- Article
Integrated Analysis of Testicular Histology, Sperm Quality, and Gene Expression (TGFB2, DMRT1) in Rooster Semen (Gallus gallus domesticus)
- Anastasiya Ivershina,
- Yuliya Silyukova and
- Elena Fedorova
- + 3 authors
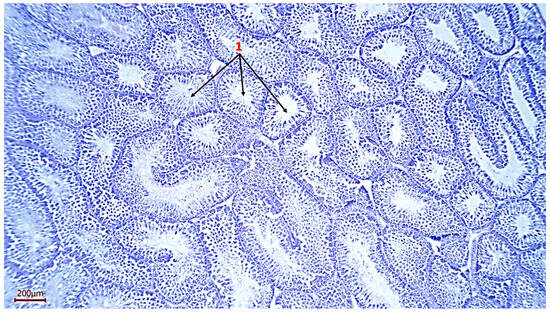
The study of the relationship between testicular morphology and sperm quality is a pressing issue, for which molecular genetic approaches, including quantitative analysis of gene expression, are being implemented. The aim of this study was to identify correlations between the histomorphological structure of the testes, fresh sperm parameters, and the expression level of key spermatogenesis genes—TGFB2 and DMRT1—in roosters. The experiment was conducted on 10 Russian Snow White roosters aged 28–32 weeks. Sperm quality was assessed by volume, sperm concentration, total and progressive motility, and viability; histological analysis of the rooster testes was performed. The relative expression of the TGFB2 and DMRT1 genes in sperm was analyzed. Multiple correlation analysis of the data was conducted. A positive correlation was found between ejaculate volume and the number of spermatogonia (p = +0.651), a negative correlation between ejaculate volume and the number of second-order spermatocytes (p = −0.704), a negative correlation between the total cross-sectional area of the seminiferous tubules of the testes and sperm viability (p = −0.782), a negative correlation between the number of seminiferous tubules and the average diameter of their cross-section (p = −0.685), and a positive correlation between total and progressive sperm motility (p = +0.794). Analysis of TGFB2 and DMRT1 gene expression in sperm demonstrated a certain relationship between molecular genetic mechanisms and histomorphometric parameters. The expression level of the DMRT1 gene, which plays a key role in sex determination in birds during embryogenesis, had a number of negative correlations with such parameters as testicle weight (r = −0.782), total/progressive sperm motility (r = −0.552; r = −0.612), and viability (r = −0.552). Expression of the TGFB2 gene had no significant relationship with the studied parameters, but correlation analysis revealed a moderate positive relationship (r = +0.321) with DMRT1 gene expression. The data obtained indicate the expediency of integrating morphometric, cellular, and molecular analysis for an objective assessment of rooster reproductive function.
12 January 2026