Molecular Detection and Genetic Diversity of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Cat Faeces from Klang Valley, Malaysia, Using B1 and REP Genes in 2018
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Copro-Microscopy
2.2. Copro-PCR Assays
2.3. DNA Sequence Results
3. Discussion
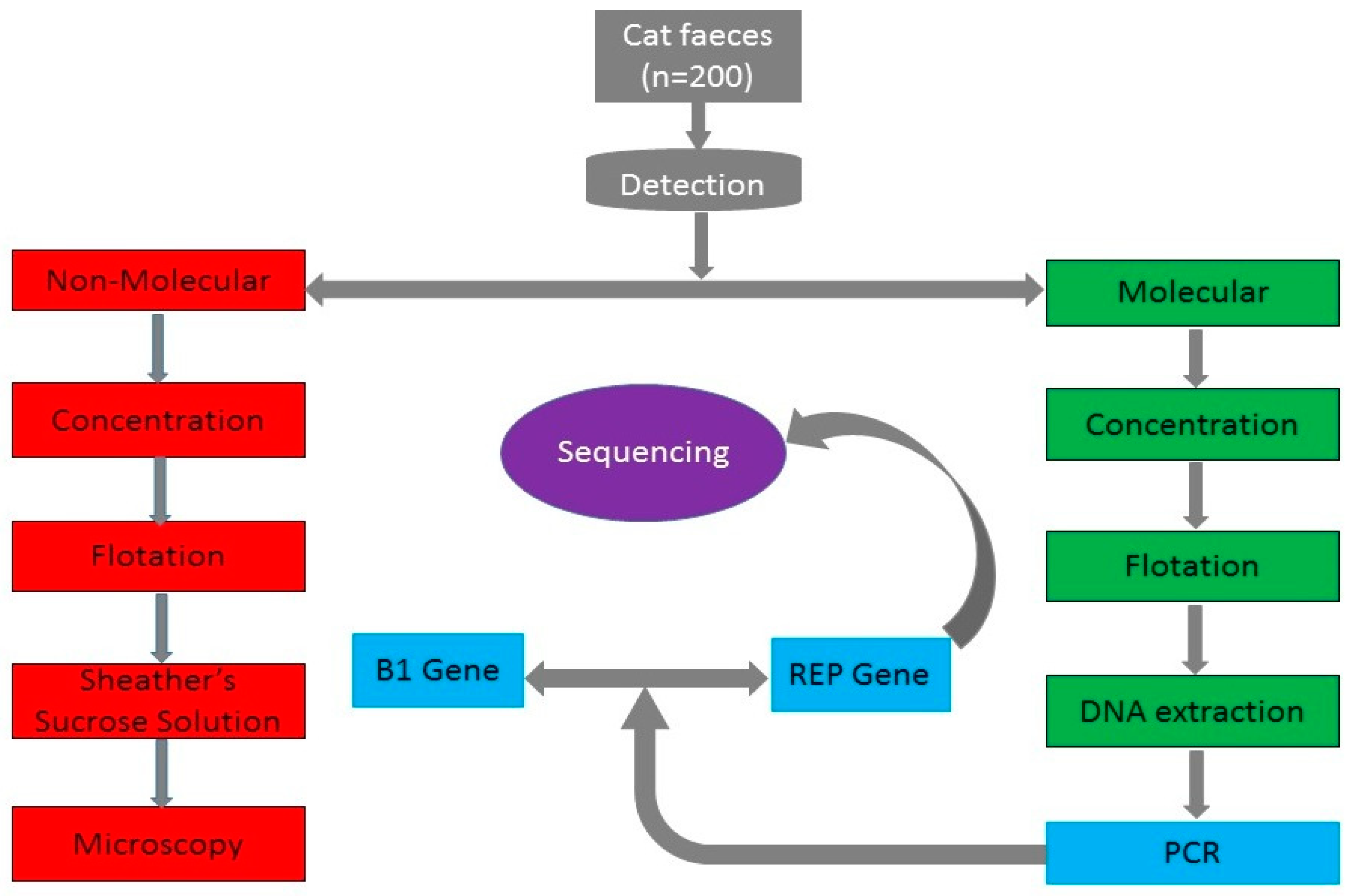
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Cat Faecal Sample Collection
4.3. Copro-Microscopic Detection of T. gondii-Like Oocysts in Faeces
4.4. Extraction of Oocyst DNA in Cat’s Faeces
4.5. Reference Samples
4.6. Copro-PCR Assays for the Detection of T. gondii in Cat Faeces
4.7. Sequencing of the REP Gene Amplified PCR Product
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dubey, J.; Jones, J. Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans and animals in the United States. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1257–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyebji, S.; Seizova, S.; Hannan, A.J.; Tonkin, C.J. Toxoplasmosis: A pathway to neuropsychiatric disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 96, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, Z.; Hajissa, K. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection among patients in Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 33, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Sahimin, N.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Ariffin, F.; Behnke, J.M.; Basáñez, M.-G.; Walker, M.; Lewis, J.W.; Noordin, R.; Abdullah, K.A.; Mohd Zain, S.N. Socio-demographic determinants of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence in migrant workers of Peninsular Malaysia. Parasit Vectors 2017, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemoh, W.; Farhana, N.; Noor, A. Prevalence and risk factors of Toxoplasma infection—An update in Malaysian pregnant women. Trop. Biomed. 2019, 36, 694–702. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, D.E.; Chirukandoth, S.; Dubey, J.P. Biology and epidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii in man and animals. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2005, 6, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumètre, A.; Dardé, M.-L. How to detect Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in environmental samples? FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4200-9236-3. [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Darde, M.-L. Epidemiology of and Diagnostic Strategies for Toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, J.; Dubey, J.; Miller, N.L. Toxoplasma gondii in cats: Fecal stages identified as coccidian oocysts. Science 1970, 167, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichan, P.; Mercier, A.; Galal, L.; Mahittikorn, A.; Ariey, F.; Morand, S.; Boumédiène, F.; Udonsom, R.; Hamidovic, A.; Murat, J.B.; et al. Geographical distribution of Toxoplasma gondii genotypes in Asia: A link with neighboring continents. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 53, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.T.E.; Amal, R.N.; Noor Hayati, M.I.; Kino, H.; Anisah, N.; Norhayati, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Mohammed Abdullah, M.; Fatmah, M.S.; Roslida, A.R. Seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis among migrant workers from different Asian countries working in Malaysia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2008, 39, 9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Enter, B.J.D.; Lau, Y.-L.; Ling, C.L.; Watthanaworawit, W.; Sukthana, Y.; Lee, W.-C.; Nosten, F.; McGready, R. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Refugee and Migrant Pregnant Women along the Thailand-Myanmar Border. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, E.; Germain, E.; Poulle, M.-L.; Ruette, S.; Devillard, S.; Say, L.; Villena, I.; Aubert, D.; Gilot-Fromont, E. Environmental determinants of spatial and temporal variations in the transmission of Toxoplasma gondii in its definitive hosts. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2013, 2, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger-Schoch, A.E.; Herrmann, D.C.; Schares, G.; Müller, N.; Bernet, D.; Gottstein, B.; Frey, C.F. Prevalence and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii in feline faeces (oocysts) and meat from sheep, cattle and pigs in Switzerland. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 177, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemoh, W.; Sawangjaroen, N.; Nissapatorn, V.; Sermwittayawong, N. Molecular investigation on the occurrence of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in cat feces using TOX-element and ITS-1 region targets. Vet. J. 2016, 215, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabritz, A.A.; Miller, M.A.; Atwill, E.R.; Gardner, I.A.; Leutenegger, C.M.; Melli, A.C.; Conrad, P.A. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii-like oocysts in cat feces and estimates of the environmental oocyst burden. J. Am. Vet. Med Assoc. 2007, 231, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, D.C.; Pantchev, N.; Vrhovec, M.G.; Barutzki, D.; Wilking, H.; Fröhlich, A.; Lüder, C.G.K.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G. Atypical Toxoplasma gondii genotypes identified in oocysts shed by cats in Germany. Int. J. Parasitol. 2010, 40, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancianti, F.; Nardoni, S.; Ariti, G.; Parlanti, D.; Giuliani, G.; Papini, R.A. Cross-sectional survey of Toxoplasma gondii infection in colony cats from urban Florence (Italy). J. Feline Med. Surg. 2010, 12, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schares, G.; Vrhovec, M.G.; Pantchev, N.; Herrmann, D.C.; Conraths, F.J. Occurrence of Toxoplasma gondii and Hammondia hammondi oocysts in the faeces of cats from Germany and other European countries. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 152, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokelainen, P.; Simola, O.; Rantanen, E.; Näreaho, A.; Lohi, H.; Sukura, A. Feline toxoplasmosis in Finland: Cross-sectional epidemiological study and case series study. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, T.R.; Nunes, C.M.; Luvizotto, M.C.R.; de Moura, A.B.; Lopes, W.D.Z.; da Costa, A.J.; Bresciani, K.D.S. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in environmental samples from public schools. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 171, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramini, J.J.; Stephen, C.; Dubey, J.P.; Engelstoft, C.; Schwantje, H.; Ribble, C.S. Potential contamination of drinking water with Toxoplasma gondii oocysts. Epidemiol. Infect. 1999, 122, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Zhu, X.Q.; Sundar, N.; Zhang, H.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Su, C. Genetic and biologic characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolates of cats from China. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 145, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salant, H.; Hamburger, J.; Spira, D.T. A Comparative Analysis of Coprologic Diagnostic Methods for Detection of Toxoplama gondii in Cats. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilly, E.L.; Wortham, C.D. High prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii oocyst shedding in stray and pet cats (Felis catus) in Virginia, United States. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronesi, F.; Santoro, A.; Milardi, G.L.; Diaferia, M.; Morganti, G.; Ranucci, D.; Gabrielli, S. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii in faeces of privately owned cats using two PCR assays targeting the B1 gene and the 529-bp repetitive element. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Masatoshi, N.; Sudhir, K. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Razik, K.A.; Barakat, A.M.A.; Hussein, H.A.; Younes, A.M.; Elfadaly, H.A.; Eldebaky, H.A.; Soliman, Y.A. Seroprevalence, isolation, molecular detection and genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii from small ruminants in Egypt. J. Parasit. Dis. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.F.; Ngui, R.; Muhammad Aidil, R.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Rohela, M. Current status of parasitic infections among Pangkor Island community in Peninsular Malaysia. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 31, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andiappan, H.; Nissapatorn, V.; Sawangjaroen, N.; Nyunt, M.H.; Lau, Y.-L.; Khaing, S.L.; Aye, K.M.; Mon, N.C.N.; Tan, T.-C.; Kumar, T.; et al. Comparative study on Toxoplasma infection between Malaysian and Myanmar pregnant women. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andiappan, H.; Nissapatorn, V.; Sawangjaroen, N.; Khaing, S.-L.; Salibay, C.C.; Cheung, M.M.M.; Dungca, J.Z.; Chemoh, W.; Xiao Teng, C.; Lau, Y.-L.; et al. Knowledge and practice on Toxoplasma infection in pregnant women from Malaysia, Philippines, and Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon-Mong, G.-J.; Che Mat Seri, N.A.A.; Sharma, R.S.-K.; Andiappan, H.; Tan, T.-C.; Lim, Y.A.-L.; Nissapatorn, V. Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasmosis among People Having Close Contact with Animals. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantlay, J.C.; Ingram, D.J.; Meredith, A.L. A Review of Zoonotic Infection Risks Associated with the Wild Meat Trade in Malaysia. EcoHealth 2017, 14, 361–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrawathani, P.; Nurulaini, R.; Zanin, C.M.; Premaalatha, B.; Adnan, M.; Jamnah, O.; Khor, S.K.; Khadijah, S.; Lai, S.Z.; Shaik, M.A.B.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in pigs, goats, cattle, dogs and cats in peninsular Malaysia. Trop. Biomed. 2008, 25, 257–258. [Google Scholar]
- Emelia, O.; Rahana, A.R.; Mohamad Firdaus, A.; Cheng, H.S.; Nursyairah, M.S.; Fatinah, A.S.; Azmawati, M.N.; Siti, N.A.M.; Aisah, M.Y. IgG avidity assay: A tool for excluding acute toxoplasmosis in prolonged IgM titer sera from pregnant women. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 31, 633–640. [Google Scholar]
- Fazly, Z.; Nurulaini, R.; Shafarin, M.; Fariza, N.; Zawida, Z.; Muhamad, H.; Adnan, M.; Premaalatha, B.; Erwanas, A.; Zaini, C. Zoonotic parasites from exotic meat in Malaysia. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 30, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Normaznah, Y.; Azizah, M.A.; Azuan, M.I.; Latifah, I.; Rahmat, S.; Nasir, M.A. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Rodents from Various Locations in Peninsular Malaysia. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2015, 46, 388–395. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, A.; Bakar, O.C.; Adam, N.F.; Osman, H.; Osman, A.; Suleiman, A.H.; Manaf, M.R.A.; Selamat, M.I. Seropositivity and serointensity of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies and DNA among patients with schizophrenia. Korean J. Parasitol. 2015, 53, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, W.A.; Manimegalai, V.; Chandrawathani, P.; Nurulaini, R.; Zaini, C.M.; Premaalatha, B. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Malaysian Cattle. Malays. J. Vet. Res. 2011, 2, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ching, X.T.; Fong, M.Y.; Lau, Y.L. Evaluation of Immunoprotection Conferred by the Subunit Vaccines of GRA2 and GRA5 against Acute Toxoplasmosis in BALB/c Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emelia, O.; Zeehaida, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Rohela, M.; Saadatnia, G.; Yeng, C.; Rahmah, N. An Assay for Selection of Sera with Circulating Toxoplasma gondii Antigens. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2009, 31, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajissa, K.; Zakaria, R.; Suppian, R.; Mohamed, Z. An evaluation of a recombinant multiepitope based antigen for detection of Toxoplasma gondii specific antibodies. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling Lau, Y.; Yik Fong, M. Toxoplasma gondii: Serological characterization and immunogenicity of recombinant surface antigen 2 (SAG2) expressed in the yeast Pichia pastoris. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 119, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatnia, G.; Ghaffarifar, F.; Khalilpour, A.; Amerizadeh, A.; Rahmah, N. Saadatnia et al_ 2011_A Toxoplasma gondii 10 kDa in vitro excretory secretory antigen reactive with human IgM and IgA antibodies.pdf. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 28, 606–614. [Google Scholar]
- Puvanesuaran, V.R.; Noordin, R.; Balakrishnan, V. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii Isolates from Wild Boars in Peninsular Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puvanesuaran, V.R.; Noordin, R.; Balakrishnan, V. Isolation and Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii from Free-Range Ducks in Malaysia. Avian Dis. 2013, 57, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolören, Z.; Dubey, J.P. A review of toxoplasmosis in humans and animals in Turkey. Parasitology 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, K.; Bahia-Oliveira, L.; Dixon, B.; Dumètre, A.; de Wit, L.A.; VanWormer, E.; Villena, I. Environmental transmission of Toxoplasma gondii: Oocysts in water, soil and food. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, E.; Lemoine, M.; Poulle, M.-L.; Ravat, M.-C.; Romand, S.; Thulliez, P.; Villena, I.; Aubert, D.; Rabilloud, M.; Riche, B.; et al. Spatial distribution of soil contamination by Toxoplasma gondii in relation to cat defecation behaviour in an urban area. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotteland, C.; Gilot-Fromont, E.; Aubert, D.; Poulle, M.-L.; Dupuis, E.; Dardé, M.-L.; Forin-Wiart, M.-A.; Rabilloud, M.; Riche, B.; Villena, I. Spatial distribution of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in soil in a rural area: Influence of cats and land use. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 205, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lass, A.; Pietkiewicz, H.; Modzelewska, E.; Dumètre, A.; Szostakowska, B.; Myjak, P. Detection of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in environmental soil samples using molecular methods. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kappany, Y.M.; Rajendran, C.; Ferreira, L.R.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Abu-Elwafa, S.A.; Hilali, M.; Dubey, J.P. High Prevalence of Toxoplasmosis in Cats from Egypt: Isolation of Viable Toxoplasma gondii, Tissue Distribution, and Isolate Designation. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, V.; Foley, P. Infectious disease prevalence in a feral cat population on Prince Edward Island, Canada. Can. Vet. J. 2011, 52, 979–982. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Choudhary, S.; Tilahun, G.; Tiao, N.; Gebreyes, W.A.; Zou, X.; Su, C. Genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from Ethiopian feral cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Su, C.; Cortés, J.A.; Sundar, N.; Gomez-Marin, J.E.; Polo, L.J.; Zambrano, L.; Mora, L.E.; Lora, F.; Jimenez, J.; et al. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in cats from Colombia, South America and genetic characterization of T. gondii isolates. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 141, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatepe, B.; Babür, C.; Karatepe, M.; Kiliç, S.; Dündar, B. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies and intestinal parasites in stray cats from Nigde, Turkey. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 7, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miró, G.; Montoya, A.; Jiménez, S.; Frisuelos, C.; Mateo, M.; Fuentes, I. Prevalence of antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii and intestinal parasites in stray, farm and household cats in Spain. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Wang, H.; Su, C.; Shan, D.; Cui, X.; Yang, N.; Lv, C.; Liu, Q. Isolation and characterization of Toxoplasma gondii strains from stray cats revealed a single genotype in Beijing, China. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 187, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavalla, M.; Asgarian, F.; Kazemi, F. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in cats of southwest of Iran. Infect. Dis. Health 2017, 22, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Feng, H.L.; Nie, H.; Tu, P.; Zhang, Q.L.; Hu, M.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Zhao, J.L. Survey on the contamination of Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in the soil of public parks of Wuhan, China. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 184, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Comparative infectivity of oocysts and bradyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii for intermediate (mice) and definitive (cats) hosts. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 140, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lass, A.; Pietkiewicz, H.; Szostakowska, B.; Myjak, P. The first detection of Toxoplasma gondii DNA in environmental fruits and vegetables samples. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 31, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, J.L. Direct and Sensitive Detection of a Pathogenic Protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii, by Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, W.L.; Vercammen, M.; Braekeleer, J.D.; Verschueren, H. Identification of a 200- to 300-fold repetitive 529 bp DNA fragment in Toxoplasma gondii, and its use for diagnostic and quantitative PCRp. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.-K.; Lee, S.-E.; Lim, H.; Cho, J.; Kim, D.-G.; Song, H.; Kim, M.-J.; Shin, E.-H.; Chai, J.-Y. Toxoplasma gondii B1 Gene Detection in Feces of Stray Cats around Seoul, Korea and Genotype Analysis of Two Laboratory-Passaged Isolates. Korean J. Parasitol. 2015, 53, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.L.; Dubey, J.P. Waterborne toxoplasmosis—Recent developments. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 124, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salant, H.; Markovics, A.; Spira, D.T.; Hamburger, J. The development of a molecular approach for coprodiagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 146, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabritz, H.A.; Conrad, P.A. Cats and Toxoplasma: Implications for Public Health. Zoonoses Public Health 2010, 57, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.A.; Kurdzielewicz, S.; Jeanniot, E.; Dupuis, E.; Marnef, F.; Aubert, D.; Villena, I.; Poulle, M.-L. Spatial distribution of soil contaminated with Toxoplasma gondii oocysts in relation to the distribution and use of domestic cat defecation sites on dairy farms. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrey, E.F.; Yolken, R.H. Toxoplasma oocysts as a public health problem. Trends Parasitol. 2013, 29, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanWormer, E.; Fritz, H.; Shapiro, K.; Mazet, J.A.; Conrad, P.A. Molecules to modeling: Toxoplasma gondii oocysts at the human–animal–environment interface. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 36, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C.; Ajioka, J.W.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Sibley, L.D. Genetic analyses of atypical Toxoplasma gondii strains reveal a fourth clonal lineage in North America. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, G.V.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. Genotyping studies of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from Africa revealed that the archetypal clonal lineages predominate as in North America and Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 155, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, E.S.; Sadraei, J.; Dalimi, A.; Namroodi, S.; Pirestani, M. Phylogenetic Analysis of Toxoplasma gondii Type II and Type III by PCRRFLP Plus Sequencing on Wild-Rats of Golestan Forest, Iran. J. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mo, X.-W.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Luo, Q.-L.; Wen, H.-Q.; Wei, W.; Zhang, A.-M.; Du, J.; Lu, F.-L. Phylogeny and virulence divergency analyses of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from China. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, H.F.J.; Gennari, S.M.; Dubey, J.P.; Su, C. Population structure and mouse-virulence of Toxoplasma gondii in Brazil. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
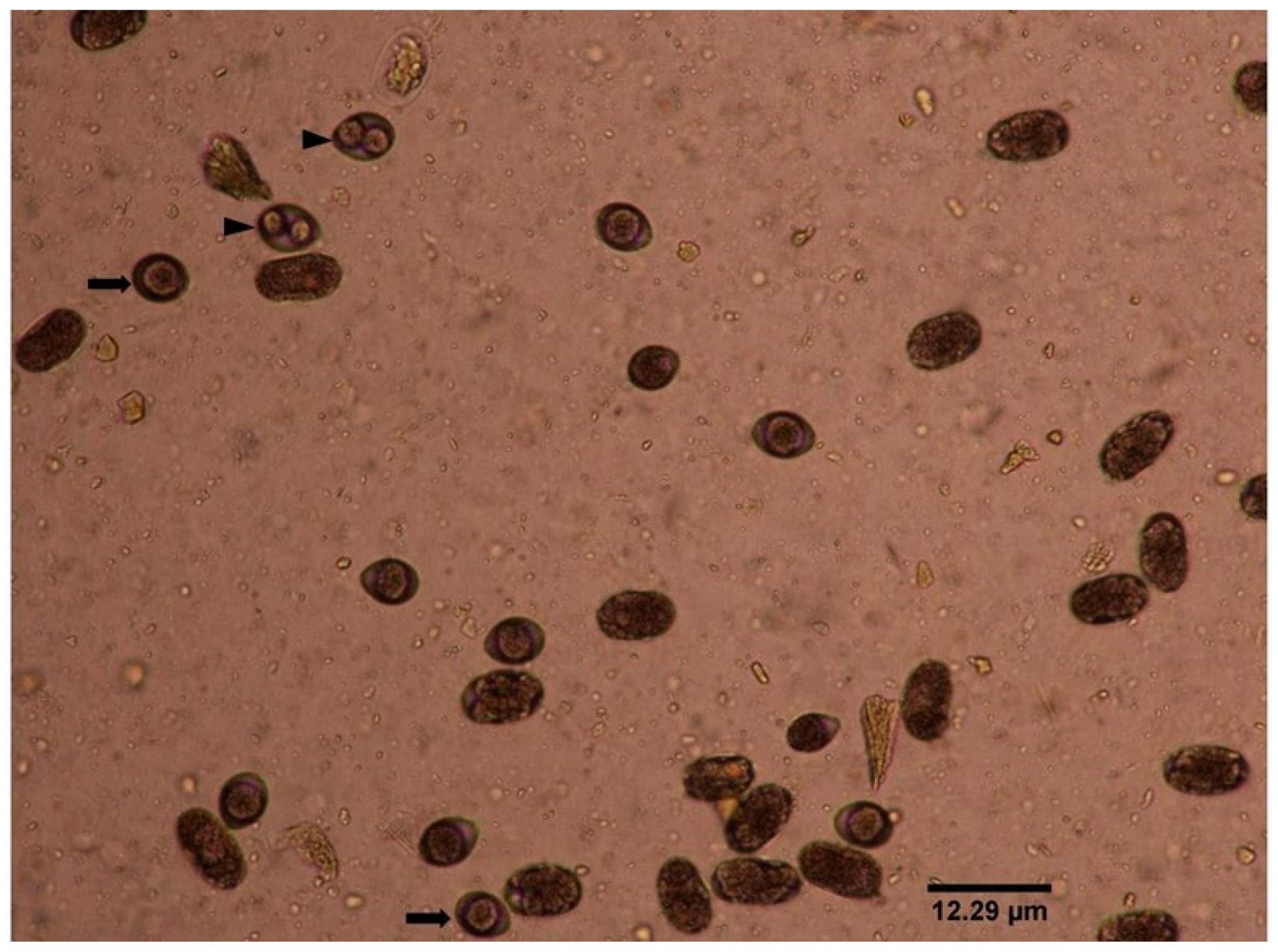



| Cats | No. of Samples Examined | Copro-Microscopy Positive (%) | Copro-PCR Positive (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 Gene | REP Gene | |||
| PC | 100 | 2 (2.0) | 4 (4.0) | 4 (4.0) |
| FRC | 100 | 5 (5.0) | 13 (13.0) | 13 (13.0) |
| Total | 200 | 7 (3.5) | 17 (8.5) | 17 (8.5) |
| Sample Number | Cat | Copro-Microscopy | Copro-PCR | Sequencing and BLAST Results of REP Gene (A146527) | Isolate Designation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | REP | Identified Specie | % Identity | GenBank Accession Number | ||||
| 2B | PC | + | + | + | T. gondii | 95.8 | KU599165 | TgCtMy01 |
| 3A | FRC | + | + | + | T. gondii | 94.4 | KX963354 | TgCtMy02 |
| 5A | FRC | − | + | + | T. gondii | 93.6 | MH560583 | TgCtMy03 |
| 6A | FRC | + | + | + | T. gondii | 93.6 | KY628128 | TgCtMy04 |
| 7A | FRC | − | + | + | T. gondii | 100 | KU873097 | TgCtMy05 |
| 8B | PC | + | + | + | T. gondii | 100 | KU873097 | TgCtMy06 |
| 9B | PC | − | + | + | T. gondii | 96.7 | KX963354 | TgCtMy07 |
| 16B | FRC | − | + | + | T. gondii | 95.8 | DQ779188 | TgCtMy08 |
| 26B | FRC | + | + | + | T. gondii | 98.9 | KX963354 | TgCtMy09 |
| 27A | FRC | − | + | + | T. gondii | 97.4 | KU599165 | TgCtMy10 |
| 36A | FRC | − | + | + | T. gondii | 97.8 | KX963354 | TgCtMy11 |
| 36B | FRC | + | + | + | T. gondii | 100 | KU873097 | TgCtMy12 |
| 37A | FRC | − | + | + | T. gondii | 100 | KX963354 | TgCtMy13 |
| 40B | PC | − | + | + | T. gondii | 97.8 | KU599811 | TgCtMy14 |
| 42B | FRC | − | + | + | T. gondii | 97.8 | KX963354 | TgCtMy15 |
| 50A | FRC | + | + | + | T. gondii | 89.7 | DQ779188 | TgCtMy16 |
| Target Gene | Primer Sequence | Amplicon Size | PCR Cycles | Annealing Temperature | GenBank Accession no. | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 gene | F (5′ GGA ACT GCA TCC GTT CAT GAG 3′) R (5′ TCT TTA AAG CGT TCG TGG TC 3′) | 194 bp | 35 | 57 °C | AF179871 | [67] |
| REP gene | F (5′ AGG CGA GGG TGA GGA TGA 3′) R (5′ TCG TCT CGT CTG GAT CGC AT 3′) | 134 bp | 35 | 62.8 °C | AF146527 | [68] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasiru Wana, M.; Mohd Moklas, M.A.; Watanabe, M.; Zasmy Unyah, N.; Alhassan Abdullahi, S.; Ahmad Issa Alapid, A.; Nordin, N.; Basir, R.; Abd Majid, R. Molecular Detection and Genetic Diversity of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Cat Faeces from Klang Valley, Malaysia, Using B1 and REP Genes in 2018. Pathogens 2020, 9, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070576
Nasiru Wana M, Mohd Moklas MA, Watanabe M, Zasmy Unyah N, Alhassan Abdullahi S, Ahmad Issa Alapid A, Nordin N, Basir R, Abd Majid R. Molecular Detection and Genetic Diversity of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Cat Faeces from Klang Valley, Malaysia, Using B1 and REP Genes in 2018. Pathogens. 2020; 9(7):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070576
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasiru Wana, Mohammed, Mohamad Aris Mohd Moklas, Malaika Watanabe, Ngah Zasmy Unyah, Sharif Alhassan Abdullahi, Ashraf Ahmad Issa Alapid, Norshariza Nordin, Rusliza Basir, and Roslaini Abd Majid. 2020. "Molecular Detection and Genetic Diversity of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Cat Faeces from Klang Valley, Malaysia, Using B1 and REP Genes in 2018" Pathogens 9, no. 7: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070576
APA StyleNasiru Wana, M., Mohd Moklas, M. A., Watanabe, M., Zasmy Unyah, N., Alhassan Abdullahi, S., Ahmad Issa Alapid, A., Nordin, N., Basir, R., & Abd Majid, R. (2020). Molecular Detection and Genetic Diversity of Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts in Cat Faeces from Klang Valley, Malaysia, Using B1 and REP Genes in 2018. Pathogens, 9(7), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9070576






