High-Precision Control of Control Moment Gyroscope Gimbal Servo Systems via a Proportional–Integral–Resonant Controller and Noise Reduction Extended Disturbance Observer
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To address multiple disturbances affecting gimbal servo systems, this paper classifies the disturbances into high-frequency periodic disturbance caused by rotor dynamic imbalance and other low-frequency disturbances based on frequency characteristics.
- (2)
- To minimize the disturbance estimation error caused by measurement noises, the integral of the virtual measurement of the lumped disturbance is derived to establish the disturbance dynamic model. Subsequently, an NREDO is designed based on the model. Innovatively, the estimation error of the augmented state is utilized to drive the convergence of NREDO error dynamics, thereby enhancing the suppression of measurement noise.
- (3)
- A resonant controller is utilized to reject rotor dynamic imbalance disturbance, instead of using a disturbance observer to estimate it. The composite speed controller is composed of a PIR controller and an NREDO. The proposed control scheme can maximize the suppression of complex disturbances, improving the speed control accuracy of gimbal servo systems.
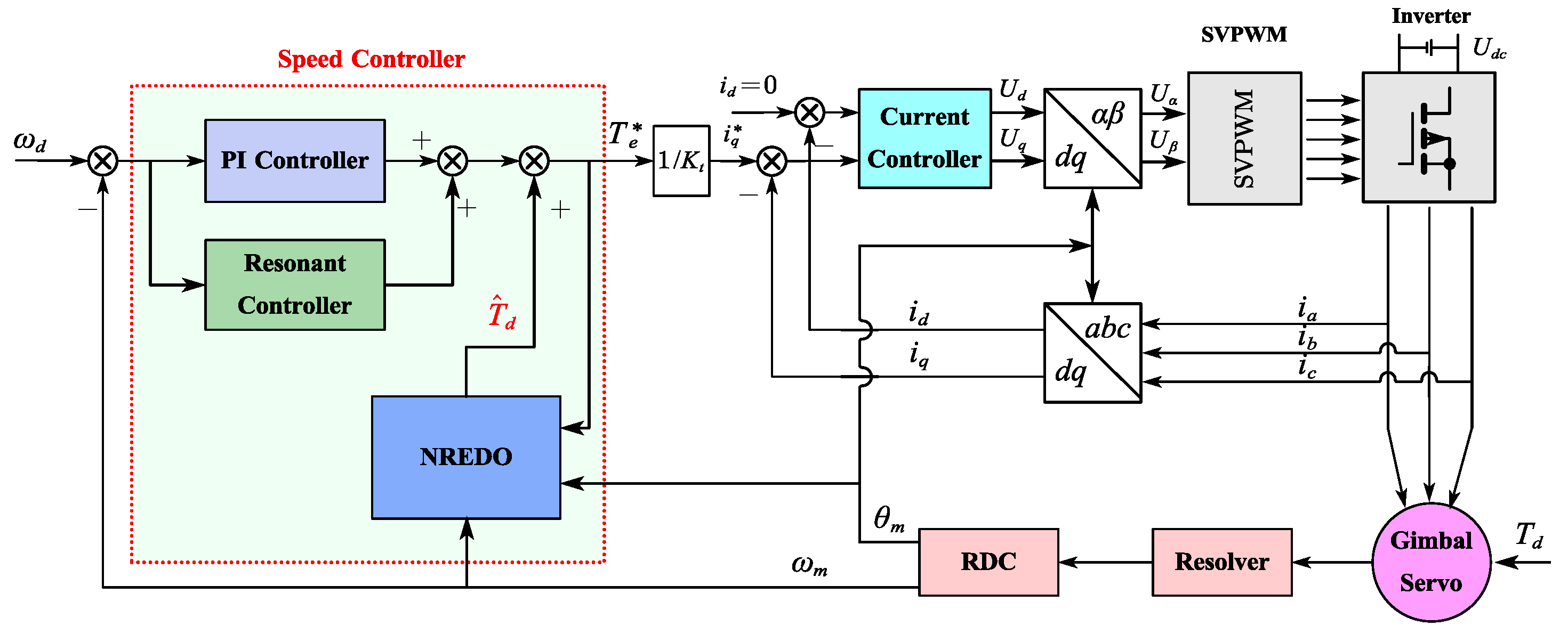
2. Mathematical Model and Problem Statement
2.1. Mathematical Model of Gimbal Servo System
2.2. Analysis of Multiple Disturbances
2.3. Problem Statement
3. PIR-NREDO Controller
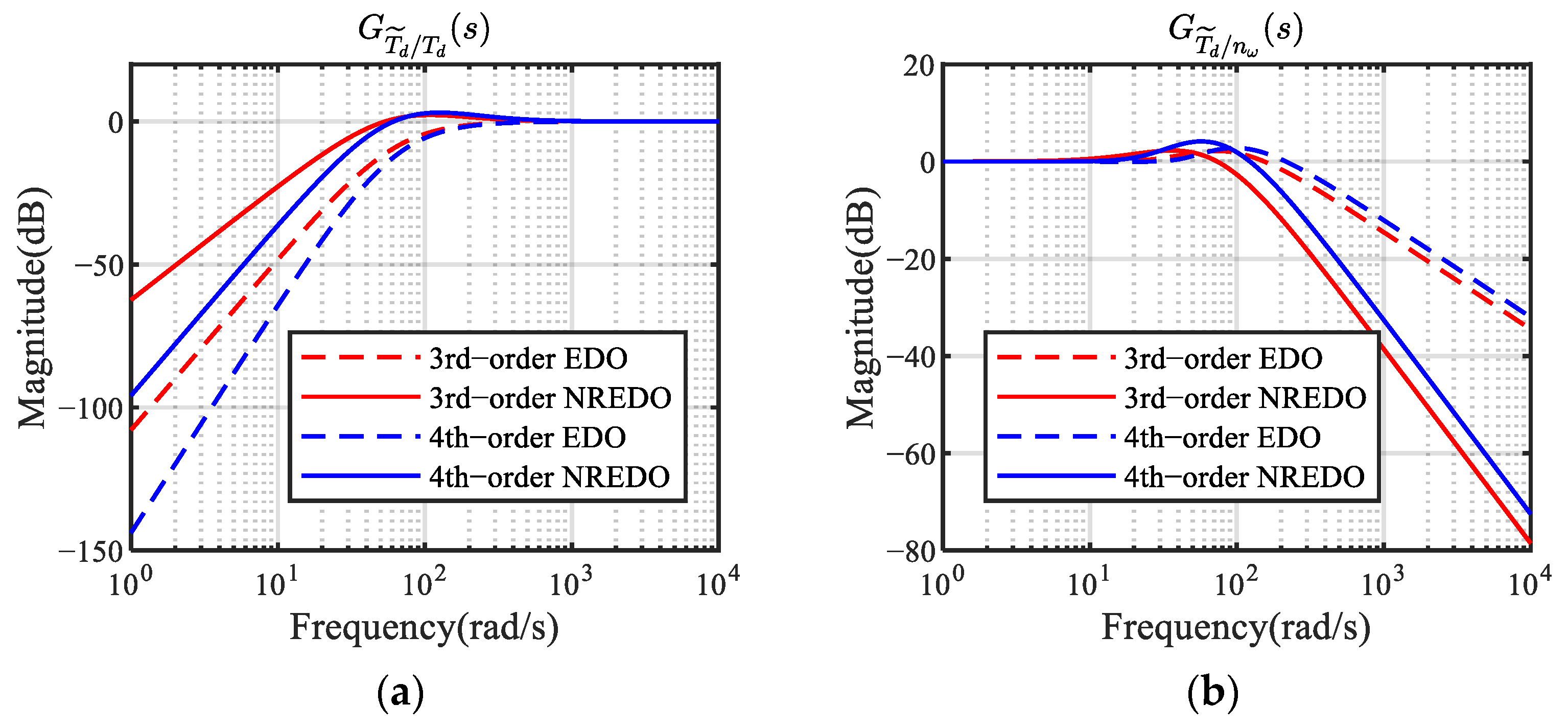
3.1. Design of NREDO
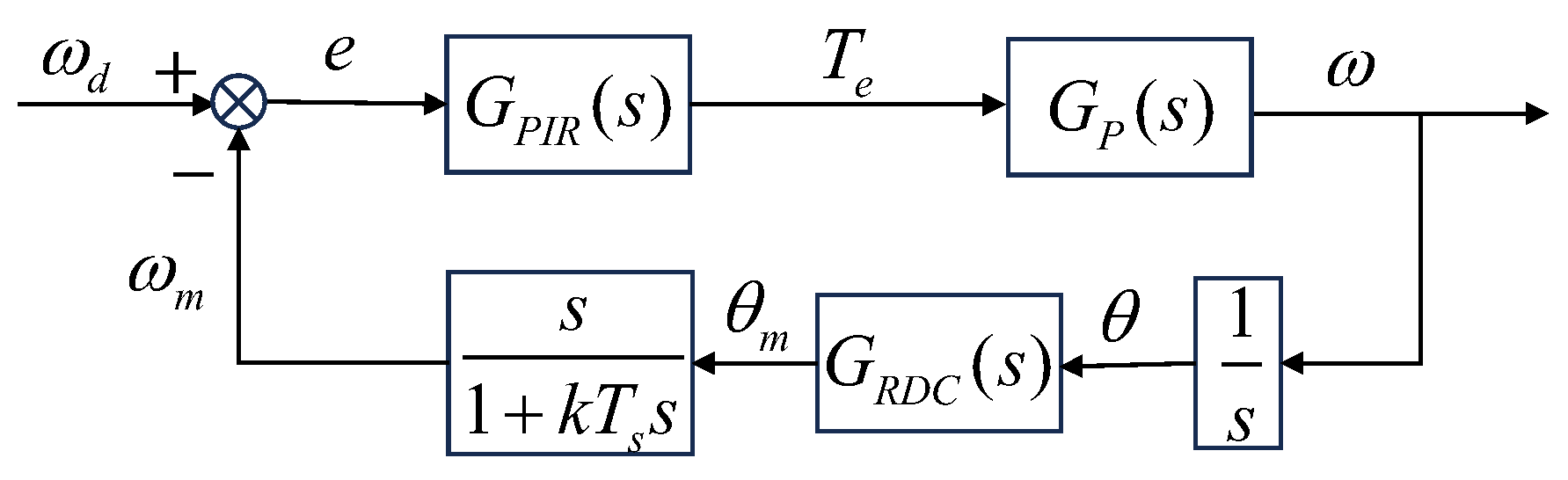
3.2. Design of PIR Controller
3.3. Stability Proof
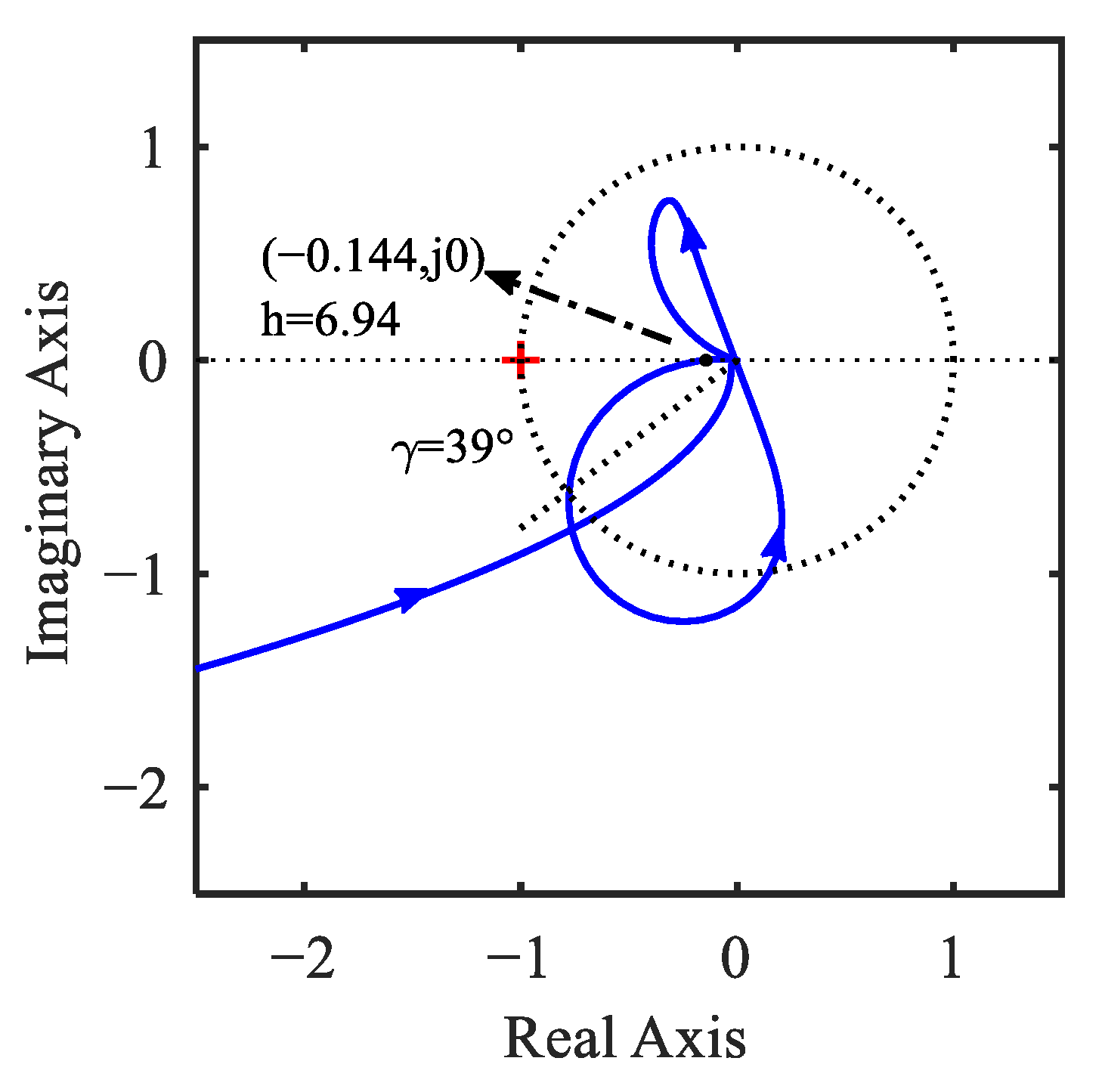
3.4. Stability Margin
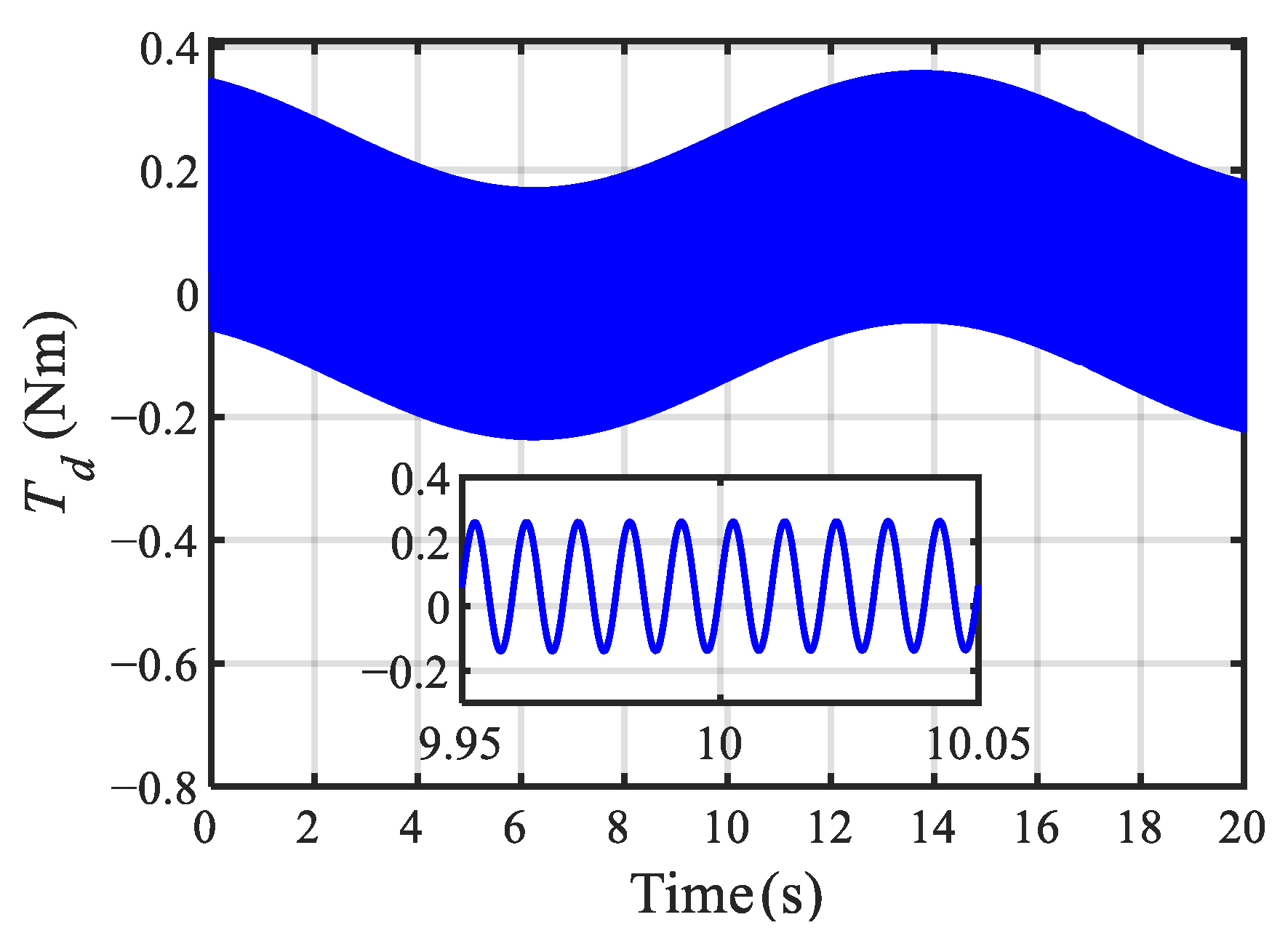
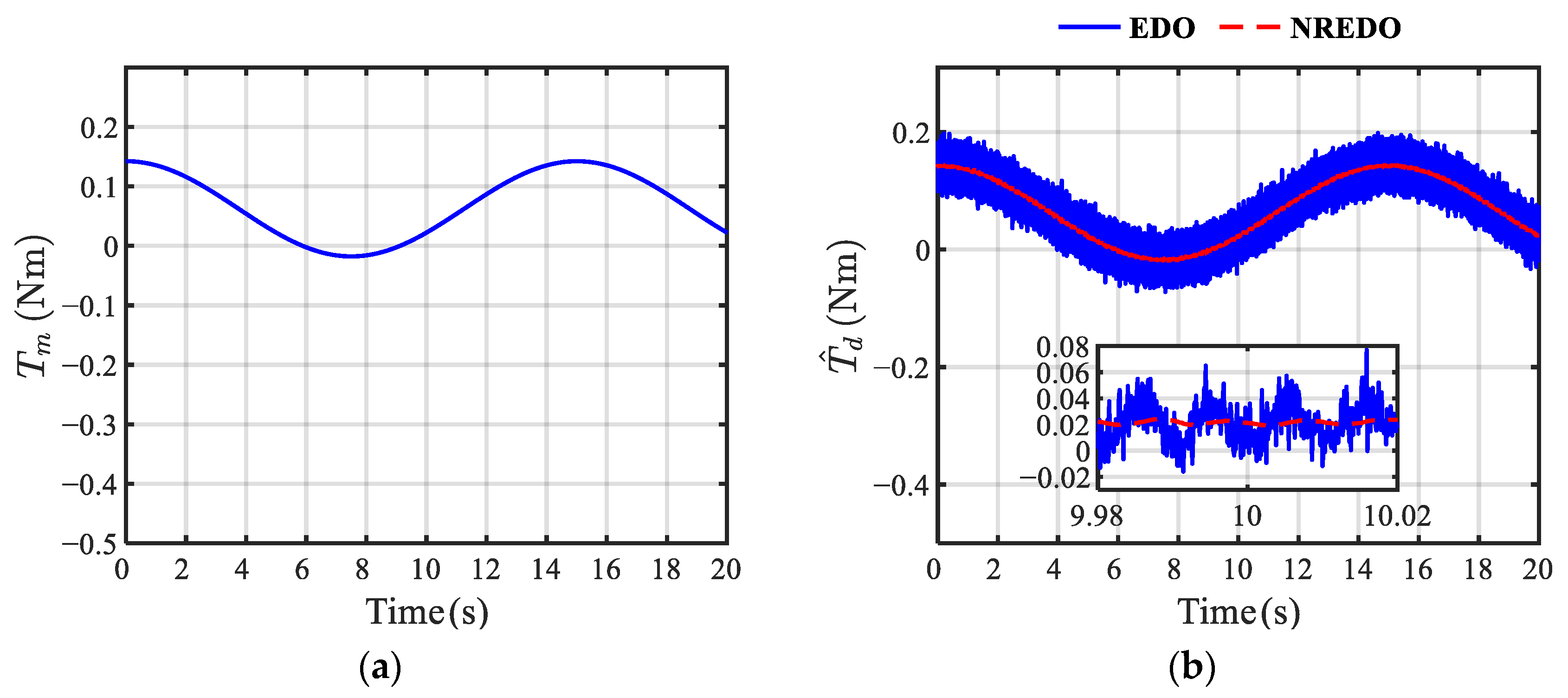
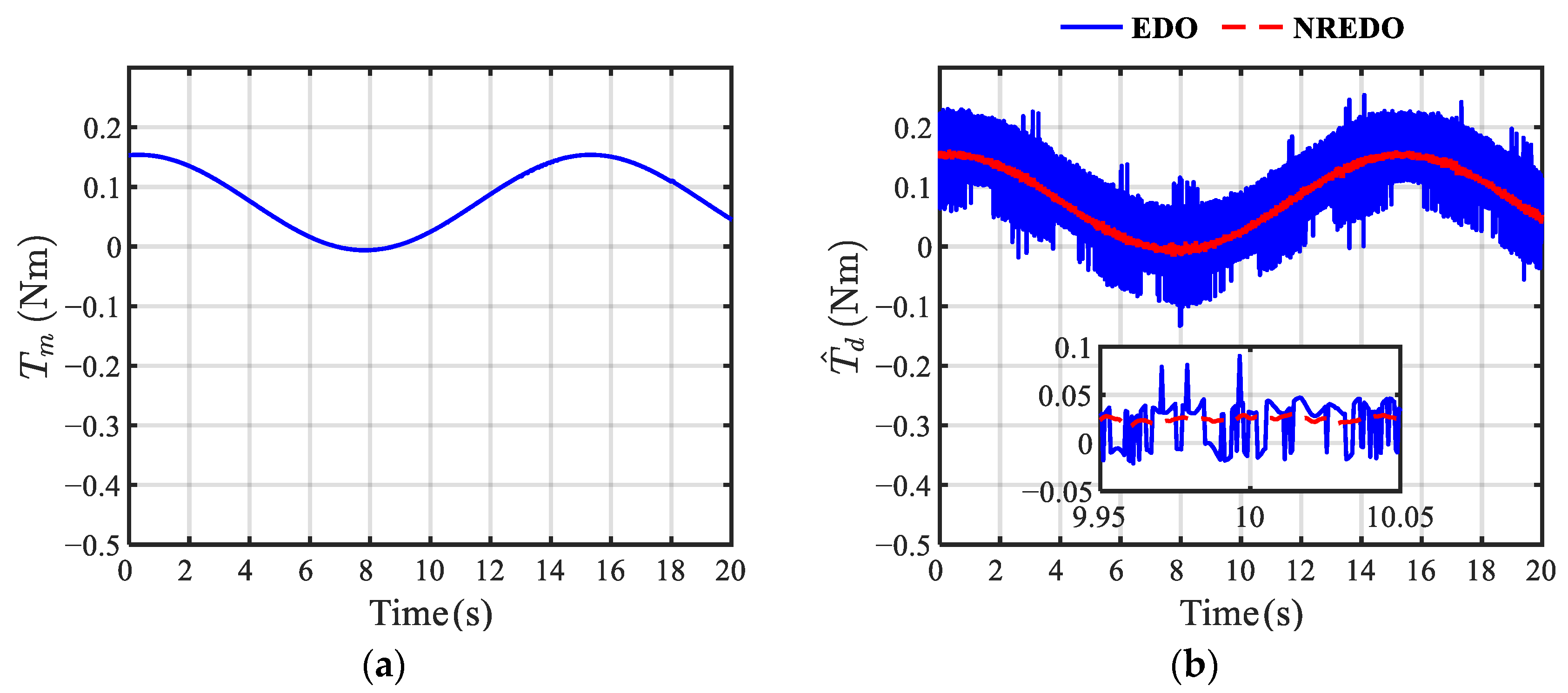
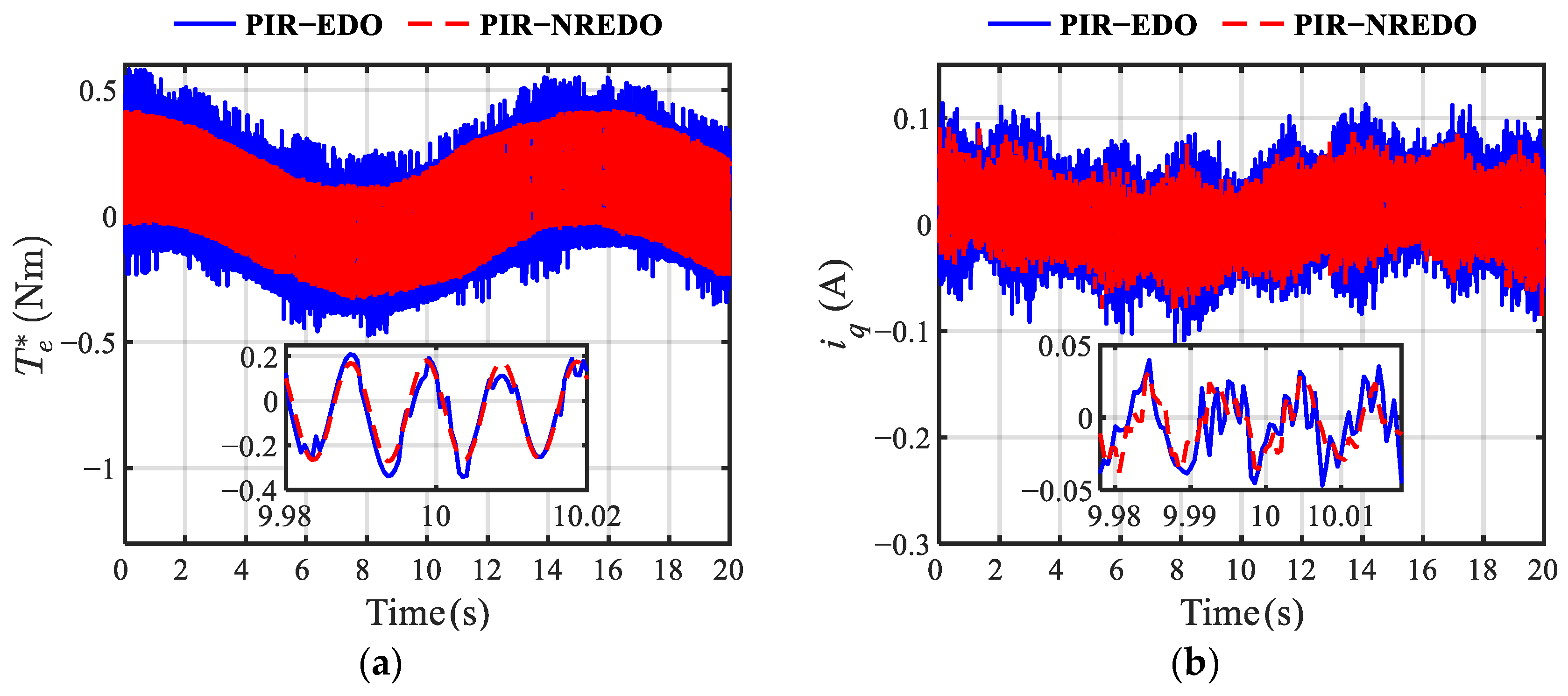
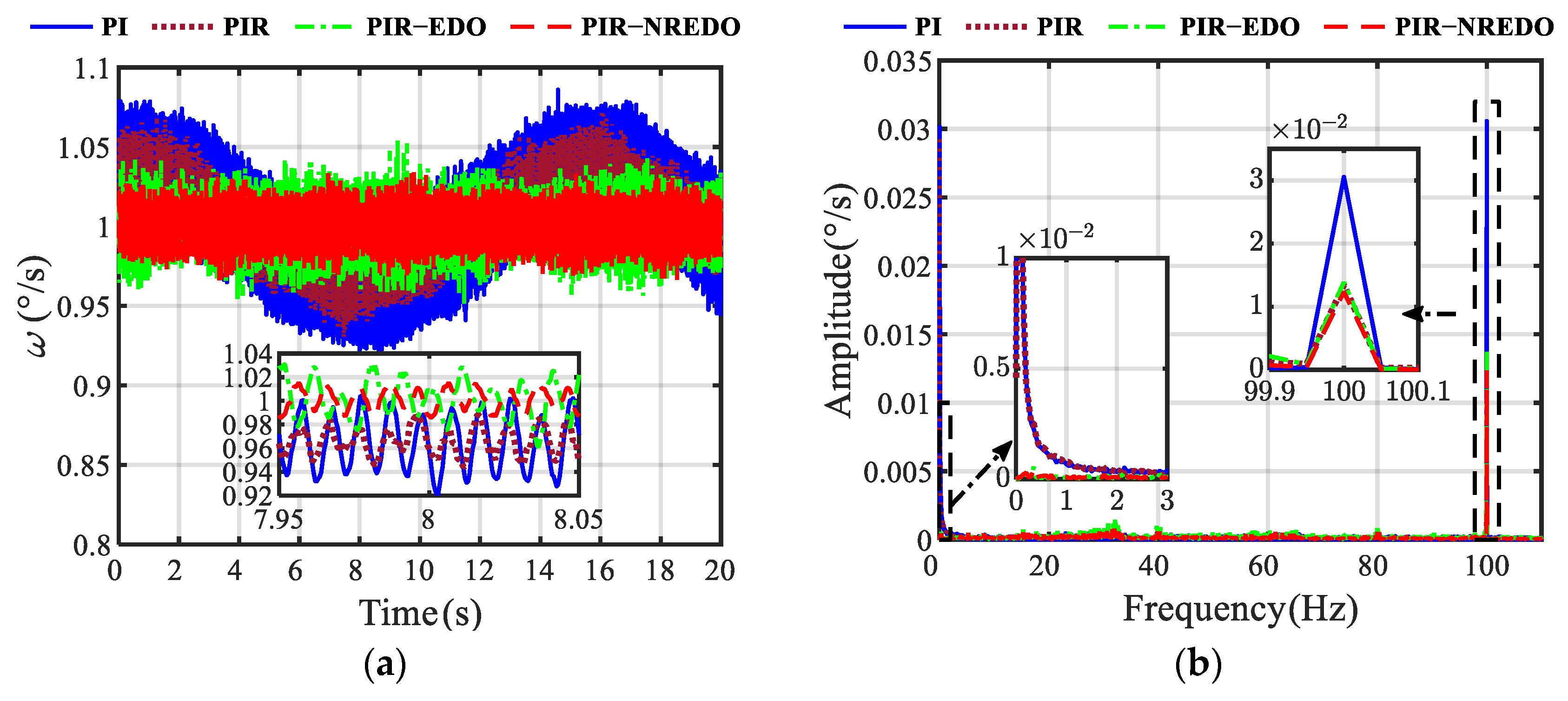
4. Simulation Results
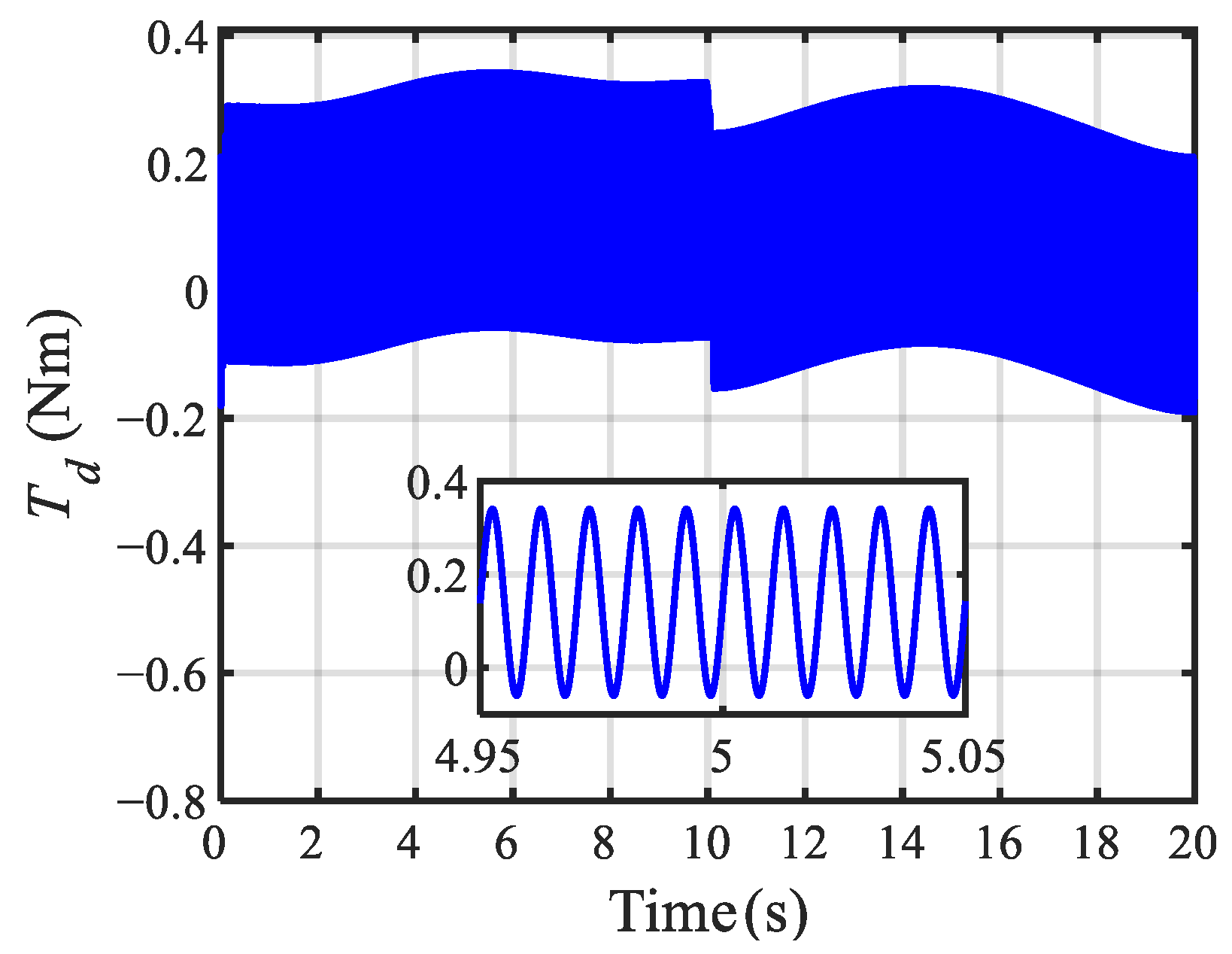
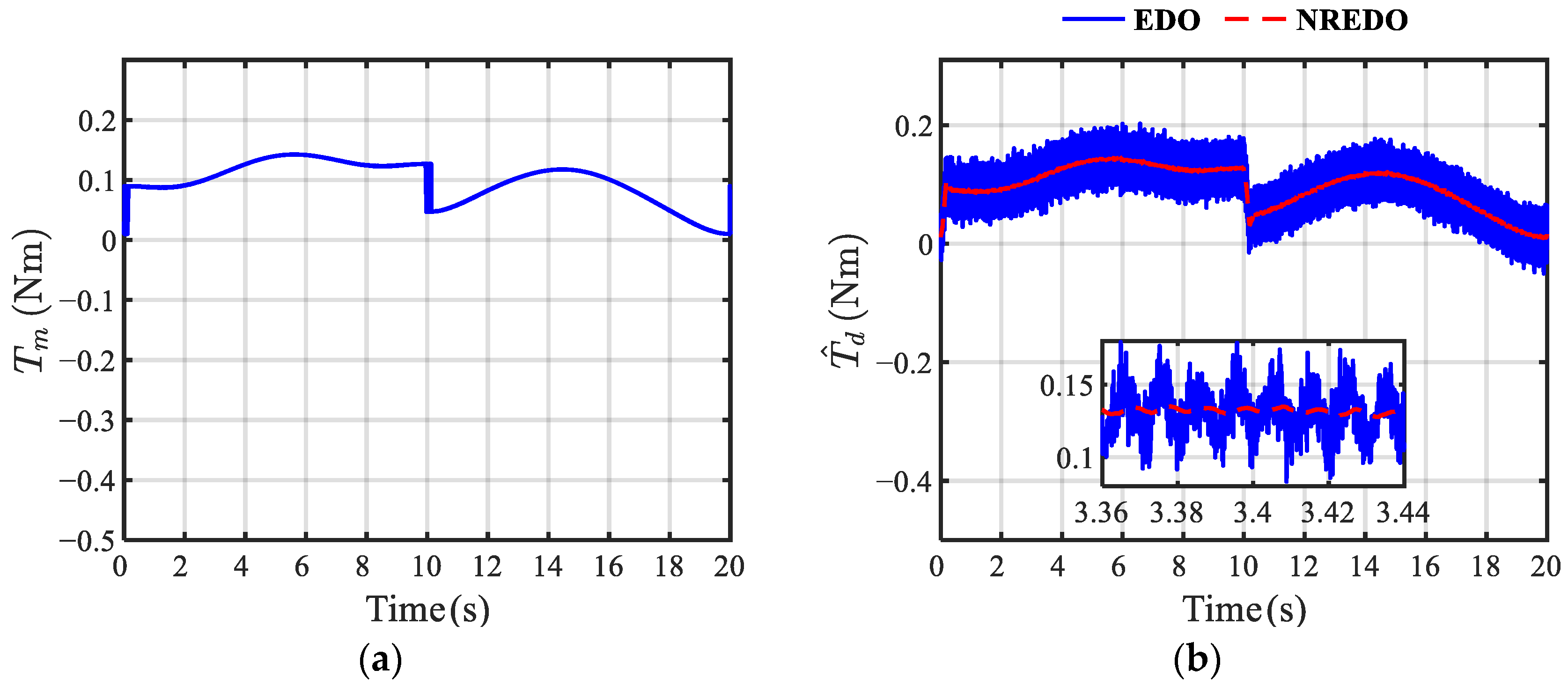
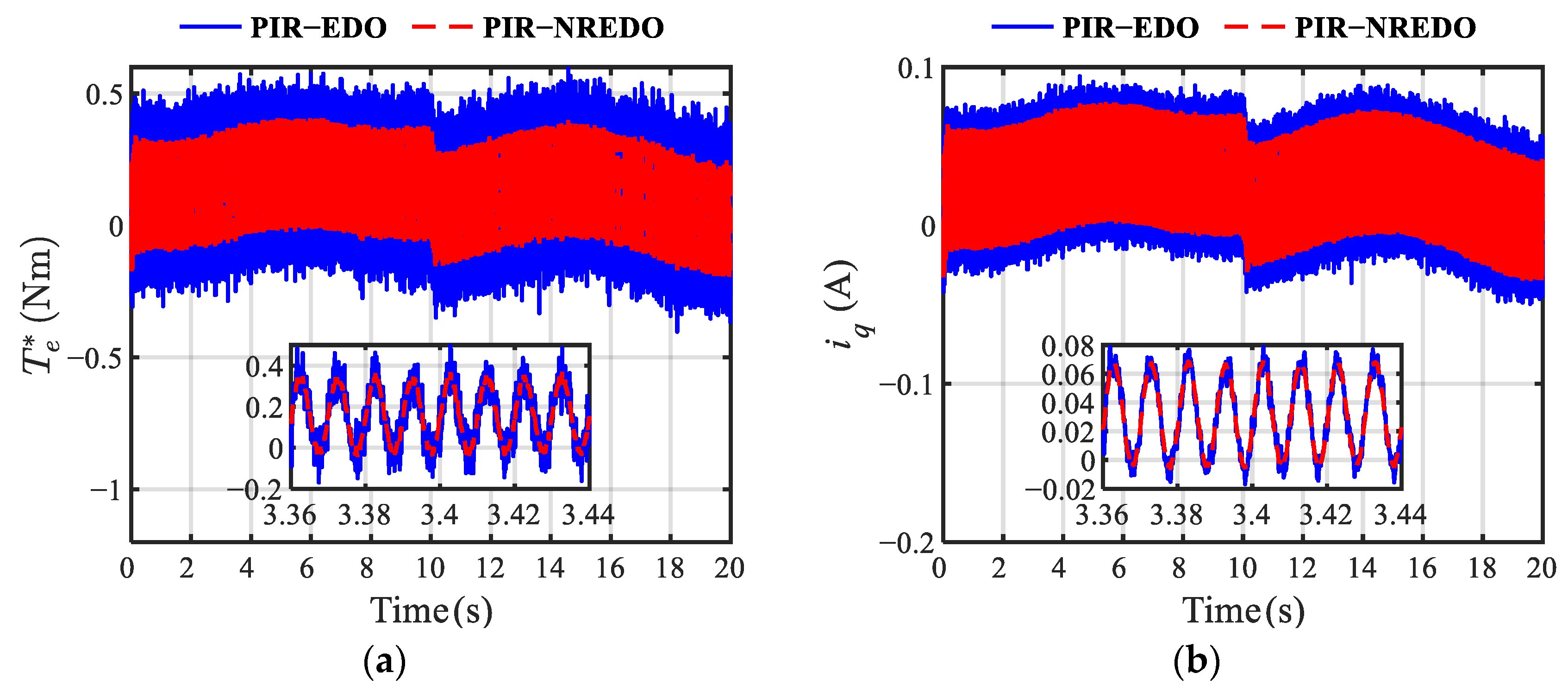
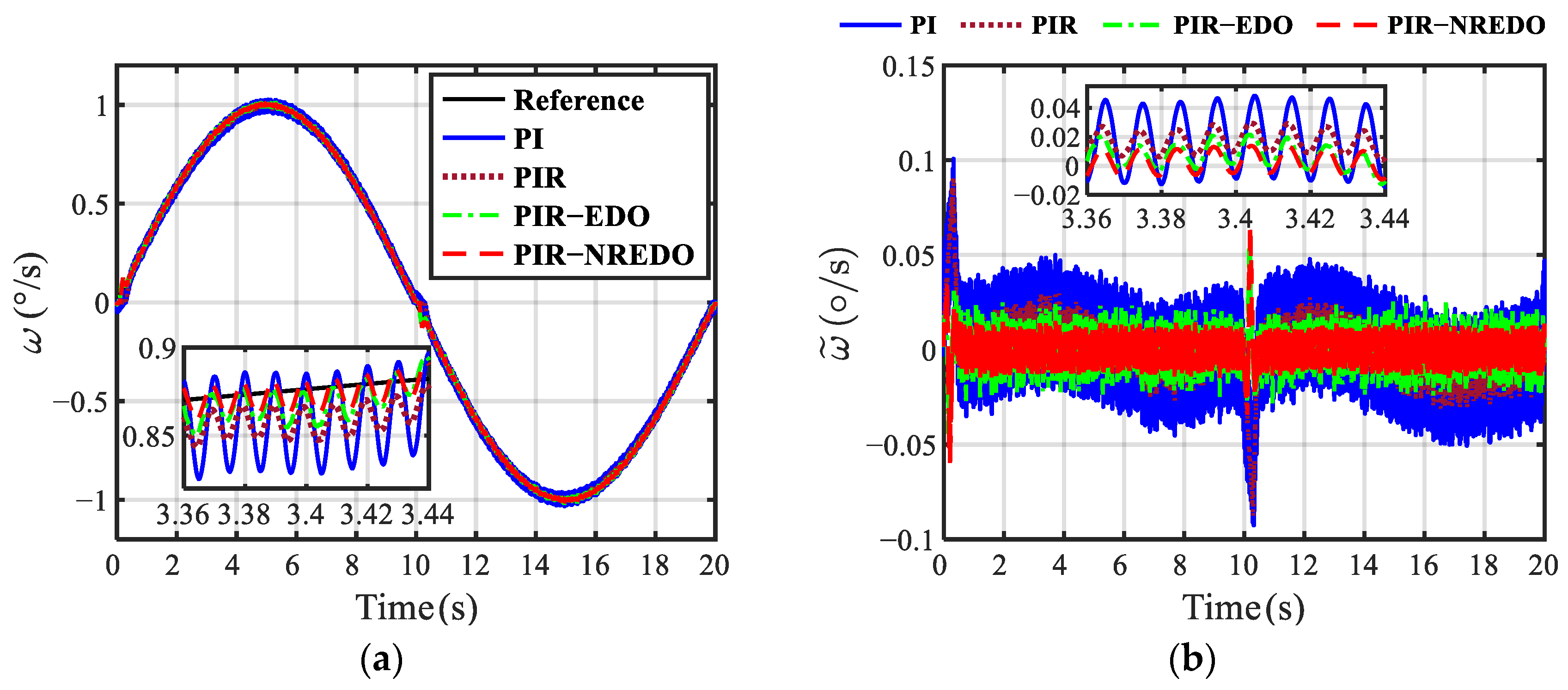
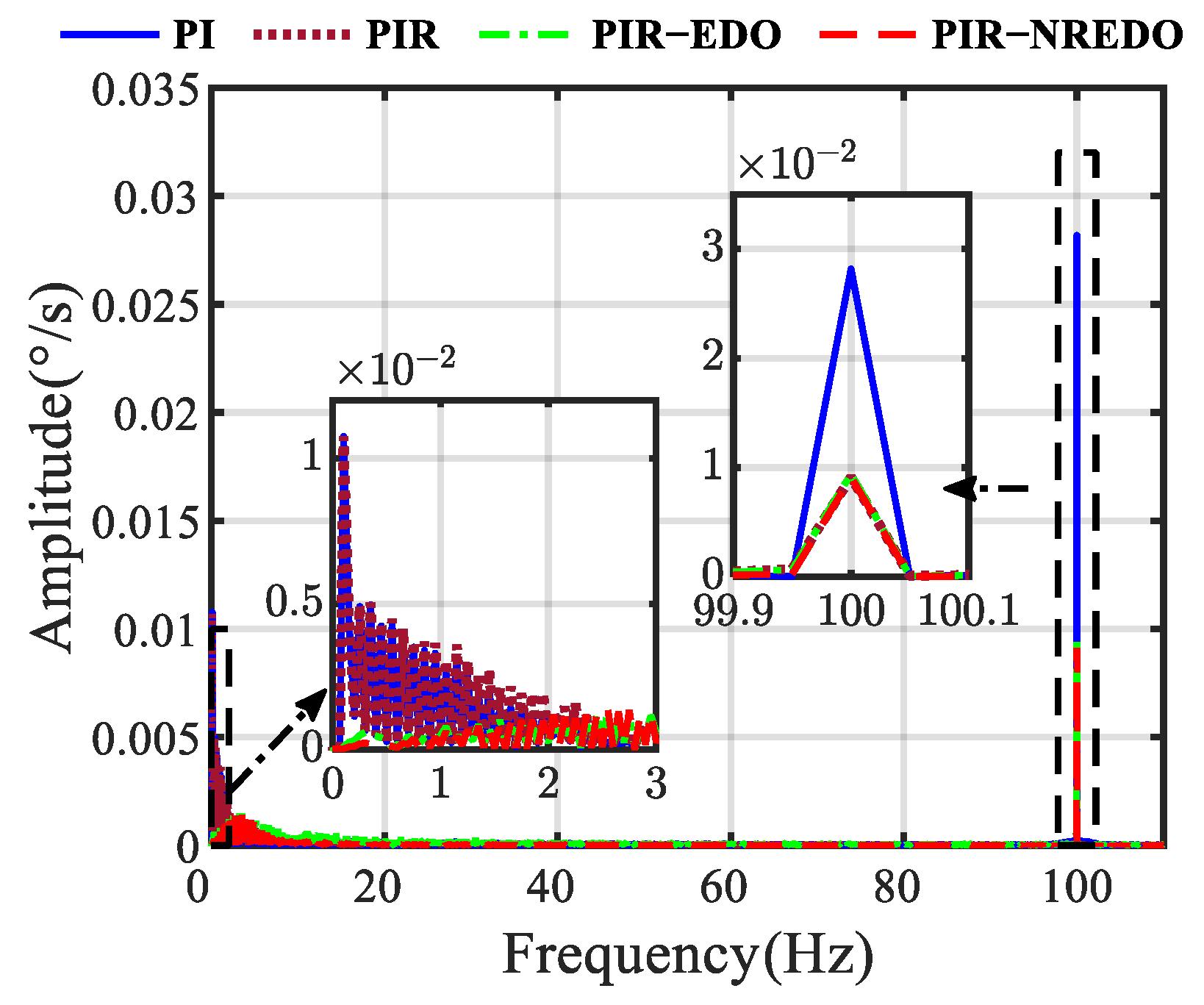
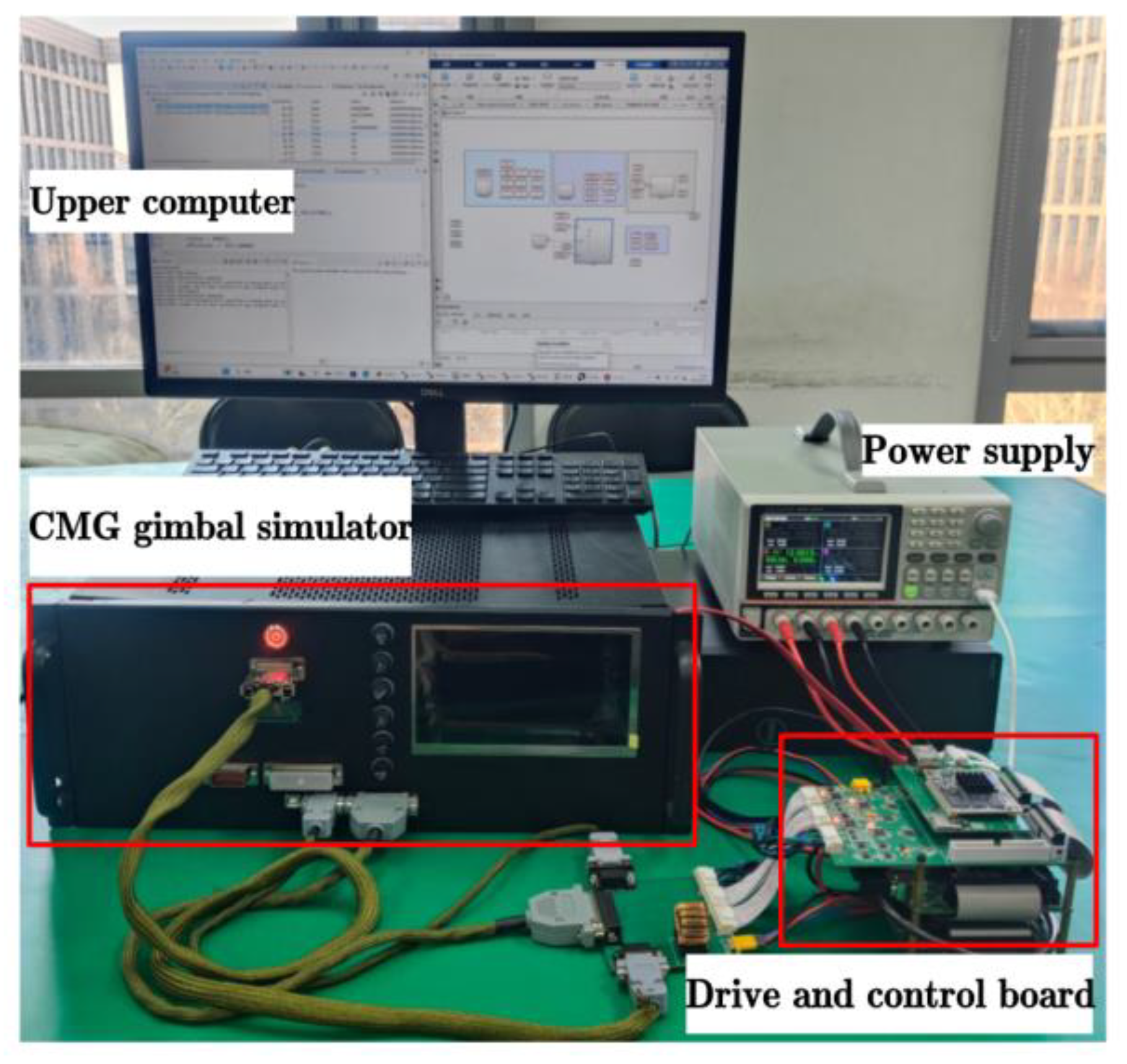
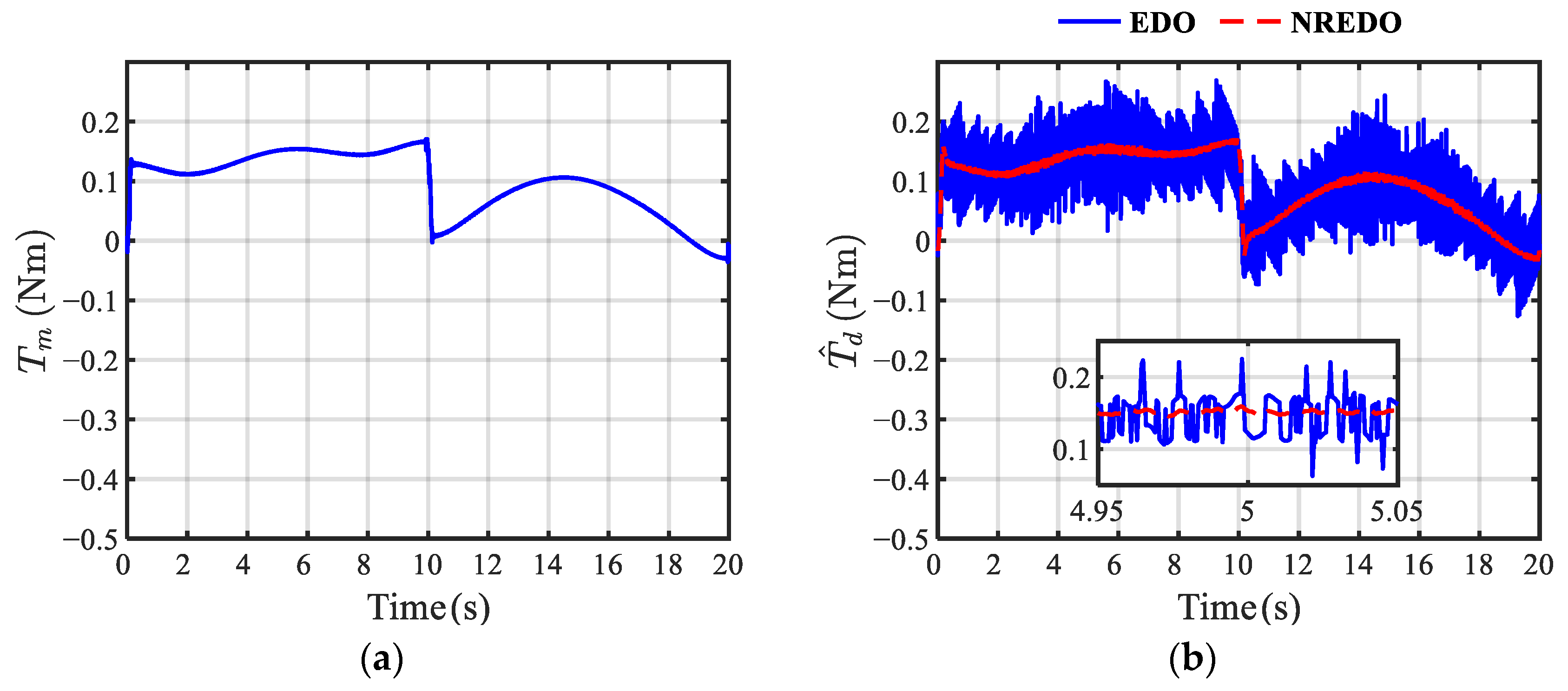
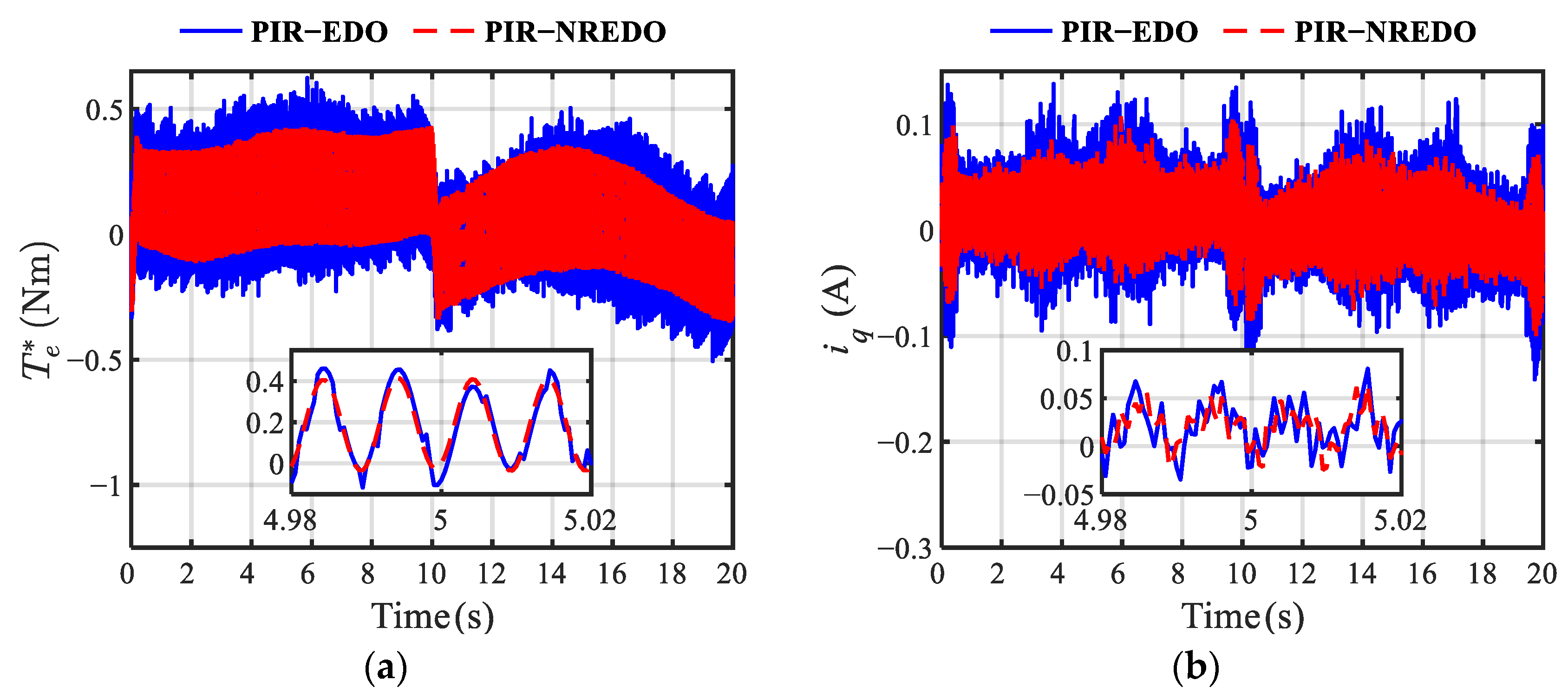
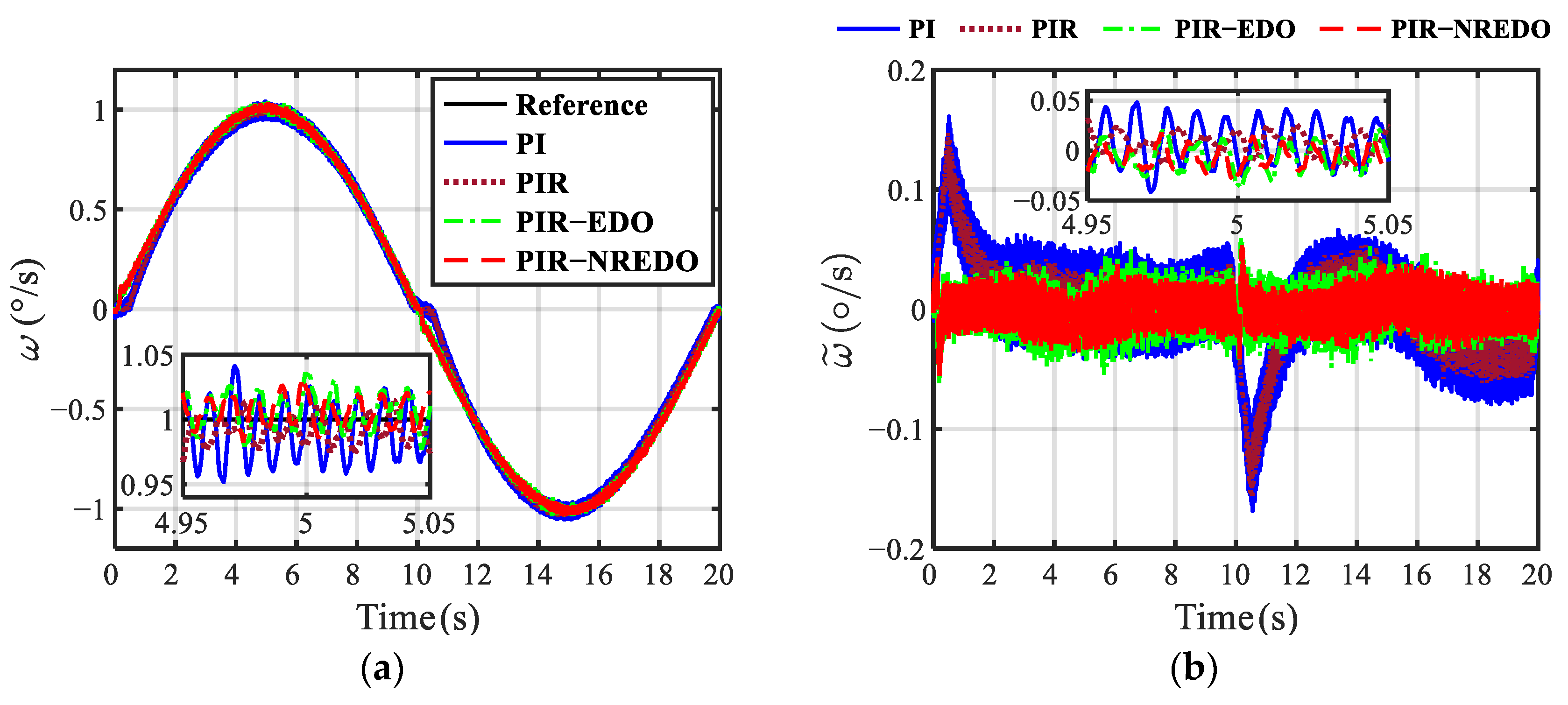
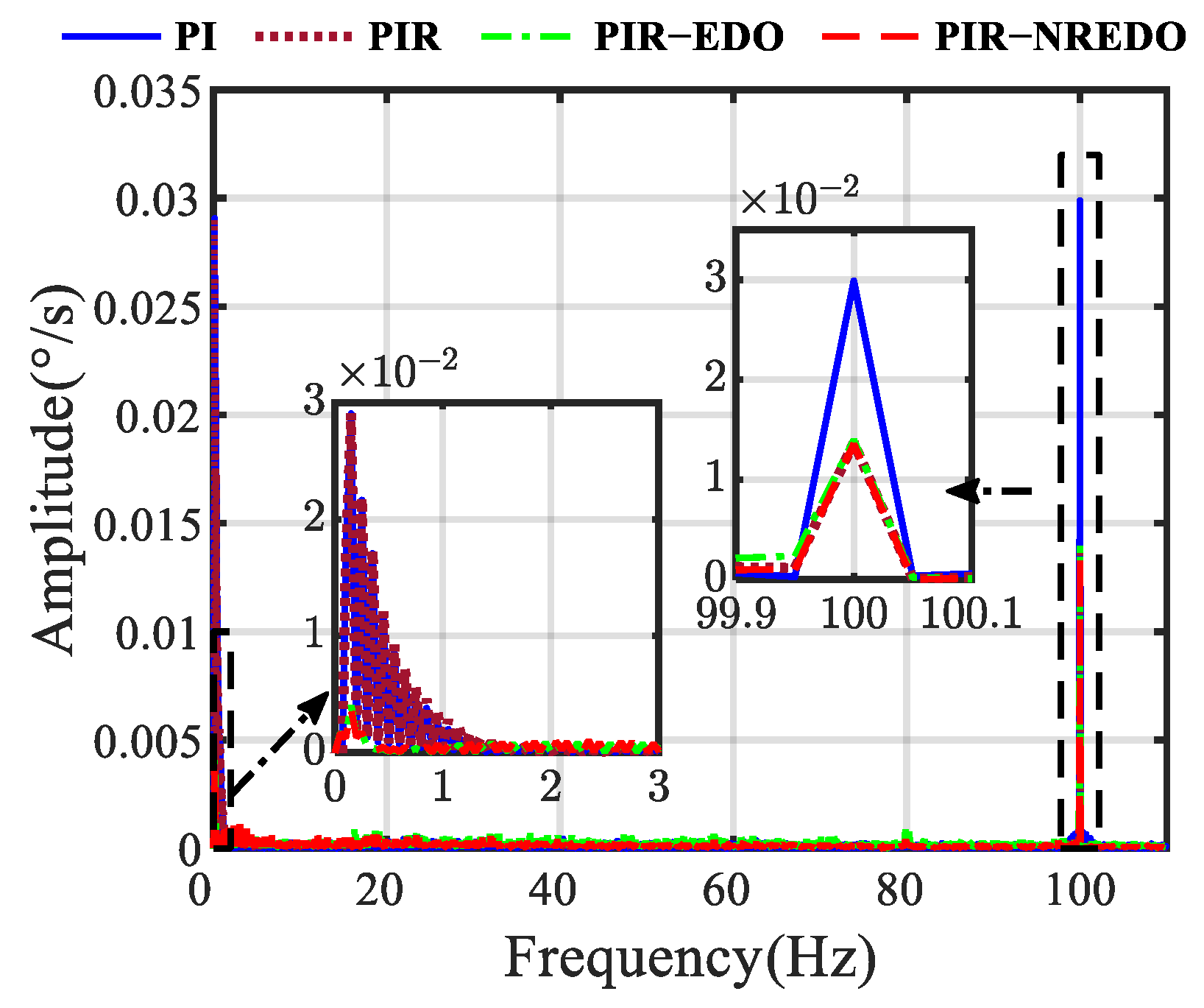
5. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, B.; Chen, X. High-Precision Composite Control Based on Dual-Sampling-Rate Extended State Observer for Ultra-Low Speed Gimbal Servo System. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 5423–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, D.; Zhang, J. High Precision Control Design for SGCMG Gimbal Servo System. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Busan, Republic of Korea, 7–11 July 2015; pp. 518–523. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Li, D.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, J.; Yang, G.; Wei, X. Dynamic Modelling and Observation of Micro-Vibrations Generated by a Single Gimbal Control Moment Gyro. J. Sound Vib. 2013, 332, 4496–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekimoglu, B. Optimal Tuning of Fractional Order PID Controller for DC Motor Speed Control via Chaotic Atom Search Optimization Algorithm. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 38100–38114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.; Moreno, J. Learning PID Structures in an Introductory Course of Automatic Control. IEEE Trans. Educ. 2001, 44, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-B.; Park, J.-G. Anti-Windup PID Controller with Integral State Predictor for Variable-Speed Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.S.; Man, K.F.; Chen, G.; Kwong, S. An Optimal Fuzzy PID Controller. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2001, 48, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Yao, B. A Globally Stable High-Performance Adaptive Robust Control Algorithm with Input Saturation for Precision Motion Control of Linear Motor Drive Systems. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2007, 12, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, G.; Formentini, A.; Papini, L.; Gerada, C.; Zanchetta, P. Performance Improvement of Bearingless Multisector PMSM With Optimal Robust Position Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 3575–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Mondragon, F.; Hernandez-Guzman, V.M.; Rodriguez-Resendiz, J. Robust Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Using Two-Degrees-of-Freedom Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6099–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wu, Z. Adaptive Learning Control of Robot Manipulators via Incremental Hybrid Neural Network. Neurocomputing 2024, 568, 127045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, S. Speed Control for a PMSM Servo System Using Model Reference Adaptive Control and an Extended State Observer. J. Power Electron. 2014, 14, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, L.; Vazquez, S.; Xu, R.; Dong, Z.; Liu, J.; Leon, J.I.; Wu, L.; Franquelo, L.G. Disturbance and Uncertainty Attenuation for Speed Regulation of PMSM Servo System Using Adaptive Optimal Control Strategy. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrific. 2023, 9, 3410–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.H.; Leu, V.Q.; Choi, Y.-S.; Jung, J.-W. Adaptive Speed Controller Design for a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2011, 5, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comanescu, M.; Xu, L.; Batzel, T.D. Decoupled Current Control of Sensorless Induction-Motor Drives by Integral Sliding Mode. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 3836–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, M.; Yu, X. Design and Implementation of Terminal Sliding Mode Control Method for PMSM Speed Regulation System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2013, 9, 1879–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yang, D.; Su, Z. Improved Sliding Mode Control for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Servo System. IET Power Electron. 2023, 16, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, A.G.; Freijedo, F.D.; Lopez, O.; Doval-Gandoy, J. Analysis and Design of Resonant Current Controllers for Voltage-Source Converters by Means of Nyquist Diagrams and Sensitivity Function. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 5231–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Ji, B.; Yan, Y. Smooth Speed Control for Low-Speed High-Torque Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Using Proportional–Integral–Resonant Controller. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Hua, W.; Ma, G.; Xu, S.; Zeng, W. Improved Current Dynamics of Proportional-Integral-Resonant Controller for a Dual Three-Phase FSPM Machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 11719–11730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Wang, B.; Yu, Y.; Dong, Q.; Xu, D. Robust Adaptive Resonant Controller for PMSM Speed Regulation Considering Uncertain Periodic and Aperiodic Disturbances. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 3362–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-S.; Rew, K.-H.; Kim, S. Disturbance Observer for Estimating Higher Order Disturbances in Time Series Expansion. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2010, 55, 1905–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Wu, Z. Attitude Stabilization of Flexible Spacecrafts via Extended Disturbance Observer Based Controller. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 133, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Wu, Z. Extended Disturbance Observer with Measurement Noise Reduction for Spacecraft Attitude Stabilization. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 66137–66147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wei, T. Aerodynamic Disturbance Estimation in Quadrotor Landing on Moving Platform via Noise Reduction Extended Disturbance Observer. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 37566–37574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, S. Multi-Frequency-Band Uncertainties Rejection Control of Flexible Gimbal Servo Systems via a Comprehensive Disturbance Observer. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 2023, 71, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Peng, J.; Pan, J. A Novel Friction Compensation Method Based on Stribeck Model with Fuzzy Filter for PMSM Servo Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 12124–12133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Q.; Deng, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Shao, M. Speed Ripple Minimization of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Model Predictive and Iterative Learning Controls. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 31791–31800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, K. High-Precision Anti-Disturbance Gimbal Servo Control for Control Moment Gyroscopes via an Extended Harmonic Disturbance Observer. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 66336–66349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Guo, L. Composite Control for Gimbal Systems with Multiple Disturbances: Analysis, Design, and Experiment. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern Syst. 2023, 53, 4789–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analog Devices. Available online: https://www.analog.com/media/en/technical-documentation/data-sheets/ad2s1210.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2025).



| Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | 5 | 50 | 430 | 220 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Moment of inertia | 0.6821 kg⋅m2 |
| Damping coefficient | 0.008 Nm/(rad⋅s−1) |
| Torque coefficient | 5 Nm/A |
| Back EMF coefficient | 5 V(rad/s) |
| Pole pairs | 6 |
| Phase inductance | 14.5 mH |
| Phase resistance | 2.5 Ω |
| Parameters | Values | Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Nm) | 0.01 | (Nm) | 0.08 |
| (Nm) | 0.04 | 24 | |
| (Nm) | 0.05 | (g⋅cm2) | 5.066 |
| (rad/s) | 0.01 | (rpm) | 6000 |
| Methods | PI | PIR | PIR-EDO | PIR-NREDO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ) | Case1 | 0.0216 | 0.0101 | 0.0077 | 0.0068 |
| Case2 | 0.0241 | 0.0157 | 0.0097 | 0.0085 | |
| Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Values | 10 | 10 | 200 | 250 |
| Methods | PI | PIR | PIR-EDO | PIR-NREDO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ) | Case1 | 0.0338 | 0.0275 | 0.0135 | 0.0108 |
| Case2 | 0.0413 | 0.0373 | 0.0143 | 0.0124 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Z.; Wu, Z. High-Precision Control of Control Moment Gyroscope Gimbal Servo Systems via a Proportional–Integral–Resonant Controller and Noise Reduction Extended Disturbance Observer. Actuators 2025, 14, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14040196
Lu Z, Wu Z. High-Precision Control of Control Moment Gyroscope Gimbal Servo Systems via a Proportional–Integral–Resonant Controller and Noise Reduction Extended Disturbance Observer. Actuators. 2025; 14(4):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14040196
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Zhihao, and Zhong Wu. 2025. "High-Precision Control of Control Moment Gyroscope Gimbal Servo Systems via a Proportional–Integral–Resonant Controller and Noise Reduction Extended Disturbance Observer" Actuators 14, no. 4: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14040196
APA StyleLu, Z., & Wu, Z. (2025). High-Precision Control of Control Moment Gyroscope Gimbal Servo Systems via a Proportional–Integral–Resonant Controller and Noise Reduction Extended Disturbance Observer. Actuators, 14(4), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14040196








