A Disturbance Observer-Based Fractional-Order Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control Approach for Elevators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A fixed-time convergent sliding mode control strategy based on fractional-order calculus theory is newly proposed for elevators to enhance the speed control performance.
- An adaptive sliding mode disturbance observer is introduced to effectively monitor and counteract external disturbances in the elevator system to improve control performance further.
- The superiority of the proposed scheme is verified by detailed simulation results in different scenarios compared with mainstream benchmark controllers.
2. Modeling and Preliminaries
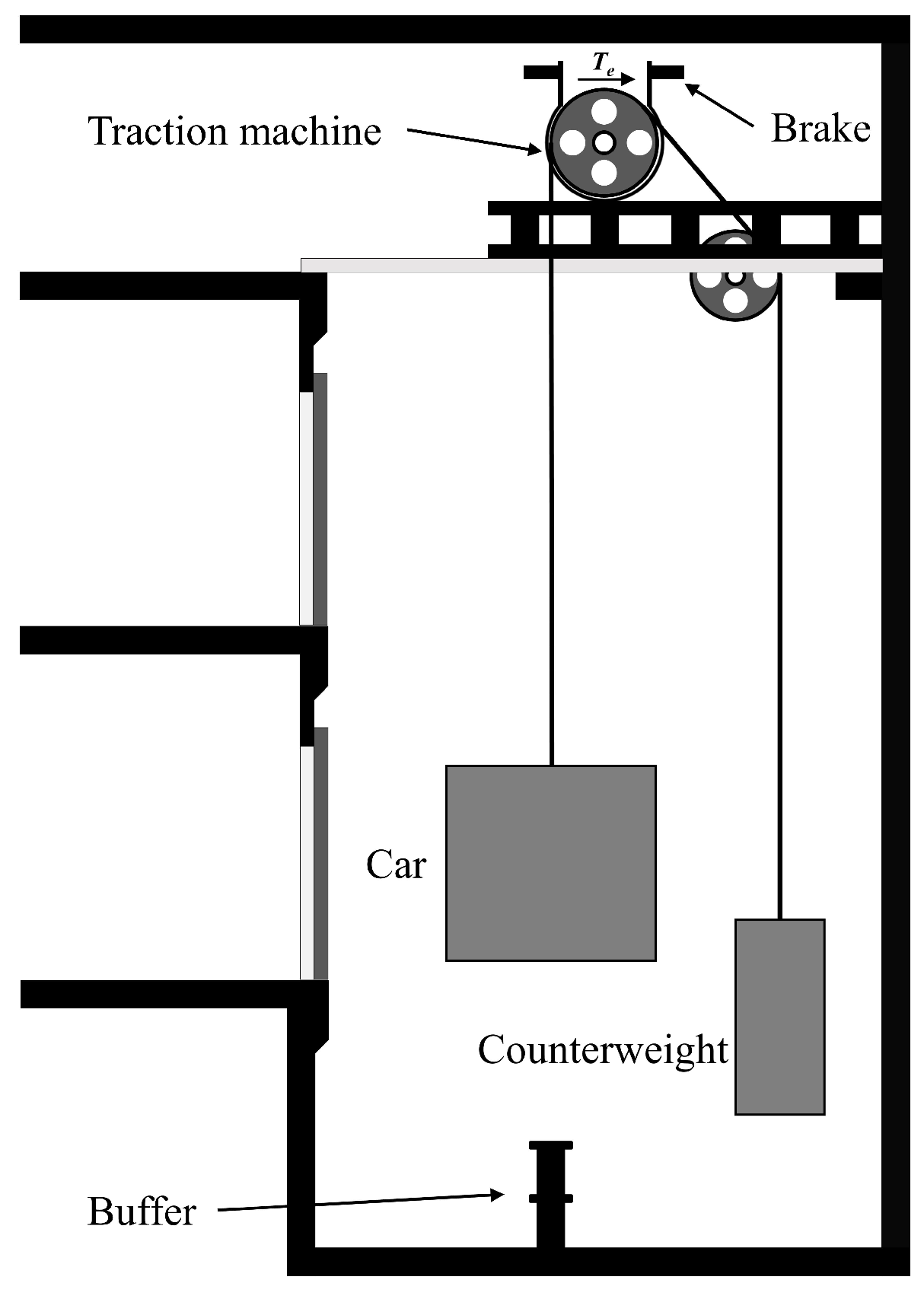
2.1. Dynamic Modeling of Elevator System
2.2. Definitions and Lemmas
3. Fixed-Time Adaptive Sliding Mode Disturbance Observer
4. Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Controller
4.1. Control Algorithm Design
4.2. Stability Analysis
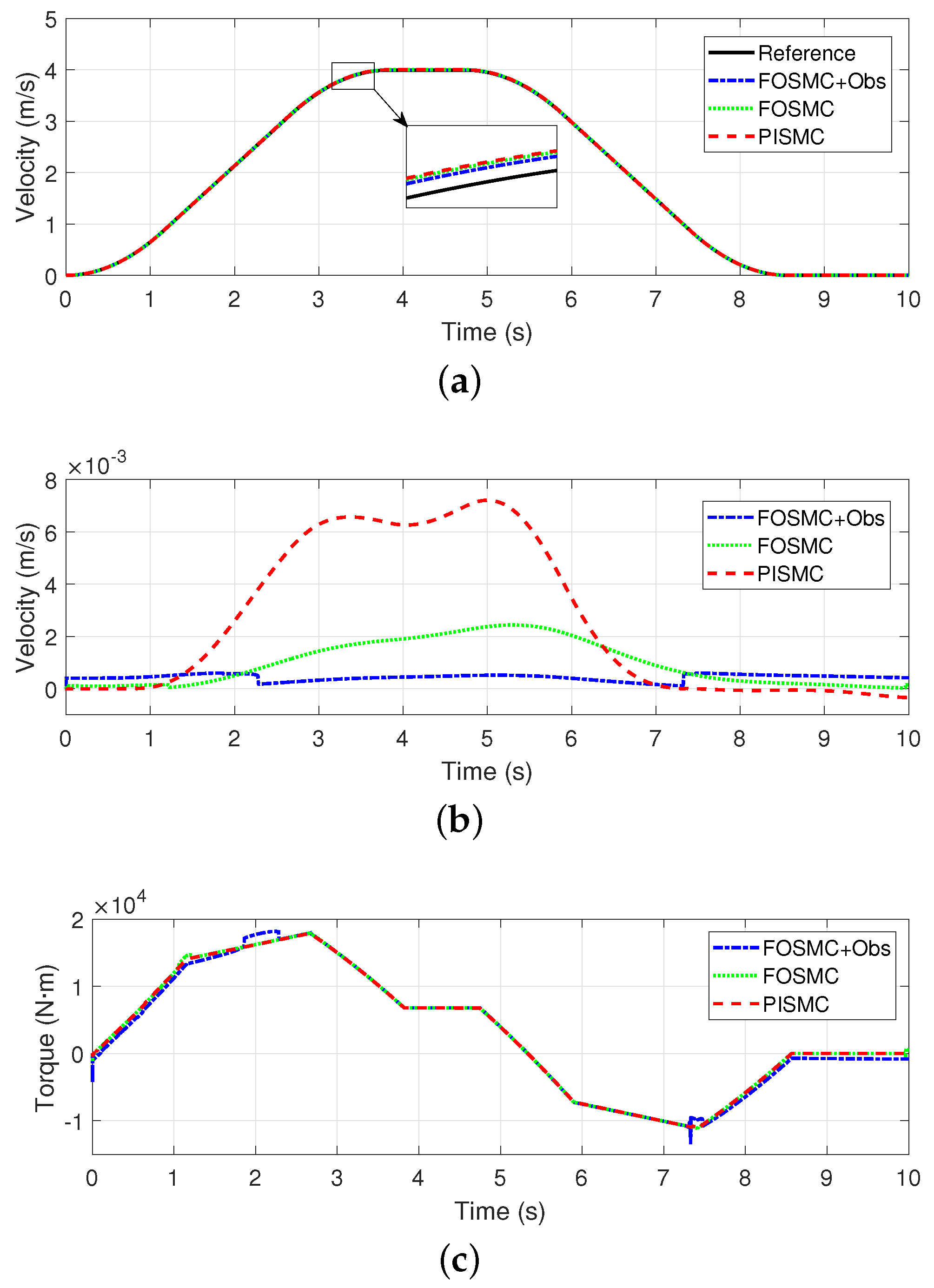
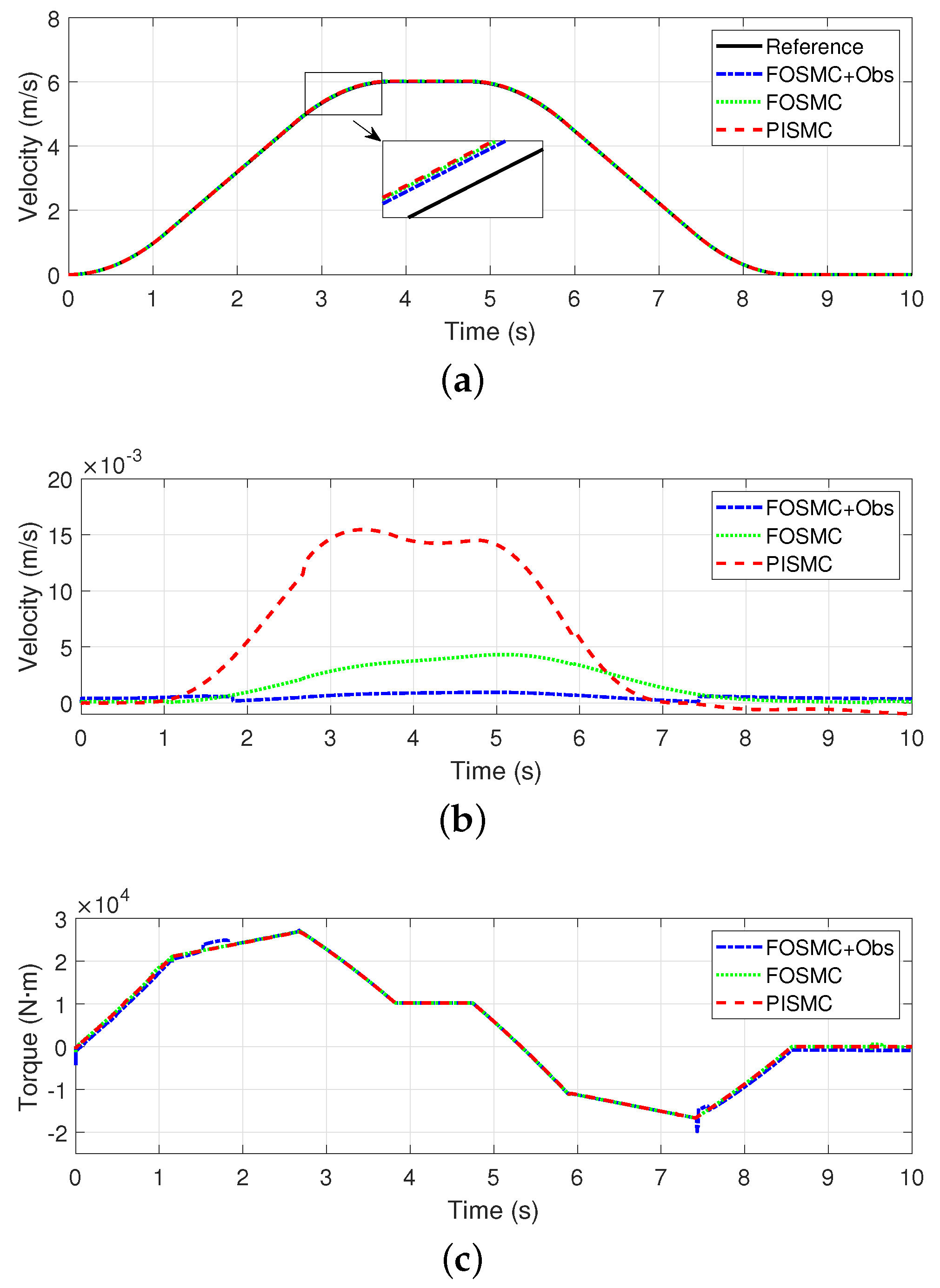
5. Simulation Results
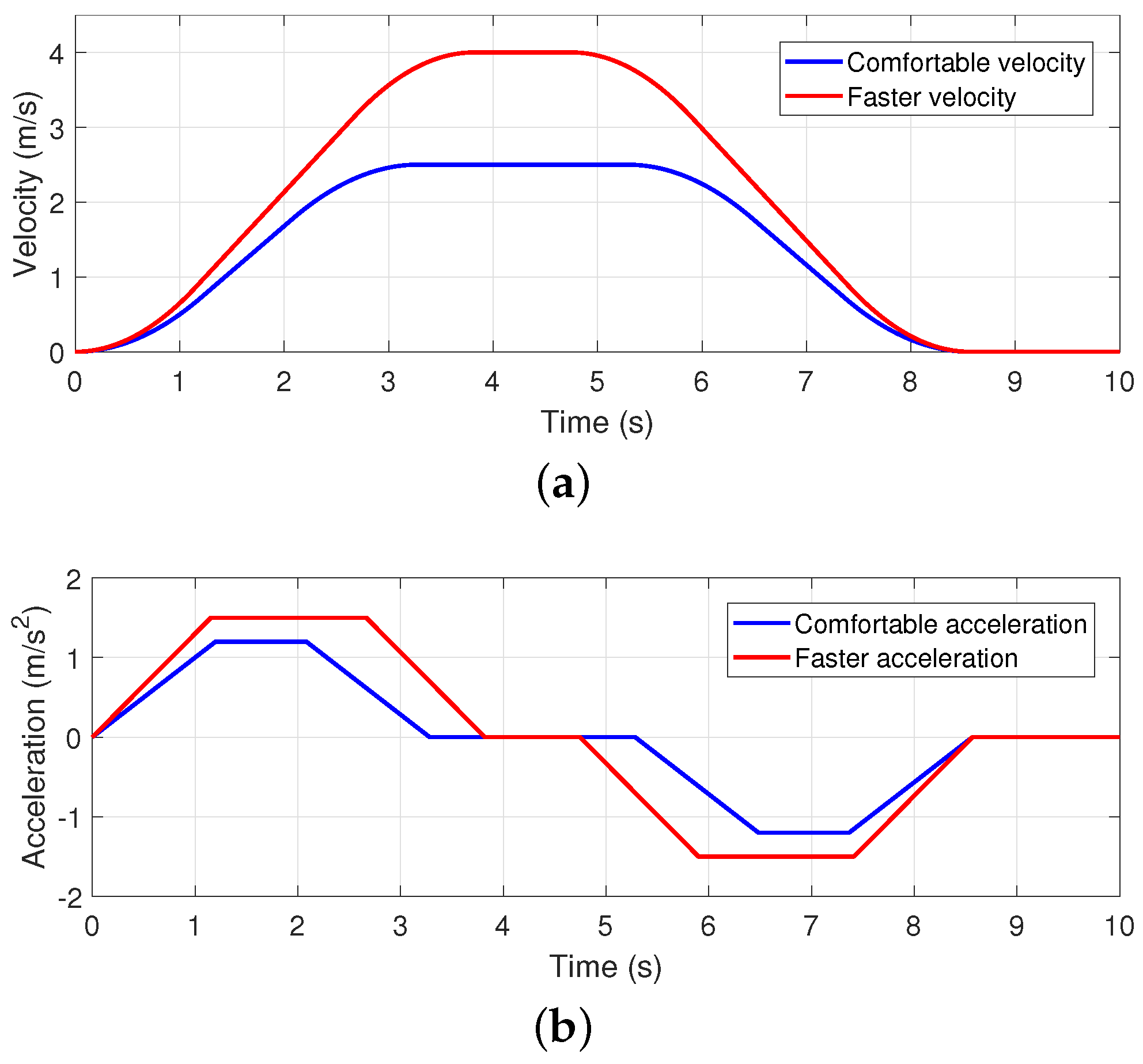
5.1. Velocity Profiles and Realization
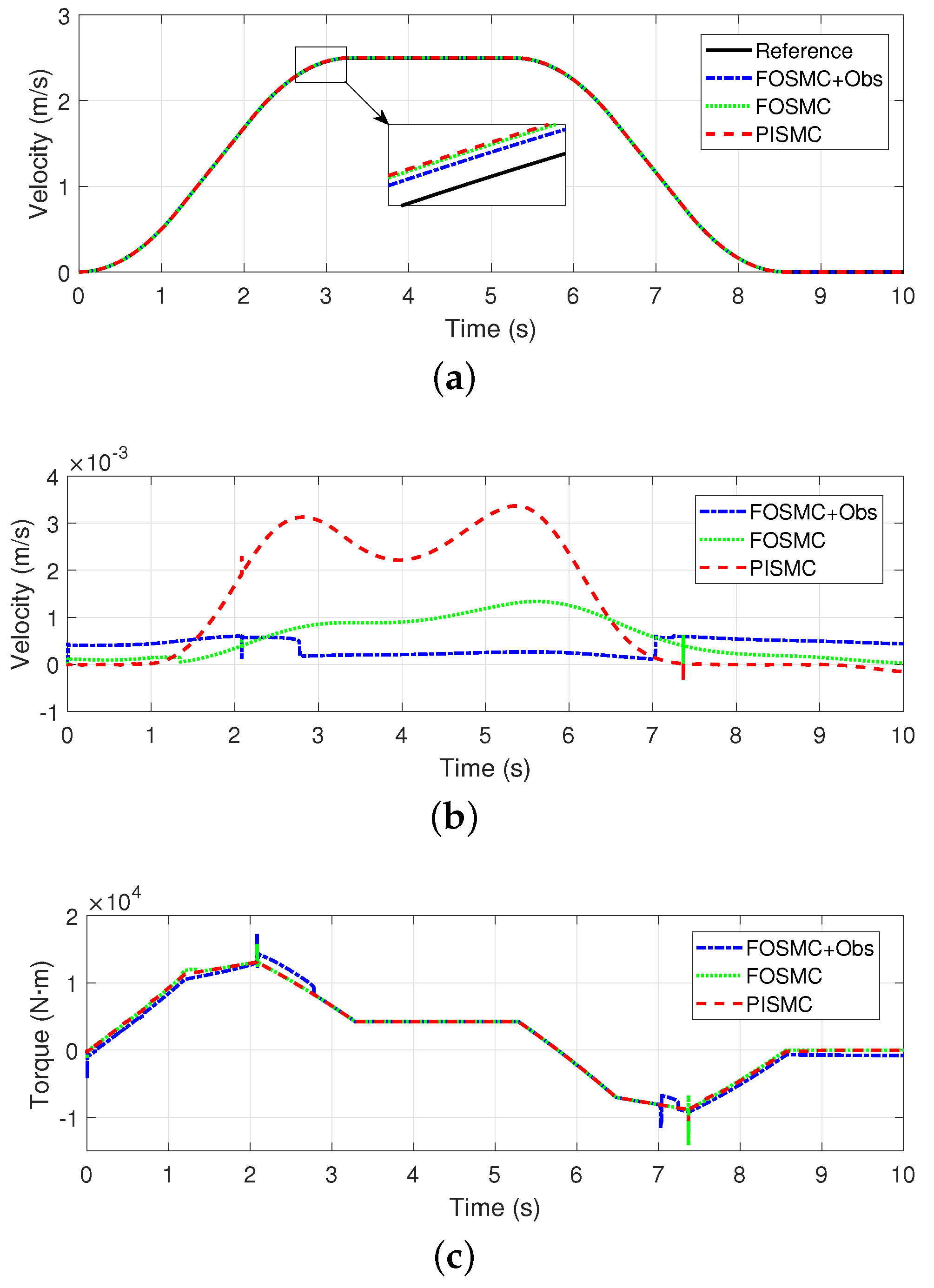
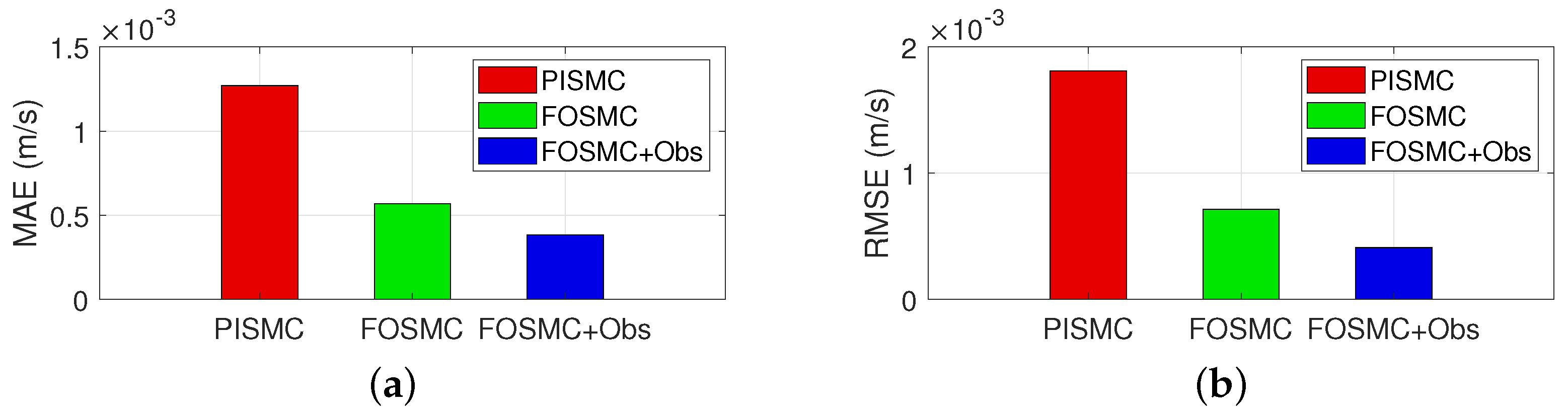
5.2. Analysis of Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ovaska, S.J. Electronics and information technology in high-range elevator systems. Mechatronics 1992, 2, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Lee, M. Modeling study on distributed control of elevators. J. Inst. Electr. Eng. 2007, 44, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ladany, S.; Hersh, M. The design of an efficient elevator operating system. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1995, 25, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X. Study of elevator safety system problems and improvement programs. J. Korean Comput. Inf. Soc. 2020, 25, 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, W.; Luo, F.; Huang, X.; Li, P. New elevator energy feedback control system design based on fuzzy PID controller. In Proceedings of 2012 Power Engineering and Automation Conference, Wuhan, China, 18–20 September 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Cao, L.; Zhang, A. Application of neural network PID controller to elevator control system. In Proceedings of the 29th Chinese Control Conference, Beijing, China, 29–31 July 2010; pp. 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Q. Speed control of hydraulic elevator by using PID controller and self-tuning fuzzy PID controller. In Proceedings of the 2017 32nd Youth Academic Annual Conference of Chinese Association of Automation (YAC), Hefei, China, 19–21 May 2017; pp. 812–817. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Tan, W. Design of PID controller with incomplete derivation based on differential evolution algorithm. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2008, 19, 578–583. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaraman, K.; Nagaraja, S.K. An elevator speed-control system using squirrel-cage induction motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1984, IE-31, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, B.; Won, C.; Hur, J. Fuzzy-logic-based vector control scheme for permanent-magnet synchronous motors in elevator drive applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 2190–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; He, Q.; Liu, L. Variable universe fuzzy control of high-speed elevator horizontal vibration based on firefly algorithm and backpropagation fuzzy neural network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 57020–57032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Z.; Palaniswami, M. Robust tracking control for rigid robotic manipulators. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1994, 39, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Zheng, J.; Man, Z.; Wang, H. Robust control of a vehicle steer-by-wire system using adaptive sliding mode. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2251–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zheng, J.; Man, Z.; Fu, M.; Lu, R. Nested adaptive super-twisting sliding mode control design for a vehicle steer-by-wire system. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 122, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-C. Disturbance-Observer-Based Sliding-Mode Speed Control for Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drives via Generalized Super-Twisting Algorithm. Actuators 2024, 13, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xie, H.; Zheng, J.; Man, Z.; He, D. Path-following control of Mecanum-wheels omnidirectional mobile robots using nonsingular terminal sliding mode. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 147, 107128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hu, S.; Xie, H.; Li, H.; Zheng, J.; Chen, B. Fuzzy adaptive recursive terminal sliding mode control for an agricultural omnidirectional mobile robot. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 105, 108529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavikumar, R.; Kaviarasan, B.; Lee, Y.G.; Kwon, O.M.; Sakthivel, R.; Choi, S.G. Robust dynamic sliding mode control design for interval type-2 fuzzy systems. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst.-Ser. S 2022, 15, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Su, C.-Y. Reinforcement Learning-Based Fractional-Order Adaptive Fault-Tolerant Formation Control of Networked Fixed-Wing UAVs With Prescribed Performance. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 3365–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.-K.; Kumar, N. Fractional order fast terminal sliding mode control scheme for tracking control of robot manipulators. ISA Trans. 2023, 142, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, L.; Fanghella, P.; Basso, D. Application of the Half-Order Derivative to Impedance Control of the 3-PUU Parallel Robot. Actuators 2022, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Ma, Z. Practical Tracking Control of Linear Motor With Adaptive Fractional Order Terminal Sliding Mode Control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2017, 22, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Ma, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhou, X. Lateral Trajectory Tracking of Self-Driving Vehicles Based on Sliding Mode and Fractional-Order Proportional-Integral-Derivative Control. Actuators 2024, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, J.; Feng, Z. Fractional-order finite-time super-twisting sliding mode control of micro gyroscope based on double-loop fuzzy neural network. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 7692–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, Z.; Huang, P.; Kuang, Z. Adaptive fractional-order sliding mode control for admittance-based telerobotic system with optimized order and force estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 5165–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chiang, H.; Liu, T.; Chang, C. Precision motion control of permanent magnet linear synchronous motors using adaptive fuzzy fractional-order sliding-mode control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2019, 24, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokic, R.; Vladic, J.; Kljajin, M.; Jovanovic, V.; Markovic, G.; Karakasic, M. Dynamic modelling, experimental identification and computer simulations of non-stationary vibration in high-speed elevators. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 67, 287–301. [Google Scholar]
- Moulay, E.; Léchappé, V.; Bernuau, E.; Plestan, F. Robust fixed-time stability: Application to sliding-mode control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 67, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilbas, A.; Srivastava, H.; Trujillo, J. Fractional integrals and fractional derivatives. In Theory and Applications of Fractional Differential Equations, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 69–133. [Google Scholar]
- Pudlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations; Academic: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, Z.; Sun, L.; Gao, H.; Tomizuka, M. Practical fractional-order variable-gain super twisting control with application to wafer stages of photolithography systems. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2022, 27, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, A. Nonlinear feedback design for fixed-time stabilization of linear control systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2012, 57, 2106–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Zuo, Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, H. A fixed-time output feedback control scheme for double integrator systems. Automatica 2017, 80, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, K.; Su, W.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, B. A Disturbance Observer-Based Fractional-Order Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control Approach for Elevators. Actuators 2024, 13, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13110438
Sun Z, Liu H, Li K, Su W, Jiang Y, Chen B. A Disturbance Observer-Based Fractional-Order Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control Approach for Elevators. Actuators. 2024; 13(11):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13110438
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhe, Huaqing Liu, Ke Li, Wanbin Su, Yefeng Jiang, and Bo Chen. 2024. "A Disturbance Observer-Based Fractional-Order Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control Approach for Elevators" Actuators 13, no. 11: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13110438
APA StyleSun, Z., Liu, H., Li, K., Su, W., Jiang, Y., & Chen, B. (2024). A Disturbance Observer-Based Fractional-Order Fixed-Time Sliding Mode Control Approach for Elevators. Actuators, 13(11), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13110438





