New Approaches for Escherichia coli Genotyping
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. BOX-PCR
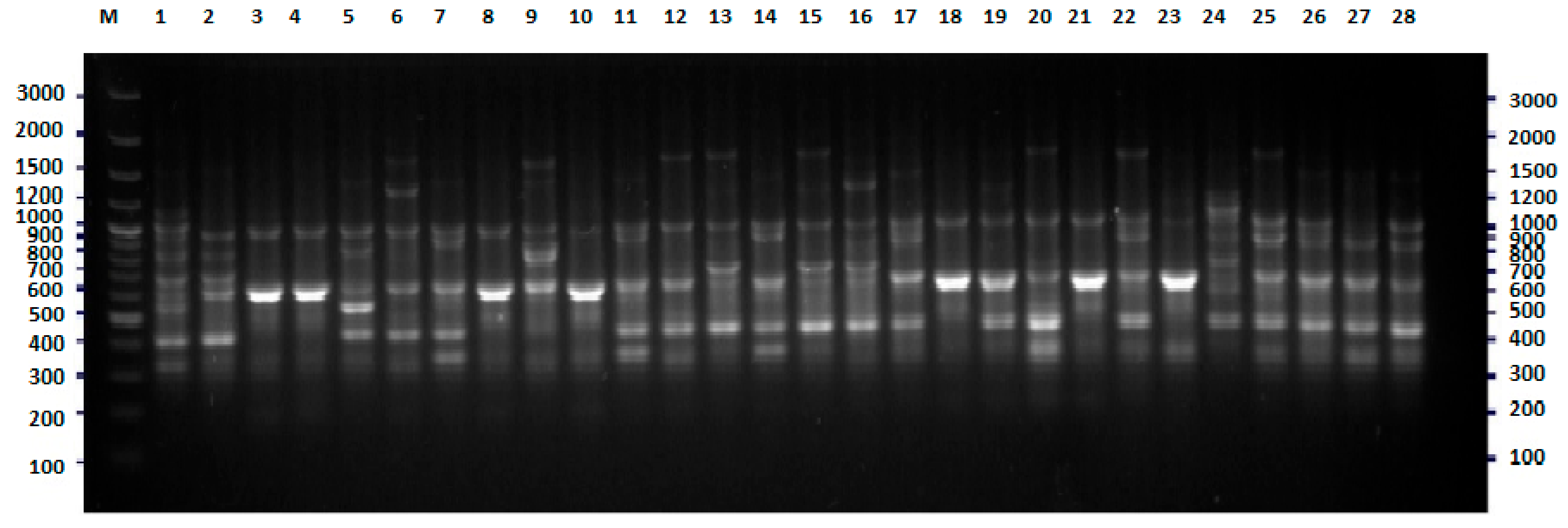
2.2. FliC PCR-RFLP
2.3. Multilocus Sequence Typing
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Isolation of Genomic DNA
4.3. BOX-PCR
4.4. Designing of Primers for Flic RFLP-PCR
4.5. Flic PCR-RFLP Analysis
4.6. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
4.7. Analysis of PCR Products
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leimbach, A.; Hacker, J.; Dobrindt, U. E. coli as an all-rounder: The thin line between commensalism and pathogenicity. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 358, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukjancenko, O.; Wassenaar, T.M.; Ussery, D.W. Comparison of 61 sequenced Escherichia coli genomes. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 60, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crossman, L.C.; Chaudhuri, R.R.; Beatson, S.A.; Wells, T.J.; Desvaux, M.; Cunningham, A.F.; Petty, N.K.; Mahon, V.; Brinkley, C.; Hobman, J.L.; et al. A commensal gone bad: Complete genome sequence of the prototypical enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain H10407. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5822–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Croxen, M.A.; Finlay, B.B. Molecular mechanisms of Escherichia coli pathogenicity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochman, H.; Selander, R.K. Standard reference strains of Escherichia coli from natural populations. J. Bacteriol. 1984, 157, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escobar-Páramo, P.; Clermont, O.; Blanc-Potard, A.B.; Bui, H.; Le Bouguénec, C.; Denamur, E. A specific genetic background is required for acquisition and expression of virulence factors in Escherichia coli. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Rothemund, D.; Curd, H.; Reeves, P.R. Species-wide variation in the Escherichia coli flagellin (H-antigen) gene. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2936–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beutin, L.; Strauch, E.; Zimmermann, S.; Kaulfuss, S.; Schaudinn, C.; Männel, A.; Gelderblom, H.R. Genetical and functional investigation of fliC genes encoding flagellar serotype H4 in wildtype strains of Escherichia coli and in a laboratory E. coli K-12 strain expressing flagellar antigen type H48. BMC Microbiol. 2005, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos Moreno, A.C.; Cabilio Guth, B.E.; Baquerizo Martinez, M. Can the fliC PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism technique replace classic serotyping methods for characterizing the H antigen of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1453–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotłowski, R. Use of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 producing recombinant colicins for treatment of IBD patients. Med. Hypotheses 2016, 93, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, B.; Humbert, O.; Camara, M.; Guenzi, E.; Walker, J.; Mitchell, T.; Andrew, P.; Prudhomme, M.; Alloing, G.; Hakenbeck, R. A highly conserved repeated DNA element located in the chromosome of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 3479–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Versalovic, J.; Koeuth, T.; Lupski, J.R. Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in eubacteria and application to fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 9, 6823–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versalovic, J.; Schneider, M.; de Bruijn, F.J.; Lupski, J.R. Genomic fingerprinting of bacteria using repetitive sequence based polymerase chain reaction. Methods Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 5, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Dombek, P.E.; Johnson, L.K.; Zimmerley, S.T.; Sadowsky, M.J. Use of repetitive DNA sequences and the PCR to differentiate Escherichia coli isolates from human and animal sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2572–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Versalovic, J.; de Bruijn, F.J.; Lupski, J. Repetitive sequence-based PCR (rep-PCR) DNA fingerprinting of bacterial genomes. In Bacterial Genomes: Physical Structure and Analysis; de Bruijn, F.J., Lupski, J.R., Weinstock, G.M., Eds.; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 437–454. [Google Scholar]
- Joensen, K.G.; Tetzschner, A.M.; Iguchi, A.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Scheutz, F. Rapid and easy in silico serotyping of Escherichia coli isolates by use of whole-genome sequencing data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2410–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banjo, M.; Iguchi, A.; Seto, K.; Kikuchi, T.; Harada, T.; Scheutz, F.; Iyoda, S.; Pathogenic E. coli Working Group in Japan. Escherichia coli H-genotyping PCR: A complete and practical platform for molecular H typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00190-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Percival, S.L.; Williams, D.W. Escherichia coli. In Microbiology of Waterborne Diseases: Microbiological Aspects and Risks; Percival, S.L., Yates, M.V., Williams, D.W., Chalmers, R.M., Gray, N.F., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2013; pp. 89–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, S.; Sadowsky, M.J. Escherichia coli in the environment: Implications for water quality and human health. Microbes Environ. 2008, 23, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carlos, C.; Alexandrino, F.; Stoppe, N.C.; Sato, M.I.; Ottoboni, L.M. Use of Escherichia coli BOX-PCR fingerprints to identify sources of fecal contamination of water bodies in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. J Environ Manag. 2012, 93, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolska, K.; Szweda, P. Genotyping techniques for determining the diversity of microorganisms. In Genetic Diversity in Microorganisms; Caliskan, M., Ed.; Intech Open: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 53–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fields, P.I.; Blom, K.; Hughes, H.J.; Helsel, L.O.; Feng, P.; Swaminathan, B. Molecular characterization of the gene encoding H antigen in Escherichia coli and development of a PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism test for identification of E. coli O157:H7 and O157:NM. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynn, S.P.; Cohen, L.K.; Kaplan, S.; Gardner, J.F. RsaI: A new sequence-specific endonuclease activity from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J. Bacteriol. 1980, 142, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fratamico, P.M.; DebRoy, C.; Liu, Y.; Needleman, D.S.; Baranzoni, G.M.; Feng, P. Advances in molecular serotyping and subtyping of Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MLST Allelic Profiles and Sequences. Available online: https://pubmlst.org/data/ (accessed on 18 December 2019).
- MLST Allelic Profiles and Sequences. Available online: https://pubmlst.org/data/ (accessed on 19 December 2019).
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: Improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotłowski, R. Identification of 20 new variable regions in the genomes of Staphylococcus aureus useful for genotyping coagulase-positive staphylococci. Med. Dośw. Mikrobiol. 2017, 69, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- Koneman, E.W.; Allen, S.D.; Janda, W.M.; Schreckenberger, P.C. Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez-Marquez, J. SQRestriction: Bio-informatics software for restriction fragment length polymorphism of batches of sequences. J. Comput. Sci. Syst. Biol. 2014, 7, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Raoult, D.; Fournier, P.E. Bacterial strain typing in the genomic era. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 892–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salipante, S.J.; SenGupta, D.J.; Cummings, L.A.; Land, T.A.; Hoogestraat, D.R.; Cookson, B.T. Application of whole-genome sequencing for bacterial strain typing in molecular epidemiology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdalhamid, B.; Mccutchen, E.L.; Bouska, A.C.; Weiwei, Z.; Loeck, B.; Hinrichs, S.H.; Iwen, P.C. Whole genome sequencing to characterize shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O26 in a public health setting. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, M.; Ciontea, A.S.; Militaru, M.; Dinu, S.; Cristea, D.; Usein, C.R. Molecular Typing of Escherichia coli O157 Isolates from Romanian Human Cases. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 71, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Genotyping Method | The Lowest Similarity between Strains Tested | Genotypes Number n = 15 * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Genomes similarity—according Kotlowski (2017) [29] | 91.15 | 15 |
| 2 | E. coli #1; MLST (adk; fumC; gyrB; icd; mdh; purA; recA)— Achtman scheme [26] | 99.63 | 12 |
| 3 | E. coli #2; MLST (dinB; icdA; pabB; polB; putP; trpA; trpB; uidA)— Pasteur scheme [27] | 94.50 | 13 |
| 4 | Genotyping by Clermont O. for 7 genomic regions [28] | 63.78 | 7 |
| 5 | New PCR-MLST method—this study | 80.86 | 13 |
| Number of Genotype | Number of Strains Classified to the Genotype | Numbers of Strains Classified to the Genotype | Ward of Hospital | Year of Isolation | Gender of Patient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 4 | 8 | Internal | 2008 | Female |
| 10 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female | ||
| 18 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female | ||
| 37 | Neurology | 2008 | Female | ||
| II | 3 | 4 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male |
| 58 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female | ||
| 61 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female | ||
| III | 2 | 21 | Neurology | 2008 | Female |
| 34 | Neurology | 2008 | Male | ||
| IV | 7 | 13 | Internal | 2007 | Male |
| 15 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male | ||
| 32 | Neurology | 2007 | Female | ||
| 38 | Obstetric | 2007 | Female | ||
| 40 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female | ||
| 45 | Internal | 2007 | Female | ||
| 63 | Dialysis unit | 2008 | Female | ||
| V | 3 | 1 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 24 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male | ||
| 39 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male | ||
| VI | 2 | 7 | Orthopedics | 2008 | Female |
| 14 | Neurology | 2008 | Unknown | ||
| VII | 2 | 17 | Internal | 2008 | Female |
| 26 | Neurology | 2008 | Female | ||
| VIII | 2 | 5 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 36 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| No. | E. coli Strains | Ward of Hospital | Year of Isolation | Gender of Patient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 34 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 2 | 14653 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 3 | 2878 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 4 | 6471 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male |
| 5 | 13202 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 6 | 13917 | Pediatrics | 2007 | Male |
| 7 | 66 | Orthopedics | 2008 | Female |
| 8 | 2937 | Internal | 2008 | Female |
| 9 | 7271 | Internal | 2008 | Male |
| 10 | 7308 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 11 | 10492 | Internal | 2008 | Female |
| 12 | 15193 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 13 | 14294 | Internal | 2007 | Male |
| 14 | 863 | Neurology | 2008 | Unknown |
| 15 | 13356 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male |
| 16 | 11199 | Pediatrics | 2007 | Male |
| 17 | 7242 | Internal | 2008 | Female |
| 18 | 6897 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 19 | 2267 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 20 | 1757 | Dialysis unit | 2007 | Female |
| 21 | 14543 | Neurology | 2008 | Female |
| 22 | 9952 | Internal | 2008 | Female |
| 23 | 456 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male |
| 24 | 4838 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male |
| 25 | 9478 | Neurology | 2008 | Female |
| 26 | 1694 | Neurology | 2008 | Female |
| 27 | 2648 | Pediatrics | 2007 | Female |
| 28 | 7663 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 29 | 6780 | Dialysis unit | 2008 | Female |
| 30 | 13583 | Neurology | 2007 | Female |
| 31 | 124 | Neurology | 2008 | Female |
| 32 | 13192 | Neurology | 2007 | Female |
| 33 | 8784 | Internal | 2007 | Male |
| 34 | 4187 | Neurology | 2008 | Male |
| 35 | 8956 | Pediatrics | 2007 | Male |
| 36 | 10316 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 37 | 14158 | Neurology | 2008 | Female |
| 38 | 12921 | Obstetric | 2007 | Female |
| 39 | 8851 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male |
| 40 | 9683 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 41 | 10238 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 42 | 9010 | Internal | 2008 | Female |
| 43 | 6429 | Neurology | 2008 | Female |
| 44 | 13567 | Neurology | 2007 | Female |
| 45 | 2421 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 46 | 1368 | Internal | 2007 | Male |
| 47 | 12021 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 48 | 9898 | Internal | 2007 | Male |
| 49 | 5326 | Obstetric | 2008 | Female |
| 50 | 5660 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male |
| 51 | 10444 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 52 | 4666 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 53 | 3850 | Obstetric | 2008 | Female |
| 54 | 10136 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 55 | 947 | Dialysis unit | 2008 | Female |
| 56 | 7522 | Neurology | 2008 | Male |
| 57 | 5326 | Obstetric | 2008 | Female |
| 58 | 2310 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 59 | 7133 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male |
| 60 | 1908 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 61 | 4410 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 62 | 1036 | Internal | 2008 | Female |
| 63 | 8677 | Dialysis unit | 2008 | Female |
| 64 | 12497 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male |
| 65 | 3909 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Female |
| 66 | 11764 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 67 | 4500 | Internal | 2008 | Female |
| 68 | 3039 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 69 | 6114 | Neurology | 2008 | Male |
| 70 | 5165 | Internal | 2007 | Female |
| 71 | 9046 | Pediatrics | 2008 | Male |
| No. | Name | PCR Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Location in CP041955.1, EC2 Chromosome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ec1 | 5′-ATC-GGC-CAT-ATC-AAG-TCG-ATG-TTG-TTG-CA-3′ | 3265597-3265625 |
| Ec2 | 5′-TGC-TTA-CTT-CGC-CGT-GGA-TAC-TAC-3′ | 3265309-3265332 | |
| 2 | Ec3 | 5′-AGA-AGC-AGC-TGC-AGC-TGA-AGC-AAG-A-3′ | 3246933-3246957 |
| Ec4 | 5′-GCT-GCT-TTC-TTA-TCA-GCT-GCT-GCC-T-3′ | 3246763-3246787 | |
| 3 | Ec5 | 5′-GCC-GAA-CGT-TCA-CCA-CTA-CAA-AAG-3′ | 1578518-1578541 |
| Ec6 | 5′-CAG-ATC-GGC-TTC-GCT-TAG-CTG-3′ | 1578158-1578178 | |
| 4 | Ec7 | 5′-GTT-CAG-TGT-TTC-AAT-TTT-CAG-CTT-GAT-CCA-G-3′ | 3835984-3836014 |
| Ec8 | 5′-TGC-GGT-TGG-ATC-ACC-TCC-TTA-CCT-3′ | 3836352-3836375 | |
| 5 | Ec9 | 5′-GAA-ATT-ACG-CAA-GAT-TCG-CTG-GTG-CA-3′ | 154450-154475 |
| Ec10 | 5′-GGA-ATT-TCT-GGT-TCG-TAA-AGT-ACG-ATG-3′ | 154157-154183 | |
| 6 | Ec11 | 5′-GAA-GGA-GAA-GAA-AAT-TCA-GGA-AAT-GGA-TAA-AG-3′ | 1153234-1153265 |
| Ec12 | 5′-GCT-AAG-GGA-GTA-TGC-GGT-CAA-AAG-3′ | 1152225-1152248 | |
| 7 | Ec13 | 5′-GCG-GAT-CAA-TAA-TTG-AAG-ATT-GCCG-GGG-3′ | 4412457-4412484 |
| Ec14 | 5′-CTG-AGC-TGT-ATG-GAA-GGG-TTT-GAT-ACC-G-3′ | 4412332-4412359 |
| Target Number | Amplified Region of the Genome | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Succinate dehydrogenase iron-sulfur subunit, QGQ16019.1 | |
| 2. | Cell envelope integrity protein TolA, QGQ16014.1 | |
| 3. | Hypothetical protein QGQ14586.1, ISNCY family transposase QGQ14587.1 | |
| 4. * | Locus_tag = “FOZ67_18655”/product = “23S ribosomal RNA” | Locus_tag = “FOZ67_18670”/product = “16S ribosomal RNA”. |
| 5. * | Product = “tRNA uridine(34)/cytosine(34)/5-carboxymethylaminomethyluridine(34)-2′-O)-methyltransferase TrmL”/protein_id = “QGQ13328.1” | Gene “lldD”/product= “quinone-dependent L-lactate dehydrogenase”/protein_id = “QGQ13329.1” |
| 6. * | Locus_tag = “FOZ67_05640” tRNA/locus_tag = “FOZ67_05640”/product = “tRNA-Ser” | Gene = “yqaB”/locus_tag = “FOZ67_05665” |
| 7. * | Locus_tag = "FOZ67_21460" | Sel1 repeat family protein"/protein_id = "QGQ17016.1". |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kotłowski, R.; Grecka, K.; Kot, B.; Szweda, P. New Approaches for Escherichia coli Genotyping. Pathogens 2020, 9, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020073
Kotłowski R, Grecka K, Kot B, Szweda P. New Approaches for Escherichia coli Genotyping. Pathogens. 2020; 9(2):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020073
Chicago/Turabian StyleKotłowski, Roman, Katarzyna Grecka, Barbara Kot, and Piotr Szweda. 2020. "New Approaches for Escherichia coli Genotyping" Pathogens 9, no. 2: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020073
APA StyleKotłowski, R., Grecka, K., Kot, B., & Szweda, P. (2020). New Approaches for Escherichia coli Genotyping. Pathogens, 9(2), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020073





