Parasitic Infections in African Humans and Non-Human Primates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals and Study Area
4.2. Ethic Statement
4.3. DNA Extraction
4.4. Molecular Screening for Parasites by Real-Time PCR Assays (qPCR)
4.5. Genetic Amplification by Standard PCR, Sequencing and Phylogeny
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Consent for Publication
Availability of Data and Materials
References
- Cox, F.E.G. History of human parasitic diseases. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 18, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, B.; Guiton, P.S. Important Human Parasites of the Tropics. Front. Young Minds 2018, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devaux, C.A.; Mediannikov, O.; Medkour, H.; Raoult, D. Infectious Disease Risk Across the Growing Human-Non Human Primate Interface: A Review of the Evidence. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strait, K.; Else, J.G.; Eberhard, M.L. Parasitic diseases of non human primates. In Nonhuman Primates in Biomedical Research, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, J.M.; Nunn, C.L.; Verdú, M. Centrality in primate-parasite networks reveals the potential for the transmission of emerging infectious diseases to humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7738–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashford, R.W.; Reid, G.D.F.; Butynski, T.M. The intestinal faunas of man and mountain gorillas in a shared habitat. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1990, 84, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriuki, S.M.K.; Murugu, R.K.; Munene, E.; Karere, G.M.; Chai, D.C. Some gastro-intestinal parasites of zoonotic (public health) importance commonly observed in old world non-human primates in Kenya. Acta Trop. 1998, 71, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizeyi, J.; Cranfield, M.; Graczyk, T. Cattle near the Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, Uganda, as a reservoir of Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia duodenalis for local community and free-ranging gorillas. Parasitol. Res. 2002, 88, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leendertz, F.H.; Pauli, G.; Maetz-Rensing, K.; Boardman, W.; Nunn, C.; Ellerbrok, H.; Jensen, S.A.; Junglen, S.; Christophe, B. Pathogens as drivers of population declines: The importance of systematic monitoring in great apes and other threatened mammals. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 131, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Mahdy, A.K.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Surin, J.; Wan, K.L.; Al-Mekhlafi, M.S.H. Risk factors for endemic giardiasis: Highlighting the possible association of contaminated water and food. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlčková, K.; Kreisinger, J.; Pafčo, B.; Čížková, D.; Tagg, N.; Hehl, A.B.; Modrý, D. Diversity of Entamoeba spp. in African great apes and humans: An insight from Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, I.; Forestier, C.L.; Peeters, M.; Delaporte, E.; Raoult, D.; Bittar, F. Wild gorillas as a potential reservoir of Leishmania major. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medkour, H.; Davoust, B.; Levasseur, A.; Mediannikov, O. Molecular Evidence of Leishmania infantum and Leishmania guyanensis in Red Howler Monkey (Alouatta seniculus) From French Guiana. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2019, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Else, J.G.; Satzger, M.; Sturrock, R.F. Natural infections of schistosoma mansoni and S. Haematobium in cercopithecus monkeys in kenya. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1982, 76, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, C.; Dobson, A.P. Primate malarias: Diversity, distribution and insights for zoonotic Plasmodium. One Health 2015, 1, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Learn, G.H.; Rudicell, R.S.; Robertson, J.D.; Keele, B.F.; Ndjango, J.-B.N.; Sanz, C.M.; Morgan, D.B.; Locatelli, S.; et al. Origin of the human parasite Plasmodium falciparum in gorillas. Nature 2010, 467, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Shaw, K.S.; Learn, G.H.; Plenderleith, L.J.; Malenke, J.A.; Sundararaman, S.A.; Ramirez, M.A.; Crystal, P.A.; Smith, A.G.; et al. African origin of the malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambrecht, F.; Dunn, F.; Eyles, D. Isolation of Plasmodium knowlesi from Philippine Macaques. Nature 1961, 191, 1117–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Ray, A.; Nair, C. Isolation of a new strain of Plasmodium knowlesi. Nature 1953, 172, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.; Contacos, P.G.; Coatney, G.R.; Kimball, H.R. A naturally acquired quotidian-type malaria in man transferable to monkeys. Science 1965, 149, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Schlagenhauf, P. Plasmodium knowlesi in travellers, update 2014. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 22, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sleeman, J.M.; Meader, L.L.; Mudakikwa, A.B.; Foster, J.W.; Patton, S. Gastrointestinal Parasites of Mountain Gorillas (Gorilla Gorilla Beringei) in the Parc National Des Volcans, Rwanda. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2000, 31, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwant, S. Human Bertiella studeri (family Anoplocephalidae) infection of probable Southeast Asian origin in Mauritian children and an adult. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 70, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada, A.; Garber, P.A.; Rylands, A.B.; Roos, C.; Fernandez-Duque, E.; Di Fiore, A.; Anne-Isola Nekaris, K.; Nijman, V.; Heymann, E.W.; Lambert, J.E.; et al. Impending extinction crisis of the world’s primates: Why primates matter. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zommers, Z.; Macdonald, D.W.; Johnson, P.J.; Gillespie, T.R. Impact of human activities on chimpanzee ground use and parasitism (Pan troglodytes). Conserv. Lett. 2013, 6, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenz-Mücke, A.; Sithithaworn, P.; Petney, T.N.; Taraschewski, H. Human contact in fl uences the foraging behaviour and parasite community in long-tailed macaques. Parasitology 2013, 140, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalewski, M.M.; Gillespie, T.R. Primatology, Biocultural Diversity and Sustainable Development in Tropical Forests; UNESCO Office: Mexico City, Mexico, December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Conly, J.M.; Johnston, B.L. The infectious diseases consequences of monkey business. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 19, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidoudi, Y.; Medkour, H.; Latrofa, M.S.; Davoust, B.; Sokhna, C.; Barciela, A.; Hernandez-Aguilar, R.A.; Raoult, D.; Otranto, D.; Mediannikov, O. Zoonotic Abbreviata caucasica in Wild Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) from Senegal. Pathogens 2020, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenollar, F.; Mediannikov, O. Emerging infectious diseases in Africa in the 21st century. New Microbes New Infect. 2018, 26, S10–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, D.; Parola, P.; Sylla, K.; Ndiaye, M.; Delaunay, P.; Halfon, P.; Camiade, S.; Dieng, T.; Tine, R.C.K.; Faye, B.; et al. Performance of real-time polymerase chain reaction assays for the detection of 20 gastrointestinal parasites in clinical samples from Senegal. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landsoud-Soukate, J.; Tutin, C.E.G.; Fernandez, M. Intestinal parasites of sympatric gorillas and chimpanzees in the Lope Reserve, Gabon. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1995, 89, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, A.A.; Mehlman, P.T.; Doran, D. Intestinal parasites in gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans at Mondika research site, dzanga-ndoki national park, Central African Republic. Int. J. Primatol. 2002, 23, 555–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renquist, D.M.; Whitney, R.A. Zoonoses acquired from pet primates. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1987, 17, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygård, K.; Schimmer, B.; Søbstad, Ø.; Walde, A.; Tveit, I.; Langeland, N.; Hausken, T.; Aavitsland, P. A large community outbreak of waterborne giardiasis—delayed detection in a non-endemic urban area. BMC Public Health 2006, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillespie, T.R.; Greiner, E.C.; Chapman, C.A. Gastrointestinal Parasites of the Guenons of Western Uganda. J. Parasitol. 2004, 90, 1356–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, M.J.; Unger, M.; Yeap, Y.T.; Rogers, E.; Millet, I.; Harman, K.; Fox, M.; Kalema-Zikusoka, G.; Blake, D.P. Molecular characterisation of protist parasites in human-habituated mountain gorillas (Gorilla beringei beringei), humans and livestock, from Bwindi impenetrable National Park, Uganda. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drakulovski, P.; Bertout, S.; Locatelli, S.; Butel, C.; Pion, S.; Mpoudi-Ngole, E.; Delaporte, E.; Peeters, M.; Mallié, M. Assessment of gastrointestinal parasites in wild chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes troglodytes) in southeast Cameroon. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 2541–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, D.G. Parasites of non-human primates. In Flynn’s Parasites of Laboratory Animals, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2008; pp. 693–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruch, T.C. Diseases of Laboratory Primates. Ann. Surg. 1961, 153, 137. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, M.R.; Wang, R.; Yu, F.; Li, T.; Dong, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Jian, F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Multi-locus analysis of Giardia duodenalis from nonhuman primates kept in zoos in China: Geographical segregation and host-adaptation of assemblage B isolates. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 30, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berghe, L.; Chardome, M.; Peel, E. The Filarial Parasites of the Eastern Gorilla in the Congo. J. Helminthol. 1964, 38, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando Caserta Tencatt, L.; Ribeiro de Britto, M.; Simone Pavanelli, C. Revisionary study of the armored catfish Corydoras paleatus (Jenyns, 1842) (Siluriformes: Callichthyidae) over 180 years after its discovery by Darwin, with description of a new species. Neotrop. Ichthyol. J. 2016, 14, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pommier de Santi, V.; Briolant, S.; Mahamat, A.; Ilcinkas, C.; Blanchet, D.; de Thoisy, B.; Reynaud, Y.; Hyvert, G.; Lou Marié, J.; Edouard, S.; et al. Q fever epidemic in Cayenne, French Guiana, epidemiologically linked to three-toed sloth. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 56, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P. Overview of Rift Valley Fever. Available online: https://www.merckvetmanual.com/generalized-conditions/rift-valley-fever/overview-of-rift-valley-fever (accessed on 11 July 2020).
- Mohan, S.; Mohan, H.; Mohan, S. Infectious and Parasitic Diseases. Essent. Pathol. Dent. Stud. 2017, 166, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalifoux, L.V. Filariasis, New World Primates; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, O.; Mutafchiev, Y.; Junker, K.; Guerrero, R.; Martin, C.; Lefoulon, E.; Uni, S. Review of the genus Mansonella Faust, 1929 sensu lato (Nematoda: Onchocercidae), with descriptions of a new subgenus and a new subspecies. Zootaxa 2015, 3918, 151–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mediannikov, O.; Ranque, S. Mansonellosis, the most neglected human filariasis. New Microbes New Infect. 2018, 26, S19–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agerholm, J.S. Coxiella burnetii associated reproductive disorders in domestic animals-a critical review. Acta Vet. Scand. 2013, 55, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandosham, A.A. On Two Helminths from the Orang Utan, Leipertrema rewelli n.g., n.sp. and Dirofilaria immitis (Leidy, 1856). J. Helminthol. 1951, 25, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodhain, J. Corollaire à l’étude de E. Peel et M. Chardome sur les filaridés des chimpanzés au Congo belge. Ann. Soc. Belge Med. Trop. 1947, 26, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Park, N.; Gillespie, T.R.; Lonsdorf, E.V.; Canfield, E.P.; Meyer, D.J.; Nadler, Y.; Raphael, J.; Pusey, A.E.; Pond, J.; Pauley, J.; et al. Demographic and ecological effects on patterns of parasitism in eastern chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii) in Gombe National Park, Tanzania. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2014, 143, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muehlenbein, M.P. Parasitological analyses of the male chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii) at Ngogo, Kibale National Park, Uganda. Am. J. Primatol. 2005, 65, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrželkov, K.J.; Hasegawa, H.; Appleton, C.C.; Huffman, M.A.; Archer, C.E.; Moscovice, L.R.; Mapua, M.I.; Singh, J.; Kaur, T. Gastrointestinal parasites of the chimpanzee population introduced onto Rubondo Island National Park, Tanzania. Am. J. Primatol. 2010, 72, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Sato, H.; Fujita, S.; Nguema, P.P.M.; Nobusue, K.; Miyagi, K.; Kooriyama, T.; Takenoshita, Y.; Noda, S.; Sato, A.; et al. Molecular identification of the causative agent of human strongyloidiasis acquired in Tanzania: Dispersal and diversity of Strongyloides spp. and their hosts. Parasitol. Int. 2010, 59, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanchomnang, T.; Intapan, P.M.; Sanpool, O.; Rodpai, R.; Tourtip, S.; Yahom, S.; Kullawat, J.; Radomyos, P.; Thammasiri, C.; Maleewong, W. First molecular identification and genetic diversity of Strongyloides stercoralis and Strongyloides fuelleborni in human communities having contact with long-tailed macaques in Thailand. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 1917–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, I.; Keita, M.B.; Peeters, M.; Delaporte, E.; Raoult, D.; Bittar, F. Pathogenic eukaryotes in gut microbiota of western lowland gorillas as revealed by molecular survey. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, H.; Modrý, D.; Kitagawa, M.; Shutt, K.A.; Todd, A.; Kalousová, B.; Profousová, I.; Petrželková, K.J. Humans and Great Apes Cohabiting the Forest Ecosystem in Central African Republic Harbour the Same Hookworms. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, N.D. Diseases of Man Acquired from His Pets. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1968, 17, 906–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguti, S. Systema Helminthum. The Nematodes of Vertebrates; Interscience (Wiley): New York, NY, USA, 1962; Volume 3, p. 1261. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo, R.K.; Perera, M.S.J.; Perera, N.; Peries, T.N.; de Silva, S.; Bambaradeniya, C.N.B. A preliminary survey on the herpetofauna in the Anawilundawa wetland sanctuary: The sond Ramsar site of Sri Lanka. Tigerpaper 2008, 35, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Essa, A. Worms and human disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 57, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vyas, R. Preliminary survey of herpetofauna of Narayan sarovar Sanctuary, Gujarat. Zoos’ Print J. 2002, 17, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remfry, J. The incidence, pathogenesis and treatment of helminth infections in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Lab. Anim. 1978, 12, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toft, J.D. The pathoparasitology of nonhuman primates: A review. In Primates; Benirschke, K., Ed.; Proceedings in Life Sciences; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, J. Ecological relationships between parasites and primates—I. Helminth Parasites and Primates. Primates 1963, 4, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polderman, A.M.; Blotkamp, J. Oesophagostomum infections in humans. Parasitol. Today 1995, 11, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghai, R.R.; Chapman, C.A.; Omeja, P.A.; Davies, T.J.; Goldberg, T.L. Nodule Worm Infection in Humans and Wild Primates in Uganda: Cryptic Species in a Newly Identified Region of Human Transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dridi, B.; Henry, M.; El Khéchine, A.; Raoult, D.; Drancourt, M. High prevalence of Methanobrevibacter smithii and Methanosphaera stadtmanae detected in the human gut using an improved DNA detection protocol. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medkour, H.; Varloud, M.; Davoust, B.; Mediannikov, O. New Molecular Approach for the Detection of Kinetoplastida Parasites of Medical and Veterinary Interest. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medkour, H.; Laidoudi, Y.; Athias, E.; Bouam, A.; Dizoé, S.; Davoust, B.; Mediannikov, O. Molecular and serological detection of animal and human vector-borne pathogens in the blood of dogs from Côte d’Ivoire. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 69, 101412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmana, H.; Amanzougaghene, N.; Davoust, B.; Normand, T.; Carette, O.; Demoncheaux, J.P.; Mulot, B.; Fabrizy, B.; Scandola, P.; Chik, M.; et al. Great diversity of Piroplasmida in Equidae in Africa and Europe, including potential new species. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2019, 18, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, J.J.; Laeijendecker, D.; Brienen, E.A.T.; Van Lieshout, L.; Polderman, A.M. Detection of Cyclospora cayetanensis in travellers returning from the tropics and subtropics using microscopy and real-time PCR. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 293, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourembou, G.; Fenollar, F.; Socolovschi, C.; Lemamy, G.J.; Nzoughe, H.; Kouna, L.C.; Toure-Ndouo, F.; Million, M.; Mbiguino, A.N.; Lekana-Douki, J.B.; et al. Molecular detection of fastidious and common Bacteria as well as Plasmodium spp. in Febrile and Afebrile children in Franceville, Gabon. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauregui, L.H.; Higgins, J.; Zarlenga, D.; Dubey, J.P.; Lunney, J.K. Development of a real-time PCR assay for detection of Toxoplasma gondii in pig and mouse tissues. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcés-Sanchez, G.; Wilderer, P.A.; Munch, J.C.; Horn, H.; Lebuhn, M. Evaluation of two methods for quantification of hsp70 mRNA from the waterborne pathogen Cryptosporidium parvum by reverse transcription real-time PCR in environmental samples. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2669–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, J.J.; Blange, R.A.; Templeton, K.; Schinkel, J.; Brienen, E.A.T.; Van Rooyen, M.A.A.; Van Lieshout, L.; Polderman, A.M. Cryptosporidium parvum in fecal samples by using Multiplex real-time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.; Kabir, M.; Mondal, D.; Ali, I.K.M.; Petri, W.A.; Haque, R. Real-time-PCR assay for diagnosis of Entamoeba histolytica infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laidoudi, Y.; Davoust, B.; Varloud, M.; Niang, E.H.A.; Fenollar, F.; Mediannikov, O. Development of a multiplexed qPCRs-based approach for the diagnosis of Dirofilaria immitis, D. repens, Acanthocheilonema reconditum and the others filariosis. bioRxiv 2020, 842575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassene, H.; Sambou, M.; Fenollar, F.; Clarke, S.; Djiba, S.; Mourembou, G.; Alioune Badara, L.Y.; Raoult, D.; Mediannikov, O. High prevalence of Mansonella perstans filariasis in rural Senegal. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Touré, F.S.; Bain, O.; Nerrienet, E.; Millet, P.; Wahl, G.; Toure, Y.; Doumbo, O.; Nicolas, L.; Georges, A.J.; McReynolds, L.A.; et al. Detection of Loa loa-specific DNA in blood from occult-infected individuals. Exp. Parasitol. 1997, 86, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, J.J.; Brienen, E.A.T.; Ziem, J.; Yelifari, L.; Polderman, A.M.; Van Lieshout, L. Simultaneous detection and quantification of Ancylostoma duodenale, Necator americanus, and Oesophagostomum bifurcum in fecal samples using multiplex real-time PCR. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 77, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wichmann, D.; Panning, M.; Quack, T.; Kramme, S.; Burchard, G.D.; Grevelding, C.; Drosten, C. Diagnosing schistosomiasis by detection of cell-free parasite DNA in human plasma. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praet, N.; Verweij, J.J.; Mwape, K.E.; Phiri, I.K.; Muma, J.B.; Zulu, G.; van Lieshout, L.; Rodriguez-Hidalgo, R.; Benitez-Ortiz, W.; Dorny, P.; et al. Bayesian modelling to estimate the test characteristics of coprology, coproantigen ELISA and a novel real-time PCR for the diagnosis of taeniasis. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2013, 18, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiria, A.; Indonesia, J.; Leiden, T.; Prasetyani, M.; Hamid, F.; University, M.; Wammes, L.; Lell, B.; Hospital, A.; Ariawan, I.; et al. Does treatment of intestinal helminth infections influence malaria? Background and methodology of a longitudinal study of clinical, parasitological and immunological parameters in Nangapanda, Flores, Indonesia (ImmunoSPIN Study). BMC Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Gratz, J.; Amour, C.; Kibiki, G.; Becker, S.; Janaki, L.; Verweij, J.J.; Taniuchi, M.; Sobuz, S.U.; Haque, R.; et al. A laboratory-developed taqman array card for simultaneous detection of 19 enteropathogens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verweij, J.J.; Canales, M.; Polman, K.; Ziem, J.; Brienen, E.A.T.; Polderman, A.M.; van Lieshout, L. Molecular diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis in faecal samples using real-time PCR. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laidoudi, Y.; Ringot, D.; Watier-Grillot, S.; Davoust, B.; Mediannikov, O. A cardiac and subcutaneous canine dirofilariosis outbreak in a kennel in central France. Parasite 2019, 26, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
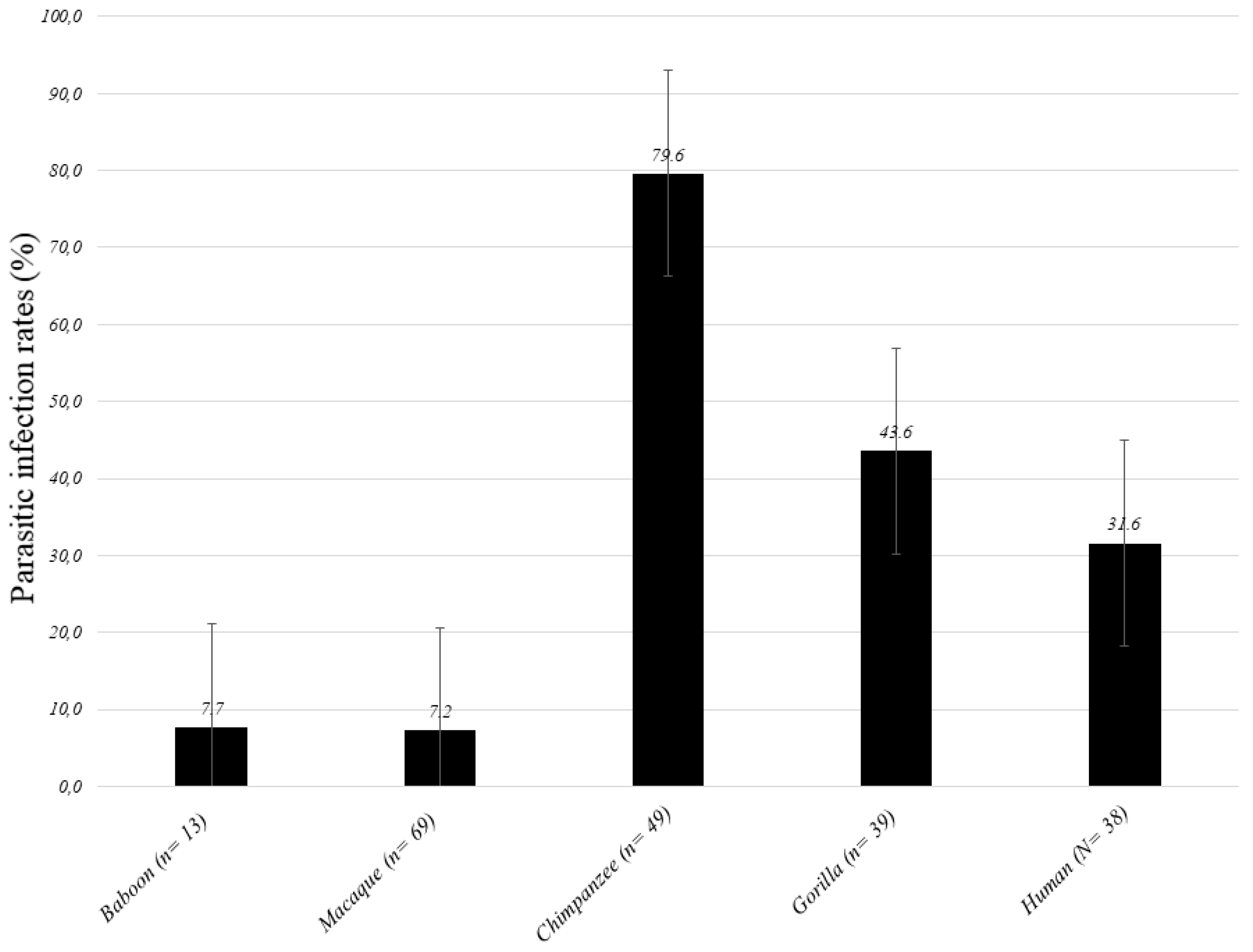

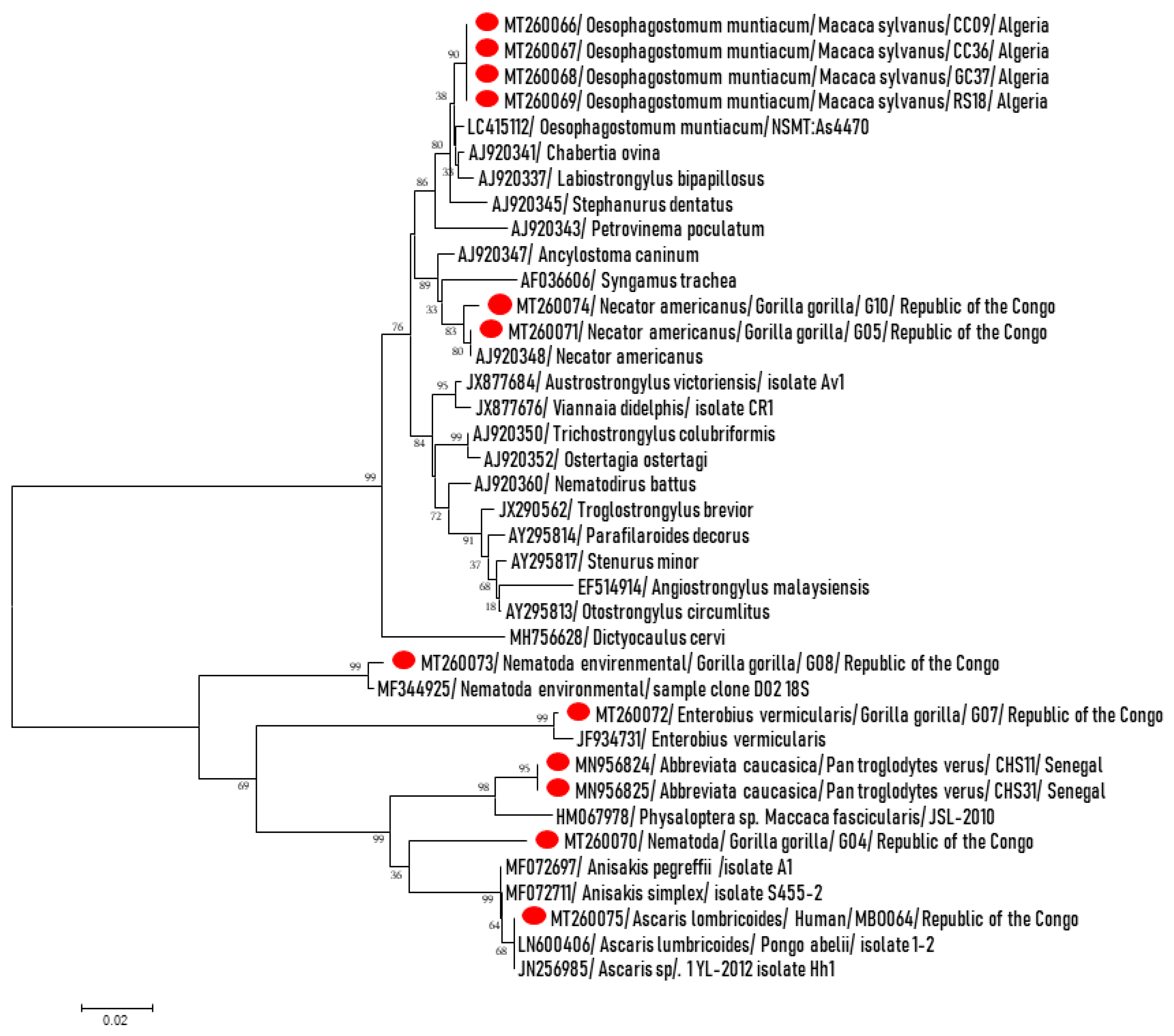
| Species (n) | Gorilla (n = 39) | Chimpanzee (n = 49) | Baboon (n = 13) | Macaque (n = 69) | NHPs (N = 170) | Human (N = 38) | Difference: p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parasitic infections | 17(43.6) | 39 (79.6) | 1 (7.7) | 5 (7.2) | 62 (36.5) | 12 (31.6) | 0.390 |
| Nematoda | 10 (25.6) | 38 (77.6) | 1 (7.7) | 4 (5.8) | 53 (31.2) | 8 (21.1) | 0.836 |
| Filarioidea | 8 (20.5) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 (4.7) | 1 (2.6) | 0.028 |
| Mansonella spp. | 4 (10.3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 (2.4) | 0 | 0.115 |
| M. perstans | 2 (5.1) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 (1.2) | 0 | 0.474 |
| Abbreviata caucasica | 0 | 28 (57.1) | 0 | 0 | 28 (16.5) | 0 | <0.0001 |
| Necator americanus | 5 (12,8) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (2.9) | 5 (13.2) | 1.000 |
| Ascaris lumbricoides | 0 | 1 (2) | 0 | 0 | 1 (0.6) | 2 (5.3) | 0.462 |
| Enterobius vermicularis | 1 (2.6) | 1 (2) | 0 | 0 | 2 (1.2) | 0 | 1.000 |
| Strongyloides stercoralis | 3 (7.7) | 1 (2) | 0 | 0 | 4 (2.4) | 1 (2.6) | 0.622 |
| Oesophagostomum muntiacum | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 (5.8) | 4 (2.4) | 0 | 1.000 |
| Unknown Nematoda | 1 (2.6) | 10 (20.4) | 1 (7.7) | 0 | 12 (7.1) | 1 (2.6) | 1.000 |
| Protozoa | 9 (23.1) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1.4) | 10 (5.9) | 4 (10.5) | 0.014 |
| Giardia lamblia | 5 (12.8) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 (2.9) | 4 (10.5) | 1000 |
| Kinetoplastida (Bodo sp.) | 4 (10.3) | 0 | 0 | 1 (1.4) | 5 (2.9) | 0 | 0.115 |
| Species | Country | Region | Coordinates | Number (date) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-human primates | 160 (2015–2018) | |||
| Chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) | Senegal | Kédougou | 12°22′57.1404″N 12°17′16.7172″W | 3 (2016) |
| 12°22′53.1732″N 12°17′26.7936″W | 7 (2016) | |||
| 12°22′47.7084″N 12°17′48.588″W | 38 (2016) | |||
| Rep. Congo | Odzala-Kokoua NP | 1.3206°”N 14.8455°”E | 1 (2017) | |
| Gorillas (Gorilla gorilla) | Rep. Congo | Lésio-Louna NP | 2°58′33.1”S 15°28′33.4”E | 16 (2015), 12 (2017) |
| Odzala-Kokoua NP | 1.3206°”N, 14.8455°”E | 10 (2017) | ||
| Nouabale-Ndoki NP | 2.5857°”N, 16.6291°”E | 1 (2017) | ||
| Baboons (Papio papio) | Senegal | Niokolo-Koba NP | 13°04′28.6”N 12°43′18.2”W | 7 (2015) |
| Baboons (Papio hamadryas) | Djibouti | Oueah | 11°29′56.1”N 42°51′14.8”E | 6 (2017) |
| Barbary macaques (Macaca sylvanus) | Algeria | Chréa NP | 36°23′42.9”N 2°45′53.6”E | 30 (2018) |
| Cap Carbon | 36°46′31.6”N 5°06′11.2”E | 39 (2018) | ||
| Humans | Rep. Congo | Mbomo village | 1.3206°”N, 14.8455°”E | 35 (2017) |
| Lésio-Louna (Eco-guards) | 2°58′33.1”S 15°28′33.4”E | 3 (2017) |
| Parasite | Target Gene | Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinetoplastida | 28s | F. 24a.5198 | AGTATTGAGCCAAAGAAGG | [71] |
| R. 24a.5412 | TTGTCACGACTTCAGGTTCTAT | |||
| P. 24a.5345 | FAM-TAGGAAGACCGATAGCGAACAAGTAG-TAMRA | |||
| Leishmania spp. | 18s | F | GGTTTAGTGCGTCCGGTG | [72] |
| R | ACGCCCCAGTACGTTCTCC | |||
| P | FAM-CGGCCGTAACGCCTTTTCAACTCA-TAMRA | |||
| Trypanosoma spp. | 5.8s | F. 5.8 S Tryp 3874 | CAACGTGTCGCGATGGATGA | |
| R. 5.8 S Tryp 3935 | ATTCTGCAATTGATACCACTTATC | |||
| S. 5.8 S Tryp 3911 | FAM-GTTGAAGAACGCAGCAAAGGCGAT-TAMRA | |||
| Piroplasmida | 5.8s | 5.8S-F5 | TCGCAGRAGTCTKCAAGTC | [73] |
| 5.8S-R | AYYKTYAGCGRTGGATGTC | |||
| 5.8S-S | FAM-TTYGCTGCGTCCTTCATCGTTGT-MGB | |||
| Cyclospora cayetanensis | 18s | Cyclo250F | TAGTAACCGAACGGATCGCATT | [74] |
| Cyclo350R | AATGCCACGTAGGCCAATA | |||
| Cyclo281T | FAM-CCGGCGATAGATCATTCAAGTTTCTGACC-TAMRA | |||
| Plasmodium spp. | Cox | Plasmo_cox_15_F | AGGAACTCGACTGGCCTACA | [75] |
| Plasmo_cox_16_R | CCAGCGACAGCGGTTATACT | |||
| Plasmo-cox_P | FAM-CGAACGCTTTTAACGCCTGACATGG-TAMRA | |||
| Toxoplasma gondii | ITS1 | Tgon_ITS1_F | GATTTGCATTCAAGAAGCGTGATAGTA | [76] |
| Tgon_ITS1_R | AGTTTAGGAAGCAATCTGAAAGCACATC | |||
| Tgon_ITS1_P | FAM-CTGCGCTGCTTCCAATATTGG-TAMRA | |||
| Cryptosporidium parvum; C. hominis | hsp70 gene | 1PSF | AACTTTAGCTCCAGTTGAGAAAGTACTC | [77] |
| 1PSR | AACTTTAGCTCCAGTTGAGAAAGTACTC | |||
| Crypt P | FAM-AATACGTGTAGAACCACCAACCAATACAACATC-TAMRA | |||
| Giardia lamblia (intestinalis or duodenalis) | 18s | Giardia-80F | GACGGCTCAGGACAACGGTT | [78] |
| Giardia-127R | TTGCCAGCGGTGTCCG | |||
| Giardia-105T | FAM-CCCGCGGCGGTCCCTGCTAG-TAMRA | |||
| Entamoeba histolytica | 18s | Ehf | AACAGTAATAGTTTCTTTGGTTAGTAAAA | [79] |
| Ehr | CTTAGAATGTCATTTCTCAATTCAT | |||
| Ehp | FAM-ATTAGTACAAAATGGCCAATTCATTCA-TAMRA | |||
| Nematoda | 5s | qNem.5S.1f | ACCACGTTGAAAGCACGMC | [29] |
| qNem.5S.110r | TGTCTACAACACCTSGRATTCC | |||
| qNem.5S.38p | FAM-AGTTAAGCAACGTTGGGCC-TAMRA | |||
| Filariae | 28S | qFil-28S-F | TTGTTTGAGATTGCAGCCCA | [80] |
| qFil-28S-R | GTTTCCATCTCAGCGGTTTC | |||
| qFil-28S-S | FAM-CAAGTACCGTGAGGGAAAGT-TAMRA | |||
| Mansonella spp. | ITS1 | Forward | CCTGCGGAAGGATCATTAAC | [81] |
| Reverse | ATCGACGGTTTAGGCGATAA | |||
| Probe | FAM-CGGTGATATTCGTTGGTGTCT-TAMRA | |||
| Mansonella perstans | ITS1 | Forward | AGGATCATTAACGAGCTTCC | |
| Reverse | CGAATATCACCGTTAATTCAGT | |||
| Probe | FAM-TTCACTTTTATTTAGCAACATGCA-TAMRA | |||
| Loa loa | LL20 15-kDa ladder antigen | 15r3-5 | CGAAAAATTATAGGGGGAAAC | [82] |
| 15r3-6 | TCGTAGACCAAACTGCGAAC | |||
| 15r3-P | FAM-TCAAGAGCCGATATACTGAAAGCTATC-TAMRA | |||
| Abbreviata caucasica | 12s | Phy.12S.f.204 | GAATTGGATTAGTACCCAAGTAAGTG | [29] |
| Phy.12S.r.305 | TGTTCCAAAAATCTTTCTAAGATCAG | |||
| Phy.12S.242p | VIC-GCGGGAGTAAAGTTAAGTTTAAACC-TAMRA | |||
| Cyclo350R | AATGCCACGTAGGCCAATA | |||
| Cyclo281T | FAM-CCGGCGATAGATCATTCAAGTTTCTGACC-TAMRA | |||
| Necator americanus | ITS2 | Na58F | CTGTTTGTCGAACGGTACTTGC | [83] |
| Na158R | ATAACAGCGTGCACATGTTGC | |||
| Na81T | FAM-CTGTACTACGCATTGTATAC-MGB | |||
| Ancylostoma duodenale | ITS2 | Ad125F | GAATGACAGCAAACTCGTTGTTG | |
| Ad195R | ATACTAGCCACTGCCGAAACGT | |||
| Ad155-XS | FAM-ATCGTTTACCGACTTTAG-MGB | |||
| Schistosoma mansoni | Tandem repeat units M61098 | SRA1 | CCACGCTCTCGCAAATAATCT | [84] |
| SRS2 | CAACCGTTCTATGAAAATCGTTGT | |||
| SRP | FAM-TCCGAAACCACTGGACGGATTTTTATGAT-TAMRA | |||
| Taenia solium | ITS | Tsol_145F | ATGGATCAATCTGGGTGGAGTT | [85] |
| Tsol_230R | ATCGCAGGGTAAGAAAAGAAGGT | |||
| Tsol_169Tq | FAM-TGGTACTGCTGTGGCGGCGG-TAMRA | |||
| Taenia saginata | ITS | Tsag_F529 | GCGTCGTCTTTGCGTTACAC | |
| Tsag_R607 | TGACACAACCGCGCTCTG | |||
| Tsag_581Tq | FAM-CCACAGCACCAGCGACAGCAGCAA-TAMRA | |||
| Ascaris lumbricoides | ITS1 | Alum96F | GTAATAGCAGTCGGCGGTTTCTT | |
| Alum183R | GCCCAACATGCCACCTATTC | [86] | ||
| Alum124T | FAM-TTGGCGGACAATTGCATGCGAT-TAMRA | |||
| Trichuris trichiura | 18s | TrichF | TTGAAACGACTTGCTCATCAACTT | [87] |
| TrichR | CTGATTCTCCGTTAACCGTTGTC | |||
| TrichP | FAM-CGATGGTACGCTACGTGCTTACCATGG-TAMRA | |||
| Strongyloides stercoralis | 18s | Stro-1530F | GAATTCCAAGTAAACGTAAGTCATTAGC | [88] |
| Stro-1630R | TGCCTCTGGATATTGCTCAGTTC | |||
| Stro-1586T | FAM-ACACACCGGCCGTCGCTGC-TAMRA | |||
| Enterobius vermicularis | 5s | EnterF | TTTCCAAGCCACAGACTCAC | |
| EnterR | ATTGCTCGTTTGCCGATTAT | [31] | ||
| EnterP | TCATGTCTGAGCCGGAACGAGA | |||
| Nematoda | 18s | Fwd.18S.631 | TCGTCATTGCTGCGGTTAAA | [89] |
| Rwd.18S.1825r | GGTTCAAGCCACTGCGATTAA | |||
| Helminths | 28s | Hspec.28S. 5748f | GGTAAGGGAAGTCGGCAAAT | This study |
| Hspec.28S.6394r | TAGGGACAGTGGGAATCTCG | |||
| Abbreviata caucasica | COI | F.Abbrev.COI.51f | TGATCAGGGTTGGGAGCTT | [29] |
| R.Abbrev.COI.601r | AAAAAGAACAATTAAAATTACGATCC |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medkour, H.; Amona, I.; Laidoudi, Y.; Davoust, B.; Bitam, I.; Levasseur, A.; Akiana, J.; Diatta, G.; Pacheco, L.; Gorsane, S.; et al. Parasitic Infections in African Humans and Non-Human Primates. Pathogens 2020, 9, 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070561
Medkour H, Amona I, Laidoudi Y, Davoust B, Bitam I, Levasseur A, Akiana J, Diatta G, Pacheco L, Gorsane S, et al. Parasitic Infections in African Humans and Non-Human Primates. Pathogens. 2020; 9(7):561. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070561
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedkour, Hacène, Inestin Amona, Younes Laidoudi, Bernard Davoust, Idir Bitam, Anthony Levasseur, Jean Akiana, Georges Diatta, Liliana Pacheco, Slim Gorsane, and et al. 2020. "Parasitic Infections in African Humans and Non-Human Primates" Pathogens 9, no. 7: 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070561
APA StyleMedkour, H., Amona, I., Laidoudi, Y., Davoust, B., Bitam, I., Levasseur, A., Akiana, J., Diatta, G., Pacheco, L., Gorsane, S., Sokhna, C., Hernandez-Aguilar, R. A., Barciela, A., Fenollar, F., Raoult, D., & Mediannikov, O. (2020). Parasitic Infections in African Humans and Non-Human Primates. Pathogens, 9(7), 561. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070561






