Snakeskin-Inspired 3D Printable Soft Robot Composed of Multi-Modular Vacuum-Powered Actuators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Concept and Design
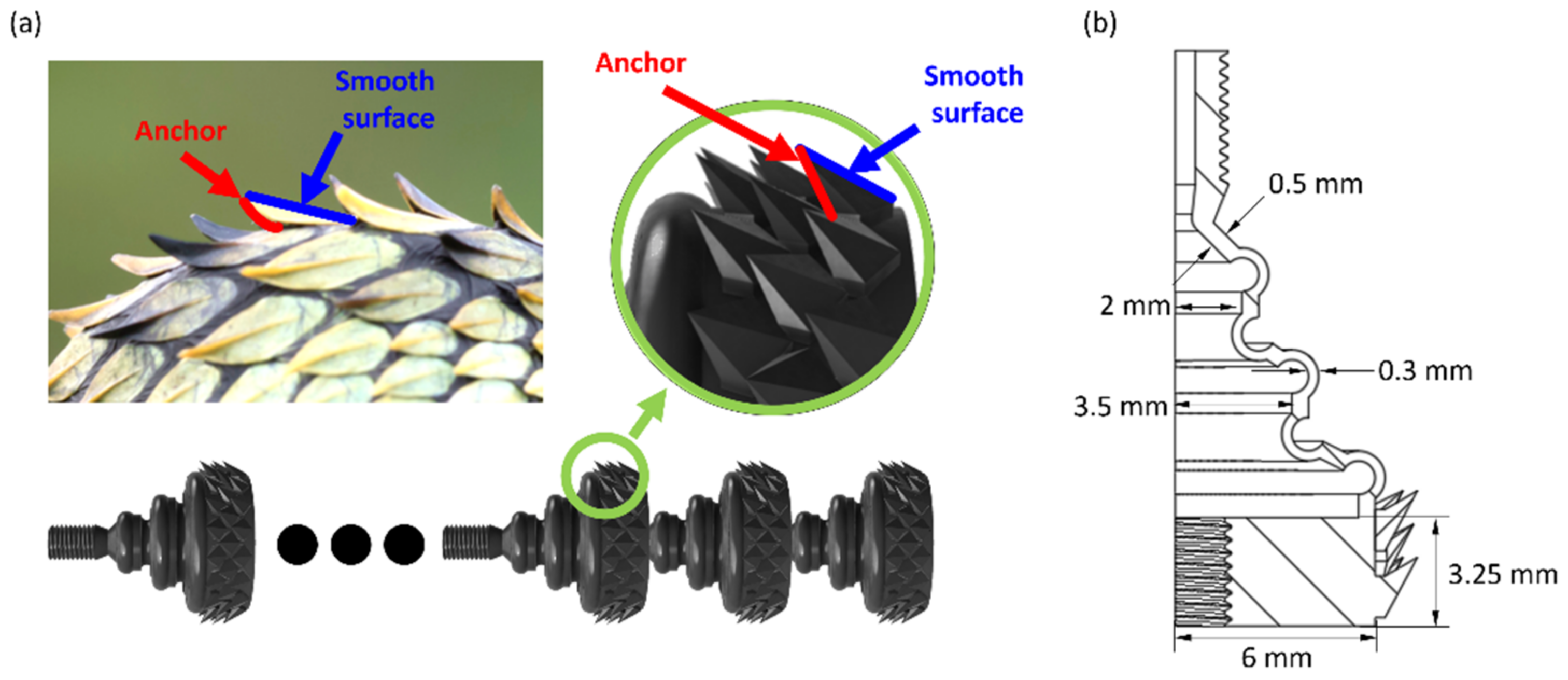
2.1. Bioinspiration from the Snakeskin
2.2. Structure Design and Fabrication of the MSSR
2.3. Mechanism for Operation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trivedi, D.; Rahn, C.D.; Kier, W.M.; Walker, I.D. Soft robotics: Biological inspiration, state of the art, and future research. Appl. Bion. Biomech. 2008, 5, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Laschi, C.; Trimmer, B. Soft robotics: A bioinspired evolution in robotics. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurzaman, S.G.; Iida, F.; Margheri, L.; Laschi, C. Soft robotics on the move: Scientific networks, activities, and future challenges. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Puranam, V.R.; Misra, S.; Venkiteswaran, V.K. A Snake-Inspired Multi-Segmented Magnetic Soft Robot Towards Medical Applications. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Fan, Y.; Yang, P.; Cao, T.; Liao, H. Worm-Like Soft Robot for Complicated Tubular Environments. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimmer, B.; Issberner, J. Kinematics of soft-bodied, legged locomotion in Manduca sexta larvae. Biol. Bull. 2007, 212, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, H.; Feng, R.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, B.; Sheng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Baoyin, H.; Zeng, X. MagWorm: A Biomimetic Magnet Embedded Worm-Like Soft Robot. Soft Robot. 2021, 8, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.L.; Nirody, J.; Scott, T.; Shelley, M.J. The mechanics of slithering locomotion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10081–10085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marvi, H.; Cook, J.P.; Streator, J.L.; Hu, D.L. Snakes move their scales to increase friction. Biotribology 2016, 5, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shepherd, R.F.; Ilievski, F.; Choi, W.; Morin, S.A.; Stokes, A.A.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Multigait soft robot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20400–20403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polygerinos, P.; Lyne, S.; Wang, Z.; Nicolini, L.F.; Mosadegh, B.; Whitesides, G.M.; Walsh, C.J. Towards a soft pneumatic glove for hand rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 1512–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, J.C.; Yap, H.K.; Xi, W.; Wang, Z.; Yeow, C.-H.; Lim, C.T. Flexible and Stretchable Strain Sensing Actuator for Wearable Soft Robotic Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1, 1600018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, J.Z.; Sajid, M.; Rehman, M.M.; Siddiqui, G.U.; Shah, I.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, J.-W.; Choi, K.H. 3D printing for soft robotics—A review. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2018, 19, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, F.; Piccin, O.; Barbé, L.; Bayle, B. Soft Robots Manufacturing: A Review. Front. Robot. AI 2018, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.; Luo, X.; Zhao, H.; Qiao, C.; Li, J.; Yi, J.; Yang, L.; Oropeza, F.J.; Hu, T.S.; Xu, Q.; et al. Recent advances in biomimetic soft robotics: Fabrication approaches, driven strategies and applications. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 7699–7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.S.; Stevens, K.R.; Yang, M.T.; Baker, B.M.; Nguyen, D.-H.T.; Cohen, D.M.; Toro, E.; Chen, A.A.; Galie, P.A.; Yu, X.; et al. Rapid casting of patterned vascular networks for perfusable engineered three-dimensional tissues. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.K.; Ng, H.Y.; Yeow, R.C.-H. High-Force Soft Printable Pneumatics for Soft Robotic Applications. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Alici, G. Bioinspired Three-Dimensional-Printed Helical Soft Pneumatic Actuators and Their Characterization. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, T.J.; Pikul, J.; Shepherd, R.F. 3D printing of soft robotic systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plott, J.; Shih, A. The extrusion-based additive manufacturing of moisture-cured silicone elastomer with minimal void for pneumatic actuators. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffner, M.; Faber, J.A.; Pianegonda, L.; Rühs, P.A.; Coulter, F.; Studart, A.R. 3D printing of robotic soft actuators with programmable bioinspired architectures. Nat. Comm. 2018, 9, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalisky, T.; Wang, Y.; Shih, B.; Drotman, D.; Jadhav, S.; Aronoff-Spencer, E.; Tolley, M.T. Differential pressure control of 3D printed soft fluidic actuators. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 6207–6213. [Google Scholar]
- MacCurdy, R.; Katzschmann, R.; Youbin, K.; Rus, D. Printable hydraulics: A method for fabricating robots by 3D co-printing solids and liquids. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3878–3885. [Google Scholar]
- Peele, B.N.; Wallin, T.J.; Zhao, H.; Shepherd, R.F. 3D printing antagonistic systems of artificial muscle using projection stereolithography. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 055003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-W.; Lee, I.H.; Cho, D.-W. Development of a micro-bellows actuator using micro-stereolithography technology. Microelectron. Eng. 2006, 83, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truby, R.L.; Lewis, J.A. Printing soft matter in three dimensions. Nature 2016, 540, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Jung, W.; Ko, K.; Hwang, Y. Wireless Micro Soft Actuator without Payloads Using 3D Helical Coils. Micromachines 2022, 13, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.; Lee, S.; Hwang, Y. Truly 3D microfluidic heating system with iterative structure of coil heaters and fluidic channels. Smart Mater. Struct. 2022, 31, 035016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawk, C.; Alici, G. A Review of 3D-Printable Soft Pneumatic Actuators and Sensors: Research Challenges and Opportunities. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Verma, M.S.; So, J.-H.; Mosadegh, B.; Keplinger, C.; Lee, B.; Khashai, F.; Lossner, E.; Suo, Z.; Whitesides, G.M. Buckling Pneumatic Linear Actuators Inspired by Muscle. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1, 1600055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Verma, M.S.; Lossner, E.; Stothers, D.; Whitesides, G.M. Negative-Pressure Soft Linear Actuator with a Mechanical Advantage. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1600164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, P.; Lin, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Zou, J. Modular Soft Robotics: Modular Units, Connection Mechanisms, and Applications. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 1900166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, B.T.; Becker, K.P.; Kurumaya, S.; Galloway, K.C.; Whittredge, G.; Vogt, D.M.; Teeple, C.B.; Rosen, M.H.; Pieribone, V.A.; Gruber, D.F. A dexterous, glove-based teleoperable low-power soft robotic arm for delicate deep-sea biological exploration. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Jin, H.; Liu, C.; Dong, E.; Xu, M.; Yang, J. A novel biomimetic jellyfish robot based on a soft and smart modular structure (SMS). In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Qingdao, China, 3–7 December 2016; pp. 708–713. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, T.; Fan, J.; Li, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J. Nonlinear Modeling and Docking Tests of a Soft Modular Robot. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 11328–11337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Pan, M.; Yang, H.; Zou, J. Advanced Artificial Muscle for Flexible Material-Based Reconfigurable Soft Robots. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1901371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, J.; Lin, Y.; Ji, C.; Yang, H. A reconfigurable omnidirectional soft robot based on caterpillar locomotion. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Xu, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, D. A new design of cellular soft continuum manipulator based on beehive-inspired modular structure. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1729881417707380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawk, C.; Panhuis, M.I.H.; Spinks, G.M.; Alici, G. Bioinspired 3d printable soft vacuum actuators for locomotion robots, grippers and artificial muscles. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashe, J. A New Bush Viper. J. East Afr. Nat. Hist. 1968, 1968, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groen, J.; Bok, B.; Tiemann, L.; Verspui, G.J. Geographic range extension of the rough-scaled bush viper, Atheris hispida (Serpentes: Viperidae) from Uganda, Africa. Herpetol. Notes 2019, 12, 241–243. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, K. Can You Estimate Modulus from Durometer Hardness for Silicones; Dow Corning Corporation: Midland, MI, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.M.; Yap, A.U.J.; Koh, W.K.; Tsai, K.T.; Lim, C.T. Measurement of Poisson’s ratio of dental composite restorative materials. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2455–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Angle | 30° | 40° | 50° | 60° |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood (Ra = 12.82) | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.20 |
| Paper (Ra = 9.82) | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.03 |
| Sandpaper (Ra = 13.21) | 0.25 | 0.59 | 0.48 | 0.38 |
| Sandpaper (Ra = 24.93) | 0.18 | 0.15 | 1.02 | 0.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Her, I.; Jung, W.; Hwang, Y. Snakeskin-Inspired 3D Printable Soft Robot Composed of Multi-Modular Vacuum-Powered Actuators. Actuators 2023, 12, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12020062
Lee S, Her I, Jung W, Hwang Y. Snakeskin-Inspired 3D Printable Soft Robot Composed of Multi-Modular Vacuum-Powered Actuators. Actuators. 2023; 12(2):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12020062
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seonghyeon, Insun Her, Woojun Jung, and Yongha Hwang. 2023. "Snakeskin-Inspired 3D Printable Soft Robot Composed of Multi-Modular Vacuum-Powered Actuators" Actuators 12, no. 2: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12020062
APA StyleLee, S., Her, I., Jung, W., & Hwang, Y. (2023). Snakeskin-Inspired 3D Printable Soft Robot Composed of Multi-Modular Vacuum-Powered Actuators. Actuators, 12(2), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12020062






