Design of High Precision Interval Observer for Robot System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Theoretical Research Related Knowledge
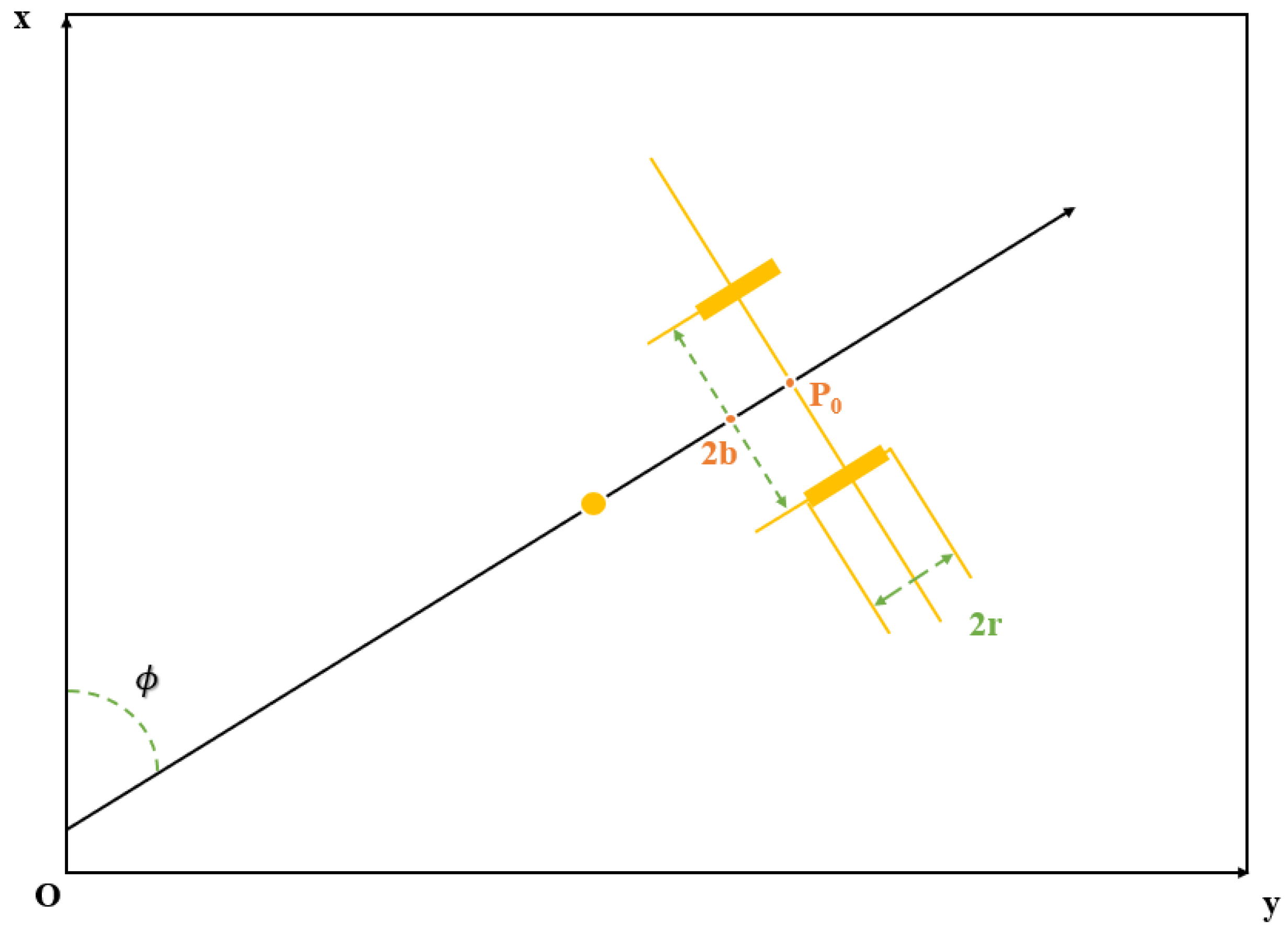
2.2. Kinematic and Dynamic Models of the Robot
2.3. Description of Trajectory Tracking Problem
2.4. Design and Analysis of High Precision Interval Observer
2.5. Stability Analysis
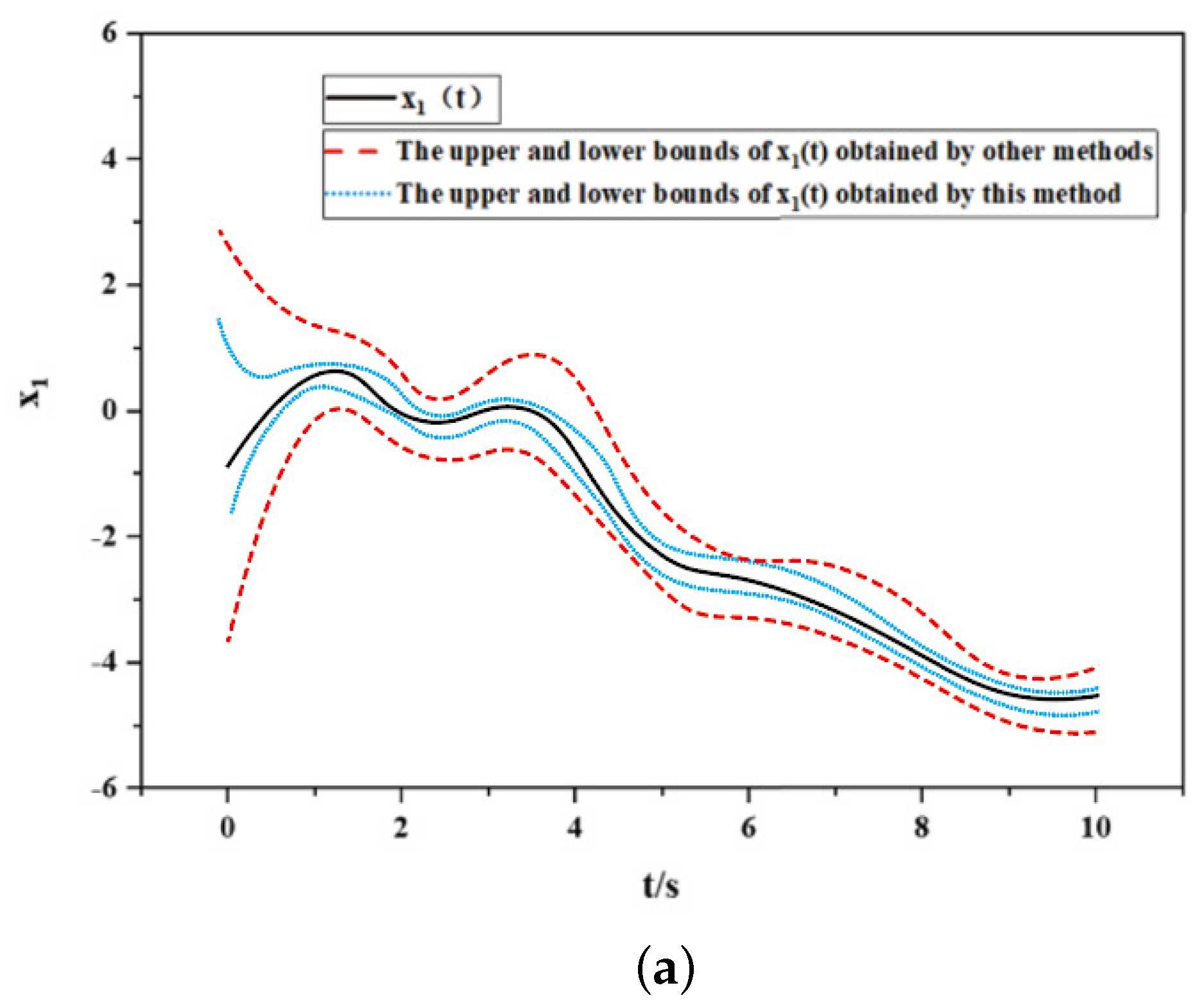
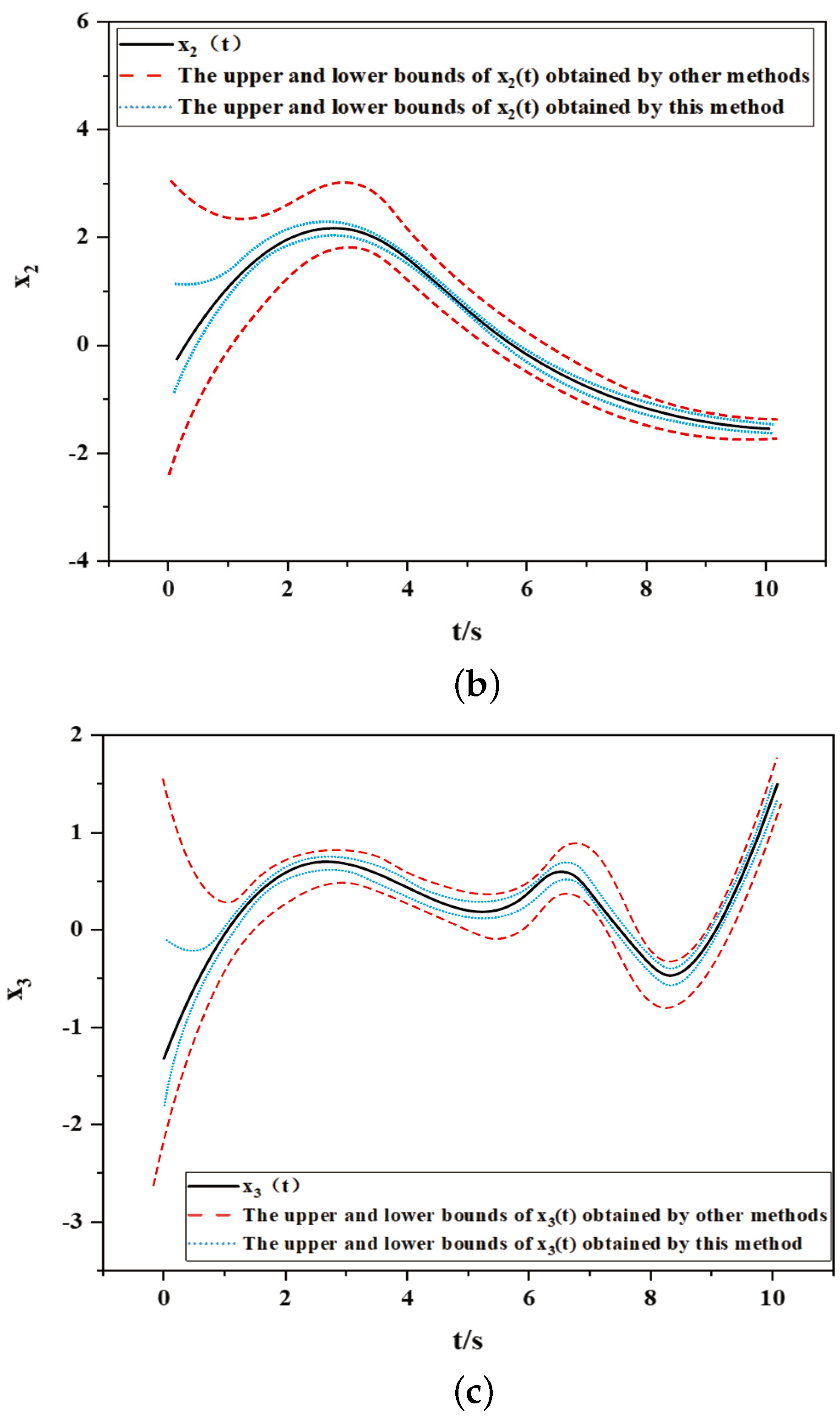
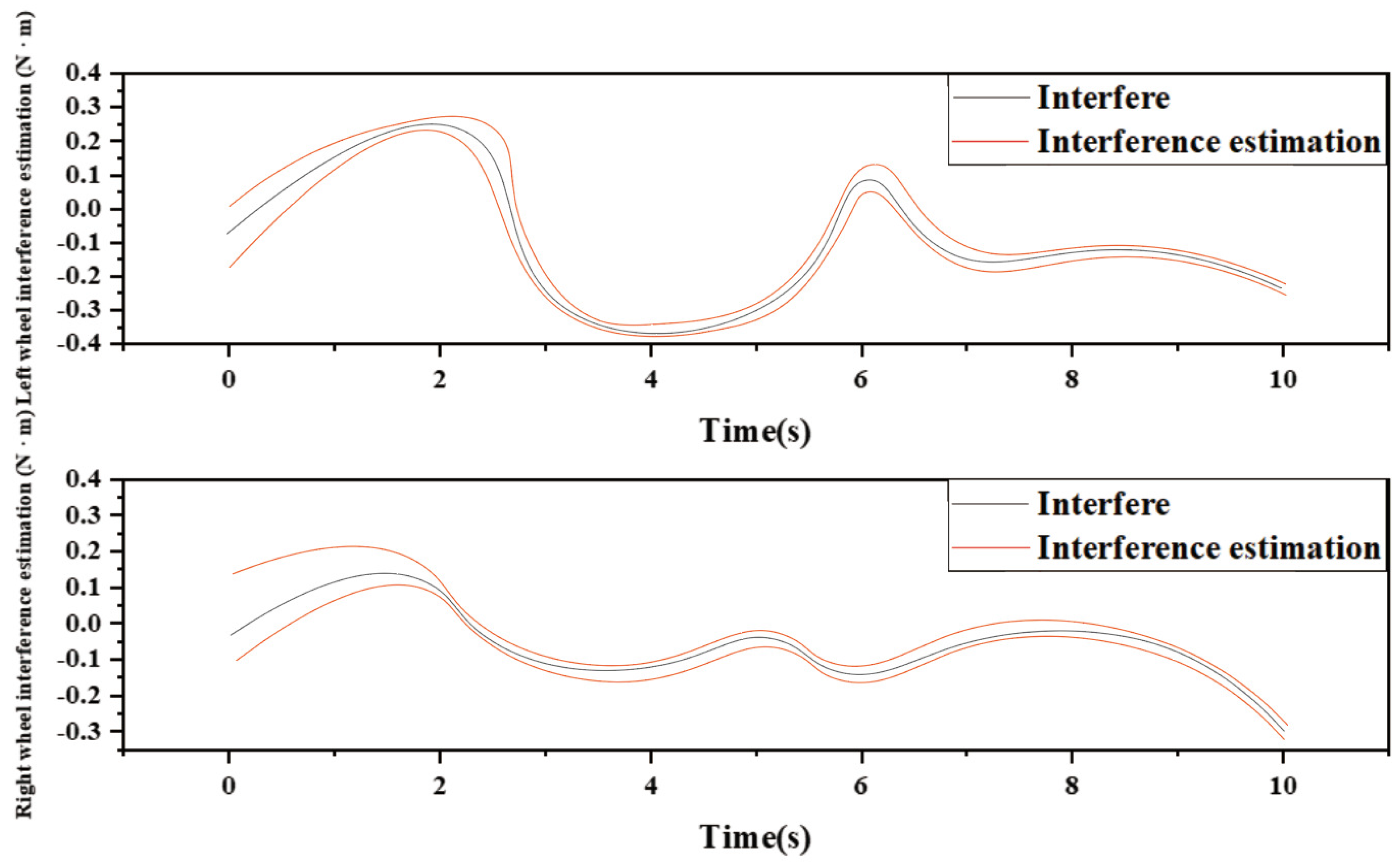
3. Simulation Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arents, J.; Greitans, M. Smart industrial robot control trends, challenges and opportunities within manufacturing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; An, D. AI-Based Posture Control Algorithm for a 7-DOF Robot Manipulator. Machines 2022, 10, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Schutter, B.D. A Unified Framework for Multi-Agent Formation with a Non-repetitive Leader Trajectory: Adaptive Control and Iterative Learning Control. TechRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, Y.; Charalambous, T. Consensus of General Linear Multi-Agent Systems with Heterogeneous Input and Communication Delays. IEEE Control. Syst. Lett. 2020, 5, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, H.; Dinh, T.N. Asymptotic and tracking guarantees in interval observer design for systems with unmeasured polytopic nonlinearities. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 5010–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbouj, Y.; Dinh, T.N.; Raissi, T.; Zouari, T.; Ksouri, M. Optimal interval observer for switched takagi–sugeno systems: An application to interval fault estimation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. Publ. IEEE Neural Netw. Counc. 2020, 29, 2296–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajenejad, M.; Jin, Z.; Yong, S.Z. Resilient interval observer for simultaneous estimation of states, modes and attack policies. In Proceedings of the 2022 American Control Conference (ACC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 8–10 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Harlamov, B.P.; Rasova, S.S. Time distribution from zero up to beginning: Of the final stop of semi-markov diffusion process on interval with unattainable boundaries. Vestnik St. Petersburg University. Mathematics 2022, 9, 38309. [Google Scholar]
- D’Angelo, G.; Perrett, A.; Iacono, M.; Furber, S.; Bartolozzi, C. Event Driven Bio-Inspired Attentive System for the Icub Humanoid Robot on Spinnaker; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bingul, Z.; Karahan, O. Real-time trajectory tracking control of stewart platform using fractional order fuzzy pid controller optimized by particle swarm algorithm. Ind. Robot. 2022, 49, 708–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neimark, J.I.; Fufaev, N.A. Dynamics of Nonholonomic Systems; Translations of Mathematical Monographs; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 1972; Volume 33. [Google Scholar]
- Dmmer, G.; Bauer, H.; Rüdiger, N.; Major, Z. Design, additive manufacturing and component testing of pneumatic rotary vane actuators for lightweight robots. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2022, 28, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shan, J.; Sun, F.; Fang, B.; Yang, Y. Multimode fusion perception for transparent glass recognition. Ind. Robot. Int. J. Robot. Res. Appl. 2022, 49, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cai, Z.; Chen, J.; Jiang, B. Observer-based integral sliding mode control of nonlinear systems with application to single-link flexible joint robotics. Complex Eng. Syst. 2021, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briskin, E.S.; Kalinin, Y.V.; Smirnaya, L.D. On determining the optimal lifting law of the walking propulsion device foot of an underwater robot from the bottom. J. Artif. Intell. Technol. 2021, 1, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, X. Barrier lyapunov function-based robot control with an augmented neural network approximator. Ind. Robot. 2022, 49, 359–367. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Rozas, S.; Alejo, D.; Caballero, F.; Merino, L. Path and trajectory planning of a tethered uav-ugv marsupial robotics system. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.01828. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, R.; Jaramaz, B. Navio Surgical System—Handheld Robotics-Science Direct. Handbook of Robotic and Image-Guided Surgery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harib, M.; Chaoui, H.; Miah, S. Evolution of adaptive learning for nonlinear dynamic systems: A systematic survey. Intell. Robot. 2022, 2, 37–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.H.; Zhu, F. Interval observers design for descriptor systems. Control. Decis. 2016, 31, 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- Khajenejad, M.; Shoaib, F.; Yong, S.Z. Interval observer synthesis for locally lipschitz nonlinear dynamical systems via mixed-monotone decompositions. In Proceedings of the 2022 American Control Conference (ACC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 8–10 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Lam, J.; Zhu, B.; Fan, C. Interval observer-based fault-tolerant control for a class of positive markov jump systems. Inf. Sci. Int. J. 2022, 590, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Tao, H.; Chen, Y.; Stojanovicc, V.; Paszke, W. An Optimal Iterative Learning Control Approach for Linear Systems with Nonuniform Trial Lengths under Input Constraints. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chu, B.; Freeman, C.T. Iterative Learning Control for Robotic Path Following With Trial-Varying Motion Profiles. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2022, 27, 4697–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, W.; Charalambous, T. Machine learning based iterative learning control for non-repetitive time-varying systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, G.; Weng, G. An active contour model driven by adaptive local pre-fitting energy function based on Jeffreys divergence for image segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 210, 118493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Weng, G.; Chen, H. An Active Contour Model Based on Local Pre-piecewise Fitting Bias Corrections for Fast and Accurate Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 5006413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Symbol | The Numerical | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| The quality of robot | M | 50 | kg |
| Driving wheel radius | r | 0.125 | m |
| Distance between two driving wheels | 2b | 0.5 | m |
| Results | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Methods In This Paper | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Method Proposed In Reference [20] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ |
| Other Methods Based On Coordinate Transformation | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, S.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; He, H. Design of High Precision Interval Observer for Robot System. Actuators 2023, 12, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12030116
Duan S, Shao Z, Chen X, Li X, Chen Y, He H. Design of High Precision Interval Observer for Robot System. Actuators. 2023; 12(3):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12030116
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Shuang, Zhida Shao, Xinyao Chen, Xuan Li, Yiyang Chen, and Haidong He. 2023. "Design of High Precision Interval Observer for Robot System" Actuators 12, no. 3: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12030116
APA StyleDuan, S., Shao, Z., Chen, X., Li, X., Chen, Y., & He, H. (2023). Design of High Precision Interval Observer for Robot System. Actuators, 12(3), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/act12030116









