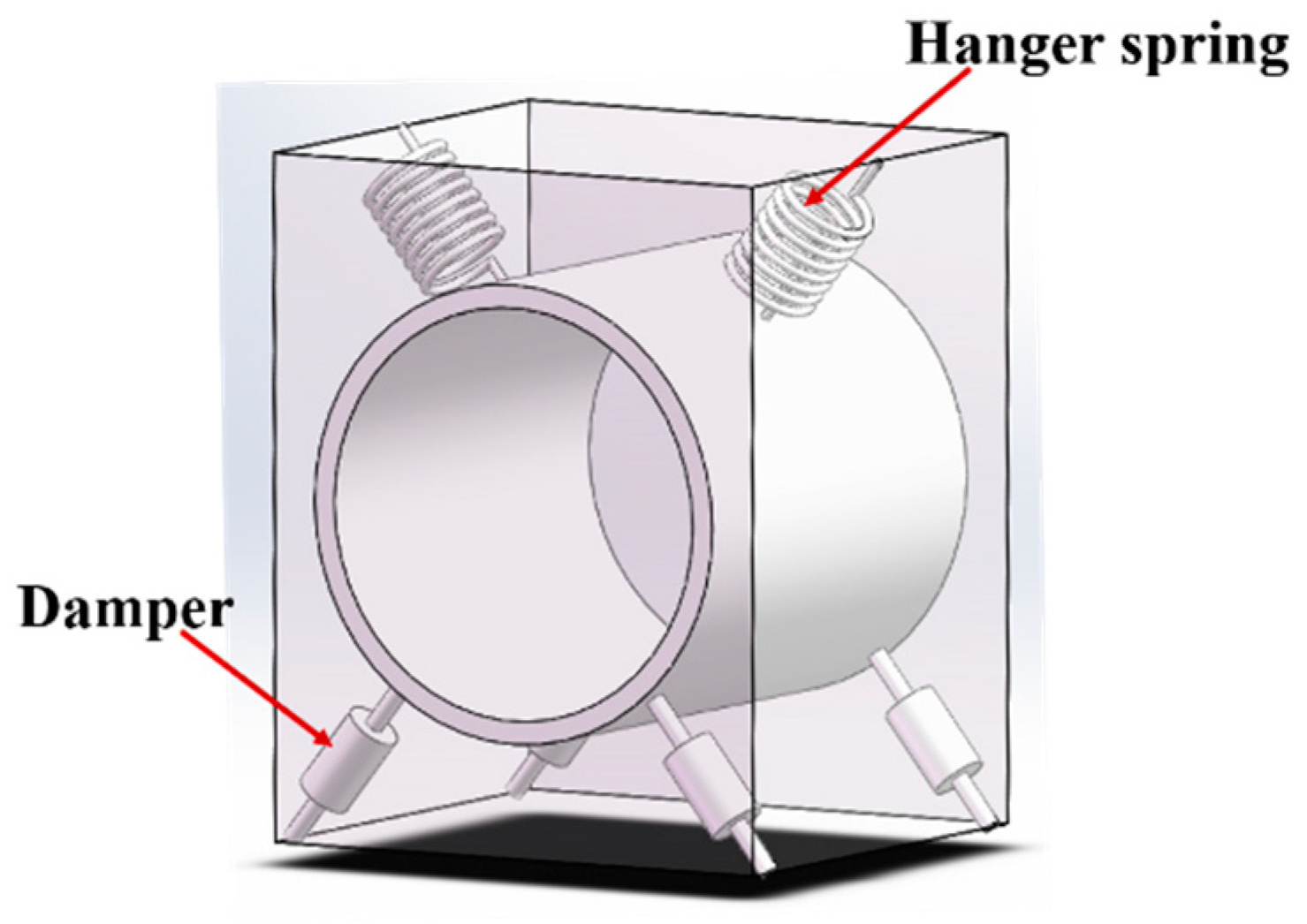
Figure 1.
Drum washing machine and its vibration-damping system.
Figure 1.
Drum washing machine and its vibration-damping system.
Figure 2.
Shear stress-shear rate relationship for fluids.
Figure 2.
Shear stress-shear rate relationship for fluids.
Figure 3.
Structural formulas of two polysaccharides: (a) carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC); (b) xanthan gum (XG).
Figure 3.
Structural formulas of two polysaccharides: (a) carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC); (b) xanthan gum (XG).
Figure 4.
Internal configuration of annular gap-type viscous damper: (a) damper with an annular gap; (b) A-A section view.
Figure 4.
Internal configuration of annular gap-type viscous damper: (a) damper with an annular gap; (b) A-A section view.
Figure 5.
Fluid state in the gap: (a) unit fluid element and flow velocity profile; (b) pressure difference.
Figure 5.
Fluid state in the gap: (a) unit fluid element and flow velocity profile; (b) pressure difference.
Figure 6.
Structure of non-Newtonian fluid variable damping damper.
Figure 6.
Structure of non-Newtonian fluid variable damping damper.
Figure 7.
Test of mechanical properties of damper.
Figure 7.
Test of mechanical properties of damper.
Figure 8.
Damper and acceleration sensor mounting location.
Figure 8.
Damper and acceleration sensor mounting location.
Figure 9.
Noise meter microphone position.
Figure 9.
Noise meter microphone position.
Figure 10.
Rheology curves of CMC/XG/B/CA solutions.
Figure 10.
Rheology curves of CMC/XG/B/CA solutions.
Figure 11.
FFT Analysis of vibration frequency.
Figure 11.
FFT Analysis of vibration frequency.
Figure 12.
Variation of apparent elastic coefficient of dampers with frequency.
Figure 12.
Variation of apparent elastic coefficient of dampers with frequency.
Figure 13.
Acceleration of the dewatering stage: (a1–a5) Top acceleration in the z-direction; (b1–b5) Bottom acceleration in the z-direction.
Figure 13.
Acceleration of the dewatering stage: (a1–a5) Top acceleration in the z-direction; (b1–b5) Bottom acceleration in the z-direction.
Figure 14.
Bottom acceleration in the z-direction for three speed stages.
Figure 14.
Bottom acceleration in the z-direction for three speed stages.
Figure 15.
Acceleration attenuation ratio.
Figure 15.
Acceleration attenuation ratio.
Figure 16.
Acceleration of the washing stage (friction damper and specimen SP-2--F3): (a1,a2) bottom acceleration in the z-direction; (b1,b2) bottom acceleration in the y-direction.
Figure 16.
Acceleration of the washing stage (friction damper and specimen SP-2--F3): (a1,a2) bottom acceleration in the z-direction; (b1,b2) bottom acceleration in the y-direction.
Figure 17.
Acceleration of the dewatering stage (friction damper and specimen SP-1--F2, SP-2--F2): (a1,a2) top acceleration in the z-direction; (b1,b2) bottom acceleration in the z-direction.
Figure 17.
Acceleration of the dewatering stage (friction damper and specimen SP-1--F2, SP-2--F2): (a1,a2) top acceleration in the z-direction; (b1,b2) bottom acceleration in the z-direction.
Figure 18.
Average acceleration for three speed stages (SP-1--F2 and SP-2--F2): (a) bottom acceleration in the z-direction; (b) bottom acceleration in the y-direction.
Figure 18.
Average acceleration for three speed stages (SP-1--F2 and SP-2--F2): (a) bottom acceleration in the z-direction; (b) bottom acceleration in the y-direction.
Figure 19.
Acceleration of the dewatering stage (the diameter of the piston head of the specimen is 18.4 mm and the number of piston heads is 4, changing the damping liquid): (a1–a4) bottom acceleration in the z-direction; (b1–b4) bottom acceleration in the y-direction.
Figure 19.
Acceleration of the dewatering stage (the diameter of the piston head of the specimen is 18.4 mm and the number of piston heads is 4, changing the damping liquid): (a1–a4) bottom acceleration in the z-direction; (b1–b4) bottom acceleration in the y-direction.
Figure 20.
Average acceleration for three speed stages (the diameter of the piston head of the specimen is 18.4 mm and the number of piston heads is 4, changing the damping liquid): (a) bottom acceleration in the z-direction; (b) bottom acceleration in the y-direction.
Figure 20.
Average acceleration for three speed stages (the diameter of the piston head of the specimen is 18.4 mm and the number of piston heads is 4, changing the damping liquid): (a) bottom acceleration in the z-direction; (b) bottom acceleration in the y-direction.
Figure 21.
Average acceleration for three speed stages (The diameter of the piston head of the specimen is 18.8 mm and the number of piston heads is 4, changing the damping liquid): (a) bottom acceleration in the z-direction; (b) bottom acceleration in y-direction.
Figure 21.
Average acceleration for three speed stages (The diameter of the piston head of the specimen is 18.8 mm and the number of piston heads is 4, changing the damping liquid): (a) bottom acceleration in the z-direction; (b) bottom acceleration in y-direction.
Figure 22.
Average acceleration for three speed stages (bottom acceleration in z-direction, the diameter of the piston head of the specimen is 18.8 mm, changing the number of piston heads): (a) ρ(p) = 2.0 g/L; (b) ρ(p) = 3.0 g/L; (c) ρ(p) = 4.0 g/L.
Figure 22.
Average acceleration for three speed stages (bottom acceleration in z-direction, the diameter of the piston head of the specimen is 18.8 mm, changing the number of piston heads): (a) ρ(p) = 2.0 g/L; (b) ρ(p) = 3.0 g/L; (c) ρ(p) = 4.0 g/L.
Figure 23.
Acceleration attenuation ratio.
Figure 23.
Acceleration attenuation ratio.
Figure 24.
Noise sound power levels (friction damper and specimens SP-2--F3, SP-2--F0, SP-2--Fp and SP-2--Fw).
Figure 24.
Noise sound power levels (friction damper and specimens SP-2--F3, SP-2--F0, SP-2--Fp and SP-2--Fw).
Figure 25.
Noise sound power levels (friction damper and specimens SP-2--F2, SP-2--F3 and SP-2--F4).
Figure 25.
Noise sound power levels (friction damper and specimens SP-2--F2, SP-2--F3 and SP-2--F4).
Table 1.
Composition of damping fluid.
Table 1.
Composition of damping fluid.
| Mass Fraction ω (%) | Mass Concentration ρ (g/L) |
|---|
| CMC | XG | B | CA | EG |
|---|
| 30 | 70 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 |
Table 2.
Main structural dimensions of the damper (all dimensions in mm).
Table 2.
Main structural dimensions of the damper (all dimensions in mm).
| Dimension | Connector | Piston Rod | Cylinder |
|---|
| Length | 25 | 50 | 110 |
| Diameter | 20 | 10 | 20 |
Table 3.
Data of apparent viscosity variation with shear rate (the unit of viscosity is Pa·s).
Table 3.
Data of apparent viscosity variation with shear rate (the unit of viscosity is Pa·s).
| Shear Rate (s−1) | ρ(p) = 1.5 g/L | ρ(p) = 2.0 g/L | ρ(p) = 3.0 g/L | ρ(p) = 4.0 g/L |
|---|
| 0.12 | 2.79 | 18.16 | 29.38 | 42.50 |
| 0.18 | 2.73 | 17.02 | 27.51 | 40.24 |
| 0.28 | 2.63 | 16.03 | 23.75 | 33.33 |
| 0.42 | 2.37 | 14.69 | 18.83 | 24.44 |
| 0.67 | 2.11 | 12.28 | 15.31 | 17.87 |
| 1.05 | 1.59 | 8.55 | 11.63 | 14.56 |
| 2.55 | 1.49 | 4.83 | 6.85 | 9.81 |
| 3.99 | 1.25 | 3.43 | 4.80 | 7.46 |
| 6.23 | 0.92 | 2.58 | 4.00 | 5.71 |
| 9.73 | 0.06 | 1.43 | 3.00 | 4.70 |
| 15.22 | 0.52 | 1.14 | 2.19 | 3.81 |
Table 4.
Specimen characters (dimensions in mm, n is number of piston heads, l is thickness of piston head, Dp is diameter of piston head, d is diameter of piston rod, h is height of gap).
Table 4.
Specimen characters (dimensions in mm, n is number of piston heads, l is thickness of piston head, Dp is diameter of piston head, d is diameter of piston rod, h is height of gap).
| Specimen | n | l | Dp | d | h | Fluid |
|---|
| SP-2--F3 | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 3.0 g/L |
| SP-2--F0 | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | None |
| SP-2--Fp | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | (C2H6OSi)n |
| SP-2--Fw | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | Water |
Table 5.
Specimen characters (dimensions in mm, n is number of piston heads, l is thickness of piston head, Dp is diameter of piston head, d is diameter of piston rod, h is height of gap).
Table 5.
Specimen characters (dimensions in mm, n is number of piston heads, l is thickness of piston head, Dp is diameter of piston head, d is diameter of piston rod, h is height of gap).
| Specimen | n | l | Dp | d | h | Fluid |
|---|
| SP-1-n4-F2 | 4 | 5 | 18.4 | 10 | 0.8 | ρ(p) = 2.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n4-F2 | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 2.0 g/L |
Table 6.
Specimen characters (dimensions in mm, n is number of piston heads, l is thickness of piston head, Dp is diameter of piston head, d is diameter of piston rod, h is height of gap).
Table 6.
Specimen characters (dimensions in mm, n is number of piston heads, l is thickness of piston head, Dp is diameter of piston head, d is diameter of piston rod, h is height of gap).
| Specimen | n | l | Dp | d | h | Fluid |
|---|
| SP-1--F1 | 4 | 5 | 18.4 | 10 | 0.8 | ρ(p) = 1.5 g/L |
| SP-1--F2 | 4 | 5 | 18.4 | 10 | 0.8 | ρ(p) = 2.0 g/L |
| SP-1--F3 | 4 | 5 | 18.4 | 10 | 0.8 | ρ(p) = 3.0 g/L |
| SP-1--F4 | 4 | 5 | 18.4 | 10 | 0.8 | ρ(p) = 4.0 g/L |
| SP-2--F1 | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 1.5 g/L |
| SP-2--F2 | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 2.0 g/L |
| SP-2--F3 | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 3.0 g/L |
| SP-2--F4 | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 4.0 g/L |
Table 7.
Specimen characters (dimensions in mm, n is number of piston heads, l is thickness of piston head, Dp is diameter of piston head, d is diameter of piston rod, h is height of gap).
Table 7.
Specimen characters (dimensions in mm, n is number of piston heads, l is thickness of piston head, Dp is diameter of piston head, d is diameter of piston rod, h is height of gap).
| Specimen | n | l | Dp | d | h | Fluid |
|---|
| SP-2-n1-F2 | 1 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 2.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n2-F2 | 2 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 2.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n3-F2 | 3 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 2.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n4-F2 | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 2.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n1-F3 | 1 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 3.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n2-F3 | 2 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 3.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n3-F3 | 3 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 3.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n4-F3 | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 3.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n1-F4 | 1 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 4.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n2-F4 | 2 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 4.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n3-F4 | 3 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 4.0 g/L |
| SP-2-n4-F4 | 4 | 5 | 18.8 | 10 | 0.6 | ρ(p) = 4.0 g/L |
Table 8.
Noise sound power levels (unit: dB).
Table 8.
Noise sound power levels (unit: dB).
| Rotations (rpm) | SP-2-n4-F3 | SP-2-n4-F0 | SP-2-n4-Fp | SP-2-n4-Fw | Friction Damper |
|---|
| 400 | 57.23 | 63.28 | 61.77 | 62.55 | 60.78 |
| 800 | 59.14 | 67.49 | 63.87 | 67.35 | 65.38 |
| 1200 | 59.78 | 70.61 | 65.71 | 69.37 | 67.12 |
| 1400 | 62.33 | 73.83 | 66.57 | 69.73 | 67.88 |
Table 9.
Materials and processing of main components.
Table 9.
Materials and processing of main components.
| Components | Raw Materials | Manufacturing Process |
|---|
| Connector | Plastic | Injection molding |
| Piston head | Plastic or Silica gel | Mold pressing |
| Piston rod | Metal tube | Stamping |
| Cylinder | Plastic | Injection molding |
| Sealing ring | Rubber | Mold processing |
| Damping fluid | Food level or industrial level powder | Dissolution |