Potential of Black Soldier Fly Production for Pacific Small Island Developing States
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
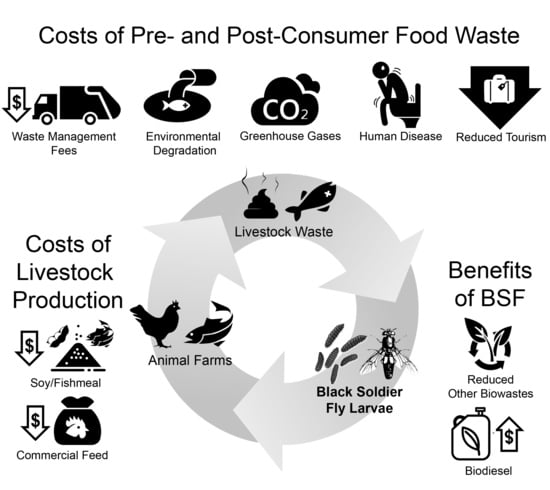
2. Black Soldier Flies
3. Pacific Small Island Developing States
4. BSF and the PSIDS
4.1. Cook Islands
4.2. Federated States of Micronesia (FSM)
4.3. Fiji
4.4. Kiribati
4.5. Marshall Islands
4.6. Nauru
4.7. Niue
4.8. Palau
4.9. Papua New Guinea
4.10. Samoa
4.11. Solomon Islands
4.12. Tonga
4.13. Tuvalu
4.14. Vanuatu
4.15. Tokelau
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nogales-Mérida, S.; Gobbi, P.; Józefiak, D.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Dudek, K.; Rawski, M.; Kierończyk, B.; Józefiak, A. Insect meals in fish nutrition. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 11, 1080–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasco, L.; Dabbou, S.; Trocino, A.; Xiccato, G.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasato, I.; Dezzutto, D.; Birolo, M.; Meneguz, M.; Schiavone, A.; et al. Effect of dietary supplementation with insect fats on growth performance, digestive efficiency and health of rabbits. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Shelomi, M. Review of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Animal Feed and Human Food. Foods 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Huis, A.; van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Muir, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2013; p. 171. [Google Scholar]
- DeFoliart, G.R.; Dunkel, F.V.; Gracer, D. The Food Insects Newsletter Volumes 1–13, 1988 through 2000; Aardvark Global Publishing Company, LLC.: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2009; p. 414. [Google Scholar]
- Fellows, P. Editorial: Insects for food and feed. Food Chain 2014, 4, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelomi, M. The meat of affliction: Insects and the future of food as seen in Expo 2015. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 56, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Muros, M.-J.; Barroso, F.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Insect meal as renewable source of food for animal feeding: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, S.Y.; Tanga, C.M.; Van Loon, J.J.; Dicke, M. Insects for sustainable animal feed: Inclusive business models involving smallholder farmers. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2019, 41, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalava, K. First respiratory transmitted food borne outbreak? Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 226, 113490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, N.D.; Daszak, P.; Kilpatrick, A.M.; Burke, N.S. Bushmeat Hunting, Deforestation, and Prediction of Zoonotic Disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1822–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, X.; Sun, X. Molecular Biology of Insect Viruses. In Advances in Microbial Control of Insect Pests; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 83–107. [Google Scholar]
- Rumpold, B.A.; Schlüter, O.K. Potential and challenges of insects as an innovative source for food and feed production. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Józefiak, A.; Engberg, R.M. Insect proteins as a potential source of antimicrobial peptides in livestock production. A review. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2017, 26, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahukar, R. Entomophagy and human food security. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2011, 31, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadeau, L.; Nadeau, I.; Franklin, F.; Dunkel, F. The Potential for Entomophagy to Address Undernutrition. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2014, 54, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Huis, A. Potential of Insects as Food and Feed in Assuring Food Security. Annu. Rev. Èntomol. 2013, 58, 563–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohri, C.R.; Diener, S.; Zabaleta, I.; Mertenat, A.; Zurbrügg, C. Treatment technologies for urban solid biowaste to create value products: A review with focus on low- and middle-income settings. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio. Technol. 2017, 16, 81–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohee, R.; Mauthoor, S.; Bundhoo, Z.M.; Somaroo, G.; Soobhany, N.; Gunasee, S.; Bundhoo, M.A.Z. Current status of solid waste management in small island developing states: A review. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graczyk, H.; Knight, R.; Gilman, R.H.; Cranfield, M.R. The role of non-biting flies in the epidemiology of human infectious diseases. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, G.R.; Durden, L.A. Medical and Veterinary Entomology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadu, Y.M.; Goselle, O.N.; Ejimadu, L.C. Microhabitats and Pathogens of Houseflies (Musca domestica): Public Health Concern. Electron. J. Biol. 2016, 12, 374–380. [Google Scholar]
- Graczyk, H.; Knight, R.; Tamang, L. Mechanical Transmission of Human Protozoan Parasites by Insects. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenberg, B. Flies and disease. In Biology and Disease Transmission; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1973; Volume 2, p. 447. [Google Scholar]
- Emerson, P.M.; Bailey, R.L.; Mahdi, O.S.; Walraven, G.E.; Lindsay, S.W. Transmission ecology of the fly Musca sorbens, a putative vector of trachoma. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2000, 94, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, V.J. I Am the Baby Killer! House Flies and the Spread of Polio. Am. Èntomol. 2016, 62, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penakalapati, G.; Swarthout, J.; Delahoy, M.; McAliley, L.; Wodnik, B.; Levy, K.; Freeman, M.C. Exposure to Animal Feces and Human Health: A Systematic Review and Proposed Research Priorities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11537–11552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woodruff, A. Appropriate Technologies. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Diener, S.; Solano, N.M.S.; Roa-Gutierrez, F.; Zurbrügg, C.; Tockner, K. Biological Treatment of Municipal Organic Waste using Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2011, 2, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabler, F. Using Black Soldier Fly for Waste Recycling and Effective Salmonella spp. Reduction. Available online: http://www.insectum.eu/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/Gabler-2014-Using-Black-Soldier-Fly-for-waste-recycling-and-effective-Salmonella-spp.-reduction.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- Esrey, S.A.; Andersson, I.; Hillers, A.; Sawyer, R. Closing the Loop: Ecological Sanitation for Food Security, 1st ed.; UNDP-SIDA: Tepoztlán, Mexico, 2001; Volume 18, p. 107. [Google Scholar]
- Cappellozza, S.; Leonardi, M.G.; Saviane, A.; Bruno, D.; Bonelli, M.; Caccia, S.; Casartelli, M.; Tettamanti, G.; Savoldelli, S.; Carminati, D.; et al. A First Attempt to Produce Proteins from Insects by Means of a Circular Economy. Animals 2019, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, L.; Cai, H.; Garza, E.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, S. From organic waste to biodiesel: Black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens, makes it feasible. Fuel 2011, 90, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Hou, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Yu, Z. Biodiesel production from rice straw and restaurant waste employing black soldier fly assisted by microbes. Energy 2012, 47, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z. Double the biodiesel yield: Rearing black soldier fly larvae, Hermetia illucens, on solid residual fraction of restaurant waste after grease extraction for biodiesel production. Renew. Energy 2012, 41, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.-T.; Hsiao, T.-Y.; Shang, N.-C.; Yu, Y.-H.; Ma, H.-W. MSW management for waste minimization in Taiwan: The last two decades. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichuk, K.M.; McCartney, D. Compost stability and maturity evaluation—Aliterature review. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2013, 8, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, G.; Oonincx, D.; Jordan, H.; Zhang, J.; Van Loon, J.; Van Huis, A.; Tomberlin, J. Standardisation of quantitative resource conversion studies with black soldier fly larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2020, 6, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoa, F.; Fry, G.; Tarte, S. The New Pacific Diplomacy at the United Nations: The rise of the PSIDS. In The New Pacific Diplomacy; Fry, G., Tarte, S., Eds.; Australian National University Press: Canberra, Australia, 2015; pp. 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Fatchurochim, S.; Geden, C.J.; Axtell, R.C. Filth fly (diptera) oviposition and larval development in poultry manure of various moisture levels. J. Èntomol. Sci. 1989, 24, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinetti, C.; Samayoa, A.C.; Hwang, S.-Y. Effects of Feeding Adults ofHermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) on Longevity, Oviposition, and Egg Hatchability: Insights Into Optimizing Egg Production. J. Insect Sci. 2019, 19, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bruno, D.; Bonelli, M.; Cadamuro, A.G.; Reguzzoni, M.; Grimaldi, A.; Casartelli, M.; Tettamanti, G. The digestive system of the adult Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae): Morphological features and functional properties. Cell Tissue Res. 2019, 378, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkegbe, E.K.; Adu-Aboagye, G.; Affedzie, O.S.; Nacambo, S.; Boafo, A.B.; Kenis, M.; Wallace, P. Potential Health and Safety Issues in the Small-Scale Production of Fly Larvae for Animal Feed—A Review. Ghana J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 9, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, S.W.; Sheppard, D.C. House fly oviposition inhibition by larvae ofHermetia illucens, the black soldier fly. J. Chem. Ecol. 1984, 10, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Fidjeland, J.; Diener, S.; Eriksson, S.; Vinneras, B. High waste-to-biomass conversion and efficient Salmonella spp. reduction using black soldier fly for waste recycling. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 35, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Brady, J.A.; Sanford, M.R.; Yu, Z. Black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae reduce Escherichia coli in dairy manure. Environ. Èntomol. 2008, 37, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.; Senecal, J.; Calvo, M.G.; Ahrens, L.; Josefsson, S.; Wiberg, K.; Vinneras, B. Fate of pharmaceuticals and pesticides in fly larvae composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charlton, A.; Dickinson, M.; Wakefield, M.E.; Fitches, E.; Kenis, M.; Han, R.; Zhu, F.; Koné, N.; Grant, M.; Devic, E.; et al. Exploring the chemical safety of fly larvae as a source of protein for animal feed. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, S.; Zurbrugg, C.; Tockner, K. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens and effects on its life cycle. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purschke, B.; Scheibelberger, R.; Axmann, S.; Adler, A.; Jäger, H. Impact of substrate contamination with mycotoxins, heavy metals and pesticides on the growth performance and composition of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) for use in the feed and food value chain. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.R.; Popa, R. Enhanced Ammonia Content in Compost Leachate Processed by Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 166, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, I.J.; Gibson, W.T.; Cameron, M.M. Growth rates of black soldier fly larvae fed on fresh human faeces and their implication for improving sanitation. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2013, 19, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.X.; Tomberlin, J.K.; VanLaerhoven, S. Ability of Black Soldier Fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larvae to Recycle Food Waste. Environ. Èntomol. 2015, 44, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertenat, A.; Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C. Black Soldier Fly biowaste treatment—Assessment of global warming potential. Waste Manag. 2019, 84, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, G.L.; Booram, C.V.; Barker, R.W.; Hale, O.M. Dried Hermetia Illucens Larvae Meal as a Supplement for Swine. J. Anim. Sci. 1977, 44, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Hilaire, S.; Cranfill, K.; A McGuire, M.; Mosley, E.E.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Newton, L.; Sealey, W.; Sheppard, C.; Irving, S. Fish Offal Recycling by the Black Soldier Fly Produces a Foodstuff High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2007, 38, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, A.; Cullere, M.; De Marco, M.; Meneguz, M.; Biasato, I.; Bergagna, S.; Dezzutto, D.; Gai, F.; Dabbou, S.; Gasco, L.; et al. Partial or total replacement of soybean oil by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.) fat in broiler diets: Effect on growth performances, feed-choice, blood traits, carcass characteristics and meat quality. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 16, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Raamsdonk, L.W.D.; Van Der Fels-Klerx, H.J.; De Jong, J. New feed ingredients: The insect opportunity. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 1384–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veldkamp, T.; Van Duinkerken, G.; Van Huis, A.; Lakemond, C.M.M.; Ottevanger, E.; Bosch, G.; Van Boekel, T. Insects as a Sustainable Feed Ingredient in Pig and Poultry Diets: A Feasibility Study = Insecten als Duurzame Diervoedergrondstof in Varkens-En Pluimveevoeders: Een Haalbaarheidsstudie; Wageningen UR Livestock Research: Lelystad, The Netherlands, 2012; p. 48. [Google Scholar]
- Moula, N.; Scippo, M.-L.; Douny, C.; Degand, G.; Dawans, E.; Cabaraux, J.F.; Hornick, J.-L.; Medigo, R.C.; Leroy, P.; Francis, F.; et al. Performances of local poultry breed fed black soldier fly larvae reared on horse manure. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 4, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacon, A.G.J.; Hasan, M.R.; Subasinghe, R.P. Use of Fishery Resources as Feed Inputs for Aquaculture Development: Trends and Policy Implications; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Derrien, C.; Boccuni, A. Current Status of the Insect Producing Industry in Europe. In Edible Insects in Sustainable Food Systems; Halloran, A., Flore, R., Vantomme, P., Roos, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 471–479. [Google Scholar]
- Halloran, A.; Vantomme, P.; Hanboonsong, Y.; Ekesi, S. Regulating edible insects: The challenge of addressing food security, nature conservation, and the erosion of traditional food culture. Food Secur. 2015, 7, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, D.; Pieterse, E. Markets, money and maggots. J. Insects Food Feed 2015, 1, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human, U. The world is feasting its eyes on insects. FarmBiz 2019, 5, 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd-Noor, S.-N.; Wong, C.-Y.; Lim, J.W.; Mah-Hussin, M.-I.-A.; Uemura, Y.; Lam, M.-K.; Ramli, A.; Bashir, M.J.; Tham, L. Optimization of self-fermented period of waste coconut endosperm destined to feed black soldier fly larvae in enhancing the lipid and protein yields. Renew. Energy 2017, 111, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dortmans, B.; Diener, S.; Verstappen, B.; Zurbrügg, C. Black Soldier Fly Biowaste Processing—A Step-by-Step Guide; Eawag-Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology: Dübendorf, Switzerland, 2017; p. 87. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, D.; Devic, E.; Subamia, I.; Talamond, P.; Baras, E. Technical Handbook of Domestication and Production of Diptera Black Soldier Fly (BSF), Hermetia Illucens, Stratiomyidae; IRD Press: Bogor, Indonesia, 2014; p. 141. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, S.; Ichiki, R.T.; Shimoda, M.; Morioka, S. Small-scale rearing of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae), in the laboratory: Low-cost and year-round rearing. Appl. Èntomol. Zoöl. 2015, 51, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, S.; Zurbrügg, C.; Tockner, K. Conversion of organic material by black soldier fly larvae: Establishing optimal feeding rates. Waste Manag. Res. 2009, 27, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liland, N.S.; Biancarosa, I.; Araújo, P.; Biemans, D.; Bruckner, C.G.; Waagbø, R.; Torstensen, B.E.; Lock, E.J. Modulation of nutrient composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae by feeding seaweed-enriched media. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Zheng, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Developmental and waste reduction plasticity of three black soldier fly strains (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) raised on different livestock manures. J. Med. Èntomol. 2013, 50, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdell, C. Poverty in the Pacific Islands. Int. J. Sociol. Soc. Policy 2000, 20, 74–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.A.; Taylor, H.R.; E Keeffe, J.; Le Mesurier, R.T. Trachoma in the Pacific Islands: Evidence from Trachoma Rapid Assessment. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.R. Development, global change and traditional food security in Pacific Island countries. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 15, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, E.; Nuttall, P.; Newell, A.; Prasad, B.; Veitayaki, J.; Bola, A.; Kaitu’u, J. Connecting the dots: Policy connections between Pacific Island shipping and global CO2and pollutant emission reduction. Carbon Manag. 2014, 5, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuttall, P.; Newell, A.; Prasad, B.; Veitayaki, J.; Holland, E. A review of sustainable sea-transport for Oceania: Providing context for renewable energy shipping for the Pacific. Mar. Policy 2014, 43, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon-Clark, M. Paradise lost? Pacific island archives threatened by climate change. Arch. Sci. 2011, 12, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, E.; Haynes, D. Solid Waste Management in Pacific Island Countries and Territories. In Progressive Development; Springer Science and Business Media LLC.: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 255–279. [Google Scholar]
- Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Programme (SPREP). Cleaner Pacific 2025: Pacific Regional Waste and Pollution Management Strategy 2016–2025; Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Programme (SPREP): Apia, Samoa, 2016; p. 68. [Google Scholar]
- Ashford, D.A.; Clark, G.G.; McReady, J.; Gubler, D.G.; Bartholomew, D.M.; Spiegel, R.A.; Vorndam, V.; Hajjeh, R.A.; Savage, H.M. Outbreak of dengue fever in Palau, Western Pacific: Risk factors for infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 69, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, A.; Mercier, A.; Lepers, C.; Hoy, D.; Duituturaga, S.; Benyon, E.; Guillaumot, L.; Souarès, Y. Concurrent outbreaks of dengue, chikungunya and Zika virus infections—An unprecedented epidemic wave of mosquito-borne viruses in the Pacific 2012–2014. Eurosurveillance 2014, 19, 20929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marks, M.E. Epidemiology of Yaws in the Solomon Islands and the Impact of a Trachoma Control Programme. Ph.D. Thesis, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, L.P.; Prasad, R. Assessing the sustainable municipal solid waste (MSW) to electricity generation potentials in selected Pacific Small Island Developing States (PSIDS). J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J. Adapting to Climate Change in Pacific Island Countries: The Problem of Uncertainty. World Dev. 2001, 29, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valdés, A.; Foster, W. Net Food-Importing Developing Countries: Who They Are, and Policy Options for Global Price Volatility; International Center for Trade and Sustainable Development: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Caddy, J.; Agnew, D. An overview of recent global experience with recovery plans for depleted marine resources and suggested guidelines for recovery planning. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2004, 14, 43–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogliano, C.; Wham, C.; Wham, C.; Burlingame, B. Can Leveraging Agrobiodiverse Food Systems Help Reverse the Rise of Malnutrition in Pacific Small Island Developing States (PSIDS)? Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2019, 37, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Central Intelligence Agency. The World Factbook. Available online: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/docs/faqs.html (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- Sheppard, D.C.; Newton, G.L.; Thompson, S.A.; Savage, S. A value added manure management system using the black soldier fly. Bioresour. Technol. 1994, 50, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohart, G.E.; Gressitt, J.L. Filth-Inhabiting Flies of Guam; Bernice, P., Ed.; Bishop Museum: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1951; Volume 204. [Google Scholar]
- Popa, R.; Green, T.R. Using black soldier fly larvae for processing organic leachates. J. Econ. Èntomol. 2012, 105, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripontan, Y.; Juntavimon, T.; Songin, S.; Chiu, C.-I. Egg-trapping of black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) with various wastes and the effects of environmental factors on egg-laying. Khon Kaen Agric. J. 2017, 45, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. Cook Islands Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. Fiji Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. The Federated States of Micronesia Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. Kiribati Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. The Marshall Islands Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. Nauru Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. Palau Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. Papua New Guinea Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. Samoa Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. Solomon Islands Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. Tonga Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. Tuvalu Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, A. Vanuatu Country Snapshot. In Solid Waste Management in the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2014; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Marsters, E.; Lewis, N.; Friesen, W. Pacific flows: The fluidity of remittances in the Cook Islands. Asia Pac. Viewp. 2006, 47, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook Islands Agriculture. Available online: http://www.mfem.gov.ck/434-cook-islands-agriculture (accessed on 9 May 2020).
- Krauss, N.L.K. Insects from Aitutaki, Cook Islands. Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 1961, 17, 415–518. [Google Scholar]
- McCormack, G. Cook Islands Biodiversity Database, version 2007.2. Available online: http://cookislands.bishopmuseum.org (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- Kumar, R. Cooks become Pacific’s first developed island nation. In Cook Islands News; Cook Island News: Rarotonga, Cook Islands, 2019; Available online: http://www.cookislandsnews.com/item/74448-cooks-become-pacific-s-first-developed-island-nation/ (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- Harris, E. The Cook Islands and the downside of developed country status. In The Interpreter; The Lowy Institute: Sydney, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chuuk State Solid Waste Management Strategy 2019–2028 (Action Plan: 2019–2023); Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Programme: Chuuk, Micronesia, 2019.
- Chong, T.L.; Matsufuji, Y.; Hassan, M.N. Implementation of the semi-aerobic landfill system (Fukuoka method) in developing countries: A Malaysia cost analysis. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanashima, M. Pollution control and stabilization process by semiaerobic landfill type: The Fukuoka method. Proc. Sard. 1999, 99, 313–325. [Google Scholar]
- Pohnpei State Solid Waste Management Strategy 2020–2029 (Action Plan: 2020–2024); Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Programme: Pohnpei, Micronesia, 2020.
- Kirk, M.D.; Kiedrzynski, T.; Johnson, E.; Elymore, A.; Wainiqolo, I. Risk factors for cholera in Pohnpei during an outbreak in 2000: Lessons for Pacific countries and territories. Pac. Health Dialog 2005, 12, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- James, M.T. Diptera: Stratiomyidae, Calliphoridae. Insects Micrones. 1962, 13, 75–127. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, C.N.; Kama, M.; Acharya, S.; Bera, U.; Clemens, J.; Crump, J.A.; Dawainavesi, A.; Dougan, G.; Edmunds, W.J.; Fox, K.; et al. Typhoid fever in Fiji: A reversible plague? Trop. Med. Int. Health 2014, 19, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, E.H.J. Notes on Insect Fauna of Fiji. Edited by Evenhuis NL. 2008. Available online: http://hbs.bishopmuseum.org/fiji/pdf/Fiji-Insect-List.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- Bezzi, M. Diptera Brachycera and Athericera of the Fiji Islands: Based on Material in the British Museum (Natural History); British Museum (Natural History): London, UK, 1928; p. 220. [Google Scholar]
- Woodley, N.E. Vitilevumyia, an enigmatic new genus of Stratiomyidae from Fiji (Diptera). Zootaxa 2011, 2821, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, S.A.; Woodley, N.E.; Hauser, M. The historical spread of the Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (L.) (Diptera, Stratiomyidae, Hermetiinae), and its establishment in Canada. J. Entomol. Soc. Ont. 2015, 146, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Evenhuis, N.L.; Bickel, D.J. The NSF-Fiji Terrestrial Arthropod Survey: Overview. Fiji Arthropods I. Bish. Mus. Occas. Pap. 2005, 82, 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Fallgren, A. A Food Culture in Transition. Perceptions of Healthy Eating and Reasoning in Food Choices—A Grounded Theory Study of Young Mothers in South Tarawa, Kiribati. Master’s Thesis, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Storey, D.; Hunter, S. Kiribati: An environmental ‘perfect storm’. Aust. Geogr. 2010, 41, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carden, Y.R. Solid Waste-level Rise on Atoll Nation States: A Less Publicised Environmental Issue in the Republic of Kiribati. Australas. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 10, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- East, A.J.; Dawes, L. Homegardening as a panacea: A case study of South Tarawa. Asia Pac. Viewp. 2009, 50, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDaniel, C.N.; Gowdy, J.M. Paradise for Sale: A Parable of Nature; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.J.; Kafoa, B.; Win, N.S.S.; Jose, M.; Bibb, W.; Luby, S.P.; Waidubu, G.; O’Leary, M.; Mintz, E. Restaurant-associated outbreak of Salmonella typhi in Nauru: An epidemiological and cost analysis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2001, 127, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenna, S.A.; Butler, D.J.; Wheatley, A. Rapid Biodiversity Assessment of Republic of Nauru, June 2013; Secretariat of the Pacific Regional Environment Programme: Apia, Samoa, 2015; p. 240. [Google Scholar]
- Allwood, A.J.; Vueti, E.T.; Leblanc, L.; Bull, R. Eradication of introduced Bactrocera species (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Nauru using male annihilation and protein bait application techniques. In Turning the Tide: The Eradication of Invasive Species; Veitch, C.R., Clout, M.N., Eds.; Hollands Printing Ltd.: Aukland, New Zealand, 2002; pp. 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Epskamp, S. Niue’s Plan for Composting to Make a Difference over Waste; Pacific Scoop: Wellington, New Zealand, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Given, B.B. List of insects collected on Niue Island during February and March, 1959. N. Z. Èntomol. 1968, 4, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenhuis, N.L. Checklist of the Diptera of Niue Island. Int. J. Entomol. 1985, 27, 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- Capuano, C.; Ozaki, M. Yaws in the Western Pacific Region: A Review of the Literature. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 2011, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wachkoo, A.A.; Shah, G.M.; Jan, U.; Akbar, S.A. A checklist of soldierflies (Diptera, Stratiomyidae) in India. J. Asia Pac. Biodivers. 2017, 10, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, M.T. A new Hermetia of potential economic importance (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Pac. Insects 1972, 14, 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi, J. Edible Insects of the World; CRC Press, Tayor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; p. 286. [Google Scholar]
- Hutton, A.F. Butterfly farming in Papua New Guinea. Oryx 1985, 19, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, R.W. Disease-bearing Insects in Samoa. Bull. Èntomol. Res. 1914, 4, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satchell, G.; Harrison, R., II. Experimental observations on the possibility of transmission of yaws by wound-feeding Diptera, in Western Samoa. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1953, 47, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kami, K.S.; Miller, S.E. Samoan Insects and Related Arthropods: Checklist and Bibliography; Bishop Museum: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1998; Volume 13, p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Rozkosný, R. A Clitellariinae, Hermediinae, Pachygasterinae and Bibliography. In Biosystematic Study of the European Stratiomyidae (Diptera); Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- James, M.T. Flies of the Family Stratiomyidae of the Solomon Islands. Proc. U. S. Natl. Mus. 1948, 98, 187–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, S.J.; Forster, T.; Himmelsbach, J.; Korte, L.; Mucke, P.; Radtke, K.; Theilbörger, P.; Weller, D. World Risk Report 2019—Focus: Water Supply; Bündnis Entwicklung Hilft: Berlin, Germany, 2019; p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Kurahashi, H. The tribe Calliphorini from Australian and Oriental regions, II. Calliphora-group (Diptera: Calliphoridae). Pac. Insects 1971, 13, 141–204. [Google Scholar]
- Swan, T.; Harding, J. The distribution and occurrence of mosquito larvae (Diptera: Culicidae) in the Tongatapu Island Group, Kingdom of Tonga. Austral. Èntomol. 2016, 56, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmaraju, E. Pest problems of crops in Tuvalu. Alafua Agric. Bull. 1980, 5, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, K.A. An Annotated Bibliography of the Natural History of Tuvalu (Ellice Islands). Pac. Sci. 1985, 39, 100–130. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Report to the Government of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony on a Survey of Insect Pests of Crops, Based on the Work of Peter D. Manser; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1974; p. 35. [Google Scholar]
- Rainbow, W.J. The Insect Fauna. In The Atoll of Funafuti, Ellice Group: Its Zoology, Botany, Ethnology and General Structure Based on Collections Made by Charles Hedley of the Australian Museum, Sydney, N.S.W.; Australian Museum: Sydney, Australia, 1900; pp. 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, K.A.; Cantrell, C. The biology and geology of Tuvalu: An annotated bibliography. Tech. Rep. Aust. Mus. 1988, 1, 1–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Waste Management and Pollution Control Strategy and Implementation Plan 2016–2020; Vanuatu Department of Environmental Protection and Conservation: Port Vila, Vanuatu, 2016; p. 59.
- James, M.T. The Stratiomyidae (Diptera) of New Caledonia and the New Hebrides with notes on the Solomon Islands forms. J. Wash. Acad. Sci. 1950, 40, 248–260. [Google Scholar]
- Jayanegara, A.; Novandri, B.; Yantina, N.; Ridla, M. Use of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) to substitute soybean meal in ruminant diet: An in vitro rumen fermentation study. Veter. World 2017, 10, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zheng, L.; Qiu, N.; Cai, H.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Yu, Z. Bioconversion of dairy manure by black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) for biodiesel and sugar production. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, H.M.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Lambert, B.; Kattes, D. Development of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae fed dairy manure. Environ. Èntomol. 2008, 37, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, K.L.; Sarty, M.; Lester, P.J. The ants of Tokelau. N. Z. J. Zoöl. 2006, 33, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinckley, A.D. Ecology of Terrestrial Arthropods on the Tokelau Atolls; The Smithsonian Institution: Washington, DC, USA, 1969; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- Muna-Brecht, C. Progress Report for FW15-041: Raising Black Soldier Fly Larvae as Chicken Feed in a Tropical Region; Sustainable Agriculture Research & Education: College Park, MD, USA, 2018; Available online: https://projects.sare.org/project-reports/fw15-041/ (accessed on 6 May 2020).
- Shiao, S.-F.; Yang, S.-T.; Kurahashi, H. Keys to the blow flies of Taiwan, with a checklist of recorded species and the description of a new species of Paradichosia Senior-White (Diptera, Calliphoridae). ZooKeys 2014, 434, 57–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.C.; Cunha, L.M.; Sousa-Pinto, B.; Fonseca, J.A. Allergic risks of consuming edible insects: A systematic review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 62, 1700030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.E. Biogeography of Pacific insects and other terrestrial invertebrates: A Status report. In The Origin and Evolution of Pacific Island Biotas, New Guinea to Eastern Polynesia: Patterns and Processes; Keast, A., Miller, S.E., Eds.; SPB Academic Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 463–475. [Google Scholar]
- Tora Vueti, E.; Allwood, A.J.; Leweniqila, L.; Ralulu, L.; Balawakula, A.; Malau, A.; Sales, F.; Peleti, K. Fruit fly fauna in Fiji, Tuvalu, Wallis and Futuna, Tokelau and Nauru. In Proceedings of the Management of Fruit Flies in the Pacific, Nadi, Fiji, 28–31 October 1996; pp. 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Anankware, P.; Fening, K.O.; Osekre, E.; Obeng-Ofori, D. Insects as food and feed: A review. Int. J. Agric. Res. Rev. 2015, 3, 143–151. [Google Scholar]
- Hounkonnou, D.; Kossou, D.; Kuyper, T.; Leeuwis, C.; Richards, P.; Röling, N.; Sakyi-Dawson, O.; Van Huis, A. Convergence of sciences: The management of agricultural research for small-scale farmers in Benin and Ghana. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2006, 53, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbi, S.; Macavei, L.I.; Fuso, A.; Luparelli, A.V.; Caligiani, A.; Ferrari, A.M.; Maistrello, L.; Montorsi, M. Valorization of seasonal agri-food leftovers through insects. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.W.; Mohd-Noor, S.-N.; Wong, C.-Y.; Lam, M.-K.; Goh, P.-S.; Beniers, J.; Chan, W.P.; Jumbri, K.; Ghani, N.A. Palatability of black soldier fly larvae in valorizing mixed waste coconut endosperm and soybean curd residue into larval lipid and protein sources. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduh, M.Y.; Manurung, R.; Faustina, A.; Affanda, E.; Siregar, I.R.H. Bioconversion of Pandanus tectorius using black soldier fly larvae for the production of edible oil and protein-rich biomass. J. Entomol. Zool Stud. 2017, 5, 803–809. [Google Scholar]
- Suantika, G.; Putra, R.E.; Hutami, R.; Rosmiati, M. Application of compost produced by bioconversion of coffee husk by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) as solid fertilizer to lettuce (Lactuca sativa Var. Crispa). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Green Technology, Rome, Italy, 18–20 July 2017; Volume 8, pp. 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Supriyatna, A.; Manurung, R.; Esyanthi, R.; Putra, R.E. Growth of black soldier larvae fed on cassava peel wastes, An agriculture waste. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2016, 4, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Hem, S.; Toure, S.; Sagbla, C.; Legendre, M. Bioconversion of palm kernel meal for aquaculture: Experiences from the forest region (Republic of Guinea). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, D.C. Toxicity of Citrus Peel, Liquids to the House Fly. J. Agric. Entomol. 1984, 1, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, C. Tap Versus Bottle: A Mixed Methods Analysis of Public Water Supply and the Bottled Water Industry in the United States. Master’s Thesis, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, Madison, WI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Saffu, K. The role and impact of culture on South Pacific island entrepreneurs. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2003, 9, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PSIDS | Population 1 | Land Area 2 | Agric. Land 2 | Agric. Labor 2 | BSF | GRW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cook Islands | 17,564 | 236 square kilometers | 8.4% | 29.0% | Yes | No |
| F.S. Micronesia | 115,023 | 702 | 25.5 | 0.9 | Yes | No |
| Fiji | 896,445 | 18,274 | 23.3 | 44.0 | - | Yes |
| Kiribati | 119,449 | 811 | 12.5 | 15.0 | Yes | No |
| Marshall Islands | 59,190 | 181 | 33.4 | 11.0 | Yes | Yes |
| Nauru | 10,824 | 21 | 20.0 | 0 | - | Yes |
| Niue | 1626 | 260 | 19.1 | - | - | No |
| Palau | 18,094 | 459 | 10.8 | 1.2 | Yes | Yes |
| PNG | 8,947,024 | 462,840 | 2.6 | 85.0 | Yes | No |
| Samoa | 198,414 | 2831 | 12.4 | 65.0 | Yes | No |
| Solomon Islands | 686,884 | 28,896 | 3.9 | 75.0 | Yes | No |
| Tokelau 3 | 1357 | 12 | 60.0 | - | - | No |
| Tonga | 105,695 | 747 | 43.1 | 27.5 | - | No |
| Tuvalu | 11,792 | 26 | 60.0 | - | - | Yes |
| Vanuatu | 307,145 | 12,189 | 15.3 | 65.0 | Yes | No |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shelomi, M. Potential of Black Soldier Fly Production for Pacific Small Island Developing States. Animals 2020, 10, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10061038
Shelomi M. Potential of Black Soldier Fly Production for Pacific Small Island Developing States. Animals. 2020; 10(6):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10061038
Chicago/Turabian StyleShelomi, Matan. 2020. "Potential of Black Soldier Fly Production for Pacific Small Island Developing States" Animals 10, no. 6: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10061038
APA StyleShelomi, M. (2020). Potential of Black Soldier Fly Production for Pacific Small Island Developing States. Animals, 10(6), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10061038