Research on the Applications of Calcium Propionate in Dairy Cows: A Review
Abstract
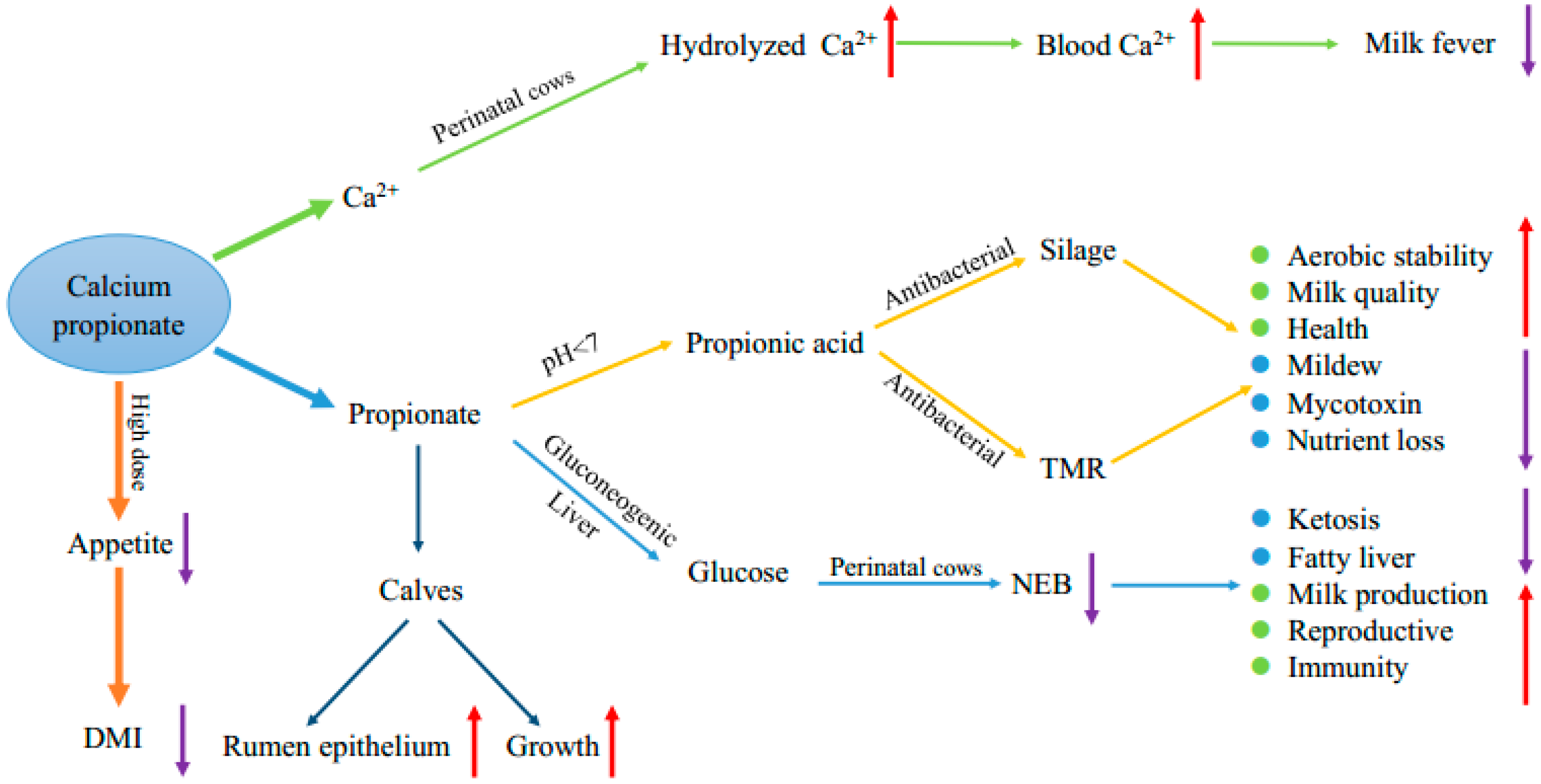
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Properties of Calcium Propionate
2.1. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Calcium Propionate
2.2. Antibacterial Properties of Calcium Propionate
2.3. Nutritive Properties of Calcium Propionate
3. The Application of Calcium Propionate in Dairy Cows
3.1. Application in Silage to Resist Mildew
3.2. Application in TMR to Increase the Aerobic Stability
3.3. Application as a Gluconeogenic Precursor to Alleviate NEB in the Perinatal Period
3.4. Application as a Source of Calcium to Prevent Milk Fever in the Perinatal Period
3.5. Application in Dairy Calves to Regulate Rumen Development or Improve Growth
4. Limitation of Calcium Propionate in Application
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Currently, research on calcium propionate in dairy cows has been mainly carried out by oral feeding alone, which is not convenient for application in practical production. Therefore, to improve the application effectiveness of calcium propionate in dairy cows, more studies are needed to determine the optimal feeding level when calcium propionate is mixed with TMR. When calcium propionate is used to prevent NEB and milk fever, the optimal feeding ratio should be revealed according to a cows’ milk production level and body condition;
- (2)
- Excessive calcium propionate feeding has been shown to inhibit the appetite and limit the intake. To avoid its adverse effects, the maximum feeding level, influencing factor, and adverse impact of calcium propionate in dairy cows need to be further studied;
- (3)
- Calcium propionate can be used as an anti-mildew additive in silage and can also be directly added to feed to prevent several metabolic diseases of dairy cows during the perinatal period. However, few studies on the effects of silage with calcium propionate on perinatal dairy cows have been conducted. Therefore, research in this field is worth exploring.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, S.M.; DeVries, T.J. Effect of diet-induced negative energy balance on the feeding behavior of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 7288–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, J.P.; Hohman, A.; Timms, L.L. Effect of subclinical and clinical hypocalcemia and dietary cation-anion difference on rumination activity in periparturient dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 2591–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Blanco, M.; Ramos, A.J.; Sanchis, V.; Marín, S. Mycotoxins occurrence and fungal populations in different types of silages for dairy cows in Spain. Fungal Biol. UK 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.R.; Prichard, A.S.; Maerz, N.L.; Prichard, A.P.; Endres, E.L.; Hernandez-Castellano, L.E.; Akins, M.S.; Bruckmaier, R.M.; Hernandez, L.L. Elevating serotonin pre-partum alters the Holstein dairy cow hepatic adaptation to lactation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequeira, S.O.; Phillips, A.J.L.; Cabrita, E.J.; Macedo, M.F. Antifungal treatment of paper with calcium propionate and parabens: Short-term and long-term effects. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2017, 120, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrazola, A.; Torrey, S. Conditioned place avoidance using encapsulated calcium propionate as an appetite suppressant for broiler breeders. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e206271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Chen, W.B.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.W.; Jiang, Y.M.; Meng, Q.X.; Zhou, Z.M. Calcium propionate supplementation improves development of rumen epithelium in calves via stimulating G protein-coupled receptors. Animal 2018, 12, 2284–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongsavee, M. Effects of 3300 del A-1061 Ter BRCA1 frameshift mutation and calcium propionate on oxidative stress and breast carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Genet. 2019, 10, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, S.; Shah, H.U.; Afzal, M.; Magan, N. Influence of calcium propionate, water activity and storage time on mold incidence and aflatoxins production in broiler starter feed. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2014, 188, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saftner, R.A.; Bai, J.; Abbott, J.A.; Lee, Y.S. Sanitary dips with calcium propionate, calcium chloride, or a calcium amino acid chelate maintain quality and shelf stability of fresh-cut honeydew chunks. Postharvest Biol. Tech. 2003, 29, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, C.A.; Dollimore, D. A study of the decomposition of calcium propionate, using simultaneous TG-DTA. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 357–358, 1–334. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Williams, T.C.; Divne, C.; Pretorius, I.S.; Paulsen, I.T. Evolutionary engineering in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals a TRK1-dependent potassium influx mechanism for propionic acid tolerance. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhr, K.I.; Nielsen, P.V. Effect of weak acid preservatives on growth of bakery product spoilage fungi at different water activities and pH values. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 95, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bintvihok, A.; Kositcharoenkul, S. Effect of dietary calcium propionate on performance, hepatic enzyme activities and aflatoxin residues in broilers fed a diet containing low levels of aflatoxin B1. Toxicon 2006, 47, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, T.Y.; Kim, N.H.; Rhee, M.S. Response surface methodology-based optimization of decontamination conditions for Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium on fresh-cut celery using thermoultrasound and calcium propionate. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 150, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, A.; Yuan, X.; Wang, J.; Desta, S.T.; Shao, T. Effects of four short-chain fatty acids or salts on dynamics of fermentation and microbial characteristics of alfalfa silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2017, 223, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, A.F.; Gamba, R.R.; Puppo, J.; Malo, N.; Gómez-Zavaglia, A.; Peláez, Á.L.; Golowczyc, M.A. Incorporation of Lactobacillus plantarum and zeolites in poultry feed can reduce aflatoxin B1 levels. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiles, A.; Hernando, I.; Perez-Munuera, I.; Lluch, M.A. Effect of calcium propionate on the microstructure and pectin methy-lesterase activity in the parenchyma of fresh-cut Fuji apples. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2007, 87, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, L.A.M.; Dal Bello, F.; Arendt, E.K. The use of sourdough fermented by antifungal LAB to reduce the amount of calcium propionate in bread. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 125, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkens, M.R.; Nelson, C.D.; Hernandez, L.L.; McArt, J.A.A. Symposium review: Transition cow calcium homeostasis—Health effects of hypocalcemia and strategies for prevention. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 2909–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemosquet, S.; Delamaire, E.; Lapierre, H.; Blum, J.W.; Peyraud, J.L. Effects of glucose, propionic acid, and nonessential amino acids on glucose metabolism and milk yield in Holstein dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3244–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemosquet, S.; Raggio, G.; Lobley, G.E.; Rulquin, H.; Guinard-Flament, J.; Lapierre, H. Whole-body glucose metabolism and mammary energetic nutrient metabolism in lactating dairy cows receiving digestive infusions of casein and propionic acid. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 6068–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duplessis, M.; Lapierre, H.; Ouattara, B.; Bissonnette, N.; Pellerin, D.; Laforest, J.P.; Girard, C.L. Whole-body propionate and glucose metabolism of multiparous dairy cows receiving folic acid and vitamin B12 supplements. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8578–8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldini, G.; Kennedy, K.M.; Allen, M.S. Temporal effects of ruminal infusion of propionic acid on hepatic metabolism in cows in the postpartum period. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9781–9790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.M. The role of TCA cycle anaplerosis in ketosis and fatty liver in periparturient dairy cows. Animals 2015, 5, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Aispura, J.A.; Sanchez-Torres, M.T.; Mendoza-Martinez, G.D.; Cordero-Mora, J.L.; Figueroa-Velasco, J.L.; Ayala-Monter, M.A.; Crosby-Galvan, M.M. Addition of calcium propionate to finishing lamb diets. Veterinaria Mexico 2018, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Rangel, H.A.; Mendoza, G.D.; González, S.S. Effect of calcium propionate and sorghum level on lamb performance. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2012, 177, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Meng, Q.X.; Lu, L.; Cui, Z.L.; Ren, L.P. The effect of calcium propionate supplementation on performance, meat quality, and mRNA expression of finishing steers fed a high-concentrate diet. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2015, 24, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, O.C.M.; Ogunade, I.M.; Weinberg, Z.; Adesogan, A.T. Silage review: Foodborne pathogens in silage and their mitigation by silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4132–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, M.O.; Stern, M.D.; Soraci, A.L.; Meronuck, R.; Olson, W.; Gold, S.; Koski-Hulbert, R.L.; Murphy, M.J. Patulin-producing molds in corn silage and high moisture corn and effects of patulin on fermentation by ruminal microbes in continuous culture. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2005, 119, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanier, C.; Richard, E.; Heutte, N.; Picquet, R.; Bouchart, V.; Garon, D. Airborne molds and mycotoxins associated with handling of corn silage and oilseed cakes in agricultural environment. Atmos. Env. 2010, 44, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Myers, C.L.; Neylon, J.M.; Taylor, C.C.; Lazartic, J.; Mills, J.A.; Whiter, A.G. The effects of buffered propionic acid-based additives alone or combined with microbial inoculation on the fermentation of high moisture corn and whole-crop barley. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Yuan, X.; Wen, A.; Desta, S.T.; Shao, T. Effects of calcium propionate on the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of alfalfa silage. Asian Austral. J. Anim. 2017, 30, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, S.; Shah, H.U.; Magan, N. Effect of calcium propionate and water activity on growth and aflatoxins production by Aspergillus flavus. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, M61–M64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wen, A.; Desta, S.T.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Effects of four short-chain fatty acids or salts on the dynamics of nitrogen transformations and intrinsic protease activity of alfalfa silage. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2017, 97, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceciliani, F.; Lecchi, C.; Urh, C.; Sauerwein, H. Proteomics and metabolomics characterizing the pathophysiology of adaptive reactions to the metabolic challenges during the transition from late pregnancy to early lactation in dairy cows. J. Proteomics 2018, 178, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingvartsen, K.L.; Andersen, J.B. Integration of metabolism and intake regulation: A review focusing on periparturient animals. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1573–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, A.I.; Burrough, E.; Forrest, J.; Corbishley, A.; Russell, G.; Shaw, D.J. Prevalence of excessive negative energy balance in commercial United Kingdom dairy herds. Vet. J. 2019, 248, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, M.A.; El-Gohary, E.S.; Gabr, A.A.; El-Hawary, A.F.; Ahmed, S.A.; Ebrahim, S.A.; Fathala, M.M. Impact of supplementing propylene glycol and calcium propionate to primiparous buffalo cows during the late gestation and early lactation period on reproductive performance and metabolic parameters. Alex. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 51, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, J.P.; Valdez, F. Adipose tissue metabolism and production responses to calcium propionate and chromium propionate. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2498–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingvartsen, K.L.; Moyes, K. Nutrition, immune function and health of dairy cattle. Animal 2013, 71, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Liu, G.; Yin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Q.; Shi, K.; Wang, Z. Effects of supplemental dietary energy source on feed intake, lactation performance, and serum indices of early-lactating Holstein cows in a positive energy balance. Adv. Biosci. Biotech. 2017, 8, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mendoza-Martinez, G.D.; Pinos-Rodriguez, J.M.; Lee-Rangel, H.A.; Hernandez-Garcia, P.A.; Rojo-Rubio, R.; Relling, A. Effects of dietary calcium propionate on growth performance and carcass characteristics of finishing lambs. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2016, 56, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Koser, S.L.; Donkin, S.S. Propionate induces mRNA expression of gluconeogenic genes in bovine calf hepatocytes. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3908–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drackley, J.K. Biology of dairy cows during the transition period: The final frontier? J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 2259–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Yang, W.Z.; Guo, G.; Yang, X.M.; He, D.C.; Dong, K.H.; Huang, Y.X. Effects of calcium propionate supplementation on lactation performance, energy balance and blood metabolites in early lactation dairy cows. J. Anim. Physiol. N. 2010, 94, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, R.S.; Sorenson, C.E.; Hippen, A.R. Effects of dietary glucogenic precursors and fat on feed intake and carbohydrate status of transition dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 2122–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, W.D.C.; Cunha, S.H.M.; Boscarato, A.G.; Lima, J.S.D.; Esteves Junior, J.D.; Uliana, G.L.T.; Pedrini, M.T.; Alberton, L.R. Blood parameters of lactating cows fed calcium salts as energetic source. Acta Sci. Vet. 2018, 46, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, W.D.C.; Mioso Cunha, S.H.; Boscarato, A.G.; de Lima, J.S.; Esteves Junior, J.D.; Uliana, G.C.; Pedrini, M.; Alberton, L.R. Calcium propionate increased milk parameters in Holstein cows. Acta Sci. Vet. 2019, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto Miranda, L.; Aaron Lee-Rangel, H.; David Mendoza-Martinez, G.; Magdalena Crosby-Galvan, M.; Enrique Relling, A.; Manuel Pinos-Rodriguez, J.; Rojo Rubio, R.; Gonzalez Hernandez, M. Influence of calcium propionate on in vitro fermentation of sorghum-based diets. Rev. Fac. Cienc. Agrar. 2017, 49, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Saborío-Montero, A.; Vargas-Leitón, B.; Romero-Zúñiga, J.J.; Camacho-Sandoval, J. Additive genetic and heterosis effects for milk fever in a population of Jersey, Holstein × Jersey, and Holstein cattle under grazing conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9128–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, R.C.; Leno, B.M.; Bach, K.D.; McArt, J.A.A. Epidemiology of subclinical hypocalcemia in early-lactation Holstein dairy cows: The temporal associations of plasma calcium concentration in the first 4 days in milk with disease and milk production. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9321–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulligan, F.J.; O’Grady, L.; Rice, D.A.; Doherty, M.L. A herd health approach to dairy cow nutrition and production diseases of the transition cow. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2006, 96, 331–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, J.P. The monitoring, prevention, and treatment of milk fever and subclinical hypocalcemia in dairy cows. Vet. J. 2008, 176, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, C.R.; Erb, H.N.; Sniffen, C.J.; Smith, R.D.; Powers, P.A.; Smith, M.C.; White, M.E.; Hillman, R.B.; Pearson, E.J. Association of parturient hypocalcemia with eight periparturient disorders in Holstein cows. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1983, 183, 559–561. [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Tereso, J.; Martens, H. Calcium and magnesium physiology and nutrition in relation to the prevention of milk fever and tetany (dietary management of macrominerals in preventing disease). Vet. Clin. North America: Food Anim. Pract. 2014, 30, 643–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Castellano, L.E.; Hernandez, L.L.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Review: Endocrine pathways to regulate calcium homeostasis around parturition and the prevention of hypocalcemia in periparturient dairy cows. Animal 2020, 14, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Castellano, L.E.; Hernandez, L.L.; Sauerwein, H.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Endocrine and metabolic changes in transition dairy cows are affected by prepartum infusions of a serotonin precursor. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 5050–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkens, M.R.; Mrochen, N.; Breves, G.; Schröder, B. Gastrointestinal calcium absorption in sheep is mostly insensitive to an alimentary induced challenge of calcium homeostasis. Comp. Biochem. Phys. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 158, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkens, M.R.; Richter, J.; Fraser, D.R.; Liesegang, A.; Breves, G.; Schröder, B. In contrast to sheep, goats adapt to dietary calcium restriction by increasing intestinal absorption of calcium. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2012, 163, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, B.; Wilkens, M.R.; Ricken, G.E.; Leonhard-Marek, S.; Fraser, D.R.; Breves, G. Calcium transport in bovine rumen epithelium as affected by luminal Ca concentrations and Ca sources. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyde, M.L.; Wilkens, M.R.; Fraser, D.R. In vivo measurement of strontium absorption from the rumen of dairy cows as an index of calcium absorption capacity. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 5699–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, J.W.; Engle, T.E.; Platter, W.R.; Lloyd, K.E.; Belk, K.E.; Horton, J. Effects of high dietary calcium propionate and dietary cation-anion balance on calcium metabolism and longissimus muscle tenderness in finishing steers. Prof. Anim. Sci. 2003, 19, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, N.; Sinedino, L.D.P.; Bisinotto, R.S.; Daetz, R.; Lopera, C.; Risco, C.A.; Galvão, K.N.; Thatcher, W.W.; Santos, J.E.P. Effects of oral calcium supplementation on mineral and acid-base status, energy metabolites, and health of postpartum dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 8397–8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goff, J.P.; Horst, R.L.; Jardon, P.W.; Borelli, C.; Wedam, J. Field trials of an oral calcium propionate paste as an aid to prevent milk fever in periparturient dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1996, 79, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehrson, B.; Svensson, C.; Jonsson, M. A comparative study of the effectiveness of calcium propionate and calcium chloride for the prevention of parturient paresis in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, C.; Orman, A.; Udum, D.; Yavuz, H.M.; Kovanlikaya, A. Effects of calcium propionate by different numbers of applications in first week postpartum of dairy cows on hypocalcemia, milk production and reproductive disorders. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 8, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Q.; Zhang, R.; Fu, T. Review of strategies to promote rumen development in calves. Animals (Basel) 2019, 9, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamate, H.; McGilliard, A.D.; Jacobson, N.L.; Getty, R. Effect of Various dietaries on the anatomical development of the stomach in the calf. J. Dairy Sci. 1962, 45, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhou, Z. Growth performance and development of internal organ, and gastrointestinal tract of calf supplementation with calcium propionate at various stages of growth period. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.Z.; Meng, Q.X.; Zhou, Z.M. Calcium propionate supplementation alters the ruminal bacterial and archaeal communities in pre- and postweaning calves. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3204–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarian-Tefaghi, M.; Ghasemi, E.; Khorvash, M. Performance, rumen fermentation and blood metabolites of dairy calves fed starter mixtures supplemented with herbal plants, essential oils or monensin. J. Anim. Physiol. N. 2018, 102, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholipour, A.; Shahraki, A.D.F.; Tabeidian, S.A.; Nasrollahi, S.M.; Yang, W.Z. The effects of increasing garlic powder and monensin supplementation on feed intake, nutrient digestibility, growth performance and blood parameters of growing calves. J. Anim. Physiol. N. 2016, 100, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.S.; Bittar, C.M.M. Performance and plasma metabolites of dairy calves fed starter containing sodium butyrate, calcium propionate or sodium monensin. Animal 2011, 5, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossenkopp, K.; Foley, K.A.; Gibson, J.; Fudge, M.A.; Kavaliers, M.; Cain, D.P.; MacFabe, D.F. Systemic treatment with the enteric bacterial fermentation product, propionic acid, produces both conditioned taste avoidance and conditioned place avoidance in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 227, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.S. Effects of diet on short-term regulation of feed intake by lactating dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1598–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, K.M.; Allen, M.S. Hepatic metabolism of propionate relative to meals for cows in the postpartum period. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 7997–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, M.; Allen, M.S. Dose-Response Effects of intrauminal infusion of propionate on feeding behavior of lactating cows in early or midlactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2922–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, M.; Allen, M.S. Extent of hypophagia caused by propionate infusion is related to plasma glucose concentration in lactating dairy cows. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Nan, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Xiong, B. Research on the Applications of Calcium Propionate in Dairy Cows: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081336
Zhang F, Nan X, Wang H, Guo Y, Xiong B. Research on the Applications of Calcium Propionate in Dairy Cows: A Review. Animals. 2020; 10(8):1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081336
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Fan, Xuemei Nan, Hui Wang, Yuming Guo, and Benhai Xiong. 2020. "Research on the Applications of Calcium Propionate in Dairy Cows: A Review" Animals 10, no. 8: 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081336
APA StyleZhang, F., Nan, X., Wang, H., Guo, Y., & Xiong, B. (2020). Research on the Applications of Calcium Propionate in Dairy Cows: A Review. Animals, 10(8), 1336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10081336




