Abstract
The impact of emerging infectious diseases is increasingly recognised as a major threat to wildlife. Wild populations of the endangered Tasmanian devil, Sarcophilus harrisii, are experiencing devastating losses from a novel transmissible cancer, devil facial tumour disease (DFTD); however, despite the rapid decline of this species, there is currently no information on the presence of haemoprotozoan parasites. In the present study, 95 Tasmanian devil blood samples were collected from four populations in Tasmania, Australia, which underwent molecular screening to detect four major groups of haemoprotozoa: (i) trypanosomes, (ii) piroplasms, (iii) Hepatozoon, and (iv) haemosporidia. Sequence results revealed Trypanosoma infections in 32/95 individuals. Trypanosoma copemani was identified in 10 Tasmanian devils from three sites and a second Trypanosoma sp. was identified in 22 individuals that were grouped within the poorly described T. cyclops clade. A single blood sample was positive for Babesia sp., which most closely matched Babesia lohae. No other blood protozoan parasite DNA was detected. This study provides the first insight into haemoprotozoa from the Tasmanian devil and the first identification of Trypanosoma and Babesia in this carnivorous marsupial.
1. Introduction
Haemoprotozoan parasites are unicellular eukaryotic organisms with complex lifecycles that involve an invertebrate vector and often alternate in their tropism between the tissues and blood of their vertebrate hosts. Four major haemoprotozoan assemblages infect mammals [1]; (i) Trypanosomatids (Kinetoplastea), which are flagellated protists that are characterised by the presence of a unique organelle, the kinetoplast; (ii) haemogregarines (Adeleorina); (iii) haemosporidia (Haemosporidia); and, (iv) piroplasms (Piroplasmida). Broadly haemoprotozoans are considered either host specific (e.g., Theileria ornithorhynchi infecting the platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus) host [2]) or generalists (e.g., Trypanosoma cruzi, which infects a wide range of mammals [3]). However, the true diversity and epidemiology of most of these species remain unknown.
The Tasmanian devil, Sarcophilus harrisii, is the largest extant marsupial carnivore. Once present across mainland Australia (~3000 years ago), the distribution of wild populations of Tasmanian devils became restricted to the island of Tasmania [4], off the southern coast of the Australian mainland. Biogeographical events have influenced declines in the effective size of devil populations and their distribution, with consequential genetic bottlenecks resulting in low genetic diversity [4,5,6]. Since 1996, a transmissible cancer (devil tumour facial disease, DFTD hereafter) gradually spread across most of the distributional range of the species and caused local population declines of upwards of 80% [7,8]. The transmission of DFTD occurs through direct transfer of live tumour cells between individuals when devils bite each other during social interactions [9,10,11]. Survival in DFTD infected individuals is usually 6–12 months after clinical signs appear; the disease is lethal in almost 100% of cases [12]. As a consequence of transmission being driven by social interactions, DFTD is still present, even in largely depleted populations of hosts [7]. Therefore, any additional pressure(s) on the host health, such as co-infections with haemoparasites, could further threaten imperilled populations, yet, little is known regarding the devil’s parasite community [13].
To date, only four protozoan parasite groups have been identified from wild devil populations; Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia spp., Toxoplasma gondii, and Sarcocystis sp. A previous study identified sporulated sporocysts consistent with Sarcocystis (family: Sarcocystidae) species from the intestinal mucosa using microscopic examination [14]. In north-west Tasmania, T. gondii prevalence was higher in carnivorous marsupials, such as the Tasmanian devil, spotted-tail quoll (Dasyurus maculatus), and eastern quoll (D. viverrinus), as compared to sympatric prey marsupials like the brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula), Bennett’s wallaby (Notamacropus rufogriseus, syn. Macropus rufogriseus) and Tasmanian pademelon (Thylogale billardierii) [15]. Recently, Cryptosporidium and Giardia spp. were also identified from faecal samples of wild devils using molecular techniques [16].
Over the past two decades, the use of molecular techniques has significantly extended our understanding of haemoprotozoan parasites. As a result, it has revealed that Australian marsupials and monotremes can host a high diversity of haemoprotozoa species, most of which are unique to Australia [17,18,19,20]. The clinical effects of co-infections in wildlife are often difficult to evaluate. One well documented case is the investigation into a canine distemper virus epidemic in Serengeti lions (Panthera leo), which identified that joint infection by haemoprotozoa was a major contributing factor to fatal outcomes [21]. While there are limited studies on the clinical and pathological consequences of such interactions in native Australian wildlife, there is evidence that co-infection and co-morbidities can place species at an increased risk of disease when challenged with the infection of haemoprotozoa [22,23,24].
The trypanosomatids are obligatory parasites with a single flagellum and include several genera that are pathogenic to humans, animals, and plants [25,26]. Because of their medical importance, trypanosomatids have been studied more intensively with trypanosome and Leishmania parasites the causative agents of sleeping sickness (Trypanosoma brucei gambiense and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense), Chagas disease (Trypanosoma cruzi), and leishmaniases [26,27]. Broadly, Trypanosoma species can be divided into two groups based on their transmission route; the salivarian trypanosomes, which are transmitted via the saliva of the tsetse fly (Glossina spp.), and stercorarian trypanosomes, which are passed to their host via the faeces of the arthropod intermediate host [28]. The vectors of Australian trypanosomes are still largely unknown, with few studies investigating the presence of trypanosomes in invertebrates. Previous studies have implicated ticks (Ixodes spp.) [29,30] and tabanid flies [31] as potential vectors.
The present study aimed to screen blood samples from Tasmanian devils for the presence of haemoprotozoan parasites. To the authors’ knowledge, the present study provides the first survey of haemoprotozoa from Tasmanian devils.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Sampling
Animal use was approved by the University of Tasmania Animal Ethics Committee permit numbers A0015835 and A0016789) and the Department of Primary Industries, Parks, Water and Environment Animal Ethics Committee (permit numbers TFA19144 and TFA18028).
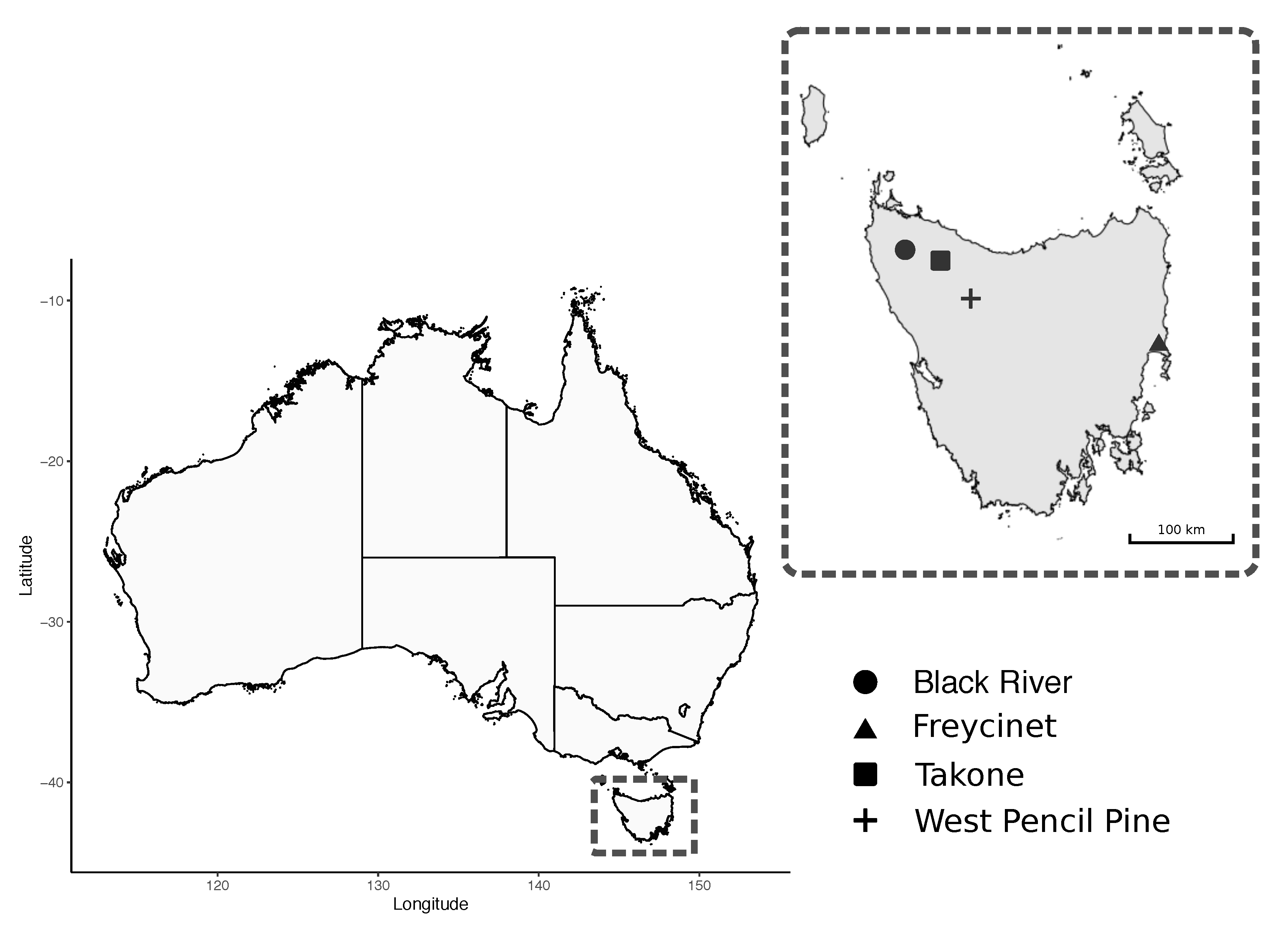
A total of 95 blood samples were collected from wild Tasmanian devils that were captured during the austral autumn (May 2018) from four sites across Tasmania: Black River, Takone, West Pencil Pine and Freycinet (Figure 1). The sampling effort at each site involved deployment of 40 PVC pipe traps during seven to 10 consecutive nights. Individual devils were identified via subcutaneously implanted microchips (AllFlex© ISO FDX-B).
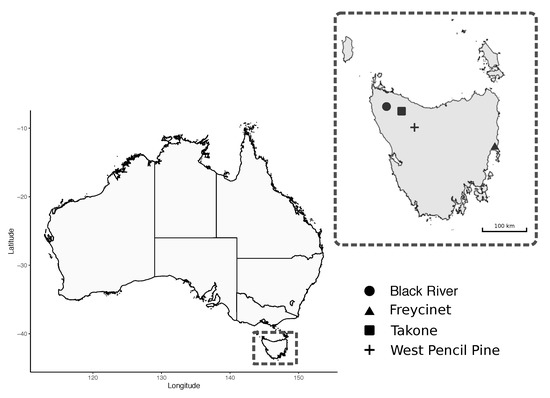
Figure 1.
Map of study sites for field collection of Tasmanian Devil (Sarcophilus harrisii) samples.
Blood was collected (between 0.3–1 mL) from either the jugular vein (Takone) or marginal ear vein (Black River, Freycinet and West Pencil Pine). The puncture site was disinfected with sterile alcohol swabs for at least 15 s prior to collection and blood was stored in ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) vacutainers. The samples were kept refrigerated at 4 and then shipped to Murdoch University, Western Australia where they were stored at −20 until analysis.
2.2. Molecular Screening
2.2.1. DNA Extraction
The total genomic DNA was extracted from 200 of blood using a MasterPure DNA purification kit (Epicentre® Biotechnologies, Madison, WI, USA) following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Where 200 of blood was not available, sterile DNA free phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was used to make samples up to 200 . Genomic DNA (gDNA) was eluted in 30 of TE buffer and stored at −20 . Extraction controls (EXBs), consisting of 200 sterile DNA free PBS, were randomly included in each extraction batch (N = 7).
2.2.2. PCR Assays
Molecular screening was carried out for haemoprotozoa on gDNA from blood samples (N = 95) and EXBs (N = 7). Reactions were carried out in 25 volumes containing 2 of gDNA or 1 of the primary product for nested and semi-nested PCR assays. Table 1 provides an overview of assays, including primer sequences.

Table 1.
List of primers used for screening of haemoprotozoa from Tasmanian Devils (Sarcophilus harrisii).
For the identification of trypanosomes (Trypanosoma and Leishmania spp.) samples were screened using a nested PCR assay targeting an ~959 bp product of the second half of the 18S ribosomal RNA (18S rRNA) locus. This assay amplifies most species of Trypanosoma [32] and it was also validated in the present study to amplify Leishmania spp. using control gDNA of Leishmania infantum from a canine bone marrow sample and Leishmania macropodum culture isolate. External primers SLF/S762R and internal primers S825F/SLIR were used as an initial screen and then sequenced as per details below. Samples that were representative of the different genotypes identified then underwent an additional secondary assay with a second set of internal primers S823/S662R to yield a near full length 18S rDNA sequence. Reactions were carried out in 25 volumes containing 0.4 of each primer and 12.5 GoTaq®Green master mix (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Thermal cycling conditions were as follows; initial cycle of 95 for 5 min, 50 for 2 min, 72 for 4 min, followed by 35 cycles of 95 for 30 s, 52 (primary) or 55 (secondary) for 30 s, 72 for 2 min. 20 s (primary) or 1 min. (secondary), and a final extension of 72 for 5 min. To obtain further phylogenetic information from the genotypes that were identified by 18S rRNA locus screening, samples underwent amplification of the glycosomal Glyceraldehyde Phosphate Dehydrogenase (gGAPDH) gene using a semi-nested PCR assay with external primers GAPDHF/GAPDHR and internal primers GAPDHF/Ga4 [32]. Reactions contained 1X buffer (KAPA Biosystems, Cape Town, South Africa), 2.0 mM (MgCl), 0.4 of each primer, 0.25 mM of each dNTP, and 0.5 U of Taq (KAPA Biosystems, Cape Town, South Africa). Thermal cycling conditions were as follows; initial cycle of 95 for 5 min, 50 for 2 min, 72 for 4 min, followed by 35 cycles of 95 for 30 s, 52 (primary) or 55 (secondary) for 30 s, 72 for 2 min. 20 s, and a final extension of 72 for 5 min.
Screening for piroplasms (Babesia and Theileria spp.) utilised a previously described nested PCR assay. Primers were used targeting an ~800 bp product of the 18S rRNA locus with external primers BT1F/BT1R and internal primers BT2F/BT2R [35]. The reactions contained 1× buffer (KAPA Biosystems, Cape Town, South Africa), 2.0 mM (MgCl), 0.4 of each primer, 0.25 mM of each dNTP, and 0.5 U of Taq (KAPA Biosystems, Cape Town, South Africa). Thermal cycling conditions were as follows; initial cycle of 95 for 2 min, 58 for 1 min, 72 for 2 min, followed by 35 cycles of 95 for 30 s, 62 for 20 s, 72 for 45 s, and a final extension of 72 for 7 min.
A genus specific assay for Hepatozoon targeting the 18S rRNA locus was used with primers HepF300/Hep900 in order to amplify an ~600 bp product [36]. Reactions contained 1× buffer (KAPA Biosystems, Cape Town, South Africa), 1.5 mM (MgCl), 0.4 of each primer, 0.25 mM of each dNTP, and 0.5 U of Taq (KAPA Biosystems, Cape Town, South Africa). Thermal cycling conditions were as follows; initial denaturation of 95 for 3 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 for 30 s, 60 for 30 s, 72 for 1 min, and a final extension of 72 for 10 min.
Screening for haemosporidia (Plasmodium spp.) utilised a previously described nested PCR assay [37]. Primers targeting an ~420 bp product of the cytochrome b (cytb) gene with external primers HAEMNF/HAEMNR2 and internal primers HAEMF/HAEMR2. Reactions contained 1× buffer (KAPA Biosystems, Cape Town, South Africa), 1.5 mM (MgCl), 0.4 of each primer, 0.25 mM of each dNTP, and 1.0 U of Taq (KAPA Biosystems, Cape Town, South Africa). The thermal cycling conditions were as follows; initial denaturation of 95 for 8 min, followed by 35 cycles of 95 for 30 s, 50 (primary) or 52 (secondary) for 30 s, 72 for 45 s, and a final extension of 72 for 10 min.
Suitable positive controls, extraction reagent blanks, and no-template PCR controls were included throughout the laboratory processes. Extractions, pre-PCR and post-PCR procedures were performed in laboratories physically separated from each other.
2.2.3. Gel Electrophoresis and Sanger Sequencing
Amplicons were electrophoresed on a 1% agarose gel stained with SYBR safe (Invitrogen, Waltman, MA, USA). Products of the correct size (see Table 1) were excised from the gel and purified while using the previously described methods [39]. Sanger sequencing was carried out in forward and reverse directions on all positive amplicons. Sequencing was performed at the Australian Genome Research Facility (Perth, Western Australia) on an Applied Biosystems 3730 using Big Dye Terminator chemistry version 3.1.
2.2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
The sequences were imported and trimmed in Geneious 10.2.6 (https://www.geneious.com) and then subjected to BLAST analysis using BLASTN 2.10.0+ [40] against nucleotide collection (nt) database [41] to identify the most similar species and genotypes. Reference sequences were retrieved from GenBank [42] (details available in Supplementary Table S1) and aligned with sequences obtained in the present study using MUSCLE [43]. Alignments of the 18S rDNA and the gGAPDH sequences were then used for phylogenetic purposes. Phylogenies were inferred while using the maximum likelihood (ML) method. The optimal evolutionary model was selected while using ModelFinder [44] based on bayesian information criterion. Phylogenetic analysis was performed in IQ-TREE v1.6.11 [45] and bootstrap support was calculated using the ultrafast (UFBoot2) method with 10,000 replicates [46].
Maximum likelihood phylogeny based on the 18S rRNA locus was performed using a 1505 bp alignment based on the transition (AC = CG, AT = GT with equal base frequencies) (TIM3e) substitution model [47], with invariable sites (I = 0.408) and a discrete gamma distribution (four categories) (G4 = 0.438) [48]. To include a wider range of neighbouring reference sequences, a second phylogenetic analysis was performed on the V7–8 hypervariable region of the 18S rRNA locus; this region is useful to differentiate between closely related trypanosome sequences [49]. A phylogeny was produced using a 559 bp alignment that was based on the Kimura Two-Parameter (K2P) substitution model [50] with discrete gamma distribution (four categories) (G4 = 0.227) [48]. A 767 bp alignment of the gGAPDH gene was used for phylogenetic reconstruction based on the Tamura-Nei (TN) substitution model [51], with empirical base frequencies (F), invariable sites (I = 0.387) and discrete gamma distribution (four categories) (G4 = 0.893) [48]. Genetic sequence similarity was calculated while using the Kimura Two-Parameter method [51].
Sequences that were generated in the present study have been submitted to GenBank nucleotide database under accession numbers MT883295–MT883326 (Trypanosoma 18S rDNA), MT514664–MT514666 (Trypanosoma GAPDH), and MW084364 (Babesia 18S rDNA).
2.3. Statisical Analysis
The overall prevalence of Trypanosoma species was compared between males and females while using two-tailed Fisher Exact test.
2.4. Microscopy of Blood Smears
Thin blood smears were prepared from animals that were sampled at Takone site only (three per individual), within 4 h of collection, and then air dried and fixed in methanol. Blood smears were then stained with modified Wright-Giemsa (Hematek®Stain Pak) using a Hema-Tek Slide Stainer (Ames Company Division, Miles Laboratories Pty Ltd., Victoria, Australia) and a coverslip was mounted using DPX neutral mounting medium (LabChem, Victoria, Australia). The smears were inspected by light microscopy (Olympus BX51) for the presence of haemoprotozoa at ×400 magnification and under oil immersion (×1000).
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Screening
Molecular screening identified 33.7% (32/95) of the blood samples were positive for Trypanosoma DNA. Sequence identity from BLAST results identified; T. copemani and T. cyclops-like in 10.5% (n = 10) and 23.2% (n = 22) of the individuals respectively (Table 2). Trypanosoma copemani was almost exclusively identified in males (90.0%, p = 0.0159), while T. cyclops-like genotypes were more commonly found in females (68.2%, p = 0.0432). All of the samples tested negative for presence of Leishmania, Hepatozoon, Plasmodium, and Theileria species.

Table 2.
Overview of Tasmanian devil sampling across survey sites showing number of individuals samples (n) and number of individuals positive for Trypanosoma species.
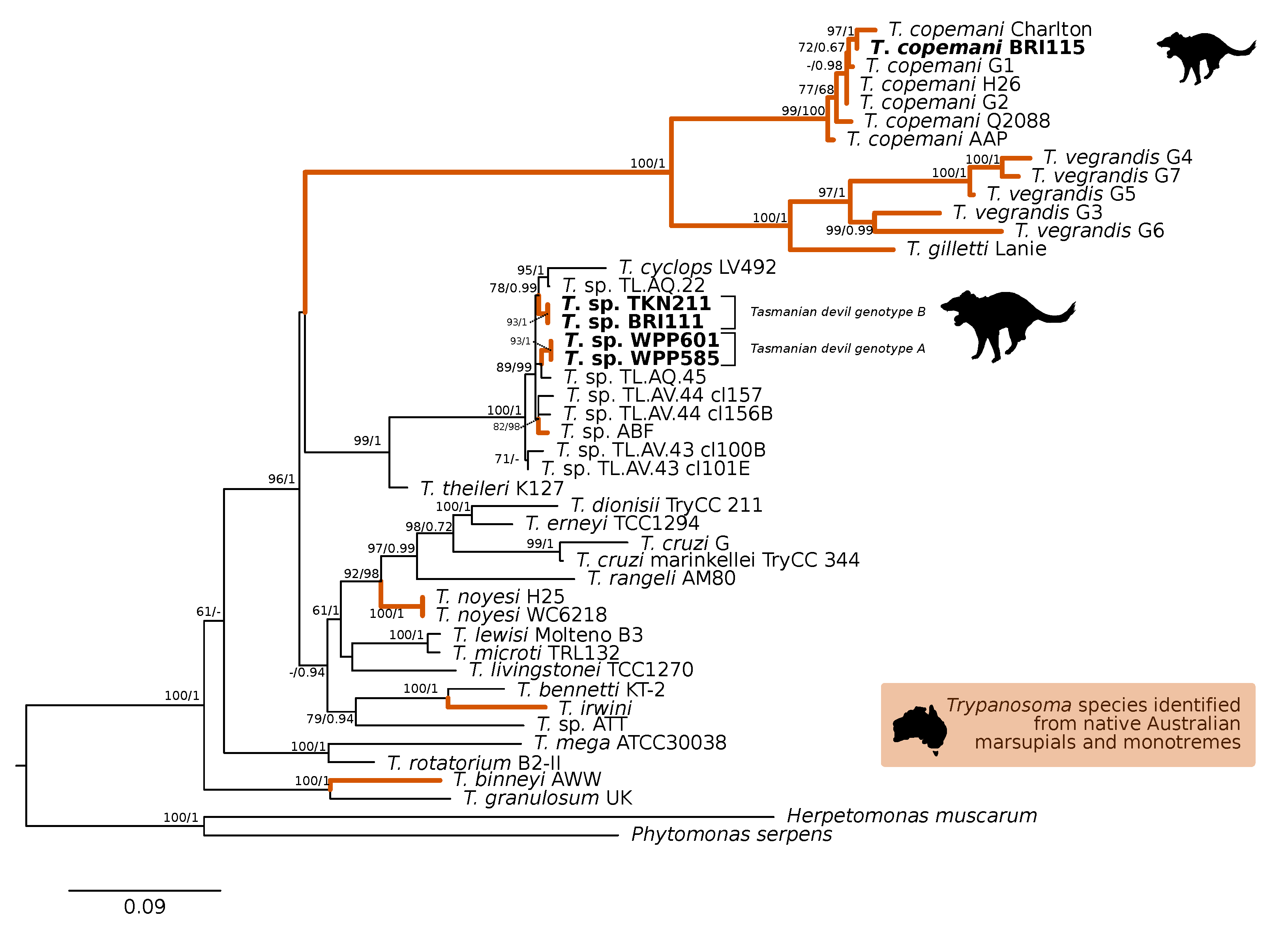
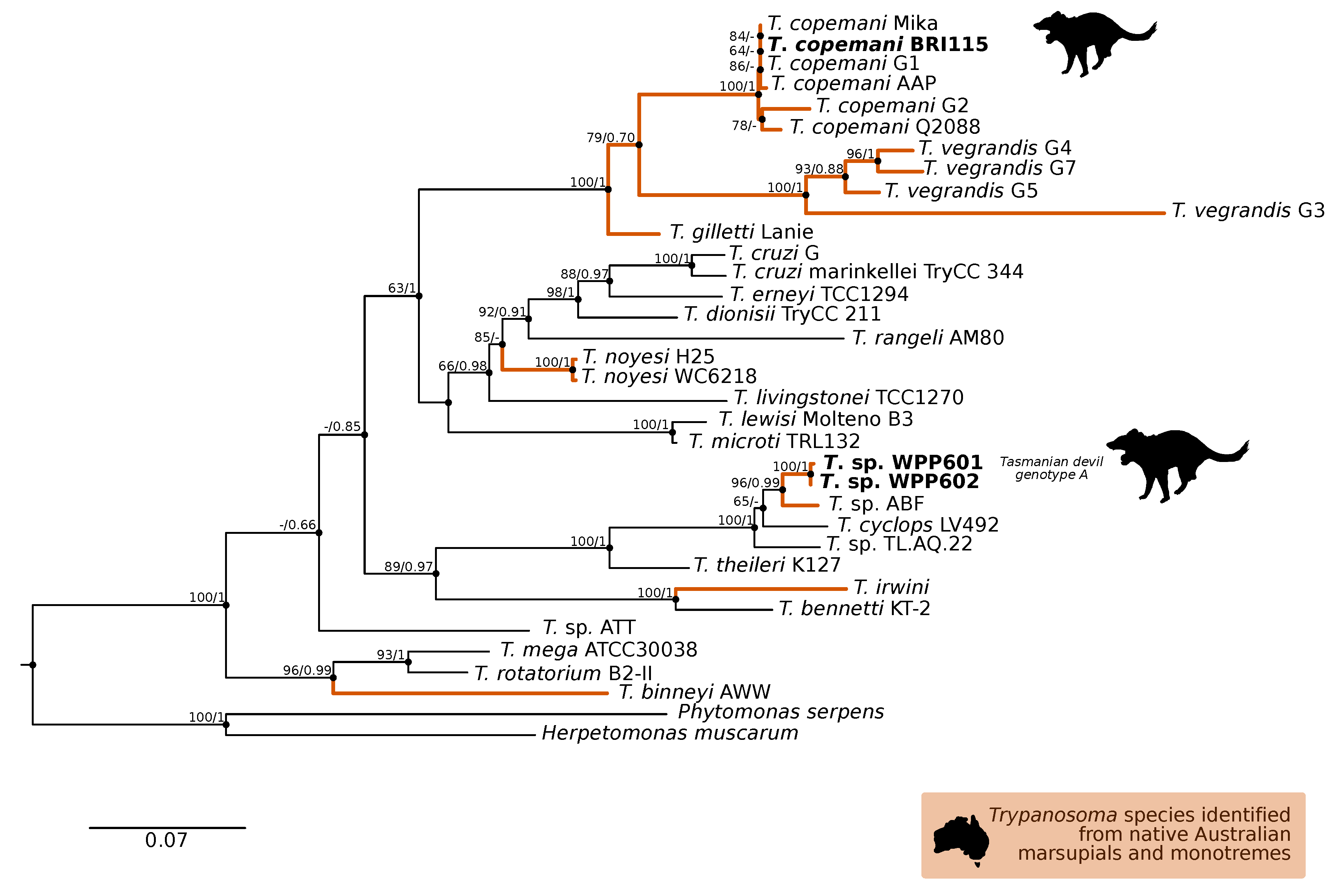
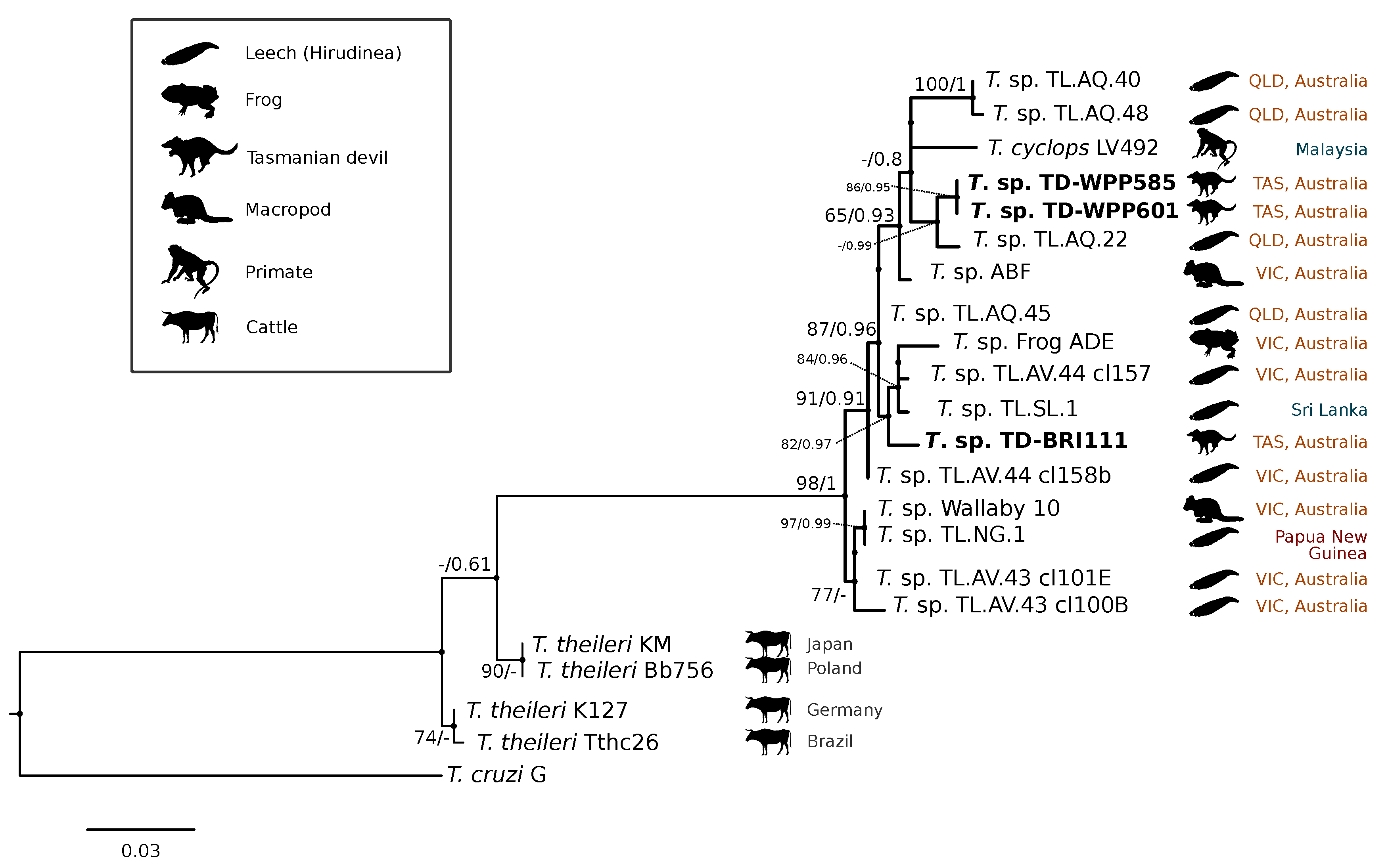
A comparison at the 18S V7-8 hypervariable region of the ten T. copemani sequences showed they were all >99% similar to each other and, as such, a representative sample (BRI115) was used for subsequent phylogeny. Analysis of long 18S alignment concluded that the BRI115 sample shared 99.1% similarity to T. copemani Charlton (GU966588) and 98.5% with T. copemani H26 (AJ009169) (Figure 2). At the gGAPDH locus BRI115 sample was identical to T. copemani Mika (GU966585), and 99.7% similar to T. copemani AAP (AJ620277) (Figure 3). There is no 18S rDNA sequence data for T. copemani Mika available. A comparison of T. copemani Charlton (GU966584) at the gGAPDH locus showed it was 99.9% similar to the BRI115 sample with one single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) (data not shown). At the 18S V7-8 hypervariable region two genotypes of the T. cyclops clade were identified, referred to as Tasmanian devil genotype A (n = 13) and genotype B (n = 9). Representatives of each genotype were used for phylogenetic reconstruction that was based on a longer alignment of 18S rDNA sequences (Figure 2). Analysis of near full length 18S rDNA alignment showed sequences were identical within each genotype (genotype A samples WPP585 and WPP601, and genotype B samples TKN211 and BRI111). The most similar 18S sequences to genotype A were Trypanosoma sp. TL.AQ.22 (AJ620574; 98.8% similar) and T. cyclops (AJ131958; 96.9% similar). Genotype B 18S sequences were most similar to Trypanosoma sp. ABF (AJ620564; 99.2% similar) and Trypanosoma sp. TL.AV.43 cl.101E (AJ620571; 99.1% similar). The gGAPDH sequences that were obtained from genotype A samples WPP601 and WPP602, were 99.9% similar to each other (Figure 3), with just one SNP. The most similar sequence was Trypanosoma sp. ABF (AJ620278), which was 97.2% and 97.4% similar to WPP601 and WPP602, respectively. The next most similar sequence was T. cyclops (FJ649493), which was 95.7% and 95.8% similar to WPP601 and WPP602, respectively. Unfortunately, GAPDH sequences from genotype B were not successfully amplified. Phylogenetic reconstruction utilising the V7-8 hypervariable region of the 18S rRNA locus showed support for a monophyletic T. cyclops clade (Figure 4). Sequences from the present study grouped with genotypes detected from Malaysia, Sri Lanka and Australia (Queensland and Victoria) with the clear distinction of two different genotypes of T. cyclops from Tasmanian devils (Supplementary Table S2).
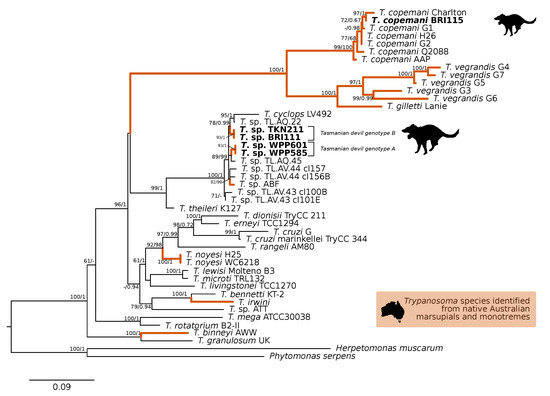
Figure 2.
Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic reconstruction of the Trypanosoma genus based on a 1505 bp alignment of the 18S rRNA locus using TIM3e + I + G4 substitution model. The node values correspond to bootstrap support/aBayes support, values less than 60 are hidden. Number of substitutions per nucleotide position is represented by the scale bar. Lineages that have been described from native Australian marsupials are denoted by orange lines. Sequences that were generated in the present study in bold. GenBank accession numbers for sequences are available in Supplementary Table S1.
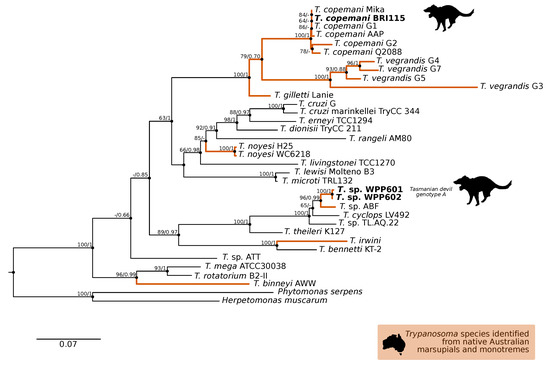
Figure 3.
Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic reconstruction of the Trypanosoma genus based on a 767 bp alignment of glycosomal Glyceraldehyde Phosphate Dehydrogenase (gGAPDH) while using TN93 + F + I + G4 substitution model. The node values correspond to bootstrap support/aBayes support, values less than 60 are hidden. Number of substitutions per nucleotide position is represented by the scale bar. Lineages that have been described from native Australian marsupials are denoted by orange lines. Sequences generated in the present study are in bold. GenBank accession numbers for sequences are available in Supplementary Table S1.
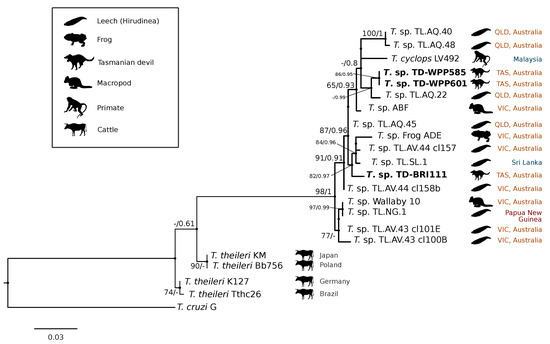
Figure 4.
Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic reconstruction of sequences from the Trypanosoma cyclops clade based on a 559 bp alignment of the 18S rRNA locus across the V7-8 hypervariable region while using K2P + G4 substitution model. Node values correspond to bootstrap support/aBayes support, values less than 60 are hidden. The number of substitutions per nucleotide position is represented by the scale bar. Australian states are abbreviated to QLD (Queensland), TAS (Tasmania), and VIC (Victoria). GenBank accession numbers for sequences are available in Supplementary Table S1.
A single sample (BRI115) obtained from Black River site was positive for a Babesia sp. and this individual was also positive for T. copemani infection. Analysis of an 800 bp fragment of the 18S rRNA locus revealed it was similar to Babesia sp. identified from Ixodes tasmani in Queensland (MG251436; 96.0% similarity) and Babesia lohae from Ixodes holocyclus in Queensland (MG593272; 95.5% similarity).
3.2. Microscopy
Microscopy of blood smears from Takone site did not yield any positive detection of haemoparasites.
4. Discussion
The present study represents the first survey of haemoprotozoa from wild populations of the endangered Tasmanian devil. Our findings of Trypanosoma infections across all four sites suggests that this infection is widespread and potentially endemic within Tasmanian devil populations. This wide distribution of Trypanosoma across populations contrasts with the absence of Leishmania, Theileria, Hepatozoon, or Plasmodium species, and the low detection of Babesia, which was only detected in a single individual.
The extension of the host range of T. copemani is notable and it supports recent research identifying this parasite in a wide range of marsupial hosts from across Australia. To date, T. copemani has been identified in all Australian states and territories, except the Northern Territory and South Australia. The identification of this parasite in Tasmanian devils is potentially significant from a health perspective as previous reports have associated it with pathological changes in the woylie (Bettongia penicillata) [22,23] and in koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus) with co-morbidities [24]. With this report, there are now at least ten Australian vertebrate host records for T. copemani; therefore, this Trypanosoma species appears to be a marsupial generalist and capable of infecting a diverse range of mammals. Further studies for mapping the complete distribution and host range of T. copemani will help to provide insights into the co-evolution of this native trypanosome in its marsupial hosts.
The identification of genotypes from the Trypanosoma cyclops clade was unexpected. Trypanosoma cyclops was described from wild caught southern pig-tail macaques (Macaca nemestrina) in jungle areas of West Malaysia [52] and Hamilton et al. [53] identified novel genotypes of this clade from Australia, Papua New Guinea, and Sri Lanka. However, since its identification, there have been very few published reports of T. cyclops. Phylogeny within the T. cyclops clade was not well resolved, as demonstrated by the polytomy in Figure 4. The identification of two distinct genotypes in devils that do not form a monophyletic group and show different levels of relatedness to sequences overseas highlights the uncovered diversity within this clade. The closest named species to T. cyclops is Trypanosoma (Megatrypanum) theileri, which has a cosmopolitan distribution and predominantly infects cattle. The most important vector of T. theileri is thought to be tabanid flies (Tabanidae) [54,55]. While this trypanosome is generally considered non-pathogenic, chronic infection has been associated with the development of secondary diseases in cattle [56].
The gGAPDH gene has been shown to be a more suitable marker than the 18S rRNA locus for determining the phylogeny within the Trypanosoma genus [34]. A comparative analysis of T. copemani shows the intra-specific sequence similarity within the clade is 97.0–100% and inter-specific similarity to the nearest named species, T. gilletti, is 91.3–92.3%. Intra-specific sequence similarity within the T. cyclops clade was 94.8–99.9%, while the inter-specific sequence similarity to nearest named species, T. theileri, is 90.4%. Therefore, there is sufficient support that the sequences generated for devils can be attributed to T. cyclops. The differentiation of genotypes within this clade are best identified by analysis of the V7-8 hypervariable region of the 18S rRNA locus (Figure 4, Supplementary Table S2). This study further supports that T. cyclops is more closely related to sequences obtained from Australia, Papua New Guinea, and Sri Lanka than it is to T. theileri. [53]. There is no geographical or host distinction between the different genotypes, further supporting the taxonomy as a single species, as shown in the phylogeny within the T. cyclops clade (Figure 4). Research on functional traits, including growth dynamics in culture coupled with morphological analysis, is needed to better understand the taxonomy of this clade. The geographical and host extensions reported here will be useful for the future work that aimed at understanding the evolutionary history of the T. cyclops and T. theileri clades and the Trypanosoma genus more broadly [57].
The description of a T. cyclops-like species in this work expands the number of Trypanosoma species in Tasmanian mammals to four. The platypus-specific T. binneyi has been observed from blood samples and subsequently described phylogenetically [29,58,59] with suggestions that leeches are the likely vector [59]. Trypanosomes have also been identified in populations of the eastern barred bandicoot (Perameles gunnii) and southern brown bandicoot (Isoodon obesulus) [60]; however, due to well-described limitations of morphological identification [61], species-level identification has not been achieved. Additionally, T. copemani was identified for the first time in Tasmania in 2020 from wild populations of the eastern quoll (Dasyurus viverrinus) [62]. The current study now brings the number of known trypanosome hosts in Tasmania to five, with the addition of Tasmanian devils, and the confirmation of a new species from the T. cyclops clade. It is interesting to note that, while previous studies have only described one species of Trypanosoma in the sampled hosts from Tasmania, in the current study we have described at least two species circulating in devils. The higher diversity of Trypanosoma species found in devils might be a consequence of our larger sample size or spatial coverage in comparison to previous studies.
Despite the molecular identification of Trypanosoma infection in devils from Takone, no trypomastigotes were observed in corresponding blood smears. This finding is consistent with other studies that have found molecular tools are more sensitive than microscopy for trypanosome detection [63,64]. The absence of patent parasitaemia (i.e. no flagellates observed in fresh blood smears) could be the result of low-level infections; however, it may also indicate that devils are not a competent host of the Trypanosoma species [65].
The phylogenetic position of the T. cyclops clade within the stercorarian group means that its potential vector(s) could be a range of arthropod(s) with transmission occurring via contact with vector faeces. While it has been hypothesised that carnivory is important in the maintenance of trypanosomes, experimental studies do not support this [66] and, instead, suggested that increased infection is attributed to insectivores who consume infected arthropod vectors [67]. However, it is interesting that, although members of this clade have been identified from leeches and frogs [53], their phylogenetic position is distinct from other aquatic and leech-associated Trypanosoma species [34,59,68,69]. The range extensions of both T. copemani and T. cyclops clades that were recorded in the present study provide additional data to aid vector identification. The large geographical range of both these Trypanosoma species suggests that any vector(s) should be equally ubiquitous and capable of biting or coming into close contact with a wide range of vertebrate hosts.
In the present study, we validated that a previously published Trypanosoma PCR assay [32] is also capable of detecting/amplifying Leishmania DNA. Two controls of genetically diverse species of Leishmania, L. infantum and L. macropodum, [70] were used. In the context of this study, we determined that generic trypanosome primers are able to amplify L. macropodum, which was identified as a cause of cutaneous leishmaniasis in kangaroos [71]. The preferred diagnostic sample for the detection of Leishmania is generally bone marrow aspirate or tissue samples; however, previous studies have recorded detection via blood samples [72,73]. Obtaining bone marrow and internal tissue samples from free ranging wildlife is not practical or ethical, especially where populations are experiencing significant declines. While the present study reported the absence of Leishmania via PCR of blood samples, it is not possible to discount occult infection and future studies utilising additional sample types would be recommended. Although co-infections of Leishmania and Trypanosoma cannot be completely ruled out in the individuals tested here, the absence of Leishmania DNA is consistent with previous studies that have utilised the same assay on other Australian mammals [17,18,74]. Therefore, reports of Australia’s only endemic Leishmania species remain confined to kangaroos and biting midges (Ceratopogonidae) in the Northern Territory [71,75,76].
An unexpected outcome was the low detection of Babesia species and lack of detection of Theileria and Hepatozoon species. Recent molecular studies in Australian wildlife have demonstrated a range of unique endemic piroplasms, with reports of up to 80–90% prevalence in some marsupial host populations [2,19,77]. Piroplasms and Hepatozoon spp. are transmitted by ticks and, therefore, dependent on the density and interactions between host and vector(s) to continue their lifecycle. Recent investigations have revealed the presence of numerous novel Babesia, Theileria, and Hepatozoon species in native Australian ticks [78,79,80]. With respect to the single identification of Babesia at the Black River site, the genetic relationship shows that it is most closely related to Babesia lohae sequences identified in Ixodes holocyclus and Ixodes tasmani ticks from the east coast of Queensland [78,79]. The low prevalence of Babesia might be attributed to the seasonality of tick infestations, as has been described in the relationship between I. tasmani ticks and brushtail possums hosts [81]. Future longitudinal sampling, including multiple seasons, are valuable to better understanding the phylogeny and epidemiology of this Babesia species circulating in devil populations.
In Tasmania, piroplasms and Hepatozoon species have been identified from three marsupial species and, more recently, from ticks (Ixodes spp.). A Hepatozoon has been identified in eastern barred bandicoots (Perameles gunnii) [82] by morphological examination of blood smears and the eastern quoll (Dasyurus viverrinus) through molecular tools [62]. Theileria species have been identified from eastern bettongs (Bettongia gaimardi) [83] and eastern quolls [62]. A molecular survey of ticks (I. tasmani) from Tasmanian devils demonstrated that 34.1% (15/44) of sample pools were positive for Hepatozoon sp. [84]. More recently, novel species of Theileria and Hepatozoon were identified from I. tasmani collected in Tasmania [78,79]. Given the high prevalence of I. tasmani parasitising sampled Tasmanian devils (Ruiz-Aravena pers. comms.), the low prevalence of piroplasms and Hepatozoon species is, therefore, unexpected. This raises important questions about the sylvatic lifecycle and reservoir hosts of these piroplasm and Hepatozoon species, suggesting potential and contrasting explanations: (i) Tasmanian devils are not competent reservoir hosts or (ii) they are natural hosts which are able to mount a sufficient immune response against the infection. In both cases, parasitaemia might be low or absent. Additional explanations could include (iii) infections by haemoprotozoa are acute and fatal to Tasmanian devils; however, the absence of Theileria and Hepatozoon in DFTD-free individuals makes this hypothesis less likely; or, (iv) the detection of haemoprotozoa in ticks is an opportunistic/accidental finding and they are not competent vectors of these organisms. Additional sampling from DFTD-free populations and capturing seasonal variation will be important for assessing the prevalence and susceptibility of Tasmanian devils to these haemoprotozoans.
The inclusion of morphological data obtained from blood smears and the application of additional molecular tools, such as next-generation sequencing to identify co-infections [85] and genome level information [86], are vital for further work. The collection of additional tissue samples may also prove to be useful in developing diagnostic tools, as well as better understanding the lifecycle of haemoprotozoa in the host. For example, bone marrow, skeletal muscle, tongue, brain, and liver samples have been tested positive for Trypanosoma DNA, while blood samples (including blood smears) were negative [87]. While there is a body of work demonstrating that Australian mammals are hosts to a range of endemic species of Trypanosoma, Leishmania, Babesia, Theileria, and Hepatozoon [17,18,19,31], the clinical impact of these haemoprotozoa is largely unknown. This is particularly important in the context of endangered species, such as the Tasmanian devil.
The results that are presented here highlight the need for additional studies on the haemoprotozoa and broader parasite community of Tasmanian devils. It is vital that the complete biology of this species be understood in order to provide meaningful information for management and conservation strategies. Conservation strategies, including translocation, captive breeding, and establishment of insurance populations, are management strategies that have been implemented in the case of Tasmanian devils. Parasite communities are an important consideration in species recovery, highlighting the need to further study host-parasite relationships [88]. For example, while the translocation of animals could facilitate introduction of parasites into new host populations, the same translocation could dilute adaptations of the receiving populations to the local parasites. This last case is particularly relevant when the local individuals in supplemented populations are outnumbered by the translocated individuals. Immediate future work is now needed in order to document the prevalence and diversity of haemoprotozoa in devils with a focus towards understanding the clinical impacts of infection and importantly impact of co-infection with DFTD.
5. Conclusions
Here, we have provided the first insights into haemoprotozoa infecting the endangered Tasmanian devil. Further research is urgently needed in order to document the full haemoprotozoan diversity in the Tasmanian devil, with a focus towards understanding the clinical significance of these infections and co-infections with DFTD. The identification of T. copemani and novel members of the T. cyclops clade provide further insights into the co-evolution of trypanosomes in marsupials, showing that Australian native fauna harbour genetically unique parasitic species. Finally, the lack of detection of major haemoprotozoa genera; Hepatozoon, Leishmania, Plasmodium, and Theileria in our study opens questions regarding the overall status of these parasites in the island ecosystem of Tasmania and whether their absence might reflect specific host-parasite interactions.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0817/9/11/873/s1. Supplementary Table S1. Trypanosoma sequences used in phylogenetic analysis in the present study. Supplementary Table S2. Pairwise genetic similarity matrix of the Trypanosoma cyclops clade at the 18S rRNA locus. Analysis conducted over at 559 bp alignment of the V7-8 hypervariable using the Kimura Two-Parameter (K2P) method.
Author Contributions
S.L.E. Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing—original draft, Funding acquisition M.R.-A. Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, methodology, Resources, Investigation, Writing—review & editing. J.M.A. Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing—review and editing. X.B. Investigation, Methodology, Writing—review & editing. D.G.H. Data curation, Investigation, Writing—review and editing. S.C. Data curation, Investigation, Writing—review and editing. R.K.H. Conceptualization, Resources, Writing—review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. U.M.R. Conceptualization, Resources, Writing—review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition. P.J.I. Conceptualization, Resources, Writing—review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. M.E.J. Conceptualization, Resources, Writing—review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. C.L.O. Conceptualization, Resources, Writing—review & editing, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was part-funded by the Australian Research Council (LP160100200), Bayer HealthCare (Germany) and Bayer Australia. S.L.E. was supported by an Australian Government Research Training Program (RTP) Scholarship. This project was also part supported by The Holsworth Wildlife Research Endowment & The Ecological Society of Australia (awarded to S.C. and S.L.E). Fieldwork and data collection were funded by the US National Institute of Health (R01-GM126563-01), the Save the Tasmanian Devil Appeal of the University of Tasmania Foundation (Eric Guiler Grant Scheme) and the Australian Research Council (DE170101116).
Acknowledgments
We thank Sarah Munns for extraction of DNA and Chris Peacock (The University of Western Australia) for provision of Leishmania macropodum control. We acknowledge the generous support of the large number of volunteers who assisted with fieldwork and data collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| 18S rDNA | 18S ribosomal DNA |
| DFTD | Devil tumour facial disease |
| gDNA | genomic DNA |
| gGAPDH | glycosomal glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase gene |
| SNP | single nucleotide polymorphism |
References
- O’Donoghue, P. Haemoprotozoa: Making biological sense of molecular phylogenies. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2017, 6, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paparini, A.; Macgregor, J.; Ryan, U.M.; Irwin, P.J. First molecular characterization of Theileria ornithorhynchi Mackerras, 1959: Yet another challenge to the systematics of the piroplasms. Protist 2015, 166, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, L.; Dietrich, M.; Markotter, W.; Fasel, N.; Monadjem, A.; López-Baucells, A.; Scaravelli, D.; Théou, P.; Pigeault, R.; Ruedi, M.; et al. Out of africa: The origins of the protozoan blood parasites of the Trypanosoma cruzi clade found in bats from Africa. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 145, 106705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüniche-Olsen, A.; Jones, M.E.; Burridge, C.P.; Murchison, E.P.; Holland, B.R.; Austin, J.J. Ancient DNA tracks the mainland extinction and island survival of the Tasmanian devil. J. Biogeogr. 2018, 45, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.E.; Paetkau, D.; Geffen, E.; Moritz, C. Genetic diversity and population structure of Tasmanian devils, the largest marsupial carnivore. Mol. Ecol. 2004, 13, 2197–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.H.; Margres, M.J.; Stahlke, A.R.; Hendricks, S.; Lewallen, K.; Hamede, R.K.; Ruiz-Aravena, M.; Ryder, O.; McCallum, H.I.; Jones, M.E.; et al. Contemporary demographic reconstruction methods are robust to genome assembly quality: A case study in Tasmanian devils. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 2906–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, H.; Jones, M.; Hawkins, C.; Hamede, R.; Lachish, S.; Sinn, D.L.; Beeton, N.; Lazenby, B. Transmission dynamics of Tasmanian devil facial tumor disease may lead to disease-induced extinction. Ecology 2009, 90, 3379–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazenby, B.T.; Tobler, M.W.; Brown, W.E.; Hawkins, C.E.; Hocking, G.J.; Hume, F.; Huxtable, S.; Iles, P.; Jones, M.E.; Lawrence, C.; et al. Density trends and demographic signals uncover the long-term impact of transmissible cancer in Tasmanian devils. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearse, A.M.; Swift, K. Allograft theory: Transmission of devil facial-tumour disease. Nature 2006, 439, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamede, R.K.; McCallum, H.; Jones, M. Biting injuries and transmission of tasmanian devil facial tumour disease. J. Anim. Ecol. 2013, 82, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, D.G.; Jones, M.E.; Cameron, E.Z.; McCallum, H.; Storfer, A.; Hohenlohe, P.A.; Hamede, R.K. Rate of intersexual interactions affects injury likelihood in Tasmanian devil contact networks. Behav. Ecol. 2019, 30, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, R.J.; Woods, G.M.; Kreiss, A. Devil facial tumor disease. Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wait, L.F.; Peck, S.; Fox, S.; Power, M.L. A review of parasites in the Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii). Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, B.L.; Mason, R.W.; Hartley, W.J.; Presidente, P.J.A.; Obendorf, D. Sarcocystis and related organisms in Australian wildife: I. Survey findings in mammals. J. Wildl. Dis. 1978, 14, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollings, T.; Jones, M.; Mooney, N.; McCallum, H. Wildlife disease ecology in changing landscapes: Mesopredator release and toxoplasmosis. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wait, L.F.; Fox, S.; Peck, S.; Power, M.L. Molecular characterization of (Cryptosporidum) and (Giardia) from the Tasmanian Devil (Sarcophilus harrisii). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austen, J.M.; Reid, S.A.; Robinson, D.R.; Friend, J.A.; Ditcham, W.G.; Irwin, P.J.; Ryan, U. Investigation of the morphological diversity of the potentially zoonotic (Trypanosoma copemani) in quokkas and Gilbert’s potoroos. Parasitology 2015, 142, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.D.; Austen, J.; Portas, T.J.; Friend, J.A.; Ahlstrom, L.A.; Oskam, C.L.; Ryan, U.M.; Irwin, P.J. Sequence analyses at mitochondrial and nuclear loci reveal a novel Theileria sp. and aid in the phylogenetic resolution of piroplasms from Australian marsupials and ticks. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northover, A.S.; Godfrey, S.S.; Keatley, S.; Lymbery, A.J.; Wayne, A.F.; Cooper, C.; Pallant, L.; Morris, K.; Thompson, R.C.A. Increased Trypanosoma spp. richness and prevalence of haemoparasite co-infection following translocation. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.K.; Thompson, R.A. Trypanosomes of Australian mammals: Knowledge gaps regarding transmission and biosecurity. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, L.; Terio, K.A.; Kock, R.; Mlengeya, T.; Roelke, M.E.; Dubovi, E.; Summers, B.; Sinclair, A.R.E.; Packer, C. Climate extremes promote fatal co-infections during canine distemper epidemics in African lions. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botero, A.; Thompson, C.K.; Peacock, C.S.; Clode, P.L.; Nicholls, P.K.; Wayne, A.F.; Lymbery, A.J.; Thompson, R.C. Trypanosomes genetic diversity, polyparasitism and the population decline of the critically endangered Australian marsupial, the brush tailed bettong or woylie (Bettongia penicillata). Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2013, 2, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.K.; Wayne, A.F.; Godfrey, S.S.; Thompson, R.C.A. Temporal and spatial dynamics of trypanosomes infecting the brush-tailed bettong (Bettongia penicillata): A cautionary note of disease-induced population decline. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, L.M.; Gillett, A.; Hanger, J.; Reid, S.A.; Ryan, U.M. The potential impact of native Australian trypanosome infections on the health of koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus). Parasitology 2011, 138, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslov, D.A.; Opperdoes, F.R.; Kostygov, A.Y.; Hashimi, H.; Lukeš, J.; Yurchenko, V. Recent advances in trypanosomatid research: Genome organization, expression, metabolism, taxonomy and evolution. Parasitology 2019, 146, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Avila-Levy, C.M.; Boucinha, C.; Kostygov, A.; Santos, H.L.C.; Morelli, K.A.; Grybchuk-Ieremenko, A.; Duval, L.; Votýpka, J.; Yurchenko, V.; Grellier, P.; et al. Exploring the environmental diversity of kinetoplastid flagellates in the high-throughput DNA sequencing era. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukeš, J.; Butenko, A.; Hashimi, H.; Maslov, D.A.; Votýpka, J.; Yurchenko, V. Trypanosomatids are much more than just trypanosomes: Clues from the expanded family tree. Trend Parasitol. 2018, 34, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.P. Genome evolution in trypanosomatid parasites. Parasitology 2015, 142, S40–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackerras, M.J. The haematozoa of Australian mammals. Aus. J. Zool. 1959, 7, 105–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austen, J.M.; Ryan, U.M.; Friend, J.A.; Ditchman, W.G.F.; Reid, S.A. Vector of Trypanosoma copemani identified as Ixodes sp. Parasitology 2011, 138, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero, A.; Cooper, C.; Thompson, C.K.; Clode, P.L.; Rose, K.; Thompson, R.A. Morphological and phylogenetic description of Trypanosoma noyesi sp. nov.: An Australian wildlife trypanosome within the T. cruzi clade. Protist 2016, 167, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, L.M.; Gillett, A.; Ryan, U.M.; Austen, J.; Campbell, R.S.; Hanger, J.; Reid, S.A. Trypanosoma irwini n. sp (Sarcomastigophora: Trypanosomatidae) from the koala (Phascolarctos cinereus). Parasitology 2009, 136, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslov, D.A.; Lukeš, J.; Jirku, M.; Simpson, L. Phylogeny of trypanosomes as inferred from the small and large Subunit rRNAs: Implications for the evolution of parasitism in the trypanosomatid protozoa. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1996, 75, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, P.B.; Stevens, J.R.; Gaunt, M.W.; Gidley, J.; Gibson, W.C. Trypanosomes are monophyletic: Evidence from genes for glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase and small subunit ribosomal RNA. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferies, R.; Ryan, U.M.; Irwin, P.J. PCR-RFLP for the detection and differentiation of the canine piroplasm species and its use with filter paper-based technologies. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 144, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujvari, B.; Madsen, T.; Olsson, M. High prevalence of Hepatozoon spp. (Apicomplexa, Hepatozoidae) infection in water pythons (Liasis fuscus) from tropical australia. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldenström, J.; Bensch, S.; Hasselquist, D.; Östman, Ö. A new nested polymerase chain reaction method very efficient in detecting Plasmodium and Haemoproteus infections from avian blood. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensch, S.; Stjernman, M.; Hasselquist, D.; Örjan, Ö.; Hannson, B.; Westerdahl, H.; Pinheiro, R.T. Host specificity in avian blood parasites: A study of Plasmodium and Haemoproteus mitochondrial DNA amplified from birds. Proc. R. Soc. B 2000, 267, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Murphy, C.; Song, Y.; Ng-Hublin, J.; Estcourt, A.; Hijjawi, N.; Chalmers, R.; Hadfield, S.; Bath, A.; Gordon, C.; et al. Specific and quantitative detection and identification of Cryptosporidium hominis and C. parvum Parvum in clinical and environmental samples. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 135, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Schwartz, S.; Wagner, L.; Miller, W. A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 2000, 7, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgulis, A.; Coulouris, G.; Raytselis, Y.; Madden, T.L.; Agarwala, R.; Schäffer, A.A. Database indexing for production MegaBLAST searches. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1757–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D37–D42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D. Using MODELTEST and PAUP* to select a model of nucleotide substitution. In Current Protocols in Bioinformatics, 1st ed.; Davison, D., Page, R., Petsko, G., Stein, L., Stormo, G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 6.5.1–6.5.14. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Fu, X.Y.; Li, W.H. Maximum likelihood estimation of the heterogeneity of substitution rate among nucleotide sites. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1995, 12, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, P.B.; Stevens, J.R. Resolving relationships between Australian trypanosomes using DNA barcoding data. Trend Parasit. 2011, 27, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the Number of Nucleotide Substitutions in the Control Region of Mitochondrial DNA in Humans and Chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinman, D. Trypanosoma cyclops n. sp.: A pigmented trypanosome from the Malaysian primates Macaca nemestrina and M. ira. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1972, 66, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, P.; Stevens, J.; Gidley, J.; Holz, P.; Gibson, W. A New Lineage of trypanosomes from Australian vertebrates and terrestrial bloodsucking leeches (Haemadipsidae). Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werszko, J.; Szewczyk, T.; Steiner-Bogdaszewska, Ż.; Wróblewski, P.; Karbowiak, G.; Laskowski, Z. Molecular detection of Megatrypanum trypanosomes in tabanid flies. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2020, 34, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoare, C.A. The Trypanosomes of Mammals: A Zoological Monograph; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, A.C.; Garcia, H.A.; Batista, J.S.; Minervino, A.H.H.; Góes-Cavalcante, G.; Maia Da Silva, F.; Ferreira, R.C.; Campaner, M.; Paiva, F.; Teixeira, M.M.G. Characterization of spliced leader genes of Trypanosoma (Megatrypanum) theileri: Phylogeographical analysis of Brazilian isolates from cattle supports spatial clustering of genotypes and parity with ribosomal markers. Parasitology 2010, 137, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, P.B.; Teixeira, M.M.; Stevens, J.R. The Evolution of Trypanosoma cruzi: The ‘bat seeding’ hypothesis. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakes, K.A.; O’Donoghue, P.J.; Adlard, R.D. Phylogenetic relationships of Trypanosoma chelodina and Trypanosoma binneyi from Australian tortoises and platypuses inferred from small subunit rRNA analyses. Parasitology 2001, 123, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paparini, A.; Macgregor, J.; Irwin, P.J.; Warren, K.; Ryan, U.M. Novel genotypes of Trypanosoma binneyi from wild platypuses (Ornithorhynchus anatinus) and identification of a leech as a potential vector. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 145, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettiol, S.S.; Jakes, K.; Le, D.D.; Goldsmid, J.M.; Hocking, G. First record of trypanosomes in Tasmanian bandicoots. J. Parasitol. 1998, 84, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukeš, J.; Skalický, T.; Týč, J.; Votýpka, J.; Yurchenko, V. Evolution of parasitism in kinetoplastid flagellates. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2014, 195, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portas, T.J.; Evans, M.J.; Spratt, D.; Vaz, P.K.; Devlin, J.M.; Barbosa, A.D.; Wilson, B.A.; Rypalski, A.; Wimpenny, C.; Fletcher, D.; et al. Baseline health and disease assessment of founder eastern quolls (Dasyurus viverrinus) during a conservation translocation to mainland Australia. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paguem, A.; Abanda, B.; Ndjonka, D.; Weber, J.S.; Ngomtcho, S.C.H.; Manchang, K.T.; Adoulmoumini, M.; Eisenbarth, A.; Renz, A.; Kelm, S.; et al. Widespread co-endemicity of Trypanosoma species infecting cattle in the Sudano-Sahelian and Guinea Savannah zones of Cameroon. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.S.; Lima, L.; Xavier, S.C.d.C.; Herrera, H.M.; Rocha, F.L.; Roque, A.L.R.; Teixeira, M.M.G.; Jansen, A.M. Uncovering Trypanosoma spp. diversity of wild mammals by the use of DNA from blood clots. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 8, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, E.M.V.; Xavier, S.C.C.; Carvalhaes, J.G.; D’Andrea, P.S.; Lemos, F.G.; Azevedo, F.C.; Cássia-Pires, R.; Jansen, A.M.; Roque, A.L.R. Trypanosomatids in small mammals of an Agroecosystem in Central Brazil: Another piece in the puzzle of parasite transmission in an anthropogenic landscape. Pathogens 2019, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roellig, D.M.; Ellis, A.E.; Yabsley, M.J. Oral transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi with opposing evidence for the theory of carnivory. J. Parasitol. 2009, 95, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, F.L.; Roque, A.L.R.; de Lima, J.S.; Cheida, C.C.; Lemos, F.G.; de Azevedo, F.C.; Arrais, R.C.; Bilac, D.; Herrera, H.M.; Mourão, G.; et al. Trypanosoma cruzi infection in neotropical wild carnivores (Mammalia: Carnivora): At the top of the T. cruzi transmission chain. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, P.B.; Gibson, W.C.; Stevens, J.R. Patterns of co-evolution between trypanosomes and their hosts deduced from ribosomal RNA and protein-coding gene phylogenies. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 44, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.; Fermino, B.R.; Simas-Rodrigues, C.; Hoffmann, L.; Silva, R.; Camargo, E.P.; Teixeira, M.M.G.; Souto-Padrón, T. Phylogenetic and morphological characterization of trypanosomes from Brazilian armoured catfishes and leeches reveal high species diversity, mixed infections and a new fish trypanosome species. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Kaufer, A.; Peters, B.; Craig, D.; Lawrence, A.; Roberts, T.; Lee, R.; McAuliffe, G.; Stark, D.; Ellis, J. Isolation of novel trypanosomatid, Zelonia australiensis sp. nov. (Kinetoplastida: Trypanosomatidae) provides support for a Gondwanan origin of dixenous parasitism in the Leishmaniinae. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, K.; Curtis, J.; Baldwin, T.; Mathis, A.; Kumar, B.; Sakthianandeswaren, A.; Spurck, T.; Low Choy, J.; Handman, E. Cutaneous leishmaniasis in red Kangaroos: Isolation and characterisation of the causative organisms. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humberg, R.M.P.; Oshiro, E.T.; e Cruz, M.d.S.P.; Ribolla, P.E.M.; Alonso, D.P.; Ferreira, A.M.T.; Bonamigo, R.A.; Tasso, N.; de Oliveira, A.G. Leishmania chagasi in opossums (Didelphis albiventris) in an urban area endemic for visceral leishmaniasis, Campo Grande, Mato Grosso Do Sul, Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 87, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Medkour, H.; Laidoudi, Y.; Lafri, I.; Davoust, B.; Mekroud, A.; Bitam, I.; Mediannikov, O. Canine vector-borne protozoa: Molecular and serological investigation for Leishmania spp., Trypanosoma spp., Babesia spp., and Hepatozoon spp. in dogs from Northern Algeria. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2020, 19, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paparini, A.; Irwin, P.J.; Warren, K.; McInnes, L.M.; de Tores, P.; Ryan, U.M. Identification of novel trypanosome genotypes in bative Australian marsupials. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 183, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougall, A.; Shilton, C.; Low Choy, J.; Alexander, B.; Walton, S. New reports of Australian cutaneous leishmaniasis in northern Australian macropods. Epidemiol. Infect. 2009, 137, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougall, A.M.; Alexander, B.; Holt, D.C.; Harris, T.; Sultan, A.H.; Bates, P.A.; Rose, K.; Walton, S.F. Evidence incriminating midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) as potential vectors of Leishmania in Australia. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.; Bunce, M.; Wayne, A.; Pacioni, C.; Ryan, U.; Irwin, P. A high prevalence of Theileria penicillata in woylies (Bettongia penicillata). Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 131, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greay, T.L.; Zahedi, A.; Krige, A.S.; Owens, J.M.; Rees, R.L.; Ryan, U.M.; Oskam, C.L.; Irwin, P.J. Endemic, exotic and novel apicomplexan parasites detected during a national study of ticks from companion animals in Australia. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, S.M.; Egan, S.; Gillett, A.; Banks, P.B.; Ryan, U.M.; Irwin, P.J.; Oskam, C.L. Molecular surveillance of piroplasms in ticks from small and medium-sized urban and peri-urban mammals in Australia. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2018, 7, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey-Lewis, B.; Mitrovic, A.; McParland, B. Molecular detection and characterisation of Babesia and Theileria in Australian hard ticks. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, F.A.; Spratt, D.M. Ecology of the common marsupial tick (Ixodes tasmani Neumann) (Acarina: Ixodidae), in eastern Australia. Aus. J. Zool. 2005, 53, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettiol, S.S.; Goldsmid, J.M.; Le, D.D.; Driessen, M. The first record of a member of the genus Hepatozoon in the eastern barred bandicoot (Perameles gunnii) in Tasmania. J. Parasitol. 1996, 82, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portas, T.; Fletcher, D.; Spratt, D.; Reiss, A.; Holz, P.; Stalder, K.; Devlin, J.; Taylor, D.; Dobroszczyk, D.; Manning, A.D. Health evaluation of free-ranging eastern bettongs (Bettongia gaimardi) during translocation for reintroduction in Australia. J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilcins, I.M.E.; Old, J.M.; Deane, E. Detection of a Hepatozoon and spotted fever group Rickettsia species in the common marsupial tick (Ixodes tasmani) collected from wild Tasmanian devils (Sarcophilus harrisii), Tasmania. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 162, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.D.; Gofton, A.W.; Paparini, A.; Codello, A.; Greay, T.; Gillett, A.; Warren, K.; Irwin, P.; Ryan, U. Increased genetic diversity and prevalence of co-infection with Trypanosoma spp. in koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus) and their ticks identified using next-generation sequencing (NGS). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis-Cunha, J.L.; Baptista, R.P.; Rodrigues-Luiz, G.F.; Coqueiro-dos-Santos, A.; Valdivia, H.O.; de Almeida, L.V.; Cardoso, M.S.; D’Ávila, D.A.; Dias, F.H.C.; Fujiwara, R.T.; et al. Whole genome sequencing of Trypanosoma cruzi field isolates reveals extensive genomic variability and complex aneuploidy patterns within TcII DTU. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northover, A.S.; Elliot, A.D.; Keatley, S.; Lim, Z.; Botero, A.; Ash, A.; Lymbery, A.J.; Wayne, A.F.; Godfrey, S.S.; Thompson, R.C.A. Debilitating disease in a polyparasitised woylie (Bettongia penicillata): A diagnostic investigation. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites. Wildl. 2018, 7, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northover, A.S.; Lymbery, A.J.; Wayne, A.F.; Godfrey, S.S.; Thompson, R.C.A. The hidden consequences of altering host-parasite relationships during fauna translocations. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 220, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).