Helminth Parasites among Rodents in the Middle East Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Search of Relevant Articles
2.3. Data Extraction and Summarizing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
3.2. Rodent Cestodes in the Middle East Countries
3.3. Rodent Nematodes in the Middle East Countries
3.4. Rodent Trematodes in the Middle East Countries
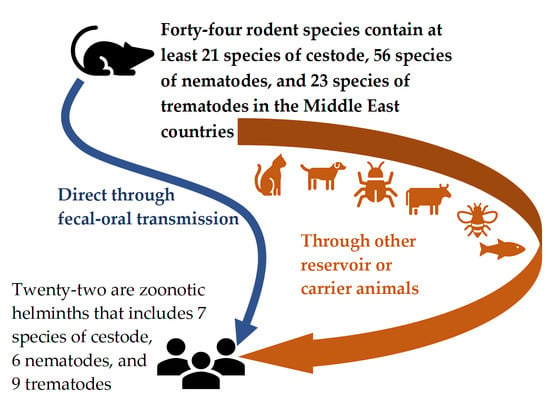
3.5. Zoonotic Importance of the Rodent Helminths in the Middle East Countries
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macpherson, C.N.L.; Craig, P.S. Parasitic Helminths and Zoonoses in Africa; Springer: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi, F. Helminth Infections and Their Impact on Global Public Health; Springer: Wien, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Torgerson, P.R.; Macpherson, C.N. The socioeconomic burden of parasitic zoonoses: Global trends. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 182, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiee, M.H.; Mahmoudi, A.; Siahsarvie, R.; Krystufek, B.; Mostafavi, E. Rodent-borne diseases and their public health importance in Iran. PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. DPDx A-Z Index. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/az.html (accessed on 5 September 2020).
- Dhaliwal, B.B.S.; Juyal, P.D. Parasitic Zoonoses; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2013; pp. 1–135. [Google Scholar]
- Meerburg, B.G.; Singleton, G.R.; Kijlstra, A. Rodent-borne diseases and their risks for public health. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 35, 221–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Population Review. The Middle East Population. Available online: http://worldpopulationreview.com/continents/the-middle-east-population/ (accessed on 21 November 2019).
- Dabrowski, M.; Wulf, L. Economic Development, Trade and Investment in the Eastern and Southern Mediterranean Region. SSRN Electron. J. 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The World Bank. GDP Growth; All Countries and Economies. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.KD.ZG (accessed on 21 November 2019).
- The World Bank. Palestine’s Economic Update—October 2019. Available online: https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/westbankandgaza/publication/economic-update-october-2019 (accessed on 21 November 2019).
- Buliva, E.; Elhakim, M.; Tran Minh, N.N.; Elkholy, A.; Mala, P.; Abubakar, A.; Malik, S.M.M.R. Emerging and Reemerging Diseases in the World Health Organization (WHO) Eastern Mediterranean Region-Progress, Challenges, and WHO Initiatives. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, F. Root causes of violent conflict in developing countries. BMJ 2002, 324, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannazadeh Baghi, H.; Alinezhad, F.; Kuzmin, I.; Rupprecht, C.E. A Perspective on Rabies in the Middle East-Beyond Neglect. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashemi Shahraki, A.; Carniel, E.; Mostafavi, E. Plague in Iran: Its history and current status. Epidemiol. Health 2016, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Neglected Tropical Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/diseases/en/ (accessed on 12 September 2020).
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd el-Wahed, M.M.; Salem, G.H.; el-Assaly, T.M. The role of wild rats as a reservoir of some internal parasites in Qalyobia governorate. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 495–503. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Gaber, R.; Abdel-Ghaffar, F.; Al Quraishy, S.; Morsy, K.; Saleh, R.; Mehlhorn, H. Morphological Re-Description and 18 S rDNA Sequence Confirmation of the Pinworm Aspiculuris tetraptera (Nematoda, Heteroxynematidae) Infecting the Laboratory Mice Mus musculus. J. Nematol. 2018, 50, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Gaber, R. Syphacia obvelata (Nematode, Oxyuridae) infecting laboratory mice Mus musculus (Rodentia, Muridae): Phylogeny and host-parasite relationship. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, F.A.; Galal, A.A.; Ali, M.K. The Role of Rodents as a Reservoir of Zoonotic Intestinal Parasites at Sohag Governorate, Egypt. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 1994, 30, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Zinadah, N.Y.; Fouad, M.A. Anti-Fasciola antibodies among rodents and sheep in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abu-Madi, M.A.; Behnke, J.M.; Mikhail, M.; Lewis, J.W.; Al-Kaabi, M.L. Parasite populations in the brown rat Rattus norvegicus from Doha, Qatar between years: The effect of host age, sex and density. J. Helminthol. 2005, 79, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Madi, M.A.; Lewis, J.W.; Mikhail, M.; El-Nagger, M.E.; Behnke, J.M. Monospecific helminth and arthropod infections in an urban population of brown rats from Doha, Qatar. J. Helminthol. 2001, 75, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hindi, A.I.; Abu-Haddaf, E. Gastrointestinal parasites and ectoparasites biodiversity of Rattus rattus trapped from Khan Younis and Jabalia in Gaza strip, Palestine. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allymehr, M.; Tavassoli, M.; Manoochehri, M.H.; Ardavan, D. Ectoparasites and Gastrointestinal Helminths of House Mice (Mus musculus) from Poultry Houses in Northwest Iran. Comp. Parasitol. 2012, 79, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Quraishy, S.; Gewik, M.M.; Abdel-Baki, A.A. The intestinal cestode Hymenolepis diminuta as a lead sink for its rat host in the industrial areas of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Qureishy, S. Lead concentrations in some organs of the rat Meriones libycus and its parasite Hymenolepis diminuta from Riyadh City, KSA. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 351–358. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniou, M.; Psaroulaki, A.; Toumazos, P.; Mazeris, A.; Ioannou, I.; Papaprodromou, M.; Georgiou, K.; Hristofi, N.; Patsias, A.; Loucaides, F.; et al. Rats as Indicators of the Presence and Dispersal of Pathogens in Cyprus: Ectoparasites, Parasitic Helminths, Enteric Bacteria, and Encephalomyocarditis Virus. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2010, 10, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzamani, K.; Salehi, M.; Mobedi, I.; Adinezade, A.; Hasanpour, H.; Alavinia, M.; Darvish, J.; Shirzadi, M.R.; Mohammadi, Z. Intestinal Helminths in Different Species of Rodents in North Khorasan Province, Northeast of Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2017, 12, 267–273. [Google Scholar]
- Ashour, A.A.; Lewis, J.W. Gongylonema aegypti n. sp. (Nematoda: Thelaziidae) from Egyptian rodents. Syst. Parasitol. 1986, 8, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcioglu, H.; Guven, E.; Balkaya, I.; Kirman, R.; Bia, M.M.; Gulbeyen, H.; Kurt, A.; Yaya, S.; Demirtas, S. First detection of Echinococcus multilocularis in rodent intermediate hosts in Turkey. Parasitology 2017, 144, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, K.M.; Abd El-Hady, E.A.; El-Abd, N. Survey of Natural Infection with Echinostoma liei in Aquatic Snails and Wild Rodents in Egypt. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest. Control. 2015, 25, 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Azzam, K.M.; El-Abd, N.M.; Abd El-Hady, E.A. Survey of endoparasites of different rodent species in Egypt. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest. Control. 2016, 26, 815–820. [Google Scholar]
- Behnke, J.M.; Barnard, C.J.; Mason, N.; Harris, P.D.; Sherif, N.E.; Zalat, S.; Gilbert, F.S. Intestinal helminths of spiny mice (Acomys cahirinus dimidiatus) from St Katherine’s Protectorate in the Sinai, Egypt. J. Helminthol. 2000, 74, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behnke, J.M.; Harris, P.D.; Bajer, A.; Barnard, C.J.; Sherif, N.; Cliffe, L.; Hurst, J.; Lamb, M.; Rhodes, A.; James, M.; et al. Variation in the helminth community structure in spiny mice (Acomys dimidiatus) from four montane wadis in the St Katherine region of the Sinai Peninsula in Egypt. Parasitology 2004, 129, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiromvand, M.; Akhlaghi, L.; Fattahi Massom, S.H.; Meamar, A.R.; Darvish, J.; Razmjou, E. Molecular Identification of Echinococcus multilocularis Infection in Small Mammals from Northeast, Iran. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borji, H.; Khoshnegah, J.; Razmi, G.; Amini, H.; Shariatzadeh, M. A survey on intestinal parasites of golden hamster (Mesocricetus auratus) in the northeast of Iran. J. Parasit. Dis. 2014, 38, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Celebi, B.; Taylan Ozkan, A.; Babur, C. Capillaria Hhepatica in mouse (Apodemus flavicollis) from Giresun Province of Turkey. Turk. Parazitol. Derg. 2014, 38, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Sharifi, Y.; Nematollahi, A. Assessment of gastrointestinal helminths among house mice (Mus musculus) caught in the north-west of Iran, with a special view on zoonotic aspects. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 25, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gindy, M.S.; Morsy, T.A.; Bebars, M.A.; Sarwat, M.A.; Arafa, M.A.; Salama, M.M. Rodents as reservoir of zoonotic intestinal helminths in Suez Canal Zone with the possible immunological changes. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1987, 17, 259–273. [Google Scholar]
- El Kady, G.A.; Gheneam, Y.M.; Bahgat, I.M. Zoonotic helminthes of commensal rodents in Talkha Center, Dakahlia Governorate. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 863–872. [Google Scholar]
- El Shazly, A.M.; Morsy, T.A.; el Kady, G.A.; Ragheb, D.A.; Handousa, A.E.; Ahmed, M.M.; Younis, T.A.; Habib, K.S. The helminthic parasites of rodents in Dakahlia Governorate, with reference to their Egyptian helminth fauna. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1994, 24, 413–428. [Google Scholar]
- Elshazly, A.M.; Awad, S.I.; Azab, M.S.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Abdel-Gawad, A.G.; Khalil, H.H.; Morsy, T.A. Helminthes of synanthropic rodents (Rodentia: Muridae) from Dakahlia and Menoufia, Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Shazly, A.M.; Romia, S.A.; el Ganayni, G.A.; Abou-Zakham, A.A.; Sabry, A.H.; Morsy, T.A. Antibodies against some zoonotic parasites in commensal rodents trapped from Dakahlia Governorate, Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1991, 21, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fair, J.M.; Schmidt, G.D.; Wertheim, G. New species of Andrya and Paranoplocephala (Cestoidea: Anoplocephalidae) from voles and mole-rats in Israel and Syria. J. Parasitol. 1990, 76, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasihi Harandi, M.; Madjdzadeh, S.M.; Ahmadinejad, M. Helminth parasites of small mammals in Kerman province, southeastern Iran. J. Parasit. Dis. 2016, 40, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garedaghi, Y.; Afshin Khaki, A. Prevalence of Gastrointestinal and Blood Parasites of Rodents in Tabriz, Iran, with Emphasis on Parasitic Zoonoses. Crescent J. Med. Biol. Sci. 2014, 1, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gholipoury, M.; Rezai, H.R.; Namroodi, S.; Arab Khazaeli, F. Zoonotic and Non-zoonotic Parasites of Wild Rodents in Turkman Sahra, Northeastern Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2016, 11, 350–357. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, Z. Helminths of mammals and birds of israel i. helminths of acomys spp. (Rodentia, Murinae). Isr. J. Ecol. Evol. 1969, 18, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurler, A.T.; Beyhan, Y.E.; Bolukbas, C.S.; Acici, M.; Umur, S. Gastro-intestinal helminths of wild rats (brown rat-Rattus norvegicus, Berkenhout 1769) in Samsun, Turkey. Ank. Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2011, 58, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridy, F.M.; Morsy, T.A.; Ibrahim, B.B.; Abdel Gawad, A.G.; Mazyad, S.A. Rattus rattus: A new host for fascioliasis. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 647–648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hasson, R.H. Zoonotic &Nonzoonotic Endoparasites of Rodents from Some Districts in Baghdad. Diyala J. Pure Sci. 2010, 6, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.; El-Azazy, O.M.E. Coelomotrema aegyptiaca sp, nov., an unusual prosthogonimid trematode from Rattus norvegicus (berkenhout) in Egypt. J. Nat. Hist. 1986, 20, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamranrashani, B.; Kia, E.; Mobedi, I.; Mohebali, M.; Zarei, Z.; Mowlavi, G.; Hajjaran, H.; Abai, M.; Sharifdini, M.; Kakooei, Z.; et al. Helminth Parasites of Rhombomys opimus from Golestan Province, Northeast Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2013, 8, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Khajeh, A.; Mohammadi, Z.; Darvish, J.; Razmi, G.R.; Ghorbani, F.; Mohammadi, A.; Mobedi, I.; Shahrokhi, A.R. A survey on endoparasites in wild rodents of the Jaz Murian depression and adjacent areas, southeast of Iran. J. Parasit. Dis. 2018, 42, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, L.F.; Hassounah, O.; Behbehani, K. Helminth parasites of rodents in Kuwait with the description of a new species Abbreviata kuwaitensis (Nematoda: Physalopteridae). Syst. Parasitol. 1979, 1, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, E.B.; Homayouni, M.M.; Farahnak, A.; Mohebai, M.; Shojai, S. Study of Endoparasites of Rodents and their Zoonotic Importance In Ahvaz, South West Iran. Iran. J. Public Health 2001, 30, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Kia, E.; Shahryary-Rad, E.; Mohebali, M.; Mahmoudi, M.; Mobedi, I.; Zahabiun, F.; Zarei, Z.; Miahipoor, A.; Mowlavi, G.; Akhavan, A.; et al. Endoparasites of rodents and their zoonotic importance in germi, dashte-mogan, ardabil province, Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2010, 5, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Meshkekar, M.; Sadraei, J.; Mahmoodzadeh, A.; Mobedi, I. Helminth Infections in Rattus ratus and Rattus norvigicus in Tehran, Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2014, 9, 548–552. [Google Scholar]
- Metwally, D.M.; Al-Enezy, H.A.; Al-Turaiki, I.M.; El-Khadragy, M.F.; Yehia, H.M.; Al-Otaibi, T.T. Gene-based molecular characterization of cox1 and pnad5 in Hymenolepis nana isolated from naturally infected mice and rats in Saudi Arabia. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikhail, M.W.; Metwally, A.M.; Allam, K.A.; Mohamed, A.S. Rodents as reservoir host of intestinal helminthes in different Egyptian agroecosystems. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 633–640. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalali, H.; Kia, E.B.; Kamranrashani, B.; Hajjaran, H.; Sharifdini, M. Molecular analysis of isolates of the cestode Rodentolepis nana from the great gerbil, Rhombomys opimus. J. Helminthol. 2016, 90, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, N.; Borji, H.; Darvish, J.; Moshaverinia, A.; Mahmoudi, A. Rodents Helminth Parasites in Different Region of Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2018, 13, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Morsy, T.A.; Michael, S.A.; Bassili, W.R.; Saleh, M.S. Studies on rodents and their zoonotic parasites, particularly leishmania, in Ismailiya Governorate, A.R. Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1982, 12, 565–585. [Google Scholar]
- Mowlavi, G.; Mobedi, I.; Abedkhojasteh, H.; Sadjjadi, S.M.; Shahbazi, F.; Massoud, J. Plagiorchis muris (Tanabe, 1922) in Rattus norvegicus in Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2013, 8, 486–490. [Google Scholar]
- Nateghpour, M.; Motevalli-Haghi, A.; Akbarzadeh, K.; Akhavan, A.A.; Mohebali, M.; Mobedi, I.; Farivar, L. Endoparasites of wild rodents in Southeastern Iran. J. Arthropod Borne Dis. 2014, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pakdel, N.; Naem, S.; Rezaei, F.; Chalehchaleh, A.A. A survey on helminthic infection in mice (Mus musculus) and rats (Rattus norvegicus and Rattus rattus) in Kermanshah, Iran. Vet. Res. Forum Int. Q. J. 2013, 4, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjbar, M.J.; Sarkari, B.; Mowlavi, G.R.; Seifollahi, Z.; Moshfe, A.; Abdolahi Khabisi, S.; Mobedi, I. Helminth Infections of Rodents and Their Zoonotic Importance in Boyer-Ahmad District, Southwestern Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2017, 12, 572–579. [Google Scholar]
- Sadighian, A.; Ghadirian, E.; Sadjadpour, E. Two new species of nematodes of lagomorphs and rodents from Iran. J. Helminthol. 1974, 48, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saoud, M.F.; Ramadan, M.M.; Ashour, A.A.; Shahawy, A.A. On the helminth parasites of rodents in the Eastern Delta. I. General survey. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1986, 16, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, M.F.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Zalat, S.M. Gastrointestinal nematode community of spiny mice (Acomys dimidiatus) from St. Katherine, South Sinai, Egypt. J. Parasit. Dis. 2015, 39, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sures, B.; Scheible, T.; Bashtar, A.R.; Taraschewski, H. Lead concentrations in Hymenolepis diminuta adults and Taenia taeniaeformis larvae compared to their rat hosts (Rattus norvegicus) sampled from the city of Cairo, Egypt. Parasitology 2003, 127, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sursal, N.; Gokpinar, S.; Yildiz, K. Prevalence of intestinal parasites in hamsters and rabbits in some pet shops of Turkey. Turk. Parazitol. Derg. 2014, 38, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanas, M.Q.; Shehata, K.K.; Rashed, A.A. Larval occurrence of Hydatigera taeniaeformis Batsch (1786) (Cestoda: Taeniidae) in the liver of wild rodents in Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1993, 23, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed; Wanas, Q.A.; Shehata, K.K.; Rashed, A.A. Studies on the nematode parasites from Egyptian rodents. I. Spirurid nematodes. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1994, 23, 851–863. [Google Scholar]
- Wertheim, G.; Chabaud, A.G. Helminths of birds and mammals of Israel. VIII.—Skrjabinocapillaria rodentium n. sp. (Nematoda Capillariidae) from gerbillid and murid rodents. Ann. De Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1979, 54, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wertheim, G.; Giladi, M. Helminths of birds and mammals of Israel. VII.—Pneumospirura rodentium n. sp. (Pneumospiruridae-Thelazioidea). Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1977, 52, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wertheim, G. Helminths of Birds and Mammals from Israel: III. Helminths from Chromosomal Forms of the Mole-Rat, Spalax ehrenbergi. J. Helminthol. 1971, 45, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, A.; Eslami, A.; Mobedi, I.; Rahbari, S.; Ronaghi, H. Helminth Infections of House Mouse (Mus musulus) and Wood Mouse (Apodemus sylvaticus) from the Suburban Areas of Hamadan City, Western Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2014, 9, 511–518. [Google Scholar]
- Yousif, F.; Ibrahim, A. The first record of Angiostrongylus cantonensis from Egypt. Z. Parasitenkdunde 1978, 56, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, Z.; Mohebali, M.; Heidari, Z.; Davoodi, J.; Shabestari, A.; Haghi, A.M.; Khanaliha, K.; Kia, E.B. Helminth infections of meriones persicus (Persian jird), Mus musculus (house mice) and cricetulus migratorius (grey ham-ster): A cross-sectional study in Meshkin-Shahr district, north-west Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2016, 11, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Nijsten, T.; Stern, R.S. How Epidemiology Has Contributed to a Better Understanding of Skin Disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neta, G.; Brownson, R.C.; Chambers, D.A. Opportunities for Epidemiologists in Implementation Science: A Primer. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 187, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, K.D. Parasitology: Protozoology and Helminthology in Relation to Clinical Medicine: With Two Hundred Fourteen Illustrations; CBS Publishers & Distributors: New Delhi, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gárate, I.; Jimenez, P.; Flores, K.; Espinoza, B. Xenopsylla cheopis record as natural intermediate host of Hymenolepis diminuta in Lima, Peru. Rev. Peru. Biol. 2011, 18, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stĕrba, J.; Barus, V. First record of Strobilocercus fasciolaris (Taenidae-larvae) in man. Folia Parasitol. 1976, 23, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, R.; Esteban, J.G. An update on human echinostomiasis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, K. Transmission Ecology of Gastrointestinal Trematodes of Small Mammals, Malham Tarn, North Yorkshire, UK. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Salford, Salford, UK, July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Loftis, A.D.; Reeves, W.K.; Szumlas, D.E.; Abbassy, M.M.; Helmy, I.M.; Moriarity, J.R.; Dasch, G.A. Surveillance of Egyptian fleas for agents of public health significance: Anaplasma, bartonella, coxiella, ehrlichia, rickettsia, and Yersinia pestis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trevisanato, S.I. The ‘Hittite plague’, an epidemic of tularemia and the first record of biological warfare. Med. Hypotheses 2007, 69, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bishara, J.; Hershkovitz, D.; Yagupsky, P.; Lazarovitch, T.; Boldur, I.; Kra-Oz, T.; Pitlik, S. Murine typhus among Arabs and Jews in Israel 1991–2001. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 19, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, T.; Michaeli, D. Murine typhus and spotted fever in Israel in the seventies. Infection 1977, 5, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaghani, R. The economic and health impact of rodent in urban zone and harbours and their control methods. Ann. Mil. Health Sci. Res. 2007, 4, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Morand, S.; Bordes, F. Parasite diversity of disease-bearing rodents of Southeast Asia: Habitat determinants and effects on sexual size dimorphism and life-traits. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radostits, O.M.; Done, S.H. Veterinary Medicine: A Textbook of the Diseases of Cattle, Sheep, Pigs, Goats, and Horses; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rodan, I.; Sparkes, A.H. Chapter 8-Preventive Health Care for Cats. In The Cat, Little, S.E., Ed.; W.B. Saunders: Saint Louis, MO, USA, 2012; pp. 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorny, P.; Praet, N.; Deckers, N.; Gabriel, S. Emerging food-borne parasites. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 163, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, H. Review of zoonotic parasites in medical and veterinary fields in the Republic of Korea. Korean J. Parasitol. 2009, 47, S133–S141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, O.M. Pathogenic micro-organisms and helminths in sewage products, Arabian Gulf, country of Bahrain. Am. J. Public Health 1988, 78, 314–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, S. Infectious Diseases of Cyprus; Incorporated Gideon e-book series; Global Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology Network Informatics: Winconsin, WI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Lahham, A.B.; Abu-Saud, M.; Shehabi, A.A. Prevalence of Salmonella, Shigella and intestinal parasites in food handlers in Irbid, Jordan. J. Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1990, 8, 160–162. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, P.K.; Khandekar, R. Intestinal parasitic infections among school children of the Dhahira Region of Oman. Saudi Med. J. 2006, 27, 627–632. [Google Scholar]
- Astal, Z. Epidemiological survey of the prevalence of parasites among children in Khan Younis governorate, Palestine. Parasitol. Res. 2004, 94, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Madi, M.A.; Behnke, J.M.; Boughattas, S.; Al-Thani, A.; Doiphode, S.H.; Deshmukh, A. Helminth infections among long-term-residents and settled immigrants in Qatar in the decade from 2005 to 2014: Temporal trends and varying prevalence among subjects from different regional origins. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alharbi, R.A.; Alwajeeh, T.S.; Assabri, A.M.; Almalki, S.S.R.; Alruwetei, A.; Azazy, A.A. Intestinal parasitoses and schistosome infections among students with special reference to praziquantel efficacy in patients with schistosomosis in Hajjah governorate, Yemen. Ann. Parasitol. 2019, 65, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Shehada, M.N. Prevalence of Toxocara ova in some schools and public grounds in northern and central Jordan. Ann. Trop Med. Parasitol. 1989, 83, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geramizadeh, B.; Baghernezhad, M. Hepatic Alveolar Hydatid Cyst: A Brief Review of Published Cases from Iran in the Last 20 Years. Hepat Mon. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Aboody, M.S.; Omar, M.A.; Alsayeqh, A.F. Epizootiology of zoonotic parasites in Middle East: A comprehensive review. Ann. Parasitol. 2020, 66, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellner, A.; Hellmann, M.A.; Kolianov, V.; Bishara, J. A non-travel related case of Angiostrongylus cantonensis eosinophilic meningomyelitis acquired in Israel. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 370, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavi, G.H.; Massoud, J.; Gutierrez, Y. Human Gongylonema infection in Iran. J. Helminthol. 2006, 80, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzayans, A.; Halim, R. Parasitic infection of Camelus dromedarius from Iran. Bull. Soc. Pathol Exot. Fil. 1980, 73, 442–445. [Google Scholar]
- Moazeni, M.; Khamesipour, F.; Anyona, D.N.; Dida, G.O. Epidemiology of taeniosis, cysticercosis and trichinellosis in Iran: A systematic review. Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenman, A.; Einat, R. A family outbreak of trichinosis acquired in Israel. Harefuah 1992, 122, 702–704, 751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haim, M.; Efrat, M.; Wilson, M.; Schantz, P.M.; Cohen, D.; Shemer, J. An outbreak of Trichinella spiralis infection in southern Lebanon. Epidemiol. Infect. 1997, 119, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, M.; Kaptan, F.; Turker, N.; Korkmaz, M.; El, S.; Ozkaya, D.; Ural, S.; Vardar, I.; Alkan, M.Z.; Coskun, N.A.; et al. Clinical and laboratory aspects of a trichinellosis outbreak in Izmir, Turkey. Parasite 2006, 13, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Shazly, A.M.; Awad, S.E.; Sultan, D.M.; Sadek, G.S.; Khalil, H.H.; Morsy, T.A. Intestinal parasites in Dakahlia governorate, with different techniques in diagnosing protozoa. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanbarzadeh, L.; Saraei, M.; Kia, E.B.; Amini, F.; Sharifdini, M. Clinical and haematological characteristics of human trichostrongyliasis. J. Helminthol. 2019, 93, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, Z.; Giladi, L.; Bashary, A.; Zahavi, H. Prevalence of intestinal parasites among Thais in Israel. Harefuah 1994, 126, 507–509, 563. [Google Scholar]
- Akdemir, C.; Helvaci, R. Evaluation of parasitology laboratory results of a group of people older than 15 years of age in Kutahya. Turk. Parazit. Derg. 2007, 31, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Nooraldeen, K. Contamination of public squares and parks with parasites in Erbil city, Iraq. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2015, 22, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhtar, A. Intestinal parasites in the state of Bahrain. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 1995, 38, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abu-Madi, M.A.; Behnke, J.M.; Ismail, A. Patterns of infection with intestinal parasites in Qatar among food handlers and housemaids from different geographical regions of origin. Acta Trop. 2008, 106, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, O.S.O.; Al-Malki, E.S.; Waly, M.I.; AlAgeel, A.; Lubbad, M.Y. Prevalence of Intestinal Parasitic Infections among Patients of King Fahd Medical City in Riyadh Region, Saudi Arabia: A 5-Year Retrospective Study. J. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yentur Doni, N.; Yildiz Zeyrek, F.; Simsek, Z.; Gurses, G.; Sahin, I. Risk Factors and Relationship Between Intestinal Parasites and the Growth Retardation and Psychomotor Development Delays of Children in Sanliurfa, Turkey. Turk. Parazitol. Derg. 2015, 39, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotez, P.J.; Savioli, L.; Fenwick, A. Neglected tropical diseases of the Middle East and North Africa: Review of their prevalence, distribution, and opportunities for control. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rollinson, D.; Knopp, S.; Levitz, S.; Stothard, J.R.; Tchuem Tchuente, L.A.; Garba, A.; Mohammed, K.A.; Schur, N.; Person, B.; Colley, D.G.; et al. Time to set the agenda for schistosomiasis elimination. Acta Trop. 2013, 128, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornstein, L.; Lederer, G.; Schechter, J.; Greenberg, Z.; Boem, R.; Bilguray, B.; Giladi, L.; Hamburger, J. Persistent Schistosoma mansoni infection in Yemeni immigrants to Israel. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1990, 26, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taha, H.A.; Soliman, M.I.; Banjar, S.A. Intestinal parasitic infections among expatriate workers in Al-Madina Al-Munawarah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Trop Biomed. 2013, 30, 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kiremit, M.C.; Cakir, A.; Arslan, F.; Ormeci, T.; Erkurt, B.; Albayrak, S. The bladder carcinoma secondary to schistosoma mansoni infection: A case report with review of the literature. Int. J. Surg. Case. Rep. 2015, 13, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Mekhlafi, A.M.; Abdul-Ghani, R.; Al-Eryani, S.M.; Saif-Ali, R.; Mahdy, M.A. School-based prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections and associated risk factors in rural communities of Sana’a, Yemen. Acta Trop. 2016, 163, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shazly, A.M.; el-Nahas, H.A.; Soliman, M.; Sultan, D.M.; Abedl Tawab, A.H.; Morsy, T.A. The reflection of control programs of parasitic diseases upon gastrointestinal helminthiasis in Dakahlia Governorate, Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 467–480. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, J.Y.; Seo, B.S.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, S.J.; Sohn, W.M. Human infections by Heterophyes heterophyes and H. dispar imported from Saudi Arabia. Kisaengchunghak Chapchi 1986, 24, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.Y.; Jung, B.K. Foodborne intestinal flukes: A brief review of epidemiology and geographical distribution. Acta Trop. 2019, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gayar, A.K. Studies on some trematode parasites of stray dogs in Egypt with a key to the identification of intestinal trematodes of dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 144, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Azazy, O.M.; Abdou, N.E.; Khalil, A.I.; Al-Batel, M.K.; Majeed, Q.A.; Henedi, A.A.; Tahrani, L.M. Potential Zoonotic Trematodes Recovered in Stray Cats from Kuwait Municipality, Kuwait. Korean J. Parasitol. 2015, 53, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.I.; El-Shahawy, I.S.; Abdelkader, H.S. Studies on some fish parasites of public health importance in the southern area of Saudi Arabia. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2014, 23, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steinmann, P.; Keiser, J.; Bos, R.; Tanner, M.; Utzinger, J. Schistosomiasis and water resources development: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, H.F.; Rizkalla, N.H.; Mehanna, S.; Abaza, S.M.; Winch, P.J. Prevalence and epidemiology of Schistosoma mansoni and S. haematobium infection in two areas of Egypt recently reclaimed from the desert. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 52, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odhiambo, G.O. Water scarcity in the Arabian Peninsula and socio-economic implications. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2479–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bordes, F.; Blasdell, K.; Morand, S. Transmission ecology of rodent-borne diseases: New frontiers. Integr. Zool. 2015, 10, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, R.J.; Enscore, R.E.; Atiku, L.A.; Zielinski-Gutierrez, E.; Mpanga, J.T.; Kajik, E.; Andama, V.; Mungujakisa, C.; Tibo, E.; MacMillan, K.; et al. Evidence that rodent control strategies ought to be improved to enhance food security and reduce the risk of rodent-borne illnesses within subsistence farming villages in the plague-endemic West Nile region, Uganda. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 2013, 59, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.M.; Laco, J. Rodent Control and Public Health: A Description of Local Rodent Control Programs. J. Environ. Health 2015, 78, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, B.; Kahn, L.H.; Monath, T.P.; Woodall, J. ‘ONE HEALTH’ and parasitology. Parasites Vectors 2009, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. One Health Basics. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/onehealth/basics/ (accessed on 2 October 2020).





| Country | Parasite | Pooled Estimates (%) | 95% CI | Heterogeneity Chi-Squared (χ2) | l2% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyprus | Nematode | 0.160 | −0.15–0.47 | 0.00 | 0 | - |
| Cestode | 14.72 | 11.94–17.50 | 0.00 | 0 | - | |
| Egypt | Nematode | 31.81 | 19.83–43.78 | 259.62 | 97.3 | <0.001 |
| Cestode | 27.49 | 23.72–31.26 | 17.18 | 70.9 | <0.001 | |
| Trematode | 15.827 | 6.56–25.1 | 344.74 | 98.5 | <0.001 | |
| Iran | Cestode | 18.21 | 11.59–24.83 | 56.08 | 87.5 | <0.001 |
| Nematode | 33.93 | 16.52–51.35 | 154.53 | 96.8 | <0.001 | |
| Trematode | 0.24 | −0.11–0.59 | 0.19 | 0 | <0.001 | |
| Palestine | Nematode | 24.39 | 11.25–37.54 | 0.00 | 0 | - |
| Cestode | 36.59 | 21.84–51.32 | 0.00 | 0 | - | |
| Qatar | Cestode | 26.64 | 8.89–44.39 | 13.94 | 92.8 | <0.001 |
| Saudi Arabia | Cestode | 57.66 | 34.63–80.70 | 6.74 | 85.6 | <0.001 |
| Trematode | 14.685 | 8.88–20.49 | 0.00 | 0 | - | |
| Turkey | Nematode | 56.24 | 11.40–101.1 | 30.10 | 96.7 | <0.001 |
| Cestode | 12.87 | 5.17–20.57 | 10.34 | 80.6 | <0.001 |
| Parasites | Host | Source of Human Infection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rodent-borne zoonotic cestodes: | |||
| Raillieitina celebensis and R. demerariensis. | DH: rodent; IH: ant and beetle | Ingestion of food contaminated with infected insects | [5,6] |
| Hymenolepis diminuta and H. nana | DH: rodent; IH: H. diminuta: flea and beetle. H. nana does not require IH. | Consumption contaminated food with rodent feces containing parasitic egg | [6,86,87] |
| Mesocestoides sp. | DH: dog and cat; 1st IH: ant and mite, 2nd IH: rodent, bird, amphibian, and reptile | Consumption of undercooked meat of amphibians and reptiles containing infective larva (tetrathyridium) | [5,6] |
| Taenia taeniaeformis | DH: cat; IH: rodent | There is a report that Taenia taeniaformis can infect humans | [88] |
| Echinococcus multilocularis | DH: dog, fox; IH: rat | Ingestion of embryonated eggs | [86] |
| Rodent-borne zoonotic nematodes: | |||
| Angiostrongylus cantonensis | DH: rat and mollusk; IH: snail, prawn, crab, and frog | Ingestion of uncooked IH or vegetables contaminated with infected larvae | [6] |
| Gongylonema pulchrum | DH: ruminant, pig, wild boar, non-human primate, carnivore, and rodent; IH: beetles and cockroaches | Ingestion of IH or drinking of water contaminated with infective larvae | [5,6] |
| Trichinella spp. | Pig, wild boar, and rodent | Ingestion of uncooked muscle with encysted larvae | [6] |
| Trichostrongylus spp. | Herbivorous animal | Consumption of food and water contaminated with animal feces containing infective larvae | [6] |
| Capillaria hepatica | Rat, carnivore, and humans | Consumption of food contaminated with feces containing embryonated eggs | [5] |
| Trichuris trichiura | Humans | Consumption of food contaminated with feces containing Trichuris egg. | [5] |
| Rodent-borne zoonotic trematodes: | |||
| Echinochasmus sp., Echinoparyphium recurvatum, and Echoinostoma sp. | DH: humans, rat, duck 1st IH: snail, 2nd IH: snail, amphibian, bivalve, fish | Ingestion of uncooked fish containing metacercariae | [2,89] |
| Fasciola hepatica | DH: herbivore; IH: snail | Ingestion of metacercariae contaminated vegetable | [6,34] |
| Haplorchis pumilio, Pygidiopsis genata, Stictodora tridactyla, Prosthodendrium spp., and Plagiorchis muris | DH: dog, cat, rat, duck, humans; 1st IH: snail, 2nd IH: fish | Eating uncooked fish harboring viable metacercariae | [88,90] |
| Schistosoma mansoni | DH: Vertebrate animal; IH: snail | Penetrate the DH skin | [6,86] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.M.; Farag, E.; Hassan, M.M.; Bansal, D.; Awaidy, S.A.; Abubakar, A.; Al-Romaihi, H.; Mkhize-Kwitshana, Z. Helminth Parasites among Rodents in the Middle East Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Animals 2020, 10, 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122342
Islam MM, Farag E, Hassan MM, Bansal D, Awaidy SA, Abubakar A, Al-Romaihi H, Mkhize-Kwitshana Z. Helminth Parasites among Rodents in the Middle East Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Animals. 2020; 10(12):2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122342
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Md Mazharul, Elmoubashar Farag, Mohammad Mahmudul Hassan, Devendra Bansal, Salah Al Awaidy, Abdinasir Abubakar, Hamad Al-Romaihi, and Zilungile Mkhize-Kwitshana. 2020. "Helminth Parasites among Rodents in the Middle East Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Animals 10, no. 12: 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122342
APA StyleIslam, M. M., Farag, E., Hassan, M. M., Bansal, D., Awaidy, S. A., Abubakar, A., Al-Romaihi, H., & Mkhize-Kwitshana, Z. (2020). Helminth Parasites among Rodents in the Middle East Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Animals, 10(12), 2342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122342