Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Growth Curve Parameters in Chinese Simmental Beef Cattle
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Resource Population and Phenotypes Collection
2.2. Genotyping and Quality Control
2.3. Growth Curve Fitting
2.4. Single-Trait GWAS
2.5. Multi-Trait GWAS
2.6. Gene Function Annotation
3. Results
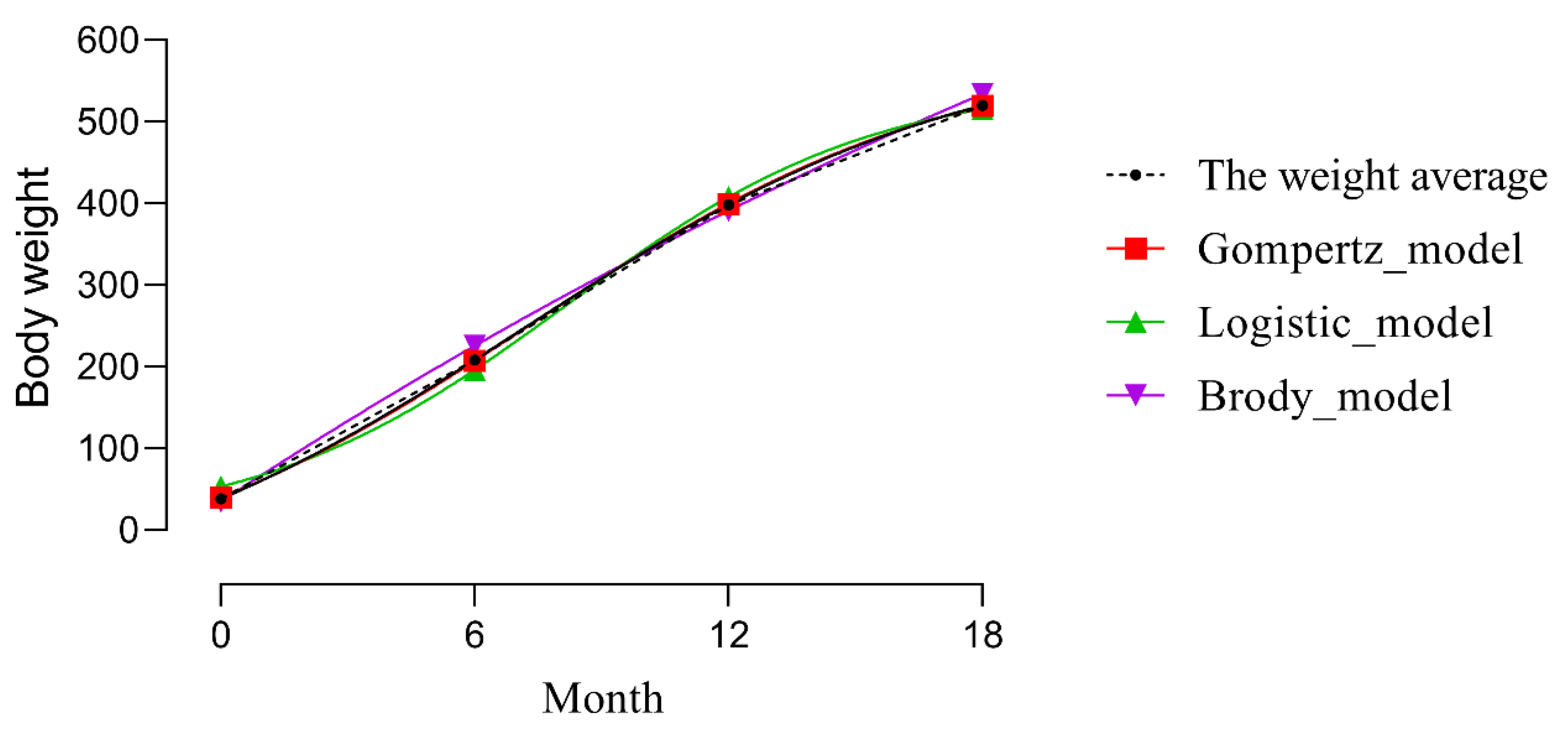
3.1. Growth Curve Fitting
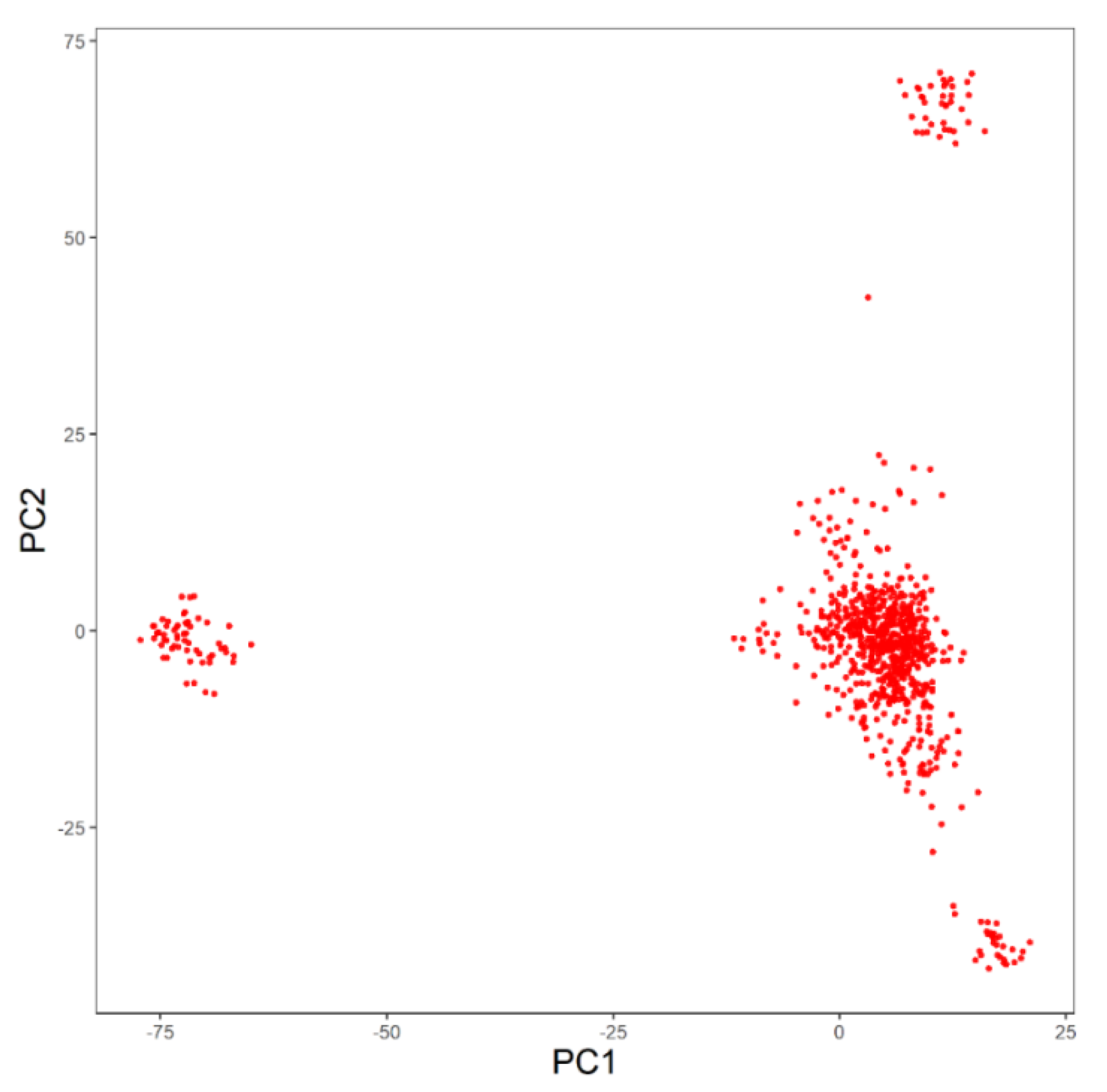
3.2. Principal Components Analysis (PCA)
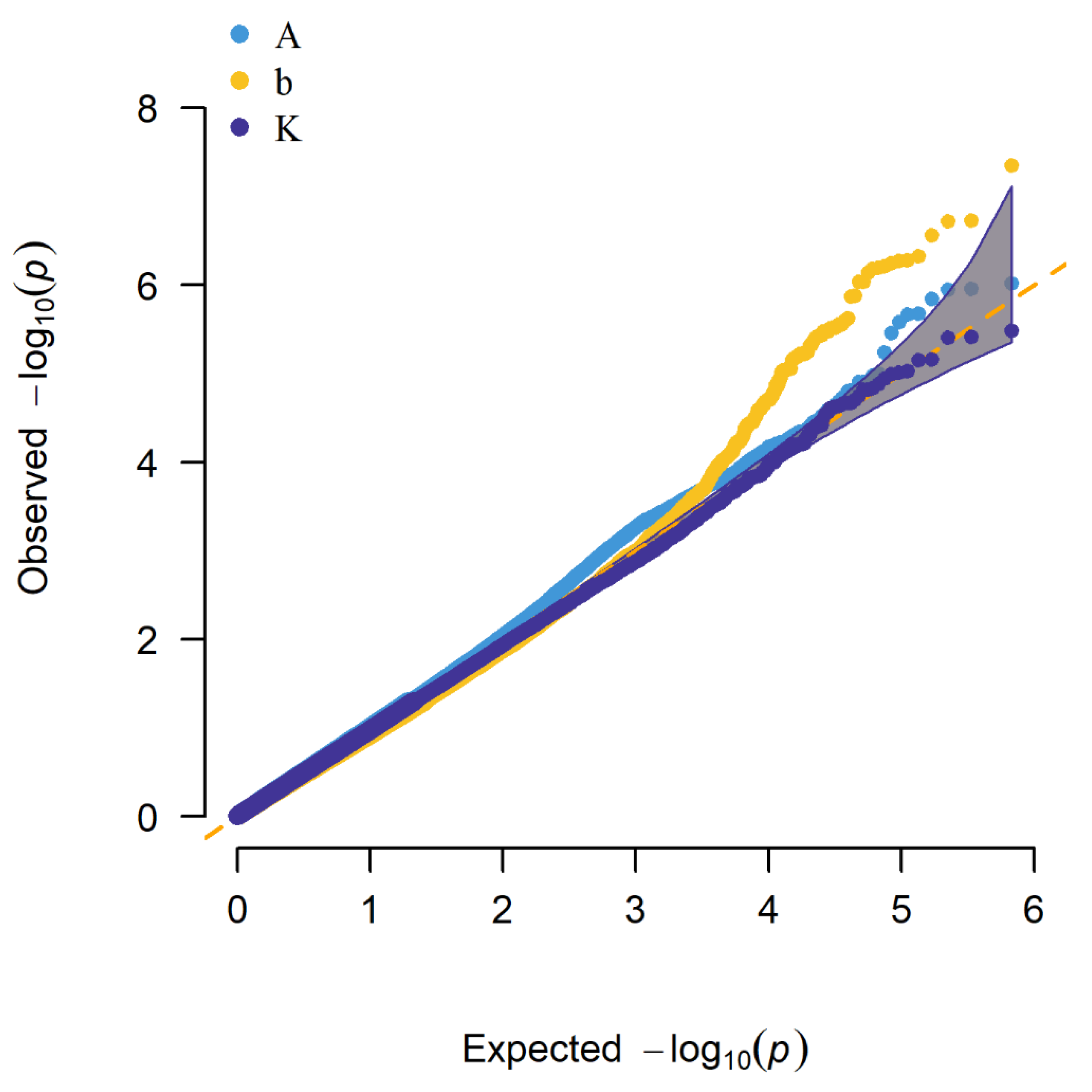
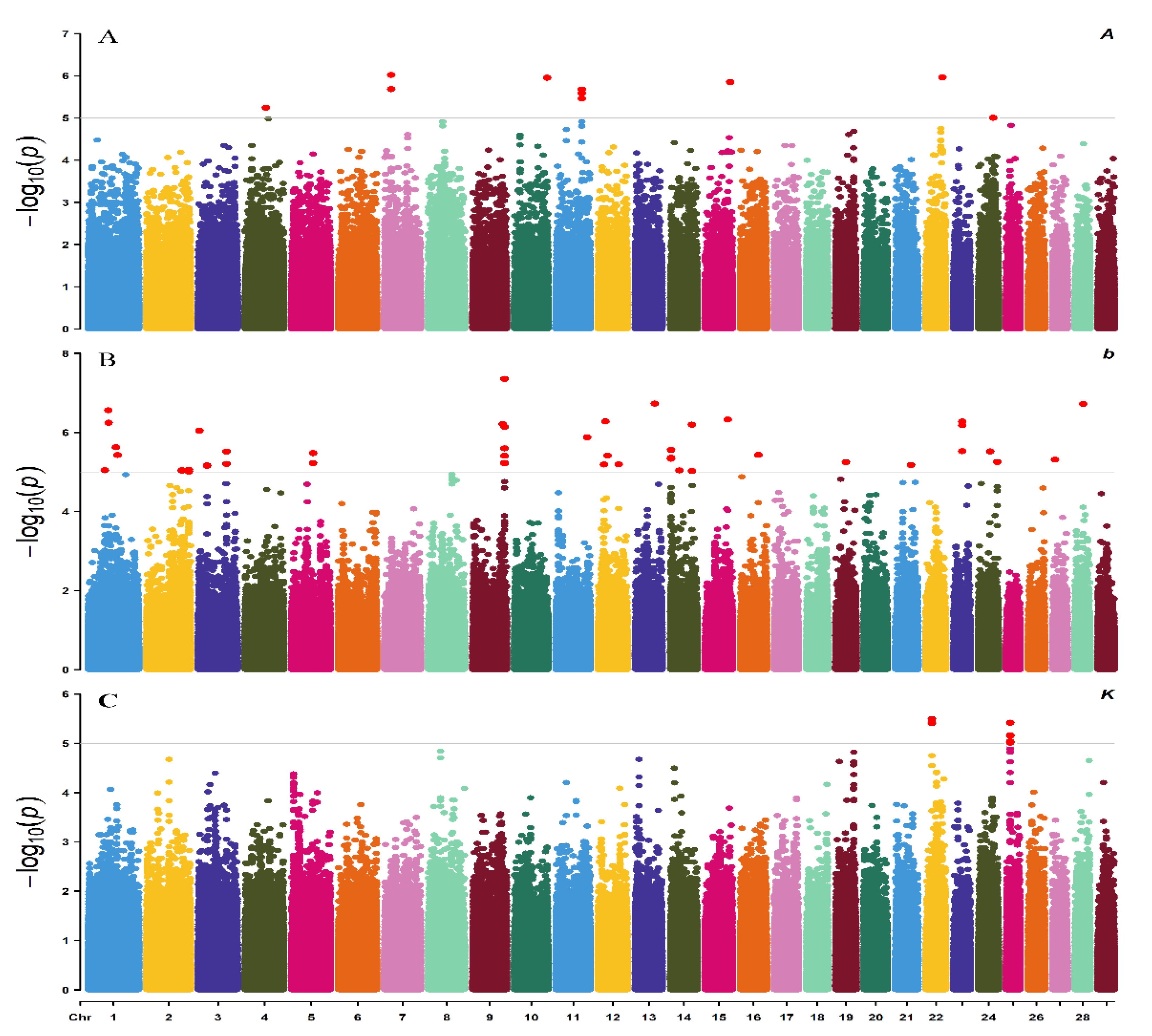
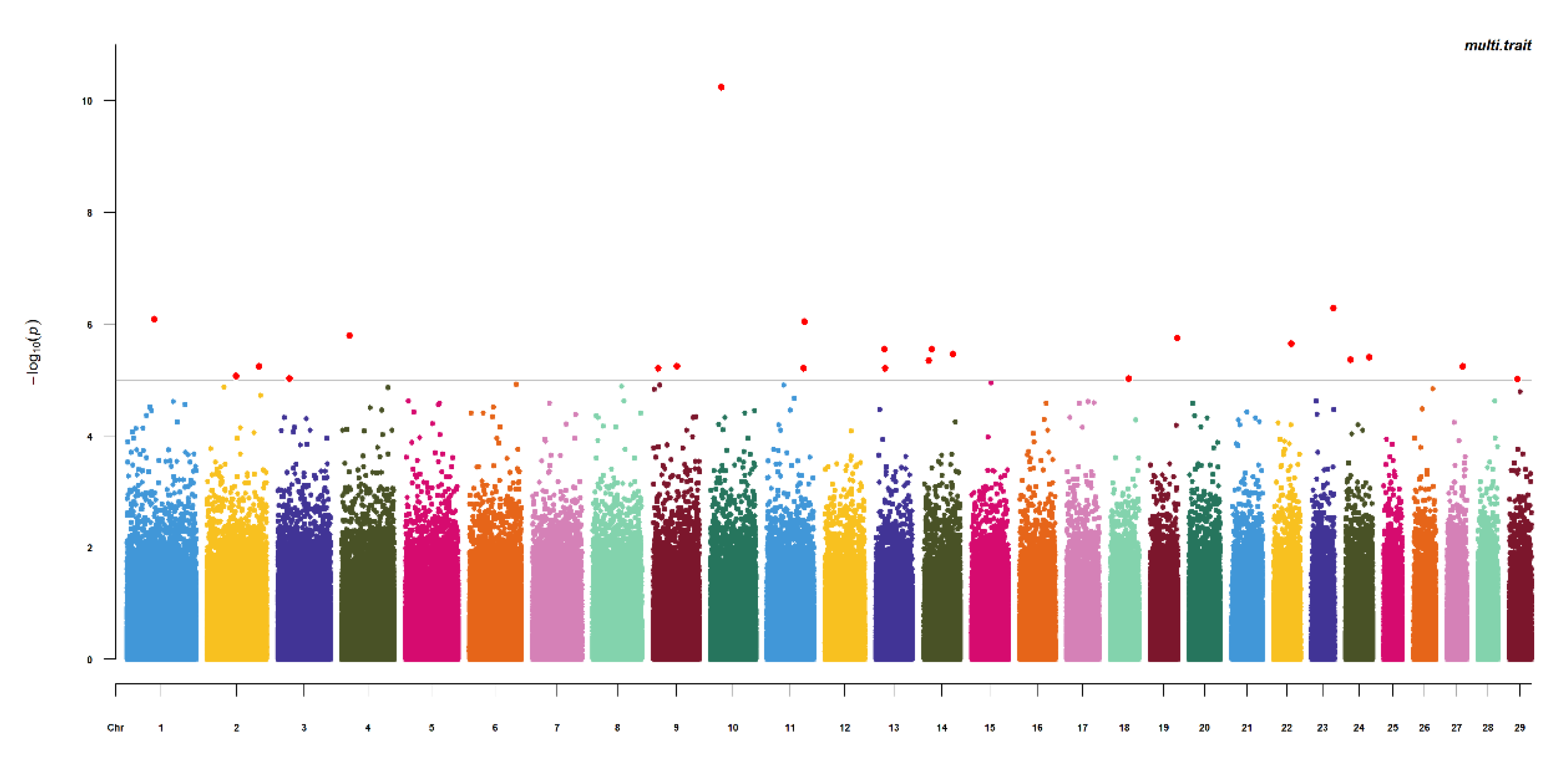
3.3. Summary of Results by Two GWAS Methods
3.4. GO and KEGG Pathway Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth Curve Fitting
4.2. GWAS, GO, and KEGG Pathway Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GWAS | genome-wide association study |
| GS | genomic selection |
| SNP | single nucleotide polymorphism |
| QTL | quantitative trait loci |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| PCA | principal components analysis |
| BTA | Bos taurus autosomes |
References
- Mao, Y.; Hopkins, D.L.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X. Consumption patterns and consumer attitudes to beef and sheep meat in China. Am. J. Food Nutr. 2016, 4, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- An, B.; Xu, L.; Xia, J.; Wang, X.; Miao, J.; Chang, T.; Song, M.; Ni, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L. Multiple association analysis of loci and candidate genes that regulate body size at three growth stages in Simmental beef cattle. BMC Genet. 2020, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Gao, H.; Wu, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, B.; Song, Y.; Bao, J.; Li, J.; et al. Detection of candidate genes for growth and carcass traits using genome-wide association strategy in Chinese Simmental beef cattle. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2018, 58, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, J.; Sun, D.; Ma, P.; Ding, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Genome wide association studies for milk pro-duction traits in Chinese Holstein population. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meredith, B.K.; Kearney, F.J.; Finlay, E.K.; Bradley, D.G.; Fahey, A.G.; Berry, D.P.; Lynn, D.J. Ge-nome-wide associations for milk production and somatic cell score in Holstein-Friesian cattle in Ireland. BMC Genet. 2012, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buzanskas, M.E.; Grossi, D.A.; Ventura, R.V.; Schenkel, F.S.; Sargolzaei, M.; Meirelles, S.L.; Mokry, F.B.; Higa, R.H.; Mudadu, M.A.; Da Silva, M.V.G.B.; et al. Genome-Wide Association for Growth Traits in Canchim Beef Cattle. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, B.; Bao, W.-J.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Xia, X.-H. In Situ Monitoring of Protein Adsorption on a Nanoparticulated Gold Film by Attenuated Total Reflection Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9460–9465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Kirkpatrick, B.W.; Rosa, G.J.M.; Khatib, H. A genome-wide association study using selective DNA pooling identifies candidate markers for fertility in Holstein cattle. Anim. Genet. 2010, 41, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahana, G.; Guldbrandtsen, B.; Bendixen, C.; Lund, M. Genome-wide association mapping for female fertility traits in Danish and Swedish Holstein cattle. Anim. Genet. 2010, 41, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Miao, J.; Chang, T.; Xia, J.; An, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; et al. Evaluation of GBLUP, BayesB and elastic net for genomic prediction in Chinese Simmental beef cattle. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Guo, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X.; Xu, L.; et al. Accuracies of genomic prediction for twenty economically important traits in Chinese Simmental beef cattle. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ning, C.; Wang, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Mrode, R.; Liu, J.-F. Eigen decomposition expedites longitudinal genome-wide association studies for milk production traits in Chinese Holstein. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Oliveira, H.R.; Lourenco, D.; Masuda, Y.; Misztal, I.; Tsuruta, S.; Jamrozik, J.; Brito, L.; Silva, F.; Cant, J.; Schenkel, F. Single-step genome-wide association for longitudinal traits of Canadian Ayrshire, Holstein, and Jersey dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9995–10011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crispim, A.C.; Kelly, M.J.; Guimaraes, S.E.; Fonseca e Silva, F.; Fortes, M.R.; Wenceslau, R.R.; Moore, S. Multi-Trait GWAS and New Candidate Genes Annotation for Growth Curve Parameters in Brahman Cattle. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- France, J.; Kebreab, E. Mathematical Modelling in Animal Nutrition; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Das, K.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Tong, C.; Fu, G.; Li, Y.; Xu, M.; Ahn, K.; Mauger, D.; Li, R.; et al. A dynamic model for genome-wide association studies. Qual. Life Res. 2011, 129, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, C.; Kang, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, A.; Fu, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.-F. Performance Gains in Genome-Wide Association Studies for Longitudinal Traits via Modeling Time-varied effects. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolormaa, S.; Pryce, J.E.; Reverter, A.; Zhang, Y.; Barendse, W.; Kemper, K.; Tier, B.; Savin, K.; Hayes, B.J.; Goddard, M.E. A Multi-Trait, Meta-analysis for Detecting Pleiotropic Polymorphisms for Stature, Fatness and Reproduction in Beef Cattle. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fortes, M.; Kemper, K.; Sasazaki, S.; Reverter, A.; Pryce, J.; Barendse, W.; Bunch, R.; McCulloch, R.; Harrison, B.; Bolormaa, S. Evidence for pleiotropism and recent selection in the PLAG 1 region in Australian Beef cattle. Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakushinskii, A.B. The problem of the convergence of the iteratively regularized Gauss-Newton method. Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 1992, 32, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Spiess, A.-N.; Neumeyer, N. An evaluation of R 2 as an inadequate measure for nonlinear models in pharmacological and biochemical research: A Monte Carlo approach. BMC Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lipka, A.E.; Tian, F.; Wang, Q.; Peiffer, J.; Li, M.; Bradbury, P.J.; Gore, M.A.; Buckler, E.S.; Zhang, Z. GAPIT: Genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2397–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to mul-tiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Bolormaa, S.; Neto, L.P.; Zhang, Y.; Bunch, R.; Harrison, B.; Goddard, M.; Barendse, W. A genome-wide as-sociation study of meat and carcass traits in Australian cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y. A new breed resource in China—Chinese Simmental cattle. J. Yellow Cattle Sci. 2002, 5, 67–69. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Jin, S.; Bao, J.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; Li, J. The Growth Curve Fitting and the Correlation Analysis between Body Weight and Body Measurements in Chinese Simmental Beef Cattle Population. Acta Vet. Zootech. Sin. 2018, 49, 497–506. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzhugh, H.A. Analysis of Growth Curves and Strategies for Altering Their Shape. J. Anim. Sci. 1976, 42, 1036–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denise, R.S.K.; Brinks, J.S. Genetic and Environmental Aspects of the Growth Curve Parameters in Beef Cows. J. Anim. Sci. 1985, 61, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zainaguli, J.; Tan, R.; Huang, X.-X.; Wang, Y.-C.; Rexiti, A.; Nuerbiye, W.; Cheng, L.-M.; Fu, X.-F.; Jia, X.-S.; Zeng, L. Fitting the Weight Growth Curve of Xinjiang Brown Cattle. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2014, 41, 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- Dekkers, J.C.M. Commercial application of marker- and gene-assisted selection in livestock: Strategies and lessons. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hou, L.; Ma, J.; Chen, C.; Ai, H.; Huang, L.-S.; Ren, J. Genome-wide detection of genetic markers associated with growth and fatness in four pig populations using four approaches. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2017, 49, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bottolo, L.; Chadeau-Hyam, M.; Hastie, D.I.; Zeller, T.; Liquet, B.; Newcombe, P.; Yengo, L.; Wild, P.S.; Schillert, A.; Ziegler, A.; et al. GUESS-ing polygenic associations with multiple phenotypes using a GPU-based evolutionary stochastic search algorithm. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Stephens, M. Genome-wide efficient mixed-model analysis for association studies. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Reilly, P.F.; Hoggart, C.J.; Pomyen, Y.; Calboli, F.C.F.; Elliott, P.; Järvelin, M.-R.; Coin, L.J. MultiPhen: Joint Model of Multiple Phenotypes Can Increase Discovery in GWAS. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covington, J.D.; Noland, R.C.; Hebert, R.C.; Masinter, B.S.; Smith, S.R.; Rustan, A.C.; Ravussin, E.; Bajpeyi, S. Perilipin 3 Differentially Regulates Skeletal Muscle Lipid Oxidation in Active, Sedentary, and Type 2 Diabetic Males. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 3683–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camera, E.; Dahlhoff, M.; Ludovici, M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Schneider, M.R. Perilipin 3 modulates specific lipogenic pathways in SZ95 sebocytes. Exp. Derm. 2014, 23, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa-Urrutia, P.; Colistro, V.; Jiménez-Osorio, A.S.; Cárdenas-Hernández, H.; Solares-Tlapechco, J.; Ramirez-Alcántara, M.; Granados, J.; Ascencio-Montiel, I.J.; Rodríguez-Arellano, M.E. Genome-Wide As-sociation Study of Body Mass Index and Body Fat in Mexican-Mestizo Children. Genes (Basel) 2019, 10, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabia, B.; Andrade, S.; Carreira, M.C.; Casanueva, F.F.; Crujeiras, A.B. A role for novel adipose tis-sue-secreted factors in obesity-related carcinogenesis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 361–376. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Uemoto, Y.; Mikawa, S.; Suzuki, K. Effect of candidate gene polymorphisms on repro-ductive traits in a Large White pig population. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Frater, J.; Lie, D.; Bartlett, P.; McGrath, J.J. Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) as a marker of cognitive decline in normal ageing: A review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2018, 42, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argente, J.; Pérez-Jurado, L.A. Genetic causes of proportionate short stature. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 32, 499–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramayo-Caldas, Y.; Fortes, M.R.; Hudson, N.J.; Porto-Neto, L.R.; Bolormaa, S.; Barendse, W.; Kelly, M.; Moore, S.S.; Goddard, M.E.; Lehnert, S.A.; et al. A marker-derived gene network reveals the regulatory role of PPARGC1A, HNF4G, and FOXP3 in intramuscular fat deposition of beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 92, 2832–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Choi, J.H.; Shi, H.; Zhang, L.; Su, S.; Wang, X. Discovery and Validation of a Novel Neutrophil Activation Marker Associated with Obesity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, A. Association of EphA4 polymorphism with swine reproductive traits and mRNA ex-pression of EphA4 during embryo implantation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 2689–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Wu, M.; Ma, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhao, F.; Wei, C.; Du, L. Genome-Wide Specific Selection in Three Domestic Sheep Breeds. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, D. The Hippo Signaling Pathway in Development and Cancer. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Beaudoin, F.; Ammah, A.A.; Bissonnette, N.; Benchaar, C.; Zhao, X.; Lei, C.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M. Deep sequencing shows microRNA involvement in bovine mammary gland adaptation to diets supplemented with linseed oil or safflower oil. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trinh, J.; Hüning, I.; Yüksel, Z.; Baalmann, N.; Imhoff, S.; Klein, C.; Rolfs, A.; Gillessen-Kaesbach, G.; Lohmann, K. A KAT6A variant in a family with autosomal dominantly inherited microcephaly and developmental delay. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 63, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, M.; Hurst, J.; Brown, S.; Bishop, N.J.; Arundel, P.; DeVile, C.; Pollitt, R.C.; Crooks, L.; Longman, D.; Caceres, J.F.; et al. Compound heterozygous variants in NBAS as a cause of atypical osteogenesis im-perfecta. Bone 2017, 94, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.D.; Kerlavage, A.R.; Fleischmann, R.D.; Fuldner, R.A.; Bult, C.J.; Lee, N.H.; Kirkness, E.F.; Weinstock, K.G.; Gocayne, J.D.; White, O. Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence. Nature 1995, 377, 3–174. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudet, P.; Livstone, M.S.; Lewis, S.E.; Thomas, P.D. Phylogenetic-based propagation of functional annotations within the Gene Ontology consortium. Brief Bioinform. 2011, 12, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Age (Month) | Max (kg) | Min (kg) | Mean (kg) | Standard Deviation (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 55.20 | 25.00 | 38.79 | 6.21 |
| 6 | 326.00 | 107.00 | 208.68 | 39.48 |
| 12 | 561.00 | 242.00 | 398.70 | 56.21 |
| 18 | 739.00 | 346.00 | 520.10 | 73.18 |
| Model | Function |
|---|---|
| Gompertz | W = Aexp(−bexp−Kt) |
| Logistic | W = A(1 + bexp−Kt)−1 |
| Brody | W = A(1 − bexp−Kt) |
| Parameter | Models | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gompertz | Logistic | Brody | |
| A | 617.900 | 551.000 | 1458.500 |
| b | 2.740 | 9.304 | 0.976 |
| K | 0.153 | 0.273 | 0.024 |
| R2 | 0.954 | 0.951 | 0.951 |
| Trait | SNP | BTA | Position | Distance | Gene | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | ARS-BFGL-NGS-14531 | 7 | 20,500,709 | 6291 | PLIN3 | 9.55 × 10−7 |
| BovineHD2200014587 | 22 | 51,133,487 | within (intronic) | BSN | 1.10 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1000029459 | 10 | 101,577,026 | within (intronic) | TTC8 | 1.12 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1500022754 | 15 | 78,218,321 | within (intronic) | C15H11ofF49 | 1.42 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0700005699 | 7 | 20461 012 | within (intronic) | UHRF1 | 2.08 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1100023174 | 11 | 80,858,593 | 14,458 | KCNS3 | 2.13 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1100023180 | 11 | 80,883,741 | 39,606 | KCNS3 | 2.61 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1100023175 | 11 | 80,860,546 | 16,411 | KCNS3 | 3.46 × 10−6 | |
| Hapmap36353-SCAFFOLD29708_3468 | 4 | 64,923,141 | 62,596 | PDE1C | 5.78 × 10−6 | |
| b | BovineHD0900028514 | 9 | 98,989,710 | within (exonic) | PRKN | 4.43 × 10−8 |
| BovineHD1300017399 | 13 | 60,669,478 | 15,189 | RSPO4 | 1.86 × 10−7 | |
| BTB-00981633 | 28 | 24,967,427 | within (intronic) | DNA2 | 1.90 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD1500020257 | 15 | 70,169,617 | 1,074,228 | LRRC4C | 4.73 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD1200006711 | 12 | 22,401,586 | 317,236 | COG6 | 5.26 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD2300007448 | 23 | 27,217,994 | within (intronic) | SKIV2L | 5.33 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD0900026419 | 9 | 93,361,299 | 12,446 | NOX3 | 6.17 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD1400018901 | 14 | 67,713,519 | within (intronic) | STK3 | 6.38 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD2300007441 | 23 | 27,195,210 | within (intronic) | C4A | 6.58 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD0900028515 | 9 | 98,990,425 | within | PRKN | 7.26 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD0300000940 | 3 | 3,186,646 | within (intronic) | TMCO1 | 9.11 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD0300000941 | 3 | 3,189,462 | within (intronic) | TMCO1 | 9.11 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD1100028458 | 11 | 97,919,703 | 60,177 | ANGPTL2 | 1.33 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1100028450 | 11 | 97,903,021 | 43,495 | ANGPTL2 | 1.34 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0100024671 | 1 | 86,573,589 | 93,224 | DNAJC19 | 2.37 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0900028520 | 9 | 99,001,573 | within (exonic) | PRKN | 2.54 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1400000353 | 14 | 2,382,595 | within (intronic) | ZC3H3 | 2.76 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1400000354 | 14 | 2,384,748 | within (intronic) | ZC3H3 | 2.76 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2300007455 | 23 | 27,227,600 | within (intronic) | CFB | 3.00 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2400010016 | 24 | 36,578,137 | 458,512 | ADCYAP1 | 3.03 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0300025174 | 3 | 87,908,532 | 16,189 | MYSM1 | 3.07 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0500018625 | 5 | 66,594,318 | within (intronic) | IGF-1 | 3.34 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0500018629 | 5 | 66,609,814 | 5314 | IGF-1 | 3.34 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0500018633 | 5 | 66,624,481 | 19,981 | IGF-1 | 3.34 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0100026284 | 1 | 92,441,255 | 1,184,964 | NLGN1 | 3.72 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1200008652 | 12 | 29,267,967 | within (exonic) | RXFP2 | 3.85 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0900028524 | 9 | 99,010,494 | within (exonic) | PRKN | 3.89 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1400000321 | 14 | 2,241,832 | 6798 | MAPK15 | 4.36 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1400000343 | 14 | 2,348,518 | 3233 | GSDMD | 4.68 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1900009534 | 19 | 32,360,589 | within (intronic) | HS3ST3A1 | 5.67 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0900028481 | 9 | 98,914,727 | within (exonic) | PRKN | 5.95 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0900028509 | 9 | 98,984,305 | within (exonic) | PRKN | 5.95 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0500018642 | 5 | 66,654,472 | 49,972 | IGF-1 | 6.01 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0900028504 | 9 | 98,967,507 | within (exonic) | PRKN | 6.05 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0300025183 | 3 | 87,959,712 | within (intronic) | MYSM1 | 6.27 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1200027060 | 12 | 64,329,068 | 1,659,351 | SLITRK5 | 6.45 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1200026793 | 12 | 18,310,824 | 9625 | RCBTB2 | 6.50 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2100014355 | 21 | 49,967,674 | 200,864 | FBXO33 | 6.69 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0300008509 | 3 | 26,888,743 | 28,039 | CD58 | 6.84 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0300008508 | 3 | 26,885,838 | 25,134 | CD58 | 6.98 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0200038336 | 2 | 131,809,255 | within (intronic) | ALPL | 8.81 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0200038337 | 2 | 131,810,815 | within (exonic) | ALPL | 8.81 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0200038343 | 2 | 131,820,288 | 7428 | ALPL | 8.81 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0200031784 | 2 | 110,303,552 | within (intronic) | EPHA4 | 9.04 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0100014672 | 1 | 52,227,088 | 136,783 | CCDC54 | 9.06 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1400008371 | 14 | 28,916,088 | 27,997 | ASPH | 9.15 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0200031783 | 2 | 110,302,531 | within (intronic) | EPHA4 | 9.19 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1400018902 | 14 | 67,716,121 | within (intronic) | STK3 | 9.42 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0200038341 | 2 | 131,817,068 | 4208 | ALPL | 9.84 × 10−6 | |
| K | BovineHD2200005378 | 22 | 18,694,612 | 60,070 | GRM7 | 3.24 × 10−6 |
| BovineHD2500003405 | 25 | 12,148,764 | 444,406 | SHISA9 | 3.82 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2200005379 | 22 | 18,697,043 | 57,639 | GRM7 | 3.89 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2500003397 | 25 | 12,122,951 | 418,593 | SHISA9 | 6.89 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2500003394 | 25 | 12,119,907 | 415,549 | SHISA9 | 7.09 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2500003411 | 25 | 12,164,708 | 460,350 | SHISA9 | 9.25 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2500003396 | 25 | 12,122,067 | 417,709 | SHISA9 | 9.70 × 10−6 | |
| Multi | BovineHD1000008269 | 10 | 25,336,507 | 11,871 | BT.86117 | 5.76 × 10−11 |
| BovineHD2300014561 | 23 | 49,948,237 | 785 | C6ORF146 | 5.11 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD0100017897 | 1 | 63,214,855 | within (intronic) | bta-mir-2285de | 8.19 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD1100024571 | 11 | 85,545,380 | 311,744 | TRIB2 | 9.06 × 10−7 | |
| BovineHD1900017810 | 19 | 61,961,078 | within (intronic) | ABVA10 | 1.78 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2200011596 | 22 | 40,545,626 | 185,054 | BT.92027 | 2.22 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1300005737 | 13 | 19,728,845 | 183,012 | NRP1 | 2.77 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1400005409 | 14 | 18,830,773 | 441,600 | BT.88023 | 2.77 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1400018913 | 14 | 67,761,416 | within (exonic) | STK3 | 3.41 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2400015566 | 24 | 54,582,317 | 107,987 | C18ORF26 | 3.89 × 10−6 | |
| Hapmap46842-BTA-57397 | 24 | 11,851,627 | 637,616 | CDH7 | 4.32 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1400003514 | 14 | 12,051,695 | 146,289 | GSDMC | 4.44 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0200034312 | 2 | 118,915,870 | within (intronic) | PSMD1 | 5.65 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0900014829 | 9 | 53,862,308 | 48,559 | GPR63 | 5.70 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2700010439 | 27 | 36,460,835 | 72,147 | KAT6A | 5.71 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1100023984 | 11 | 83,388,941 | 200,644 | NBAS | 6.15 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0900002818 | 9 | 11,192,144 | 488,896 | RIMS1 | 6.15 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1300006393 | 13 | 21,900,826 | within (intronic) | PLXDC2 | 6.15 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0200019309 | 2 | 66,721,486 | 808,880 | ACTR3 | 8.50 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD1800012623 | 18 | 42,743,057 | 295,489 | ZNF507 | 9.33 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD0300008523 | 3 | 26,920,280 | 59,576 | CD58 | 9.36 × 10−6 | |
| BovineHD2900005573 | 29 | 19,238,772 | 49,975 | GDPD4 | 9.53 × 10−6 |
| Gene Name | Term | Database | ID | DEG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALPL | Hippo signaling pathway—multiple species | KEGG pathway | bta00730 | 1 |
| biomineral tissue development | Gene Ontology | GO:0031214 | 1 | |
| ANGPTL2 | angiogenesis | Gene Ontology | GO:0001525 | 1 |
| EPHA4 | Axon guidance | KEGG pathway | bta04360 | 1 |
| nephric duct morphogenesis | Gene Ontology | GO:0072178 | 1 | |
| cochlea development | Gene Ontology | GO:0090102 | 1 | |
| KAT6A | Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | KEGG pathway | bta04550 | 1 |
| PLIN3 | lipid storage | Gene Ontology | GO:0019915 | 1 |
| PRKAG3 | Longevity regulating pathway—multiple species | KEGG pathway | bta04213 | 1 |
| Apelin signaling pathway | KEGG pathway | bta04371 | 1 | |
| fatty acid biosynthetic process | Gene Ontology | GO:0006633 | 1 | |
| ASPH | limb morphogenesis | Gene Ontology | GO:0035108 | 1 |
| roof of mouth development | Gene Ontology | GO:0060021 | 1 | |
| ASPH, STK3 | negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Gene Ontology | GO:0008285 | 2 |
| STK3 | Hippo signaling pathway | KEGG pathway | bta04390 | 1 |
| MAPK signaling pathway | KEGG pathway | bta04010 | 1 | |
| cell differentiation involved in embryonic placenta development | Gene Ontology | GO:0060706 | 1 | |
| hepatocyte apoptotic process | Gene Ontology | GO:0097284 | 1 | |
| negative regulation of organ growth | Gene Ontology | GO:0046621 | 1 | |
| positive regulation of fat cell differentiation | Gene Ontology | GO:0045600 | 1 | |
| central nervous system development | Gene Ontology | GO:0007417 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, X.; An, B.; Du, L.; Chang, T.; Liang, M.; Yang, B.-G.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; E, G.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Growth Curve Parameters in Chinese Simmental Beef Cattle. Animals 2021, 11, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010192
Duan X, An B, Du L, Chang T, Liang M, Yang B-G, Xu L, Zhang L, Li J, E G, et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Growth Curve Parameters in Chinese Simmental Beef Cattle. Animals. 2021; 11(1):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010192
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Xinghai, Bingxing An, Lili Du, Tianpeng Chang, Mang Liang, Bai-Gao Yang, Lingyang Xu, Lupei Zhang, Junya Li, Guangxin E, and et al. 2021. "Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Growth Curve Parameters in Chinese Simmental Beef Cattle" Animals 11, no. 1: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010192
APA StyleDuan, X., An, B., Du, L., Chang, T., Liang, M., Yang, B.-G., Xu, L., Zhang, L., Li, J., E, G., & Gao, H. (2021). Genome-Wide Association Analysis of Growth Curve Parameters in Chinese Simmental Beef Cattle. Animals, 11(1), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010192





