Characterization of Gut Microbiota in Prenatal Cold Stress Offspring Rats by 16S rRNA Sequencing
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
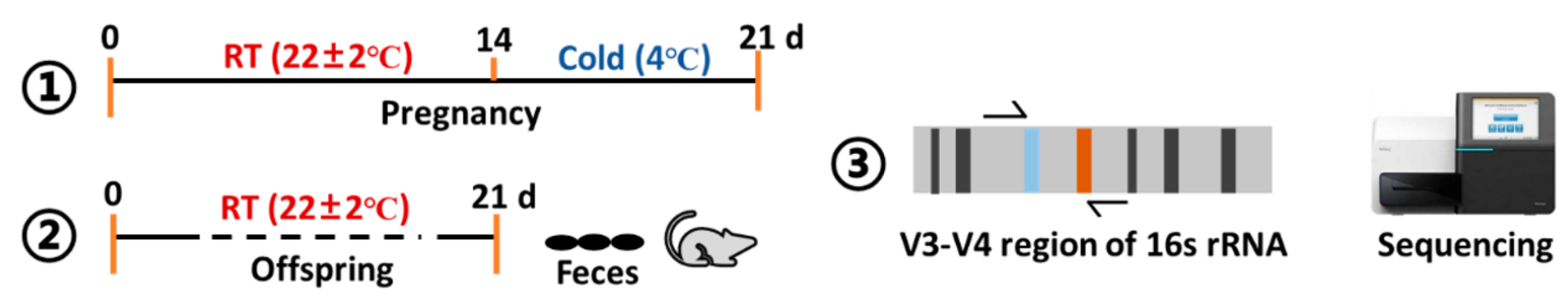
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Prenatal Stress
2.3. Microbial Sequencing-16s rRNA
2.4. Microbiome Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
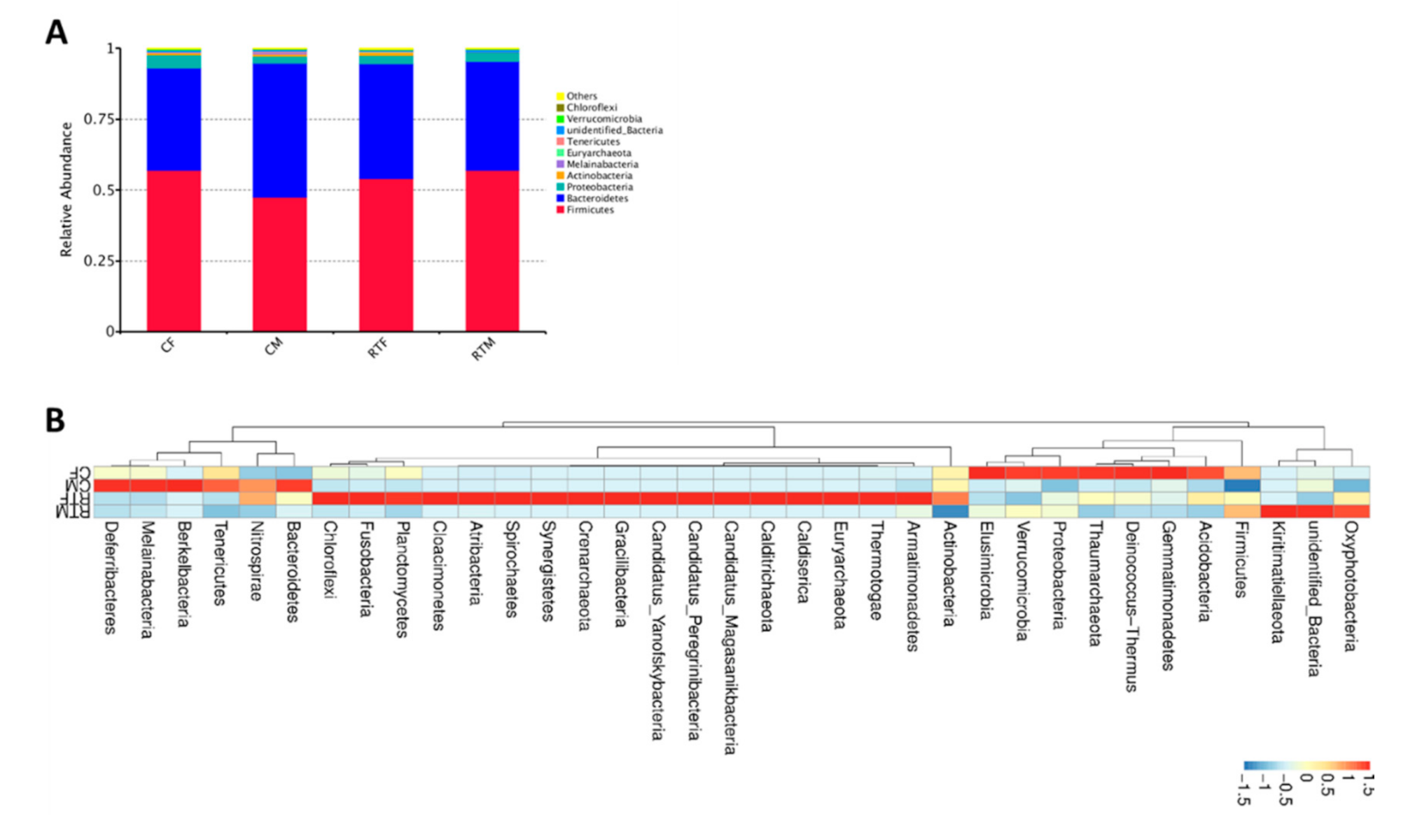
3.1. OTU Cluster Abundance Analysis
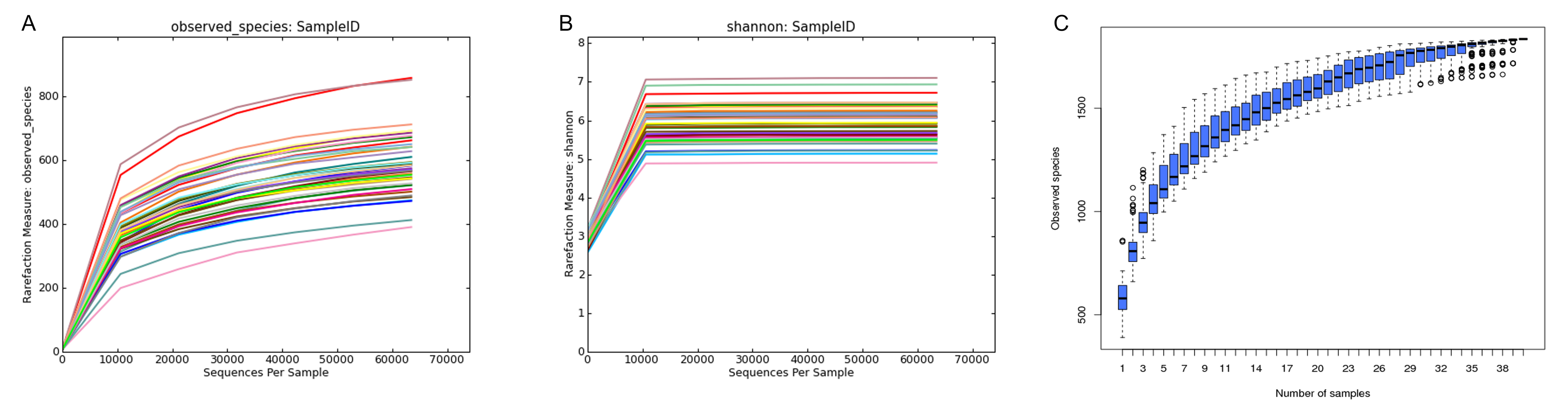
3.2. Alpha Diversity Analysis
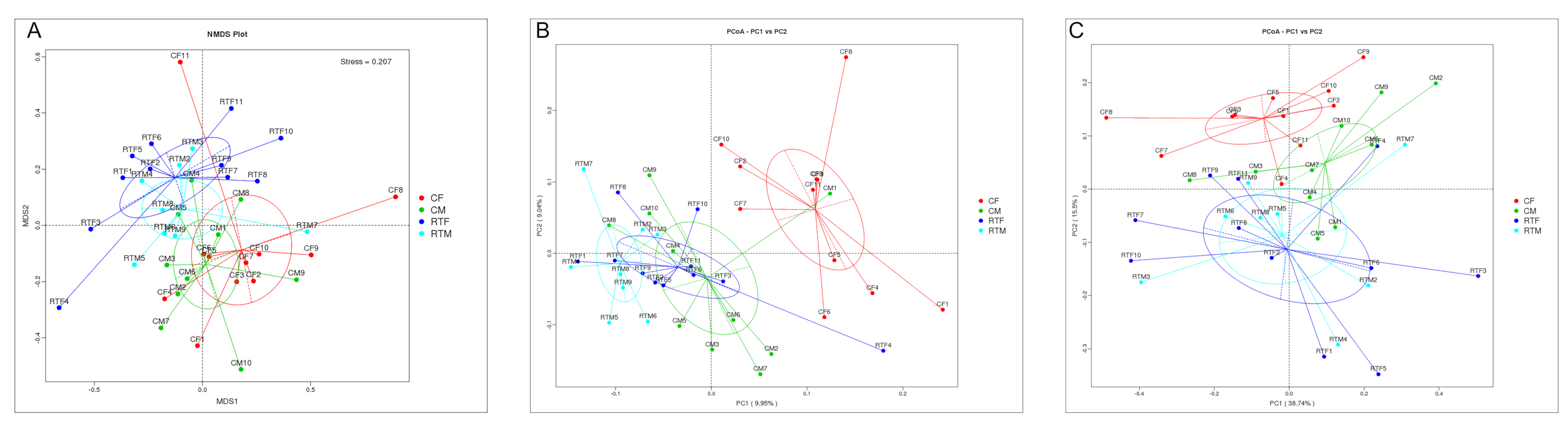
3.3. Beta Diversity Analysis
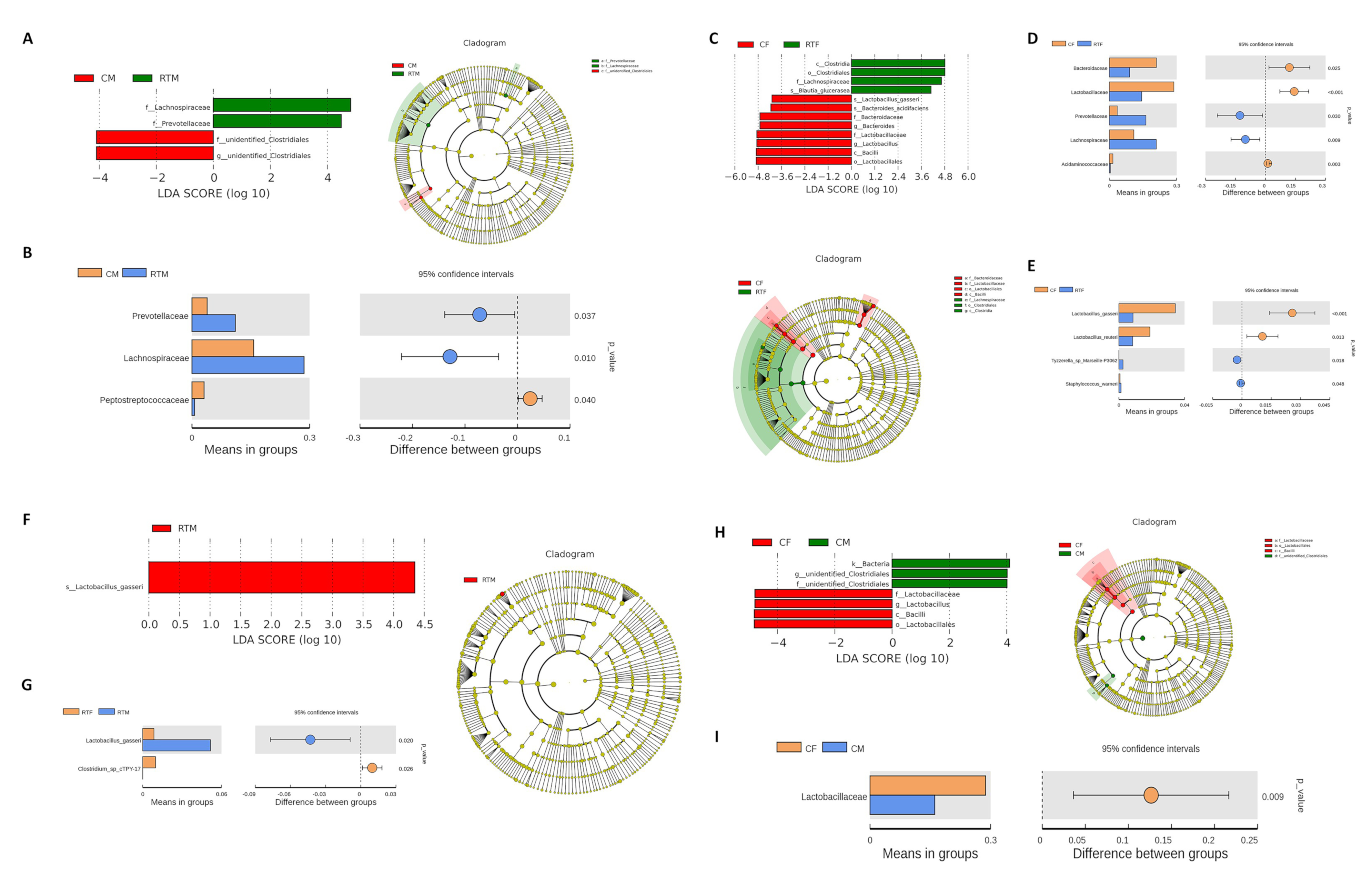
3.4. Screening of Microorganisms in Response to Prenatal Cold Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A. Living with the past: Evolution, development, and patterns of disease. Science 2004, 305, 1733–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoner, R.; Chow, M.L.; Boyle, M.P.; Sunkin, S.M.; Mouton, P.R.; Roy, S.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Colamarino, S.A.; Lein, E.S.; Courchesne, E. Patches of disorganization in the neocortex of children with autism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Entringer, S.; Buss, C.; Kumsta, R.; Hellhammer, D.H.; Wadhwa, P.D.; Wüst, S. Prenatal psychosocial stress exposure is associated with subsequent working memory performance in young women. Behav. Neurosci. 2009, 123, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glover, V.; O’Connor, T.G.; O’Donnell, K. Prenatal stress and the programming of the HPA axis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 35, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, S.; Xu, B.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Yao, R.; Ji, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Li, S.; et al. Possible mechanisms of prenatal cold stress induced-anxiety-like behavior depression in offspring rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 359, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Sun, D.; Qu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Jose, P.A.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, C. Prenatal cold exposure causes hypertension in offspring by hyperactivity of the sympathetic nervous system. Clin. Sci. 2019, 133, 1097–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, K.Y.; Kotachi, M.; Suzuki, A.; Iinuma, M.; Azuma, K. Chewing during prenatal stress prevents prenatal stress-induced suppression of neurogenesis, anxiety-like behavior and learning deficits in mouse offspring. Int. J. Med Sci. 2018, 15, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beversdorf, D.Q.; Stevens, H.E.; Jones, K.L. Prenatal Stress, Maternal Immune Dysregulation, and Their Association with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2018, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Antonson, A.M.; Rajasekera, T.A.; Patterson, J.M.; Bailey, M.T.; Gur, T.L. Prenatal stress causes intrauterine inflammation and serotonergic dysfunction, and long-term behavioral deficits through microbe- and CCL2-dependent mechanisms. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, S.; Wang, D.; Xu, B.; Guo, W.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Ji, H.; Wang, J.; Kong, F.; Zhen, L.; et al. Prenatal cold stress: Effect on maternal hippocampus and offspring behavior in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 346, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Clarke, G.; Borre, Y.E.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Serotonin, tryptophan metabolism and the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, M.P.; Zaghouani, H.; Niklas, V. Gut microbiota, the immune system, and diet influence the neonatal gut-brain axis. Pediatric Res. 2015, 77, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.T.; Dowd, S.E.; Galley, J.D.; Hufnagle, A.R.; Allen, R.G.; Lyte, M. Exposure to a social stressor alters the structure of the intestinal microbiota: Implications for stressor-induced immunomodulation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, M.T.; Dowd, S.E.; Parry, N.M.; Galley, J.D.; Schauer, D.B.; Lyte, M. Stressor exposure disrupts commensal microbial populations in the intestines and leads to increased colonization by Citrobacter rodentium. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, J.R.; Borre, Y.; O’Brien, C.; Patterson, E.; El Aidy, S.; Deane, J.; Kennedy, P.J.; Beers, S.; Scott, K.; Moloney, G.; et al. Transferring the blues: Depression-Associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 82, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, C.; Stojanović, O.; Colin, D.J.; Suarez-Zamorano, N.; Tarallo, V.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Rigo, D.; Fabbiano, S.; Stevanović, A.; Hagemann, S.; et al. Gut Microbiota Orchestrates Energy Homeostasis during Cold. Cell 2015, 163, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lian, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Ji, H.; Kong, F.; Xu, B.; Li, S.; Yang, H. Impact of prenatal cold stress on placental physiology, inflammatory response, and apoptosis in rats. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 115304–115314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, E.Y.; McBride, S.W.; Hsien, S.; Sharon, G.; Hyde, E.R.; McCue, T.; Codelli, J.A.; Chow, J.; Reisman, S.E.; Petrosino, J.F.; et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 2013, 155, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, A.V.; Bested, A.C.; Beaulne, T.M.; Katzman, M.A.; Iorio, C.; Berardi, J.M.; Logan, A.C. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study of a probiotic in emotional symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome. Gut Pathog. 2009, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takada, M.; Nishida, K.; Kataoka-Kato, A.; Gondo, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Suda, K.; Kawai, M.; Hoshi, R.; Watanabe, O.; Igarashi, T.; et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota relieves stress-associated symptoms by modulating the gut-brain interaction in human and animal models. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. Off. J. Eur. Gastrointest. Motil. Soc. 2016, 28, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, J.F.; Hsu, C.C.; Chou, G.T.; Hsu, J.S.; Liong, M.T.; Tsai, Y.C. Lactobacillus paracasei PS23 reduced early-life stress abnormalities in maternal separation mouse model. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crestani, F.; Lorez, M.; Baer, K.; Essrich, C.; Benke, D.; Laurent, J.P.; Belzung, C.; Fritschy, J.M.; Lüscher, B.; Mohler, H. Decreased GABAA-receptor clustering results in enhanced anxiety and a bias for threat cues. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargaei, Z.; Bang, J.Y.; Mahadevan, V.; Khademullah, C.S.; Bedard, S.; Parfitt, G.M.; Kim, J.C.; Woodin, M.A. Restoring GABAergic inhibition rescues memory deficits in a Huntington’s disease mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1618–E1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.; Ohta, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, H. Progressive cognitive impairment following chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced by permanent occlusion of bilateral carotid arteries in rats. Brain Res. 1994, 653, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.C.; Olson, C.A.; Hsiao, E.Y. Interactions between the microbiota, immune and nervous systems in health and disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandwitz, P.; Kim, K.H.; Terekhova, D.; Liu, J.K.; Sharma, A.; Levering, J.; McDonald, D.; Dietrich, D.; Ramadhar, T.R.; Lekbua, A.; et al. GABA-Modulating bacteria of the human gut microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunes, R.A.; Poluektova, E.U.; Dyachkova, M.S.; Klimina, K.M.; Kovtun, A.S.; Averina, O.V.; Orlova, V.S.; Danilenko, V.N. GABA production and structure of gadB/gadC genes in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains from human microbiota. Anaerobe 2016, 42, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Raw_Reads | Clean_Reads | Base(nt) | AvgLen(nt) | Q20 | GC% | Effective% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF1 | 92,260 | 89,261 | 22,514,767 | 252 | 82.14 | 52.13 | 96.75 |
| CF2 | 83,650 | 80,149 | 20,243,525 | 252 | 83.8 | 51.94 | 95.81 |
| CF3 | 83,298 | 80,401 | 20,316,690 | 252 | 82.54 | 52.07 | 96.52 |
| CF4 | 83,297 | 80,125 | 20,214,254 | 252 | 83.66 | 52.48 | 96.19 |
| CF5 | 85,330 | 80,021 | 20,190,759 | 252 | 83.37 | 51.75 | 93.78 |
| CF6 | 85,139 | 80,086 | 20,229,884 | 252 | 83.64 | 52.26 | 94.06 |
| CF7 | 84,444 | 80,156 | 20,262,129 | 252 | 82.6 | 52.91 | 94.92 |
| CF8 | 93,369 | 90,450 | 22,854,929 | 252 | 83.14 | 52.95 | 96.87 |
| CF9 | 82,300 | 80,012 | 20,193,261 | 252 | 83.36 | 49.78 | 97.22 |
| CF10 | 83,407 | 80,210 | 20,227,906 | 252 | 82.39 | 51.75 | 96.17 |
| CF11 | 77,267 | 74,592 | 18,829,804 | 252 | 88.38 | 51.82 | 96.54 |
| CM1 | 85,000 | 80,135 | 20,229,046 | 252 | 84.22 | 52.48 | 94.28 |
| CM2 | 82,853 | 80,271 | 20,229,164 | 252 | 83.8 | 50.55 | 96.88 |
| CM3 | 85,402 | 80,218 | 20,248,437 | 252 | 87.64 | 52.1 | 93.93 |
| CM4 | 82,193 | 80,067 | 20,203,569 | 252 | 89.1 | 53.63 | 97.41 |
| CM5 | 85,686 | 80,027 | 20,196,156 | 252 | 82.52 | 53 | 93.4 |
| CM6 | 85,413 | 80,192 | 20,234,272 | 252 | 81.6 | 51.65 | 93.89 |
| CM7 | 83,505 | 80,110 | 20,252,100 | 252 | 80.29 | 51.82 | 95.93 |
| CM8 | 82,851 | 80,161 | 20,257,659 | 252 | 82.13 | 52.09 | 96.75 |
| CM9 | 83,032 | 80,250 | 20,225,862 | 252 | 85.33 | 50.51 | 96.65 |
| CM10 | 94,549 | 91,345 | 23,051,906 | 252 | 86.17 | 51.74 | 96.61 |
| RTF1 | 89,793 | 85,797 | 21,722,030 | 253 | 85.33 | 52.34 | 95.55 |
| RTF2 | 84,096 | 80,166 | 20,241,950 | 252 | 87.34 | 53.06 | 95.33 |
| RTF3 | 85,131 | 80,209 | 20,322,631 | 253 | 81.71 | 52.24 | 94.22 |
| RTF4 | 82,078 | 80,181 | 20,237,808 | 252 | 82.2 | 51.82 | 97.69 |
| RTF5 | 103,541 | 99,559 | 25,148,508 | 252 | 88.31 | 52.24 | 96.15 |
| RTF6 | 85,361 | 80,235 | 20,254,767 | 252 | 88.53 | 51.95 | 93.99 |
| RTF7 | 71,314 | 68,814 | 17,387,481 | 252 | 78.71 | 53.17 | 96.49 |
| RTF8 | 84,943 | 80,114 | 20,195,893 | 252 | 83.01 | 52.6 | 94.32 |
| RTF9 | 84,557 | 80,148 | 20,248,562 | 252 | 83.97 | 52.43 | 94.79 |
| RTF10 | 82,732 | 80,286 | 20,269,324 | 252 | 84.38 | 53.05 | 97.04 |
| RTF11 | 83,449 | 80,090 | 20,217,831 | 252 | 88.04 | 52.86 | 95.97 |
| RTM2 | 83,144 | 80,084 | 20,225,142 | 252 | 84.92 | 51.63 | 96.32 |
| RTM3 | 83,169 | 80,105 | 20,284,526 | 253 | 81.31 | 52.78 | 96.32 |
| RTM4 | 83,560 | 80,200 | 20,254,101 | 252 | 87.61 | 52.47 | 95.98 |
| RTM5 | 85,973 | 79,380 | 20,034,819 | 252 | 85.79 | 52.68 | 92.33 |
| RTM6 | 83,612 | 80,295 | 20,278,888 | 252 | 81.36 | 52.74 | 96.03 |
| RTM7 | 82,830 | 80,147 | 20,222,220 | 252 | 84.19 | 50.56 | 96.76 |
| RTM8 | 84,339 | 80,215 | 20,236,766 | 252 | 88.18 | 52.92 | 95.11 |
| RTM9 | 83,915 | 80,047 | 20,206,904 | 252 | 81.54 | 52.35 | 95.39 |
| Groups | Firmicutes | Bacteroidetes | Proteobacteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| RYM | 57.02% | 38.04% | 3.18% |
| CM | 47.57% | 47.28% | 2.48% |
| RTF | 54.11% | 40.40% | 3.06% |
| CF | 57.00% | 36.17% | 4.57% |
| Groups | Bacte | Lacto | Romb | Un-Lachn | Blaua | Fusica | Un-Clostri | Un-Entero | Lachn | Roseb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RYM | 15.51 | 18.28 | 0.67 | 1.54 | 9.38 | 3.78 | 0.04 | 0.74 | 2.53 | 2.94 |
| CM | 22.93 | 16.11 | 3.09 | 1.72 | 4.76 | 2.96 | 2.34 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.87 |
| RTF | 9.03 | 14.39 | 8.20 | 5.84 | 5.52 | 3.24 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.41 | 0.76 |
| CF | 20.97 | 28.75 | 4.99 | 1.52 | 2.40 | 0.31 | 0.59 | 1.21 | 0.51 | 0.37 |
| Group | A | Observed-Delta | Expected-Delta | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CF-RTF | 0.05108 | 0.6782 | 0.7147 | 0.001 |
| RTF-RTM | 0.02732 | 0.683 | 0.7022 | 0.035 |
| CF-RTM | 0.04646 | 0.652 | 0.6837 | 0.001 |
| CM-RTF | 0.04115 | 0.6967 | 0.7266 | 0.004 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, J.; Zhu, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Lian, S. Characterization of Gut Microbiota in Prenatal Cold Stress Offspring Rats by 16S rRNA Sequencing. Animals 2020, 10, 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091619
Zheng J, Zhu T, Wang L, Wang J, Lian S. Characterization of Gut Microbiota in Prenatal Cold Stress Offspring Rats by 16S rRNA Sequencing. Animals. 2020; 10(9):1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091619
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Jiasan, Tingting Zhu, Lipeng Wang, Jianfa Wang, and Shuai Lian. 2020. "Characterization of Gut Microbiota in Prenatal Cold Stress Offspring Rats by 16S rRNA Sequencing" Animals 10, no. 9: 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091619
APA StyleZheng, J., Zhu, T., Wang, L., Wang, J., & Lian, S. (2020). Characterization of Gut Microbiota in Prenatal Cold Stress Offspring Rats by 16S rRNA Sequencing. Animals, 10(9), 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10091619





