The Design of a Tracking Controller for Flexible Ball Screw Feed System Based on Integral Sliding Mode Control with a Generalized Extended State Observer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
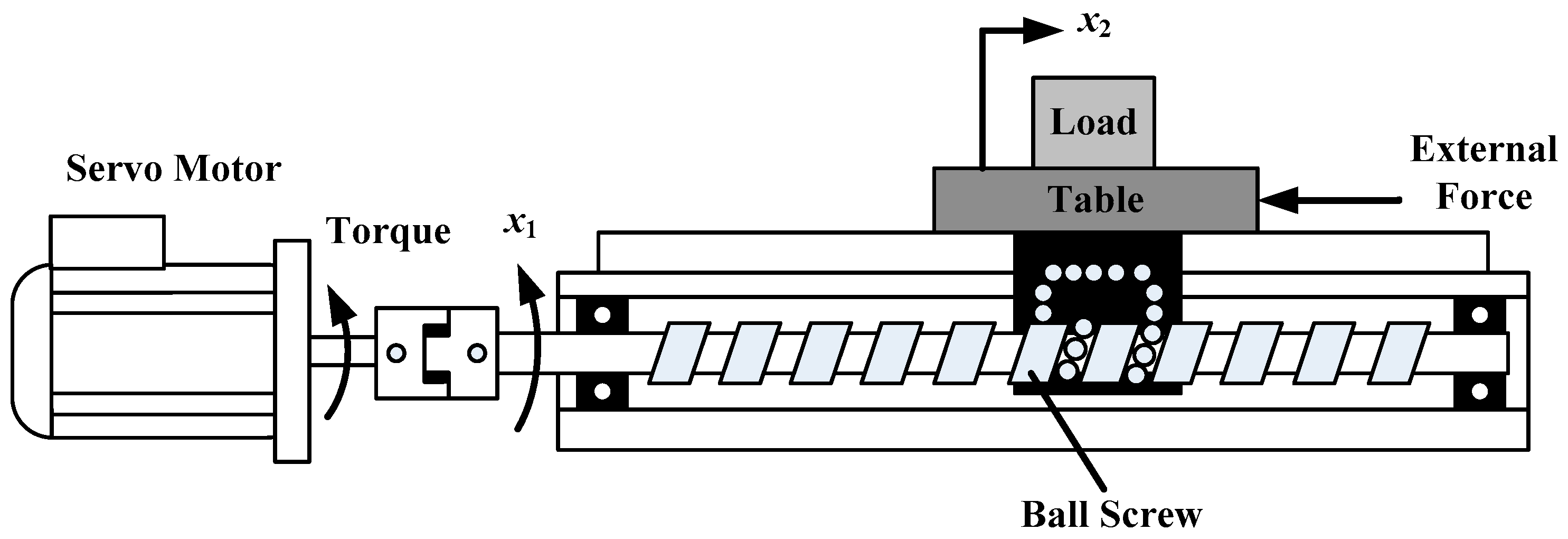
2. Ball Screw Drive Model
3. Integral Sliding Mode Control with Generalized Extended State Observer
3.1. Design of Integral Sliding Mode Controller for Flexible Drives
3.2. Design of Generalized Extended State Observer for Flexible Drives
3.3. Integral Sliding Mode Controller with GESO for Flexible Drives
3.4. Stability and Perturbation Rejection Analysis
3.5. Vibration Compensation Design
4. Simulation and Experimental Verification
4.1. Experimental Setup and Modeling
4.2. Simulation Verification
- (1) Case 1: GESOISMC with vibration compensation;
- (2) Case 2: ISMC.

4.2.1. Tracking Performance Only with Matched Perturbation
4.2.2. Tracking Performance with Matched and Mismatched Perturbations
4.2.3. Tracking Performance with Uncertainties
4.2.4. Tracking Performance with Vibration
4.3. Experimental Verification
4.3.1. Tracking Performance
4.3.2. Robustness Performance against System Uncertainties
4.3.3. Vibration Suppression Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masih, H. Linear Parameter-Varying Control of CNC Machine Tool Feed-Drives with Dynamic Variations. Master’s Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Altintas, Y.; Verl, A.; Brecher, C.; Uriarte, L.; Pritschow, G. Machine tool feed drives. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 60, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepasi, D. Modeling of linear systems with parameter variations: Applications in hard disk and ball screw drives. Master’s Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pritschow, G. On the influence of the velocity gain factor on the path deviation. CIRP Annals Manuf. Technol. 1996, 45, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.U.; Le, Q.N.; Jeon, J.W. An FPGA-based multiple-axis motion control chip. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 856–870. [Google Scholar]
- Wai, R.J.; Lee, J.D.; Chuang, K.L. Real-time pid control strategy for maglev transportation system via particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkorkmaz, K.; Kamalzadeh, A. High bandwidth control of ball screw drives. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2006, 55, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Al-Majed, M.; Tomizuka, M. High-performance robust motion control of machine tools: An adaptive robust control approach and comparative experiments. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2002, 2, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Boucher, P.; Dumur, D.; Rodriguez, P. Robustification of CNC Controllers for Machine Tools Motor Drives. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2003, 52, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.G.; Tran, D.T.; Ahn, K.K. Disturbance observer-based chattering-attenuated terminal sliding mode control for nonlinear systems subject to matched and mismatched disturbances. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskarwar, T.; Hawari, H.F.; Nor, N.B.M.; Chile, R.H.; Waghmare, D.; Aole, S. Sliding Mode Controller with Generalized Extended State Observer for Single Link Flexible Manipulator. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalzadeh, A.; Erkorkmaz, K. Compensation of axial vibrations in ball screw drives. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 56, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwudire, C.; Altintas, Y. Minimum tracking error control of flexible ball screw drives using a discrete-time sliding mode controller. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2009, 131, 051006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaludin, Z.; Van Brussel, H.; Swevers, J. Quadrant glitch compensation using friction model-based feedforward and an inverse-model-based disturbance observer. In Proceedings of the 2008 10th IEEE International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control, Trento, Italy, 26–28 March 2008; pp. 212–217. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Tang, W.C. Adaptive backstepping sliding mode control of flexible ball screw drives with time-varying parametric uncertainties and disturbances. ISA Trans. 2014, 53, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.J.; Erkorkmaz, K. Accurate control of ball screw drives using pole-placement vibration damping and a novel trajectory prefilter. Precis. Eng. 2013, 7, 308–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Y.; Khoshdarregi, M.R. Contour error control of CNC machine tools with vibration avoidance. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 61, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, H.; Takemura, T. High-precision control of ball-screw-driven stage based on repetitive control using n-times learning filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3694–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.S.; Yen, C.L.; Yau, H.T. Integration of an empirical mode decomposition algorithm with iterative learning control for high-precision machining. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, Y. Tracking control of ball screw drives using ADRC and equivalent-error-model-based feedforward control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7682–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, N.; Abolmasoumi, A.H.; Soleymani, M. Sliding mode trajectory tracking control of a ball-screw-driven shake table based on online state estimations using EKF/UKF. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2018, 25, e2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.C.; Lee, J.M.; Han, S.I. Tracking error constrained terminal sliding mode control for ball-screw driven motion systems with state observer. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2018, 19, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Pritschow, G.; Zahn, P. A novel cascade control principle for feed drives of machine tools. CIRP Ann. 2018, 67, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simba, K.R.; Bui, B.D.; Msukwa, M.R.; Uchiyama, N. Robust iterative learning contouring controller with disturbance observer for machine tool feed drives. ISA Trans. 2018, 75, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Jiang, Y.; Li, T.; Ehmann, K.F. Compensation of dynamic mechanical tracking errors in ball screw drives. Mechatronics 2018, 55, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Fujimoto, H.; Isaoka, Y. Projection-based iterative learning control for ball-screw-driven stage with consideration of rolling friction compensation. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2020, 9, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Fujimoto, H.; Isaoka, Y. Negative quadrant glitch suppression control of ball-screw-driven stage for machine tool by friction compensation and initial value compensation. Electr. Eng. Jpn. 2022, 215, e23402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sencer, B.; Dumanli, A. Optimal control of flexible drives with load side feedback. CIRP Ann. 2017, 66, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumanli, A.; Sencer, B. Optimal high-bandwidth control of ball-screw drives with acceleration and jerk feedback. Precis. Eng. 2018, 54, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Ni, Q.; Liu, X. Vibration suppression and over-quadrant error mitigation methods for a ball-screw driven servo system with dual-position feedback. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 213758–213771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvani, H.K.; Hosseinkhani, Y.; Erkorkmaz, K. Suppression of harmonic positioning errors in ball-screw drives using Adaptive Feedforward Cancellation. Precis. Eng. 2021, 68, 235–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-L.; Wang, T.; Li, M.; Yu, Y. Sliding Mode Control of Servo Feed System Based on Fuzzy Reaching Law. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Tang, W.C.; Bao, D.F. Interpolating gain-scheduled H∞ loop shaping design for high speed ball screw feed drives. ISA Trans. 2015, 55, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifzadegan, M.; Nagamune, R. Tracking and structural vibration control of flexible ball–screw drives with dynamic variations. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, C. Gain scheduling control of ball screw feed drives based on linear parameter varying model. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 11–12, 4493–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.A.; Anwar, M.N.; Laskar, S.H. Tuning of PIDF controller in parallel control structure for integrating process with time delay and inverse response characteristic. J. Control. Autom. Electr. Syst. 2020, 31, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S. Dynamic Analysis of Ball Screw Feed System with the Effects of Excitation Amplitude and Design Parameters. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.; Shi, J. Integral sliding mode in systems operating under uncertainty conditions. In Proceedings of the 35th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Kobe, Japan, 13 December 1996; pp. 4591–4596. [Google Scholar]
- Bejarano, F.J.; Fridman, L.M.; Poznyak, A.S. Output integral sliding mode for min-max optimization of multi-plant linear uncertain systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2009, 54, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamayun, M.T.; Edwards, C.; Alwi, H. Fault Tolerant Control Schemes Using Integral Sliding Modes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Shi, P.; Yao, D. Observer-based adaptive sliding mode control for nonlinear Markovian jump systems. Automatica 2016, 64, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.-H.; Chen, X. Generalized extended state observer based control for systems with mismatched uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 4792–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z. Active disturbance rejection control: A paradigm shift in feedback control system design. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 14–16 June 2006; pp. 2399–2405. [Google Scholar]













| m1 (V·s2/m) | m2 (V·s2/m) | b1 (V·s/m) | b2 (V·s/m) | k (V/m) | c (V·s/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.6512 | 0.0771 | 4.1571 × 10−4 | 0.8052 | 2.1153 × 104 | 2.6775 |
| Case | Maximum Absolute Value of Tracking Error [μm] | RMS [μm] | Positioning Error [μm] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No workpiece | 1 | 12.79 | 4.02 | 8.2 × 10−11 |
| 2 | 25.96 | 5.47 | 2.31 | |
| Addition of 25 kg workpiece | 1 | 14.84 | 4.45 | 0.42 |
| 2 | 35.51 | 7.43 | 1.25 | |
| Vibration interference | 1 | 15.98 | 4.86 | 0.25 |
| 2 | 24.93 | 6.831 | 3.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, M.; Bao, D.; Huang, X. The Design of a Tracking Controller for Flexible Ball Screw Feed System Based on Integral Sliding Mode Control with a Generalized Extended State Observer. Actuators 2023, 12, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12100387
Zhu M, Bao D, Huang X. The Design of a Tracking Controller for Flexible Ball Screw Feed System Based on Integral Sliding Mode Control with a Generalized Extended State Observer. Actuators. 2023; 12(10):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12100387
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Muzhi, Dafei Bao, and Xingrong Huang. 2023. "The Design of a Tracking Controller for Flexible Ball Screw Feed System Based on Integral Sliding Mode Control with a Generalized Extended State Observer" Actuators 12, no. 10: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12100387
APA StyleZhu, M., Bao, D., & Huang, X. (2023). The Design of a Tracking Controller for Flexible Ball Screw Feed System Based on Integral Sliding Mode Control with a Generalized Extended State Observer. Actuators, 12(10), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12100387





