Characterization of the Rumen Microbiota and Volatile Fatty Acid Profiles of Weaned Goat Kids under Shrub-Grassland Grazing and Indoor Feeding
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Experimental Design and Collection of Rumen Fluid
2.3. Measurement of VFAs and DNA Extraction
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Concentrations of VFAs Among the Three Feeding Systems
3.2. Rumen Microbial Diversity and Similarities Among the Three Feeding Systems
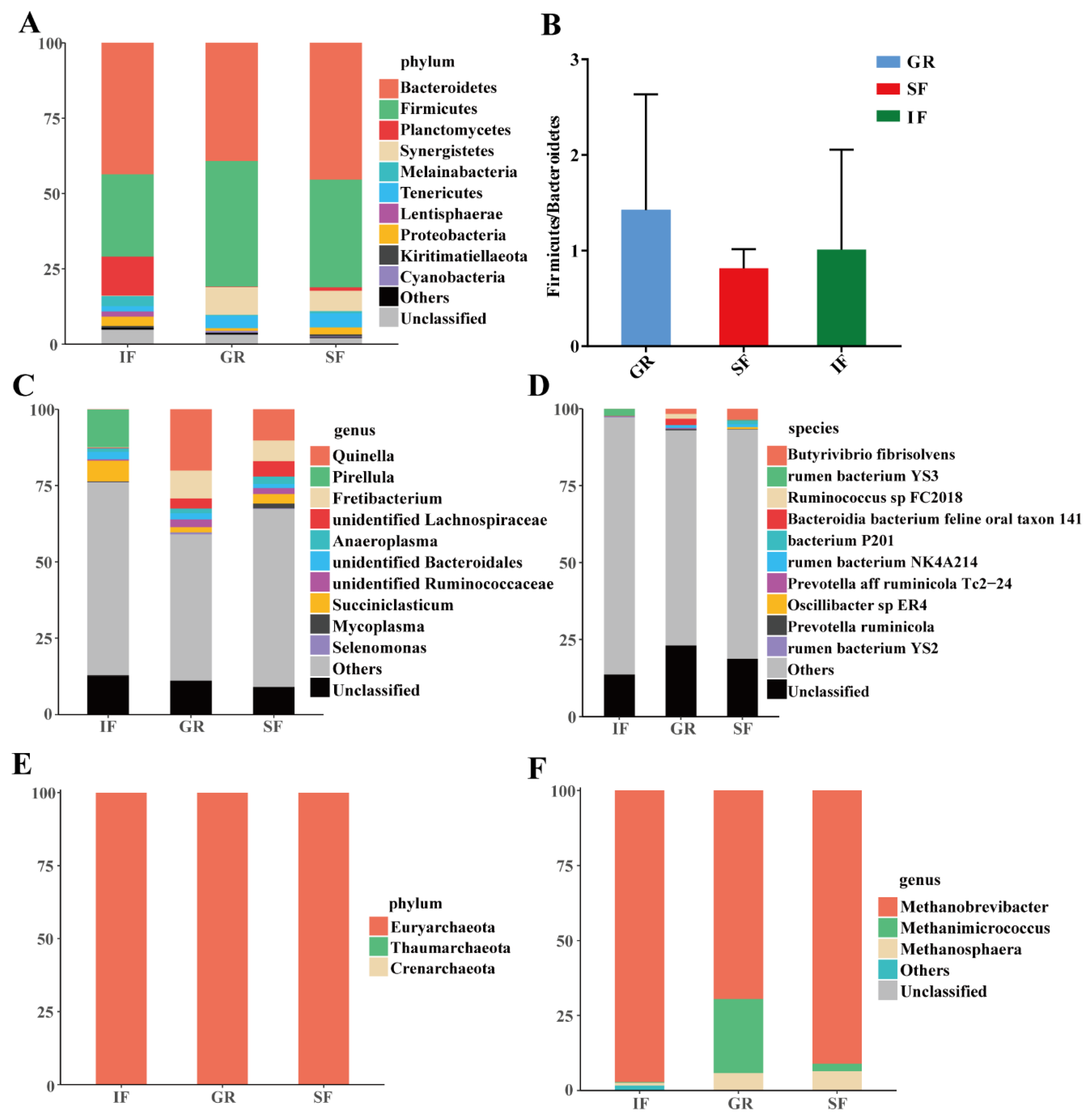
3.3. Rumen Microbial Community Composition Across the Three Feeding Systems
3.4. Effects of the Feeding Systems on Rumen Microbial Compositions Among the Three Feeding Systems
3.5. Spearman Correlations Between Microbial Biomarkers and VFAs in the Rumen Fluid
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russell, J.B.; Rychlik, J.L. Factors that alter rumen microbial ecology. Science 2001, 292, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgavi, D.; Forano, E.; Martin, C.; Newbold, C. Microbial ecosystem and methanogenesis in ruminants. Animal 2010, 4, 1024–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; McAllister, T.A. Rumen Microbes, Enzymes and Feed Digestion-A Review. Asian Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2002, 15, 1659–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Morrison, M.; Yu, Z. Status of the phylogenetic diversity census of ruminal microbiomes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 76, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janssen, P.H.; Kirs, M. Structure of the Archaeal Community of the Rumen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petri, R.M.; Schwaiger, T.; Penner, G.B.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Forster, R.J.; McKinnon, J.J.; McAllister, T.A. Characterization of the Core Rumen Microbiome in Cattle during Transition from Forage to Concentrate as Well as during and after an Acidotic Challenge. PLoS ONE 2014, 8, e83424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henderson, G.; Cox, F.; Ganesh, S.; Jonker, A.; Young, W.; Global Rumen Census, C.; Abecia, L.; Angarita, E.; Aravena, P.; Nora Arenas, G.; et al. Rumen microbial community composition varies with diet and host, but a core microbiome is found across a wide geographical range. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Yang, Y.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Qu, L.; Chen, Y. Rumen Bacterial Diversity of 80 to 110-Day-Old Goats Using 16S rRNA Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, Q.; Kong, F.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Mishra, S.; Li, Y. Exploring the Goat Rumen Microbiome from Seven Days to Two Years. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jami, E.; Israel, A.; Kotser, A.; Mizrahi, I. Exploring the bovine rumen bacterial community from birth to adulthood. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, W.; Liu, J.; Mao, S. Effect of dietary forage sources on rumen microbiota, rumen fermentation and biogenic amines in dairy cows. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Q.; Gao, C.; Gao, Z.; Rahman, A.M.; He, Y.; Cao, B.; Su, H. Temporal Dynamics in Rumen Bacterial Community Composition of Finishing Steers during an Adaptation Period of Three Months. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Menezes, A.B.; Lewis, E.; O’Donovan, M.; O’Neill, B.F.; Clipson, N.; Doyle, E.M. Microbiome analysis of dairy cows fed pasture or total mixed ration diets. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belanche, A.; Kingston-Smith, A.H.; Griffith, G.W.; Newbold, C.J. A Multi-Kingdom Study Reveals the Plasticity of the Rumen Microbiota in Response to a Shift from Non-grazing to Grazing Diets in Sheep. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Fang, L.; Meng, Q.; Li, S.; Chai, S.; Liu, S.; Schonewille, J.T. Assessment of Ruminal Bacterial and Archaeal Community Structure in Yak (Bos grunniens). Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grilli, D.J.; Fliegerová, K.; Kopečný, J.; Lama, S.P.; Egea, V.; Sohaefer, N.; Pereyra, C.; Ruiz, M.S.; Sosa, M.A.; Arenas, G.N.; et al. Analysis of the rumen bacterial diversity of goats during shift from forage to concentrate diet. Anaerobe 2016, 42, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Effect of dietary concentrate to forage ratios on ruminal bacterial and anaerobic fungal populations of cashmere goats. Anaerobe 2019, 59, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.-Y.; Huo, W.-J.; Zhu, W.-Y. Microbiome–metabolome analysis reveals unhealthy alterations in the composition and metabolism of ruminal microbiota with increasing dietary grain in a goat model. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Shen, Z. Antibiotic pretreatment minimizes dietary effects on reconstructure of rumen fluid and mucosal microbiota in goats. MicrobiologyOpen 2018, 7, e00537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunha, I.S.; Barreto, C.C.; Costa, O.Y.A.; Bomfim, M.A.; Castro, A.P.; Kruger, R.H.; Quirino, B.F. Bacteria and Archaea community structure in the rumen microbiome of goats (Capra hircus) from the semiarid region of Brazil. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Version 3.5.3; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 11 March 2019).
- Jiao, J.; Zhou, C.; Guan, L.L.; McSweeney, C.S.; Tang, S.; Wang, M.; Tan, Z. Shifts in Host Mucosal Innate Immune Function Are Associated with Ruminal Microbial Succession in Supplemental Feeding and Grazing Goats at Different Ages. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.C.; Purvis, H.T.; Najar, F.Z.; Sukharnikov, L.O.; Krehbiel, C.R.; Nagaraja, T.G.; Roe, B.A.; DeSilva, U. Rumen Microbial Population Dynamics during Adaptation to a High-Grain Diet. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belanche, A.; de la Fuente, G.; Pinloche, E.; Newbold, C.J.; Balcells, J. Effect of diet and absence of protozoa on the rumen microbial community and on the representativeness of bacterial fractions used in the determination of microbial protein synthesis. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 3924–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Wang, L.; Yan, T.; Wang, Z.; Xue, B.; Peng, Q. Relationship between the structure and composition of rumen microorganisms and the digestibility of neutral detergent fibre in goats. Asian Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jami, E.; Mizrahi, I. Composition and Similarity of Bovine Rumen Microbiota across Individual Animals. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tapio, I.; Snelling, T.J.; Strozzi, F.; Wallace, R.J. The ruminal microbiome associated with methane emissions from ruminant livestock. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Indugu, N.; Vecchiarelli, B.; Pitta, D.W. Associative patterns among anaerobic fungi, methanogenic archaea, and bacterial communities in response to changes in diet and age in the rumen of dairy cows. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reis, M.P.; Dias, M.F.; Costa, P.S.; Ávila, M.P.; Leite, L.R.; de Araújo, F.M.G.; Salim, A.C.M.; Bucciarelli-Rodriguez, M.; Oliveira, G.; Chartone-Souza, E.; et al. Metagenomic signatures of a tropical mining-impacted stream reveal complex microbial and metabolic networks. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharenko, A.S.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Morozov, I.V.; Shubenkova, O.V.; Morozov, A.A.; Ivanov, V.G.; Pimenov, N.V.; Krasnopeev, A.Y.; Zemskaya, T.I. Bacterial Communities in Areas of Oil and Methane Seeps in Pelagic of Lake Baikal. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, C.J.; Banfield, J.F. Major New Microbial Groups Expand Diversity and Alter our Understanding of the Tree of Life. Cell 2018, 172, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sieber, C.M.K.; Paul, B.G.; Castelle, C.J.; Hu, P.; Tringe, S.G.; Valentine, D.L.; Andersen, G.L.; Banfield, J.F. Unusual metabolism and hypervariation in the genome of a Gracilibacteria (BD1-5) from an oil degrading community. bioRxiv 2019, 595074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, R.; Schnürer, A.; Arthurson, V.; Bertilsson, J. Methanogenic Population and CH4 Production in Swedish Dairy Cows Fed Different Levels of Forage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6172–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hook, S.E.; Steele, M.A.; Northwood, K.S.; Wright, A.-D.G.; McBride, B.W. Impact of High-Concentrate Feeding and Low Ruminal pH on Methanogens and Protozoa in the Rumen of Dairy Cows. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 62, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cersosimo, L.M.; Lachance, H.; St-Pierre, B.; van Hoven, W.; Wright, A.-D.G. Examination of the Rumen Bacteria and Methanogenic Archaea of Wild Impalas (Aepyceros melampus melampus) from Pongola, South Africa. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allison, M.J.; Mayberry, W.R.; McSweeney, C.S.; Stahl, D.A. Synergistes jonesii, gen. nov., sp.nov: A Rumen Bacterium That Degrades Toxic Pyridinediols. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1992, 15, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumas-Bilak, E.; Roudière, L.; Marchandin, H. Description of ‘Synergistetes’ phyl. nov. and emended description of the phylum ‘Deferribacteres’ and of the family Syntrophomonadaceae, phylum ‘Firmicutes’. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, T.; Yoshiguchi, K.; Ariesyady, H.D.; Okabe, S. Identification of a novel acetate-utilizing bacterium belonging to Synergistes group 4 in anaerobic digester sludge. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, S.R.; Pop, M.; DeBoy, R.T.; Eckburg, P.B.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I.; Relman, D.A.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Nelson, K.E. Metagenomic Analysis of the Human Distal Gut Microbiome. Science 2006, 312, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maldonado-Contreras, A.; Goldfarb, K.C.; Godoy-Vitorino, F.; Karaoz, U.; Contreras, M.; Blaser, M.J.; Brodie, E.L.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G. Structure of the human gastric bacterial community in relation to Helicobacter pylori status. ISME J. 2011, 5, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrou, C.; Sambe, B.; Armougom, F.; Raoult, D.; Drancourt, M. Molecular diversity of the Planctomycetes in the human gut microbiota in France and Senegal. APMIS 2013, 121, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhler, T.; Stingl, U.; Meuser, K.; Brune, A. Novel lineages of Planctomycetes densely colonize the alkaline gut of soil-feeding termites (Cubitermes spp.). Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.M.; Judd, C.; Kuske, C.R.; Smith, C. Analysis of Stomach and Gut Microbiomes of the Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica) from Coastal Louisiana, USA. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michalet-Doreau, B.; Fernandez, I.; Peyron, C.; Millet, L.; Fonty, G. Fibrolytic activities and cellulolytic bacterial community structure in the solid and liquid phases of rumen contents. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2001, 41, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Weimer, P.J. Competition among three predominant ruminal cellulolytic bacteria in the absence or presence of non-cellulolytic bacteria. Microbiology 2001, 147, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biddle, A.; Stewart, L.; Blanchard, J.; Leschine, S. Untangling the Genetic Basis of Fibrolytic Specialization by Lachnospiraceae and Ruminococcaceae in Diverse Gut Communities. Diversity 2013, 5, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Duncan, S.H.; Louis, P.; Forano, E. Microbial degradation of complex carbohydrates in the gut. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Chung, J.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Ren, N. Characteristics of rumen microorganisms involved in anaerobic degradation of cellulose at various pH values. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 40303–40310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y. Bacterial community in the rumen of Tibetan sheep and Gansu alpine fine-wool sheep grazing on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Pei, C.X.; Zhang, S.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, Z.W.; Yang, W.Z.; Wang, H.; Guo, G.; et al. Effects of isovalerate supplementation on growth performance and ruminal fermentation in pre- and post-weaning dairy calves. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 154, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Pei, C.X.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; He, J.P.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.Z.; et al. Effects of isovalerate supplementation on microbial status and rumen enzyme profile in steers fed on corn stover based diet. Livest. Sci. 2014, 161, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.B.; Bi, Y.L.; Tu, Y.; Beckers, Y.; Du, H.C.; Diao, Q.Y. Early Feeding Regime of Waste Milk, Milk, and Milk Replacer for Calves Has Different Effects on Rumen Fermentation and the Bacterial Community. Animals 2019, 9, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poulsen, M.; Schwab, C.; Borg Jensen, B.; Engberg, R.M.; Spang, A.; Canibe, N.; Højberg, O.; Milinovich, G.; Fragner, L.; Schleper, C.; et al. Methylotrophic methanogenic Thermoplasmata implicated in reduced methane emissions from bovine rumen. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buddle, B.M.; Denis, M.; Attwood, G.T.; Altermann, E.; Janssen, P.H.; Ronimus, R.S.; Pinares-Patiño, C.S.; Muetzel, S.; Neil Wedlock, D. Strategies to reduce methane emissions from farmed ruminants grazing on pasture. Vet. J. 2011, 188, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirel, B.; Scherer, P. The roles of acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methanogens during anaerobic conversion of biomass to methane: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2008, 7, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ufnar, J.A.; Wang, S.Y.; Ufnar, D.F.; Ellender, R.D. Methanobrevibacter ruminantium as an indicator of domesticated-ruminant fecal pollution in surface waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7118–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leahy, S.C.; Kelly, W.J.; Altermann, E.; Ronimus, R.S.; Yeoman, C.J.; Pacheco, D.M.; Li, D.; Kong, Z.; McTavish, S.; Sang, C.; et al. The Genome Sequence of the Rumen Methanogen Methanobrevibacter ruminantium Reveals New Possibilities for Controlling Ruminant Methane Emissions. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Martin, G.B.; Wen, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Shi, B.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, S. Linseed oil and heated linseed grain supplements have different effects on rumen bacterial community structures and fatty acid profiles in cashmere kids1. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 2099–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Covián, D.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Margolles, A.; Gueimonde, M.; de los Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.; Salazar, N. Intestinal Short Chain Fatty Acids and their Link with Diet and Human Health. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flint, H.J.; Duncan, S.H.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P. Interactions and competition within the microbial community of the human colon: Links between diet and health. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, T.; Boland, T.; Storey, S.; Doyle, E. Linseed Oil Supplementation of Lambs’ Diet in Early Life Leads to Persistent Changes in Rumen Microbiome Structure. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandri, M.; Manfrin, C.; Pallavicini, A.; Stefanon, B. Microbial biodiversity of the liquid fraction of rumen content from lactating cows. Animal 2014, 8, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, X.; Xue, F.; Nan, X.; Tang, Z.; Wang, K.; Beckers, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xiong, B. Illumina Sequencing Approach to Characterize Thiamine Metabolism Related Bacteria and the Impacts of Thiamine Supplementation on Ruminal Microbiota in Dairy Cows Fed High-Grain Diets. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Grieneisen, L.E.; Alberts, S.C.; Archie, E.A.; Wu, M. Development, diet and dynamism: Longitudinal and cross-sectional predictors of gut microbial communities in wild baboons. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1312–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hicks, A.L.; Lee, K.J.; Couto-Rodriguez, M.; Patel, J.; Sinha, R.; Guo, C.; Olson, S.H.; Seimon, A.; Seimon, T.A.; Ondzie, A.U.; et al. Gut microbiomes of wild great apes fluctuate seasonally in response to diet. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smits, S.A.; Leach, J.; Sonnenburg, E.D.; Gonzalez, C.G.; Lichtman, J.S.; Reid, G.; Knight, R.; Manjurano, A.; Changalucha, J.; Elias, J.E.; et al. Seasonal cycling in the gut microbiome of the Hadza hunter-gatherers of Tanzania. Science 2017, 357, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Cheng, F.; Shi, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J. Seasonal diets overwhelm host species in shaping the gut microbiota of Yak and Tibetan sheep. bioRxiv 2018, 481374. [Google Scholar]




| VFAs | GR | SF | IF | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total VFA (mM) | 17.09 b | 24.72 b | 46.68 a | <0.01 |
| Acetate (molar%) | 67.13 b | 69.49 ab | 72.77 a | 0.011 |
| Propionate (molar%) | 17.28 | 15.57 | 17.09 | 0.505 |
| Butyrate (molar%) | 9.21 ab | 10.33 a | 7.66 b | <0.01 |
| Iso-butyrate (molar%) | 2.43 a | 1.69 b | 0.86 c | <0.01 |
| Valerate (molar%) | 0.95 a | 0.64 b | 0.54 b | 0.015 |
| Iso-valerate (molar%) | 2.99 a | 2.28 a | 1.07 b | <0.01 |
| Acetate: propionate | 4.00 | 4.55 | 4.36 | 0.492 |
| Item | Bacteria | Archaea | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GR | SF | IF | p-Value | GR | SF | IF | p-Value | |
| Observed species | 93 a | 93 a | 59 b | 0.02 | 142.67 | 151.50 | 119.00 | 0.06 |
| Shannon | 5.49 ab | 5.88 a | 4.56 b | 0.04 | 3.71 | 3.49 | 3.35 | 0.21 |
| Simpson | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 0.21 | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.40 |
| Chao1 | 215.04 | 148.79 | 99.21 | 0.18 | 169.05 a | 177.80 a | 131.56 b | 0.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Li, P.; Liu, S.; Miao, B.; Zeng, B.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H. Characterization of the Rumen Microbiota and Volatile Fatty Acid Profiles of Weaned Goat Kids under Shrub-Grassland Grazing and Indoor Feeding. Animals 2020, 10, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020176
Guo J, Li P, Liu S, Miao B, Zeng B, Jiang Y, Li L, Wang L, Chen Y, Zhang H. Characterization of the Rumen Microbiota and Volatile Fatty Acid Profiles of Weaned Goat Kids under Shrub-Grassland Grazing and Indoor Feeding. Animals. 2020; 10(2):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020176
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jiazhong, Pengfei Li, Shuai Liu, Bin Miao, Bo Zeng, Yahui Jiang, Li Li, Linjie Wang, Yu Chen, and Hongping Zhang. 2020. "Characterization of the Rumen Microbiota and Volatile Fatty Acid Profiles of Weaned Goat Kids under Shrub-Grassland Grazing and Indoor Feeding" Animals 10, no. 2: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020176
APA StyleGuo, J., Li, P., Liu, S., Miao, B., Zeng, B., Jiang, Y., Li, L., Wang, L., Chen, Y., & Zhang, H. (2020). Characterization of the Rumen Microbiota and Volatile Fatty Acid Profiles of Weaned Goat Kids under Shrub-Grassland Grazing and Indoor Feeding. Animals, 10(2), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10020176





