Giardia duodenalis Induces Apoptosis in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Parasite Culture
2.3. LDH Detection
2.4. Apoptosis Analysis
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
2.7. Detections of Intracellular ROS and Glutathione (GSH) Level
2.8. Western Blots Analysis
2.9. Immunofluorescence Assays
2.10. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) Analysis
2.11. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) Assay
2.12. Cell Viability Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Giardia Trophozoites Promote Apoptosis and Induce Cell Cycle Arrest
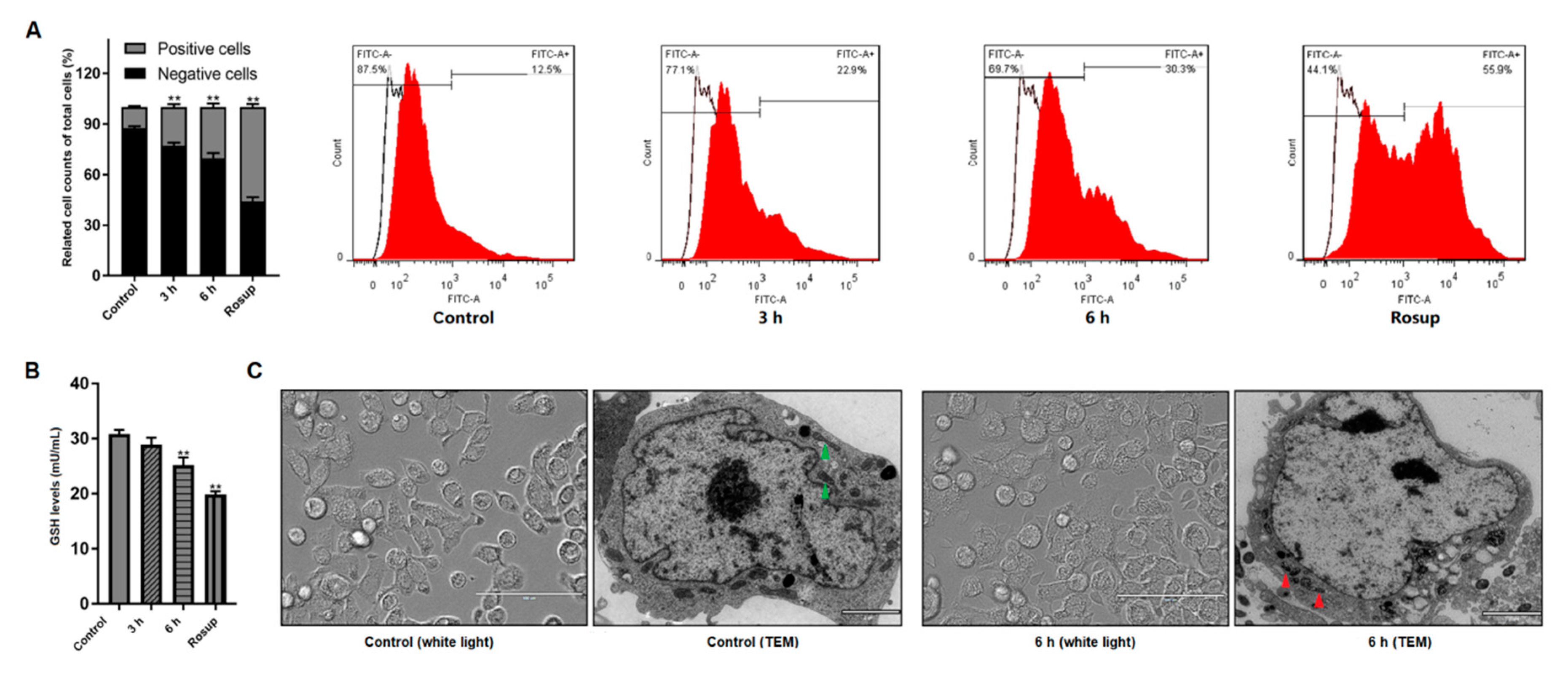
3.2. Giardia Trophozoites Trigger ROS Accumulation and Induce Mitochondria Damage in Caco-2 Cells
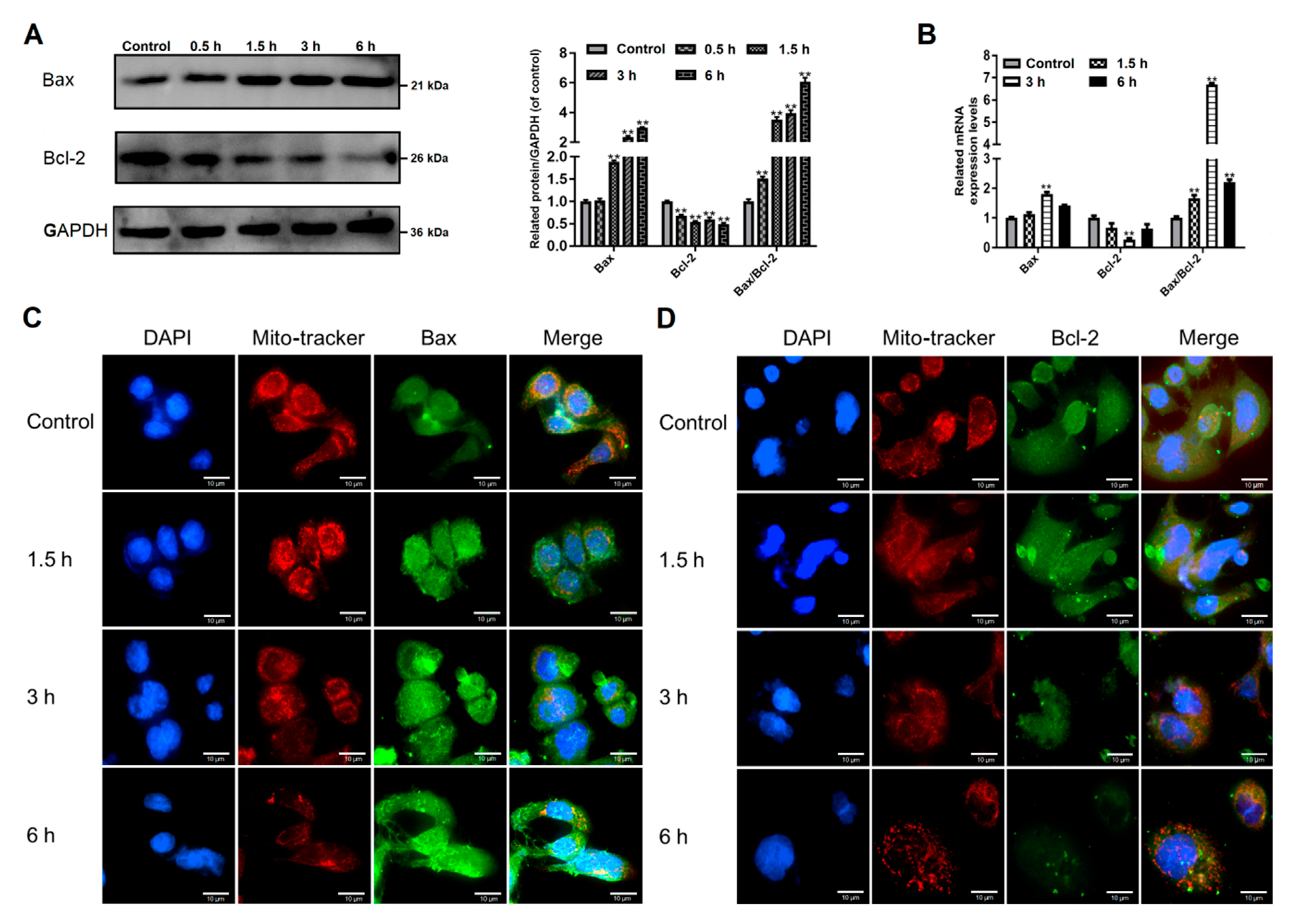
3.3. Giardia Trophozoites Regulate Expression of Bax/Bcl-2 and Localization of Bax in Caco-2 Cells
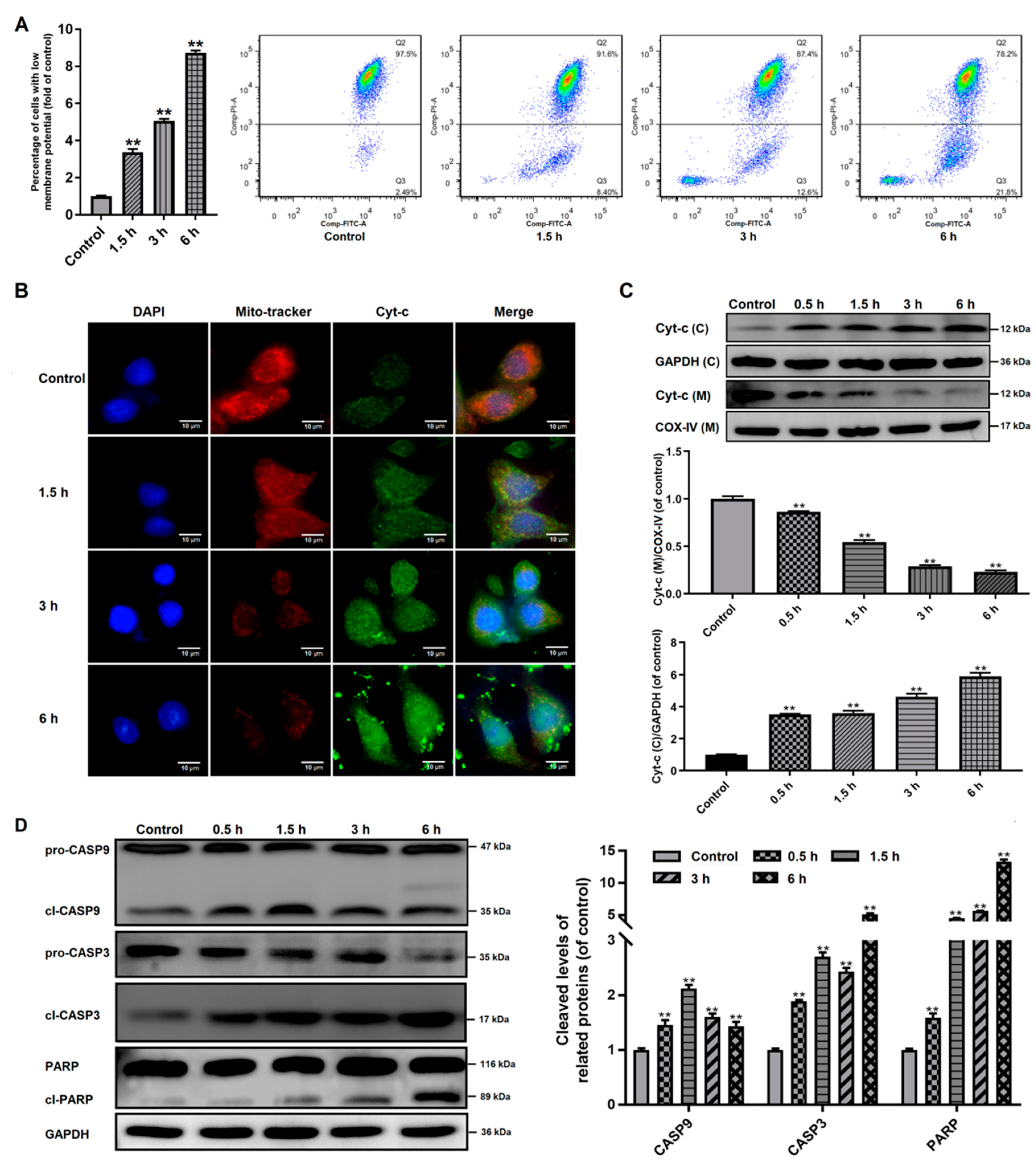
3.4. Effects of Giardia Trophozoite Treatment on Mitochondrial Function and Regulation of Apoptotic-Related Proteins in Caco-2 Cells
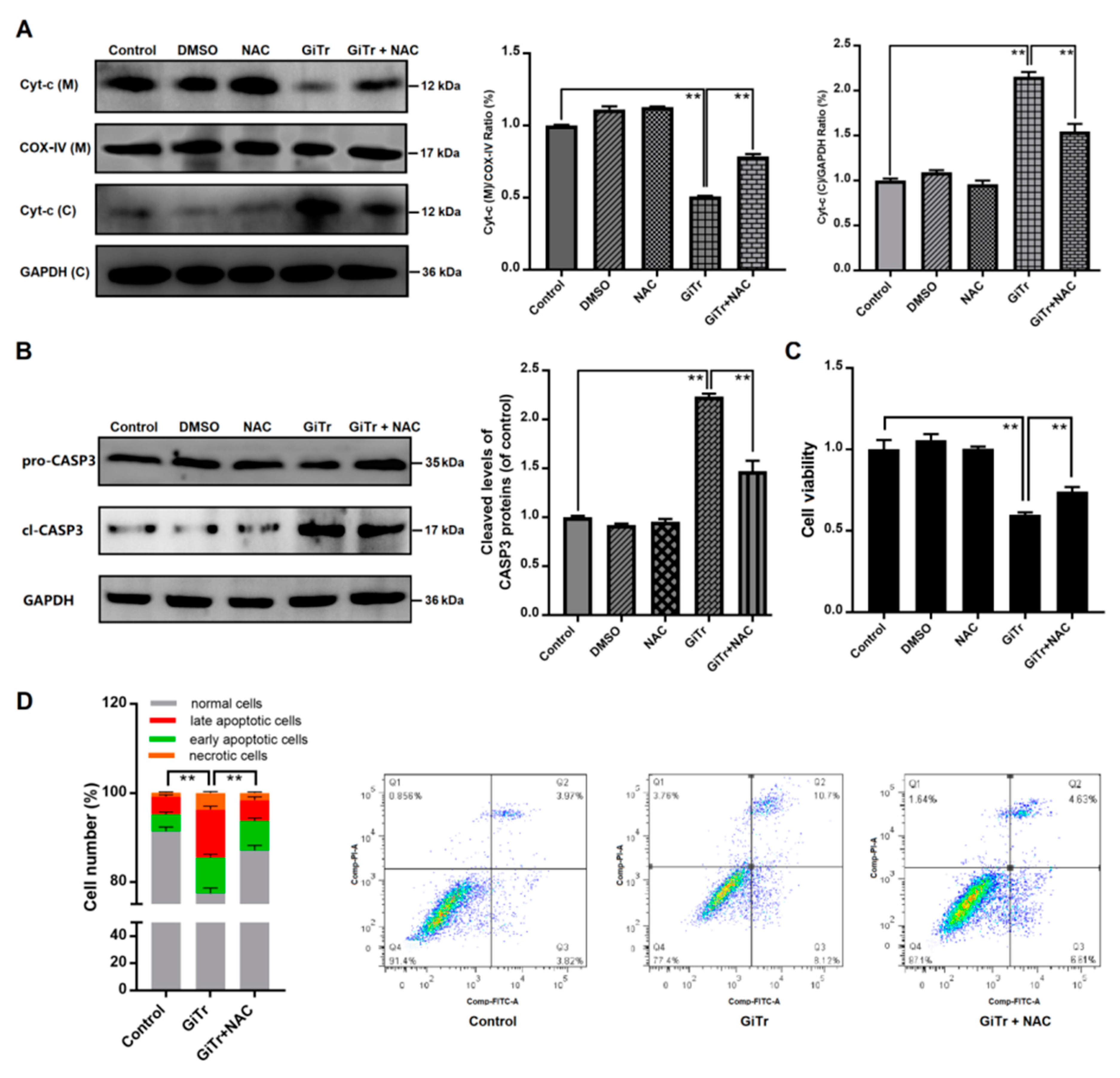
3.5. The Role of ROS Production in Giardia Trophozoites-Induced Caco-2 Cell Apoptosis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vivancos, V.; González-Alvarez, I.; Bermejo, M.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, M. Giardiasis: Characteristics, pathogenesis and new insights about treatment. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1287–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einarsson, E.; Ma’ayeh, S.; Svärd, S.G. An up-date on Giardia and giardiasis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 34, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotton, J.A.; Beatty, J.K.; Buret, A.G. Host parasite interactions and pathophysiology in Giardia infections. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogawski, E.T.; Bartelt, L.A.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Seidman, J.C.; Samie, A.; Havt, A.; Babji, S.; Trigoso, D.R.; Qureshi, S.; Shakoor, S.; et al. Determinants and impact of Giardia infection in the first 2 years of life in the MAL-ED Birth Cohort. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2017, 6, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minetti, C.; Chalmers, R.M.; Beeching, N.J.; Probert, C.; Lamden, K. Giardiasis. BMJ 2016, 355, i5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambuy, Y.; De Angelis, I.; Ranaldi, G.; Scarino, M.L.; Stammati, A.; Zucco, F. The Caco-2 cell line as a model of the intestinal barrier: Influence of cell and culture-related factors on Caco-2 cell functional characteristics. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2005, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiloglu, S.; Capanoglu, E.; Grootaert, C.; Van Camp, J. Anthocyanin absorption and metabolism by human intestinal Caco-2 cells—A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21555–21574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxström-Lindquist, K.; Ringqvist, E.; Palm, D.; Svärd, S. Giardia lamblia-induced changes in gene expression in differentiated Caco-2 human intestinal epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 8204–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma’ayeh, S.Y.; Liu, J.; Peirasmaki, D.; Hörnaeus, K.; Bergström Lind, S.; Grabherr, M.; Bergquist, J.; Svärd, S.G. Characterization of the Giardia intestinalis secretome during interaction with human intestinal epithelial cells: The impact on host cells. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ma’ayeh, S.; Peirasmaki, D.; Lundström-Stadelmann, B.; Hellman, L.; Svärd, S.G. Secreted Giardia intestinalis cysteine proteases disrupt intestinal epithelial cell junctional complexes and degrade chemokines. Virulence 2018, 9, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia-Brigagão, C.; Morgado-Díaz, J.A.; De Souza, W. Giardia disrupts the arrangement of tight, adherens and desmosomal junction proteins of intestinal cells. Parasitol. Int. 2012, 61, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma’ayeh, S.Y.; Knörr, L.; Sköld, K.; Garnham, A.; Ansell, B.R.E.; Jex, A.R.; Svärd, S.G. Responses of the differentiated intestinal epithelial cell line Caco-2 to infection with the Giardia intestinalis GS isolate. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panaro, M.A.; Cianciulli, A.; Mitolo, V.; Mitolo, C.I.; Acquafredda, A.; Brandonisio, O.; Cavallo, P. Caspase-dependent apoptosis of the HCT-8 epithelial cell line induced by the parasite Giardia intestinalis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 51, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, A.C.; Teoh, D.A.; Scott, K.G.; Meddings, J.B.; Macnaughton, W.K.; Buret, A.G. Strain-dependent induction of enterocyte apoptosis by Giardia lamblia disrupts epithelial barrier function in a caspase-3-dependent manner. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3673–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, E.; Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, A.N.; Nozaki, T.; Ganguly, S. Oxidative stress-induced cell cycle blockage and a protease-independent programmed cell death in microaerophilic Giardia lamblia. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2009, 3, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, S.; Gupta, D. Crosstalk of toll-like receptors signaling and Nrf2 pathway for regulation of inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, B.R.; Roy, B. Cysticercus fasciolaris infection induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in rat liver: A strategy for host-parasite cross talk. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 2617–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; He, L.; Zhang, A.; Li, Q.; Hu, W.; Chen, H.; Du, J.; Shen, J. Toxoplasma gondii isolate with genotype Chinese 1 triggers trophoblast apoptosis through oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in mice. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 154, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, K.; Das, J.; Pal, P.B.; Sil, P.C. Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1157–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wei, Z.; Fang, R.; Li, X.; Li, W. Giardia duodenalis induces extrinsic pathway of apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells through activation of TNFR1 and K63 de-ubiquitination of RIP1 in vitro. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, B.J.; Gillin, F.D. Methods for Giardia culture, cryopreservation, encystation, and excystation in vitro. Giardia 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, L.; Seeger, W.; Ermert, L.; Hänze, J.; Stahl, U.; Grimminger, F.; Kummer, W.; Bohle, R.M. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR after laser-assisted cell picking. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, J.H.; Kang, B.H.; Yang, J.B.; Rhee, Y.E.; Noh, H.T.; Choi, I.W.; Cha, G.H.; Yuk, J.M.; Lee, Y.H. Trichomonas vaginalis induces SiHa cell apoptosis by NF-κB inactivation via reactive oxygen species. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 3904870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Blanco, A.; García-Sáez, A.J. Bax, Bak and beyond-mitochondrial performance in apoptosis. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkinshaw, R.W.; Czabotar, P.E. The BCL-2 family of proteins and mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilisation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Shamoto-Nagai, M.; Maruyama, W.; Osawa, T.; Naoi, M. Phytochemicals prevent mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and protect SH-SY5Y cells against apoptosis induced by PK11195, a ligand for outer membrane translocator protein. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, R.; Kheirollahi, A.; Davoodi, J. Apaf-1: Regulation and function in cell death. Biochimie 2017, 135, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery-Corbin, S.J.; Vuong, D.; Lacey, E.; Svärd, S.G.; Ansell, B.R.E.; Jex, A.R. Proteomic diversity in a prevalent human-infective Giardia duodenalis sub-species. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enea, M.; Pereira, E.; de Almeida, M.P.; Araújo, A.M.; de Lourdes Bastos, M.; Carmo, H. Gold nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and apoptosis in human kidney cells. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.Y.; Stovall, K.; Franklin, J.L. The intrinsic apoptotic pathway lies upstream of oxidative stress in multiple organs. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 158, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Hu, L.; Yang, B.; Fang, X.; Gao, Z.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wu, X.; Shu, Y.; et al. Erlotinib promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated injury in the intestinal epithelium. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 278, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.M.; Duckworth, C.A.; Watson, A.J.M.; Frey, M.R.; Miguel, J.C.; Burkitt, M.D.; Sutton, R.; Hughes, K.R.; Hall, L.J.; Caamaño, J.H.; et al. A mouse model of pathological small intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis and shedding induced by systemic administration of lipopolysaccharide. Dis. Models Mech. 2013, 6, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudzińska, E.; Gryzinska, M.; Ognik, K.; Gil-Kulik, P.; Kocki, J. Oxidative stress and effect of treatment on the oxidation product decomposition processes in IBD. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 7918261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diebold, L.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial ROS regulation of proliferating cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Chang, H.; Li, H.; Wang, S. Induction of reactive oxygen species: An emerging approach for cancer therapy. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Wu, C.-Q.; Li, Z.-J.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, Q.-J.; Ding, R.-G. Characterizing the mechanism of thiazolidinedione-induced hepatotoxicity: An in vitro model in mitochondria. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmcol. 2015, 284, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Yang, C.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Sai, N.; Dong, X.; Yin, X.; Ni, J. Matrine exerts hepatotoxic effects via the ROS-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis pathway and inhibition of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1045345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santucci, R.; Sinibaldi, F.; Cozza, P.; Polticelli, F.; Fiorucci, L. Cytochrome c: An extreme multifunctional protein with a key role in cell fate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Chen, Q.; Dou, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Shao, H.; Ling, P.; Liu, F.; Wang, F. Lower range of molecular weight of xanthan gum inhibits cartilage matrix destruction via intrinsic bax-mitochondria cytochrome c-caspase pathway. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, C. Porcine deltacoronavirus induces caspase-dependent apoptosis through activation of the cytochrome c-mediated intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. Virus Res. 2018, 253, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, H. Induction of apoptosis in TNF-treated L929 cells in the presence of necrostatin-1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldar, S.; Khaniani, M.S.; Derakhshan, S.M.; Baradaran, B. Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis and roles in cancer development and treatment. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 2129–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, C.H.; Singer, S.M. Recent advances in the Giardia-host relationship reveal danger lurking behind the smile. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargantini, P.R.; Serradell, M.D.C.; Ríos, D.N.; Tenaglia, A.H.; Luján, H.D. Antigenic variation in the intestinal parasite Giardia lamblia. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 32, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Ghosh, S.; Samra, H.; Vinayak, V.K.; Ganguly, N.K. Identification and characterization of an excretory-secretory product from Giardia lamblia. Parasitology 2001, 123, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, T.T.; Ellis, C.C.; Grajeda, B.I.; De Chatterjee, A.; Almeida, I.C.; Das, S. A targeted mass spectrometric analysis reveals the presence of a reduced but dynamic sphingolipid metabolic pathway in an ancient protozoan, Giardia lamblia. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Accession No. | Primer (5′ to 3′) | Product Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bax | NM_138763.4 | Forward: CCCGAGAGGTCTTTTTCCGAG, Reverse: CCAGCCCATGATGGTTCTGAT | 155 bp |
| Bcl-2 | XM_017025917.2 | Forward: GGTGGGGTCATGTGTGTGG, Reverse: CGGTTCAGGTACTCAGTCATCC | 89 bp |
| GAPDH | NM_001357943.2 | Forward: ACAACTTTGGTATCGTGGAAGG, Reverse: GCCATCACGCCACAGTTTC | 101 bp |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Fang, R.; Wei, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Li, W. Giardia duodenalis Induces Apoptosis in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway In Vitro. Pathogens 2020, 9, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090693
Liu L, Fang R, Wei Z, Wu J, Li X, Li W. Giardia duodenalis Induces Apoptosis in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway In Vitro. Pathogens. 2020; 9(9):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090693
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lin, Rui Fang, Ziyan Wei, Jingxue Wu, Xiaoyun Li, and Wei Li. 2020. "Giardia duodenalis Induces Apoptosis in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway In Vitro" Pathogens 9, no. 9: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090693
APA StyleLiu, L., Fang, R., Wei, Z., Wu, J., Li, X., & Li, W. (2020). Giardia duodenalis Induces Apoptosis in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway In Vitro. Pathogens, 9(9), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090693






