The Host-Specific Intestinal Microbiota Composition Impacts Campylobacter coli Infection in a Clinical Mouse Model of Campylobacteriosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Association of Microbiota-Depleted IL-10−/− Mice with a Murine or Human Fecal Microbiota Prior C. coli Infection
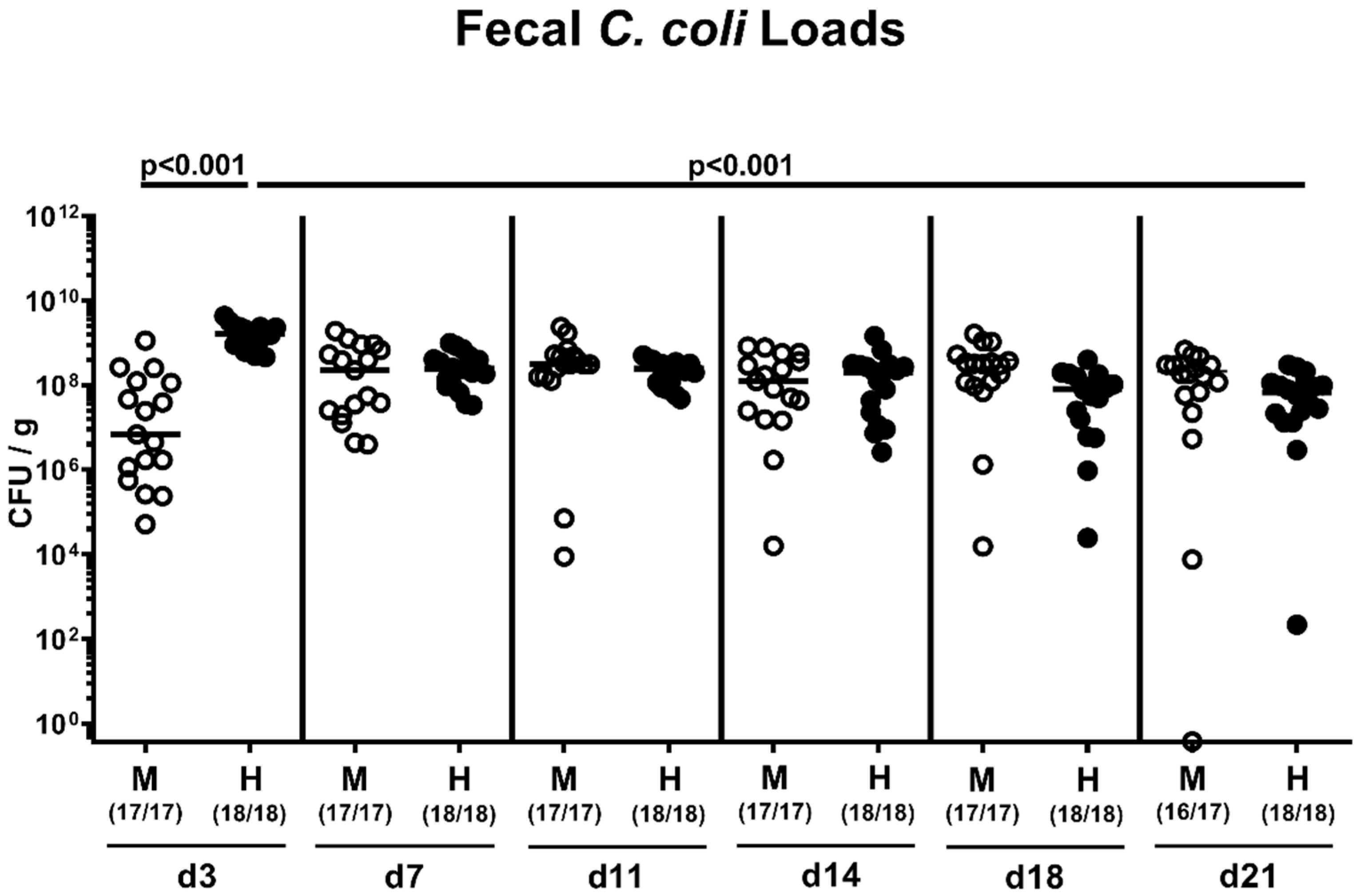
2.2. Fecal Pathogen Shedding after Oral C. coli Infection of Microbiota-Depleted IL-10−/− Mice that Had Been Subjected to Human or Murine Fecal Microbiota Transplantations
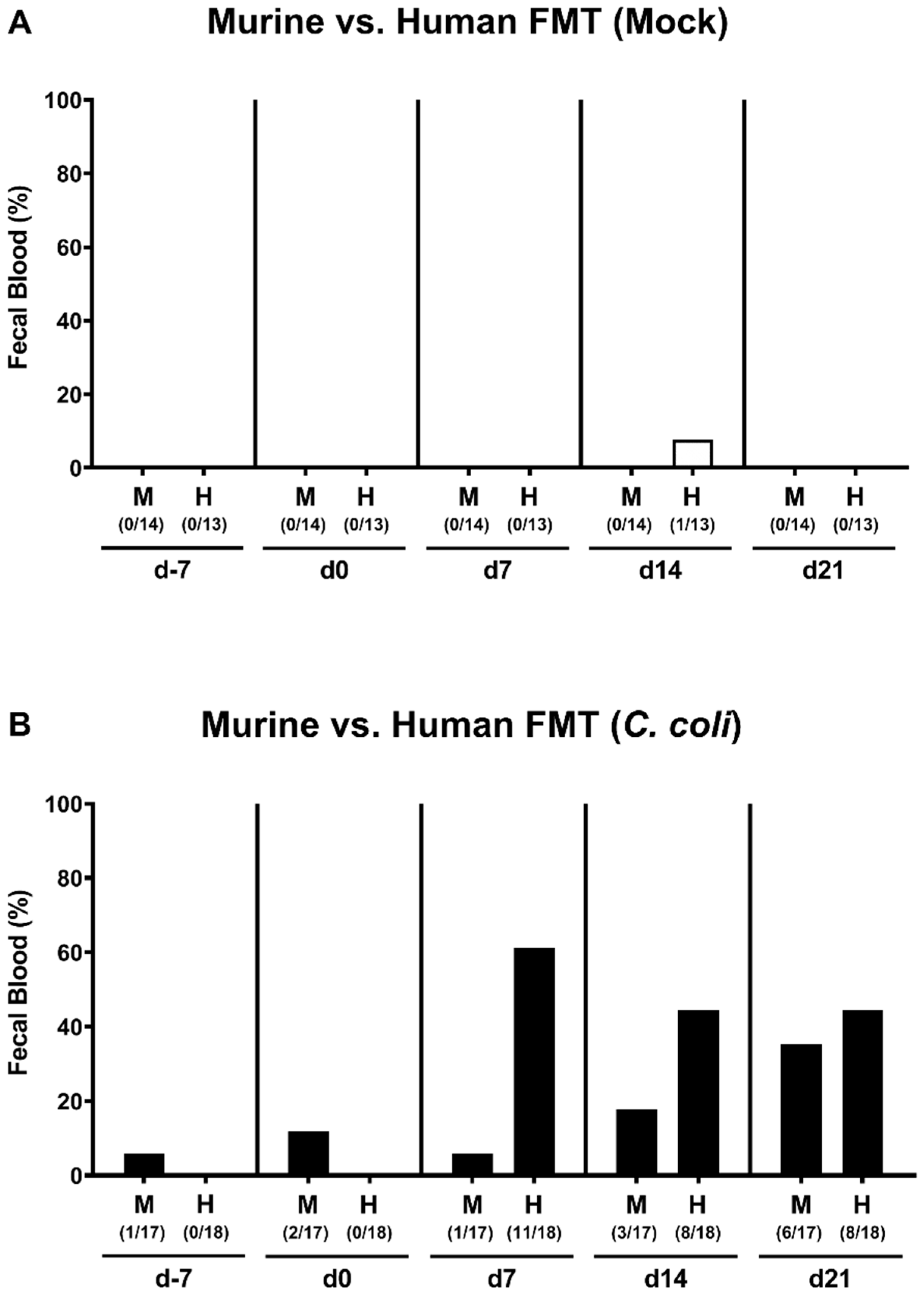
2.3. Kinetic Assessment of Clinical Conditions Following Peroral C. coli Infection of Microbiota-Depleted IL-10−/− Mice That Had Been Subjected to Human or Murine Fecal Microbiota Transplantations
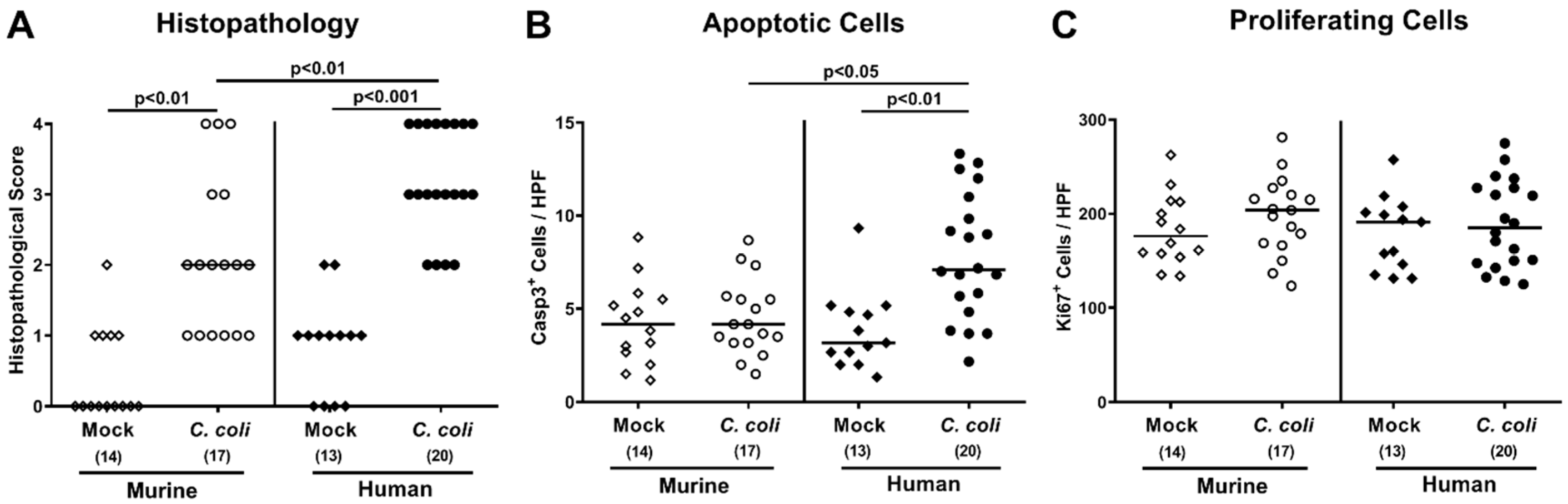
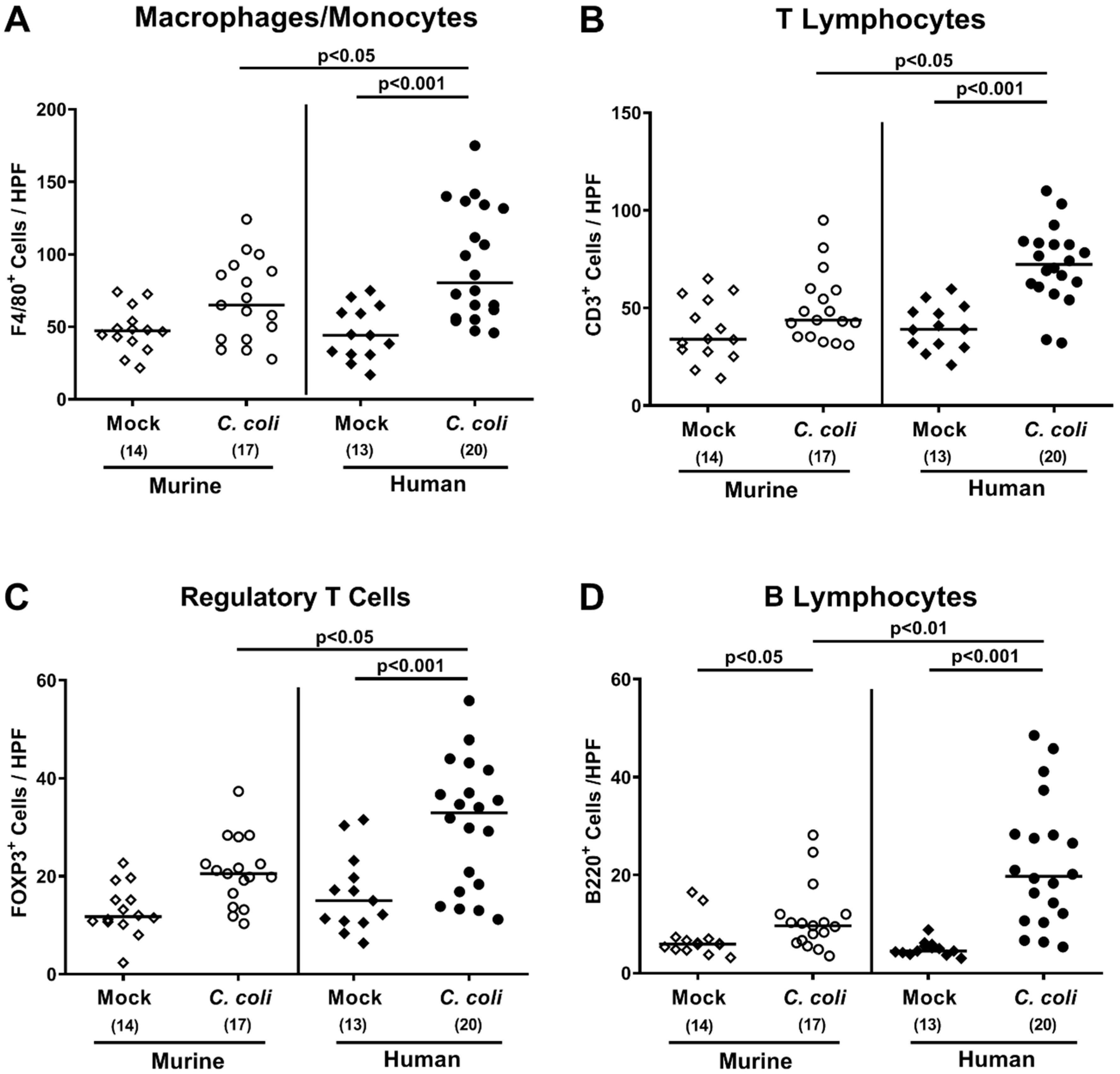
2.4. Intestinal Histopathological, Apoptotic, and Pro-Inflammatory Immune Responses upon Peroral C. coli Infection of Microbiota-Depleted IL-10−/− Mice That Had Been Subjected to Human or Murine Fecal Microbiota Transplantations
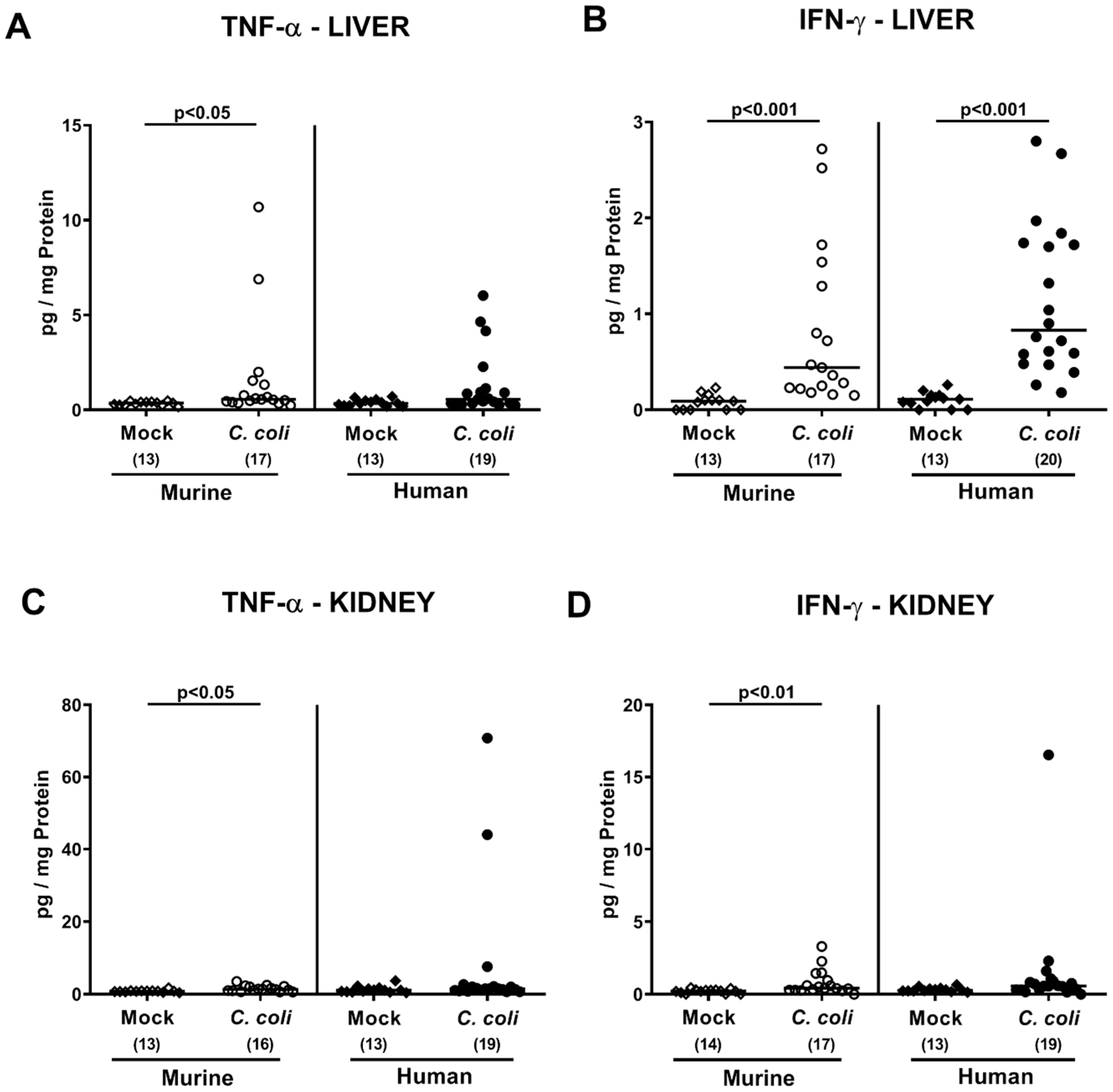
2.5. Extra-Intestinal Including Systemic Pro-Inflammatory Immune Responses upon Peroral C. coli Infection of Microbiota-Depleted IL-10−/− Mice That Had Been Subjected to Human or Murine Fecal Microbiota Transplantations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Generation of Microbiota-Depleted Mice
4.3. Fecal Microbiota Transplantations
4.4. C. coli Infection, Colonisation Properties, and Translocation
4.5. Analyses of the Intestinal Microbiota Composition
4.6. Clinical Conditions
4.7. Sampling Process
4.8. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
4.9. Immunohistochemistry
4.10. Pro-Inflammatory Mediator Measurements in Intestinal, Extra-Intestinal, and Systemic Compartments
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Campylobacter. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/campylobacter (accessed on 4 June 2020).
- Wagenaar, J.A.; French, N.P.; Havelaar, A.H. Preventing Campylobacter at the source: Why is it so difficult? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, K.T.; Davis, L.M.; Dirita, V.J. Campylobacter jejuni: Molecular biology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backert, S.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Cróinín, T.Ó.; Boehm, M.; Heimesaat, M.M. Chapter 1—Human campylobacteriosis. In Campylobacter; Klein, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kist, M.; Bereswill, S. Campylobacter jejuni. Contrib. Microbiol. 2001, 8, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, R.; Krogfelt, K.A.; Cawthraw, S.A.; van Pelt, W.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Owen, R.J. Host-pathogen interactions in Campylobacter infections: The host perspective. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, K. Campylobacters in water, sewage and the environment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 68S–79S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, K.; Jones, K. Cattle and sheep farms as reservoirs of Campylobacter. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrocks, S.M.; Anderson, R.C.; Nisbet, D.J.; Ricke, S.C. Incidence and ecology of Campylobacter jejuni and coli in animals. Anaerobe 2009, 15, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Leite, D.; Fernandes, M.; Mena, C.; Gibbs, P.A.; Teixeira, P. Campylobacter spp. as a foodborne pathogen: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alter, T.; Gaull, F.; Kasimir, S.; Gurtler, M.; Mielke, H.; Linnebur, M.; Fehlhaber, K. Prevalences and transmission routes of Campylobacter spp. strains within multiple pig farms. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 108, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shibiny, A.; Connerton, P.L.; Connerton, I.F. Enumeration and diversity of campylobacters and bacteriophages isolated during the rearing cycles of free-range and organic chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheppard, S.K.; Maiden, M.C. The evolution of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a018119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Castano-Rodriguez, N.; Mitchell, H.M.; Man, S.M. Global Epidemiology of Campylobacter Infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 687–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiebiger, U.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Dissecting the Interplay Between Intestinal Microbiota and Host Immunity in Health and Disease: Lessons Learned from Germfree and Gnotobiotic Animal Models. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 6, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bereswill, S.; Fischer, A.; Plickert, R.; Haag, L.M.; Otto, B.; Kuhl, A.A.; Dasti, J.I.; Zautner, A.E.; Munoz, M.; Loddenkemper, C.; et al. Novel murine infection models provide deep insights into the “menage a trois” of Campylobacter jejuni, microbiota and host innate immunity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, L.S.; Bell, J.A.; Wilson, D.L.; Murphy, A.J.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Rathinam, V.A.; Fierro, B.R.; Linz, J.E.; Young, V.B. C57BL/6 and congenic interleukin-10-deficient mice can serve as models of Campylobacter jejuni colonization and enteritis. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 1099–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippert, E.; Karrasch, T.; Sun, X.; Allard, B.; Herfarth, H.H.; Threadgill, D.; Jobin, C. Gnotobiotic IL-10; NF-kappaB mice develop rapid and severe colitis following Campylobacter jejuni infection. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Novel Clinical Campylobacter jejuni Infection Models Based on Sensitization of Mice to Lipooligosaccharide, a Major Bacterial Factor Triggering Innate Immune Responses in Human Campylobacteriosis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haag, L.M.; Fischer, A.; Otto, B.; Plickert, R.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Campylobacter jejuni induces acute enterocolitis in gnotobiotic IL-10-/- mice via Toll-like-receptor-2 and -4 signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Bereswill, S. Murine infection models for the investigation of Campylobacter jejuni—Host interactions and pathogenicity. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2015, 128, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Grundmann, U.; Alutis, M.E.; Fischer, A.; Bereswill, S. Absence of Nucleotide-Oligomerization-Domain-2 Is Associated with Less Distinct Disease in Campylobacter jejuni Infected Secondary Abiotic IL-10 Deficient Mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereswill, S.; Plickert, R.; Fischer, A.; Kühl, A.A.; Loddenkemper, C.; Batra, A.; Siegmund, B.; Göbel, U.B.; Heimesaat, M.M. What you eat is what you get: Novel Campylobacter models in the quadrangle relationship between nutrition, obesity, microbiota and susceptibility to infection. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2011, 1, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genger, C.; Kløve, S.; Mousavi, S.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. The conundrum of colonization resistance against Campylobacter reloaded: The gut microbota composition in conventional mice does not prevent from Campylobacter coli infection. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2020, 10, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erben, U.; Loddenkemper, C.; Doerfel, K.; Spieckermann, S.; Haller, D.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Zeitz, M.; Siegmund, B.; Kühl, A.A. A guide to histomorphological evaluation of intestinal inflammation in mouse models. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 4557–4576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Escher, U.; Giladi, E.; Dunay, I.R.; Bereswill, S.; Gozes, I.; Heimesaat, M.M. Anti-inflammatory Effects of the Octapeptide NAP in Human Microbiota-Associated Mice Suffering from Subacute Ileitis. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 8, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Mrazek, K.; Bereswill, S. Murine Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Alleviates Intestinal and Systemic Immune Responses in Campylobacter jejuni Infected Mice Harboring a Human Gut Microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Klitzing, E.; Ekmekciu, I.; Kühl, A.A.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Intestinal, extra-intestinal and systemic sequelae of Toxoplasma gondii induced acute ileitis in mice harboring a human gut microbiota. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Klitzing, E.; Ekmekciu, I.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Acute ileitis facilitates infection with multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in human microbiota-associated mice. Gut. Pathog. 2017, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Klitzing, E.; Ekmekciu, I.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Intestinal and systemic immune responses upon multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonization of mice harboring a human gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Mrazek, K.; Bereswill, S. Murine fecal microbiota transplantation lowers gastrointestinal pathogen loads and dampens pro-inflammatory immune responses in Campylobacter jejuni infected secondary abiotic mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereswill, S.; Escher, U.; Grunau, A.; Kühl, A.A.; Dunay, I.R.; Tamas, A.; Reglodi, D.; Heimesaat, M.M. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide-A neuropeptide as novel treatment option for subacute ileitis in mice harboring a human gut microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Escher, U.; Grunau, A.; Fiebiger, U.; Bereswill, S. Peroral Low-Dose Toxoplasma gondii Infection of Human Microbiota-Associated Mice—A Subacute Ileitis Model to Unravel Pathogen-Host Interactions. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 8, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Boelke, S.; Fischer, A.; Haag, L.M.; Loddenkemper, C.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S. Comprehensive postmortem analyses of intestinal microbiota changes and bacterial translocation in human flora associated mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- von Klitzing, E.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Induce Systemic Pro-Inflammatory Immune Responses in Colonized Mice. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 7, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Bereswill, S.; Fischer, A.; Fuchs, D.; Struck, D.; Niebergall, J.; Jahn, H.K.; Dunay, I.R.; Moter, A.; Gescher, D.M.; et al. Gram-negative bacteria aggravate murine small intestinal Th1-type immunopathology following oral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8785–8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Fischer, A.; Siegmund, B.; Kupz, A.; Niebergall, J.; Fuchs, D.; Jahn, H.K.; Freudenberg, M.; Loddenkemper, C.; Batra, A.; et al. Shift towards pro-inflammatory intestinal bacteria aggravates acute murine colitis via Toll-like receptors 2 and 4. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Fischer, A.; Jahn, H.K.; Niebergall, J.; Freudenberg, M.; Blaut, M.; Liesenfeld, O.; Schumann, R.R.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S. Exacerbation of murine ileitis by Toll-like receptor 4 mediated sensing of lipopolysaccharide from commensal Escherichia coli. Gut 2007, 56, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muñoz, M.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Danker, K.; Struck, D.; Lohmann, U.; Plickert, R.; Bereswill, S.; Fischer, A.; Dunay, I.R.; Wolk, K. Interleukin (IL)-23 mediates Toxoplasma gondii–induced immunopathology in the gut via matrixmetalloproteinase-2 and IL-22 but independent of IL-17. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 3047–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erridge, C.; Duncan, S.H.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. The induction of colitis and ileitis in mice is associated with marked increases in intestinal concentrations of stimulants of TLRs 2, 4, and 5. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Nogai, A.; Bereswill, S.; Plickert, R.; Fischer, A.; Loddenkemper, C.; Steinhoff, U.; Tchaptchet, S.; Thiel, E.; Freudenberg, M.A.; et al. MyD88/TLR9 mediated immunopathology and gut microbiota dynamics in a novel murine model of intestinal graft-versus-host disease. Gut 2010, 59, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereswill, S.; Munoz, M.; Fischer, A.; Plickert, R.; Haag, L.M.; Otto, B.; Kuhl, A.A.; Loddenkemper, C.; Gobel, U.B.; Heimesaat, M.M. Anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol, curcumin and simvastatin in acute small intestinal inflammation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haag, L.M.; Fischer, A.; Otto, B.; Plickert, R.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Intestinal microbiota shifts towards elevated commensal Escherichia coli loads abrogate colonization resistance against Campylobacter jejuni in mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kløve, S.; Genger, C.; Mousavi, S.; Weschka, D.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Toll-Like Receptor-4 Dependent Intestinal and Systemic Sequelae Following Peroral Campylobacter coli Infection of IL10 Deficient Mice Harboring a Human Gut Microbiota. Pathogens 2020, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekmekciu, I.; von Klitzing, E.; Fiebiger, U.; Escher, U.; Neumann, C.; Bacher, P.; Scheffold, A.; Kühl, A.A.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Immune responses to broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment and fecal microbiota transplantation in mice. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rausch, S.; Held, J.; Fischer, A.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Kühl, A.A.; Bereswill, S.; Hartmann, S. Small intestinal nematode infection of mice is associated with increased enterobacterial loads alongside the intestinal tract. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Alutis, M.; Grundmann, U.; Fischer, A.; Tegtmeyer, N.; Bohm, M.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Backert, S.; Bereswill, S. The role of serine protease HtrA in acute ulcerative enterocolitis and extra-intestinal immune responses during Campylobacter jejuni infection of gnotobiotic IL-10 deficient mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alutis, M.E.; Grundmann, U.; Fischer, A.; Hagen, U.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. The Role of Gelatinases in Campylobacter Jejuni Infection of Gnotobiotic Mice. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 5, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alutis, M.E.; Grundmann, U.; Hagen, U.; Fischer, A.; Kuhl, A.A.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Mediates Intestinal Immunopathogenesis in Campylobacter Jejuni-Infected Infant Mice. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 5, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Lugert, R.; Fischer, A.; Alutis, M.; Kuhl, A.A.; Zautner, A.E.; Tareen, A.M.; Gobel, U.B.; Bereswill, S. Impact of Campylobacter jejuni cj0268c knockout mutation on intestinal colonization, translocation, and induction of immunopathology in gnotobiotic IL-10 deficient mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heimesaat, M.M.; Genger, C.; Kløve, S.; Weschka, D.; Mousavi, S.; Bereswill, S. The Host-Specific Intestinal Microbiota Composition Impacts Campylobacter coli Infection in a Clinical Mouse Model of Campylobacteriosis. Pathogens 2020, 9, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100804
Heimesaat MM, Genger C, Kløve S, Weschka D, Mousavi S, Bereswill S. The Host-Specific Intestinal Microbiota Composition Impacts Campylobacter coli Infection in a Clinical Mouse Model of Campylobacteriosis. Pathogens. 2020; 9(10):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100804
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeimesaat, Markus M., Claudia Genger, Sigri Kløve, Dennis Weschka, Soraya Mousavi, and Stefan Bereswill. 2020. "The Host-Specific Intestinal Microbiota Composition Impacts Campylobacter coli Infection in a Clinical Mouse Model of Campylobacteriosis" Pathogens 9, no. 10: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100804
APA StyleHeimesaat, M. M., Genger, C., Kløve, S., Weschka, D., Mousavi, S., & Bereswill, S. (2020). The Host-Specific Intestinal Microbiota Composition Impacts Campylobacter coli Infection in a Clinical Mouse Model of Campylobacteriosis. Pathogens, 9(10), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9100804





