Exploring the Genetic Background of the Differences in Nest-Building Behavior in European Rabbit
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Test Animals
2.3. Housing
2.4. Studying Behavior
2.5. Determining Hormones from Feces
2.6. Sequencing PGR
2.7. Statistical Processing
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Point Mutations
3.2. Examine of Genotype Distributions
3.3. The Linkage Between Point Mutations
3.4. The Relationship between Hay-Carrying Behavior, the Amount of Hay in the Nest and Polymorphisms in the PGR Gene
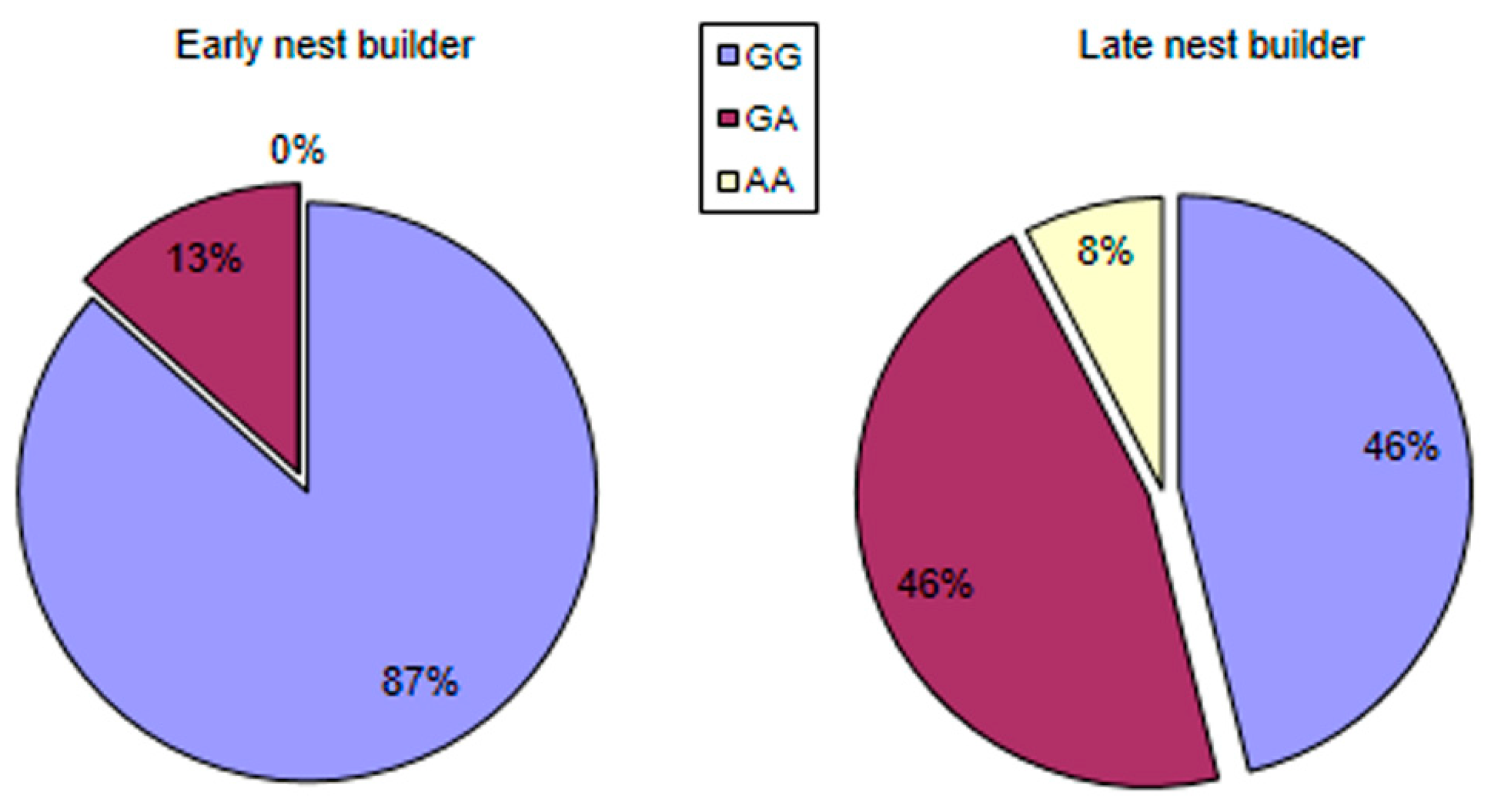
3.5. Allele Distribution in Groups Formed as a Result of Behavioral Cluster Analysis and Heritability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, F.S.; Barth, M.; Johnson, S.L.; Gotlib, I.H.; Johnson, S.C. Oxytocin receptor (OXTR) polymorphisms and attachment in human infants. Front. Psychol. 2011, 2, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumsta, R.; Heinrichs, M. Oxytocin, stress and social behavior: Neurogenetics of the human oxytocin system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kis, A.; Bence, M.; Lakatos, G.; Pergel, E.; Turcsán, B.; Pluijmakers, J.; Vas, J.; Elek, Z.; Brúder, I.; Földi, L.; et al. Oxytocin receptor gene polymorphisms are associated with human directed social behavior in dogs (Canis familiaris). PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hejjas, K.; Vas, J.; Topal, J.; Szantai, E.; Ronai, Z.; Szekely, A.; Kubinyi, E.; Horvath, Z.; Sasvari-Szekely, M.; Miklosi, A. Association of polymorphisms in the dopamine D4 receptor gene and the activity-impulsivity endophenotype in dogs. Anim. Genet. 2007, 38, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Hejjas, K.; Ronai, Z.; Elek, Z.; Sasvari-Szekely, M.; Champagne, F.A.; Miklósi, Á.; Kubinyi, E. DRD 4 and TH gene polymorphisms are associated with activity, impulsivity and inattention in Siberian Husky dogs. Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forstmeier, W.; Mueller, J.C.; Kempenaers, B. A polymorphism in the oestrogen receptor gene explains covariance between digit ratio and mating behaviour. Biol. Sci. 2010, 277, 3353–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, J.A. Nest building behaviour of domestic rabbits under semi-natural conditions. Anim. Behav. 1957, 5, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, R.; Distel, H. The pattern of behaviour of rabbit pups in the nest. Behaviour 1982, 79, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mykytowycz, R. Territorial marking by rabbits. Sci. Am. 1968, 218, 116–129. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/24926233 (accessed on 6 May 2018). [CrossRef]
- von Holst, D.; Hutzelmeyer, H.; Kaetzke, P.; Khaschei, M.; Rödel, H.G.; Schrutka, H. Social rank, fecundity and lifetime reproductive success in wild European rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2002, 51, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltmann, M.W.; Rangassamy, M.; Zapka, M.; Hoffman, K.L.; Rödel, H.G. Timing of maternal nest building and perinatal offspring survival in a group-living small mammal. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2017, 71, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, K.L.; Morales, R.I.R. Toward an understanding of the neurobiology of “just right” perceptions: Nest building in the female rabbit as a possible model for compulsive behavior and the perception of task completion. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 204, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mariscal, G.; Melo, A.I.; Jiménez, P.; Beyer, C.; Rosenblatt, J.S. Estradiol, progesterone, and prolactin regulate maternal nest-building in rabbits. J. Neuroendocrinol. 1996, 8, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mariscal, G.; Cuamatzi, E.; Rosenblatt, J.S. Hormones and external factors: Are they “on/off” signals for maternal nest-building in rabbits? Horm. Behav. 1998, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mariscal, G.; Melo, A.I.; Parlow, A.F.; Beyer, C.; Rosenblatt, J.S. Pharmacological evidence that prolactin acts from late gestation to promote maternal behaviour in rabbits. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2000, 12, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mariscal, G. Neuroendocrinology of maternal behavior in the rabbit. Horm. Behav. 2001, 40, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mariscal, G.; Martínez-Gómez, M.; Bautista, A.; Hudson, R. Mothers and offspring: The rabbit as a model system in the study of mammalian maternal behavior and sibling interactions. Horm. Behav. 2016, 77, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, K.L.; González-Mariscal, G. Progesterone receptor activation signals behavioral transitions across the reproductive cycle of the female rabbit. Horm. Behav. 2006, 50, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocé, M.L.; Santacreu, M.A.; Climent, A.; Blasco, A. The effect of divergent selection for uterine capacity on prenatal survival in rabbits: Maternal and embryonic genetic effects. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 82, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, N.; Boice, R. Mouse (Mus) burrows: Effects of age, strain, and domestication. Anim. Learn. Behav. 1981, 9, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bult, A.; Lynch, C.B. Multiple selection responses in house mice bidirectionally selected for thermoregulatory nest-building behavior: Crosses of replicate lines. Behav. Genet. 1996, 26, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiró, R.; Merchan, M.; Santacreu, M.A.; Argente, M.J.; García, M.L.; Folch, J.M.; Blasco, A. Identification of single-nucleotide polymorphism in the progesterone receptor gene and its association with reproductive traits in rabbits. Genetics 2008, 180, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peiró, R.; Herrler, A.; Santacreu, M.A.; Merchán, M.; Argente, M.J.; García, M.L.; Folch, J.M.; Blasco, A. Expression of progesterone receptor related to the polymorphism in the PGR gene in the rabbit reproductive tract. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caba, M.; Rovirosa, M.J.; Beyer, C.; González-Mariscal, G. Immunocytochemical detection of progesterone receptor in the female rabbit forebrain: Distribution and regulation by oestradiol and progesterone. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2003, 15, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongrácz, P.; Altbäcker, V.; Fenes, D. Human handling might interfere with conspecific recognition in the European rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Dev. Psychobiol. 2001, 39, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilkó, Á.; Altbäcker, V. Regular handling early in the nursing period eliminates fear responses toward human beings in wild and domestic rabbits. Dev. Psychobiol. 2000, 36, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touma, C.; Palme, R. Measuring fecal glucocorticoid metabolites in mammals and birds: The importance of validation. Ann. Ny. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1046, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monclús, R.; Rödel, H.G.; Palme, R.; Von Holst, D.; De Miguel, J. Non-invasive measurement of the physiological stress response of wild rabbits to the odour of a predator. Chemoecology 2006, 16, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, N.; Nakao, T. Direct enzyme immunoassay of fecal estrone derivatives in dairy cows. Anim. Sci. J. 2005, 76, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, P.S.; Metzger, D.A.; Higuchi, R. Chelex 100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material. Biotechniques 1991, 10, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goujon, M.; McWilliam, H.; Li, W.; Valentin, F.; Squizzato, S.; Paern, J.; Lopez, R. A new bioinformatics analysis tools framework at EMBL-EBI. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2010, 38, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peakall, R.O.D.; Smouse, P.E. GENALEX 6: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2537–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalinowski, S.T.; Taper, M.L.; Marshall, T.C. Revising how the computer program CERVUS accommodates genotyping error increases success in paternity assignment. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falconer, D.S.; Mackay, T.F.C. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics, 4th ed.; Longmans Green, Harlow: Essex, UK, 1996; pp. 125–147. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, C.P.; Romero, L.M. Chronic captivity stress in wild animals is highly species-specific. Conserv. Physiol. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabezas, S.; Blas, J.; Marchant, T.A.; Moreno, S. Physiological stress levels predict survival probabilities in wildrabbits. Horm Behav. 2007, 51, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, C.; Aurich, C.; Aurich, J. Stress effects on the regulation of parturition in different domestic animal species. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 207, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aksher, S.H.; Sherif, H.S.; Khalil, M.H.; El-Garhy, H.A.; Ramadan, S. Molecular analysis of a new synthetic rabbit line and their parental populations using microsatellite and SNP markers. Gene Rep. 2017, 8, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, E. Molecular-genetic analysis as component of organization selection process in rabbit breeding. Рoзведення Генетика Тварин 2015, 50, 177. Available online: https://www.irbis-nbuw.gov.ua (accessed on 27 April 2020).
- Mocé, M.L.; Santacreu, M.A. Genetic improvement of litter size in rabbits. In Proceedings of the 9th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production, Leipzig, Germany, 1–6 August 2010; Species Breeding: Breeding of Further Species (Rabbits, Grass Cutter, Companion Animals etc.)—Lecture Sessions. p. 0025. [Google Scholar]
- Canali, E.; Ferrante, V.; Todeschini, R.; Verga, M.; Carenzi, C. Rabbit nest construction and its relationship with litter development. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 1991, 31, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rödel, H.G.; Hudson, R.; Von Holst, D. Optimal litter size for individual growth of European rabbit pups depends on their thermal environment. Oecologia 2008, 155, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rödel, H.G.; Starkloff, A.; Seltmann, M.W.; Prager, G.; von Holst, D. Causes and predictors of nest mortality in a Europeanrabbit population. Mamm. Biol. 2009, 74, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakatos, K.; Toth, I.; Nemoda, Z.; Ney, K.; Sasvari-Szekely, M.; Gervai, J. Dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) gene polymorphism is associated with attachment disorganization in infants. Mol. Psychiatry 2000, 5, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeRijk, R.H.; de Kloet, E.R.; Zitman, F.G.; van Leeuwen, N. Mineralocorticoid receptor gene variants as determinants of HPA axis regulation and behavior. Endocr. Dev. 2011, 20, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukefahr, S.D.; Hamilton, H.H. Heritability and repeatability estimates of maternal performance traits in purebred and crossbred does. World Rabbit Sci. 1997, 5, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferraz, J.B.S.; Johnson, R.K.; van Vleck, L.D. Estimation of genetic trends and genetic parameters for reproductive and growth traits of rabbits raised in subtropics with animal models. World Rabbit Sci. 1992, 15, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi, R.K.; Lukefahr, S.D.; Lauckner, F.B. Maternal heritability and repeatability for litter traits in rabbits in a humid tropical environment. Livest Prod. Sci. 2000, 67, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, I.; Radnai, I.; Nagyné-Kiszlinger, H.; Farkas, J.; Szendrő, Z. Genetic parameters and genetic trends of reproduction traits in synthetic Pannon rabbits using repeatability and multi-trait animal models. Arch. Tierz. 2011, 54, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.T. Genetic analyses of nest-building behavior in laboratory mice (Mus musculus). Behav. Genet. 1973, 3, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, P.; Kluen, E.; Brommer, J.E. Low heritability of nest construction in a wild bird. Biol. Lett. 2017, 13, 20170246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, P.T.; Hansell, M.; Borello, W.D.; Healy, S.D. Repeatability of nest morphology in African weaver birds. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
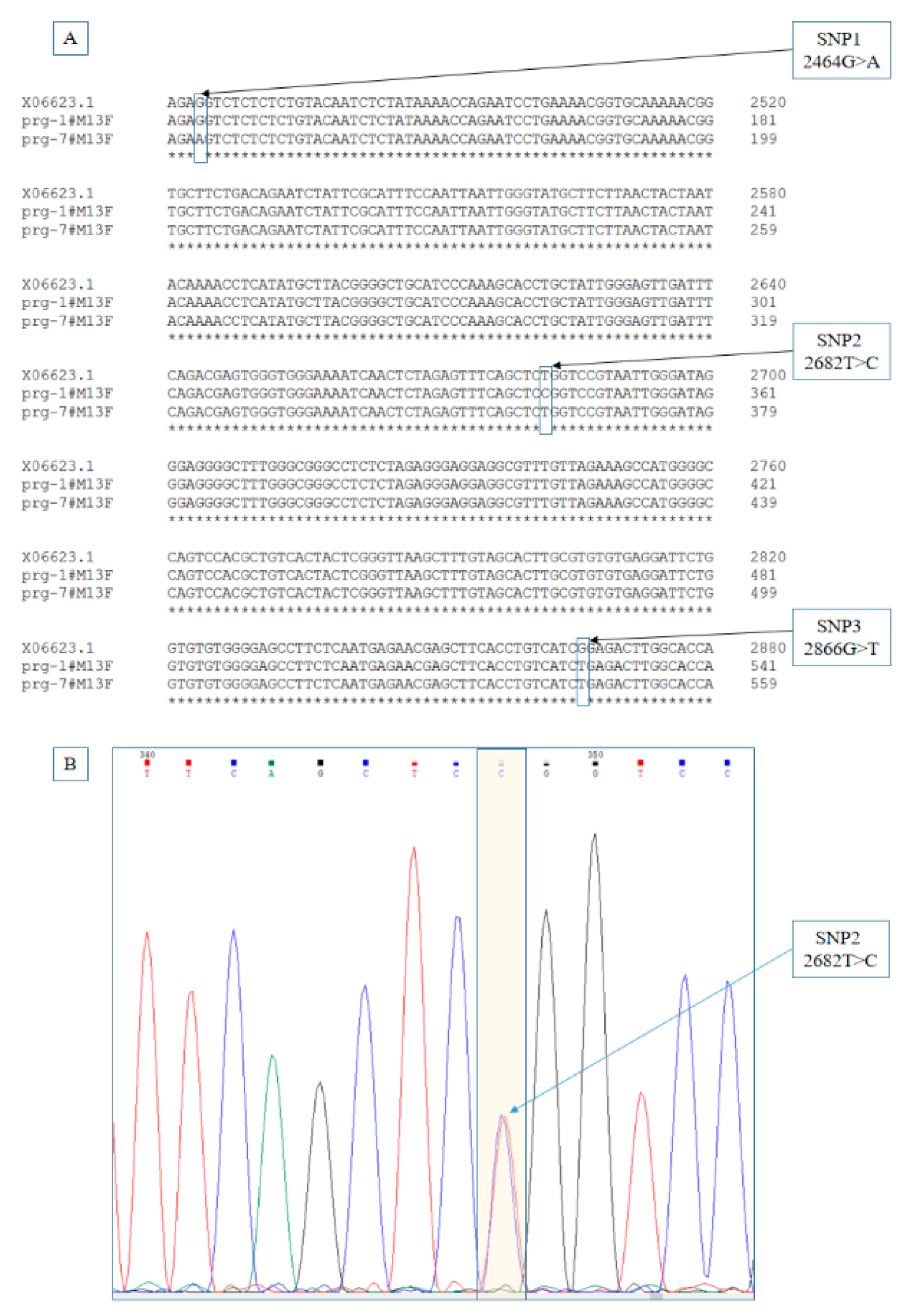
| SNP | Observed Genotype | Ho | uHe | HWE | Ne | PIC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2 | Prob. | |||||||||||
| 2464G > A | GG | 19 | GA | 8 | AA | 1 | 0.286 | 0.299 | 0.019 | 0.890 | 1.415 | 0.250 |
| 2682T > C | TT | 17 | TC | 11 | CC | 0 | 0.393 | 0.321 | 1.673 | 0.196 | 1.461 | 0.266 |
| 2866G > T | GG | 13 | GT | 14 | TT | 1 | 0.500 | 0.416 | 1.418 | 0.234 | 1.690 | 0.325 |
| Allele Frequency | Haplotype Frequency | D’ | r | χ2 | P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP1-2 | G | 0.82 | GT | 0.67 | 0.018 | 0.016 | 0.029 | NS |
| A | 0.18 | GC | 0.16 | |||||
| T | 0.80 | AT | 0.13 | |||||
| C | 0.20 | AC | 0.03 | |||||
| SNP1-3 | T | 0.80 | TT | 0.56 | −0.632 | −0.181 | 3.651 | NS |
| C | 0.20 | TG | 0.24 | |||||
| T | 0.71 | CT | 0.15 | |||||
| G | 0.29 | CG | 0.04 | |||||
| SNP2-3 | G | 0.82 | GT | 0.55 | −0.239 | −0.077 | 0.662 | NS |
| A | 0.18 | GG | 0.27 | |||||
| T | 0.71 | AT | 0.16 | |||||
| G | 0.29 | AG | 0.02 | |||||
| Trait | N | Mean | S.D. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time of Hay Carrying (Day) | 28 | 2.3 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 5.0 |
| Hay Weight (g) | 28 | 169.2 | 61.5 | 90.5 | 331.1 |
| Rate of Fur (%) | 28 | 18.9 | 16.4 | 3.7 | 74.5 |
| df | Hay Carrying Behavior | Hay Weight | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Square | F | P | Partial Eta Squared | Mean Square | F | P | Partial Eta Squared | ||
| Intercept | 1 | 10.94 | 6.877 | 0.018 | 0.288 | 85041.200 | 21.614 | 0.001 | 0.560 |
| Progesterone | 1 | 9.873 | 6.203 | 0.023 | 0.267 | 1473.090 | 0.374 | 0.549 | 0.022 |
| Cortisol | 1 | 8.298 | 5.214 | 0.036 | 0.235 | 2543.257 | 0.646 | 0.433 | 0.037 |
| SNP1 | 2 | 7.085 | 4.452 | 0.028 | 0.344 | 1132.699 | 0.288 | 0.753 | 0.033 |
| SNP2 | 1 | 0.299 | 0.188 | 0.670 | 0.011 | 1914.580 | 0.487 | 0.495 | 0.028 |
| SNP3 | 2 | 1.595 | 1.002 | 0.388 | 0.105 | 236.410 | 0.060 | 0.942 | 0.007 |
| SNP1 * SNP2 | 1 | 0.129 | 0.081 | 0.780 | 0.005 | 5301.626 | 1.347 | 0.262 | 0.073 |
| SNP1 * SNP3 | 1 | 0.035 | 0.022 | 0.883 | 0.001 | 5662.326 | 1.439 | 0.247 | 0.078 |
| SNP2 * SNP3 | 1 | 0.333 | 0.209 | 0.653 | 0.012 | 18,082.703 | 4.596 | 0.047 | 0.213 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benedek, I.; Altbӓcker, V.; Zsolnai, A.; Molnár, T. Exploring the Genetic Background of the Differences in Nest-Building Behavior in European Rabbit. Animals 2020, 10, 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091579
Benedek I, Altbӓcker V, Zsolnai A, Molnár T. Exploring the Genetic Background of the Differences in Nest-Building Behavior in European Rabbit. Animals. 2020; 10(9):1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091579
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenedek, Ildikó, Vilmos Altbӓcker, Attila Zsolnai, and Tamás Molnár. 2020. "Exploring the Genetic Background of the Differences in Nest-Building Behavior in European Rabbit" Animals 10, no. 9: 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091579
APA StyleBenedek, I., Altbӓcker, V., Zsolnai, A., & Molnár, T. (2020). Exploring the Genetic Background of the Differences in Nest-Building Behavior in European Rabbit. Animals, 10(9), 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091579






