Control of a Round Jet Intermittency and Transition to Turbulence by Means of an Annular Synthetic Jet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
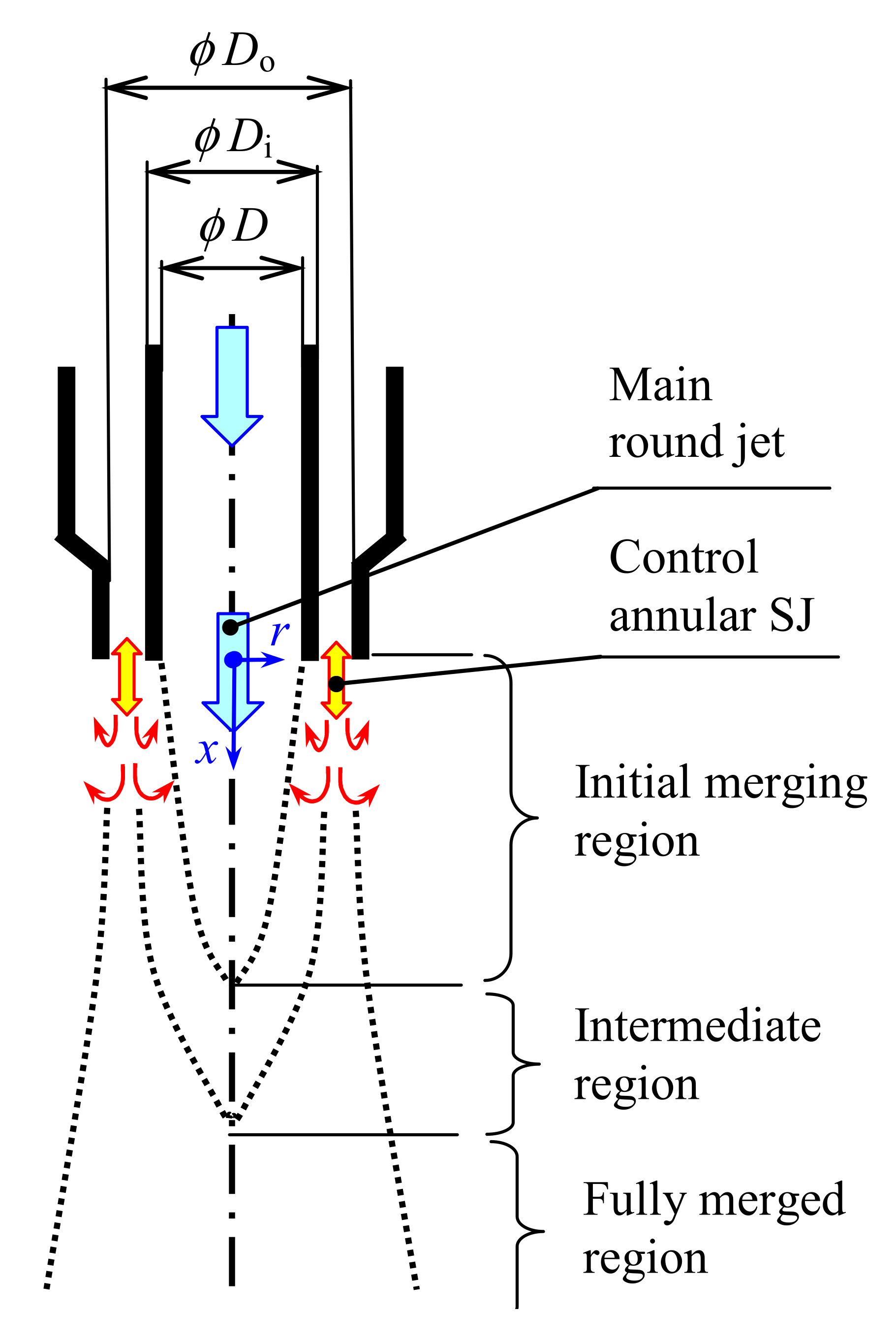
Problem Parameters
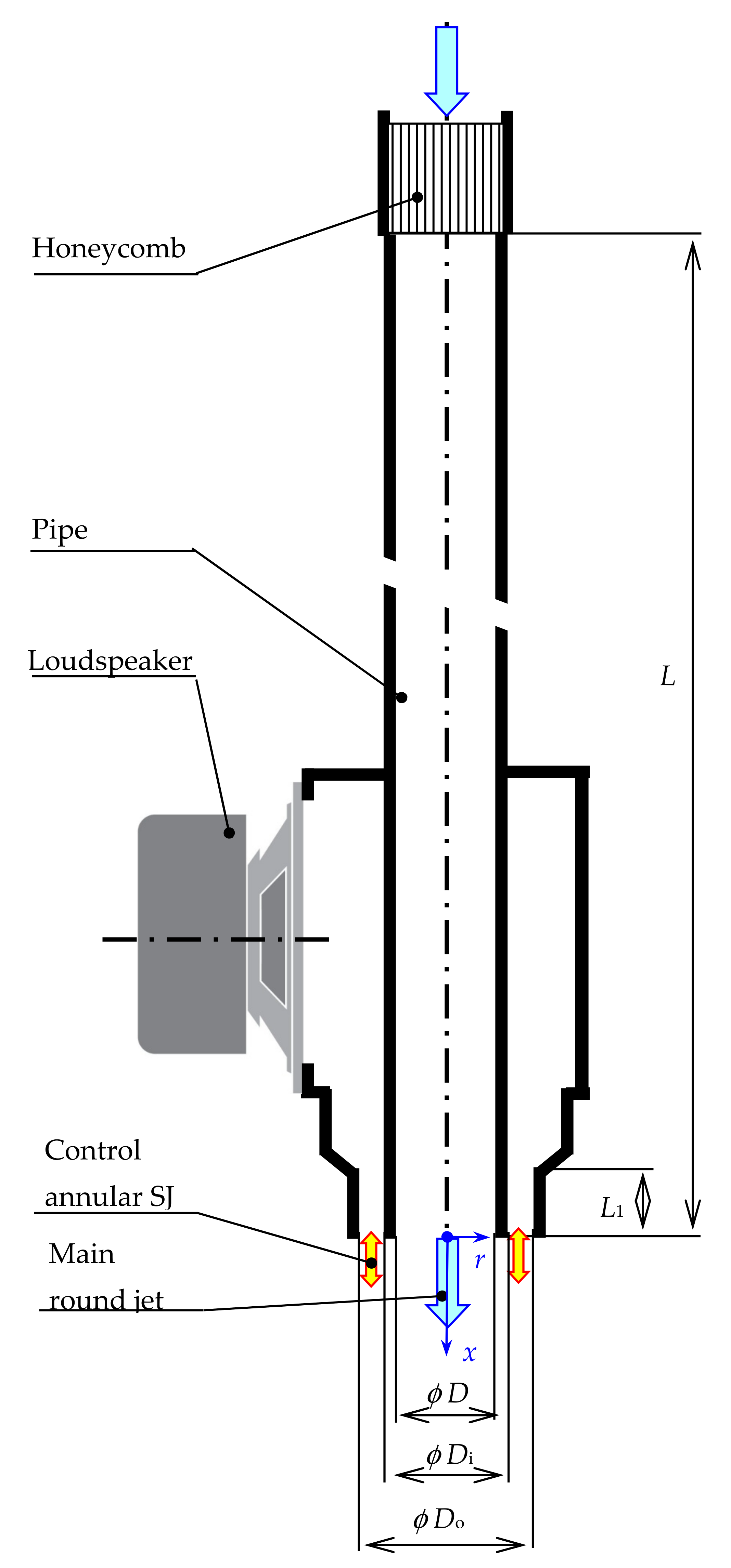
2. Experimental Setup and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Frequency Characteristics of the SJ Actuator
3.2. Parameters of Examined Jets
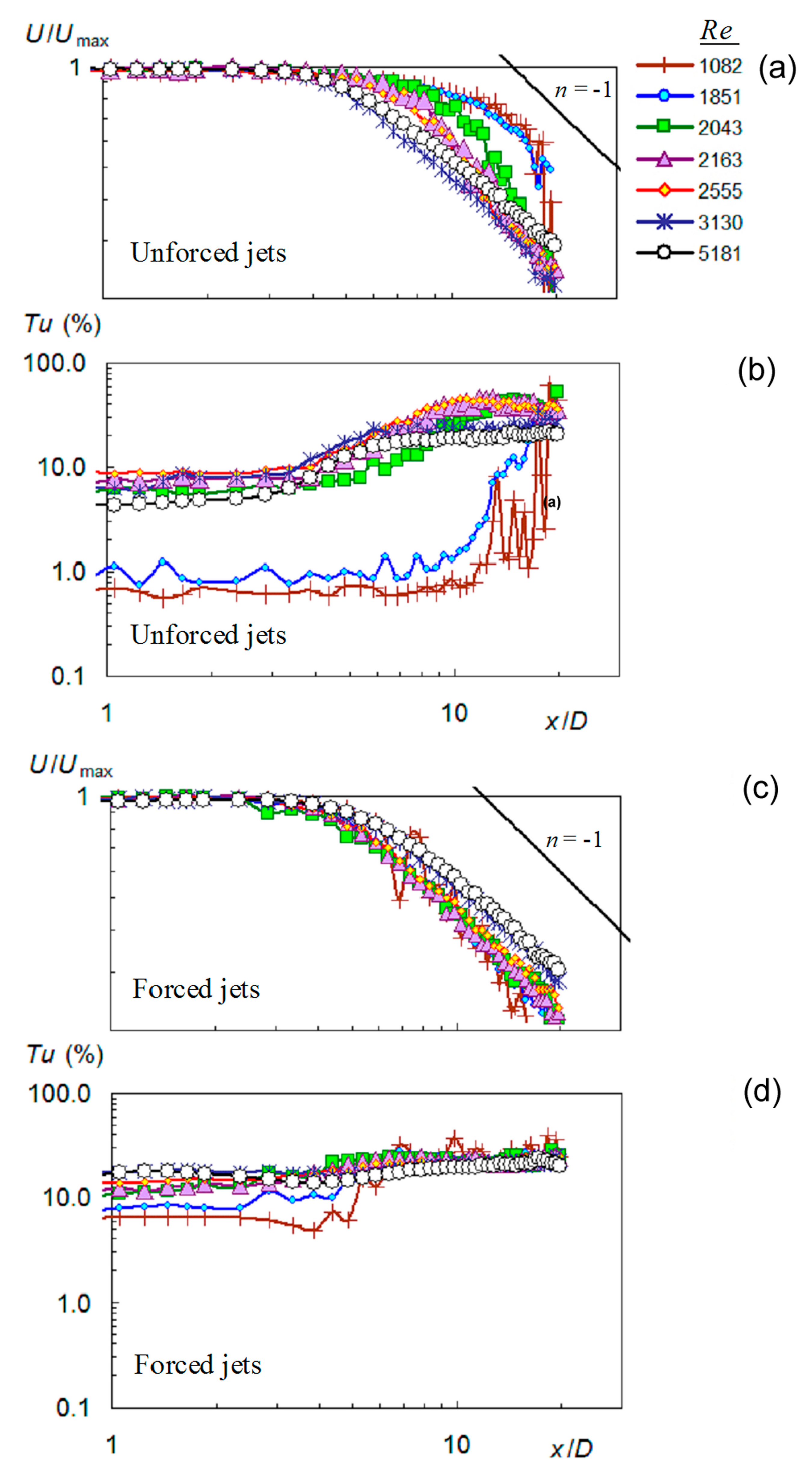
3.3. Velocity Fields
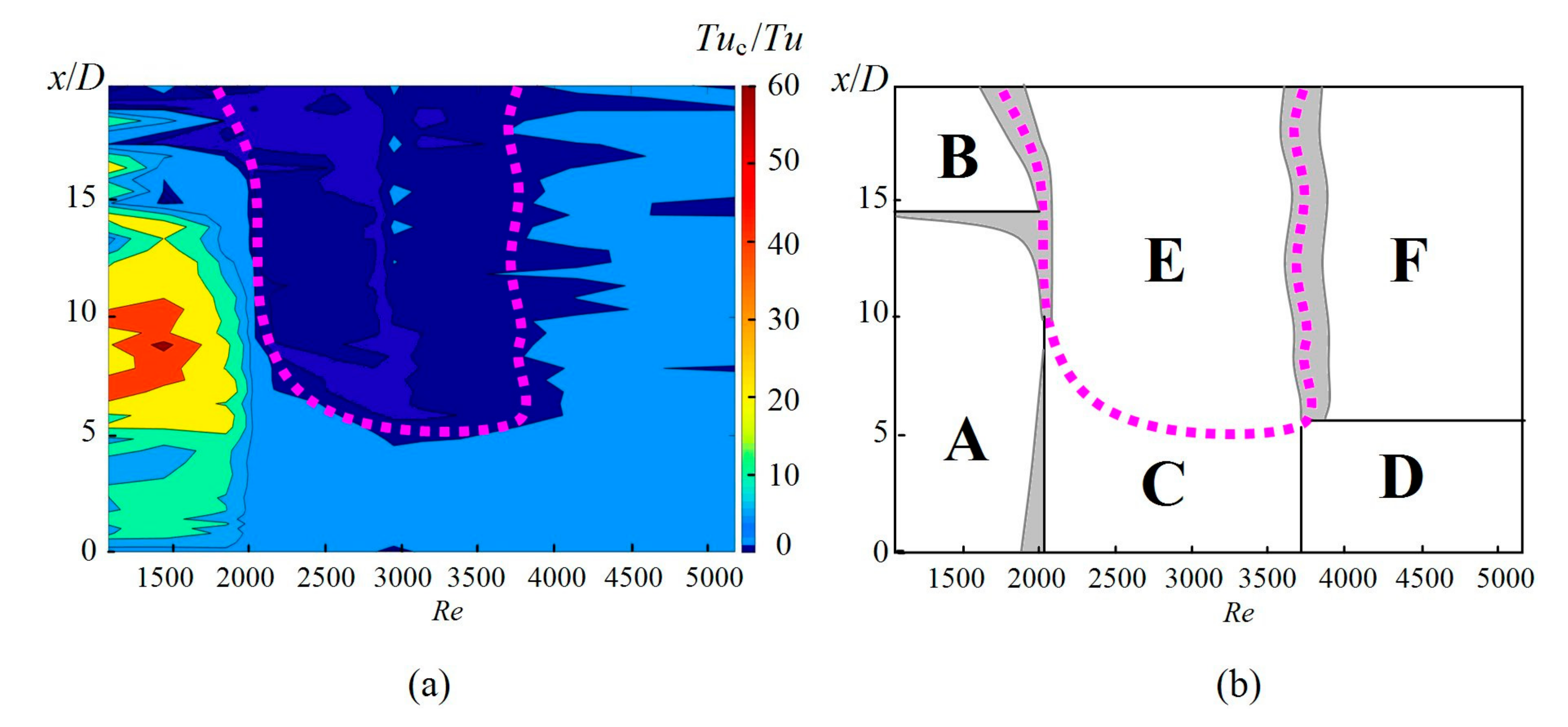
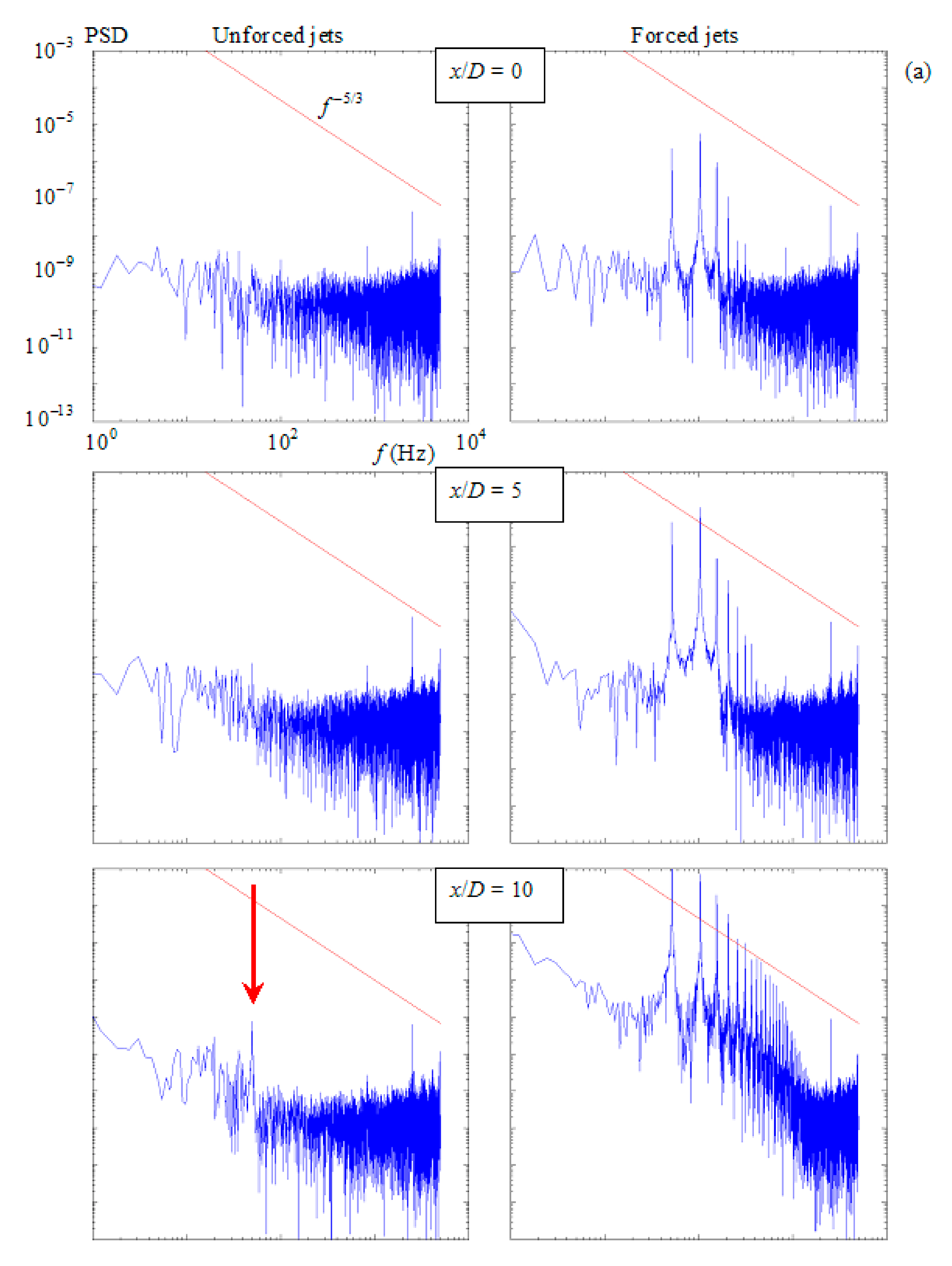
3.4. Power Spectral Density of Velocity Fluctuations
3.4.1. Unforced Jets
3.4.2. Forced Jets
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| B | width of the annular slot, B = (Do − Di)/2 |
| Di | inner diameter of annular nozzle |
| Do | outer diameter of annular nozzle |
| f | driving frequency (Hz) |
| k | velocity ratio, k = Umax/Um |
| r | radial coordinate, see Figure 1 and Figure 2 |
| Re | Reynolds number of round jet, Re = Um D/ν |
| ReSJ | Reynolds number of control SJ, ReSJ = U0Do/ν |
| SJ | synthetic jet |
| t | time |
| T | time period, T = 1/f |
| Tu | turbulence intensity, Tu = uRMS/U |
| uRMS | fluctuation velocity, (m/s) |
| u0 | velocity of the SJ at the nozzle exit, x = 0 |
| U | time-mean velocity, (m/s) |
| U0 | time-mean orifice velocity of SJ, see Equation (1) |
| Um | mean exit velocity of the main jet, (m/s) |
| Umax | maximum velocity in the exit profile of the main round jet, (m/s) |
| x | axial coordinate, see Figure 1 and Figure 2 |
| ν | kinematic viscosity of the working fluid (air) |
| ρ | density of the working fluid (air) |
| γ | intermittency factor |
References
- Schlichting, H. Boundary-Layer Theory; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Abramovich, G.N. The Theory of Turbulent Jets; The MitPress: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevins, R.D. Applied Fluid Dynamics Handbook; Krieger Publishing: Malabar, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bejan, A. Convection Heat Transfer; Wiley Interscience Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Crow, S.C.; Champagne, F.H. Orderly structure in jet turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 1971, 48, 547–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yule, A.J. Large-scale structure in the mixing layer of a round jet. J. Fluid Mech. 1978, 89, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.K.M.F.; Husain, H.S. Passive and active control of jet turbulence. In Turbulence Management and Relaminarisation; Liepmann, H.W., Narasimha, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, K.B.M.Q. Axis switching and spreading of an asymmetric jet: The role of coherent structure dynamics. J. Fluid Mech. 1996, 316, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, S.; Ueda, H. The large-scale coherent structure in the intermittent region of the self-preserving round free jet. J. Fluid Mech. 1985, 152, 337–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.O. Structure of mixing layers and jets. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1991, 44, 119–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T.; Sakakibara, J. On the vortical structure in a round jet. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 25106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiedler, H.; Fernholz, H.-H. On management and control of turbulent shear flows. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 1990, 27, 305–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad-el-Hak, M. Modern developments in flow control. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1996, 49, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Sullivan, J. Heat transfer and flow structures in an excited circular impinging jet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1996, 39, 3695–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibens, V. Discrete noise spectrum generated by acoustically excited jet. AIAA J. 1980, 18, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasov, E.V.; Ginevskii, A.S. The aeroacoustic interaction problem. Sov. Phys. Acoust. 1980, 26, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lepičovský, J.K.K.; Ahuja, R.H.; Burrin, R.H. Tone excited jets, part III: Flow measurements. J. Sound Vibr. 1985, 102, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.K.; Yoo, J.Y.; Choi, H. Vortex pairing in an axisymmetric jet using two-frequency acoustic forcing at low to moderate strouhal numbers. Exp. Fluids 1998, 25, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejrazka, J.; Tihon, J.; Marty, P.; Sobolík, V. Effect of an external excitation on the flow structure in a circular impinging jet. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 105102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, C.; Cho, H. Heat transfer and flow structures in axisymmetric impinging jet controlled by vortex pairing. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2001, 22, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, J.; Sigurdson, L. Cross-jet influenced by a concentric synthetic jet. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koso, T.; Kinoshita, T. agitated turbulent flowfield of a circular jet with an annular synthetic jet actuator. J. Fluid Sci. Technol. 2008, 3, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, B.L.; Glezer, A. The formation and evolution of synthetic jets. Phys. Fluids 1998, 10, 2281–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinson, S.G.; Reizes, J.A.; Hong, G. An experimental and numerical study of synthetic jet flow. Aeronaut. J. 2001, 105, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glezer, A.; Amitay, M. Synthetic jets. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2002, 34, 503–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, K.; Mittal, R. Synthetic Jets, Fundamentals and Applications; CRC Press Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pack, L.G.; Seifert, A. periodic excitation for jet vectoring and enhanced spreading. J. Aircr. 2001, 38, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cater, J.E.; Soria, J. The evolution of round zero-net-mass-flux jets. J. Fluid Mech. 2002, 472, 167–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauphinee, T.M. Acoustic air pump. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1957, 28, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallas, Q.; Holman, R.; Nishida, T.; Carroll, B.; Sheplak, M.; Cattafesta, L. Lumped element modeling of piezoelectric-driven synthetic jet actuators. AIAA J. 2003, 41, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holman, R.; Utturkar, Y.; Mittal, R.; Smith, B.L.; Cattafesta, L. Formation criterion for synthetic jets. AIAA J. 2005, 43, 2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Tang, H.; Zhong, S. Vortex roll-up criterion for synthetic jets. AIAA J. 2009, 47, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trávníček, Z.; Broučková, Z.; Kordík, J. Formation criterion for axisymmetric synthetic jets at high stokes numbers. AIAA J. 2012, 50, 2012–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, L.; Girfoglio, M.; Coppola, G. Modeling and experimental validation of the frequency response of synthetic jet actuators. AIAA J. 2014, 52, 1733–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, C.S.; Cardone, G.; Soria, J. On the behaviour of impinging zero-net-mass-flux jets. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 810, 25–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilarranz, J.L.; Traub, L.W.; Rediniotis, O.K. A new class of synthetic jet actuators—Part I: Design, fabrication and bench top characterization. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2005, 127, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trávníček, Z.; Vít, T.; Tesař, V. Hybrid synthetic jet as the non-zero-net-mass-flux jet. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 081701-1–081701-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.S.; Ro, J.J.; Yang, M.T.; Chang, W.H. Investigation of piezoelectrically generated synthetic jet flow. J. Vis. 2009, 12, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shan, R.; Zhang, C.; Feng, L. Experimental investigation of a novel two-dimensional synthetic jet. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 2010, 29, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordík, J.; Travnicek, Z. Optimal diameter of nozzles of synthetic jet actuators based on electrodynamic transducers. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2017, 86, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.L.; Glezer, A. Jet vectoring using synthetic jets. J. Fluid Mech. 2002, 458, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Rampunggoon, P. On the virtual aeroshaping effect of synthetic jets. Phys. Fluids 2002, 14, 1533–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amitay, M.; Glezer, A. Controlled transients of flow reattachment over stalled airfoils. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2002, 23, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tensi, J.; Boué, I.; Paillé, F.; Dury, G. Modification of the wake behind a circular cylinder by using synthetic jets. J. Vis. 2002, 5, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Chiekh, M.; Béra, J.-C.; Sunyach, M. Synthetic jet control for flows in a diffuser: Vectoring, spreading and mixing enhancement. J. Turbul. 2003, 4, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Millet, F.; Wood, N.J. The behaviour of circular synthetic jets in a laminar boundary layer. Aeronaut. J. 2005, 109, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G. Effectiveness of micro synthetic jet actuator enhanced by flow instability in controlling laminar separation caused by adverse pressure gradient. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 132, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamburello, D.A.; Amitay, M. Three-dimensional interactions of a free jet with a perpendicular synthetic jet. J. Turbul. 2007, 8, N38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassour, Y.; Stricker, J.; Wolfshtein, M. Heat transfer from a small pulsating jet. In Proceedings of the International Heat Transfer Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–22 August 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kercher, D.S.; Lee, J.-B.; Brand, O.; Allen, M.G.; Glezer, A. Microjet cooling devices for thermal management of electronics. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 2003, 26, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trávníček, Z.; Tesař, V. Annular synthetic jet used for impinging flow mass–transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 46, 3291–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillespie, M.B.; Black, W.Z.; Rinehart, C.; Glezer, A. Local convective heat transfer from a constant heat flux flat plate cooled by synthetic air jets. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 990–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arik, M. An investigation into feasibility of impingement heat transfer and acoustic abatement of meso scale synthetic jets. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 1483–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiorgue, P.; Persoons, T.; McGuinn, A.; Murray, D. Heat transfer mechanisms in an impinging synthetic jet for a small jet-to-surface spacing. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2009, 33, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mangate, L.D.; Chaudhari, M.B. Experimental study on heat transfer characteristics of a heat sink with multiple-orifice synthetic jet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 103, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persoons, T.; McGuinn, A.; Murray, D.B. A general correlation for the stagnation point Nusselt number of an axisymmetric impinging synthetic jet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 3900–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Yeoh, G.; Timchenko, V.; Reizes, J. Heat transfer enhancement in micro-channel with multiple synthetic jets. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 48, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trávníček, Z.; Antošová, Z. Impingement heat transfer to the synthetic jet issuing from a nozzle with an oscillating cross section. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 153, 106349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Llanca, L.; Ortega, A. Vortex dynamics and mechanisms of heat transfer enhancement in synthetic jet impingement. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 112, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broučková, Z.; Trávníček, Z.; Vit, T. Synthetic and continuous jets impinging on a circular cylinder. Heat Transf. Eng. 2018, 40, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broučková, Z. Active Control of the Jet Flow in Coaxial Arrangement. Master’s Thesis, Czech Technical University, Prague, Czech Republic, 2012. (In Czech). [Google Scholar]
- Trávníček, Z.; Fedorchenko, A.I.; Wang, A.-B. Enhancement of synthetic jets by means of an integrated valve-less pump, Part I: Design of the actuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2005, 120, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, R.E.; Gendrich, C.P. The turbulence burst detection algorithm of Z. Zaric. In Proceedings of the 1988 Zoltan Zaric Memorial Conference on Near-Wall Turbulence, Dubrovnik, Yugoslavia, May 1988; Kline, S., Afgan, N.H., Eds.; Hemisphere Publishing Corp.: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 911–931. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1990nrw..book..911F/abstract (accessed on 20 June 2021).

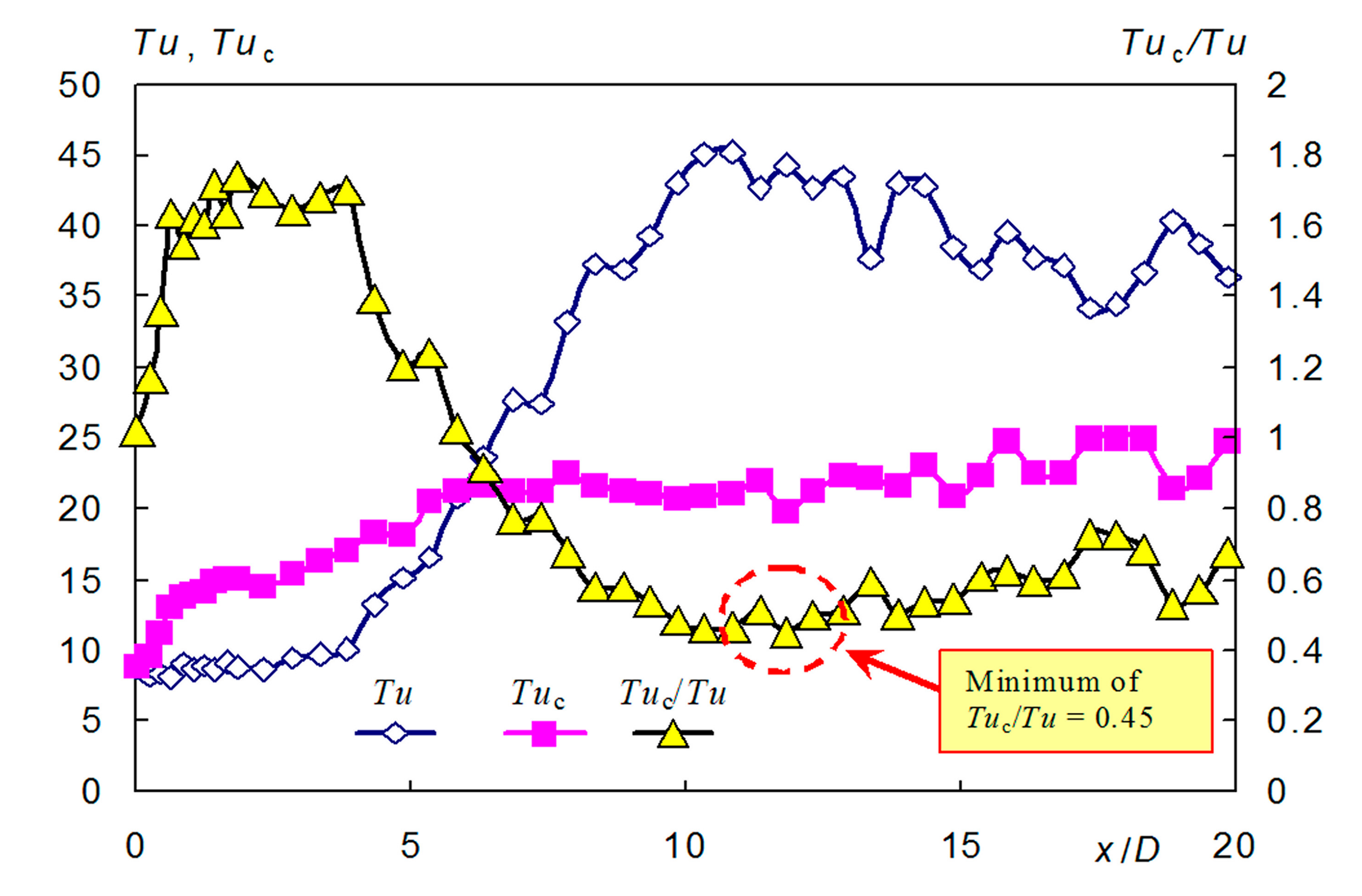
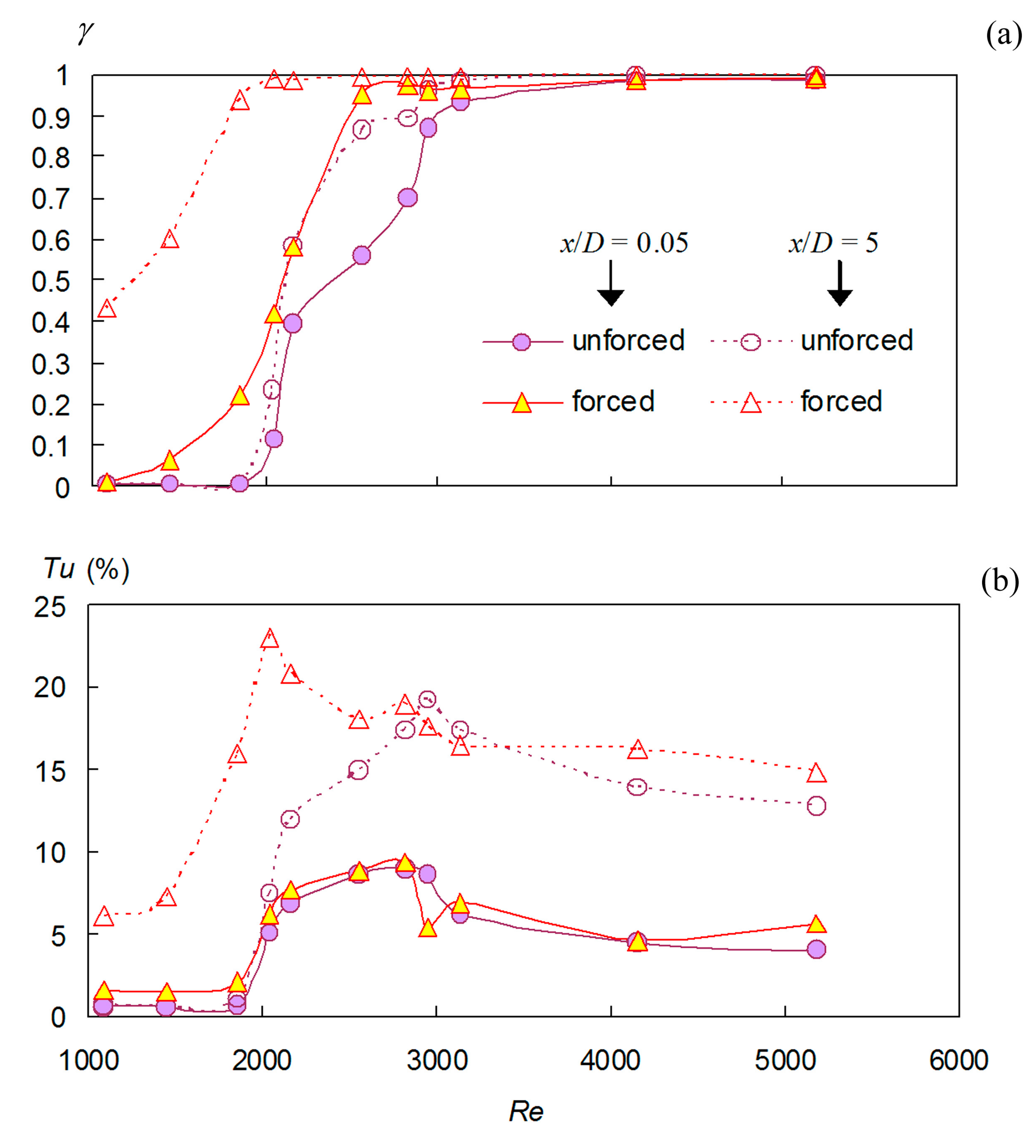
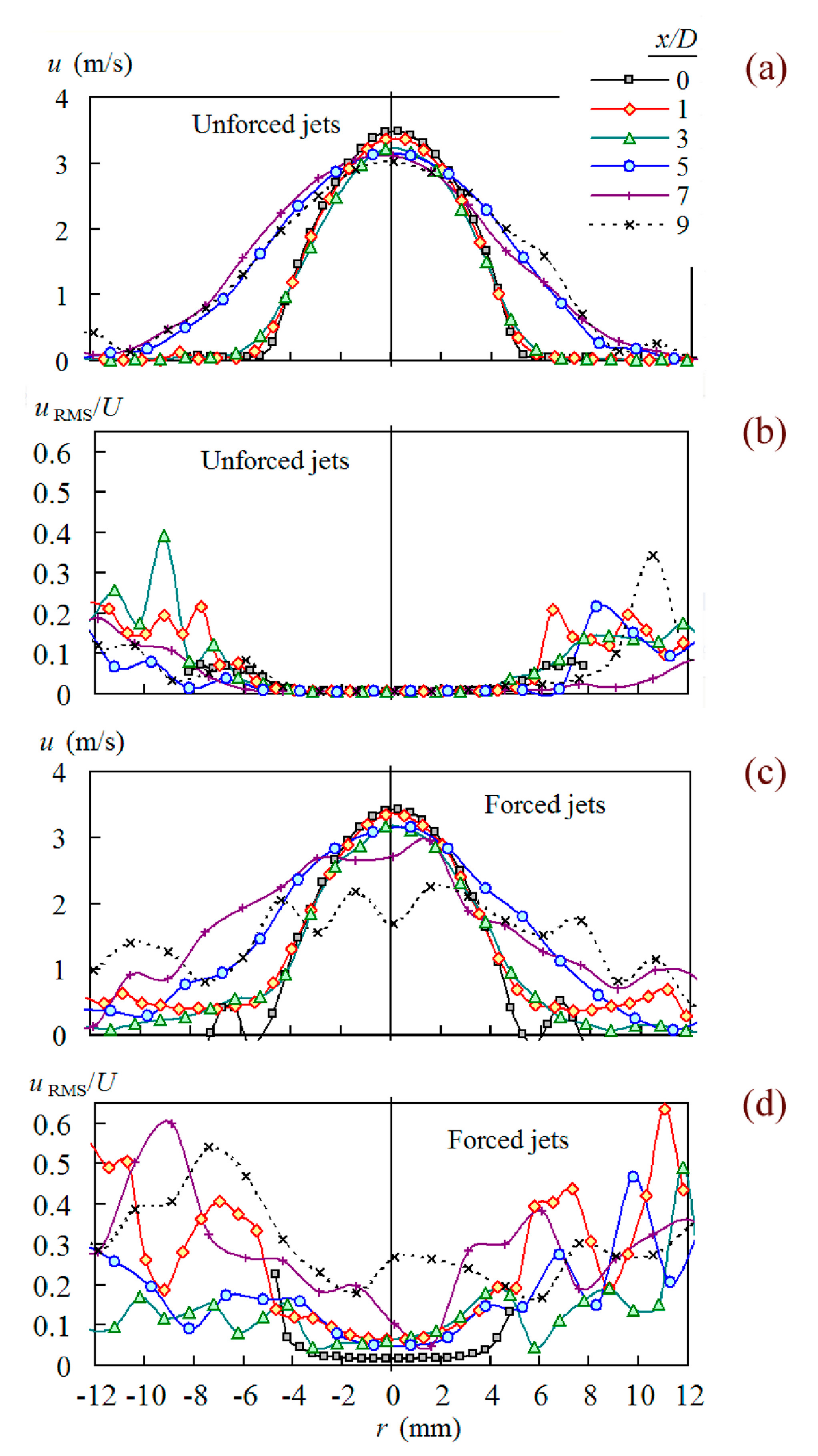

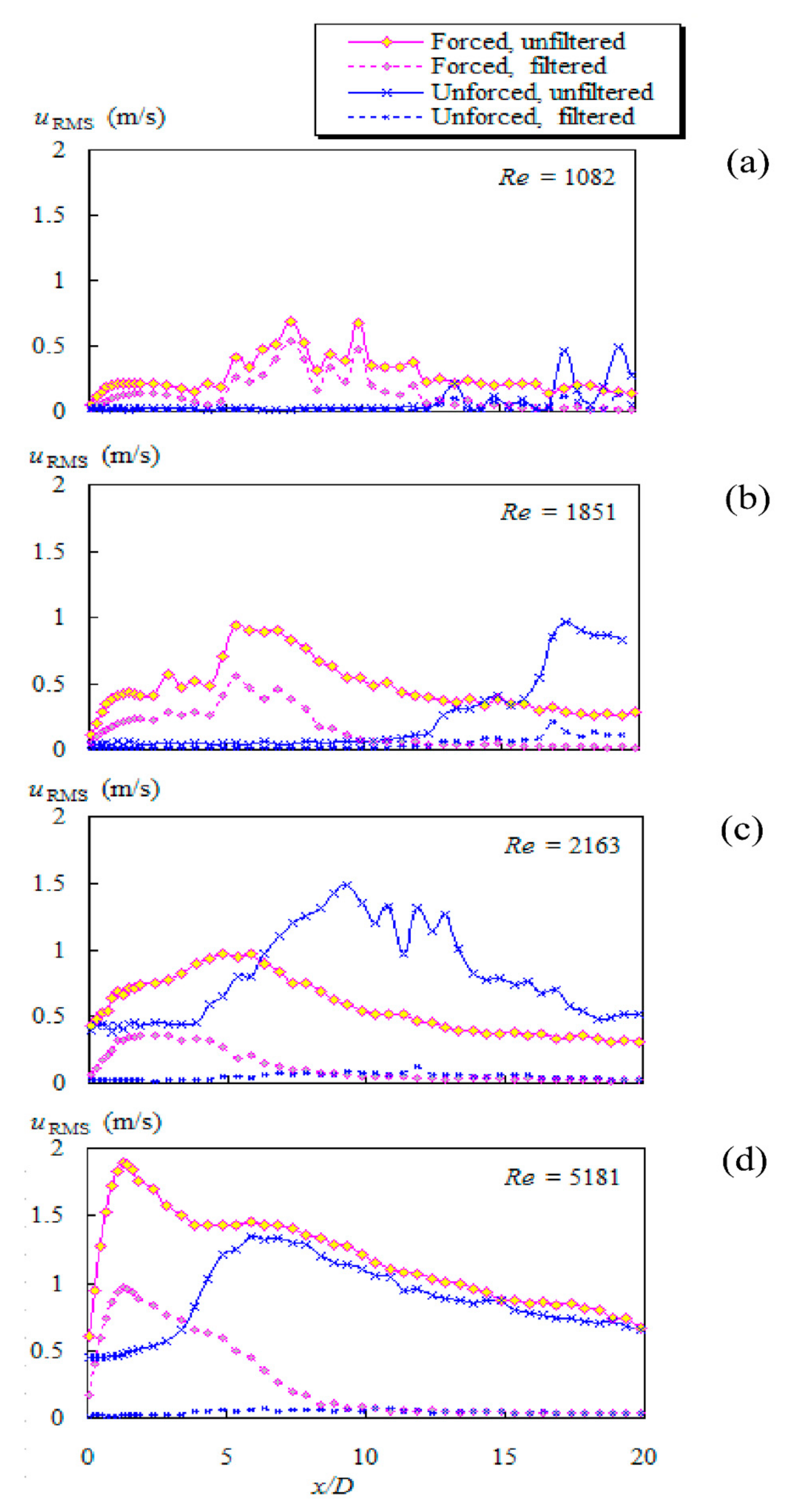


| Re | Um (m/s) | k = Umax/Um | ReSJ | U0 (m/s) | f (Hz) | P (W) | cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1082 | 1.74 | 2.0 | 169 | 0.86 | 52 | 0.13 | 0.49 |
| 1445 | 2.32 | 2.0 | 223 | 1.14 | 69 | 0.10 | 0.49 |
| 1851 | 2.97 | 1.9 | 311 | 1.58 | 89 | 0.08 | 0.53 |
| 2043 | 3.27 | 1.9 | 333 | 1.69 | 98 | 0.06 | 0.52 |
| 2163 | 3.47 | 2.0 | 320 | 1.63 | 103 | 0.04 | 0.47 |
| 2555 | 4.07 | 1.8 | 416 | 2.12 | 121 | 0.04 | 0.52 |
| 2820 | 4.49 | 1.6 | 459 | 2.34 | 134 | 0.06 | 0.52 |
| 2947 | 4.69 | 1.5 | 443 | 2.26 | 140 | 0.06 | 0.48 |
| 3130 | 4.98 | 1.4 | 478 | 2.43 | 149 | 0.10 | 0.49 |
| 4151 | 6.61 | 1.3 | 637 | 3.24 | 197 | 0.70 | 0.49 |
| 5181 | 8.25 | 1.3 | 754 | 3.83 | 246 | 2.23 | 0.46 |
| Tuc/Tu (max) | Tuc/Tu (Average) | |
|---|---|---|
| A | 66.7 | 19.0 |
| B | 29.5 | 3.9 |
| C | 3.1 | 1.7 |
| D | 4.1 | 2.4 |
| E | 1.1 | 0.7 |
| F | 1.2 | 1.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antošová, Z.; Trávníček, Z. Control of a Round Jet Intermittency and Transition to Turbulence by Means of an Annular Synthetic Jet. Actuators 2021, 10, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080185
Antošová Z, Trávníček Z. Control of a Round Jet Intermittency and Transition to Turbulence by Means of an Annular Synthetic Jet. Actuators. 2021; 10(8):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080185
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntošová, Zuzana, and Zdeněk Trávníček. 2021. "Control of a Round Jet Intermittency and Transition to Turbulence by Means of an Annular Synthetic Jet" Actuators 10, no. 8: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080185
APA StyleAntošová, Z., & Trávníček, Z. (2021). Control of a Round Jet Intermittency and Transition to Turbulence by Means of an Annular Synthetic Jet. Actuators, 10(8), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080185






