorgačevski, J.; Zorec, R. Astrocytes in Flavivirus Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, M.; Khasa, R.; Sharma, M.; Nain, M.; Vrati, S. Japanese encephalitis virus infects neuronal cells through a clathrin-independent endocytic mechanism. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Yu, X.; Xu, A.; Xu, J.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Wu, X.; Tang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Japanese encephalitis virus induces apoptosis by inhibiting Foxo signaling pathway. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 220, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Sengupta, N.; Chaudhuri, A.; Akbar, I.; Singh, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Suryawanshi, A.R.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Basu, A. PLVAP and GKN3 Are Two Critical Host Cell Receptors Which Facilitate Japanese Encephalitis Virus Entry Into Neurons. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.P.; Ong, K.C.; Perera, D.; Wong, K.T. Neuronal transcriptomic responses to Japanese encephalitis virus infection with a special focus on chemokine CXCL11 and pattern recognition receptors RIG-1 and MDA5. Virology 2019, 527, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kalita, J.; Saxena, V.; Khan, M.Y.; Khanna, V.K.; Sharma, S.; Dhole, T.N.; Misra, U.K. Some observations on the tropism of Japanese encephalitis virus in rat brain. Brain Res. 2009, 1268, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, V.; Roy, U.; Panwar, A.; Raizada, A. Japanese Encephalitis Complicated with Obstructive Hydrocephalus. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, OD18-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, A.; Rai, M.K.; Agarval, V.; Dhole, T.N. Role of CD4+T cell subsets in the determination of the clinical outcome of Japanese encephalitis infection. IJPSR 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkari, N.B.S.; Thacker, A.K.; Barthwal, S.P.; Mishra, V.K.; Prapann, S.; Srivastava, D.; Sarkari, M. Japanese encephalitis (JE) part II: 14 years’ follow-up of survivors. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, K.; Hayasaka, D.; Kitaura, K.; Takasaki, T.; Morita, K.; Suzuki, R.; Kurane, I. Qualitative differences in brain-infiltrating T cells are associated with a fatal outcome in mice infected with Japanese encephalitis virus. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.S.; Khanna, V.K.; Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K. Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection Results in Transient Dysfunction of Memory Learning and Cholinesterase Inhibition. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4705–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mathur, A.; Prakash, V.; Kulshreshtha, R.; Kumar, R.; Chaturvedi, U.C. Japanese encephalitis virus latency in peripheral blood lymphocytes and recurrence of infection in children. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1991, 85, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongtan, T.; Cheepsunthorn, P.; Chaiworakul, V.; Rattanarungsan, C.; Wikan, N.; Smith, D.R. Highly permissive infection of microglial cells by Japanese encephalitis virus: A possible role as a viral reservoir. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongtan, T.; Thepparit, C.; Smith, D.R. The involvement of microglial cells in Japanese encephalitis infections. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 890586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goic, B.; Saleh, M.-C. Living with the enemy: Viral persistent infections from a friendly viewpoint. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Benito, J.S.; de Nova-Ocampo, M. Viral Interference and Persistence in Mosquito-Borne Flaviviruses. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 873404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wispelaere, M.; Khou, C.; Frenkiel, M.-P.; Desprès, P.; Pardigon, N. A Single Amino Acid Substitution in the M Protein Attenuates Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Mammalian Hosts. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 2676–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neufeldt, C.J.; Cortese, M.; Acosta, E.G.; Bartenschlager, R. Rewiring cellular networks by members of the Flaviviridae family. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnis, P.R.; Ravi, V.; Desai, A.; Turtle, L.; Solomon, T. Innate immune mechanisms in Japanese encephalitis virus infection: Effect on transcription of pattern recognition receptors in mouse neuronal cells and brain tissue. Viral Immunol. 2013, 26, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Ye, J.; Zhu, B.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.; Cao, S. Roles of TLR3 and RIG-I in mediating the inflammatory response in mouse microglia following Japanese encephalitis virus infection. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 787023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazmi, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Kundu, K.; Dutta, K.; Mahadevan, A.; Shankar, S.K.; Basu, A. TLR7 is a key regulator of innate immunity against Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 69, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhu, B.; Fu, Z.F.; Chen, H.; Cao, S. Immune evasion strategies of flaviviruses. Vaccine 2013, 31, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.; Khan, S.A. Differential Expression Levels of Inflammatory Chemokines and TLRs in Patients Suffering from Mild and Severe Japanese Encephalitis. Viral Immunol. 2019, 32, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleyas, A.G.; George, J.A.; Han, Y.W.; Rahman, M.M.; Kim, S.J.; Han, S.B.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, K.; Eo, S.K. Functional modulation of dendritic cells and macrophages by Japanese encephalitis virus through MyD88 adaptor molecule-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2462–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ravi, V.; Desai, A. Japanese encephalitis virus interacts with vimentin to facilitate its entry into porcine kidney cell line. Virus Res. 2011, 160, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry Sum, M.S. The involvement of microtubules and actin during the infection of Japanese encephalitis virus in neuroblastoma cell line, IMR32. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 695283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.-H.; Burckhardt, C.J.; Yakimovich, A.; Greber, U.F. Imaging, Tracking and Computational Analyses of Virus Entry and Egress with the Cytoskeleton. Viruses 2018, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.-W.; Li, W.; Zhao, D.-M.; Wang, H.; Hua, R.-H.; Bu, Z.-G. Host Factor SPCS1 Regulates the Replication of Japanese Encephalitis Virus through Interactions with Transmembrane Domains of NS2B. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhu, N.; Chen, S.; Zhao, P.; Ren, H.; Zhu, S.; Tang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Qi, Z. E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Nedd4 Promotes Japanese Encephalitis Virus Replication by Suppressing Autophagy in Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B.; Ashraf, U.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, B.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Microarray Analysis Identifies the Potential Role of Long Non-Coding RNA in Regulating Neuroinflammation during Japanese Encephalitis Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Okabayashi, T.; Yamashita, T.; Zhao, Z.; Wakita, T.; Yasui, K.; Hasebe, F.; Tadano, M.; Konishi, E.; Moriishi, K.; et al. Nuclear localization of Japanese encephalitis virus core protein enhances viral replication. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3448–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wei, J.; Shi, Z.; Yan, W.; Wu, Z.; Shao, D.; Li, B.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Tumor suppressor p53 functions as an essential antiviral molecule against Japanese encephalitis virus. J. Genet. Genom. 2016, 43, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Lyoo, H.R.; Koo, E.S.; Kim, M.S.; Jeong, Y.S. Extended stability of cyclin D1 contributes to limited cell cycle arrest at G1-phase in BHK-21 cells with Japanese encephalitis virus persistent infection. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.A.; Rengifo, A.C.; Sarmiento, L.; Díaz, T.; Laiton-Donato, K.; Gracia, M.; Camacho, S.; Velandia-Romero, M.; Castellanos, J.; Caldas, M.L. Nuclei ultrastructural changes of C6/36 cells infected with virus dengue type 2. Biomedica 2018, 38, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, V.; Sharma, K.B.; Gupta, V.; Saha, D.; Dhapola, P.; Sharma, M.; Sen, U.; Kitajima, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Kalia, M.; et al. ATF3 negatively regulates cellular antiviral signaling and autophagy in the absence of type I interferons. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Okamoto, T.; Katoh, H.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kusakabe, S.; Tokunaga, M.; Hirano, J.; Miyata, Y.; Fukuhara, T.; Ikawa, M.; et al. Infection with flaviviruses requires BCLXL for cell survival. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchil, P.D.; Kumar, A.V.A.; Satchidanandam, V. Nuclear localization of flavivirus RNA synthesis in infected cells. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5451–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicenzi, E.; Pagani, I.; Ghezzi, S.; Taylor, S.L.; Rudd, T.R.; Lima, M.A.; Skidmore, M.A.; Yates, E.A. Subverting the mechanisms of cell death: Flavivirus manipulation of host cell responses to infection. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-C.; Lai, C.-C.; Shiu, S.-L.; Chuang, P.-H.; Tzou, B.-C.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Tsai, F.-J.; Lin, C.-W. Japanese encephalitis virus down-regulates thioredoxin and induces ROS-mediated ASK1-ERK/p38 MAPK activation in human promonocyte cells. Microbes Infect. 2010, 12, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.-H.; Nadar, M.; Chen, C.-C.; Weng, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chang, R.-Y. Small noncoding RNA modulates Japanese encephalitis virus replication and translation in trans. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villordo, S.M.; Filomatori, C.V.; Sánchez-Vargas, I.; Blair, C.D.; Gamarnik, A.V. Dengue virus RNA structure specialization facilitates host adaptation. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiyoshi, H.; Hoke, C.H.; Trent, D.W. Infectious Japanese encephalitis virus RNA can be synthesized from in vitro-ligated cDNA templates. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 5425–5431. [Google Scholar]
- Lannes, N.; Garcia-Nicolàs, O.; Démoulins, T.; Summerfield, A.; Filgueira, L. CX3CR1-CX3CL1-dependent cell-to-cell Japanese encephalitis virus transmission by human microglial cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Teillon, J.; Koulakoff, A.; Berry, H.; Giaume, C. Monitoring gap junctional communication in astrocytes from acute adult mouse brain slices using the gap-FRAP technique. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 303, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapato, A.S.; Tiwari-Woodruff, S.K. Connexins and pannexins: At the junction of neuro-glial homeostasis & disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Li, L.; Engelhart, A.E.; Gan, J.; Wang, J.; Szostak, J.W. Structural insights into the effects of 2’-5’ linkages on the RNA duplex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3050–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemcke, H.; Peukert, J.; Voronina, N.; Skorska, A.; Steinhoff, G.; David, R. Applying 3D-FRAP microscopy to analyse gap junction-dependent shuttling of small antisense RNAs between cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016, 98, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Li, Y.; Lv, H.; Deng, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tang, P. Exchange of genetic material: A new paradigm in bone cell communications. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 1989–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Dang, S.; Ma, X.; Liu, F.; Xu, M.; Lv, Z.; Han, D.; Fang, X.; et al. Long-distance intercellular connectivity between cardiomyocytes and cardiofibroblasts mediated by membrane nanotubes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 92, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ady, J.; Thayanithy, V.; Mojica, K.; Wong, P.; Carson, J.; Rao, P.; Fong, Y.; Lou, E. Tunneling nanotubes: An alternate route for propagation of the bystander effect following oncolytic viral infection. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2016, 3, 16029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayanithy, V.; O’Hare, P.; Wong, P.; Zhao, X.; Steer, C.J.; Subramanian, S.; Lou, E. A transwell assay that excludes exosomes for assessment of tunneling nanotube-mediated intercellular communication. Cell Commun. Signal. 2017, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Grein, S.G.; Defourny, K.A.Y.; Rabouw, H.H.; Galiveti, C.R.; Langereis, M.A.; Wauben, M.H.M.; Arkesteijn, G.J.A.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.M. Picornavirus infection induces temporal release of multiple extracellular vesicle subsets that differ in molecular composition and infectious potential. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
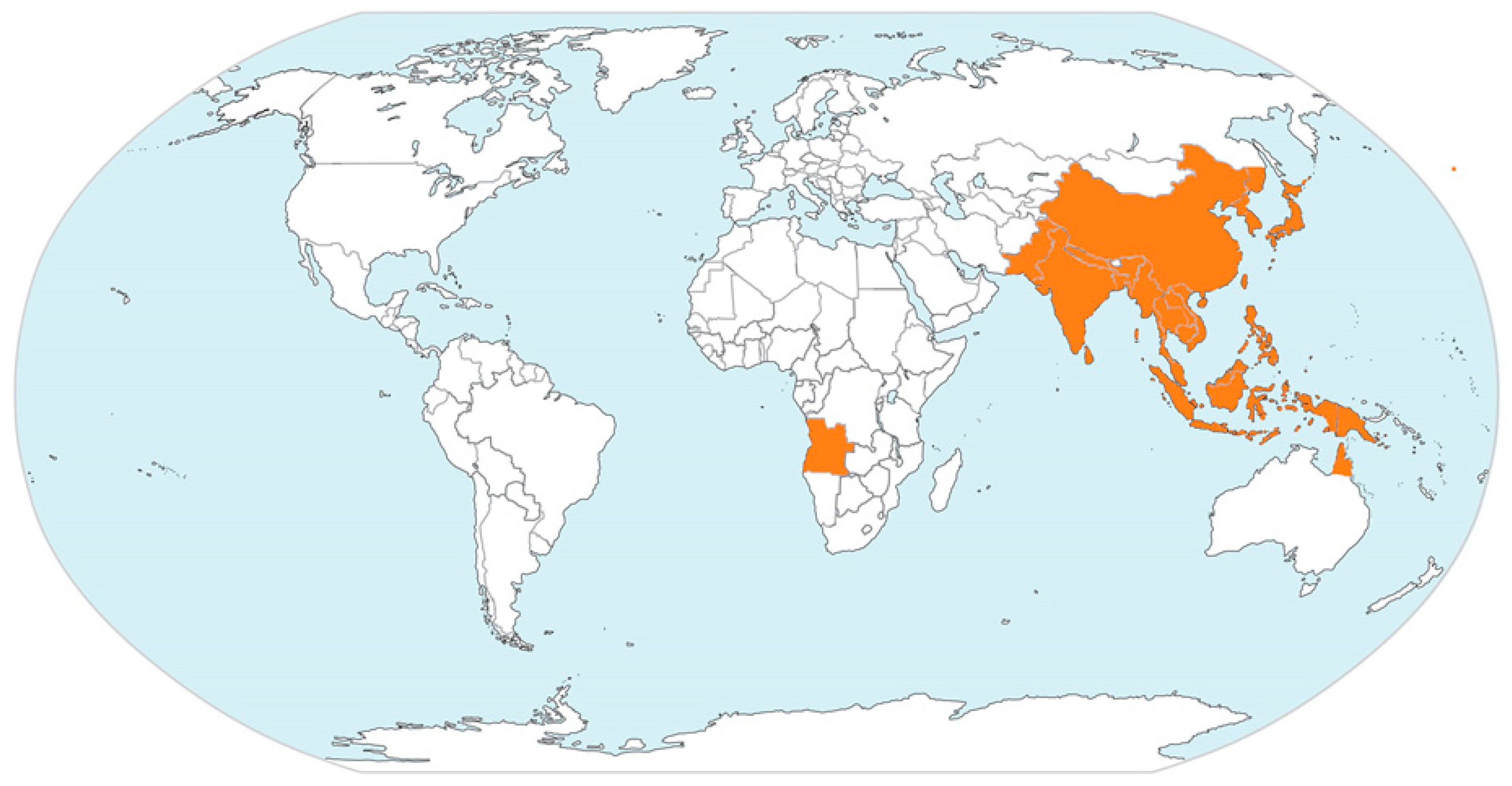


| Geographic Region | Countries/Territories/Provinces |
|---|---|
| East Asia | China (including Tibet) |
| Japan | |
| North Korea | |
| Russia (Far East Provinces) | |
| South Korea | |
| Taiwan | |
| South Asia | Bangladesh |
| India | |
| Nepal | |
| Pakistan | |
| Sri Lanka | |
| Southeast Asia | Brunei |
| Cambodia | |
| Indonesia | |
| Laos | |
| Malaysia | |
| Myanmar | |
| Papua New Guinea | |
| Philippines | |
| Singapore | |
| Thailand | |
| Timor-Leste | |
| Vietnam | |
| Australia | Cape York Peninsula of Queensland |
| Top End of Northern Territory |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filgueira, L.; Lannes, N. Review of Emerging Japanese Encephalitis Virus: New Aspects and Concepts about Entry into the Brain and Inter-Cellular Spreading. Pathogens 2019, 8, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8030111
Filgueira L, Lannes N. Review of Emerging Japanese Encephalitis Virus: New Aspects and Concepts about Entry into the Brain and Inter-Cellular Spreading. Pathogens. 2019; 8(3):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8030111
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilgueira, Luis, and Nils Lannes. 2019. "Review of Emerging Japanese Encephalitis Virus: New Aspects and Concepts about Entry into the Brain and Inter-Cellular Spreading" Pathogens 8, no. 3: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8030111
APA StyleFilgueira, L., & Lannes, N. (2019). Review of Emerging Japanese Encephalitis Virus: New Aspects and Concepts about Entry into the Brain and Inter-Cellular Spreading. Pathogens, 8(3), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8030111





