Mechanical Design and Performance Analyses of a Rubber-Based Peristaltic Micro-Dosing Pump
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design Concept and Challenges
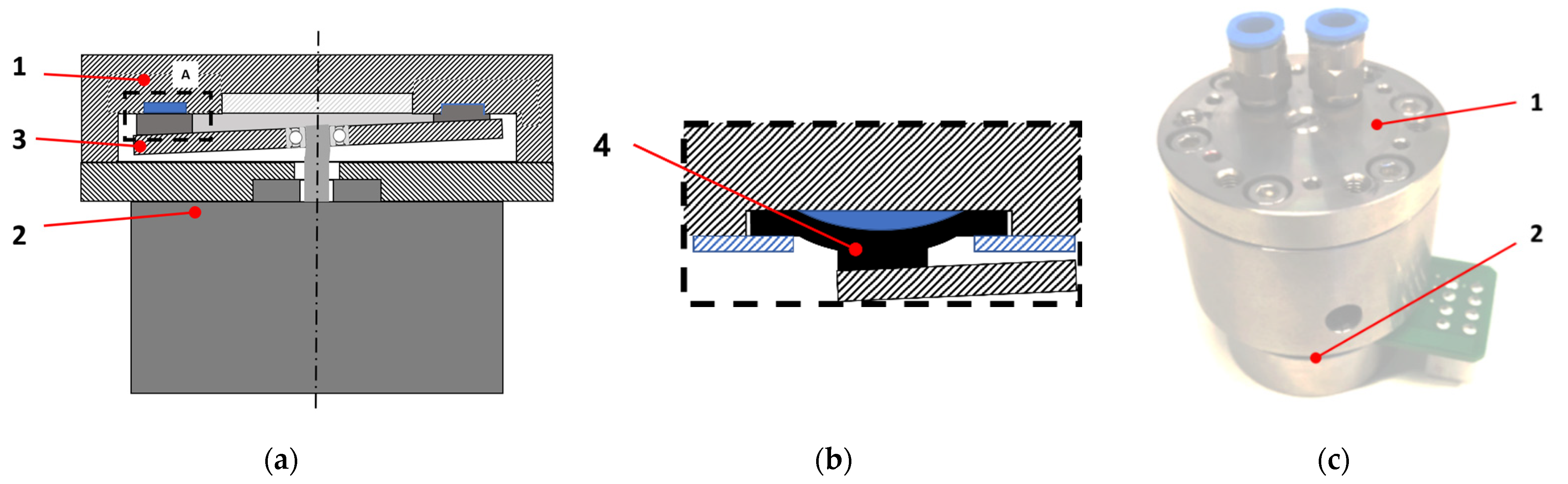
2.1. Mechanical Design
2.1.1. FE-Calculations and Design Hypothesis
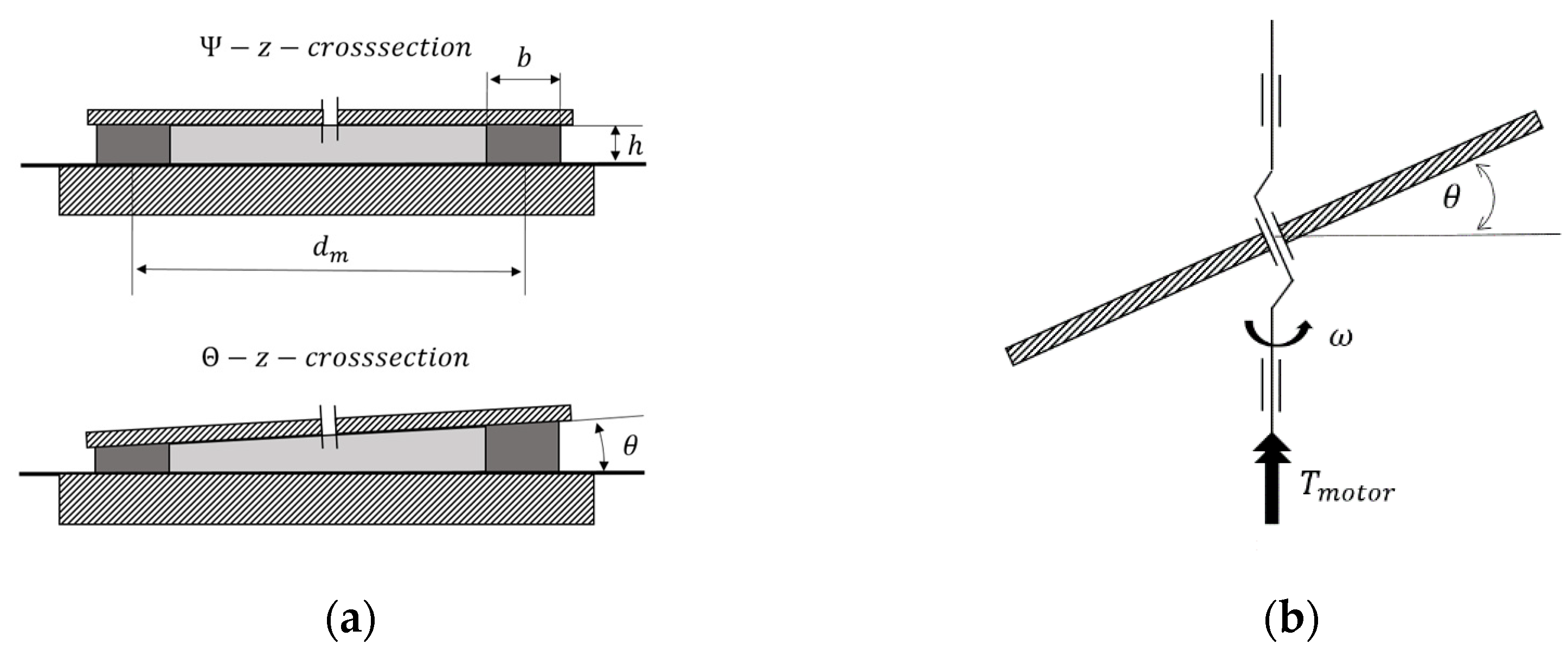
2.1.2. Analytical Model for the Estimation for the Drive Torque
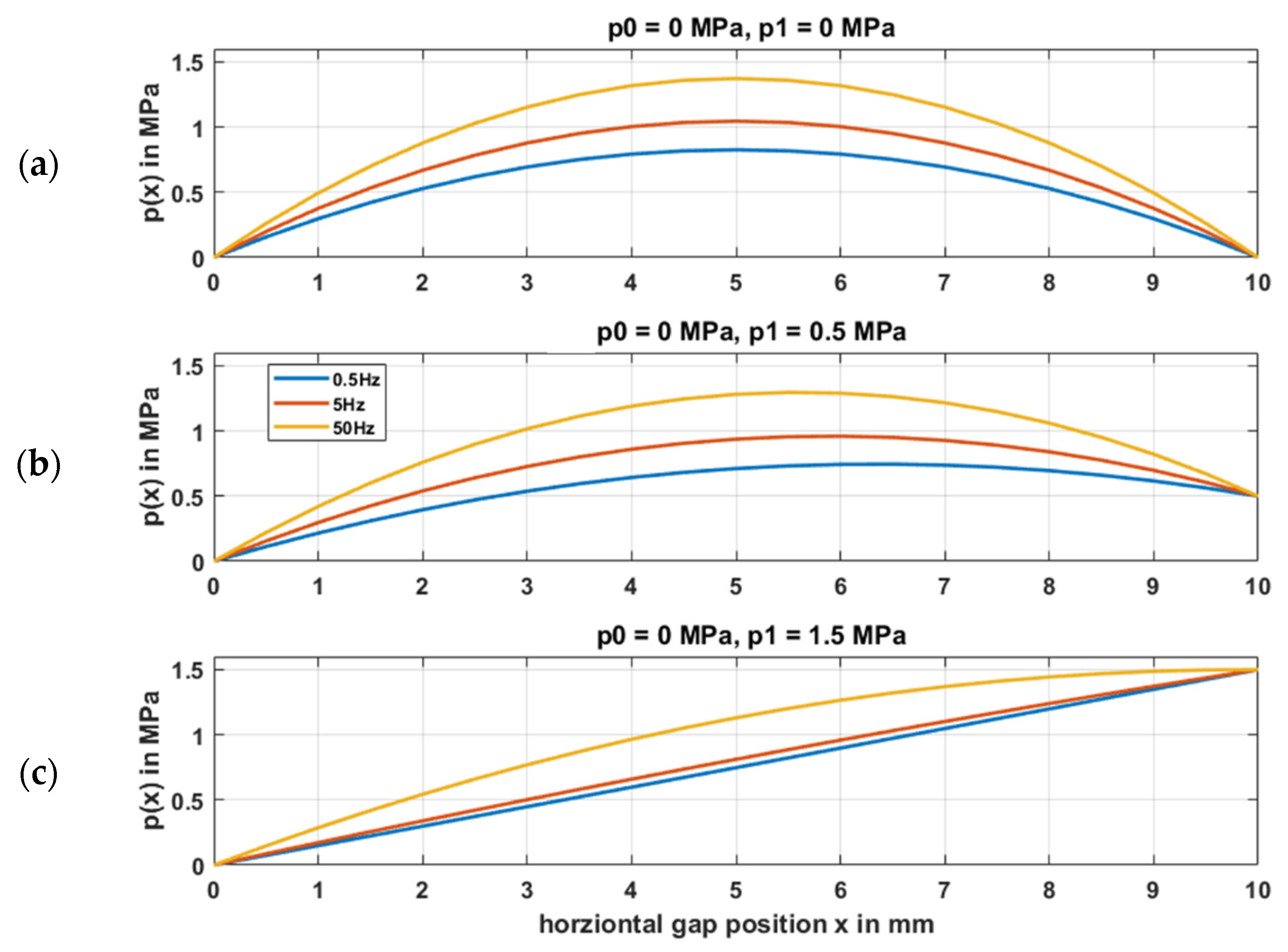
2.1.3. Dynamic Fluid Gap
2.1.4. Wobble Plate Design
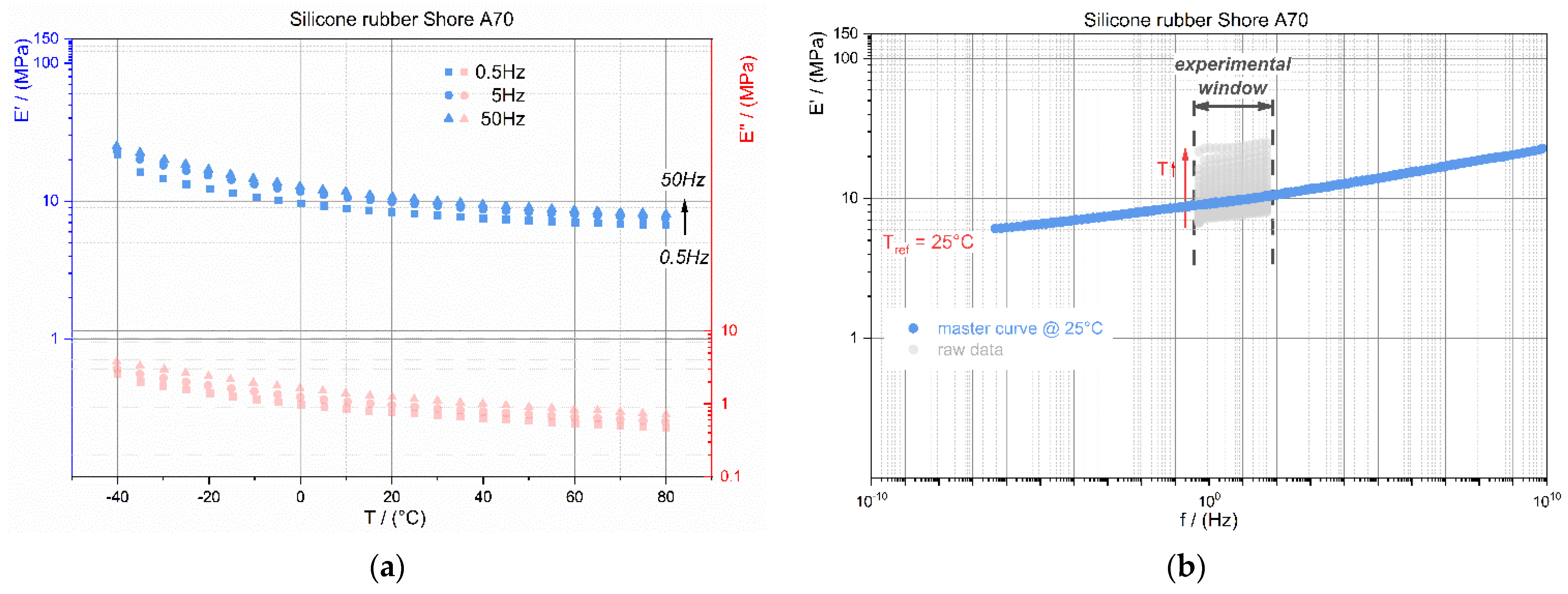
2.2. Material Selection for the Soft Layer of the Wobbling Plate
- constant storage modulus E′ for low and balanced sealing pressures,
- low loss modulus E″ for low drive torques,
- low Poisson’s ratio ν (rubber is incompressible, hence, ν = 0.5),
- low viscoelasticity and elastic deformability up to 25% strain
2.2.1. Candidate Materials (Rubbers)
2.2.2. Experimental
2.3. Evaluation Procedure of the Pump Prototype
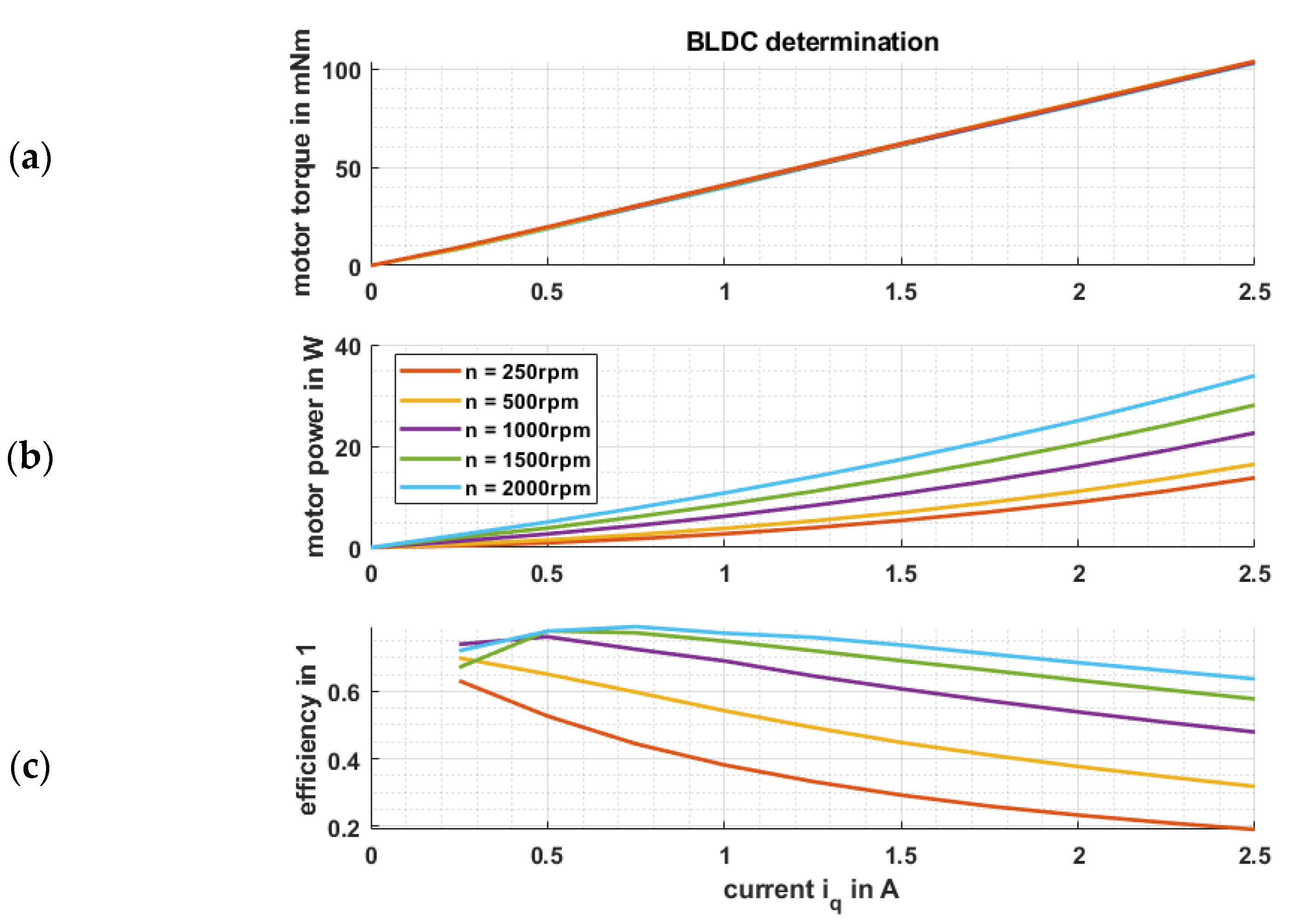
2.3.1. Electrical Drive and Performance Determination
2.3.2. Test Rig
2.3.3. Definition of the Test Cycle
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Material Selection of Wobble Plate’s Soft Layer
3.2. Bonding between the Wobble Plate’s Soft and Rigid Layers
3.3. Determination of the Static Displacement
3.4. Pump Testing
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Böge, A. Technische Mechanik; Vieweg+Teubner Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2011; pp. 142–221, 401–415. [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann, P. Faszination Hydraulischer Widder; Weinmann Sondermaschinenbau GmbH: Hersbruck, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.W. The Handbook of Fluid Dynamics; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gülich, J.F. Kreiselpumpen, Handbuch für Entwicklung, Anlagenplanung und Betrieb, 4. Auflage ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, K.; Murrenhoff, H. Gundlagen der Fluidtechnik: Teil1: Hydraulik; Shaker: Düren, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Leati, E.; Poltschak, F.; Scheidl, R. An electromagnetically actuated high frequency oscillation pump. Mechatronics 2017, 47, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, K. Hydraulische Kolbenmaschinen; Friedr. Vieweg & Sohn Verlagsgesellschaft mbH: Braunschweig, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Dallas, T.; Berg, J.M. Persitaltic Pumps. In Encyclopedia of Micro- and Nanofluidics; Springer: Bosten, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, X.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Smart magnetorheological elastomer peristaltic pump. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2019, 30, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideris, E.A.; Delange, H.C. Pumps operated by solid-state electromechanical smart material actuators—A review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 307, 111915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenke, C.; Rubio, J.P.; Kibler, S.; Häfner, J.; Richter, M.; Kutter, C. The Combination of Micro Diaphragm Pumps and Flow Sensors for Single Stroke Based Liquid Flow Control. Sensors 2017, 17, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cakmak, U.D.; Major, Z. Experimental Thermomechanical Analysis of Elastomers under Uni- and Biaxial Tensile Stress State. Exp. Mech. 2014, 54, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmak, U.D.; Kallaí, I.; Major, Z. Temperature dependent bulge test for elastomers. Mech. Res. Commun. 2014, 60, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmak, U.D.; Fischlschweiger, M.; Graz, I.; Major, Z. Adherence Kinetics of a PDMS Gripper with Inherent Surface Tackiness. Polymers 2020, 12, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschoegl, N.W.; Knauss, W.G.; Emri, I. The effect of temperature and pressure on the mechanical properties of thermo-and/or piezorheologically simple polymeric materials in thermodynamic equilibrium—A critical review. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 2002, 6, 53–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.F. Materials Selection in Mechanical Design, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, D. Elektrische Antriebe-Regelung von Antriebssystemen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Abaqus/CAE 2018; Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp.: Johnston, RI, USA, 2018.
- Marth, E. Beiträge zur Auslegung von Rotorsystemen mit Permanentmagnetisch Passiv Stabilisierten Radial- und Kippfreiheitsgraden. Linz, Austria, June 2017; pp. 21–36. Available online: https://epub.jku.at/obvulihs/content/titleinfo/2196947 (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Röthemeyer, F.; Sommer, F. Kautschuktechnologie Werkstoffe—Verarbeitung—Produkte; Carl Hanser Verlag: München, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Resch, M. Beiträge zum Verhalten von Newtonschen und Magnetorheologischen Flüssigkeiten in Engen Quetschspalten; Trauner Verlag: Linz, Austria, 2010; ISBN 978-3854998440. [Google Scholar]
- Spurk, J. Strömungslehre—Eine Einführung in die Theorie der Strömungen, 5. Auflage ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Warsi, Z. Fluid Dynamics—Theoretical and Computatilnal Approaches, 2nd ed.; CRC Press LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Troughton, M.J. Handbook of Plastics Joining, 2nd ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, New York, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Formato, G.; Romano, R.; Formato, A.; Sorvari, J.; Koiranen, T.; Pellegrino, A.; Villecco, F. Fluid–Structure Interaction Modeling Applied to Peristaltic Pump Flow Simulations. Machines 2019, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cakmak, U.D.; Grestenberger, G.; Major, Z. A novel test method for quantifying surface tack of polypropylene compound surfaces. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataplasm Test. Available online: https://leitfaden.klebstoffe.com/6-7-langzeitbestaendigkeit/ (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- X2C (2019) v6.1.1632; Linz Center of Mechatronics: Linz, Austria, 2019.
- LCM-ECU-10HB-10A-80V. Available online: https://x2c.lcm.at/power-inverters/ (accessed on 8 January 2021).
- Plöckinger, A.; Huova, M.; Scheidl, R. Simulation and Expterimential Results of PWM Control for Digitalhydraulics. In Proceedings of the Fitfth Workshop on Digital Fluid Power, DFP’12, Tampere, Finland, 24–25 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Plöckinger, A.; Winkler, B.; Foschum, P.; Scheidl, R. Digital Hydraulics for an Industrial Micro-Positioning System. In Proceedings of the 9th International Fluid Power Conference, 9. IFK, Aachen, Germany, 24–26 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Plöckinger, A.; Scheidl, R.; Winkler, B. Combined PWM- and Hysteresis Switching Control For A Digital Hydraulic Actuator. In Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Digital Fluid Power, DFP’10, Tampere, Finland, 13–14 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zehetbauer, T. Advancement and demonstration of the new generation of LCM’s FSVi4.1. In Proceedings of the Ninth Workshop on Digital Fluid Power, Aalborg, Denmark, 7–8 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- MATLAB. Version 7.10.0 (R2010a); The MathWorks Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Automation Studio 4.5.2 (2019); B&R Industrial Automation GmbH: Eggelsberg, Austria, 2019.
- Scheidl, R.; Gradl, C.; Plöckinger, A. The Cushioning Groove for Solenoid Switching Valves—Concept and Theoretical Analyses. JFPS Int. J. Fluid Power Syst. 2014, 8, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



























Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zehetbauer, T.; Plöckinger, A.; Emminger, C.; Çakmak, U.D. Mechanical Design and Performance Analyses of a Rubber-Based Peristaltic Micro-Dosing Pump. Actuators 2021, 10, 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080198
Zehetbauer T, Plöckinger A, Emminger C, Çakmak UD. Mechanical Design and Performance Analyses of a Rubber-Based Peristaltic Micro-Dosing Pump. Actuators. 2021; 10(8):198. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080198
Chicago/Turabian StyleZehetbauer, Thomas, Andreas Plöckinger, Carina Emminger, and Umut D. Çakmak. 2021. "Mechanical Design and Performance Analyses of a Rubber-Based Peristaltic Micro-Dosing Pump" Actuators 10, no. 8: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080198
APA StyleZehetbauer, T., Plöckinger, A., Emminger, C., & Çakmak, U. D. (2021). Mechanical Design and Performance Analyses of a Rubber-Based Peristaltic Micro-Dosing Pump. Actuators, 10(8), 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10080198





