Whole Genome Sequencing of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Cultured from Blood Stream Infections Reveals Three Major Phylogenetic Groups Including a Novel Lineage Expressing Serotype a Membrane O Polysaccharide
Abstract
1. Introduction
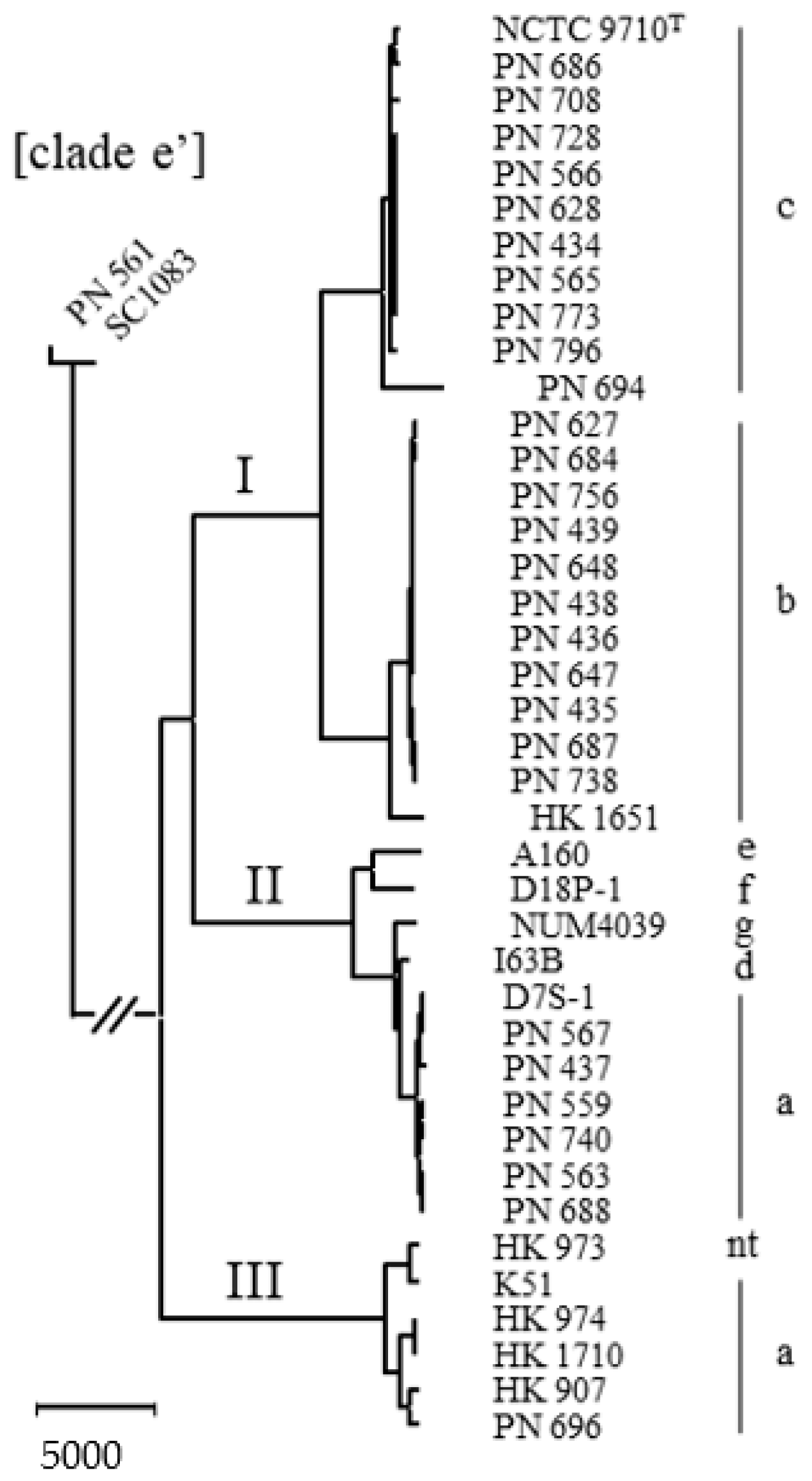
2. Results
2.1. Delineation of the Species
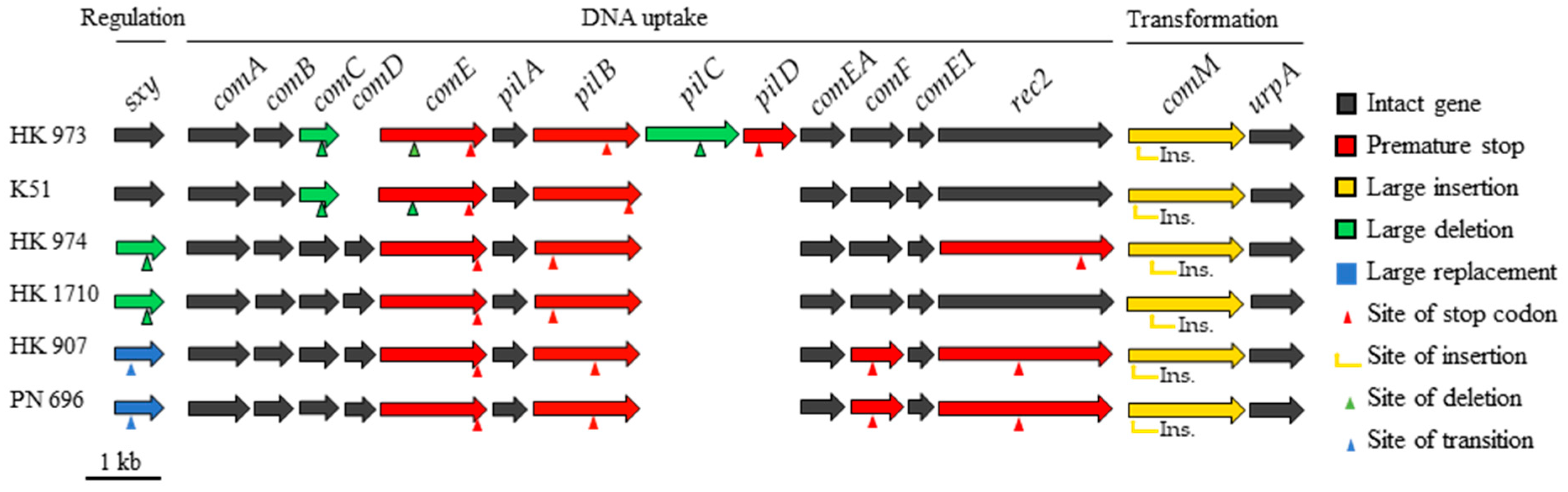
2.2. Natural Competence and Genomic Characteristics of Lineages
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and DNA Accession Numbers
4.2. Identification and Phenotyping
4.3. DNA Sequencing, Genome Assembly, and Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Ethical Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Karched, M.; Furgang, D.; Planet, P.J.; DeSalle, R.; Fine, D.H. Genome Sequence of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans RHAA1, Isolated from a Rhesus Macaque, an Old World Primate. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 1275–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nørskov-Lauritsen, N. Classification, identification, and clinical significance of Haemophilus and Aggregatibacter species with host specificity for humans. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 214–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, B.; Ward, J.M.; Ready, D. Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans: A triple A* periodontopathogen? Periodontology 2000 2010, 54, 78–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haubek, D.; Ennibi, O.K.; Poulsen, K.; Vaeth, M.; Poulsen, S.; Kilian, M. Risk of aggressive periodontitis in adolescent carriers of the JP2 clone of Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans in Morocco: A prospective longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 2008, 371, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, D.H.; Patil, A.G.; Velusamy, S.K. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans (Aa) Under the Radar: Myths and Misunderstandings of Aa and Its Role in Aggressive Periodontitis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lützen, L.; Olesen, B.; Voldstedlund, M.; Christensen, J.J.; Moser, C.; Knudsen, J.D.; Fuursted, K.; Hartmeyer, G.N.; Chen, M.; Søndergaard, T.S.; et al. Incidence of HACEK bacteraemia in Denmark: A 6-year population-based study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 68, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, H.S.; Chambers, S.T.; Roberts, S.A.; Holland, D.J.; Julian, K.A.; Raymond Beardsley, J.; Read, K.M.; Murdoch, D.R. Association between HACEK bacteraemia and endocarditis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 892–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, K.; Theilade, E.; Lally, E.T.; Demuth, D.R.; Kilian, M. Population structure of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: A framework for studies of disease-associated properties. Microbiology 1994, 140, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kaplan, J.B.; Schreiner, H.C.; Furgang, D.; Fine, D.H. Population Structure and Genetic Diversity of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Strains Isolated from Localized Juvenile Periodontitis Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubek, D.; Poulsen, K.; Kilian, M. Microevolution and patterns of dissemination of the JP2 clone of Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) Actinomycetemcomitans. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 3080–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittichotirat, W.; Bumgarner, R.E.; Asikainen, S.; Chen, C. Identification of the Pangenome and Its Components in 14 Distinct Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Strains by Comparative Genomic Analysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorth, P.; Whiteley, M. An Evolutionary Link between Natural Transformation and CRISPR Adaptive Immunity. MBio 2012, 3, e00309-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittichotirat, W.; Bumgarner, R.E.; Chen, C. Evolutionary Divergence of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambon, J.J.; Umemoto, T.; De Nardin, E.; Nakazawa, F.; Christersson, L.A.; Genco, R.J. Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in the pathogenesis of human periodontal disease. Adv. Dent. Res. 1988, 2, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paju, S.; Carlson, P.; Jousimies-Somer, H.; Asikainen, S. Heterogeneity of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Strains in Various Human Infections and Relationships between Serotype, Genotype, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Rylev, M.; Kilian, M. Prevalence and distribution of principal periodontal pathogens worldwide. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 3, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.P.; Göker, M. Genome sequencebased species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, L.; Brenner, D.J.; Colwell, R.R.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Kandler, O.; Krichevsky, M.I.; Moore, L.H.; Moore, W.E.C.; Murray, R.G.E.; Stackebrandt, E.; et al. Report of the Ad Hoc Committee on Reconciliation of Approaches to Bacterial Systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1987, 37, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Ouk Kim, Y.; Park, S.C.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevers, D.; Cohan, F.M.; Lawrence, J.G.; Spratt, B.G.; Coenye, T.; Feil, E.J.; Stackebrandt, E.; Van de Peer, Y.; Vandamme, P.; Thompson, F.L.; et al. Opinion: Re-evaluating prokaryotic species. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Goodman, S.D.; Redfield, R.J.; Chen, C. Natural transformation and DNA uptake signal sequences in Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 3442–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nørskov-Lauritsen, N.; Kilian, M. Reclassification of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Haemophilus aphrophilus, Haemophilus paraphrophilus and Haemophilus segnis as Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans gen. nov., comb. nov., Aggregatibacter aphrophilus comb. nov. and Aggregatibacter segnis comb. nov., and emended description of Aggregatibacter aphrophilus to include V factor-dependent and V factor-independent isolates. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Murra, M.; Lützen, L.; Barut, A.; Zbinden, R.; Lund, M.; Villesen, P.; Nørskov-Lauritsen, N. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Aggregatibacter Species Isolated from Human Clinical Specimens and Description of Aggregatibacter kilianii sp. nov. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00053-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, A.B.; Haubek, D.; Claesson, R.; Johansson, A.; Nørskov-Lauritsen, N. Comprehensive antimicrobial susceptibility testing of a large collection of clinical strains of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans does not identify resistance to amoxicillin. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, K.; Bostanci, N.; Thurnheer, T.; Grossmann, J.; Wolski, W.E.; Thay, B.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Oscarsson, J. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans H-NS promotes biofilm formation and alters protein dynamics of other species within a polymicrobial oral biofilm. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2018, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cummins, C.A.; Hunt, M.; Wong, V.K.; Reuter, S.; Holden, M.T.; Fookes, M.; Falush, D.; Keane, J.A.; Parkhill, J. Roary: Rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3691–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nedergaard, S.; Kobel, C.M.; Nielsen, M.B.; Møller, R.T.; Jensen, A.B.; Nørskov-Lauritsen, N. Whole Genome Sequencing of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Cultured from Blood Stream Infections Reveals Three Major Phylogenetic Groups Including a Novel Lineage Expressing Serotype a Membrane O Polysaccharide. Pathogens 2019, 8, 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040256
Nedergaard S, Kobel CM, Nielsen MB, Møller RT, Jensen AB, Nørskov-Lauritsen N. Whole Genome Sequencing of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Cultured from Blood Stream Infections Reveals Three Major Phylogenetic Groups Including a Novel Lineage Expressing Serotype a Membrane O Polysaccharide. Pathogens. 2019; 8(4):256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040256
Chicago/Turabian StyleNedergaard, Signe, Carl M. Kobel, Marie B. Nielsen, Rikke T. Møller, Anne B. Jensen, and Niels Nørskov-Lauritsen. 2019. "Whole Genome Sequencing of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Cultured from Blood Stream Infections Reveals Three Major Phylogenetic Groups Including a Novel Lineage Expressing Serotype a Membrane O Polysaccharide" Pathogens 8, no. 4: 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040256
APA StyleNedergaard, S., Kobel, C. M., Nielsen, M. B., Møller, R. T., Jensen, A. B., & Nørskov-Lauritsen, N. (2019). Whole Genome Sequencing of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Cultured from Blood Stream Infections Reveals Three Major Phylogenetic Groups Including a Novel Lineage Expressing Serotype a Membrane O Polysaccharide. Pathogens, 8(4), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040256




