Soft Robotics: A Review of Recent Developments of Pneumatic Soft Actuators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Control Systems
3. Materials and Construction
4. Modeling
5. Sensors
6. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saigo, H.; Naruse, M.; Okamura, K.; Hori, H.; Ojima, I. Analysis of Soft Robotics Based on the Concept of Category of Mobility. Complexity 2019, 2019, 1490541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiva, A.; Stilli, A.; Noh, Y.; Faragasso, A.; De Falco, I.; Gerboni, G.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A.; Althoefer, K.; Wurdemann, H.A. Tendon-Based Stiffening for a Pneumatically Actuated Soft Manipulator. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 1, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawlowski, B.; Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J. Modeling of Soft Robots Acuated by Twisted-and-Coiled Actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, D.; Tolley, M.T. Design, Fabrication, and Control of Soft Robots. Naure 2015, 521, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zinn, M.; Khatib, O.; Roth, B.; Salisbury, J.K. Actuation Methods for Human-Centered Robotics and Associated Control Challenges. In Control Problems in Robotics; Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 4, pp. 105–119. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, R.F.; Stokes, A.A.; Freake, J.; Barber, J.; Snyder, P.W.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Cademartiri, L.; Morin, S.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Using Explosions to Power a Soft Robot. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 7868–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumbre, G.; Fiorito, G.; Flash, T.; Hochner, B. Octopu uses Human-Like Strategy to Control Point-to-Point Arm Movement. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webster, R.J.; Jones, B.A. Design and Kinematic Modeling of Constant Curvature Continuum Robotics: A Review. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.A.; Walker, I.D. Kinematics for Multisection Continuum Robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2006, 22, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onal, C.D.; Chen, X.; Whitesides, G.M.; Rus, D. Soft Mobile Robots with on-board Chemical Pressure Generation. In International Symposium on Robotics Research; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 100, pp. 525–540. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, B.; Christianson, C.; Gillespie, K.; Lee, S.; Mayeda, J.; Huo, Z.; Tolley, M.T. Design Considerations for 3D Printed, Soft, Multimaterial Resistive Sensors for Soft Robotics. Front. Robot. AI 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skorina, E.H.; Luo, M.; Oo, W.Y.; Tao, W.; Chen, F.; Youssefian, S.; Rahbar, N.; Onal, C.D. Reverse Pneumatic Artificial Muscles (RPAMs): Modeling, Integration, and Control. PLoS ONE 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Elsamadisi, A.; Shepherd, R. Scalable Manufacturing of High Force Wearable Soft Actuators. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2015, 3, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschi, C.; Cianchetti, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Margheri, L.; Follador, M.; Dario, P. Soft robot arm inspired by the octopus. Adv. Robot. 2012, 26, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintake, J.; Cacucciolo, V.; Floreano, D.; Shea, H. Soft Robotic Grippers. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kellaris, N.; Venkata, V.G.; Smith, G.M.; Mitchell, S.K.; Keplinger, C. Peano-hasel Actuators: Muscle-mimetic, Electrohydraulic Transducers that Linearly Contract on Activation. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Fumiya, I. Deformation in Soft-Matter Robotiics: A Categorization and Quanitative Characterization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2015, 22, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, N.; Correll, N. A soft pneumatic actuator that can sense grasp and touch. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 2317–2323. [Google Scholar]
- Marchese, A.D.; Katzschmann, R.K.; Rus, D. A recipe for soft fluicic elastomer robots. Soft Robot. 2015, 2, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilievski, F.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Shepherd, R.F.; Chen, X.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft Robotics for Chemists. Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, M.; Tolley, M.T.; Mengüç, Y.; Park YMozika, A.; Ding, Y.; Onal, C.; Shepherd, R.F.; Whitesides, G.M. Pneumatic Energy Sources for Autonomous and Wearable Soft Robotics. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decker, M. Soft Robotics and Emergent Materials in Architecture. In Proceedings of the Real Time eCAADe Conference, Vienna, Austria, 16–18 September 2015; Volume 2, pp. 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, H.K.; Ng, H.Y.; Yeow, C.H. High-force Soft Printable Pneumatics for Soft Robotic Applications. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peele, B.N.; Wallin, T.J.; Zhao, H.; Shepherd, R.F. 3D Printing Antagonistic Systems of Artificial Muscle Using Projection Stereolithography. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCurdy, R.; Katzschmann, R.; Kim, Y.; Rus, D. Printable Hydraulics: A Method for Fabricating Robots by 3D co-printing Solids and Liquids. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Truby, R.L.; Wehner, M.; Grosskopf, A.K.; Vogt, D.M.; Uzel, S.G.; Wood, R.J.; Lewis, J.A. Soft Somatosensitive Actuators via Embedded 3D Printing. Adv. Mater. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, N.; Chastain, P.; Crowther, M.; Shin, M. Development of Fast Prototyping Pneumatic Actuated Grippers. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 20, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward-Cherrier, B.; Pestell, N.; Cramphorn, L.; Winstone, B.; Giannaccini, M.E.; Rossiter, J.; Lepora, N.F. The TacTip Family: Soft Optical Tactile Sensors with 3D-Printed Biomimetic Morphologies. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, M.; Agheli, M.; Onal, C.D. Theoretical Modeling and Experimental Analysis of a Pressure-operated Soft Robotic Snake. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deimel, R.; Brock, O. A Novel Type of Compliant, Underactuated Robotic Hand for Dexterous Grasping. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 35, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, I.D.; Dawson, D.M.; Flash, T.; Grasso, F.W.; Hanlon, R.T.; Hochner, B.; Kier, W.M.; Pagano, C.C.; Rahn, C.D.; Zhang, Q.M. Continuum Robot Arms Inspired by Cephalopods. Proc. SPIE 2005, 5804, 303–314. [Google Scholar]
- Runge, G.; Raatz, A. A Framework for the Automated Design and Modelling of Soft Robotic Systems. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 66, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napp, N.; Araki, B.; Tolley, M.T.; Nagpal, R.; Wood, R.J. Simple Passive Valves for Addressable Pneumatic Actuation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 1440–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, H.K.; Lim, J.H.; Nasrallah, F.; Goh JC, H.; Yeow RC, H. A Soft Exoskeleton for Hand Assistive and Rehabilitation Application Using Pneumatic Actuators with Variable Stiffness. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 4967–4972. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.T.; Leisk, G.G.; Trimmer, B. GoQBot: A Caterpillar-inspired Soft-bodied Rolling Robot. BioInspir. Biomim. 2011, 6, 026007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschi, C.; Mazzolai, B. Lessons from Animals and Plants: The Symbiosis of Morphological Computation and Soft Robotics. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikas, V.; Cohen, E.; Grassi, R.; Sozer, C.; Trimmer, B. Design and Locomotion Control of a Soft Robot Using Friction Manipulation and Motor–Tendon Actuation. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faudzi, A.A.M.; Ooga, J.; Goto, T.; Takeichi, M.; Suzumori, K. Index Finger of a Human-Like Robotic Hand Using Thin Soft Muscles. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 3, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Wood, R.J. Smart Pneumatic Artificial Muscle Actuator with Embedded Microfluidic Sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–6 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ranzani, T.; Gerboni, G.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A. A Bioinspired Soft Manipulator for Minimally Invasive Surgery. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, W.K.; Yeow, C.-H. 3D Printed Soft Pneumatic Actuators with Intent Sensing for Hand Rehabilitative Exoskeletons. In Proceedings of the Internation Conference on Robotics and Automation, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Berring, J.; Kianfar, K.; Lira, C.; Menon, C.; Scarpa, F. A Smart Hydraulic Joint for Future Implementation in Robotic Structures. Robotica 2010, 28, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, A.D.; Tedrake, R.; Rus, D. Dynamics and Trajectory Optimization for a Soft Spatial Fluidic Elastomer Manipulator. J. Robot. Res. 2016, 35, 1000–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzschmann, R.K.; Marchese, A.D.; Rus, D. Hydraulic Autonomous Soft Robotics Fish for 3D Swimming. In International Symposium on Experimental Robotics; Marrakech & Essaouira: Essaouira, Morocco, 2014; pp. 405–420. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Pre-Charged Pneumatic Soft Gripper with Closed-Loop Control. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 2, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuruthel, T.G.; Falotico, E.; Manti, M.; Laschi, C. Stable Open Loop Control of Soft Robotic Manipulators. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh, B.; Polygerinos, P.; Keplinger, C.; Wennstedt, S.; Shepherd, R.F.; Gupta, U.; Shim, J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.; Whiteshides, G.M. Pneumatic Networks for Soft Robotics that Actuate Rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanan, S.; Lynn, P.S.; Griffith, S.T. Pneumatic Torsional Actuators for Inflatable Robots. J. Mech. Robot. 2014, 6, 031003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.H.; Cheng, N.; Khin, P.M.; Thakor, N.V.; Kukreja, S.L.; Ren, H.L.; Yeow, C.H. A Bidirectional Soft Pneumatic Fabric-based Actuator for Grasping Applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tolley, M.T.; Shepherd, R.F.; Karpelson, M.; Bartlett, N.; Galloway, K.C.; Wehner, M.; Nunes, R.; Whitesides, G.M.; Wood, R.J. An Untethered Jumping Soft Robot. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 561–566. [Google Scholar]
- Majidi, C.; Shepherd, R.F.; Kramer, R.K.; Whitesides, G.M.; Wood, R.J. Influence of Surface Traction on Soft Robot Undulation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amend, J.R.; Brown, E.M.; Rodenberg, N.; Jaeger, H.M.; Lipson, H. A Positive Pressure Universal Gripper Based on the Jamming of Granular Material. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahn, J.M.; Fabbro, F.; Menon, C. A Soft-touch Gripper for Grasping Delicate Objects. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drotman, D.; Ishida, M.; Jadhav, S.; Tolley, M.T. Application-Driven Design of Soft, 3D Printed, Pneumatic Actuators with Bellows. IEEE Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgeneidy, K.; Lohse, N.; Jackson, M. Bending Angle Prediction and Control of Soft Pneumatic Actuators with Embedded Flex Sensors—A Data-driven Approach. Mechatronics 2018, 50, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deimel, R.; Brock, O. A Compliant Hand Based on a Novel Pneumatic Actuator. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 2047–2053. [Google Scholar]
- Memarian, M.; Gorbet, R.; Kulić, D. Control of Soft Pneumatic Finger-like Actuators for Affective Motion Generation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 1691–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Della Santina, C.; Bianchi, M.; Grioli, G.; Angelini, F.; Catalano, M.; Garabini, M.; Bicchi, A. Controlling Soft Robots: Balancing Feedback and Feedforward Elements. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2017, 24, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Srivastava, S.; Gupta, J.R.P. Online Modeling and Adaptive Control of Robotic Manipulators Using Gaussian Radial Basis Function Networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 30, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somm, L.; Hahn, D.; Kumar, N.; Coros, S. Expanding Foam as the Material for Fabrication, Prototyping and Experimental Assessment of Low-Cost Soft Robots with Embedded Sensing. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohta, P.; Valle, L.; King, J.; Low, K.; Yi, J.; Atkeson, C.; Park, Y. Design of a Lightweight Soft Robotic Arm Using Pneumatic Artificial Muscles and Inflatable Sleeves. Soft Robot. 2017, 5, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Case, J.C.; Yuen, M.C.; Jacobs, J.; Kramer-Bottiglio, R. Robotic Skins That Learn to Control Passive Structures. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerboni, G.; Diodato, A.; Ciuti, G.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A. Feedback Control of Soft Robot Actuators via Commercial Flex Bend Sensors. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintake, J.; Rosset, S.; Schubert, B.; Floreano, D.; Shea, H. Versatile Soft Grippers with Intrinsic Electroadhesion Based on Multifunctional Polymer Actuators. Adv. Mater. 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, C.; Goldberg, N.N.; Deheyn, D.; Cai, S.; Tolley, M.T. Translucent Soft Robots Driven by Frameless Fluid Electrode Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaat1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
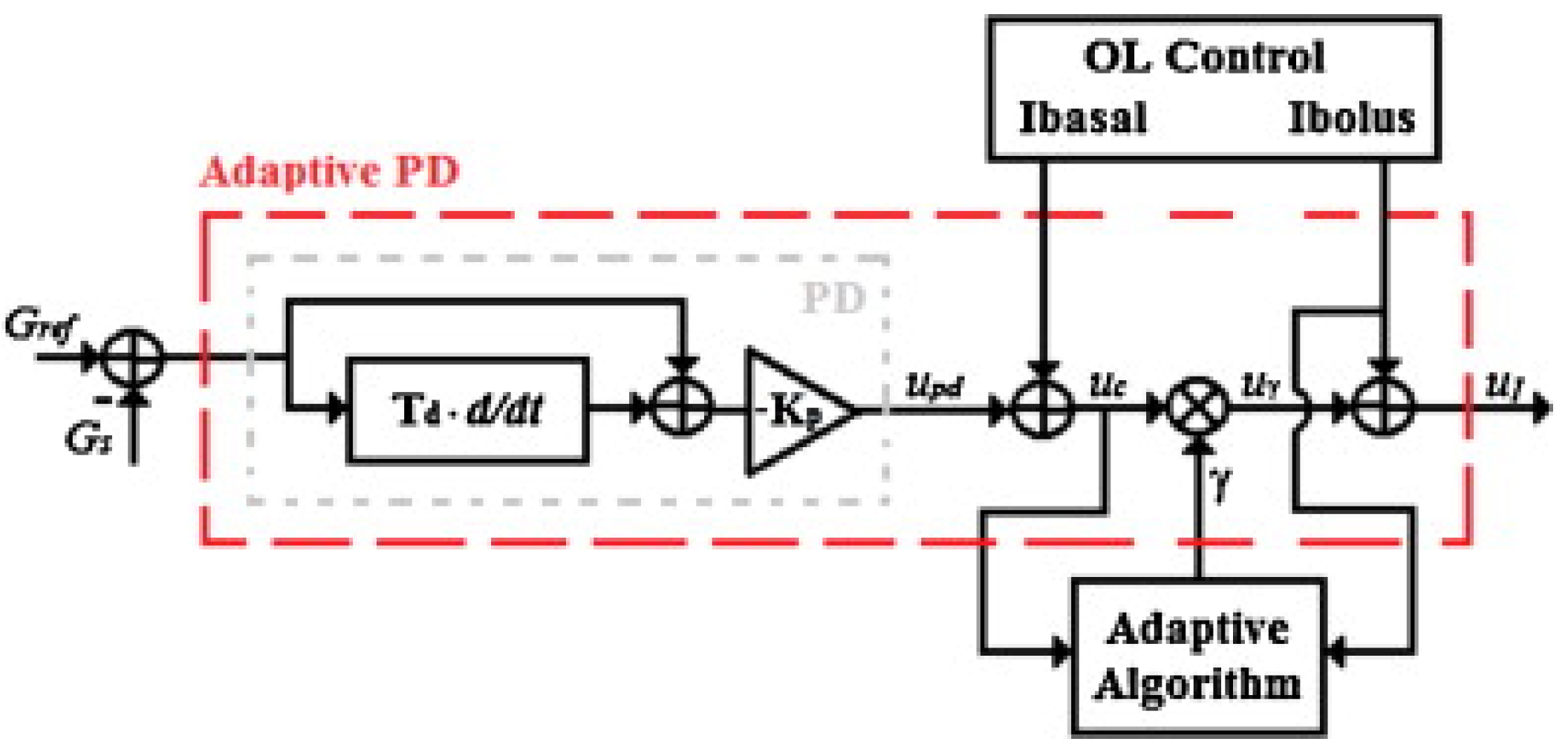
- León-Vargas, F.; Garelli, F.; De Battista, H.; Vehí, J. Postprandial Blood Glucose Control Using a Hybrid Adaptive PD Controller with Insulin-on-board Limitation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2013, 8, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, R.; Sariyildiz, E.; Nozaki, T.; Alici, G. Design of a Multi-Stage Stiffness Enhancing Unit for a Soft Robotic Finger and its Robust Motion Control. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2018), Washington, WA, USA, 20–23 October 2018; pp. 5074–5079. [Google Scholar]
- Haghshenas-Jaryani, M.; Pande, C.; Muthu Wijesundara, B.J. Soft Robotic Bilateral Hand Rehabilitation System for Fine Motor Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2019; p. 337. [Google Scholar]
- Kalisky, T.; Wang, Y.; Shih, B.; Drotman, D.; Jadhav, S.; Aronoff-Spencer, E.; Tolley, M.T. Differential Pressure Control of 3D Printed Soft Fluidic Actuators. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, S.; Ranzani, T.; Walsh, C.J.; Wood, R.J. An Additive Millimeter-Scale Fabrication Method for Soft Biocompatible Actuators and Sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1700135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Ren, T.; Hu, Y. Passive and Active Particle Damping in Soft Robotic Actuators. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 20–25 May 2018; pp. 1547–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y. Passive Particle Jamming and Its Stiffening of Soft Robotic Grippers. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hirai, S. Soft Gripper Dynamics Using a Line-Segment Model with an Optimization-Based Parameter Identification Method. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, J.Y.; Tan, C.P.; Nurzaman, S.G. H-infinity Based Extended Kalman Filter for State Estimation in Highly Non-linear Soft Robotic System. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference (ACC), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–12 July 2019; pp. 5154–5160. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Koh, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Cho, K. Deformable Wheel Robot Based on Soft Material. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainla, A.; Verma, M.S.; Yang, D.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft, Rotating Pneumatic Actuator. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagaoka, T.; Mao, Z.; Takemura, K.; Yokota, S.; Kim, J. ECF (Electro-conjugate fluid) Finger with Bidirectional Motion and its Application to a Flexible Hand. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, R.F.; Morin, S.A.; Ilievski, F.; Whitesides, G.M. A Hybrid Combining Hard and Soft Robots. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, Y.; Wolf, A.; Gabor, K. Bi-bellows: Pneumatic Bending Actuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 167, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Verma, M.S.; So, J.; Mosadegh, B.; Keplinger, C.; Lee, B.; Khashai, F.; Lossner, E.; Suo, Z.; Whitesides, G.M. Buckling Pneumatic Linear Actuators Inspired by Muscle. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, Y.; Lekakou, C.; Geng, T.; Saaj, C. Design Optimization of Soft Silicone Pneumatic Actuators Using Finite Element Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Besacon, France, 8–11 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, Y.; Paydar, O.H.; Candler, R.N. Pneumatic microfinger with Balloon Fins for Linear Motion Using 3D Printed Molds. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 234, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakimoto, S.; Koichi, S.; Keiko, O. Miniature Pneumatic Curling Rubber Actuator Generating Bidirectional Motion with One Air-Supply Tube. Adv. Robot. 2011, 25, 1311–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilodeau RA, R.; White, E.L.; Kramer, R.K. Monolithic Fabrication of Sensors and Actuators in a Soft Robotic Gripper. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Niiyama, R.; Rus, D.; Kim, S. Pouch Motors: Printable/inflatable Soft Actuators for Robotics. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 6332–6337. [Google Scholar]
- Gorissen, B.; Reynaerts, D.; Konishi, S.; Yoshida, K.; Kim, J.; De Volder, M. Elastic Inflatable Actuators for Soft Robotic Applications. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintake, J.; Sonar, H.; Piskarev, E.; Paik, J.; Floreano, D. Soft Pneumatic Gelatin Actuator for Edible Robotics. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Takashima, K.; Sugitani, K.; Morimoto, N.; Sakaguchi, S.; Noritsugu, T.; Mukai, T. Pneumatic Artificial Rubber Muscle Using Shape-memory Polymer Sheet with Embedded Electrical Heating Wire. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comber, D.; Slightam, J.; Barth, E.J.; Gervasi, V.R.; Webster, R.J. Design and Precision Control of an MR-Compatible Flexible Fluidic Actuator. In Proceedings of the ASME/BATH 2013 Symposium on Fluid Power and Motion Control, Sarasota, FL, USA, 6–9 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Niiyama, R.; Sun, X.; Sung, C.; An, B.; Rus, D.; Kim, S. Pouch Motors: Printable Soft Actuators Integrated with Computational Design. Soft Robot. 2015, 2, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.K.; Sakhaei, A.H.; Layani, M.; Zhang, B.; Ge, Q.; Magdassi, S. Highly Stretchable and UV Curable Elastomers for Digital Light Processing Based 3D Printing. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, M.A.; Sadeghi, H.; Florez, J.M.; Paik, J. Soft Pneumatic Actuator Fascicles for High Force and Reliability. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, E.; Rodenberg, N.; Amend, J.; Mozeika, A.; Steltz, E.; Zakin, M.R.; Lipson, H.; Jaeger, H. Universal Robotic Gripper Based on the Jamming of Granular Material. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18809–18814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amend, J.; Cheng, N.; Fakhouri, S.; Culley, B. Soft Robotics Commercialization: Jamming Grippers from Research to Product. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, J.; Cho, I.; Kim, J. Microrobotic tentacles with spiral bendingcapability based on shape-engineered elastomeric microtubes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 2045–2322. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, S.; Rueben, J.; Van Volkenburg, T.; Hemleben, S.; Grimm, C.; Simonsen, J.; Mengüç, Y. Using an environmentally benign and degradable elastomer in soft robotics. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2017, 1, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
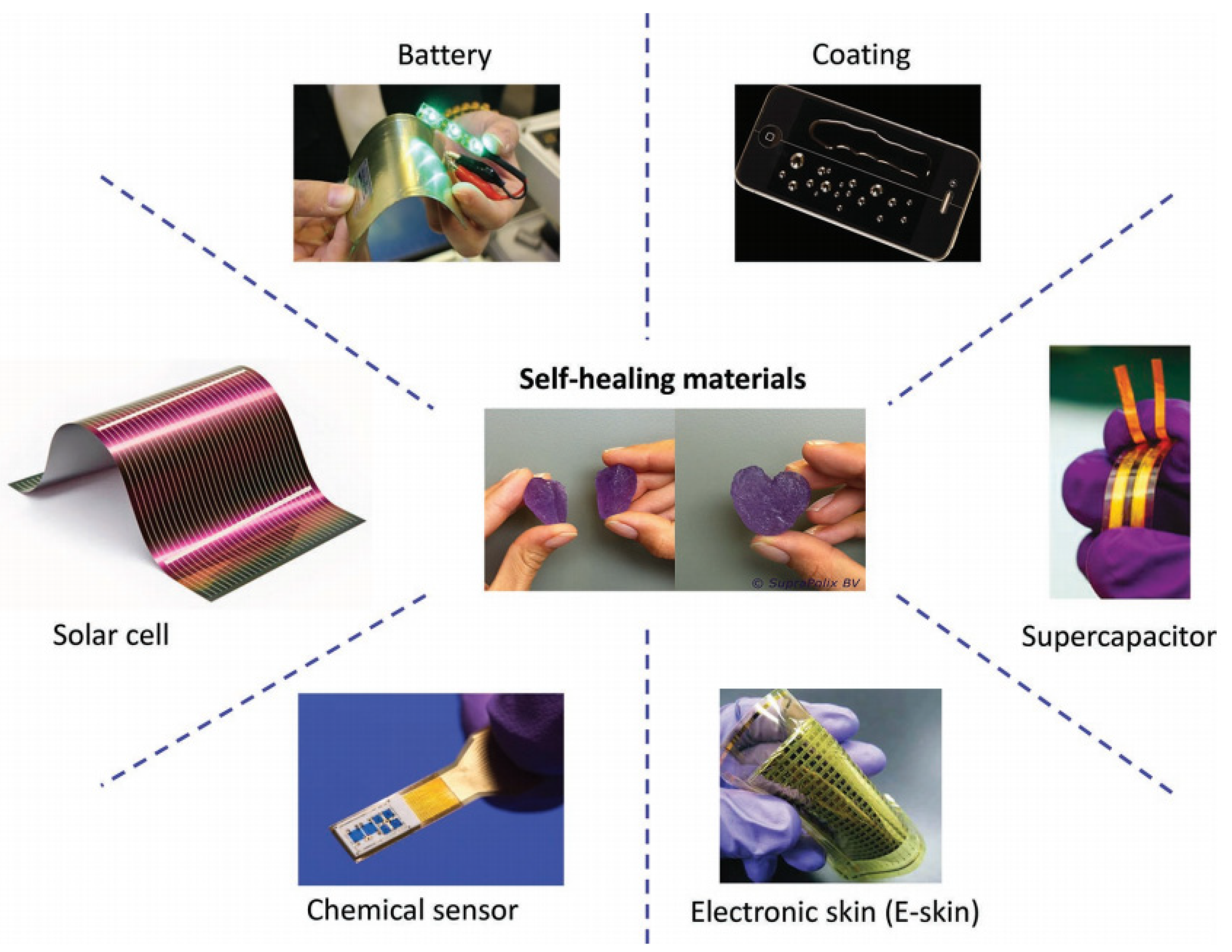
- Huynh, T.P.; Hossam, H. Advanced Materials of Use in Soft Self-Healing Devices. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rueben, J.; Walker, S.; Huhn, S.; Simonsen, J.; Mengüç, Y. Developing a UV-Curable, Environmentally Benign and Degradable Elastomer for Soft Robotics. Biomater. Soft Mater. 2018, 3, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, E.A.; Taylor, L.D.; Swensen, J.P. Smart material composites for discrete stiffness materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzumori, K.; Endo, S.; Kanda, T.; Kato, N.; Suzuki, H. A bending pneumatic rubber actuator realizing soft-bodied manta swimming robot. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Rome, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 4975–4980. [Google Scholar]
- Belding, L.; Baytekin, B.; Baytekin, H.T.; Rothemund, P.; Verma, M.S.; Nemiroski, A.; Sameoto, D.; Grzybowski, B.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Slit Tubes for Semisoft Pneumatic Actuators. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldfarb, M.; Barth, E.; Gogola, M.A.; Wehrmeyer, J.A. Design and energetic characterization of a liquid-propellant-powered actuator for self-powered robots. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2003, 8, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghooa, F.; Stilli, A.; Noh, Y.; Althoefer, K.; Wurdemann, H. Tendon and pressure actuation for a bio-inspired manipulator based on an antagonistic principle. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; ISBN 978-1-4799-6923-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fraś, J.; Czarnowski, J.; Maciaś, M.; Główka, J.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A. New STIFF-FLOP module construction idea for improved actuation and sensing. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, H.; Hongliang, R. Optimizing Double-Network Hydrogel for Biomedical Soft Robots. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, H.; Lin, S.; Ma, C.; Takaffoli, M.; Fang, N.X.; Zhao, X. Hydraulic hydrogel actuators and robots optically and sonically camouflaged in water. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terryn, S.; Brancart, J.; Lefeber, D.; Van Assche, G.; Vanderborght, B. Self-healing soft pneumatic robots. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaan4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Murray, B.C.; An, X.; Robinson, S.S.; van Meerbeek, I.M.; O’Brien, K.W.; Zhao, H.; Shepherd, R.F. Poroelastic Foams for Simple Fabrication of Complex Soft Robots. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1521–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, K.C.; Becker, K.P.; Phillips, B.; Kirby, J.; Licht, S.; Tchernov, D.; Wood, R.J.; Gruber, D.F. Soft Robotic Grippers for Biological Sampling on Deep Reefs. Galloway. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.; Howard, D.; Wu, S.; Wang, C. An Ultrasensitive 3D Printed Tactile Sensor for Soft Robotics. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Austria, 20–25 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner, M.; Faber, J.A.; Pianegonda, L.; Rühs, P.A.; Coulter, F.; Studart, A.R. 3D printing of Robotic Soft Actuators with Programmable Bioinspired Architectures. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, A.D.; Komorowski, K.; Onal, C.D.; Rus, D. Design and Control of a soft and continuously deformable 2D robotics manipulation system. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Hong Kong, China, 1 May–7 June 2014; pp. 2189–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, S.A.; Shepherd, R.F.; Kwok, S.W.; Stokes, A.A.; Nemiroski, A.; Whitesides, G.M. Camouflage and Display for Soft Machines. Science 2012, 337, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cianchetti, M.; Ranzani, T.; Gerboni, G.; Falco, I.D.; Laschi, C.; Menciassi, A. Stiff-flop surgical manipulator: Mechanical design and experimental characterization of the single module. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 3576–3581. [Google Scholar]
- Moseley, P.; Florez, J.M.; Sonar, H.A.; Agarwal, G.; Curtin, W.; Paik, J. Modeling, Design, and Development of Soft Pneumatic Actuators with Finite Element Method. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Mutlu, R.; Li, W.; Alici, G. A Structural Optimisation Method for a Soft Pneumatic Actuator. Robotics 2018, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alici, G.; Canty, T.; Mutlu, R.; Hu, W.; Sencadas, V. Modeling and Experimental Evaluation of Bending Behavior of Soft Pneumatic Actuators Made of Discrete Actuation Chambers. Soft Robot. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shepherd, R.F.; Ilievski, F.; Choi, W.; Morin, S.A.; Stokes, A.A.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Multigait soft robot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20400–20403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Della Santina, C.; Pallottino, L.; Rus, D.; Bicchi, A. Exact Task Execution in Highly Under-Actuated Soft Limbs: An Operational Space Based Approach. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2508–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolley, M.T.; Shepherd, R.F.; Mosadegh, B.; Galloway, K.C.; Wehner, M.; Karpelson, M.; Wood, R.J.; Whitesides, G.M. A resilient, untethered soft robot. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, C.M.; Gillespie, M.T.; Hyatt, P.; Rupert, L.; Sherrod, V.; Killpack, M.D. A New Soft Robot Control Method: Using Model Predictive Control for a Pneumatically Actuated Humanoid. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2016, 23, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, M.; Kogan, B.; Bryant, M.; Garcia, E. Model-based Feedforward and Cascade Control of Hydraulic McKibben Muscles. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 275, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, T.; Ren, Z.; Gong, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Guan, S.; Wen, L. Modeling and experiments of a soft robotic gripper in amphibious environments. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1729881417707148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Low, J.H.; Liang, X.; Lee, J.S.; Wong, Y.R.; Yeow, R.C.H. A Hybrid Soft Robotic Surgical Gripper System for Delicate Nerve Manipulation in Digital Nerve Repair Surgery. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fahaam, H.; Davis, S.; Nefti-Meziani, S. The Design and Mathematical Modelling of Novel Extensor Bending Pneumatic Artificial Muscles (EBPAMs) for Soft Exoskeletons. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2018, 99, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, V.; Deimel, R.; Brock, O. Selective Stiffening of Soft Actuators Based on Jamming. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 252–257. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y. A novel versatile robotic palm inspired by human hand. Eng. Res. Express 2019, 1, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, S. Design and Implementation of a Soft Robotic Arm Driven by SMA Coils. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 6108–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiser, I.; Schulz, S.; Breitwieser, H.; Bretthauer, G.T. Enhanced Flexible Fluidic Actuators for Biologically Inspired Lightweight Robots with Inherent Compliance. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Tianjin, China, 14–18 December 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Camarillo, D.B.; Carlson, C.R.; Salisbury, J.K. Configuration tracking for continuum manipulators with coupled tendon drive. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2009, 25, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Leisk, G.; Trimmer, B. Soft robots in space: A perspective for soft robotics. Acta Futura 2013, 6, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Onal, C.D.; Rus, D. Autonomous undulatory serpentine locomotion utilizing body dynamics of a fluidic soft robot. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coevoet, E.; Morales-Bieze, T.; Largilliere, F.; Zhang, Z.; Thieffry, M.; Sanz-Lopez, M.; Carrez, B.; Marchal, D.; Goury, O.; Durlez, D. Software Toolkit for Modeling, Simulation, and Control of Soft Robots. Adv. Robot. 2017, 31, 1208–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.; Culha, U.; Giardina, F.; Guenther, F.; Rosendo, A.; Iida, F. Soft manipulators and grippers: A review. Front. Robot. 2016, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonar, H.A.; Paik, J. Soft pneumatic actuator skin with piezoelectric sensors for vibrotactile feedback. Front. Robot. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White Edward, L.; Case Jennifer, C.; Kramer Rebecca, K. Multi-Mode Strain and Curvature Sensors for Soft Robotic Applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 253, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozel, S.; Keskin, N.A.; Khea, D.; Onal, C.D. A Precise Embedded Curvature Sensor Module for Soft-Bodied Robots. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 236, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, T.; Ribeiro, P.; Neto, M.; Cardoso, S.; Schmitz, A.; Santos-Victor, J.; Bernardino, A.; Jamone, L. Low-Cost 3-Axis Soft Tactile Sensors for the Human-Friendly Robot Vizzy. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; de Boer, G.; Kow, J.; Alazmani, A.; Ghajari, M.; Hewson, R.; Culmer, P. Design Methodology for Magnetic Field-Based Soft Tri-Axis Tactile Sensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devaraj, H.; Yellapantula, K.; Stratta, M.; McDaid, A.; Aw, K. Embedded Piezoresistive Pressure Sensitive Pillars from Piezoresistive Carbon Black Composites towards a Soft Large-Strain Compressive Load Sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 285, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, B.; Yan, Z.; Shang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z. Touch Locating and Stretch Sensing Studies of Conductive Hydrogels with Applications to Soft Robots. Sensors 2018, 18, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shih, B.; Drotman, D.; Christianson, C.; Hou, Z.; White, R.; Christensen, H.I.; Tolley, M.T. Custom Soft Robotic Gripper Sensor Skins for Haptic Object Visualization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Homberg, B.S.; Katzschmann, R.K.; Dogar, M.R.; Rus, D. Haptic Identification of Objects using a Modular Soft Robotic Gripper. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Truby, R.L.; Katzschmann, R.K.; Lewis, J.A.; Rus, D. Soft Robotic Fingers with Embedded Ionogel Sensors and DiscreteActuation Modes for Somatosensitive Manipulation. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Seoul, Korea, 14–18 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yanlin, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Sun, G.; Lou, X.; Dong, M. Optical Fiber Sensor Performance Evaluation in Soft Polyimide Film with Different Thickness Ratios. Sensors 2019, 19, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, H.; Sun, G.; Zhu, L. Polyimide Sensing Layer for Bending Shape Measurement in Soft Surgical Manipulators. Optik 2019, 183, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, K.; Narumi, K.; Niiyama, R.; Yoshihiro, K. Electric phase-change actuator with inkjet printed flexible circuit for printable and integrated robot prototyping. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference, Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Koivikko, A.; Raei, E.S.; Sariola, V.; Mosallaei, M.; Mantysalo, M. Soft Actuators with Screen Printed Curvature Sensors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors, Glasgow, UK, 29 October–1 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bobrow, J.E.; McDonell, B.W. Modeling, identification, and controlof a pneumatically actuated, force controllable robot. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1998, 14, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caldwell, D.G.; Medrano-Cerda, G.A.; Goodwin, M. Control of pneumatic muscle actuators. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 1995, 15, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ren, T.; Li, Y.; Choi, S.H. Precharged pneumaticsoft actuators and their applications to untethered soft robots. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, F.; Henning, A.; Tang, K.; Cai, L. Soft damper for quick stabilizationof soft robotic actuator. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Real-time Computing and Robotics, Angkor Wat, Cambodia, 6–10 June 2016; pp. 466–471, ISBN 978-1-4673-8959-4. [Google Scholar]
- Al Abeach, L.A.; Nefti-Meziani, S.; Davis, S. Design of a Variable Stiffness Soft Dexterous Gripper. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, F.; Rojas, D.; Tang, K.; Cai, L.; Asfour, T. A jumpingrobot using soft pneumatic actuator. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 3154–3159. [Google Scholar]
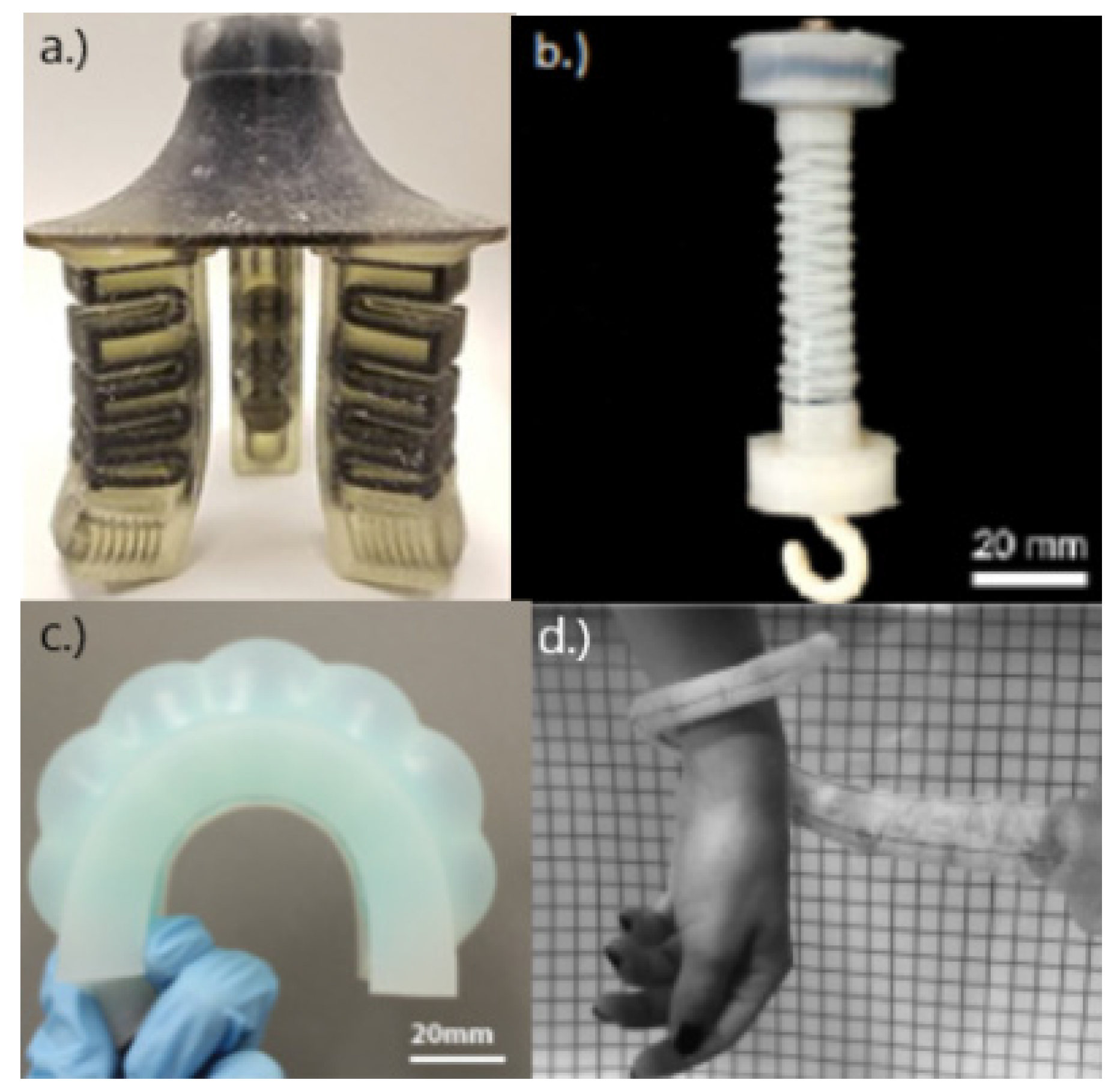



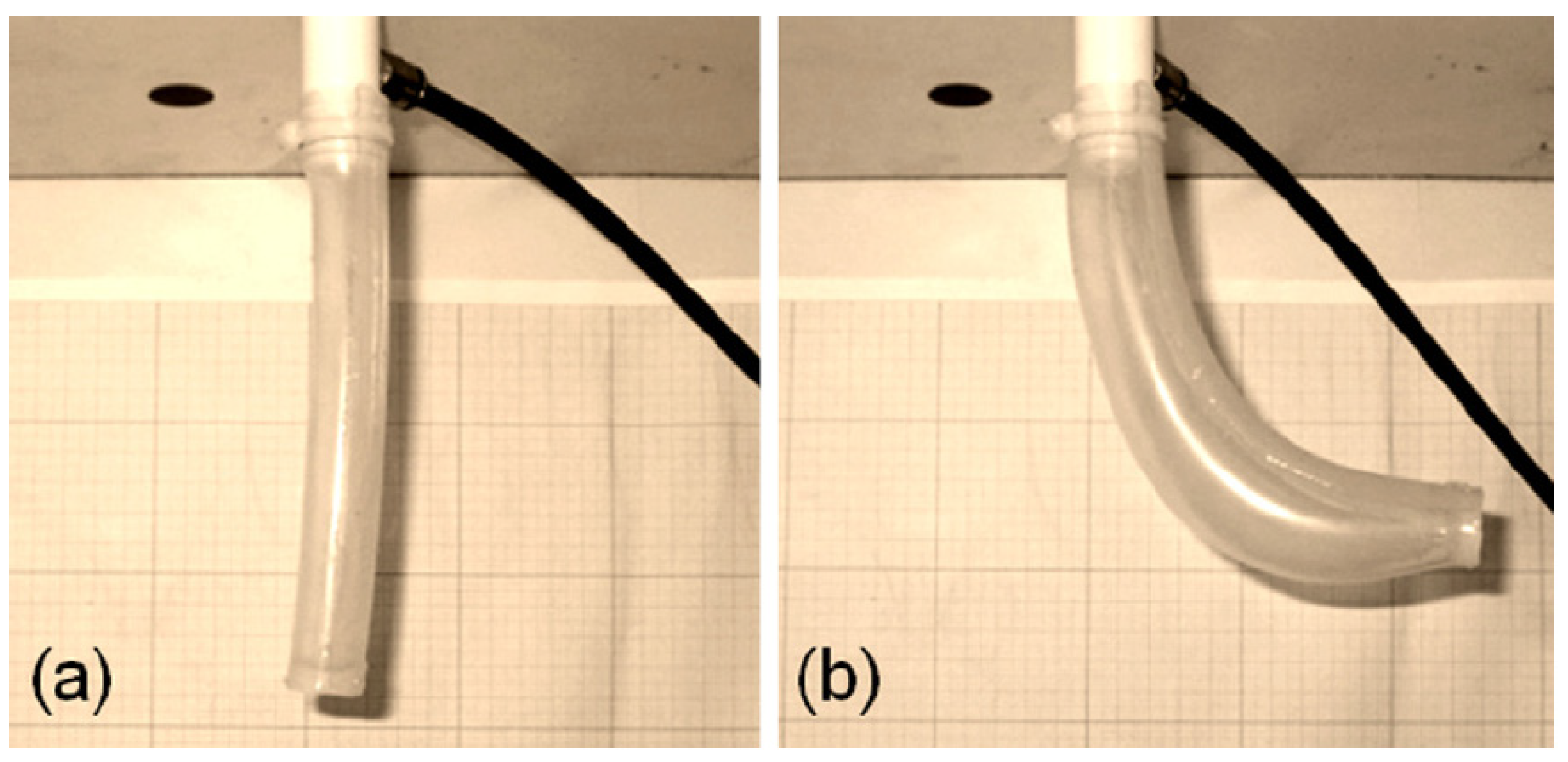
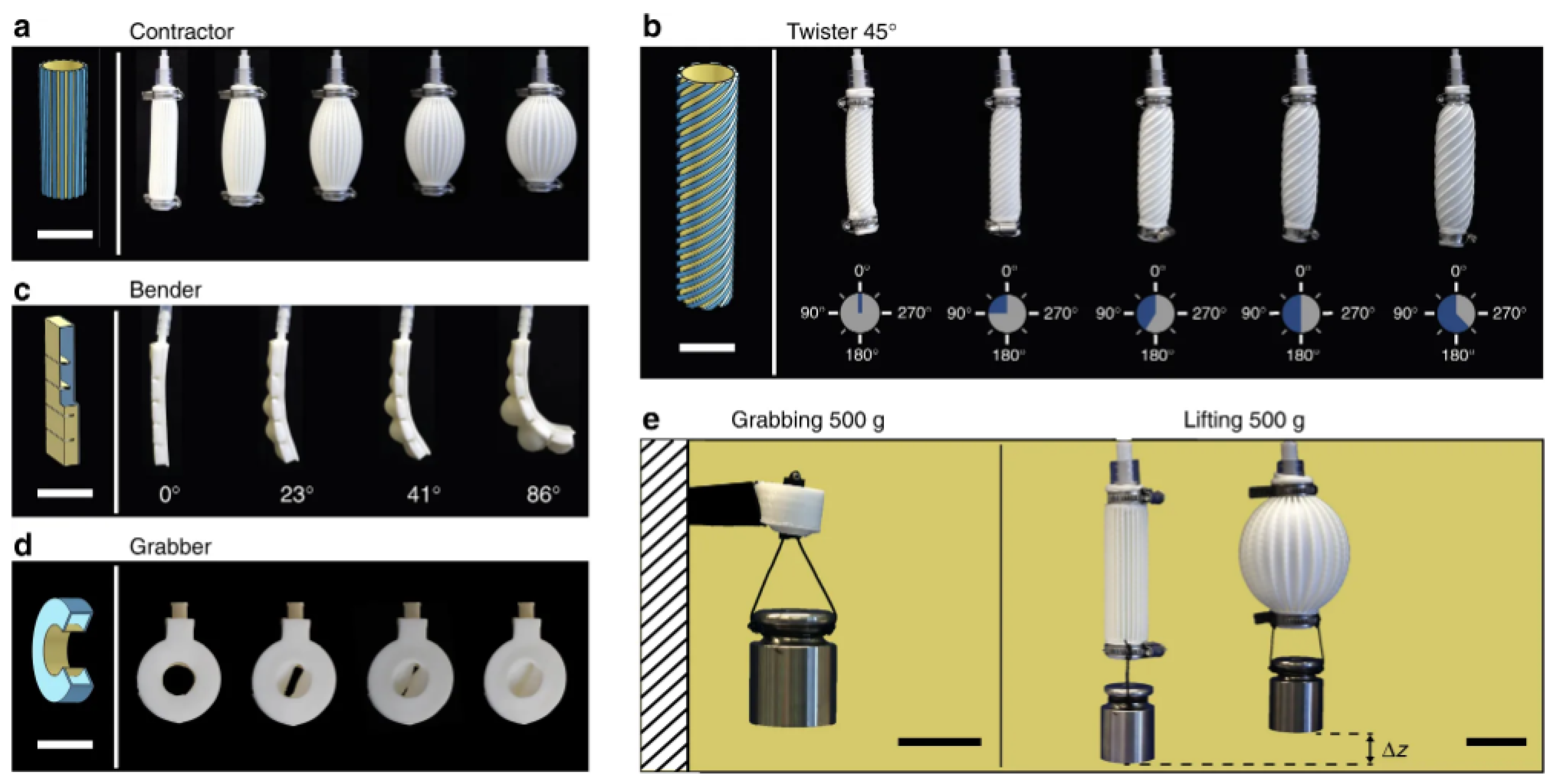
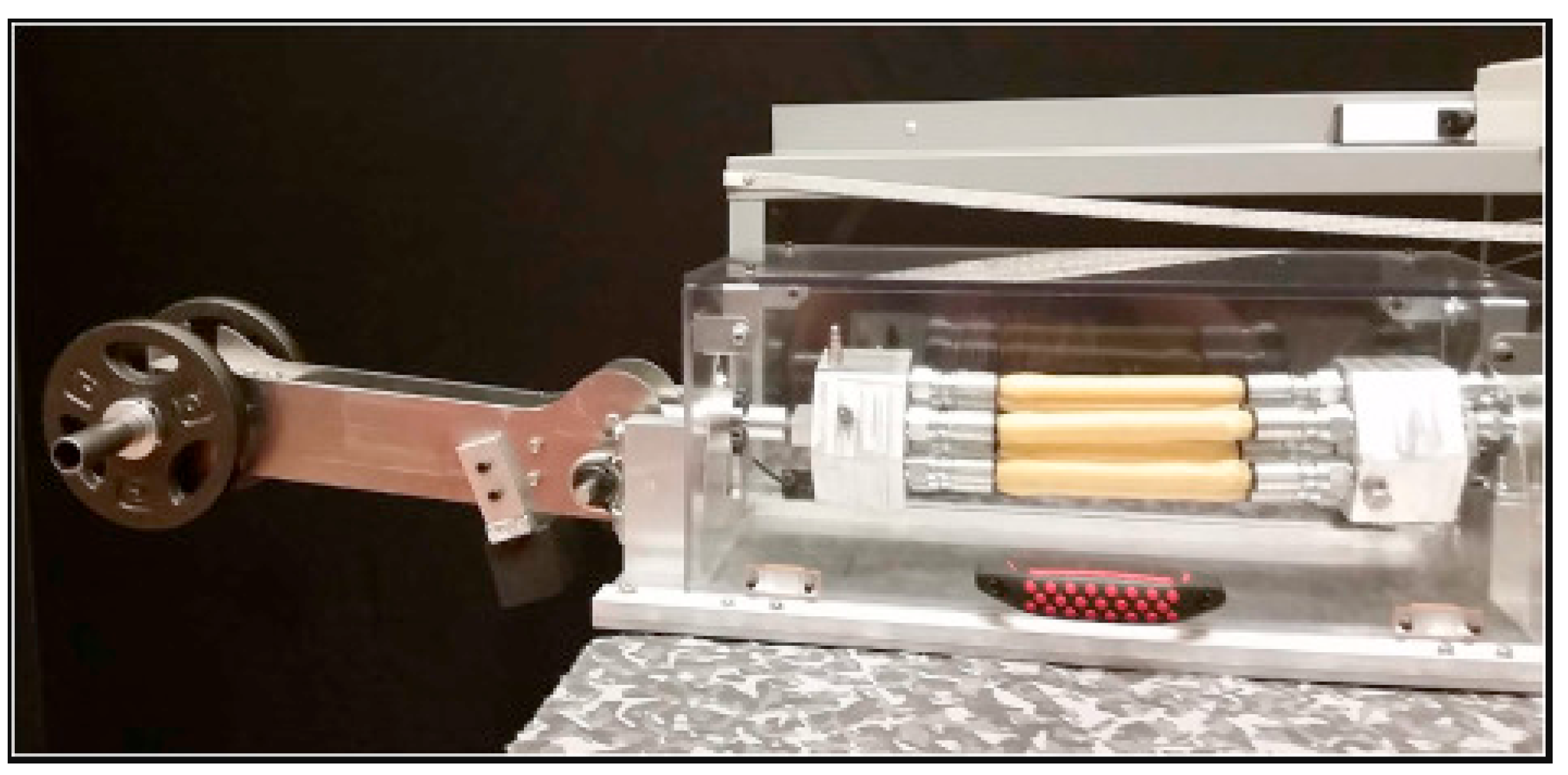
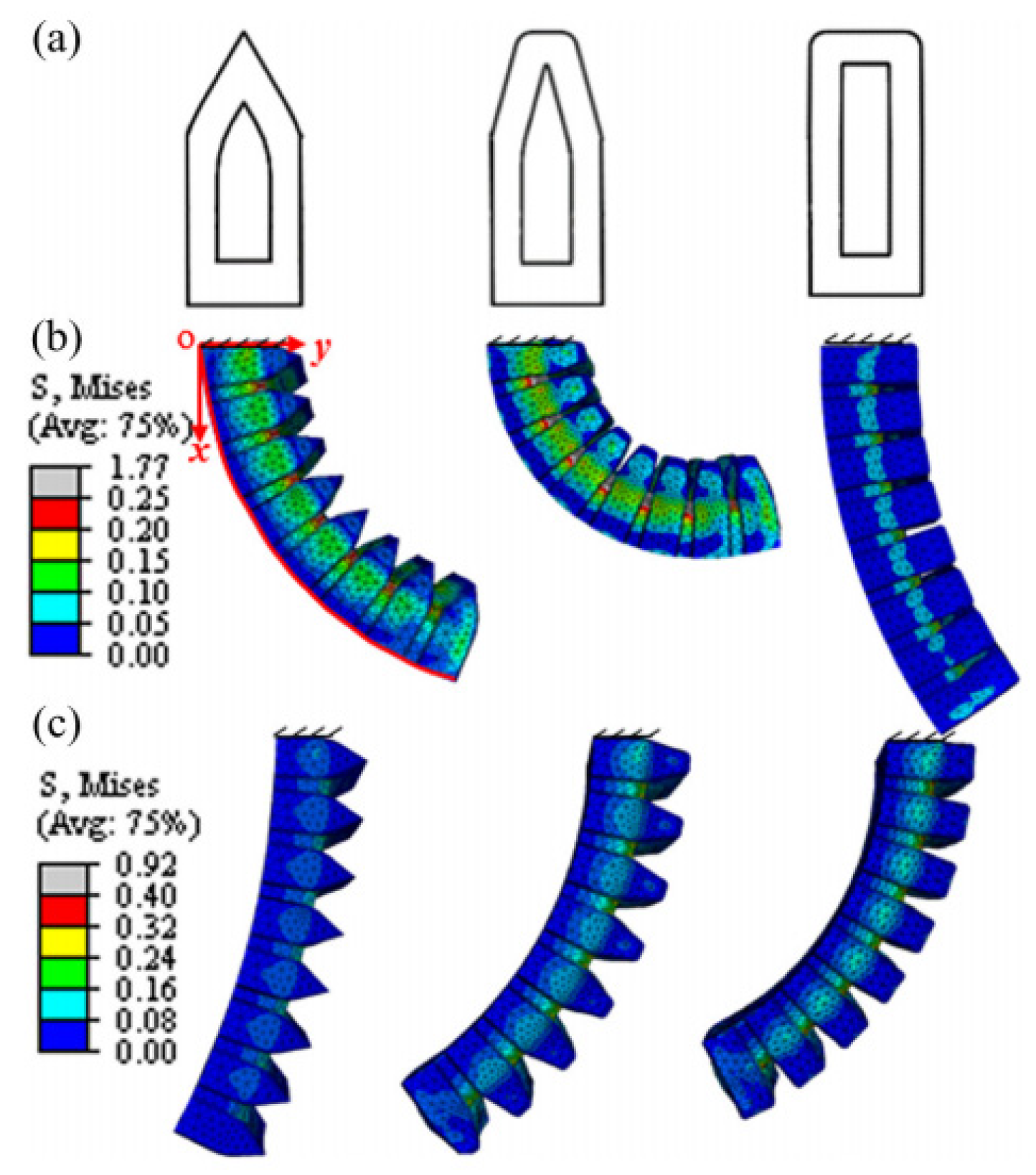

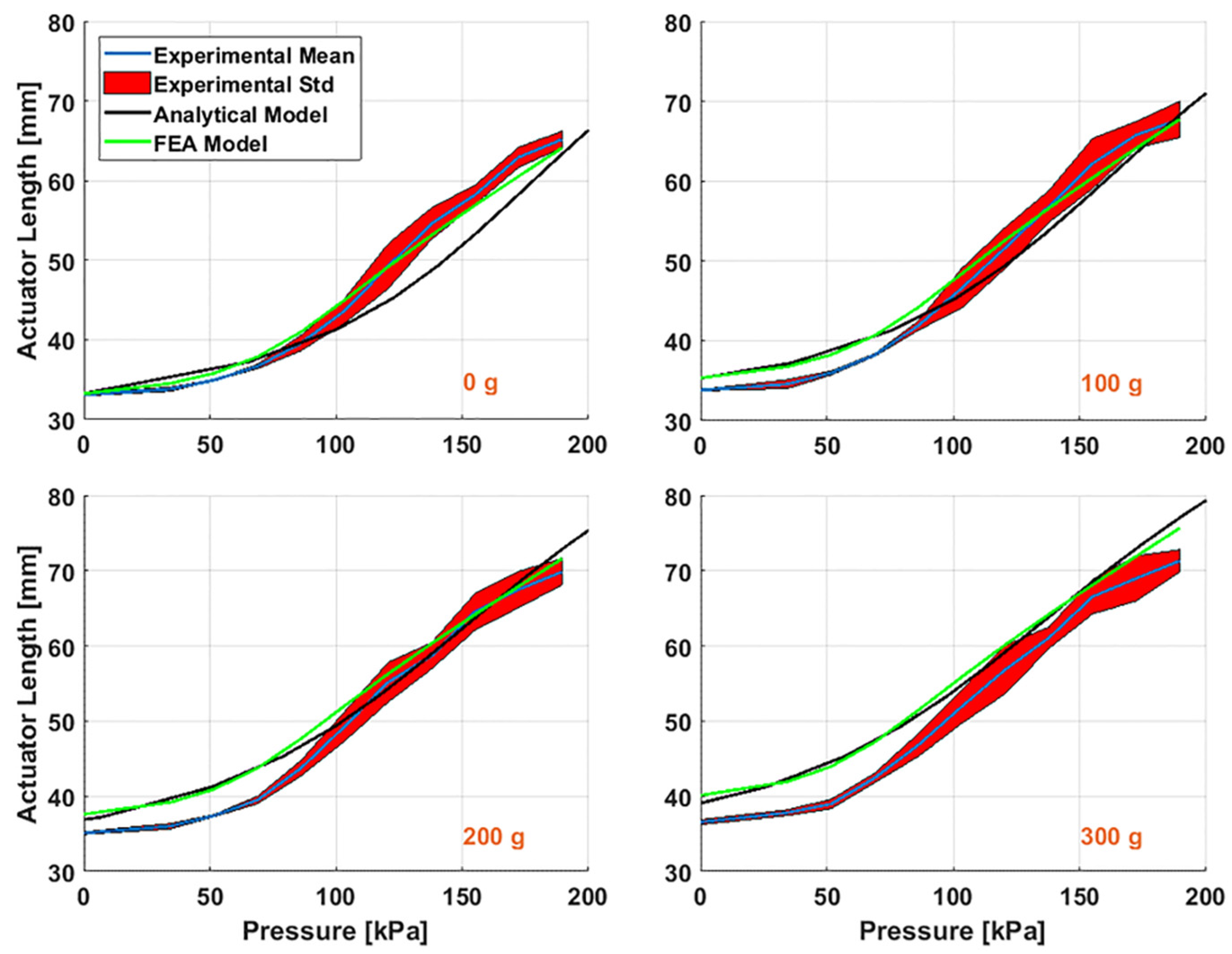
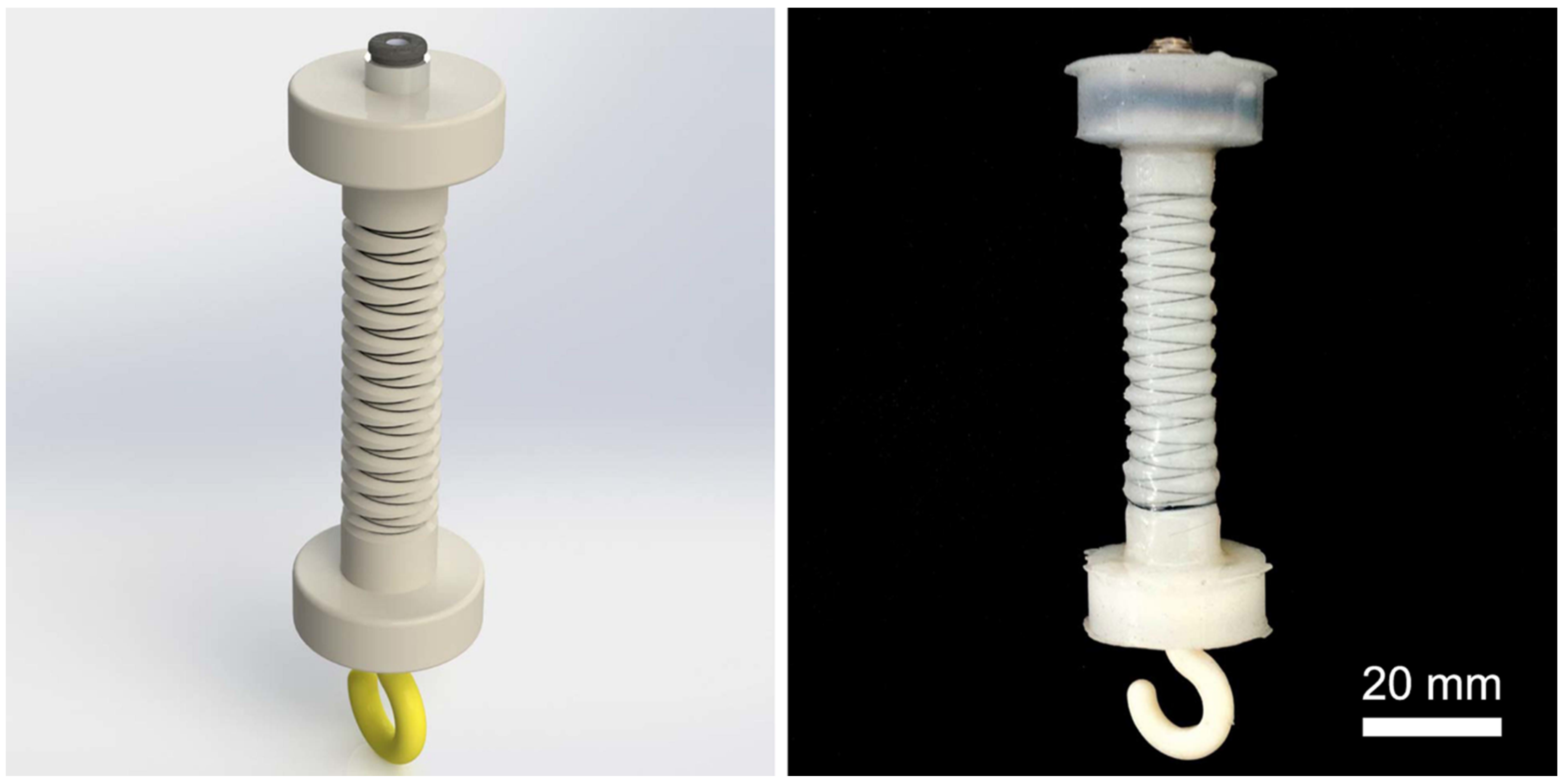
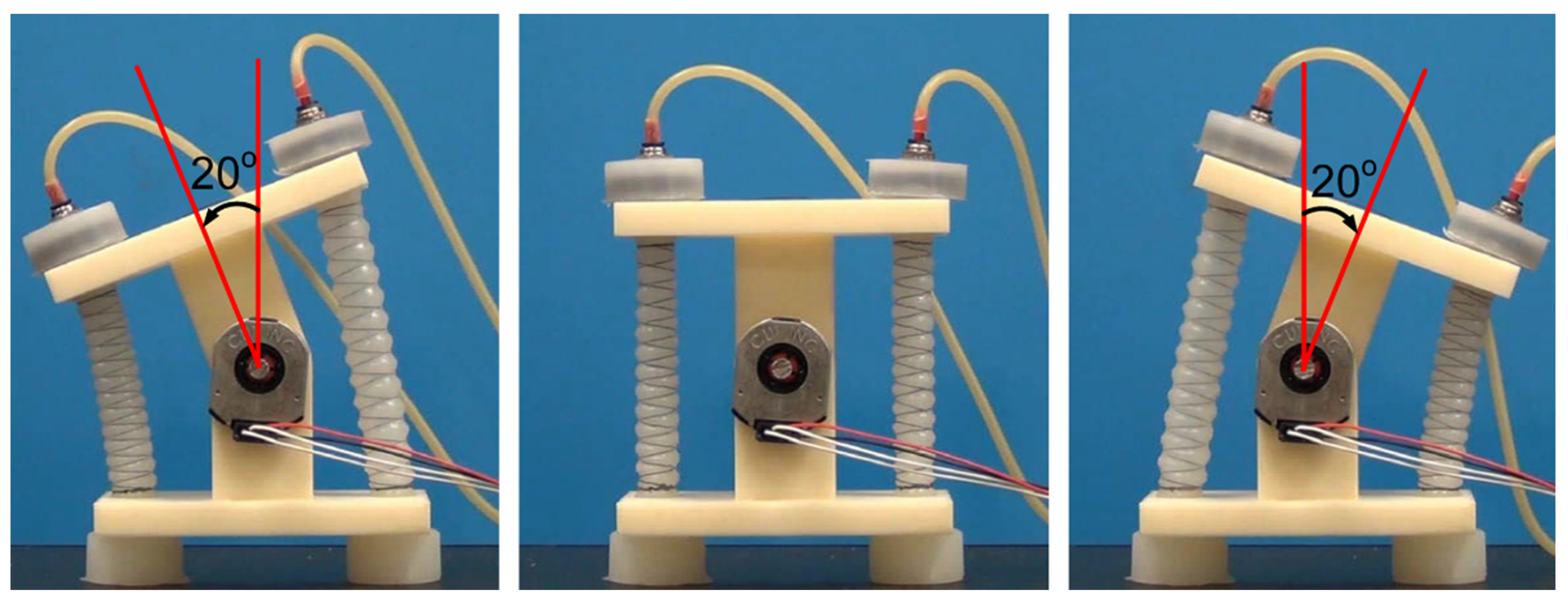
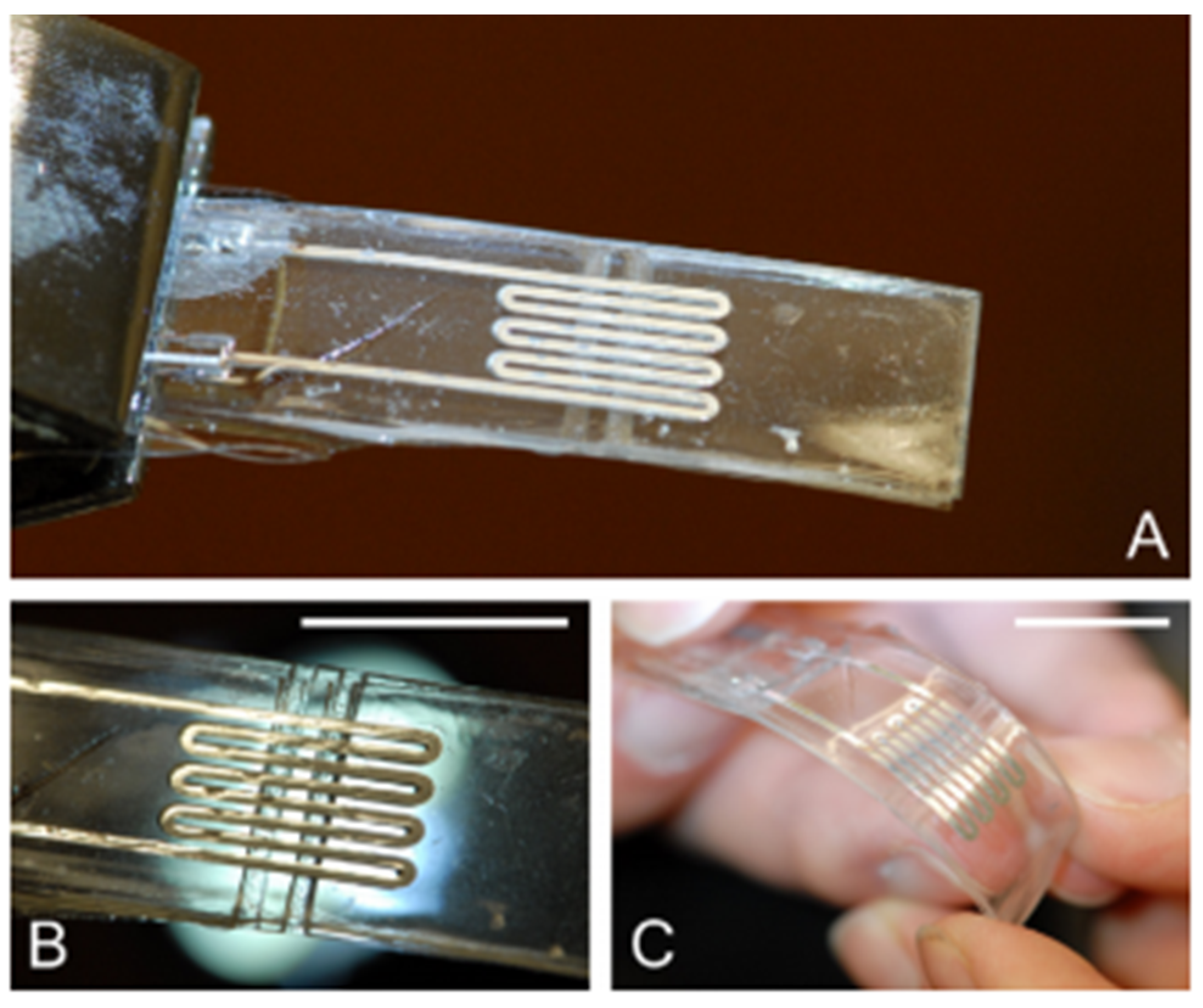
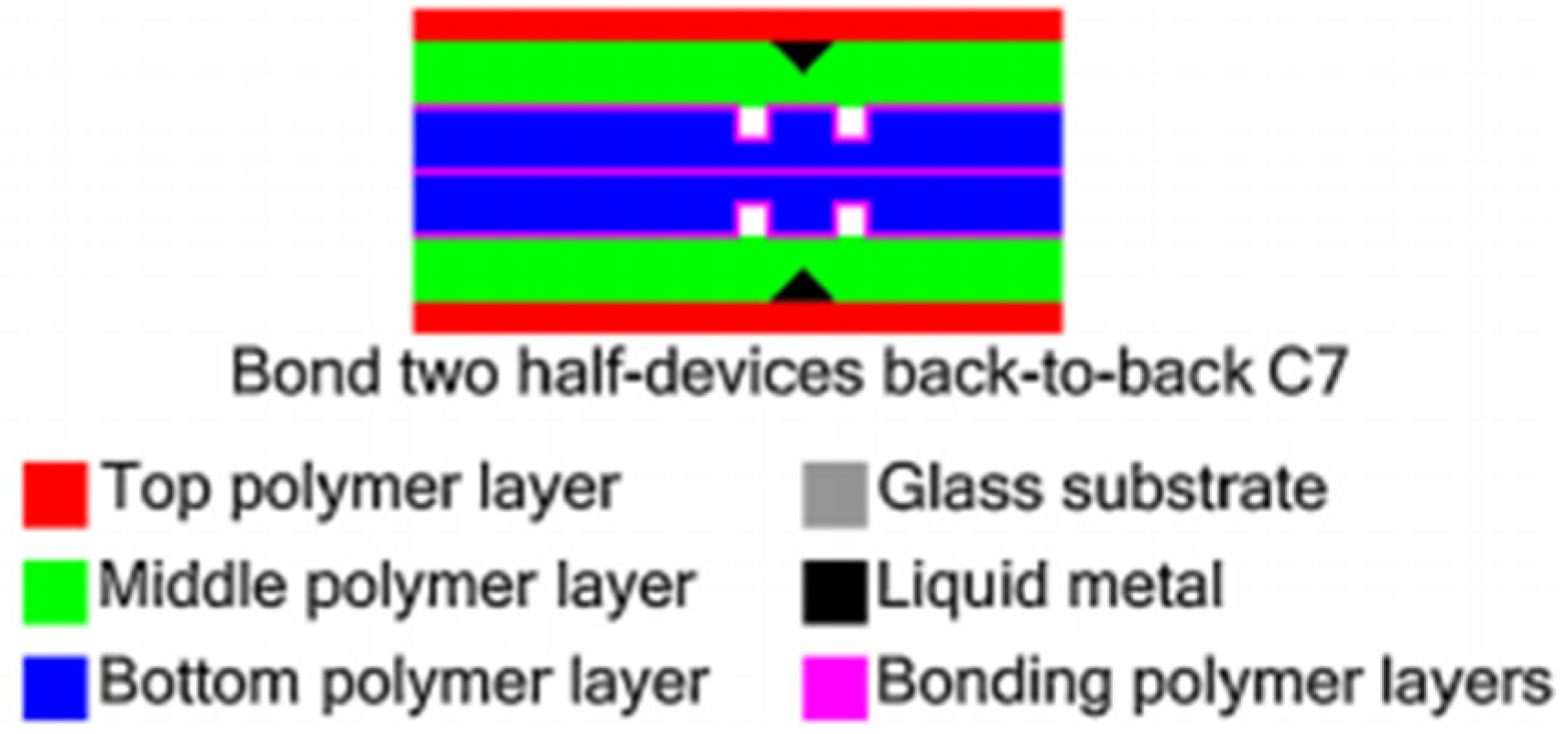

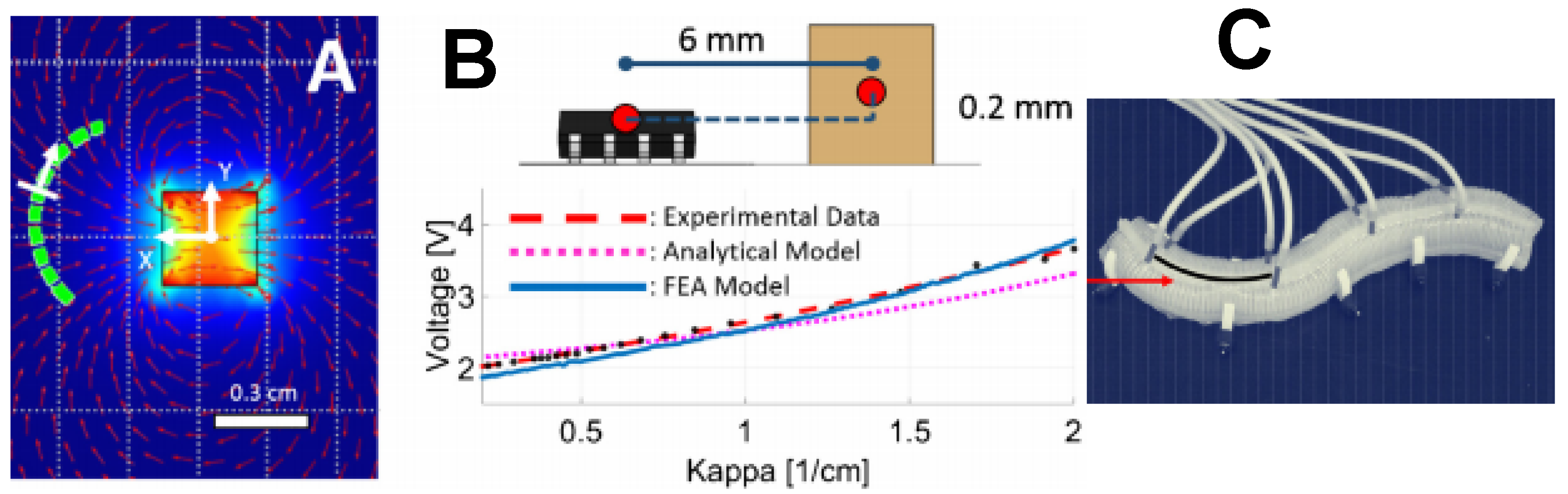
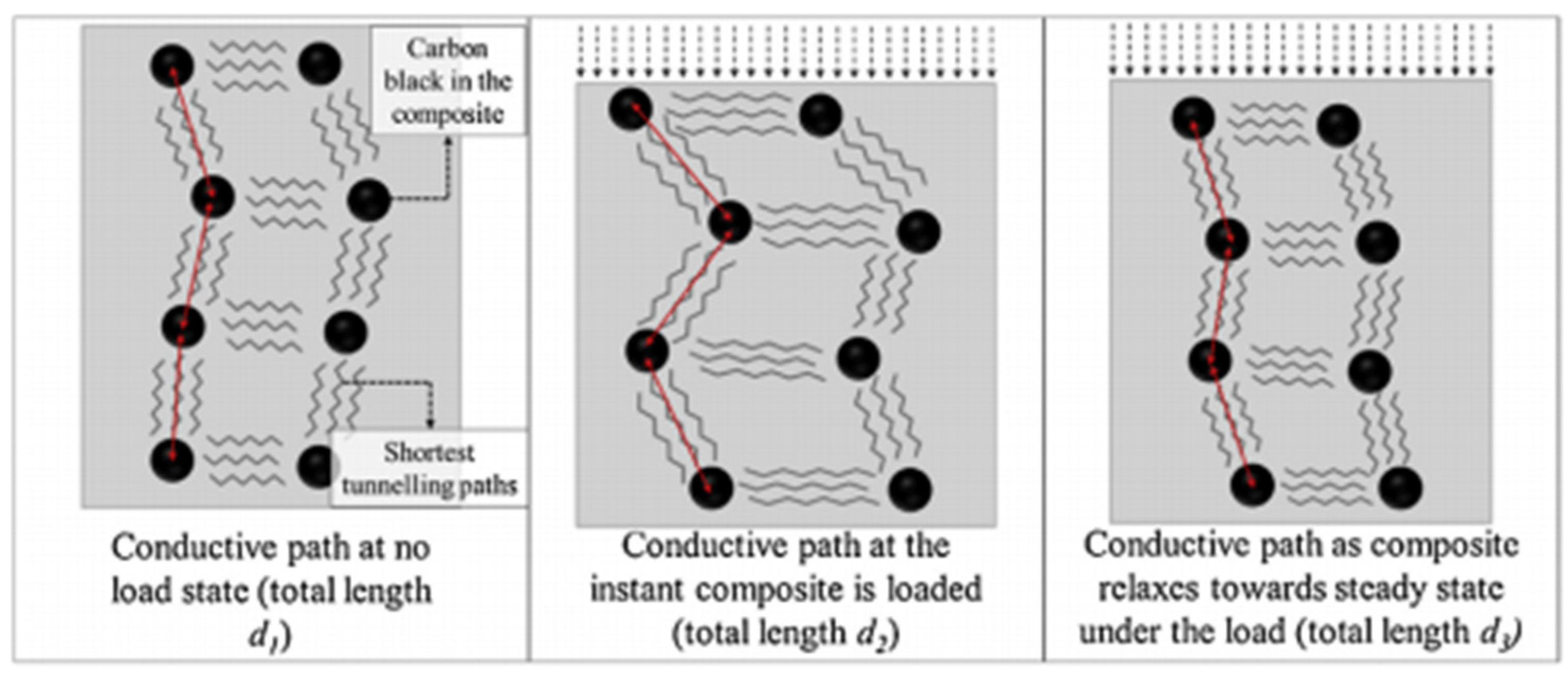
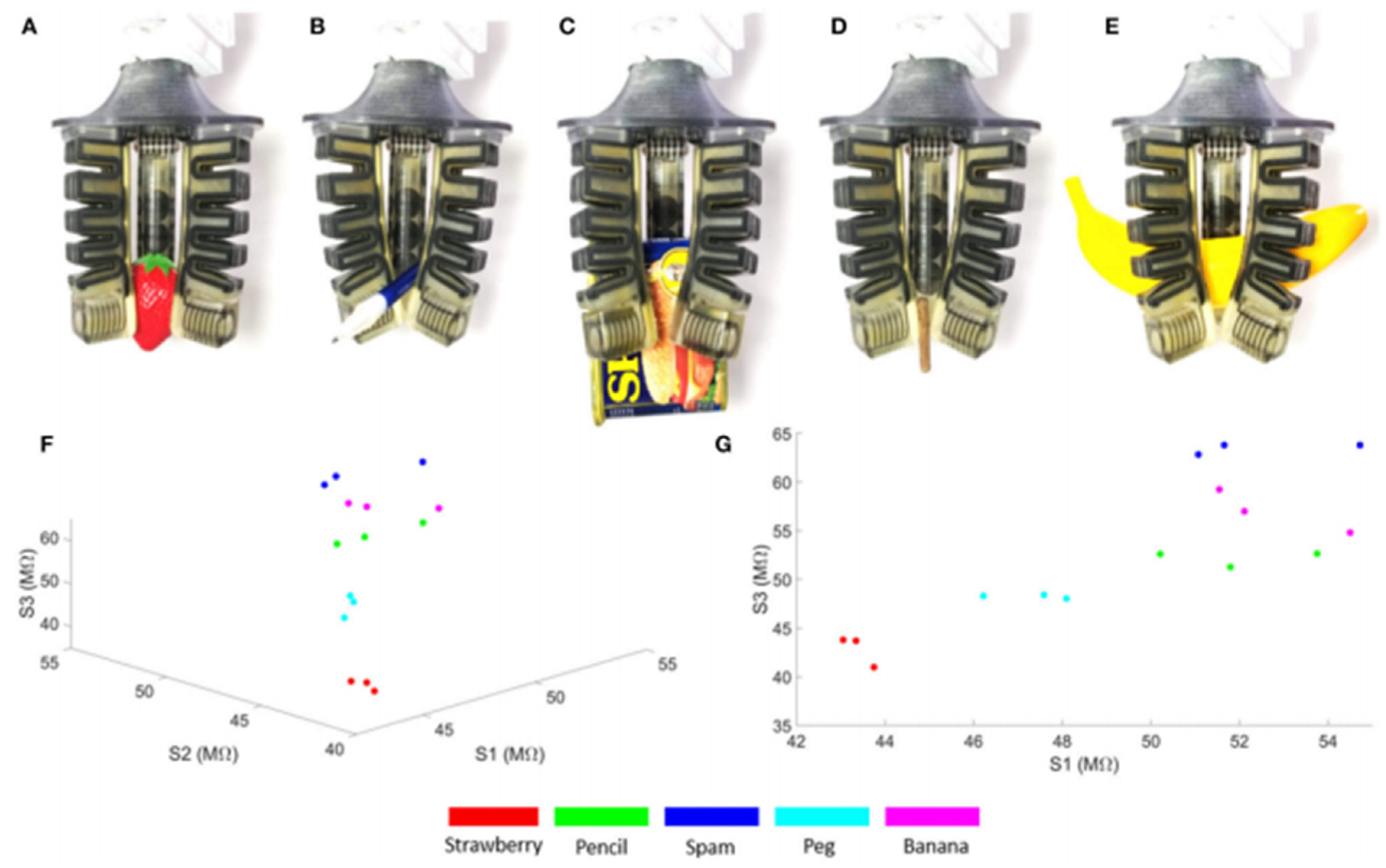


| Driving Systems | Controller | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
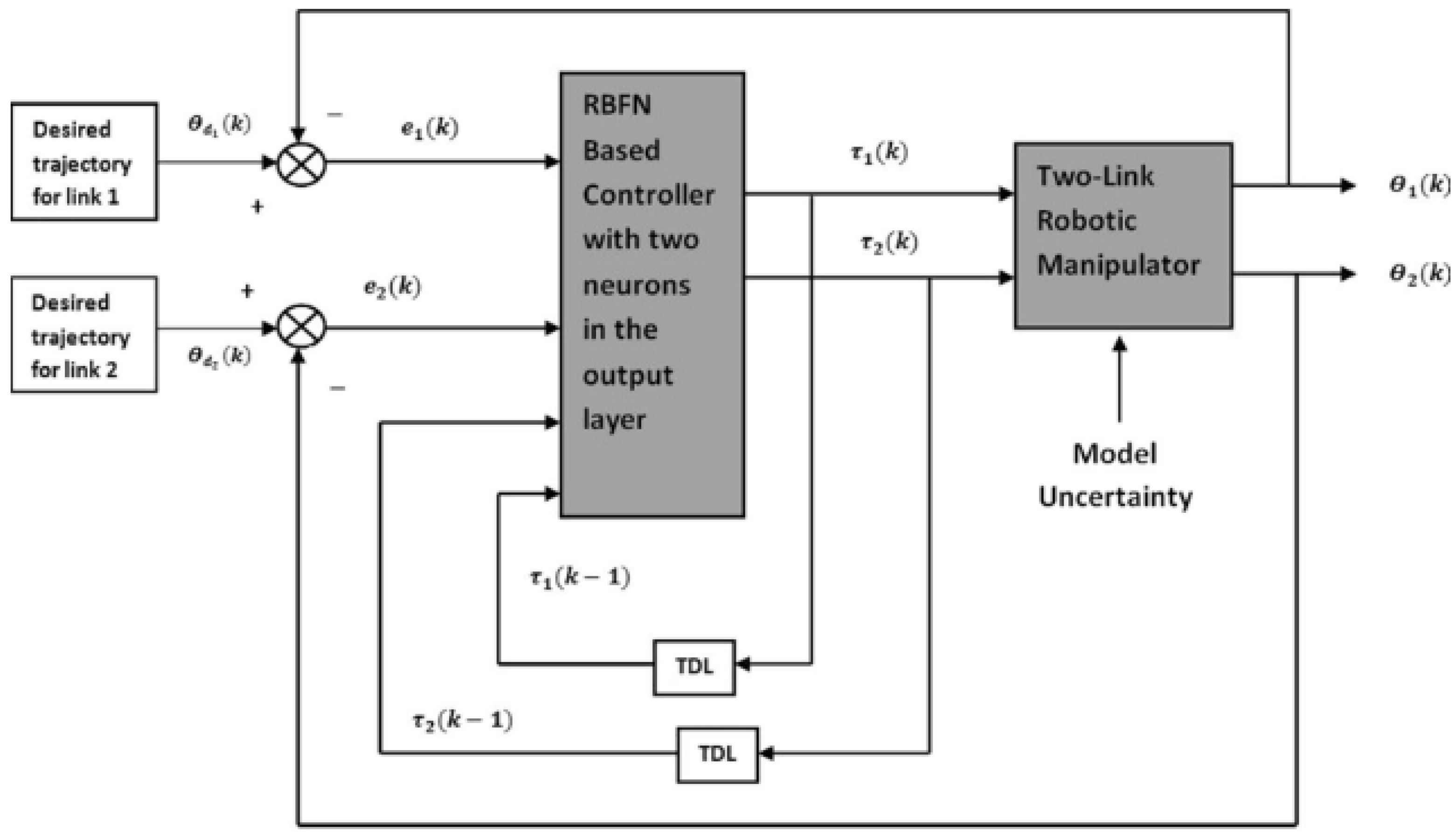
| Cables and Servos | RBFN [59] Radial basis function network |
|
|
| Disturbance Observer (Dob) [67] |
|
| |
| MLFFNN [59] Multilayer Feed-forward Neural Network |
|
| |
| PD (Proportional-Derivative) [68,69,70] |
|
| |
| PID [35,67] Proportional-Integral-Derivative |
|
| |
| Electromagnetic & Electroactive polymers (EAP) | Microcontrollers [61] |
|
|
| Pressure Sensor | PI [71] Proportional-Integral |
|
|
| Linear [72,73] |
|
| |
| None (Theoretical Model) | Extended Kalman Filter [74] |
|
|
| Material | Purpose/Functionality | Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Silicon Rubber [75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84] | Pneumatic Flexible Finger Tube; Robot leg and gripper; Bi-bellows actuator; Buckling Linear Actuators | Chamber; Bidirectional motion Locomotive and manipulative role; Ecoflex-50; Elastosil |
| Sheet Material [85] | Pouch Motor | Mass-fabricable; heat bonding; |
| 3D printing materials (NinjaFlex, EP, Nylon 12, and EAA & AUD) [23,24,25,26,89,90,91] | Soft pneumatic actuator; Flexible fluidic actuator | Various 3D printing method type (FDM; DMP-SL; SLS; DLP); High degree of freedom |
| Polychloroprene-based membrane [93,94] | Single mass granular material gripper | Hold the object without sensory feedback |
| PDMS [95] | Microscale inward spiraling tentacle actuators | ~185 μm radius, ~0.78 mN grabbing force |
| PGSI [98] | Environment friendly and biodegradable polymers | 134 to 193 kPa UTS; 57 to 131 kPa moduli; |
| Smart material (Nitinol, PCL, Field’s metal) [99] | Smart composite finger | Discrete levels of stiffness |
| DN Hydrogels; Agrar/PAM [105,106] | Bending actuator | 3-DOF; easily customizable; delicate in small millimeter scale; biocompatible |
| Electro Active Polymer [31] | OCTARM (artificial manipulator) | PVDF based and dielectric |
| Diels-Alder Polymer [107] | Self-healing elastomers | Thermo-reversible covalent network; heal micro and macroscopic damage |
| Open-celled elastomeric foam [108] | Fluidic elastomer actuators | Low density; |
| Technology | Modeling Method | Gripper size (mm) | Object Mass (g) | Supplied Power | Force (N) | Surface Conditions (Dry, Wet) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tendon-Based Stiffening [2] | Beam Theory (Mathematical Model) | 47 × 23 | No Object | N/A | 3.3 | Dry |
| Twisted-and-Coiled Actuator [3] | Physics-Based | N/A | 1, 2 and 3 | N/A | 0.013 | Dry |
| Pneumatic Finger [27] | ANSYS | 67 × 3.2 | 15.3 | 12V | 0.15 | Dry |
| SMA Coils [128] | Physics-Based Kinematics | 80 × 55 | N/A | 0-5V | N/A | Both |
| ECF (electro-conjugate fluid) [77] | Physics-Based | 18 × 5 | No Object | .5kV-4kV | 0.007 | Dry |
| Transducer Mechanism | Material | Functionality | Characteristic | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistive sensors | Liquid metal [136] | Strain, Curvature | Laser engraved microchannel, Flexible system | Linearity and low coupling between summation and differential channels in response to strain and curvature. |
| Conductive Hydrogel [141] | Touch location stretch | Location of touch points are determined by its polar radius | Conductive Hydrogel has tensile elastic modulus of 1.335 kPa; Gel resistance increases with stretching. | |
| Photopolymers (Tango+, Tangoblack+, VeroClear, SUP705) [11] | Strain | 3D–printed, Multimaterial with various conductivities | – | |
| Piezoresistive sensors | Composite (TPU & PLA–G) [110] | Tactile | 3D–printed (FDM), high sensitivity, excellent recovery to bending strain, wide range of pressure detecting | Detectable pressure Range: 292 Pa to 487 kPa Bending angle range: 0.1 °–26.3° |
| Composite (Carbon black) [140] | Elastomeric force | Controllable composite film thickness | Response rise time upon applied load: 600 ms | |
| Magnetic | Hall sensors and permanent magnets [137] | Curvature | Contract–free | Sensitivity with noise filtering: 0.0012 cm−1 Sensitivity without noise filtering: 0.05 cm−1 |
| Hall sensors and permanent magnets [138] | Tactile | High sensitivity, low hysteresis, good repeatability, Easy fabrication | Minimum Sensed force: 7.2 mN; Recovery time: 0.3 s; Noise level: ± 2.5 mN | |
| Optical | Photopolymer (TangoBlack+) [28] | Tactile | 3D printed, Biomimetic Morphology, High accuracy | Sensor Localization accuracy average: ± 0.205 |
| FBG, Polyimide film [145] | Curvature | Reliable sensitivity, good repeatability | Range of sensitivity of the sensor: 1.96 to 50.65 pm/m−1 The curvature ranges up to 30 m−1 | |
| FBG, Polyimide film [146] | Curvature | Flexible system | Range of sensitivity of the sensor: 9.73 to 212.8 pm/m−1 Sensor error average: 1.82% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walker, J.; Zidek, T.; Harbel, C.; Yoon, S.; Strickland, F.S.; Kumar, S.; Shin, M. Soft Robotics: A Review of Recent Developments of Pneumatic Soft Actuators. Actuators 2020, 9, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9010003
Walker J, Zidek T, Harbel C, Yoon S, Strickland FS, Kumar S, Shin M. Soft Robotics: A Review of Recent Developments of Pneumatic Soft Actuators. Actuators. 2020; 9(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalker, James, Thomas Zidek, Cory Harbel, Sanghyun Yoon, F. Sterling Strickland, Srinivas Kumar, and Minchul Shin. 2020. "Soft Robotics: A Review of Recent Developments of Pneumatic Soft Actuators" Actuators 9, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9010003
APA StyleWalker, J., Zidek, T., Harbel, C., Yoon, S., Strickland, F. S., Kumar, S., & Shin, M. (2020). Soft Robotics: A Review of Recent Developments of Pneumatic Soft Actuators. Actuators, 9(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/act9010003





