Effect of Medetomidine, Dexmedetomidine, and Their Reversal with Atipamezole on the Nociceptive Withdrawal Reflex in Beagles
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Size, Design
2.2. Animals
2.3. Randomization, Blinding and Treatment
2.4. Animal Preparation
2.5. NWR Threshold Determination
2.6. Sedation
2.7. Physiological Variables
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phase 1 (T0–T44, MED Versus DEX)
3.1.1. Sedation
3.1.2. Nociceptive Withdrawal Reflexes
3.1.3. Physiological Variables
3.2. Phase 2 (T45–T210, ATI Versus SAL)
3.2.1. Sedation
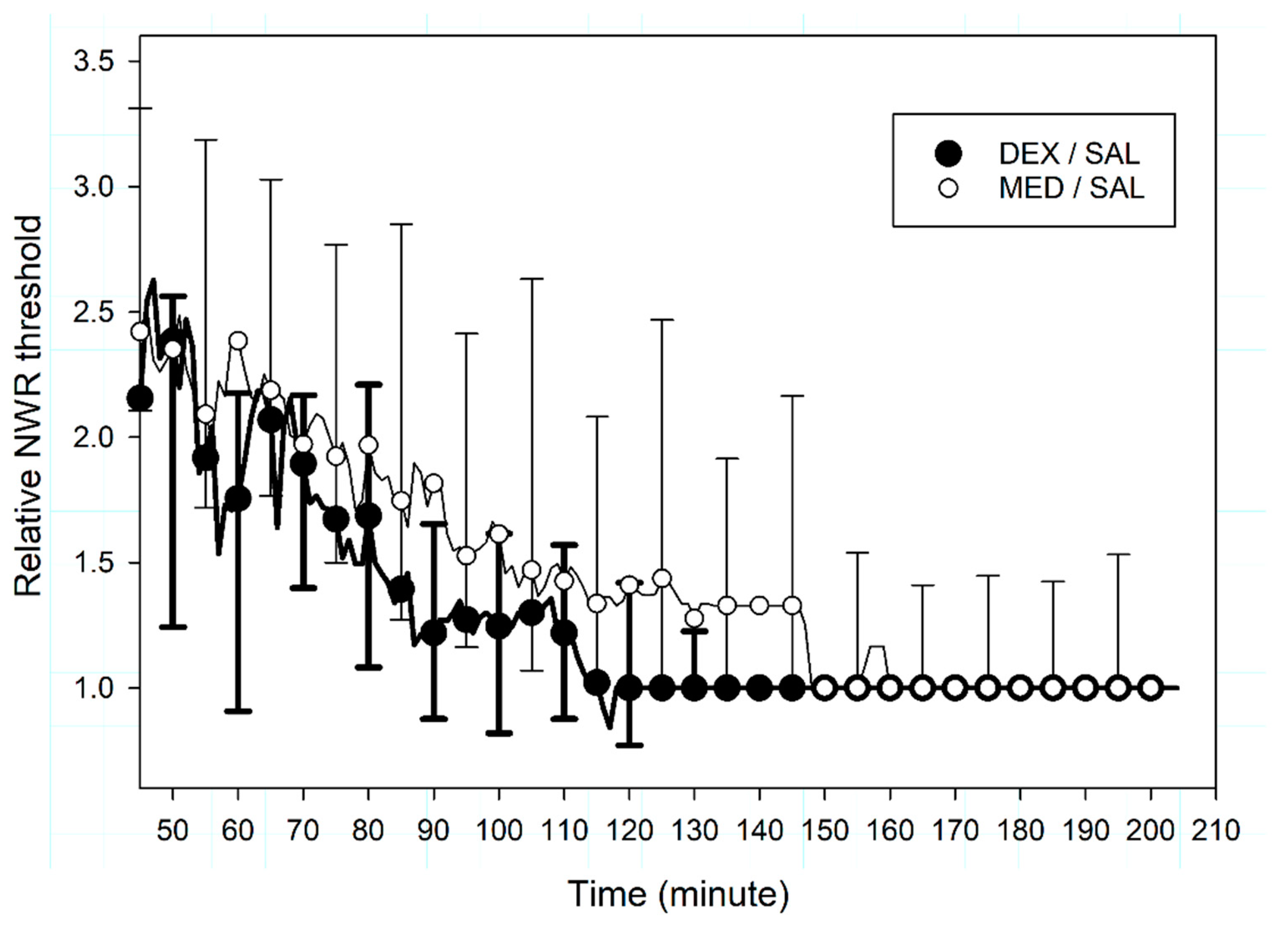
3.2.2. Nociceptive Withdrawal Reflexes
3.2.3. Physiological Variables
3.3. Additional Observations on the Effect Offset
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpretation
4.2. Limitations
4.3. Harm
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Truchetti, G.; Otis, C.; Brisville, A.C.; Beauchamp, G.; Pang, D.; Troncy, E. Management of veterinary anaesthesia in small animals: A survey of current practice in Quebec. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, J.C.; Hellebrekers, L.J. Medetomidine and dexmedetomidine: A review of cardiovascular effects and antinociceptive properties in the dog. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2005, 32, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuusela, E.; Raekallio, M.; Anttila, M.; Falck, I.; Molsa, S.; Vainio, O. Clinical effects and pharmacokinetics of medetomidine and its enantiomers in dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 23, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granholm, M.; McKusick, B.C.; Westerholm, F.C.; Aspegren, J.C. Evaluation of the clinical efficacy and safety of intramuscular and intravenous doses of dexmedetomidine and medetomidine in dogs and their reversal with atipamezole. Vet. Rec. 2007, 160, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, E.; Scheinin, M.; Scheinin, H.; Virtanen, R. Comparison of the behavioral and neurochemical effects of the two optical enantiomers of medetomidine, a selective alpha-2-adrenoceptor agonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1991, 259, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuusela, E.; Raekallio, M.; Vaisanen, M.; Mykkanen, K.; Ropponen, H.; Vainio, O. Comparison of medetomidine and dexmedetomidine as premedicants in dogs undergoing propofol-isoflurane anesthesia. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Villamandos, R.J.; Palacios, C.; Benitez, A.; Granados, M.M.; Dominguez, J.M.; Lopez, I.; Ruiz, I.; Aguilera, E.; Santisteban, J.M. Dexmedetomidine or medetomidine premedication before propofol-desflurane anaesthesia in dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 29, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raszplewicz, J.; Macfarlane, P.; West, E. Comparison of sedation scores and propofol induction doses in dogs after intramuscular premedication with butorphanol and either dexmedetomidine or medetomidine. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2013, 40, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vainio, O.; Vaha-Vahe, T.; Palmu, L. Sedative and analgesic effects of medetomidine in dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1989, 12, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyner, C.L.; Woody, B.J.; Reid, J.S.; Chafetz, E.P.; Lederer, H.A.; Norton, J.F.; Keefe, T.J.; Jochle, W. Multicenter clinical comparison of sedative and analgesic effects of medetomidine and xylazine in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1997, 211, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Barnhart, M.D.; Hubbell, J.A.; Muir, W.W. Evaluation of the analgesic properties of acepromazine maleate, oxymorphone, medetomidine and a combination of acepromazine-oxymorphone. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2000, 27, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, K.A.; Tranquilli, W.J.; Thurmon, J.C.; Benson, G.J. Duration of nonresponse to noxious stimulation after intramuscular administration of butorphanol, medetomidine, or a butorphanol-medetomidine combination during isoflurane administration in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 61, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, R.C.; Salla, K.M.; Raekallio, M.R.; Hanninen, L.; Rinne, V.M.; Scheinin, M.; Vainio, O.M. Effects of MK-467 on the antinociceptive and sedative actions and pharmacokinetics of medetomidine in dogs. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 39, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.; Horais, K.A.; Tozier, N.A.; Rathbun, M.L.; Shtaerman, Y.; Yaksh, T.L. Development of a canine nociceptive thermal escape model. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 168, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuusela, E.; Vainio, O.; Kaistinen, A.; Kobylin, S.; Raekallio, M. Sedative, analgesic, and cardiovascular effects of levomedetomidine alone and in combination with dexmedetomidine in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergadano, A.; Andersen, O.K.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Schatzmann, U.; Spadavecchia, C. Quantitative assessment of nociceptive processes in conscious dogs by use of the nociceptive withdrawal reflex. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2006, 67, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, H.; Zeiter, S.; Andersen, O.K.; Wieling, R.; Spadavecchia, C. Quantitative assessment of the nociceptive withdrawal reflex in healthy, non-medicated experimental sheep. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 129, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadavecchia, C.; Spadavecchia, L.; Andersen, O.K.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Leandri, M.; Schatzmann, U. Quantitative assessment of nociception in horses by use of the nociceptive withdrawal reflex evoked by transcutaneous electrical stimulation. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2002, 63, 1551–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergadano, A.; Andersen, O.K.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Spadavecchia, C. Modulation of nociceptive withdrawal reflexes evoked by single and repeated nociceptive stimuli in conscious dogs by low-dose acepromazine. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2009, 36, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergadano, A.; Andersen, O.K.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Theurillat, R.; Thormann, W.; Spadavecchia, C. Plasma levels of a low-dose constant-rate-infusion of ketamine and its effect on single and repeated nociceptive stimuli in conscious dogs. Vet. J. 2009, 182, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levionnois, O.L.; Menge, M.; Thormann, W.; Mevissen, M.; Spadavecchia, C. Effect of ketamine on the limb withdrawal reflex evoked by transcutaneous electrical stimulation in ponies anaesthetised with isoflurane. Vet. J. 2010, 186, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lervik, A.; Haga, H.A.; Ranheim, B.; Spadavecchia, C. The influence of a continuous rate infusion of dexmedetomidine on the nociceptive withdrawal reflex and temporal summation during isoflurane anaesthesia in dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2012, 39, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrbach, H.; Korpivaara, T.; Schatzmann, U.; Spadavecchia, C. Comparison of the effects of the alpha-2 agonists detomidine, romifidine and xylazine on nociceptive withdrawal reflex and temporal summation in horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2009, 36, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spadavecchia, C.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Andersen, O.K.; Spadavecchia, L.; Schatzmann, U. Effect of romifidine on the nociceptive withdrawal reflex and temporal summation in conscious horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2005, 66, 1992–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Dincklage, F.; Hackbarth, M.; Schneider, M.; Baars, J.H.; Rehberg, B. Introduction of a continual RIII reflex threshold tracking algorithm. Brain Res. 2009, 1260, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaha-Vahe, A.T. The clinical effectiveness of atipamezole as a medetomidine antagonist in the dog. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1990, 13, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleyers, T.; Siegenthaler, J.; Levionnois, O.L.; Spadavecchia, C.; Raillard, M. Investigation of selected respiratory effects of (dex)medetomidine in healthy beagles. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2020, Accepted, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugelberg, E.; Eklund, K.; Grimby, L. An electromyographic study of the nociceptive reflexes of the lower limb. Mechanism of the plantar responses. Brain 1960, 83, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, D.; Cescon, C.; Merletti, R. Influence of anatomical, physical, and detection-system parameters on surface EMG. Biol. Cybern. 2002, 86, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergadano, A.; Andersen, O.K.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Spadavecchia, C. Noninvasive assessment of the facilitation of the nociceptive withdrawal reflex by repeated electrical stimulations in conscious dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2007, 68, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grint, N.J.; Burford, J.; Dugdale, A.H. Does pethidine affect the cardiovascular and sedative effects of dexmedetomidine in dogs? J. Small Anim. Pract. 2009, 50, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez Bernal, S.; Studer, N.; Thormann, W.; Spadavecchia, C.; Levionnois, O. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling of the antinociceptive effect of a romifidine infusion in standing horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2020, 47, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McShane, B.B.; Gal, D. Statistical significance and the dichotomization of evidence. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2007, 112, 885–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserstein, R.L.; Schirm, A.L.; Lazar, N.A. Moving to a world beyond “p<0.05”. Am. Stat. 2009, 73, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela, E. Dexmedetomidine and Levomedetomidine, the Isomers of Medetomidine, in Dogs. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland, 2004; p. 69. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, J.C.; Fox, S.M.; Mandsager, R.E. Sedative and cardiorespiratory effects of medetomidine, medetomidine-butorphanol, and medetomidine-ketamine in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 216, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansah, O.B.; Raekallio, M.; Vainio, O. Comparison of three doses of dexmedetomidine with medetomidine in cats following intramuscular administration. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 21, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.C.; Hecker, K.G.; Pang, D.S.J. Sedation levels in dogs: A validation study. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, R.G.; Sheridan, B.C.; Segal, I.S.; Maze, M. Anesthetic and hemodynamic effects of the stereoisomers of medetomidine, an alpha 2-adrenergic agonist, in halothane-anesthetized dogs. Anesth. Analg. 1988, 67, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granholm, M.; McKusick, B.C.; Westerholm, F.C.; Aspegren, J.C. Evaluation of the clinical efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine or medetomidine in cats and their reversal with atipamezole. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2006, 33, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragiotta, G.; Pierelli, F.; Coppola, G.; Conte, C.; Perrotta, A.; Serrao, M. Effect of phobic visual stimulation on spinal nociception. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 206, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhudy, J.L.; Meagher, M.W. Fear and anxiety: Divergent effects on human pain thresholds. Pain 2000, 84, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neziri, A.Y.; Andersen, O.K.; Petersen-Felix, S.; Radanov, B.; Dickenson, A.H.; Scaramozzino, P.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Curatolo, M. The nociceptive withdrawal reflex: Normative values of thresholds and reflex receptive fields. Eur. J. Pain 2010, 14, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, D.J.; France, C.R.; France, J.L.; Arnott, L.F. The influence of acute anxiety on assessment of nociceptive flexion reflex thresholds in healthy young adults. Pain 2005, 114, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillingim, R.B.; Ness, T.J. Sex-related hormonal influences on pain and analgesic responses. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.W.; Dallaire, M. Subjective pain sensation is linearly correlated with the flexion reflex in man. Brain Res. 1989, 479, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikasa, Y.; Ogasawara, S.; Takase, K. Alpha adrenoceptor subtypes involved in the emetic action in dogs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1992, 261, 746–754. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, M.D. A review of the physiological effects of alpha2-agonists related to the clinical use of medetomidine in small animal practice. Can. Vet. J. 2003, 44, 885–897. [Google Scholar]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siegenthaler, J.; Pleyers, T.; Raillard, M.; Spadavecchia, C.; Levionnois, O.L. Effect of Medetomidine, Dexmedetomidine, and Their Reversal with Atipamezole on the Nociceptive Withdrawal Reflex in Beagles. Animals 2020, 10, 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071240
Siegenthaler J, Pleyers T, Raillard M, Spadavecchia C, Levionnois OL. Effect of Medetomidine, Dexmedetomidine, and Their Reversal with Atipamezole on the Nociceptive Withdrawal Reflex in Beagles. Animals. 2020; 10(7):1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071240
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiegenthaler, Joëlle, Tekla Pleyers, Mathieu Raillard, Claudia Spadavecchia, and Olivier Louis Levionnois. 2020. "Effect of Medetomidine, Dexmedetomidine, and Their Reversal with Atipamezole on the Nociceptive Withdrawal Reflex in Beagles" Animals 10, no. 7: 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071240
APA StyleSiegenthaler, J., Pleyers, T., Raillard, M., Spadavecchia, C., & Levionnois, O. L. (2020). Effect of Medetomidine, Dexmedetomidine, and Their Reversal with Atipamezole on the Nociceptive Withdrawal Reflex in Beagles. Animals, 10(7), 1240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10071240




