Simple Summary
Monitoring the health status of cats ensures their welfare and control of infections transmissible to other domestic and wild animals, as well as to humans. In the present survey, blood samples and ticks were collected, between February 2018 and October 2019, from 85 stray cats living in registered colonies in Emilia Romagna (northern Italy), with the aim of investigating the presence and infection level of a wide range of pathogens transmitted by arthropods (arthropod-borne pathogens—ABPs). The collected samples were subjected to serological and DNA-based methods. The presence of pathogens was observed in 71 cats (83.5%) using serological methods and in 47 cats (55.3%) by applying DNA-based analysis. Coinfections (presence of two or more pathogens) were observed in 21 cats (24.7%). While ABPs in privately owned cats are more easily prevented and managed through standard veterinary care, stray cats may be particularly at risk as they live outdoors, have constant exposure to arthropods such as ticks and fleas, and generally do not receive regular antiparasitic treatment. Indeed, the results of the present study show a widespread presence of ABPs, suggesting that stray cats may represent a potential health threat to companion animals and people and the need for improved management.
Abstract
Cats may be affected by a wide range of arthropod-borne pathogens (ABPs) of medical and veterinary interest. Between February 2018 and October 2019, 85 blood samples were collected from stray cats from the Emilia Romagna region (northern Italy). Ticks (n = 28) on the examined cats were also collected. Serological and molecular methods were applied to search for infection by Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Bartonella henselae, Coxiella burnetii, Ehrlichia canis, Leishmania spp., Babesia spp., Hepatozoon spp., and Cytauxzoon spp. A total of 71 sera (83.5%) had antibodies to at least one investigated pathogen: 39 (45.9%) were positive for B. henselae, 32 (37.6%) positive for C. burnetii, 12 (14.1%) positive for E. canis, four (4.7%) positive for A. phagocytophilum, and two (2.4%) positive for Leishmania spp. A total of 47 (55.3%) DNA samples were positive by PCR for at least one investigated pathogen: 25 (29.4%) were positive for C. burnetii, 23 (27.1%) positive for B. henselae, two (2.4%) positive for E. canis, five (5.9%) positive for Leishmania spp., and two (2.4%) positive for Cytauxzoon spp. Coinfections were observed in 21 cats (24.7%). No positivity was found for A. phagocytophilum, Babesia spp., or Hepatozoon spp. All ticks were negative. A widespread presence of ABPs in the investigated area of northern Italy was shown. Accurate information on their prevalence may be relevant for feline veterinary medicine, as well as from a One Health perspective.
1. Introduction
Domestic cats (Felis catus) may host a wide range of protozoa and bacteria of medical and veterinary interest [1,2,3,4,5,6], and they are often exposed to hematophagous arthropods, including sand flies, fleas, and ticks [7]. Infections by different arthropod-borne pathogens (ABPs) have been investigated in feline populations, even though less frequently than in dogs [7,8]. In fact, epidemiological data related to the spreading of ABPs among pets, in Europe and in the rest of the world, have been performed mainly in dogs [9,10]. Moreover, whereas laboratory diagnosis for arthropod-borne infections on the basis of clinical signs is often requested for this latter species, these infections are not frequently diagnosed and, thus, underestimated in feline populations [7]. Arthropod-borne diseases, caused by ABPs, have emerged or re-emerged in the past few years due to human factors and climatic changes [11]. Thus, improved knowledge of various aspects of these infections in feline hosts, such as occurrence and distribution in different geographic areas, is required [8,12].
Among the most relevant protozoan ABPs are feline leishmaniosis, babesiosios, cytauxzoonosis, and hepatozoonosis. Feline leishmaniosis (FeL), caused by Leishmania infantum, is reported from areas endemic for canine leishmaniosis [4,13]. Cat infection is frequent and clinical signs occur mostly as nodular skin lesions; when these appear, specific treatment is needed, although cats frequently do not fully recover. These animals have been recognized able to infect phlebotomine vectors, playing a role as minor reservoirs [14]. Feline babesiosis is considered rare in Europe [15]. Two clinical cases were reported from Germany and Poland, caused by a large Babesia morphologically very similar to B. canis. The affected animals showed fever, anemia, and hematuria and responded to treatment with imidocarb [16,17]. In general, cats may be infected by several Babesia spp., recently reviewed by Penzhorn and Oosthuizen [15]. Cytauxzoonosis, an emerging tick-borne protozoan disease affecting domestic and wild felids, is caused by piroplasms of the genus Cytauxzoon, specifically C. felis, C. manul, and Cytauxzoon sp. [18]. The most common clinical features are fever, anorexia, lethargy, and icterus [19]. C. felis, which is limited to the American continent (United States and Brazil) [20,21], was previously considered responsible for life-threatening infections leading to the death of domestic cats within a few days [22]. However, a different pathogenicity, depending on the strains, was recently reported [22], and even domestic cats developing subclinical and persistent blood parasitaemia have been described [23,24,25], suggesting they may play a role as reservoir of infection [25]. Fewer epidemiological and clinical data on infections by species other than C. felis are available, especially for Europe [18,26], although several studies have been published lately [27,28,29,30]. Finally, Hepatozoon felis, H. canis, and H. silvestris are the etiological agents of feline hepatozoonosis [2,31,32]. The infection is primarily transmitted by the ingestion of infected ticks. Hepatozoonosis in cats is usually asymptomatic but may develop as a muscle disease [27].
Among the bacterial ABPs, Bartonella henselae is the most known agent affecting cats. Other relevant bacteria species are Coxiella burnetii, Anaplasma phagocytophilum, and Ehrlichia canis. The Bartonella genus includes several species able to infect domestic and wild animals. These bacteria are transmitted by blood-sucking arthropods, including fleas, lice, and sandflies, whereas it is not clear if ticks may be considered as potential vectors [33]. In particular, B. henselae is transmitted by the flea Ctenocephalides felis and is associated with cat scratch disease (CSD) in humans [34]. Coxiella burnetii is an obligate intracellular Gram-negative bacterium, which causes a zoonosis called Q Fever. Several domestic and wild animal species are known to be susceptible to this agent, even though Q Fever is usually related to cattle and small ruminants. Coxiellosis-associated abortion has been documented in cats; however, the organism has also been isolated from cats after normal parturition [35,36]. Anaplasma phagocytophilum and E. canis are two obligate intracellular Gram-negative bacteria responsible for well-known canine diseases. They are mainly transmitted by Ixodes ricinus and Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks, respectively. Clinical signs and abnormal laboratory findings related to feline ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are similar to those observed in dogs, and include anorexia, hyperesthesia, lethargy, weight loss, joint pain, dyspnea, lymphadenomegaly, anemia, and hyperglobulinemia [37,38].
All these diseases should not be overlooked, as, for instance, feline leishmaniosis is increasingly recognized as a disease of cats in endemic areas [4,13]. Many surveys conducted in cats examined only one parasitic agent, but studies should ideally examine several pathogens [39]. In particular, studies on stray colony cats are particularly valuable for assessing the epidemiology and emergence of ABPs, as they generally do not receive regular antiparasitic treatment [5,6,12,40]. Thus, this survey aimed to investigate the occurrence of bacterial ABPs, specifically A. phagocytophilum, B. henselae, C. burnetii, and E. canis, and protozoan ABPs, including Leishmania spp., Babesia spp., Cytauxzoon spp., and Hepatozoon spp., in stray cats from northern Italy (Emilia Romagna region) and in ticks collected on the same animals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
Between February 2018 and October 2019, 85 venous blood samples were collected from stray cats (37 females and 48 males), during ovariohysterectomy and orchiectomy activities conducted by veterinarians of the Italian National Health Service (local unit of Bologna). All stray cats belonged to registered colonies of the province of Bologna and Rimini (Emilia Romagna region, northern Italy). No sex, age, or clinical condition inclusion criteria was applied. Body condition score (BCS) was evaluated (score 1–9) [41]. Blood samples were collected in EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) and serology tubes from the jugular vein after trichotomy and disinfection of the neck region with ethyl alcohol, with the animal under general anesthesia. Serum was collected from clotted blood samples after centrifugation at 1200× g for 10 min.
Ticks occurring on the examined cats were removed, placed in 1.5 mL tubes with 70% ethanol. Blood, serum, and tick samples were then transferred to the Department of Veterinary Sciences of the University of Pisa for the analytical procedures. Herein, the ticks were morphologically identified [42]. Serum, blood, and tick samples were stored at −20 °C until used.
2.2. Serological Analysis
2.2.1. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay for Bacterial Pathogens
An indirect immunofluorescent assay (IFA) was carried out to detect antibodies against the investigated bacterial pathogens. Commercial IFA slides (Fuller Laboratories, Fullerton, CA, USA) with the following coated antigens were used: A. phagocytophilum, B. henselae, C. burnetii (separate phase I and phase II antigens), and E. canis. A commercial fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated sheep anti-cat immunoglobulin G (IgG) (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) diluted 1:50 in Evans Blue (Sigma-Aldrich) solution was used as secondary antibody.
Antibody titers of 1:40 and 1:64 were considered the cut-off values for A. phagocytophilum/E. canis and B. henselae/C. burnetii, respectively [43,44,45]. Two-fold dilutions of the positive sera were tested to determine the endpoint titer.
2.2.2. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay for Leishmania
An IFA test was applied for the detection of antibodies against Leishmania spp., as described by Mancianti and Meciani [46], using cultured promastigotes fixed on Multiwell glass slides as antigens. Sera were tested starting from a 1:10 dilution.
2.3. Molecular Analysis
2.3.1. DNA Extraction
Total DNA was extracted from the sediment (200 µL) obtained after centrifugation of the blood samples and from ticks using the DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Milano, Italy), following the manufacturer’s blood and tissues protocols, respectively. Each DNA sample was stored at −20 °C until used in PCR assays.
2.3.2. DNA Amplification and Sequencing
Different PCR approaches were employed to detect the investigated pathogens in DNA extracted from blood and ticks, following the protocols previously described and summarized in Table 1. For some pathogens, such as Leishmania spp., A. phagocytophilum, and E. canis, a nested PCR protocol was used. All DNA samples resulted positive for Bartonella spp. were successively tested with a PCR protocol to identify B. henselae and distinguish type I and type II, using reverse type-specific primers BH1 or BH2 in combination with the forward broad-host-range primer 16SF [47]. In addition, DNA extracted from ticks was used for specific identification of the host, targeting a fragment of the mitochondrial 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) gene [48].

Table 1.
Gene target, amplicon length, primer pairs, and PCR conditions used for the different pathogens.
PCR assays were performed with Wonder Taq (EUROCLONE, Italy) in an automated thermal cycler (Gene-Amp PCR System 2700, Perkin Elmer, Norwalk, CT, USA). Sterile distilled water was used instead of DNA in the negative control. DNA extracted from slides used for indirect immunofluorescent assay coated with A. phagocytophilum, E. canis, C. burnetii, and B. henselae (Fuller Laboratories, Fullerton, CA, USA) and known positive samples, previously sequenced, of B. annae [49], Cytauxzoon sp. [18], H. canis [49], and L. infantum were included as positive controls [50].
PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis on 2% agarose gel stained with GelRed® Nucleic Acid Gel Stain (Biotium). SharpMass™ 100 Plus Ladder (Euroclone, Milano, Italy) was used as a DNA marker and for visual estimation of the PCR products’ concentration.
For Cytauxzoon spp., PCR products of the expected length and with a sufficient concentration were forward and reverse Sanger sequenced by an external company. Nucleotide sequences were analyzed using Bioedit version 7.0.9 [51]. Adjustments were made after visual checking and consensus sequences were compared against those deposited in GenBank by using the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). A neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogram was constructed using Bioedit and MEGA-X software including the DNA sequences obtained in the present study and other sequences of Cytauxzoon spp. previously deposited in GenBank [18,26,28,30,52,53,54,55,56,57]. Sequencing and phylogenetic analysis was conducted only on Cytauxzoon spp. to determine the species involved and as reports of this parasite in Italy are still quite uncommon.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The detection rate was calculated for each pathogen and each test, together with the 95% confidence interval (CI).
3. Results
The overall results of the serological and molecular analysis are reported in Table 2. Briefly, the highest seropositivity rate was observed for B. henselae (45.9%), followed by C. burnetii (37.6%), E. canis (14.1%), A. phagocytophilum (4.7%), and Leishmania sp. (2.4%). The detection rate found by PCR were generally lower; all cats positive by PCR to the bacterial pathogens were also seropositive, while three cats PCR-positive to Leishmania were seronegative (see Section 4). Coinfections by two or more pathogens were observed in 21 cats (24.7%) (Table 3). Overall, the BCS most frequently scored 5, whereas only a minority of cats scored 7 (5.9%) or 3 (3.5%).

Table 2.
Results of the serological (indirect immunofluorescent assay, IFA) and molecular (PCR) tests for protozoa and bacteria of the 85 cats analyzed. CI, confidence interval.

Table 3.
Details of the cats with coinfections of two or more pathogens. ID, identifier.
3.1. Serological Analysis
A total of 71 (83.5%; 95% CI 75.6–91.4%) sera had antibodies to at least one investigated pathogen. With regard to bacterial pathogens, 39 cats (45.9%; 95% CI 35.3–56.5) were positive for B. henselae (n = 18 titer 1:64, n = 21 titer ≥1:128), 32 cats (37.6%; 95% CI 27.3–47.9) for C. burnetii (phase II antigen, n = 14 titer 1:64, n = 18 titer ≥1:1.128), 12 cats (14.1%; 95% CI 6.7–21.5) for E. canis (n = 9 titer 1:40, n = 3 titer ≥1:80), and four cats (4.7%; 95% CI 2–9.2%) for A. phagocytophilum (titer 1:40). Serological tests for protozoan showed that two (2.4%, 95% CI 0–5.6%) of the sampled cats were positive for Leishmania sp. with a titer 1/10.
3.2. Molecular Analysis
A total of 47 (55.3%; 95% CI 44.7–65.9%) DNA samples were positive by PCR for at least one investigated pathogen. Among these, 25 (29.4%; 95% CI 19.7–39.1%) cats were positive for C. burnetii, 23 (27.1%; 95% CI 17.6–36.5%) for B. henselae (16 genotype I and 7 genotype II%), and two (2.4%; 95% CI 0–5.6%) for E. canis. No cats were positive at PCR for A. phagocytophilum.
The molecular analysis confirmed positivity for Leishmania in the two seropositive cats, and DNA of this parasite was also found in three additional cats (overall prevalence 5.9%; 95% CI 0.9–10.9%). Moreover, DNA of Cytauxzoon sp. (confirmed by sequencing) was found in two cats (2.4%; 95% CI 0–5.6%), while no positivity was found for Babesia spp. or Hepatozoon spp.
The two sequences of Cytauxzoon sp. were deposited in GenBank (MW165870-MW165871). The BLAST analysis retrieved 100–99.75% identity with sequences deposited as Cytauxzoon sp. isolated from domestic cats in Germany (MN629916 [30]), in Switzerland (MF503141-8 [29]; KU306940-4, KU306945-8, Willi et al., Tochtermann et al. unpublished), in France (KX881967 [28]; EU622908 [52]), and in Portugal (KU710344, [26]), as well as with isolates from the European lynx and the wild cat in Romania (KT361070-2, KT361074, KT361076, KT361079-81 [53]) and from the Iberian lynx in Spain (EF094468-70 [54]). Accordingly, in the NJ dendrogram the sequences obtained in this study clustered with other Cytauxzoon sp. isolates obtained from wild and domestic felids from Italy, Spain, France, Switzerland, Germany, Portugal, and Romania and with C. manul found in Pallas’s cats (Otocolobus manul) from Mongolia [55,66]. As already observed in other studies [18,26,56], isolates of C. felis from the American continent belong to a different cluster (Figure 1).
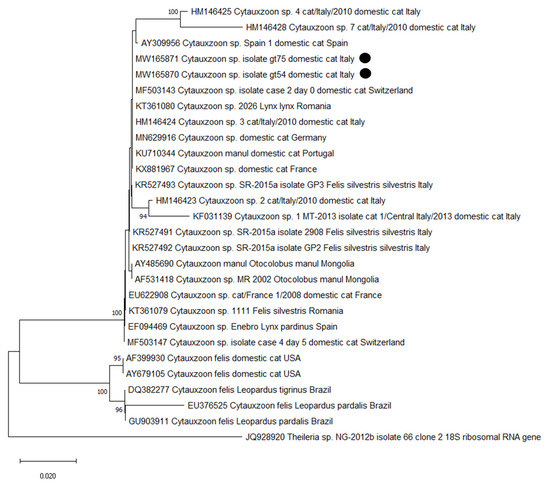
Figure 1.
Neighbor-joining phylogram created with the two sequences of the small subunit (18S) ribosomal RNA gene obtained in the present survey (highlighted with a black dot), 20 sequences of Cytauxzoon sp., and five sequences of Cytauxzoon felis from other studies in domestic and wild animals.
The majority of the 28 ticks were molecularly identified as I. ricinus (92.8%), followed by R. sanguineus (7.2%). No pathogen DNA was found in ticks.
4. Discussion
Data obtained in the present investigation show that ABPs are widespread among stray cats from the investigated geographic areas. Feline ABP occurrence and distribution among Italian cat populations are described in many studies, mainly focusing on southern regions and insular areas [4,8,67,68,69,70], while northern [5,6,56] and central Italy had since recently received little attention [7,43,44]. A large survey investigating owned cats from northern, central, and southern Italy was also recently published [71].
The high percentage of cats that resulted PCR-positive to C. burnetii is worthy of attention. This pathogen is traditionally related to farm animals, mainly ruminants, in which it causes reproductive disorders. The presence of a large number of bacteria mainly in placenta, birth fluids, and milk causes a high risk of infection for workers having contact with infected animals and their products. Moreover, raw milk and unpasteurized dairy products may be cause of infection for consumers. C. burnetii is able to infect other mammals, and infections in cats have been previously reported. Cases of abortion have been described, although the organism has also been isolated from cats after normal parturition [35,36]. Data about the spreading of C. burnetii in domestic and stray feline populations are scant, but information to better understand the role of cats in the epidemiology of Q fever is necessary in view of the One Health concept. Whereas, according to some authors who did not find C. burnetii DNA in cats’ samples, cats are not important reservoirs for human Q Fever infection [72], our results, with a 29.4% of bacteremic animals, suggest that cats are involved in the epidemiology of coxiellosis and could be source of infection for other animals and people. Owners, as well as veterinarians, breeders, and other persons having contact with cats, may be at risk of infection mainly with the abortion products; however, urine, feces, and respiratory secretions could also contain coxiellae. Other than the transmission through oral and inhalatory routes, C. burnetii may be transmitted by tick bites [73]. During our study, C. burnetii DNA was not found in the analyzed ticks. Positive reactions to the agent found in the tested cats could be related to the ingestion of infected roditors and/or contact with them, which is more frequent in stray cats. In fact, rodents are considered natural reservoirs of this pathogen [74]. Among the examined cats, 14.1% had antibodies against E. canis, and, in 2.4%, DNA of the pathogen was found. Overall, 4.7% of the cats were seropositive for A. phagocytophilum, even though all them were PCR-negative, indicating exposure to the pathogen but not active infection. While, for the Emilia Romagna region, data are scanty, a previous serological survey in cats from the neighbouring region Tuscany found seroprevalence values of 6.4% and 4.5% to E. canis and A. phagocytophilum, respectively [44]. The lower prevalence to E. canis detected in the previous survey could be related to the better life condition of the cats that lived in private catteries and domestic environments. On the other hand, the molecular prevalence values detected in this study were lower than those observed among stray cats from urban colonies in Milan (northern Italy). In fact, Spada et al. [5] found 17.7% of PCR-positive cats for A. phagocytophilum and 5.4% for Ehrlichia spp. On the contrary, no DNA of Ehrlichia/Anaplasma spp. was found in another recent study including cats from throughout Italy [71]. E. canis and A. phagocytophilum are usually transmitted to dogs by R. sanguineus, Ixodes spp., Amblyomma spp., and Dermacentor spp. ticks [75]. It has been supposed that these pathogens are also transmitted by ticks to cats, even though the transmission mechanism in these animals is actually not fully understood. In the present study, DNAs of the two pathogens were not found in the examined ticks. Cats could contract E. canis and/or A. phagocytophilum from other ticks that previously fed on them or from other hematophagous arthropods. Ctenocephalides felis fleas, which are proven vectors of other feline pathogens and infest cats more frequently than ticks, should also be investigated to determine if they are able to transmit E. canis and A. phagocytophilum [44].
The present survey found a high seroprevalence (45.9%) to B. henselae. Moreover, 27.1% of the tested cats had B. henselae DNA in their blood. Both detected percentages were higher than those reported in a previous investigation carried out in domestic cats that lived in private houses and/or gardens [43]. Our prevalence value is higher than the value found by Latrofa and collaborators [71], where 24 out of 958 (2.5%) cats tested PCR-positive for Bartonella spp., with 1.6% for B. henselae and 0.9% for B. clarridgeiae. The present investigation, as well as the above-cited study, found a higher number of cats positive to B. henselae genotype I, suggesting that it is more widespread than genotype II. However, previous studies demonstrated that the prevalence of the two genotypes may vary in relation to the considered geographic area [76]. Cats are usually asymptomatic when infected with both genotype I and genotype II; conversely, it seems that the two types may induce varying pathologic features in infected people. In particular, genotype I is considered more pathogenic for humans than genotype II [77,78]. It is well known that B. henselae is transmitted by C. felis, whereas it is not clear if ticks may be considered as potential vectors. In fact, there is little evidence that Bartonella spp. can replicate within ticks and no definitive evidence of transmission by a tick to a vertebrate host [33]. The absence of B. henselae DNA in the examined ticks could confirm that these arthropods are not important in the epidemiology of the agent.
With regard to protozoan ABPs, the presence of Leishmania sp. is an interesting finding. Feline leishmaniosis (FeL) due to L. infantum was firstly described in Italy in a cat from Imperia (Liguria, Italy) [13], thus living in a highly endemic area for canine leishmaniosis. Thenceforth, along with the improvement of feline medicine and veterinary clinical diagnostic tools, the reports from Europe have become more and more frequent. The seroprevalence values range from more than 60% to 0% [79] depending on the canine seroprevalence range. Moreover, the positivity to specific parasitological tests is not necessarily related to an ability to develop an overt disease. Serological testing is considered to have a very low sensitivity, although it has shown 100% specificity [80]. It is believed that the immune response to Leishmania strongly differs between dogs and cats. The seroprevalence, as well as the antibody titers in epidemiological surveys, is lower than reported in dogs. Another basic issue impacting on the seroprevalence/PCR positivity estimation, such as for dogs, is the season of testing. In fact, in some cats, a transient disseminated infection would occur during the transmission period. The cats of the present study were sampled between October and June; thus, the positivity rate should not be overestimated. The finding of antibodies and/or parasite DNA would indicate that the animals were infected; nevertheless, the occurrence of DNA in seronegative cats can be explained with the very low humoral response in this animal species. Considering that, in the Bologna province, a stable focus of canine leishmaniosis has been reported [81], the finding of low prevalence of infection in cats is not surprising. In accordance, the spread of L. infantum infection in cats was also observed in a study on owned cats sampled at a veterinary university hospital in Bologna (P 12.5%) [82]. A slightly lower prevalence (8.6% considering PCR and IFA results combined) of FeL was recently found in Milan (northern Italy), a non-endemic area for this parasitic disease. Although it was not clear if these were imported cases or if Leishmania vectors are present in the area, the study showed a stable FeL situation among the stray cats of the city compared to previously available studies [83].
The finding of Cytauxzoon sp. in two cats confirms the presence of this pathogen in Italy, as already observed both in domestic cats [2,56,57] and in wild cats [18]. As mentioned, C. felis, the first described species of the genus, is distributed in the New World where, in addition to cases in domestic cats, it is traditionally associated with the wild felid Lynx rufus (bobcat), the reservoir in endemic areas [21,22]. A closely related piroplasm was reported in Pallas’s cats (O. manul) from Mongolia and described as a new species, C. manul, on the basis of a significant sequence divergence [55,66]. In Europe, cytauxzoonosis by C. felis has not been described; however, in the past decade, infections with a genetically distinct species described as Cytauxzoon sp. have been increasingly reported [28] in several European countries, both in domestic cat [26,27,28,29,30,56,57] and in wild felids, including the Iberian lynx (L. pardinus), the European lynx (Lynx lynx), and the European wild cat (Felis silvestris silvestris) [18,52,53,54,84,85]). The sequences described from Europe as Cytauxzoon sp. are closely related and may belong to the same species [28]. On the contrary, isolates of C. felis from the United States of America (USA) and from South America cluster separately from the European ones and from each other (Figure 1). The negligible differences between the 18S rDNA gene from European wild and domestic felids and the available sequences of C. manul suggest their conspecificity [26]. However, different genes with higher variability than 18S rRNA, such as the internal transcribed spacer1 (ITS1) and ITS2 [86] or the III subunit of the cytochrome oxidase [87], are needed to further clarify the taxonomy of the species of Cytauxzoon described until now [56]. Thus, life cycle and genetic markers need to be fully understood before referring the European Cytauxzoon isolates to C. manul [53].
Clinical cytauxzoonosis in domestic cats has been recently described in Germany, Switzerland, France, and Portugal. In Italy, following the detection of three clinical cases in cats from Trieste (northeastern Italy), an epidemiological study was carried out in colony (n = 63) and owned (n = 52) cats from the same city, finding Cytauxzoon sp. in 23% of the examined cats. A subsequent report of two other clinical cases from the same authors confirmed the presence of the pathogen in northeastern Italy, as well as showed its presence in central Italy [57]. On the contrary, this protozoan ABP was not detected in cats in other Italian surveys [5,7,70]. In the Italian cases, infection was mainly subclinical, as clinical disease was observed only in seven cats [56]. Thus, it has been suggested that Cytauxzoon sp. in Europe is less virulent than C. felis and that the disease could develop preferentially in the case of concurrent disease or immunodeficiency [28,56]. In general, such infections are likely to be underdiagnosed, and causes and impacts of feline cytauxzoonosis have not yet been clarified [7]. Furthermore, the epidemiology of the infection in this country is still not fully clear. The only study on wild felids in Italy found a prevalence of 14.3% [18], similar to the value detected in Iberian lynxes from Spain (15%) [54].
As for the arthropod host, ticks known to be able to transmit C. felis infection (mainly A. americanum and Dermacentor varibilis) are not described in Italy; thus, it is hypothesized that other Ixodid ticks commonly found in the country, i.e., I. ricinus or Dermacentor sp., might be involved in the transmission of Cytauxzoon sp. [56]. However, as in the present study, the arthropods collected in the focus of cytauxzoonosis in domestic cats of northeastern Italy (one R. sanguineus s. l., nine I. ricinus, and 28 fleas C. felis) were all negative by PCR, even when collected from five Cytauxzoon-positive cats [57]. In general, very low prevalence values for several pathogens (A. phagocytophilum, B. henselae, Hepatozoon sp.) were observed in a large-scale molecular study on ticks from cats in the United Kingdom (UK) [88].
The observed negativity for Babesia sp. agrees with other recent Italian surveys [7,71]. However, in other Italian studies, B. microti DNA was detected in cat blood samples [6], and a seropositivity rate around 20–24% was also observed [69,70]. In addition to the two clinical cases previously mentioned from Germany and Poland [16,17], the presence of piroplasm species primarily associated with dogs, such as B. vogeli and B. canis, has been sporadically described in cats in Europe [89]. Further details on Babesia spp. reported from domestic cats in Europe and worldwide are available in Penzhorn and Oosthuizen [15].
The absence of Hepatozoon spp. DNA agrees with the results of a recent survey on cats from northern, central, and southern Italy [71]. Data on the occurrence of this parasite in cats is minimal. In Italy, a single record of H. felis was described in 2017 in a cat, out of 330 examined, living on the Aeolian Islands [4]. A subsequent epidemiological study involving 196 cats from three provinces of southern Italy (Bari, Lecce, and Matera) found Hepatozoon spp. DNA in 10 cats (5.1%, CI: 3–9%), with the BLAST analysis revealing the presence of three species, H. canis, H. felis, and H. silvestris and, thus, demonstrating for the first time H. silvestris infection in a domestic cat [2]. This parasite was described as a novel species in European wild cats from Bosnia and Herzegovina shortly before [90] and subsequently reported as responsible for a fatal infection in a domestic cat from Switzerland [32]. The presence of H. felis in cat blood samples has been found, with variable prevalence values, in several European countries, including France (1.7% [52]), Spain (1.6% [27]; 16% [91]), and Portugal (15.6% [89]). Recently, it was described as the cause of a clinical case in Switzerland [92].
5. Conclusions
The results of the present study show a widespread presence of ABPs, suggesting that stray cats may represent a potential health threat to companion animals and people and the need for improved management. While these diseases in privately owned cats can be prevented and managed through standard veterinary care, appropriate dewormers, and effective ectoparasiticides, investigating free-roaming, stray, or feral cats may be particularly interesting as they live outdoors, have constant exposure to ticks and fleas, and prey on wildlife that may harbor pathogens. Additionally, stray cats are often neither monitored nor treated for vector-borne pathogens. Considering the obtained results, it would be worthy to conduct further epidemiological surveys investigating other ABPs, responsible for diseases such as rickettsiosis or borreliosis. Knowledge of pathogens in feline populations is helpful for veterinary clinicians in the prevention and control of such agents. Moreover, data about the prevalence of ABPs in feline populations can aid physicians in the diagnosis and control of these zoonotic diseases. Therefore, accurate information on the prevalence of feline pathogens may also be relevant from a One Health perspective.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.V.E. and F.M. (Francesca Mancianti); methodology, V.V.E. and F.M. (Francesca Mancianti); software, L.G.; validation, V.V.E. and F.M. (Francesca Mancianti); investigation, L.G., I.A., S.N., F.M. (Federica Marra), and V.V.E.; resources, V.V.E. and F.M. (Federica Marra).; data curation, L.G., I.A., S.N., F.M. (Federica Marra), and V.V.E.; writing—original draft preparation, L.G., S.N., I.A., and F.M. (Federica Marra); writing—review and editing, V.V.E. and F.M. (Francesca Mancianti). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Fabrizia Veronesi, Department of Veterinary Medicine, University of Perugia, for kindly providing a positive control for Cytauxzoon sp.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gerhold, R.W.; Jessup, D.A. Zoonotic diseases associated with free-roaming cats. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannelli, A.; Latrofa, M.S.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Hodžić, A.; Greco, G.; Attanasi, A.; Annoscia, G.; Otranto, D.; Baneth, G. Three different Hepatozoon species in domestic cats from southern Italy. Tick Tick Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancianti, F.; Nardoni, S.; Mugnaini, L.; Zambernardi, L.; Guerrini, A.; Gazzola, V.; Papini, R.A. A retrospective molecular study of select intestinal protozoa in healthy pet cats from Italy. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2015, 17, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otranto, D.; Napoli, E.; Latrofa, M.S.; Annoscia, G.; Tarallo, V.D.; Greco, G.; Lorusso, L.; Gulotta, L.; Falsone, L.; Solari Basano, F.; et al. Feline and canine leishmaniosis and other vector-borne diseases in the Aeolian Islands: Pathogen and vector circulation in a confined environment. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 236, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spada, E.; Proverbio, D.; Galluzzo, P.; Della Pepa, A.; Perego, R.; Bagnagatti De Giorgi, G.; Ferro, E. Molecular study on selected vector-borne infections in urban stray colony cats in northern Italy. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2014, 16, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, E.; Proverbio, D.; Galluzzo, P.; Perego, R.; Bagnagatti De Giorgi, G.; Roggero, N.; Caracappa, S. Frequency of piroplasms Babesia microti and Cytauxzoon felis in stray cats from northern Italy. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 943754. [Google Scholar]
- Morganti, G.; Veronesi, F.; Stefanetti, V.; Di Muccio, T.; Fiorentino, E.; Diaferia, M.; Santoro, A.; Passamonti, F.; Gramiccia, M. Emerging feline vector-borne pathogens in Italy. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otranto, D.; Dantas-Torres, F. Canine and feline vector-borne diseases in Italy: Current situation and perspectives. Parasites Vectors 2010, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, R.G.; Krämer, F. A review on the occurrence of companion vector-borne diseases in pet animals in Latin America. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabar, M.D.; Movilla, R.; Serrano, L.; Altet, L.; Francino, O.; Roura, X. PCR evaluation of selected vector-borne pathogens in dogs with pericardial effusion. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 59, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beugnet, F.; Marié, J.L. Emerging arthropod-borne diseases of companion animals in Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 163, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakou, A.; Di Cesare, A.; Accettura, P.M.; Barros, L.; Iorio, R.; Paoletti, B.; Frangipane di Regalbono, A.; Halos, L.; Beugnet, F.; Traversa, D. Intestinal parasites and vector-borne pathogens in stray and free-roaming cats living in continental and insular Greece. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, A.; Abramo, F.; Barsotti, P.; Leva, S.; Gramiccia, M.; Ludovisi, A.; Mancianti, F. Feline leishmaniosis due to Leishmania infantum in Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 106, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroli, M.; Pennisi, M.G.; Di Muccio, T.; Khoury, C.; Gradoni, L.; Gramiccia, M. Infection of sandflies by a cat naturally infected with Leishmania infantum. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 145, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzhorn, B.L.; Oosthuizen, M.C. Babesia species of domestic cats: Molecular characterization has opened Pandora’s box. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaszek, L.; Winiarczyk, S.; Lukaszewska, J.; Heile, C. Feline babesiosis. J. Small Anim. Prac. 2010, 55, 624–634. [Google Scholar]
- Moik, K.; Gothe, R. Babesia infections of the felids: A case description in a cat in Germany. Vet. Prac. 1997, 25, 532–535. [Google Scholar]
- Veronesi, F.; Ravagnan, S.; Cerquetella, M.; Carli, E.; Olivieri, E.; Santoro, A.; Pesaro, S.; Berardi, S.; Rossi, G.; Ragni, B.; et al. First detection of Cytauxzoon spp. infection in European wildcats (Felis silvestris silvestris) of Italy. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2016, 7, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrill, M.K.; Cohn, L.A. Cytauxzoonosis: Diagnosis and treatment of an emerging disease. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2015, 17, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, M.R.; Herrera, H.M.; de Jesus Fernandes, S.; de Sousa, K.C.M.; Goncalves, L.R.; Domingos, I.H.; de Macedo, G.C.; Machado, R.Z. Tick-borne agents in domesticated and stray cats from the city of Campo Grande state of Mato Grosso do Sul, midwestern Brazil. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2015, 6, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shock, B.C.; Murphy, S.M.; Patton, L.L.; Shock, P.M.; Olfenbutte, L.C.; Beringer, J.; Prange, S.; Grove, D.M.; Peek, M.; Butfiloski, J.W.; et al. Distribution and prevalence of Cytauxzoon felis in bobcats (Lynx rufus), the natural reservoir, and other wild felids in thirteen states. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 175, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Li, T.T.; Liu, G.H.; Zhu, X.Q.; Yao, C. Two tales of Cytauxzoon felis infections in domestic cats. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 861–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haber, M.D.; Tucker, M.D.; Marr, H.S.; Levy, J.K.; Burgess, J.; Lappin, M.R.; Birkenheuer, A.J. The detection of Cytauxzoon felis in apparently healthy free-roaming cats in the USA. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 146, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamori, Y.; Slovak, J.E.; Reichard, M.V. Prevalence of Cytauxzoon felis infection in healthy free roaming cats in North-Central Oklahoma and Central Iowa. J. Feline Med. Surg. Open Rep. 2016, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, T.E.; Reichard, M.V.; Cohn, L.A.; Birkenheuer, A.J.; Taylor, J.D.; Meinkoth, J.H. Prevalence of Cytauxzoon felis infection in healthy cats from enzootic areas in Arkansas, Missouri, and Oklahoma. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alho, A.M.; Silva, J.; Fonseca, M.J.; Santos, F.; Nunes, C.; de Carvalho, L.M.; Rodrigues, M.; Cardoso, L. First report of Cytauxzoon sp. infection in a domestic cat from Portugal. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Regañón, D.; Villaescusa, A.; Ayllón, T.; Rodríguez-Franco, F.; Baneth, G.; Calleja-Bueno, L.; García-Sancho, M.; Agulla, B.; Sainz, A. Molecular detection of Hepatozoon and Cytauxzoon sp. in domestic and stray cats from Madrid, Spain. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legroux, J.P.; Halos, L.; René-Martellet, M.; Servonnet, M.; Pingret, J.L.; Bourdoiseau, G.; Baneth, G.; Chabanne, L. First clinical case report of Cytauxzoon sp. infection in a domestic cat in France. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nentwig, A.; Meli, M.L.; Schrack, J.; Reichler, I.M.; Riond, B.; Gloor, C.; Howard, J.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Willi, B. First report of Cytauxzoon sp. infection in domestic cats in Switzerland: Natural and transfusion-transmitted infections. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panait, L.C.; Stock, G.; Globokar, M.; Balzer, J.; Groth, B.; Mihalca, A.D.; Pantchev, N. The first case of feline cytauxzoonosis in Germany: Clinical description and molecular confirmation. Res. Sq. 2020. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneth, G.; Sheiner, A.; Eyal, O.; Hahn, S.; Beaufils, J.P.; Anug, Y.; Talmi-Frank, D. Redescription of Hepatozoon felis (Apicomplexa: Hepatozoidae) based on phylogenetic analysis, tissue and blood form morphology, and possible transplacental transmission. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kegler, K.; Nufer, U.; Alic, A.; Posthaus, H.; Olias, P.; Basso, W. Fatal infection with emerging apicomplexan parasite Hepatozoon silvestris in a domestic cat. Parasites Vectors 2013, 11, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelakis, E.; Billeter, S.A.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Chomel, B.B.; Raoult, D. Potential for tick-borne bartonelloses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guptill, L. Bartonellosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, K.; Brewer, M.; Lappin, M.R. Prevalence of Coxiella burnetii DNA in vaginal and uterine samples from healthy cats of north-central Colorado. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2007, 9, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, C.E. Francisella and Coxiella infections. In Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat, 4th ed.; Greene, C.E., Ed.; Saunders: St Louis, MO, USA, 2012; pp. 476–484. [Google Scholar]
- Beaufils, J.P.; Martin-Granel, J.; Jumelle, P.; Barbault-Jumelle, M. Ehrlichiose probable chez le chat: Etude retrospective sur 21 cas. Prat. Méd. Chir. Anim. Cie. 1999, 34, 587–596. [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs, C.J.; Holland, C.J.; Reif, J.S.; Wheeler, S.; Lappin, R. Feline ehrlichiosis. Comp. Cont. Ed. Pract. Vet. 2000, 22, 307–318. [Google Scholar]
- Mugnaini, L.; Papini, R.; Gorini, G.; Passantino, A.; Merildi, V.; Mancianti, F. Pattern and predictive factors of endoparasitism in cats in Central Italy. Rev. Med. Vet. 2012, 163, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Spada, E.; Canzi, I.; Baggiani, L.; Perego, R.; Vitale, F.; Migliazzo, A.; Proverbio, D. Prevalence of Leishmania infantum and co-infections in stray cats in northern Italy. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 45, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflamme, D.P.; Kealy, R.D.; Schmidt, D.A. Estimation of body fat by body condition score. J. Vet. Int. Med. 1994, 8, 154. [Google Scholar]
- Kolonin, G.V. Fauna of Ixodid Ticks of the World (Acari, Ixodidae). 2009. Available online: http://www.kolonin.org/ (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Ebani, V.V.; Bertelloni, F.; Fratini, F. Occurrence of Bartonella henselae types I and II in Central Italian domestic cats. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebani, V.V.; Bertelloni, F. Serological evidence of exposure to Ehrlichia canis and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Central Italian healthy domestic cats. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, S.; Komiya, T.; Celebi, B.; Aydin, N.; Saito, J.; Toriniwa, H.; Karatepe, B.; Babur, C. Seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii in stray cats in Central Anatolia. Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2008, 32, 483–486. [Google Scholar]
- Mancianti, F.; Meciani, N. Specific serodiagnosis of canine leishmaniasis by indirect immunofluorescence, indirect hemagglutination, and counterimmunoelectrophoresis.is. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1988, 49, 1409. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmans, A.M.C.; Schellekens, J.F.P.; Van Embden, J.D.A.; Schouls, L.M. Predominance of two Bartonella henselae variants among cat scratch disease patients in The Netherlands. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Oliveira, C.; Van der Weide, M.; Jacquiet, P.; JongeJan, F. Detection of Theileria annulata by the PCR in ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) collected from cattle in Mauritania. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 1997, 21, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebani, V.V.; Rocchigiani, G.; Nardoni, S.; Bertelloni, F.; Vasta, V.; Papini, R.A.; Verin, R.; Poli, A.; Mancianti, F. Molecular detection of tick-borne pathogens in wild red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) from Central Italy. Acta Trop. 2017, 172, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchigiani, G.; Ebani, V.V.; Nardoni, S.; Bertelloni, F.; Bascherini, A.; Leoni, A.; Mancianti, F.; Poli, A. Molecular survey on the occurrence of arthropod-borne pathogens in wild brown hares (Lepus europaeus) from Central Italy. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 59, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Criado-Fornelio, A.; Buling, A.; Pingret, J.L.; Etievant, M.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Alongi, A.; Agnone, A.; Torina, A. Hemoprotozoa of domestic animals in France: Prevalence and molecular characterization. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 159, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallusová, M.; Jirsová, D.; Mihalca, A.D.; Gherman, C.M.; D’Amico, G.; Qablan, M.A.; Modrý, D. Cytauxzoon infections in wild felids from Carpathian-Danubian- Pontic space: Further evidence for a different Cytauxzoon species in European felids. J. Parasitol. 2016, 102, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, J.; Naranjo, V.; Rodríguez, A.; de la Lastra, J.M.; Mangold, A.J.; de la Fuente, J. Prevalence of infection and 18S rRNA gene sequences of Cytauxzoon species in Iberian lynx (Lynx pardinus) in Spain. Parasitology 2007, 134, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketz-Riley, C.J.; Reichard, M.V.; Van den Bussche, R.A.; Hoover, J.P.; Meinkoth, J.; Kocan, A.A. An intraerythrocytic small piroplasm in wild-caught Pallas’s cats (Otocolobus manul) from Mongolia. J. Wildl. Dis. 2003, 39, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, E.; Trotta, M.; Chinelli, R.; Drigo, M.; Sinigoi., L.; Tosolini, P.; Furlanello, T.; Millotti, A.; Caldin, M.; Solano-Gallego, L. Cytauxzoon sp. infection in the first endemic focus described in domestic cats in Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 183, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, E.; Trotta, M.; Bianchi, E.; Furlanello, T.; Caldin, M.; Pietrobelli, M.; Solano-Gallego, L. Cytauxzoon sp. infection in two free ranging young cats: Clinicopathological findings, therapy and follow up. Türkiye Parazitol. Derg. 2014, 38, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massung, R.F.; Slater, K.; Owens, J.H.; Nicholson, W.L.; Mather, T.N.; Solberg, V.B.; Olson, J.G. Nested PCR assay for detection of granulocytic ehrlichiae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relman, D.A.; Falkow, S.; Lepp, P.W.; Schmidt, T.M. The causative agent of bacillary angiomatosis is closely related to Bartonella bacilliformis. In Programs and Abstracts of the 31st Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Chicago, Illinois, 29 September–2 October 1991; American Society for Microbiology: Chicago, IL, USA, 1991; Abstract Number 443. [Google Scholar]
- Berri, M.; Rekiki, A.; Boumedine, A.; Rodolakis, A. Simultaneous differential detection of Chlamydophila abortus, Chlamydophila pecorum, and Coxiella burnetii from aborted ruminant’s clinical samples using multiplex PCR. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocan, A.A.; Levesque, G.C.; Whitworth, L.C.; Murphy, G.L.; Ewing, S.A.; Barker, R.W. Naturally occurring Ehrlichia chaffeensis infection in coyotes from Oklahoma. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eys, G.J.J.M.; Schoone, G.J.; Kroon, N.C.; Ebeling, S.B. Sequence analysis of small subunit ribosomal RNA genes and its use for detection and identification of Leishmania parasites. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1992, 51, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, R.; VoJta, L.; MrlJak, V.; Marinculić, A.; Beck, A.; Živičnjak, T.; Cacciò, S.M. Diversity of Babesia and Theileria species in symptomatic and asymptomatic dogs in Croatia. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmeda, A.S.; Armstrong, P.M.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Valladares, B.; Del Castillo, A.; De Armas, F.; Miguelez, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Rodrıguez Rodrıguez, J.A.; Spielman, A.; et al. A subtropical case of human babesiosis. Acta Trop. 1997, 67, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inokuma, H.; Okuda, M.; Ohno, K.; Shimoda, K.; Onishi, T. Analysis of the 18S rRNA gene sequence of a Hepatozoon detected in two Japanese dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 106, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, M.V.; Van Den Bussche, R.A.; Meinkoth, J.H.; Hoover, J.P.; Kocan, A.A. A new species of Cytauxzoon from Pallas’ cats caught in Mongolia and comments on the systematics and taxonomy of piroplasmids. J. Parasitol. 2005, 91, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.G.; Lupo, T.; Malara, D.; Masucci, M.; Migliazzo, A.; Lombardo, G. Serological and molecular prevalence of Leishmania infantum infection in cats from southern Italy. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2012, 14, 656–657. [Google Scholar]
- Pennisi, M.G.; Persichetti, M.F. Feline leishmaniosis: Is the cat a small dog? Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 251, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persichetti, M.F.; Solano-Gallego, L.; Serrano, L.; Altet, L.; Reale, S.; Masucci, M.; Pennisi, M.G. Detection of vector-borne pathogens in cats and their ectoparasites in southern Italy. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persichetti, M.F.; Pennisi, M.G.; Vullo, A.; Masucci, M.; Migliazzo, A.; Solano-Gallego, L. Clinical evaluation of outdoor cats exposed to ectoparasites and associated risk for vector-borne infections in southern Italy. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latrofa, M.S.; Iatta, R.; Toniolo, F.; Furlanello, T.; Ravagnan, S.; Capelli, G.; Schunack, B.; Chomel, B.; Zatelli, A.; Mendoza-Roldan, J.; et al. A molecular survey of vector-borne pathogens and haemoplasmas in owned cats across Italy. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.C.; Norris, J.M.; Mathews, K.O.; Chandra, S.; Šlapeta, J.; Bosward, K.L.; Ward, M.P. New insights on the epidemiology of Coxiella burnetii in pet dogs and cats from New South Wales, Australia. Acta Trop. 2020, 105416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knap, N.; Žele, D.; Biškup, U.G.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Vengušt, G. The prevalence of Coxiella burnetii in ticks and animals in Slovenia. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerburg, B.G.; Reusken, C.B.E.M. The role of wild rodents in spread and transmission of Coxiella burnetii needs further elucidation. Wildl. Res. 2011, 38, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, S.F. Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis in dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. 2010, 40, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomel, B.B.; Kasten, R.W.; Henn, J.B.; Molia, S. Bartonella infection in domestic cats and wild felids. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1078, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchouicha, R.; Durand, B.; Monteil, M.; Chomel, B.B.; Berrich, M.; Arvand, M.; Birtles, R.J.; Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Koehler, J.E.; Maggi, R.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of feline and human Bartonella henselae isolates. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woestyn, S.; Olivé, N.; Bigaignon, G.; Avesani, V.; Delmee, M. Study of genotypes and virB4 secretion gene of Bartonella henselae strains from patients with clinically defined cat scratch disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, M.G.; Cardoso, L.; Baneth, G.; Bourdeau, P.; Koutinas, A.; Miró, G.; Oliva, G.; Solano-Gallego, L. LeishVet update and recommendations on feline leishmaniosis. Parasites Vectors 2015, 4, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzis, M.K.; Leontides, L.; Athanasiou, L.V.; Papadopoulos, E.; Kasabalis, D.; Mylonakis, M.; Rallis, T.; Koutinas, A.F.; Andreadou, M.; Ikonomopoulos, J.; et al. Evaluation of indirect immunofluorescence antibody test and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis of infection by Leishmania infantum in clinically normal and sick cats. Exp. Parasitol. 2014, 147, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollicone, E.; Battelli, G.; Gramiccia, M.; Maroli, M.; Baldellii, R. A stable focus of canine leishmaniosis in the Bologna Province, Italy. Parassitologia 2003, 45, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- Urbani, L.; Tirolo, A.; Salvatore, D.; Tumbarello, M.; Segatore, S.; Battilani, M.; Balboni, A.; Dondi, F. Serological, molecular and clinicopathological findings associated with Leishmania infantum infection in cats in Northern Italy. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2020, 22, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spada, E.; Perego, R.; Vitale, F.; Bruno, F.; Castelli, G.; Tarantola, G.; Baggiani, L.; Magistrelli, S.; Proverbio, D. Feline Leishmania spp. Infection in a non-endemic area of Northern Italy. Animals 2020, 10, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barandika, J.F.; Espí, A.; Oporto, B.; Del Cerro, A.; Barral, M.; Povedano, I.; García-Pérez, A.L.; Hurtado, A. Occurrence and genetic diversity of piroplasms and other apicomplexa in wild carnivores Parasitol. Open 2016, 2, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Hodžić, A.; Alić, A.; Duscher, G.G. High diversity of blood-associated parasites and bacteria in European wild cats in Bosnia and Herzegovina: A molecular study. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, H.M.; Berghaus, R.D.; Latimer, K.S.; Britt, J.O.; Rakich, P.M.; Peterson, D.S. Genetic variability of Cytauxzoon felis from 88 infected domestic cats in Arkansas and Georgia. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2009, 21, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreeg, M.E.; Marr, H.S.; Griffith, E.H.; Tarigo, J.L.; Bird, D.M.; Reichard, M.V.; Cohn, L.A.; Levy, M.G.; Birkenheuer, A.J. PCR amplification of a multi-copy mitochondrial gene (Cox3) improves detection of Cytauxzoon felis infection as compared to a ribosomal gene (18S). Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 225, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duplan, F.; Davies, S.; Filler, S.; Abdullah, S.; Keyte, S.; Newbury, H.; Helps, C.R.; Wall, R.; Tasker, S. Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Bartonella spp., haemoplasma species and Hepatozoon spp. in ticks infesting cats: A large-scale survey. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilhena, H.; Martinez-Díaz, V.L.; Cardoso, L.; Vieira, L.; Altet, L.; Francino, O.; Pastor, J.; Silvestre-Ferreira, A.C. Feline vector-borne pathogens in the north and centre of Portugal. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodžić, A.; Alić, A.; Prašović, S.; Otranto, D.; Baneth, G.; Duscher, G.G. Hepatozoon silvestris sp. nov.: Morphological and molecular characterization of a new species of Hepatozoon (Adeleorina: Hepatozoidae) from the European wild cat (Felis silvestris silvestris). Parasitology 2017, 144, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuño, A.; Castellà, J.; Criado-Fornelio, A.; Buling, A.; Barba-Carretero, J.C. Molecular detection of a Hepatozoon species in stray cats from a feline colony in North-eastern Spain. Vet. J. 2008, 177, 134–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, W.; Görner, D.; Globokar, M.; Keidel, A.; Pantchev, N. First autochthonous case of clinical Hepatozoon felis infection in a domestic cat in Central Europe. Parasitol. Int. 2019, 72, 101945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).