Molecular Detection and Antibiotyping of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Isolated from Houseflies in a Fish Market
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Selection and Interviews
2.2. Sample Size Determination
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
2.4. Isolation and Identification of Salmonella spp.
2.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test
2.6. Molecular Detection of the Resistance Genes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
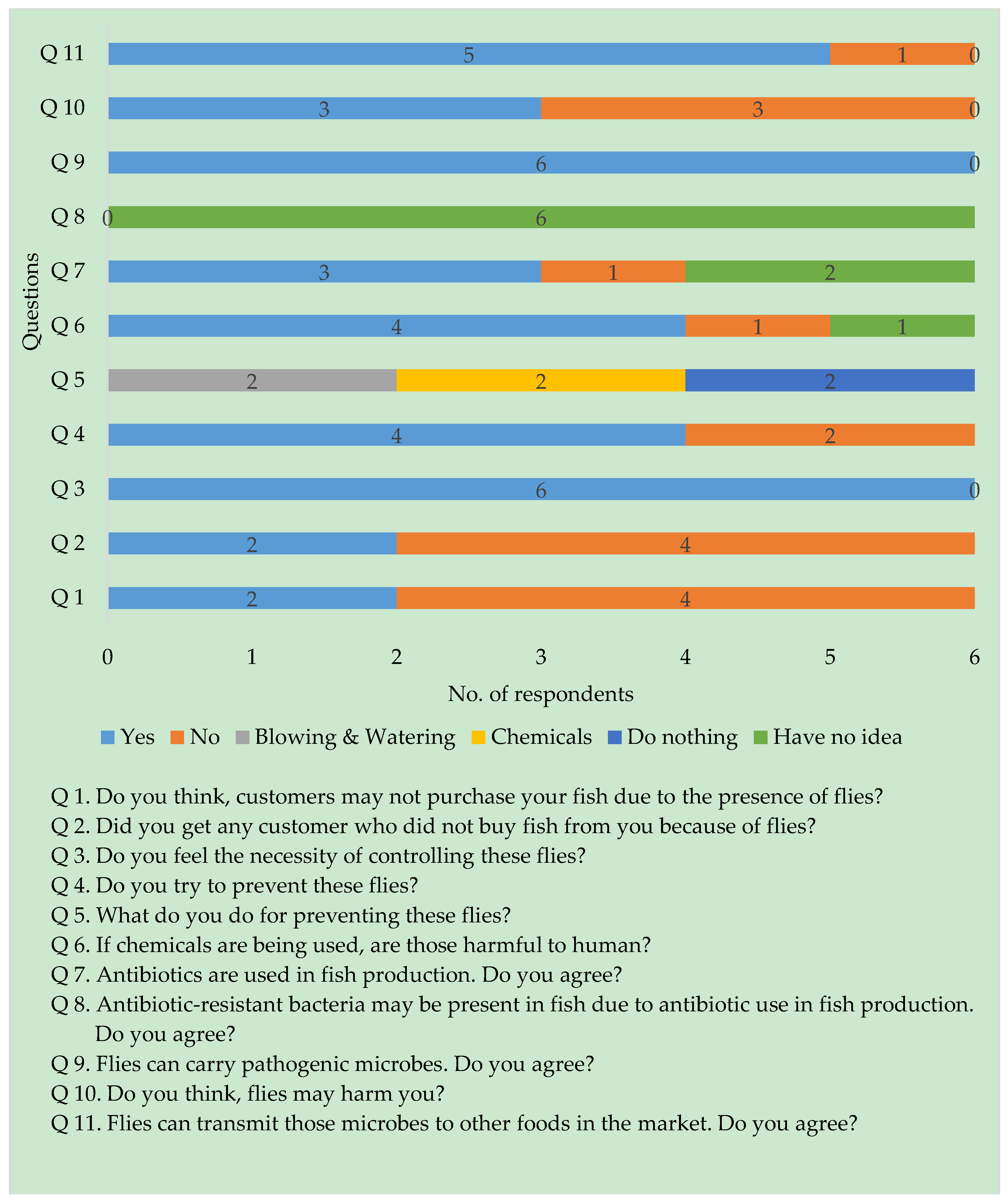
3.1. Semi-Structured Interviews
3.2. Prevalence of Salmonella spp.
3.3. Antibiogram of Salmonella spp.
3.4. Antibiotyping
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franco, B.E.; Martínez, M.A.; Rodríguez, M.A.S.; Wertheimer, A.I. The determinants of the antibiotic resistance process. Infect. Drug Resist. 2009, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choo, L.; Saleha, A.; Wai, S.; Fauziah, N. Isolation of Campylobacter and Salmonella from houseflies (Musca domestica) in a university campus and a poultry farm in Selangor, Malaysia. Trop.Biomed. 2011, 28, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Songe, M.; Hang’ombe, B.; Knight-Jones, T.; Grace, D. Antimicrobial resistant enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. in houseflies infesting fish in food markets in Zambia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurek, L.; Ghosh, A. Insects represent a link between food animal farms and the urban environment for antibiotic resistance traits. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3562–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.L.F.; Rudan, I.; Liu, L.; Nair, H.; Theodoratou, E.; Bhutta, Z.A.; OBrien, K.L.; Campbell, H.; Black, R.E. Global burden of childhood pneumonia and diarrhoea. Lancet 2013, 381, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohar, A.; Abdeltawab, N.F.; Fahmy, A.; Amin, M.A. Development of safe, effective and immunogenic vaccine candidate for diarrheagenic Escherichia coli main pathotypes in a mouse model. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havelaar, A.H.; Kirk, M.D.; Torgerson, P.R.; Gibb, H.J.; Hald, T.; Lake, R.J.; Praet, N.; Bellinger, D.C.; De Silva, N.R.; Gargouri, N. World Health Organization global estimates and regional comparisons of the burden of foodborne disease in 2010. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, M.; Klimpel, S.; Sievert, K. The house fly (Musca domestica) as a potential vector of metazoan parasites caught in a pig-pen in Germany. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 160, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestmann, F.; Förster, M.; Mehlhorn, H.; Sievert, K.; Messler, S.; Neuhausen, N.; Petersdorf, S.; Pfeffer, K. Flies as vectors of microorganisms potentially inducing severe diseases in humans and animals. In Arthropods as Vectors of Emerging Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 195–226. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, A.N.; Abdel-Latef, G.K.; Abdel-Azeem, N.M.; El-Dakhly, K.M. Ecological study on antimicrobial-resistant zoonotic bacteria transmitted by flies in cattle farms. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 3889–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, G.; Durden, L. Medical and Veterinary Entomology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nazni, W.; Seleena, B.; Lee, H.; Jeffery, J.; Rogayah, T.; Sofian, M. Bacteria fauna from the house fly, Musca domestica (L.). Trop. Biomed. 2005, 22, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, P.S.; Geden, C.J.; Moore, R.W.; Gast, R.K. Isolation of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis from houseflies (Musca domestica) found in rooms containing Salmonella serovar Enteritidis-challenged hens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 6030–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahuma, N.; Ghenghesh, K.; Ben Aissa, R.; Elamaari, A. Carriage by the housefly (Musca domestica) of multiple-antibiotic-resistant bacteria that are potentially pathogenic to humans, in hospital and other urban environments in Misurata, Libya. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2005, 99, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R. Effect of Curcuma longa (Turmeric) on biochemical aspects of House Fly, Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae). Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2013, 54, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chuang, H.-L.; Chiu, C.-C.; Yeh, K.-S.; Chang, C.-C.; Hsuan, S.-L.; Lin, W.-H.; Chen, T.-H. Transmission of Salmonella between swine farms by the housefly (Musca domestica). J. Food Prot. 2011, 74, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Österberg, J.; Lewerin, S.S.; Wallgren, P. Direct and indirect transmission of four Salmonella enterica serotypes in pigs. Acta Vet. Scand. 2010, 52, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Yi, W.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, N.; Qin, P. Characteristic diversity and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella from gastroenteritis. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, V.V.; Gole, V.C.; McWhorter, A.R.; Abraham, S.; Chousalkar, K.K. Antimicrobial resistance of non-typhoidal Salmonella isolates from egg layer flocks and egg shells. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 203, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelle, B.W.; Bearson, S.M.D.; Bearson, B.L. Tetracycline accelerates the temporally-regulated invasion response in specific isolates of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pribul, B.R.; Festivo, M.L.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Costa, R.G.; Rodrigues, E.C.d.P.; de Souza, M.; Rodrigues, D.d.P. Characteristics of quinolone resistance in Salmonella spp. isolates from the food chain in Brazil. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.-S.; Lauderdale, T.-L.; Phung, D.C.; Watanabe, H.; Kuo, J.-C.; Wang, P.-J.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Liang, S.-Y.; Chen, P.-C. Antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi isolates from Bangladesh, Indonesia, Taiwan, and Vietnam. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6501–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ed-dra, A.; Filali, F.R.; Karraouan, B.; El Allaoui, A.; Aboulkacem, A.; Bouchrif, B. Prevalence, molecular and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from sausages in Meknes, Morocco. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okanda, T.; Haque, A.; Ehara, T.; Huda, Q.; Ohkusu, K.; Miah, R.A.; Matsumoto, T. Characteristics of resistance mechanisms and molecular epidemiology of fluoroquinolone-nonsusceptible Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi and Paratyphi a isolates from a tertiary hospital in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 1460–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aftabuddin, S.; Islam, M.N.; Bhuyain, M.A.B.; Mannan, M.A.; Alam, M.M. Fish diseases and strategies taken by the farmers in freshwater aquaculture at southwestern Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Zool. 2016, 44, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.Z. Aquaculture drugs used for fish and shellfish health management in the Southwestern Bangladesh. Asian J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 7, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Das, M.; Hafiz, F.; Ahmed, M.K.; Parveen, S. Microbiological analysis of some raw fish samples. Bangladesh J. Microbiol. 2007, 24, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Mojumder, P.K.; Baten, A.; Sayeed, A. Bacteriological quality of frozen and unfrozen pabda (Ompok pabda: Siluriformes) in a fish processing plant. J. Asiat. Soc. Bangladesh Sci. 2016, 42, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Seel, S.; Kabir, S.; Islam, M. Molecular detection and characterization of Salmonella spp. isolated from fresh fishes sold in selected upazila markets of Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Vet. Med. 2016, 14, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, M.A.K.; Marzan, M.; Khatun, F.; Ahmed, M.F.; Mahmud, S.A.; Rahman, S.R. Isolation of multidrug resistant pathogenic bacteria from common flies in Dhaka, Bangladesh. J. Entomol. 2016, 13, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrusfield, M. Veterinary Epidemiology, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Roesel, K.; Grace, D. Food Safety and Informal Markets: Animal Products in sub-Saharan Africa; Routledge: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan Dey, M.; Rab, M.A.; Paraguas, F.J.; Piumsombun, S.; Bhatta, R.; Ferdous Alam, M.; Ahmed, M. Fish consumption and food security: A disaggregated analysis by types of fish and classes of consumers in selected Asian countries. Aquacult. Econ. Manag. 2005, 9, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konemann, E.; Allen, S.; Janda, W. Mycobacteria in: Koneman’s Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 6th ed.; Lippincott William & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vazirianzadeh, B.; Solary, S.S.; Rahdar, M.; Hajhossien, R.; Mehdinejad, M. Identification of bacteria which possible transmitted by Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae) in the region of Ahvaz, SW Iran. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2008, 1, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.H. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 5th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1939; pp. 404–405. [Google Scholar]
- Dashti, A.A.; Jadaon, M.M.; Abdulsamad, A.M.; Dashti, H.M. Heat treatment of bacteria: A simple method of DNA extraction for molecular techniques. Kuwait Med. J. 2009, 41, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugasundaram, M.; Radhika, M.; Murali, H.; Batra, H. Detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium by selective amplification of fliC, fljB, iroB, invA, rfbJ, STM2755, STM4497 genes by polymerase chain reaction in a monoplex and multiplex format. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudzicki, J. Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Test Protocol-2009; ASM MicrobeLibrary, American Society for Microbiology: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–23. Available online: https://www.asm.org/getattachment/2594ce26-bd44-47f6-8287-0657aa9185ad/Kirby-Bauer-Disk-Diffusion-Susceptibility-Test-Protocol-pdf.pdf (accessed on 29 August 2019).
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: 17th Informational Supplement; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, M.T.; Lubbers, B.V.; Schwarz, S.; Watts, J.L. Applying definitions for multidrug resistance, extensive drug resistance and pandrug resistance to clinically significant livestock and companion animal bacterial pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1460–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobur, M.A.; Sabuj, A.A.M.; Sarker, R.; Rahman, A.M.M.T.; Kabir, S.M.L.; Rahman, M.T. Antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. associated with dairy cattle and farm environment having public health significance. Vet. World 2019, 12, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Sánchez, J.; Cruz-Trujillo, E.; Barrios, H.; Reyna-Flores, F.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Garza-Ramos, U.; Consortium, B.R. Characterization of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance (PMQR) genes in extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae pediatric clinical isolates in Mexico. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77968. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, I.; Rabbi, M.B.; Sultana, S. Antibiotic resistance in Bangladesh: A systematic review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 80, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.S.; Shiraj-Um-Mahmuda, S.; Hazzaz-Bin-Kabir, M. Antibiotic usage patterns in selected broiler farms of Bangladesh and their Public Health Implications. J. Public Health Dev. Ctries. 2016, 2, 276–284. [Google Scholar]
- Clifford, K.; Desai, D.; da Costa, C.P.; Meyer, H.; Klohe, K.; Winkler, A.S.; Rahman, T.; Islam, T.; Zaman, M.H. Antimicrobial resistance in livestock and poor quality veterinary medicines. Bull. World Health Organ. 2018, 96, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Tao, J.; Kang, X.; Jiao, Y.; Guo, R.; Wang, G.; Pan, Z.; Jiao, X. Salmonella isolated from the slaughterhouses and correlation with pork contamination in free market. Food Control 2016, 59, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wales, A.; Breslin, M.; Davies, R.H. Assessment of cleaning and disinfection in Salmonella-contaminated poultry layer houses using qualitative and semi-quantitative culture techniques. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 116, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, K.L.; Davies, R.H.; Threlfall, E.J. Mechanisms of quinolone resistance in Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Recent developments. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strahilevitz, J.; Jacoby, G.A.; Hooper, D.C.; Robicsek, A. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance: A multifaceted threat. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 664–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, T.T.H.; Chin, J.; Chapman, T.; Tran, L.T.; Coloe, P.J. Safety of raw meat and shellfish in Vietnam: An analysis of Escherichia coli isolations for antibiotic resistance and virulence genes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 124, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquali, F.; De Cesare, A.; Ricci, A.; Kehrenberg, C.; Schwarz, S.; Manfreda, G. Phage types, ribotypes and tetracycline resistance genes of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium strains isolated from different origins in Italy. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 103, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, P.G.; Caballes, M.B.D.; Rivera, W.L. Antimicrobial resistance in Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. isolates from fresh produce and the impact to food safety. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2017, 52, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics are Urgently Needed; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.who.int/medicines/publications/WHO-PPL-Short_Summary_25Feb-ET_NM_WHO.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y. WHO Pathogens Priority List Working Group. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: The WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Target Genes | Primer Sequence (5’-3’) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Annealing Temp. (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| invA | F: ATCAGTACCAGTCGTCTTATCTTGAT R:TCTGTTTACCGGGCATACCAT | 211 | 58 | [38] |
| tetA | F: GGTTCACTCGAACGACGTCA R: CTGTCCGACAAGTTGCATGA | 577 | 57 | [42] |
| tetB | F: CCTCAGCTTCTCAACGCGTG R: GCACCTTGCTGATGACTCTT | 634 | 56 | [42] |
| qnrA | F: ATTTCTCACGCCAGGATTTG R: GATCGGCAAAGGTTAGGTCA | 516 | 53 | [43] |
| Antibiotics | No. of Resistant Isolates (%) |
|---|---|
| Tetracycline | 34 (100) |
| Ampicillin | 28 (80) |
| Azithromycin | 26 (76.5) |
| Meropenem | 25 (73.5) |
| Oxytetracycline | 25 (73.5) |
| Streptomycin | 23 (67.6) |
| Imipenem | 12 (35.5) |
| Ciprofloxacin | 10 (29.4) |
| Chloramphenicol | 7 (20.6) |
| Gentamicin | 2 (5.9) |
| Pattern No. | Antibiotic Resistance Pattern | No. of Antibiotics (Classes) | Isolate No.c. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | S, TE | 2 (2) | 41, 50 |
| 2 | AZM, O, TE | 3 (2) | 15 b |
| 3 | AMP, MEM, O, TE | 4 (3) | 5 |
| 4 | MEM, O, S, TE | 4 (3) | 10 |
| 5 | AMP, AZM, O, TE | 4 (3) | 22 b, 51 b |
| 6 | AMP, AZM, C, TE | 4 (4) | 8 b |
| 7 | AMP, AZM, IPM, TE | 4 (4) | 58 |
| 8 | AZM, C, CIP, O, TE | 5 (4) | 28 a |
| 9 | AMP, AZM, MEM, O, TE | 5 (4) | 30 |
| 10 | AMP, C, MEM, S, TE | 5 (5) | 20 b |
| 11 | AMP, IPM, MEM, O, S, TE | 6 (4) | 14 |
| 12 | AZM, IPM, MEM, O, S, TE | 6 (4) | 26 |
| 13 | AMP, AZM, IPM, MEM, O, TE | 6 (4) | 35 |
| 14 | AMP, IPM, MEM, O, S, TE | 6 (4) | 44 b |
| 15 | AMP, AZM, CIP, O, S, TE | 6 (4) | 55 |
| 16 | AMP, CIP, IPM, MEM, S, TE | 6 (5) | 1 a |
| 17 | AMP, AZM, MEM, O, S, TE | 6 (5) | 29 b, 43, 45 b |
| 18 | AMP, AZM, CIP, MEM, O, TE | 6 (5) | 38 a,b |
| 19 | AMP, AZM, C, MEM, S, TE | 6 (6) | 37 |
| 20 | AMP, AZM, IPM, MEM, O, S, TE | 7 (5) | 9 b, 21, 24 b |
| 21 | AMP, AZM, C, CIP, GEN, MEM, TE | 7 (6) | 12 a,b |
| 22 | AMP, AZM, CIP, MEM, O, S, TE | 7 (6) | 16 a, 36 b, 52 |
| 23 | AMP, AZM, MEM, C, O, S, TE | 7 (6) | 40 b |
| 24 | AMP, AZM, C, GEN, IPM, MEM, S, TE | 8 (6) | 31 b |
| 25 | AMP, AZM, CIP, IPM, MEM, O, S, TE | 8 (6) | 53 b, 57 a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobur, A.; Hasan, M.; Haque, E.; Mridul, A.I.; Noreddin, A.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Rahman, T. Molecular Detection and Antibiotyping of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Isolated from Houseflies in a Fish Market. Pathogens 2019, 8, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040191
Sobur A, Hasan M, Haque E, Mridul AI, Noreddin A, El Zowalaty ME, Rahman T. Molecular Detection and Antibiotyping of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Isolated from Houseflies in a Fish Market. Pathogens. 2019; 8(4):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040191
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobur, Abdus, Mehedi Hasan, Emdadul Haque, Asmaul Iqbal Mridul, Ayman Noreddin, Mohamed E. El Zowalaty, and Tanvir Rahman. 2019. "Molecular Detection and Antibiotyping of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Isolated from Houseflies in a Fish Market" Pathogens 8, no. 4: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040191
APA StyleSobur, A., Hasan, M., Haque, E., Mridul, A. I., Noreddin, A., El Zowalaty, M. E., & Rahman, T. (2019). Molecular Detection and Antibiotyping of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Isolated from Houseflies in a Fish Market. Pathogens, 8(4), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040191








