Steroid Receptor Coregulators Can Modulate the Action of Progesterone Receptor during the Estrous Cycle in Cow Endometrium
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Collection
2.2. Progesterone Concentrations
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription
2.5. Real-Time PCR
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. HAT and HDAC Activity
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Immunohistochemistry
3.2. Progesterone Concentrations
3.3. mRNA Levels of Coregulators, PGRA, and PGRB Isoforms in the Endometrium
3.4. The Protein Levels of Coregulators in the Endometrium
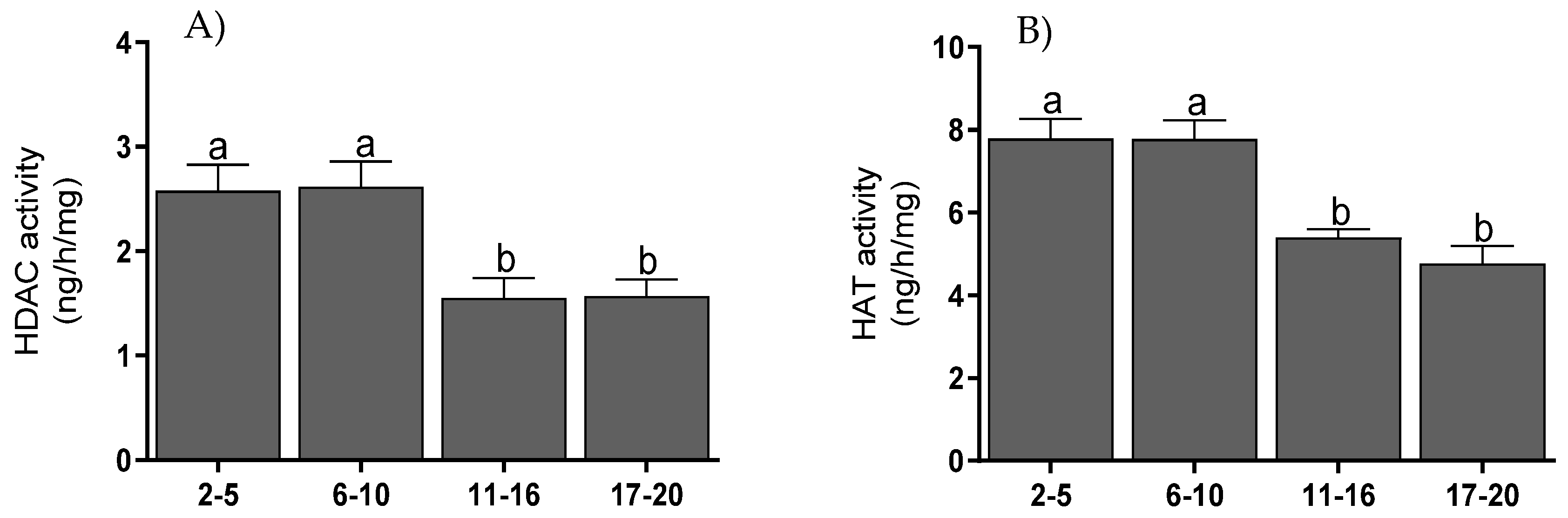
3.5. Histone Acetyltransferase and Histone Deacetylase Activities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krzymowski, T.; Stefańczyk-Krzymowska, S. Uterine Blood Supply as a Main Factor Involved in the Regulation of the Estrous Cycle—A New Theory. Reprod. Biol. 2002, 2, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krzymowski, T.; Stefańczyk-Krzymowska, S. The Oestrous Cycle and Early Pregnancy—A New Concept of Local Endocrine Regulation. Vet. J. 2004, 168, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulac-Jericevic, B.; Conneely, O.M. Reproductive Tissue Selective Actions of Progesterone Receptors. Reproduction 2004, 128, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, D.X.; Xu, Y.F.; Mais, D.E.; Goldman, M.E.; McDonnell, D.P. The A and B Isoforms of the Human Progesterone Receptor Operate through Distinct Signaling Pathways within Target Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 8356–8364. [Google Scholar]
- Pieber, D.; Allport, V.C.; Bennett, P.R. Progesterone Receptor Isoform A Inhibits Isoform B-Mediated Transactivation in Human amnion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 427, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, T.; Shih, H.-C.; Miyamoto, T.; Feng, Y.-Z.; Uchikawa, J.; Itoh, K.; Konishi, I. Cyclic Changes in the Expression of Steroid Receptor Coactivators and Corepressors in the Normal Human Endometrium. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Glass, C.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Coactivator and Corepressor Complexes in Nuclear Receptor Function. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1999, 9, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanstein, B.; Eckner, R.; DiRenzo, J.; Halachmi, S.; Liu, H.; Searcy, B.; Kurokawa, R.; Brown, M. P300 Is a Component of an Estrogen Receptor Coactivator Complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11540–11545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bevan, C.L.; Hoare, S.; Claessens, F.; Heery, D.M.; Parker, M.G. The AF1 and AF2 Domains of the Androgen Receptor Interact with Distinct Regions of SRC1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 8383–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKay, L.I.; Cidlowski, J.A. CBP (CREB Binding Protein) Integrates NF-KappaB (Nuclear Factor-KappaB) and Glucocorticoid Receptor Physical Interactions and Antagonism. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyler, J.K.; Kadonaga, J.T. The “Dark Side” of Chromatin Remodeling: Repressive Effects on Transcription. Cell 1999, 99, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazar, M.A. Nuclear Receptor Corepressors. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2003, 1, e001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonard, D.M.; Lanz, R.B.; O’Malley, B.W. Nuclear Receptor Coregulators and Human Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lonard, D.M.; O’Malley, B.W. Nuclear Receptor Coregulators: Modulators of Pathology and Therapeutic Targets. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekawiecki, R.; Kowalik, M.K.; Kotwica, J. The Expression of Progesterone Receptor Coregulators MRNA and Protein in Corpus Luteum and Endometrium of Cows during the Estrous Cycle. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2017, 183, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireland, J.J.; Murphee, R.L.; Coulson, P.B. Accuracy of Predicting Stages of Bovine Estrous Cycle by Gross Appearance of the Corpus Luteum. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, M.J.; Fields, P.A. Morphological Characteristics of the Bovine Corpus Luteum during the Estrous Cycle and Pregnancy. Theriogenology 1996, 45, 1295–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, P.C.; Walton, J.S.; Hansel, W. Oxytocin-Specific RNA, Oxytocin and Progesterone Concentrations in Corpora Lutea of Heifers Treated with Oxytocin. J. Reprod. Fertil. 1990, 89, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwica, J.; Skarzynski, D.J.; Jaroszewski, J.J.; Bogacki, M. Noradrenaline Affects Secretory Function of Corpus Luteum Independently on Prostaglandins in Conscious Cattle. Prostaglandins 1994, 48, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single-Step Method of RNA Isolation by Acid Guanidinium Thiocyanate-Phenol-Chloroform Extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.C.; Berkelman, T.; Yadav, G.; Hammond, M. A Defined Methodology for Reliable Quantification of Western Blot Data. Mol. Biotechnol. 2013, 55, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Fernald, R.D. Comprehensive Algorithm for Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Comput. Biol. 2005, 12, 1047–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekawiecki, R.; Dobrzyn, K.; Kotwica, J.; Kowalik, M.K. Progesterone Receptor Coregulators as Factors Supporting the Function of the Corpus Luteum in Cows. Genes 2020, 11, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boos, A.; Meyer, W.; Schwarz, R.; Grunert, E. Immunohistochemical Assessment of Oestrogen Receptor and Progesterone Receptor Distribution in Biopsy Samples of the Bovine Endometrium Collected throughout the Oestrous Cycle. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 1996, 44, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, I.; Torres Neto, R.; Oba, E.; Buratini, J.; Binelli, M.; Laufer-Amorim, R.; Ferreira, J.C.P. Immunohistochemical Detection of Receptors for Oestrogen and Progesterone in Endometrial Glands and Stroma during the Oestrous Cycle in Nelore (Bos taurus indicus) Cows. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2008, 43, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalik, M.K.; Slonina, D.; Rekawiecki, R.; Kotwica, J. Expression of Progesterone Receptor Membrane Component (PGRMC) 1 and 2, Serpine MRNA Binding Protein 1 (SERBP1) and Nuclear Progesterone Receptor (PGR) in the Bovine Endometrium during the Estrous Cycle and the First Trimester of Pregnancy. Reprod. Biol. 2013, 13, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niswender, G.D.; Juengel, J.L.; Silva, P.J.; Rollyson, M.K.; McIntush, E.W. Mechanisms Controlling the Function and Life Span of the Corpus Luteum. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misao, R.; Nakanishi, Y.; Iwagaki, S.; Fujimoto, J.; Tamaya, T. Expression of Progesterone Receptor Isoforms in Corpora Lutea of Human Subjects: Correlation with Serum Oestrogen and Progesterone Concentrations. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1998, 4, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekawiecki, R.; Kowalik, M.K.; Kotwica, J. Cloning and Expression of Progesterone Receptor Isoforms A and B in Bovine Corpus Luteum. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2015, 27, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, B.G.; O’Malley, B.W. Progesterone Receptor Coactivators. Steroids 2000, 65, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosh, J.A.; Banu, S.K.; Chapdelaine, P.; Madore, E.; Sirois, J.; Fortier, M.A. Prostaglandin Biosynthesis, Transport, and Signaling in Corpus Luteum: A Basis for Autoregulation of Luteal Function. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, M.; Yoshioka, S.; Tasaki, Y.; Okuda, K. Remodeling of Bovine Endometrium throughout the Estrous Cycle. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2013, 142, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmins, S.; MacLaren, L.A. Oestrous Cycle and Pregnancy Effects on the Distribution of Oestrogen and Progesterone Receptors in Bovine Endometrium. Placenta 2001, 22, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, P.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Pintilie, G.D.; Foulds, C.E.; Lanz, R.B.; Ludtke, S.J.; Schmid, M.F.; Chiu, W.; O’Malley, B.W. Structure of a Biologically Active Estrogen Receptor-Coactivator Complex on DNA. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Billhaq, D.H.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, S. The Potential Function of Endometrial-Secreted Factors for Endometrium Remodeling during the Estrous Cycle. Anim. Sci. J. 2020, 91, e13333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heery, D.M.; Kalkhoven, E.; Hoare, S.; Parker, M.G. A Signature Motif in Transcriptional Co-Activators Mediates Binding to Nuclear Receptors. Nature 1997, 387, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perissi, V.; Staszewski, L.M.; McInerney, E.M.; Kurokawa, R.; Krones, A.; Rose, D.W.; Lambert, M.H.; Milburn, M.V.; Glass, C.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Molecular Determinants of Nuclear Receptor-Corepressor Interaction. Genes. Dev. 1999, 13, 3198–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagy, L.; Kao, H.Y.; Love, J.D.; Li, C.; Banayo, E.; Gooch, J.T.; Krishna, V.; Chatterjee, K.; Evans, R.M.; Schwabe, J.W. Mechanism of Corepressor Binding and Release from Nuclear Hormone Receptors. Genes. Dev. 1999, 13, 3209–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tagami, T.; Gu, W.-X.; Peairs, P.T.; West, B.L.; Jameson, J.L. A Novel Natural Mutation in the Thyroid Hormone Receptor Defines a Dual Functional Domain That Exchanges Nuclear Receptor Corepressors and Coactivators. Mol. Endocrinol. 1998, 12, 1888–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, L.J.; Brooks, M.W.; Laufer, E.M.; Land, H. Negative Autoregulation of C-Myc Transcription. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, D.; Colangelo, C.; Williams, K.; Gerstein, M. Comparing Protein Abundance and MRNA Expression Levels on a Genomic Scale. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lonard, D.M.; O’malley, B.W. Nuclear Receptor Coregulators: Judges, Juries, and Executioners of Cellular Regulation. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, S.K.; Farquhar, C.M.; Mitchell, M.D.; Ponnampalam, A.P. Epigenetic Regulation of Endometrium during the Menstrual Cycle. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 16, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gujral, P.; Mahajan, V.; Lissaman, A.C.; Ponnampalam, A.P. Histone Acetylation and the Role of Histone Deacetylases in Normal Cyclic Endometrium. Reprod. Biol. Endocrin. 2020, 18, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peserico, A.; Simone, C. Physical and Functional HAT/HDAC Interplay Regulates Protein Acetylation Balance. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 371832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Icardi, L.; De Bosscher, K.; Tavernier, J. The HAT/HDAC Interplay: Multilevel Control of STAT Signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012, 23, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
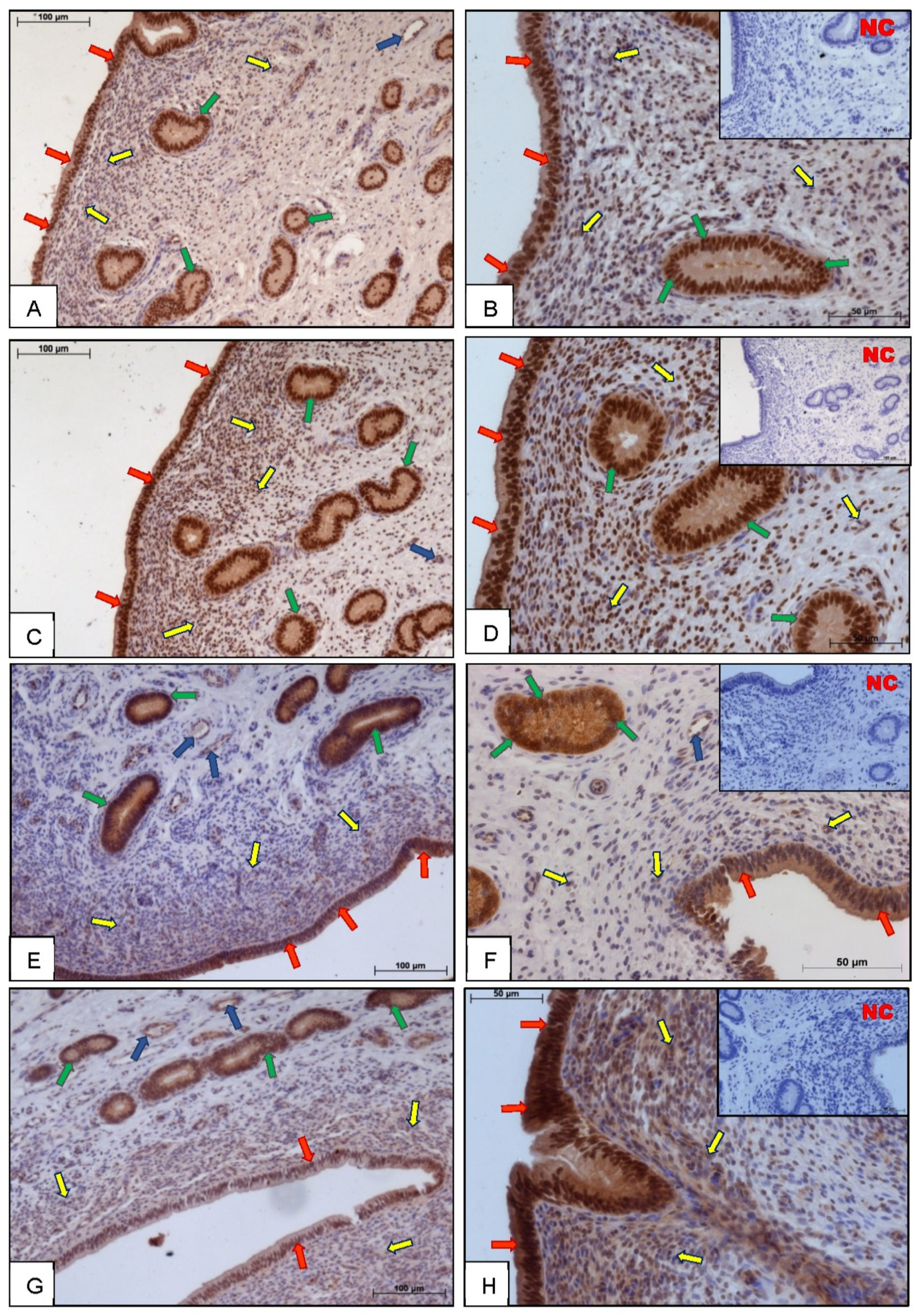
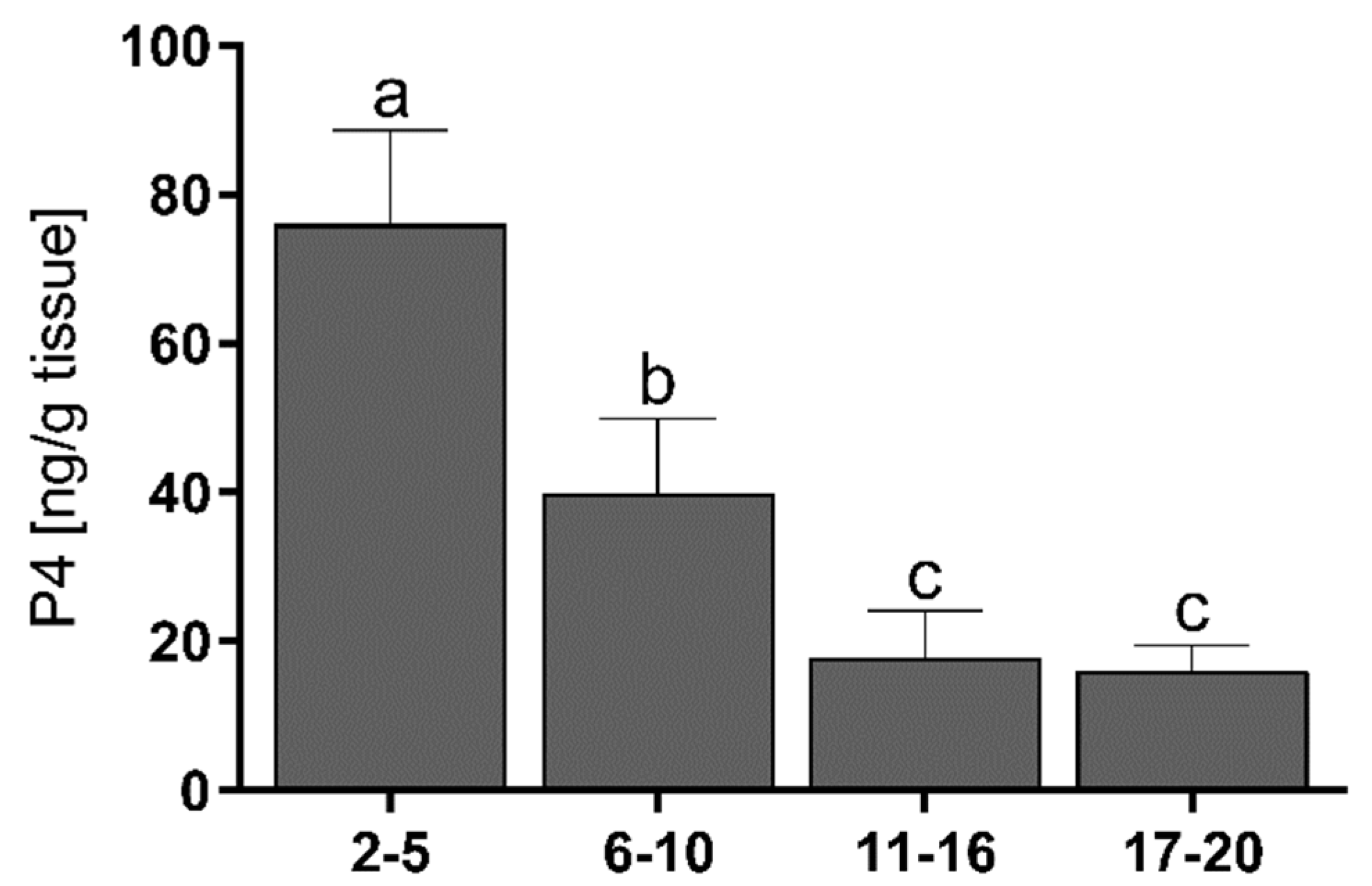
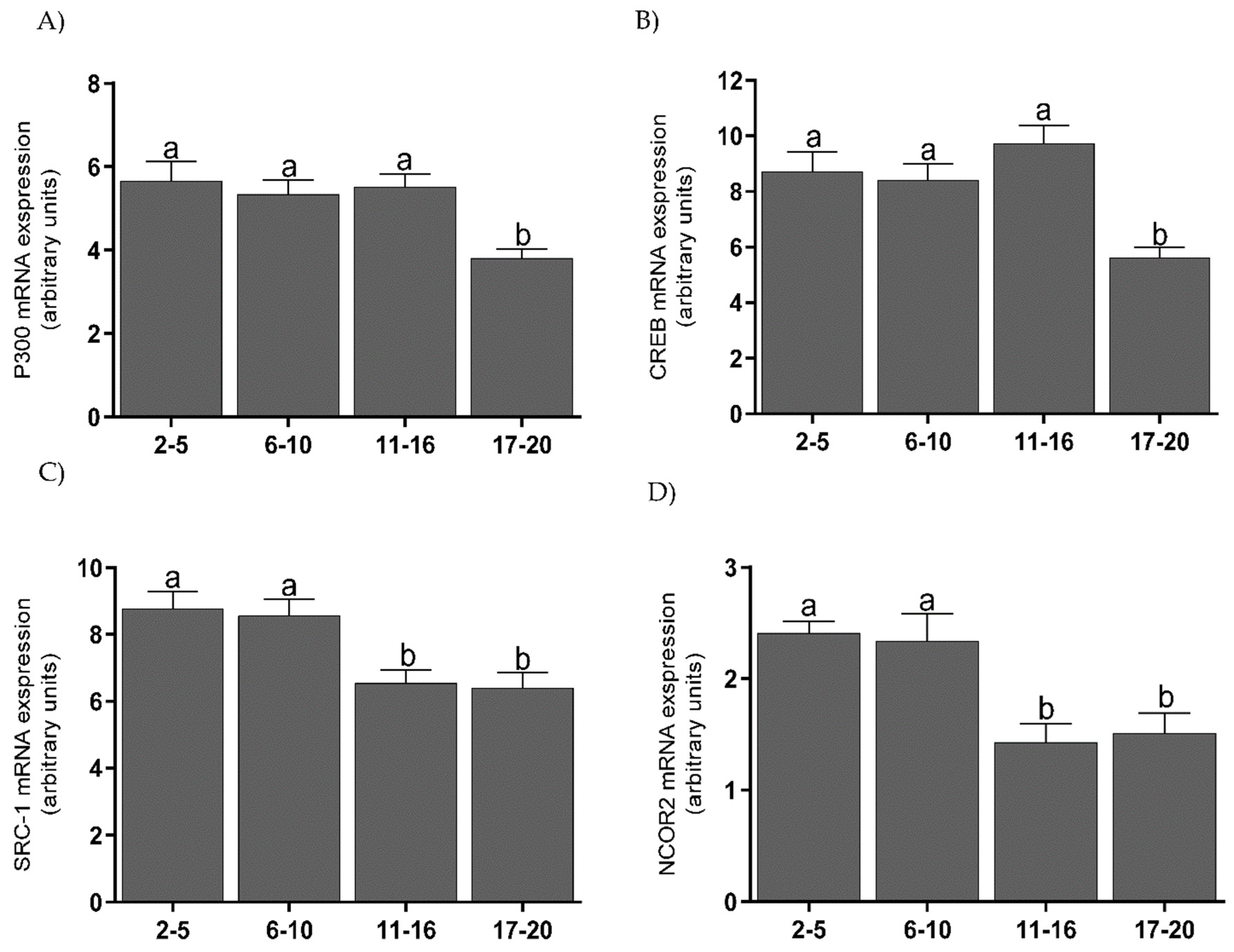
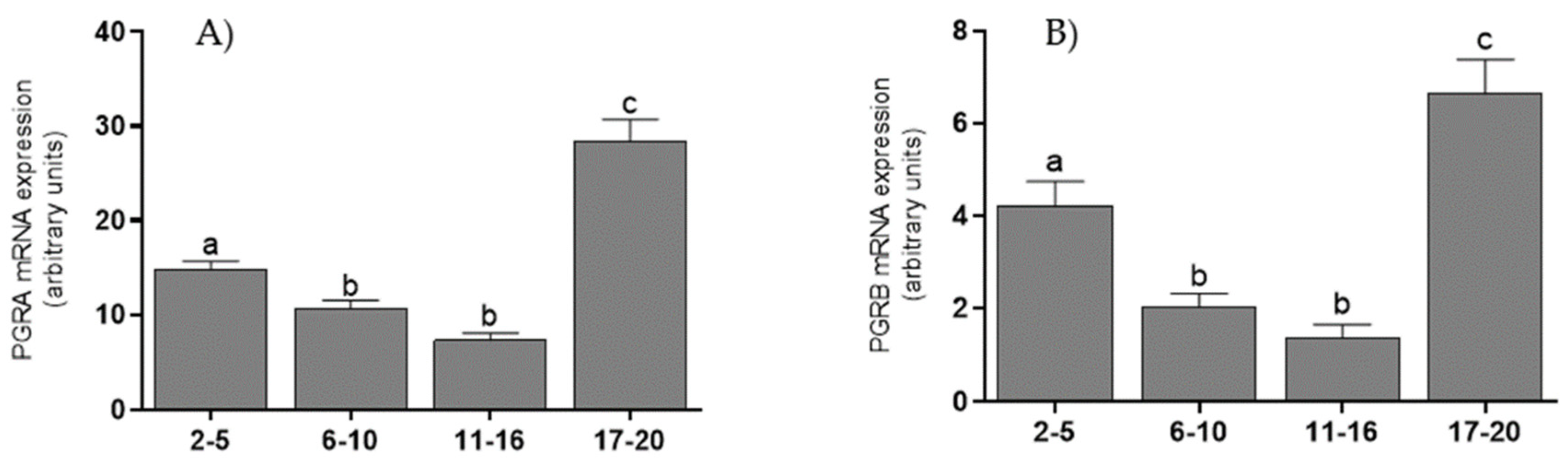

| Gen Name | Primers | GenBank Accession Number | Amplicon Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| P300 | Forward: CCATGAGCAACATGAGTGCTAGT Reverse: CATTGTCACTCATCAGTGGGTTTT | XM_027540695.1 | 129 |
| CBP | Forward: TGAAGTGAAGGTCGAAGCTAAAGA Reverse: GTACAGAGCTTCCAGGGTTGACAT | XM_024984694.1 | 147 |
| SRC-1 | Forward: CCCAGGCAGACGCTAAACAG Reverse: TCAAGATAGCTTGCCGATTTTG | XM_028514416.1 | 114 |
| NCOR-2 | Forward: AGCCCTCGAGGCAAAAGC Reverse: CATGCGGAGAGGCCTTGA | XM_024977670.1 | 177 |
| TBP | Forward: CAGAGAGCTCCGGGATCGT Reverse: ACACCATCTTCCCAGAACTGAATAT | NM_001075742 | 194 |
| PGRB | Custom Plus TaqMan RNA, Assay ID: AJY9X9P | - | |
| PGRA | Forward: GGCAATTGGTTTGAGGCAAA Reverse: TCTTGGGTAACTGTGCAGCAA Probe: TTGTCCCTAGCTCACAGCGTTTCTATCAGC | AJ557823.1 | 196 |
| TBP | Forward: CAGAGAGCTCCGGGATCGT Reverse: ACACCATCTTCCCAGAACTGAATAT Probe: AATCCCAAGCGTTTTGCTGCTGTAATCA | NM_001075742 | 194 |
| P300 | CBP | SRC-1 | NCOR-2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P4-mRNA | ns | ns | r = 0.70 p < 0.0001 | r = 0.61 p < 0.001 |
| P4-protein | ns | r = 0.69 p < 0.0001 | r = 0.83 p < 0.0001 | r = 0.78 p < 0.0001 |
| mRNA-protein | r = −0.57 p < 0.01 | ns | ns | ns |
| HAT-mRNA | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| HAT-protein | ns | r = 0.72 p < 0.0001 | ns | r = 0.56 p < 0.05 |
| HDAC-mRNA | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| HDAC-protein | ns | r = 0.60 p < 0.001 | r = 0.49 p < 0.05 | r = 0.51 p < 0.05 |
| HAT-HDAC | r = 0.58 p < 0.001 | |||
| PGRA mRNA-mRNA | ns | ns | ns | r = −0.54 p < 0.05 |
| PGRB mRNA-mRNA | ns | r = −0.50 p < 0.05 | r = −0.58 p < 0.05 | r = −0.65 p < 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rekawiecki, R.; Dobrzyn, K.; Kowalik, M.K. Steroid Receptor Coregulators Can Modulate the Action of Progesterone Receptor during the Estrous Cycle in Cow Endometrium. Animals 2021, 11, 3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113217
Rekawiecki R, Dobrzyn K, Kowalik MK. Steroid Receptor Coregulators Can Modulate the Action of Progesterone Receptor during the Estrous Cycle in Cow Endometrium. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113217
Chicago/Turabian StyleRekawiecki, Robert, Karolina Dobrzyn, and Magdalena K. Kowalik. 2021. "Steroid Receptor Coregulators Can Modulate the Action of Progesterone Receptor during the Estrous Cycle in Cow Endometrium" Animals 11, no. 11: 3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113217
APA StyleRekawiecki, R., Dobrzyn, K., & Kowalik, M. K. (2021). Steroid Receptor Coregulators Can Modulate the Action of Progesterone Receptor during the Estrous Cycle in Cow Endometrium. Animals, 11(11), 3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113217






