Developmental and Degenerative Characterization of Porcine Parthenogenetic Fetuses during Early Pregnancy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Information and Ethics Statement
2.2. In Vitro Maturation
2.3. Generation of PA and AI Embryos
2.4. Karyotype and Histological Analysis
2.5. Analysis of Apoptosis in Fetuses
2.6. Methylation Status of Fetuses
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
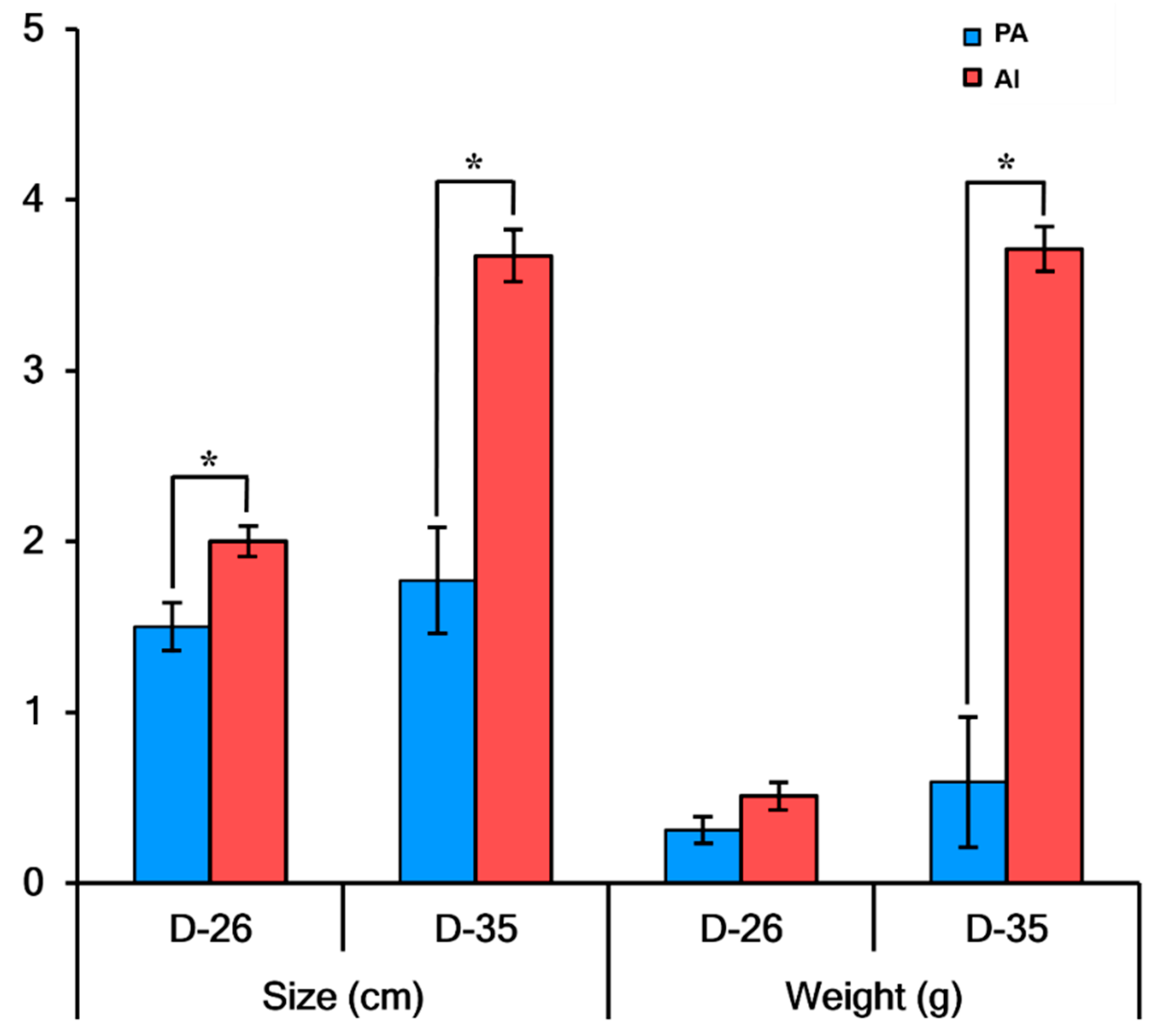
3.1. Developmental Characteristics of PA Embryos and Fetuses
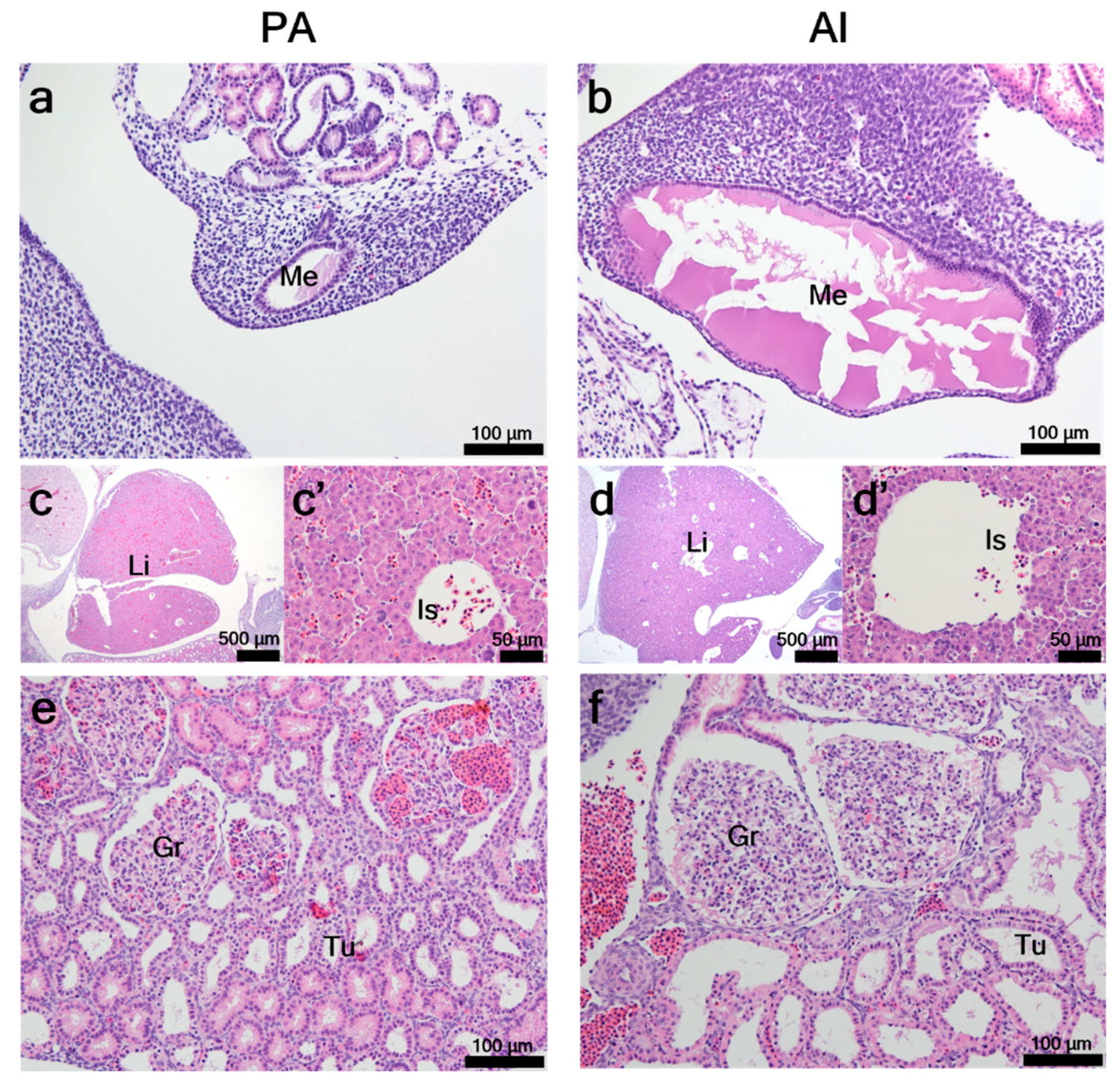
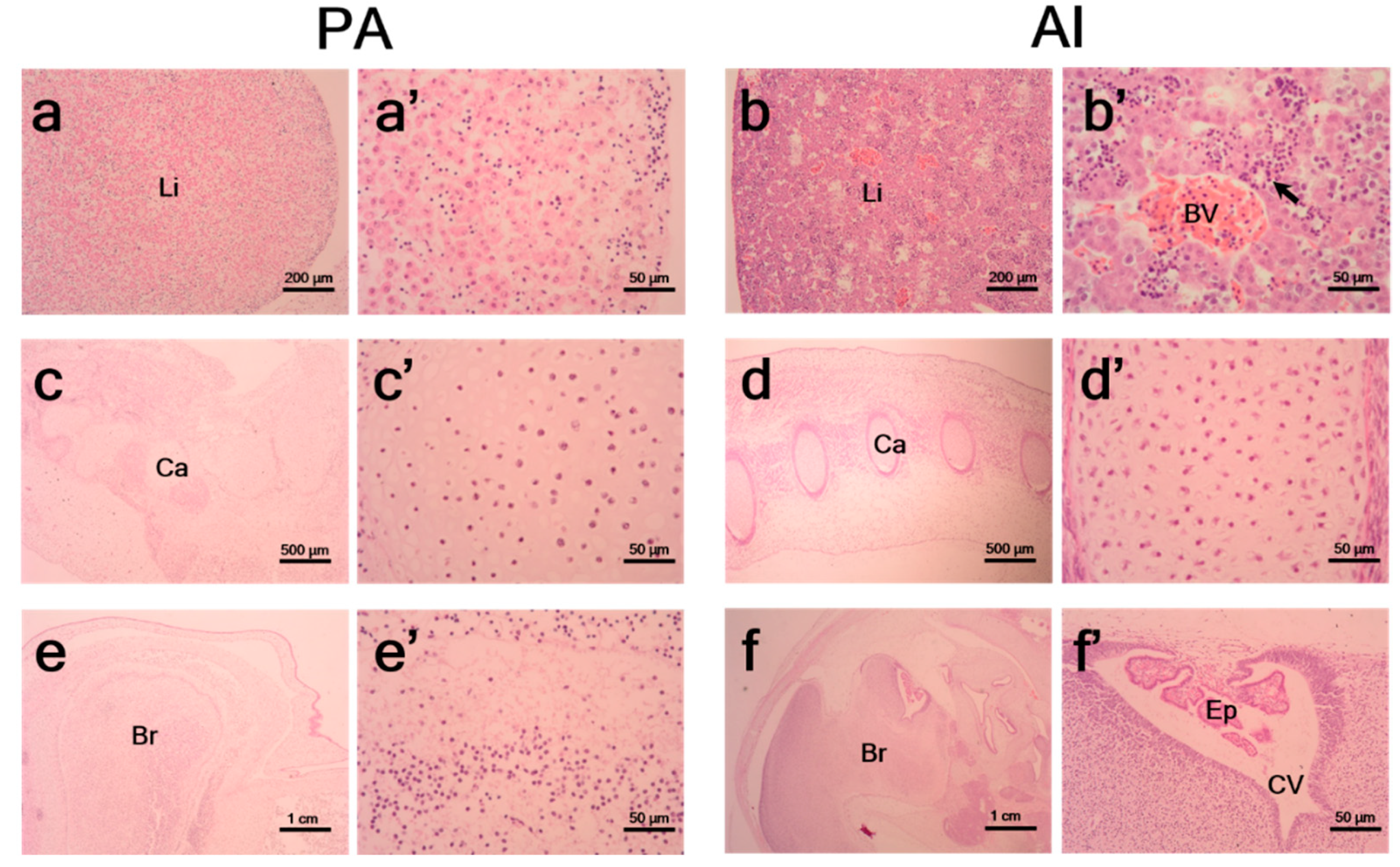
3.2. Histological Characteristics of PA Embryos and Fetuses
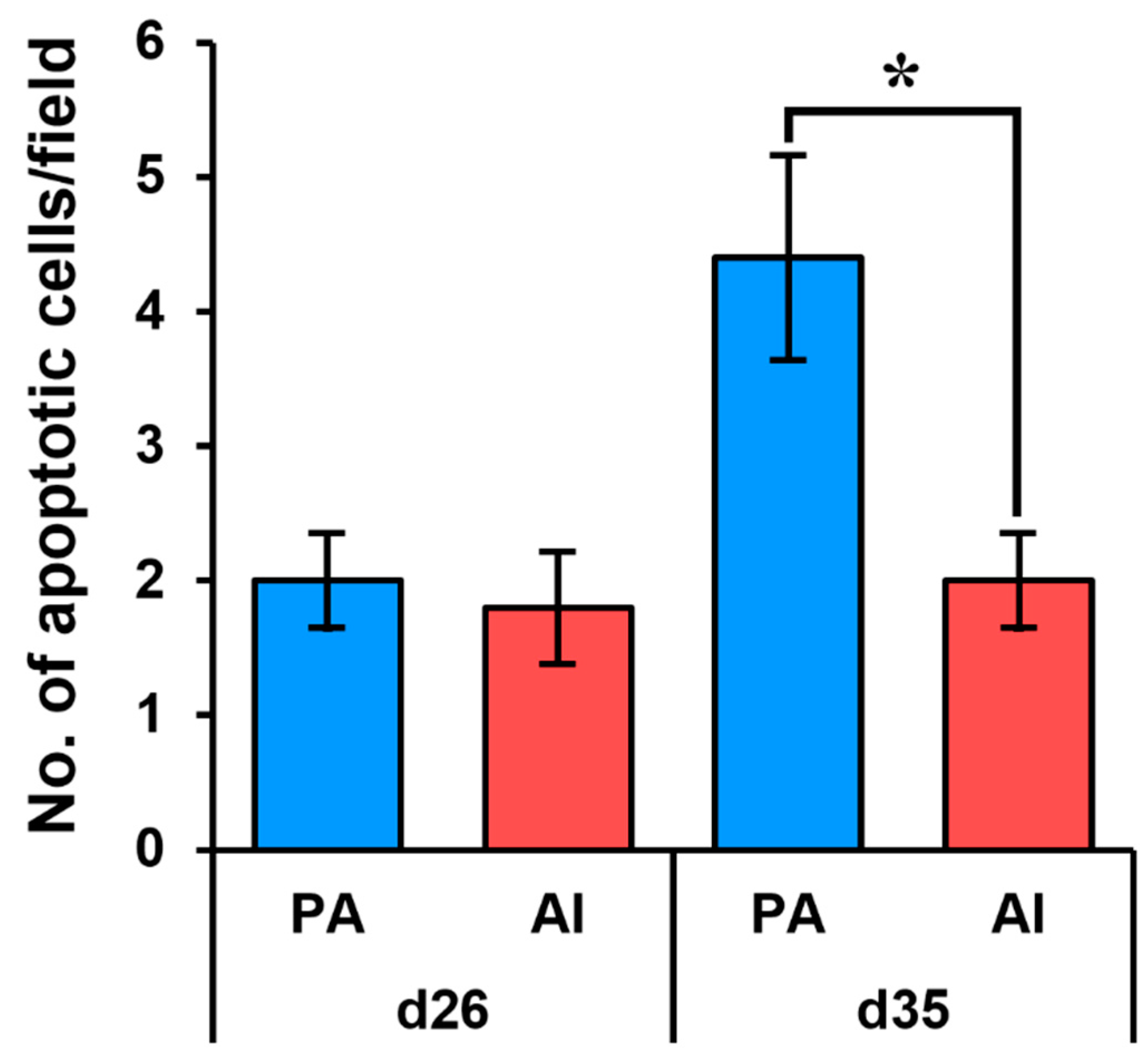
3.3. Analysis of Apoptosis in PA Embryos and Fetuses
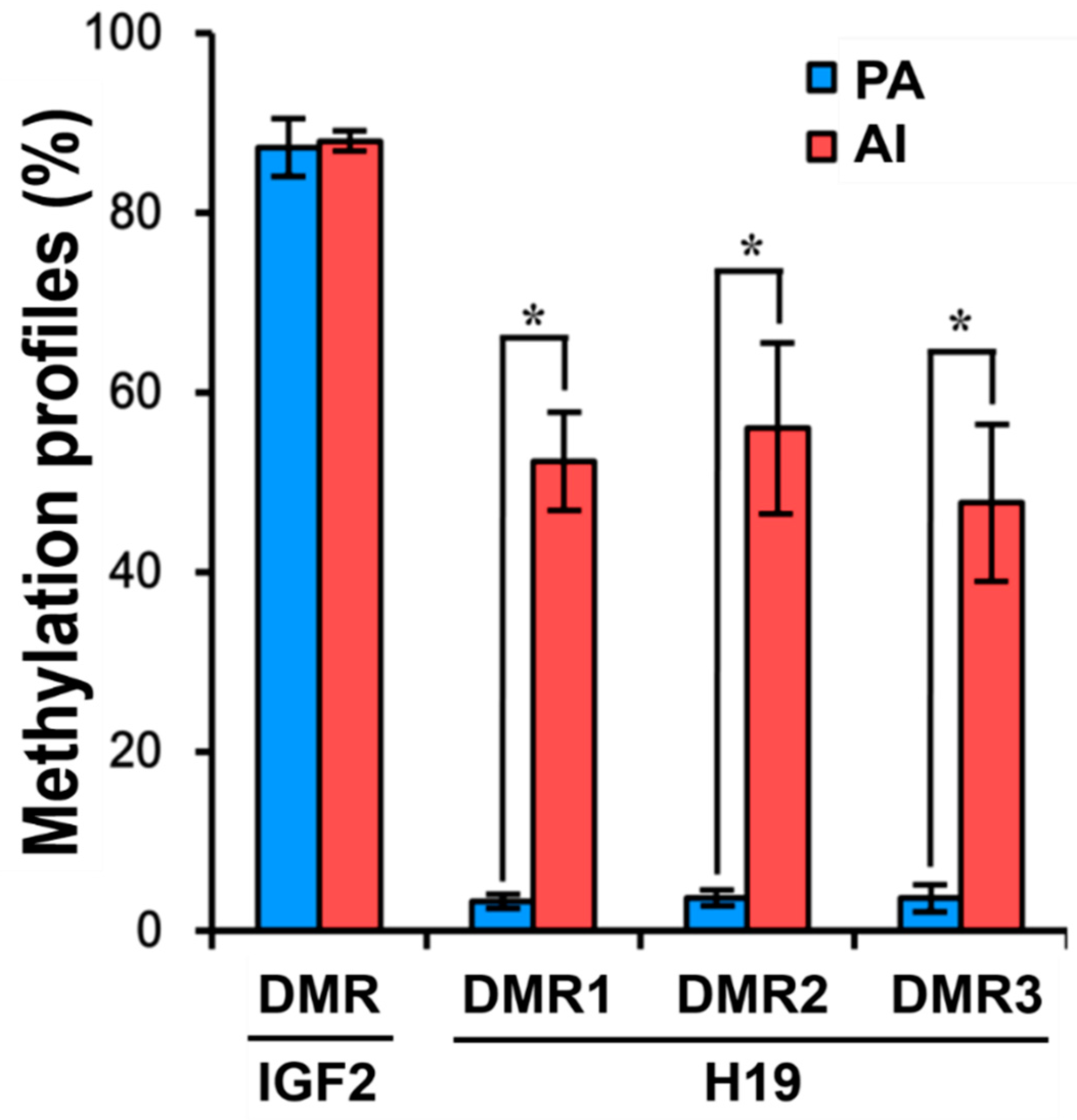
3.4. DNA Methylation Patterns in PA Fetuses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Deemeh, M.R.; Tavalaee, M. Artificial oocyte activation and intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 94, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.G.; Hur, C.G.; Park, M.R.; Park, J.Y.; Hwang, K.C.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.K. Electrical activation enhances pre-implantation embryo development following sperm injection into in vitro matured pig oocytes. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, R.; Fahmy, I.; Tawab, N.A.; Kamal, A.; El-Demery, Y.; Aboulghar, M.; Serour, G. Electrical activation of oocytes after intracytoplasmic sperm injection: A controlled randomized study. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 91, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagida, K.; Katayose, H.; Yazawa, H.; Kimura, Y.; Sato, A.; Yanagimachi, H.; Yanagimachi, R. Successful fertilization and pregnancy following ICSI and electrical oocyte activation. Hum. Reprod. 1999, 14, 1307–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.W.; Blaszcyzk, A.; Grifo, J.A.; Ozil, J.; Haberman, E.; Adler, A.; Krey, L.C. Electrical activation and in vitro development of human oocytes that fail to fertilize after intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil. Steril. 1999, 72, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, P.A.; Dobrinsky, J.R.; Zhu, J.; Archibald, A.L.; Ainslie, A.; Bosma, W.; Bowering, J.; Bracken, J.; Ferrier, P.M.; Fletcher, J.; et al. Somatic cell nuclear transfer in the pig: Control of pronuclear formation and integration with improved methods for activation and maintenance of pregnancy. Biol. Reprod. 2002, 66, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.S.; Takahashi, Y.; Katagiri, S.; Kanagawa, H. Sucrose-exposed chemically enucleated mouse oocytes support blastocyst development of reconstituted embryos. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2006, 18, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, N.J. Stability of cyclin B protein during meiotic maturation and the first mitotic cell division in mouse oocytes. Biol. Cell 1997, 89, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanski, Z.; Ledan, E.; Brunet, S.; Louvet, S.; Verlhac, M.H.; Kubiak, J.Z.; Maro, B. Cyclin synthesis controls the progression of meiotic maturation in mouse oocytes. Development 1998, 125, 4989–4997. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Miller, D.C.; Harman, R.; Antczak, D.F.; Clark, A.G. Paternally expressed genes predominate in the placenta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10705–10710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.J.; Dobrinsky, J.R.; Zhu, J.; Finlayson, H.A.; Bosma, W.; Harkness, L.; Ritchie, W.A.; Travers, A.; McCorquodale, C.; Day, B.N.; et al. Embryo development and establishment of pregnancy after embryo transfer in pigs: Coping with limitations in the availability of viable embryos. Reproduction 2002, 123, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, American Society for Reproductive Medicine, Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology. 2016 Assisted Reproductive Technology Fertility Clinic Success Rates Report; US Dept of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018.
- van Gruting, I.M.A.; Muller, M.A.; van Groningen, K.; Exalto, N. Macroscopic and microscopic morphology of first trimester miscarriage and subsequent pregnancy outcome—An exploratory study. Placenta 2017, 53, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.S.; Kwon, D.J.; Kwak, T.U.; Lee, J.Y.; Hyung, N.W.; Yang, H.; Oh, K.B.; Ock, S.A.; Park, E.W.; Im, G.S.; et al. Effect of a short-term in vitro exposure time on the production of in vitro produced piglets. J. Anim. Reprod. Biotechnol. 2016, 31, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Wu, H.; Lee, J.; Hwang, I.S.; Yu, D.; Ahn, J.S.; Lee, J.W.; Hwang, S.; Lee, K. Identification of a novel imprinted transcript in the porcine GNAS complex locus using methylome and transcriptome of parthenogenetic fetuses. Genes 2020, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.; Jang, W.-G.; Kim, E.-J.; Do, M.; Oh, K.-B.; Hwang, S.; Shim, H.; Choo, Y.-K.; Kwon, D.-J.; Lee, J.-W. Methylation and expression changes in imprinted genes H19 and Igf2 during serial somatic cell nuclear transfer using piglet fibroblasts. Anim. Cells Syst. 2015, 19, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Oh, K.B.; Kwon, D.J.; Ock, S.A.; Lee, J.W.; Im, G.S.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, K.; Park, J.K. Improvement of cloning efficiency in minipigs using post-thawed donor cells treated with roscovitine. Mol. Biotechnol. 2013, 55, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Lee, H.; Oh, K.B.; Hwang, I.S.; Yang, H.; Park, M.R.; Ock, S.A.; Woo, J.S.; Im, G.S.; Hwang, S. Production and breeding of transgenic cloned pigs expressing human CD 73. Dev. Reprod. 2017, 21, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.A. Embryology Carnegie Stage Comparison. Available online: https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Carnegie_Stage_Comparison (accessed on 16 September 2019).
- Marrable, A.W. The embryonic membranes of the pig. Vet. Rec. 1969, 84, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rahilly, R. Early human development and the chief sources of information on staged human embryos. Eur. J. Obs. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 1979, 9, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polge, C.; Rowson, L.E.; Chang, M.C. The effect of reducing the number of embryos during early stages of gestation on the maintenance of pregnancy in the pig. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1966, 12, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisert, R.D.; Zavy, M.T.; Moffatt, R.J.; Blair, R.M.; Yellin, T. Embryonic steroids and the establishment of pregnancy in pigs. J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 1990, 40, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.H.; Park, M.R.; Yang, B.C.Y.; Ko, Y.G.; Oh, K.B.; Lee, J.W.; Woo, J.S.; Park, E.W.; Park, S.B.; Hwang, S. Developmental characteristics of SCNT pig embryos knocked-out of alpha-1,3-Galactosyltransferase gene. Reprod. Dev. Biol. 2009, 33, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, L.; Kolber-Simonds, D.; Park, K.W.; Cheong, H.T.; Greenstein, J.L.; Im, G.S.; Samuel, M.; Bonk, A.; Rieke, A.; Day, B.N.; et al. Production of alpha-1,3-galactosyltransferase knockout pigs by nuclear transfer cloning. Science 2002, 295, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, P.; Ledda, S.; Fulka, J., Jr.; Cappai, P.; Moor, R.M. Development of parthenogenetic and cloned ovine embryos: Effect of activation protocols. Biol. Reprod. 1998, 58, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Kim, M.J.; Ha, S.K.; Hong, S.G.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, G.A.; Park, E.J.; Kang, J.T.; Saadeldin, I.M.; Jang, G.; et al. Altered cell cycle gene expression and apoptosis in post-implantation dog parthenotes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, T.; Obata, Y.; Yoshimzu, T.; Nakahara, T.; Carroll, J. Epigenetic modifications during oocyte growth correlates with extended parthenogenetic development in the mouse. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, D.; Koppel, J.; Maddox-Hyttel, P. Apoptotic processes during mammalian preimplantation development. Theriogenology 2005, 64, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Haldar, S. The relationship between BcI2, Bax and p53: Consequences for cell cycle progression and cell death. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 4, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joza, N.; Susin, S.A.; Daugas, E.; Stanford, W.L.; Cho, S.K.; Li, C.Y.; Sasaki, T.; Elia, A.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Ravagnan, L.; et al. Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death. Nature 2001, 410, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, J.; Solter, D. Completion of mouse embryogenesis requires both the maternal and paternal genomes. Cell 1984, 37, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.E.; Schnieke, A.E.; McCreath, K.J.; Wieckowski, S.; Konfortova, G.; Fernandes, K.; Ptak, G.; Kind, A.J.; Wilmut, I.; Loi, P.; et al. Conservation of IGF2-H19 and IGF2R imprinting in sheep: Effects of somatic cell nuclear transfer. Mech. Dev. 2003, 120, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surani, M.A.; Barton, S.C.; Norris, M.L. Development of reconstituted mouse eggs suggests imprinting of the genome during gametogenesis. Nature 1984, 308, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, T.; Obata, Y.; Wu, Q.; Niwa, K.; Ono, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Park, E.S.; Seo, J.S.; Ogawa, H. Birth of parthenogenetic mice that can develop to adulthood. Nature 2004, 428, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Enkemann, S.A.; Liang, P.; Hersmus, R.; Zanazzi, C.; Huang, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, Z.; Looijenga, L.H.; Keefe, D.L.; et al. Genome-wide gene expression profiling reveals aberrant MAPK and Wnt signaling pathways associated with early parthenogenesis. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 2, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, I.; Saito, C.; Mizuno, Y.; Meguro, M.; Bono, H.; Kadomura, M.; Kono, T.; Morris, G.A.; Lyons, P.A.; Oshimura, M.; et al. Discovery of imprinted transcripts in the mouse transcriptome using large-scale expression profiling. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 1402–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, A.; Heeson, S.; Reik, W. Interaction between differentially methylated regions partitions the imprinted genes Igf2 and H19 into parent-specific chromatin loops. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Song, Y.; Huang, Y.; Duan, F.; Lv, Q.; Ouyang, H.; Lai, L.; Li, Z. Genomic imprinting analysis of Igf2/H19 in porcine cloned fetuses using parthenogenetic somatic cells as nuclear donors. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sembon, S.; Iwamoto, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Oishi, T.; Fuchimoto, D.; Suzuki, S.; Yazaki, S.; Onishi, A. Porcine androgenetic embryos develop to fetal stage in recipient mothers. Theriogenology 2012, 78, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, I.-S.; Park, M.-R.; Lee, H.-S.; Kwak, T.-U.; Son, H.-Y.; Kang, J.-K.; Lee, J.-W.; Lee, K.; Park, E.-W.; Hwang, S. Developmental and Degenerative Characterization of Porcine Parthenogenetic Fetuses during Early Pregnancy. Animals 2020, 10, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10040622
Hwang I-S, Park M-R, Lee H-S, Kwak T-U, Son H-Y, Kang J-K, Lee J-W, Lee K, Park E-W, Hwang S. Developmental and Degenerative Characterization of Porcine Parthenogenetic Fetuses during Early Pregnancy. Animals. 2020; 10(4):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10040622
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, In-Sul, Mi-Ryung Park, Hae-Sun Lee, Tae-Uk Kwak, Hwa-Young Son, Jong-Koo Kang, Jeong-Woong Lee, Kichoon Lee, Eung-Woo Park, and Seongsoo Hwang. 2020. "Developmental and Degenerative Characterization of Porcine Parthenogenetic Fetuses during Early Pregnancy" Animals 10, no. 4: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10040622
APA StyleHwang, I.-S., Park, M.-R., Lee, H.-S., Kwak, T.-U., Son, H.-Y., Kang, J.-K., Lee, J.-W., Lee, K., Park, E.-W., & Hwang, S. (2020). Developmental and Degenerative Characterization of Porcine Parthenogenetic Fetuses during Early Pregnancy. Animals, 10(4), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10040622




