Piezoelectric Motors, an Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Early Structures of Piezoelectric Motors
3. Resonance-Drive (Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Motors)
- Number of vibrating elements that generate needed microscopic motion,
- Number of mechanical modes that are excited at the operating frequency of the vibrating element,
- Number of driving signals applied to a vibrating element,
- Full or partial drive of a piezoelectric element in a vibrator, and
- Unidirectional or bidirectional motion, if bidirectional; the method of changing direction such as frequency, phase, or excited part.
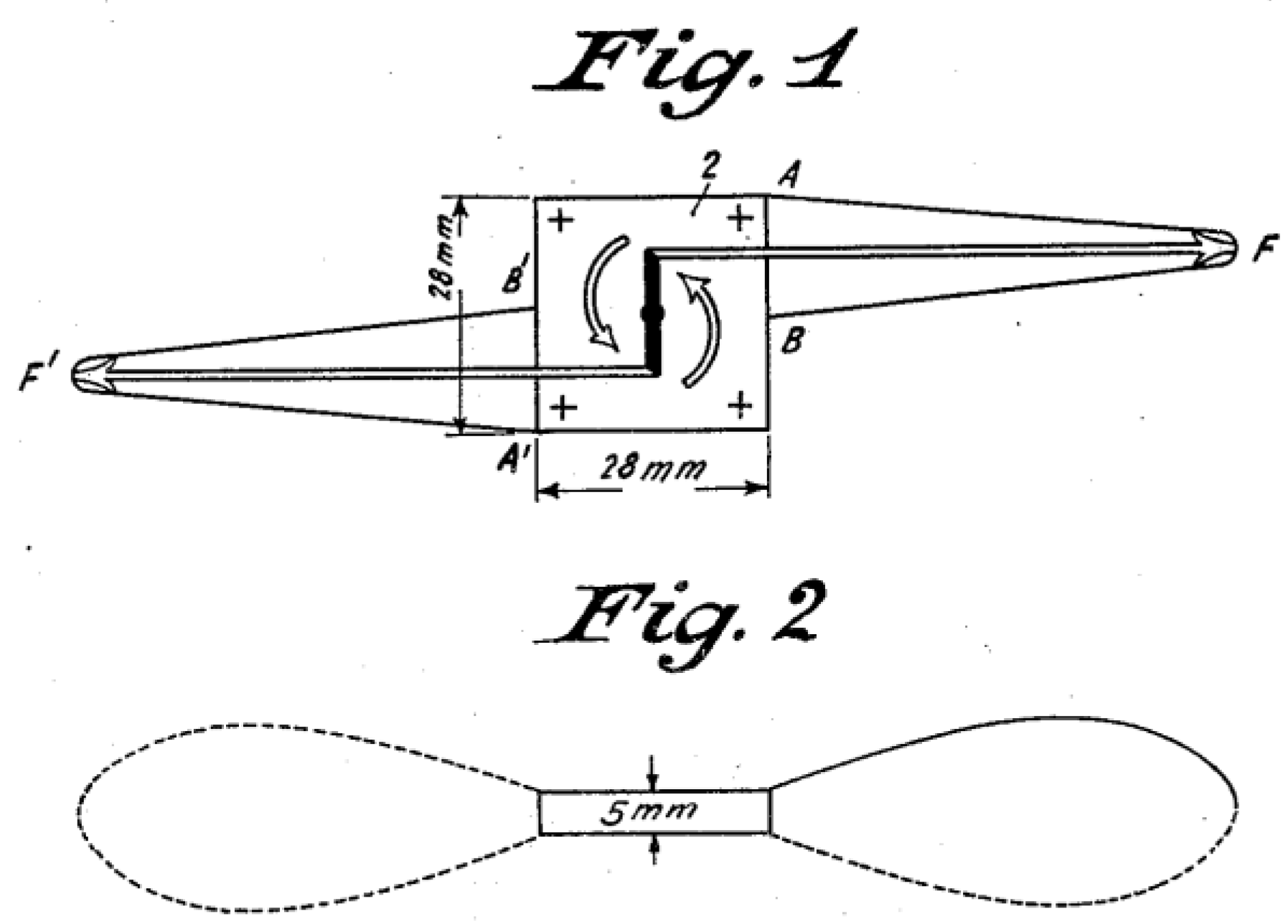
3.1. Single-Mode Excitation Type
3.1.1. Piezoelectric Element Is Fully Driven
3.1.2. Piezoelectric Element Is Partially Driven
3.2. Multi-Mode Excitation-Type Motors
- One Driving Source
- -Piezoelectric element is fully driven
- -Frequency change controls the direction
- -Piezoelectric element is partially driven
- -Driven part controls the direction
- Multiple Driving Sources
- -Piezoelectric element is fully driven
- -Phase change between the driving sources controls the direction
3.2.1. One Driving Source (Frequency Change Controls the Direction)
3.2.2. One Driving Source (Driven Part Controls the Direction)
3.2.3. Multiple Driving Sources (Phase Change between the Driving Sources Controls the Direction)
4. Inertia-Drive-Type Piezoelectric Motors
5. Piezo-Walk-Drive-Type Piezoelectric Motors
6. Discussions
7. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meissner, A. Converting electrical oscillations into mechanical movement. US Patent 1,804,838 A, 12 May 1931. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.L.W.; Brown, W.J. Piezoelectric Motor. US Patent 2,439,499, 13 April 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Lavrinenko, V.; Nekrasov, M. Electrical Motor. USSR Patent 217,509, 10 May 1965. (In Russian)[Google Scholar]
- Tehon, S.W. Electromechanical transducer motors. US Patent 3,211,931, 10 December 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Wischnewskiy, V.; Kavertsev, V.L.; Kartashev, I.A.; Lavrinenko, V.; Nekrasov, M.; Prez, A.A. Piezoelectric motor structures. US Patent 4,019,073, 12 August 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Wischnewskiy, V.; Gultajeva, L.; Kartashev, I.; Lavrinenko, V. Piezoelectric motor. USSR Patent 851,560, 16 February 1976. (In Russian)[Google Scholar]
- Bansevicius, R. Piezoelectric motor. USSR Patent 693,493, 18 July 1977. (In Russian)[Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev, P.E.; Vasilievich, A. Vibration Motor Control. GB Patent 2,020,857, 24 April 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Bansevicius, R.; Ragulskis, K. Vibromotors; MOKSLAS Publishing House: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1981. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ragulskis, K.; Bansevicius, R.; Barauskas, R.; Kulvietis, G. Vibro-motors for Precision Micro-robots, Application of Vibration Series; Rivin, E., Ed.; Hemisphere Publishing Co.: Detroit, MI, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Stibitz, G. Incremental feed mechanisms. US Patent 3,138,749, 5 March 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Ueha, U.; Tomikawa, Y. Ultrasonic Motors: Theory and Applications; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Sashida, T.; Kenjo, T. An Introduction to Ultrasonic Motors; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Uchino, K. Piezoelectric Actuators and Ultrasonic Motors; Kluwer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C. Ultrasonic Motors: Technologies and Applications; Science Press: Beijing, China; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kumada, A. Ultrasonic motor Using Bending, Longitudinal and Torsional Vibrations. US Patent 4,642,509, 21 February 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Kumada, A. Piezo Electric Motor. US Patent 4,947,076, 16 December 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Barth, H.V. Ultrasonic Drive Motor. IBM Tech. Discl. Bull. 1973, 16, 2263. [Google Scholar]
- Zhelyaskov, V.R.; Petrenko, S. Piezoelectric rotary motor with high rotation speed and bi-directional operation. US Patent 8,183,742, 1 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wishnewskiy, W.; Kovalev, S.; Vyshnevskyy, A. A New Ultrasonic Piezoelectric Actuator for Nanopositioning. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on New Actuators, Bremen, Germany, 14–16 June 2004; pp. 118–122.
- Spanner, K.; Wishnewskiy, O.; Vyshnevskyy, W. New Linear Ultrasonic Micro motors for Precision Mechatronic Systems. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on New Actuators, Bremen, Germany, 14–16 June 2006; pp. 439–443.
- Piezo Technology. Available online: http://www.physikinstrumente.com/technology.html (accessed on 24 November 2015).
- Yokoyama, K.; Tamura, H.; Masuda, K.; Takano, T. Single-Phase Drive Ultrasonic Linear Motor Using a Linked Twin Square Plate Vibrator. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 07HE03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodolite. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Theodolite (accessed on 30 November 2015).
- Takano, T.; Tomikawa, Y.; Kusakabe, C. Same Phase Drive-Type Ultrasonic Motors Using Two Degenerate Bending Vibration Modes of a Disk. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. 1992, 39, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Chiarot, P.R.; Park, S. A single Vibration Mode Tubular Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Motor. IEEE Trans. UFFC 2011, 58, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Magnussen, B.; Varadi, P.C.; Hagemann, B.; Schuler, D.A.; Davidson, E.M. Vibratory motors and methods of making and using same. US Patent 7,368,853, 22 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Z.; He, B.; Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Dong, S. A Miniature Cylindrical Piezoelectric Motor with an Asymmetric Vibrator. IEEE UFFC 2013, 60, 1498–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchino, K.; Ohnishi, K. Linear motor. US Patent 4,857,791, 3 June 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Zumeris, J. Ceramic motor. US Patent 5,453,653, 3 August 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, G.R.; Louw, D.F.; McBeth, P.B.; Fielding, T.; Gregoris, D.J. Microsurgical robot system. US Patent 8,005,571, 3 July 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Koc, B.; Ko, H.-P. Piezoelectric actuator and lens driving device. US Patent 7,764,449, 29 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Koc, B.; Ko, H.; Jeong, H.S. A miniature Piezoelectric Motor for Phone Camera Auto Focusing Application. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on New Actuators, Bremen, Germany, 9–11 June 2008; pp. 184–187.
- Koc, B.; Tressler, J.F.; Uchino, K. A Miniature Piezoelectric Rotary Motor Using Two Orthogonal Bending Modes of a Hollow Cylinder. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on New Actuators, Bremen, Germany, 19–21 June 2000; pp. 242–245.
- Sashida, T. Motor device utilizing ultrasonic oscillation. US Patent 4,562,374, 16 May 1984. [Google Scholar]
- We Evolve Our Ultrasonic Motor. Available online: http://www.shinsei-motor.com/English/index.html (accessed on 24 November 2015).
- Takano, T.; Tomikawa, Y.; Ogasawara, T.; Sugawara, S.; Konno, M. Ultrasonic Motors Using Piezoelectric Ceramic Multimode Vibrators. IEEE Trans. UFFC 1990, 37, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamai, J.; Okumura, I.; Tsukimoto, T.; Fujimoto, K. Vibration wave driving apparatus and a vibration member, and manufacturing method of the apparatus and the member. US Patent 5,949,178, 22 April 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Focus and Zoom Drive Mechanisms Using Ultrasonic Vibration. Available online: http://www.canon.com/technology/canon_tech/explanation/cp_tech.html#usm (accessed on 28 January 2016).
- Wischnewskiy, W. Piezoelectric drive excited by longitudinal and flexural waves. US Patent 6,806,620, 31 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ueha, S.; Kurosawa, M.; Masuda, M. Ultrasonic Driven Type Motor. US Patent 4,885,499, 10 February 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Marth, H. Untersuchungen zur Dimensieonierung und zum Betriebsverhalten von Vibrationslinearmotoren und deren Einsatz in Positioniereinrichtungen für Magnetköpfe. Ph.D. Thesis, TU, Dresden, Germany, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, K.; Ogiso, T. Actuator. US Patent 4,613,782, 18 March 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa, M.K.; Kodaira, O.; Tsuchitoi, Y.; Higuchi, T. Transducer for High Speed and Large Thrust Ultrasonic Linear Motor Using Two Sandwich-Type Vibrators. IEEE Trans. UFFC 1999, 45, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hills, C. Piezo-Electric Motor. US Patent 6,373,170, 10 March 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Iula, A.; Pappalardo, M. A High-Power Traveling Wave Ultrasonic Motor. IEEE Trans. UFFC 2006, 53, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Kurosawa, M.K.; Higuchi, T. Cylindrical Micro Ultrasonic Motor Utilizing Bulk Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT). Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 38, 3347–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SQUIGGLE Micro Motor Technology. Available online: http://www.newscaletech.com (accessed on 20 November 2015).
- Kurosawa, M.; Nakamura, K.; Okamoto, T.; Ueha, S. An Ultrasonic Motors Using Bending Vibrations of a Short Cylinder. IEEE Trans. UFFC 1989, 36, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichiro, O. Electro-mechanical energy conversion element and a vibration wave actuator using the electro-mechanical energy conversion element. US Patent 5,814,919, 23 April 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Koc, B.; Thelen, M. Piezoelectric Rotary Motor with Independently Driven Orthogonal Electrodes of a Piezoelectric Plate. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on New Actuators, Bremen, Germany, 18–20 June 2012; pp. 258–261.
- Pohl, D.W. Dynamic Piezoelectric Transducer Devices. Rev. Sci. Instrum 1987, 58, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Watanabe, M. Apparatus for effecting fine movement by impact force produced by piezoelectric or electrostrictive element. US Patent 4,894,579, 23 May 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Miyano, M.; Kawasaki, T.; Kuwana, M.; Miyazawa, M.; Ueyama, M.; Tasaka, Y. Lens Moving Apparatus. US Patent 5,587,846, 24 December 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, R.; Okamoto, Y.; Higuchi, T.; Hamamatsu, A. Development of Smooth Impact Drive Mechanism (SIDM). J. JSPE 1999, 65, 111–115. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Niedermann, P.; Emch, R.; Descouts, P. Simple Piezoelectric translation Device. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1988, 59, 368–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howald, L.; Rudin, H.; Güntherodt, H.J. Piezoelectric inertial stepping motor with spherical rotor. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1992, 63, 3909–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrovich, B.V.; Viktorovic, B.A.; Evich, K.V.V. Inertia Step Motor. RU Patent 2,465,712, 27 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, P.; Desailly, R. Optical adjustment mounts with piezoelectric inertia drive. Patent WO2008087469A2, 18 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kortschack, A.; Rass, C. Method for controlling a multi-actuator drive. Patent WO2013128032A1, 4 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huebner, R. Piezoelectric rotary drive for a shaft. US Patent 9,106,158B2, 1 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Takagi, T. Vibration Driven Motor. US Patent 5,917,268, 29 June 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kanbara, T. Electro-Mechanical Transducer lens drive mechanism for a vibration compensating system. US Patent 5,768,016, 26 July 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Karrai, K.; Heines, M. Inertial rotation device. US Patent 6,940,210B2, 4 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata, Y.; Higuchi, T.; Saeki, H.; Ishimaru, H. Ultrahigh vacuum precise positioning device utilizing rapid deformations of Piezoelectric Elements. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1990, 8, 4098–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Sqalli, O.; Lorenz, H.; Karrai, K. Slip-stick step-scanner for scanning probe microscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2005, 76, 063706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansevičius, B.; Blechertas, V. Ultrasonic motors for mass-consumer products. Ultragarsas 2006, 4, 50–52. [Google Scholar]
- Koc, B. Piezoelectric Motor, Operates by Exciting Multiple Harmonics of a Square Plate. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on New Actuators, Bremen, Germany, 14–16 June 2010.
- Morita, T.; Yoshida, R.; Hosaka, H. Resonant-Type Smooth Impact Drive Mechanism Actuator Operating at Lower Input Voltages. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 07HE05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncdemir, S.; Ural, S.O.; Koc, B.; Uchino, K. Design of Translation Rotary Ultrasonic Motor with Slanted Piezoelectric Ceramics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisbane, A.D. Position Control Device. US Patent 3,377,489, 9 April 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Galutva, G.V.; Ryazantsev, A.I.; Presnyakov, G.S.; Modestov, J.K. Device for Precision Displacement of a Solid Body. US Patent 3,684,904, 15 April 1970. [Google Scholar]
- May, W.G. Piezoelectric Electromechanical Translation Apparatus. US Patent 3,902,084, 30 May 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Marth, H.; Gloess, R. Verstelleantrieb aus Bimorphelementen. DE Patent 4,408,618A1, 15 March 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Johanson, S.; Bexell, M.; Lithell, B.O. Fine Walking Actuator. US Patent 6,798,117, 10 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, K.D.; Marth, H.; Pertsch, P.; Gloess, R.; Zhao, X. Piezo-Based, Long-Travel Actuators for Special Environmental Conditions. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on New Actuators, Bremen, Germany, 14–16 June 2006; pp. 149–153.
- Eriksson, T.; Holmgren, B. Particle accelerators having electromechanical motors and methods of operating and manufacturing the same. US Patent 8,653,762, 23 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Maeno, T.; Takayuki, T.; Miyaki, A. Finite-Element Analysis of the Rotor/Stator Contact in a Ring-Type Ultrasonic Motor. IEEE Trans. UFFC 1992, 39, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagedorn, P.; Wallaschek, J. Traveling wave ultrasonic motors, part I: Working principle and mathematical modelling of the stator. J. Sound Vib. 1992, 155, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagood, N.W.; McFarland, A.J. Modeling of a piezoelectric rotary ultrasonic motor. IEEE Trans. UFFC 1995, 42, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Kato, K. Fundamental properties of friction and wear on friction drive by traveling wave type ultrasonic. Jpn. J. Tribol. 1993, 47, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, A.M. Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Motors. Ph.D. Thesis, MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA, December 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta, S.; Sinatra, R.; Meschini, A. Evaluation of the Effect of Preload Force on Resonance Frequencyies for a Traveling Wave Ultrasonic Motor. IEEE Trans. UFFC 2006, 53, 746–753. [Google Scholar]
- Sattel, T.; Hagedorn, P.; Schmidt, J. The Contact Problem in Ultrasonic Traveling–Wave Motors. J. Appl. Mech. 2010, 77, 031014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashimo, T.; Terashima, K. Dynamic analysis of an ultrasonic motor using point contact model. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 233, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunovic, T.; Golubovic, E.; Sabanovic, A. Piezo LEGS Driving Principle Based on Coordinate Transformation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashimo, T.; Terashima, K. Experimental Verification of Elliptical Motion Model in Traveling Wave Ultrasonic Motors. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 2699–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, T.; Ishii, T.; Nakamura, K.; Ueha, S. An ultrasonic actuator with multi degree of freedom using bending and longitudinal vibrations of a single stator. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonic Symposium, Sendai, Japan, 5–8 October 1998; Volume 1, pp. 667–670.
- Mashimo, T.; Toyama, S.; Ishida, H. Design and Implementation of Spherical Ultrasonic Motor. IEEE Trans. UFFC 2009, 56, 2614–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masayuki, M.; Toyotoshi, K.; Minoru, K.; Masayuki, M.; Yoshihiro, T. Lens moving apparatus. US Patent 5,587,846, 14 July 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.-W.; Lim, J.-H.; Park, S.-H. Vibrating element, fabrication method thereof, and ultrasonic motor having the same. US Patent 8,237,330, 10 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Gehlbach, P.L.; Kang, J.U. Active tremor cancellation by a “Smart” handheld vitreoretinal microsurgical tool using swept source optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 23414–23421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifabadi, R.; Song, S.E.; Krieger, A.; Cho, N.B.; Tokuda, J.; Fichtinger, G.; Iordachita, I. Robotic system for MRI-guided prostate biopsy: feasibility of tele operated needle insertion and ex vivo phantom study. Int. J. CARS 2012, 7, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Weijian, S.; Cole, G.A.; Harrington, K.; Fischer, G.S. Haptic System Design for MRI-Guided Needle Based Prostate Brachytherapy. In Proceedings of the IEEE Haptics Symposium, Waltham, MA, USA, 25–26 March 2010; pp. 483–488.
- Yang, S.; MacLachlan, A.R.; Riviere, N.C. Manipulator Design and Operation of a Six-Degree-of-Freedom Handheld Tremor-Canceling Microsurgical Instrument. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priester, A.M.; Natarajan, S.; Culjat, M.O. Robotic Ultrasound Systems in Medicine. IEEE UFFC 2013, 60, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















| Single-Mode Excitation Type | Multi-Mode Excitation Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oblique motion | Elliptical motion: By exciting two orthogonal mechanical resonance modes at the same time. | |||
| One Driving Source | One Driving Source | Multiple Driving Sources | ||
| Piezo-element is fully driven | Piezo-element is partially driven | Piezo-element is fully driven | Piezo-element is partially driven | Piezo-element is fully driven |
| Unidirectional | Bidirectional: Driven part controls the direction | Bidirectional: Frequency change controls the direction | Bidirectional: Driven part controls the direction | Bidirectional: Phase change between the driving sources controls the direction (traveling wave-motor) |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spanner, K.; Koc, B. Piezoelectric Motors, an Overview. Actuators 2016, 5, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5010006
Spanner K, Koc B. Piezoelectric Motors, an Overview. Actuators. 2016; 5(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpanner, Karl, and Burhanettin Koc. 2016. "Piezoelectric Motors, an Overview" Actuators 5, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5010006
APA StyleSpanner, K., & Koc, B. (2016). Piezoelectric Motors, an Overview. Actuators, 5(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/act5010006





