Managing Gut Microbiota through In Ovo Nutrition Influences Early-Life Programming in Broiler Chickens
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Development of Gut Microbiota in Newly Hatched Chicks
1.2. Function of Gut Microbiota
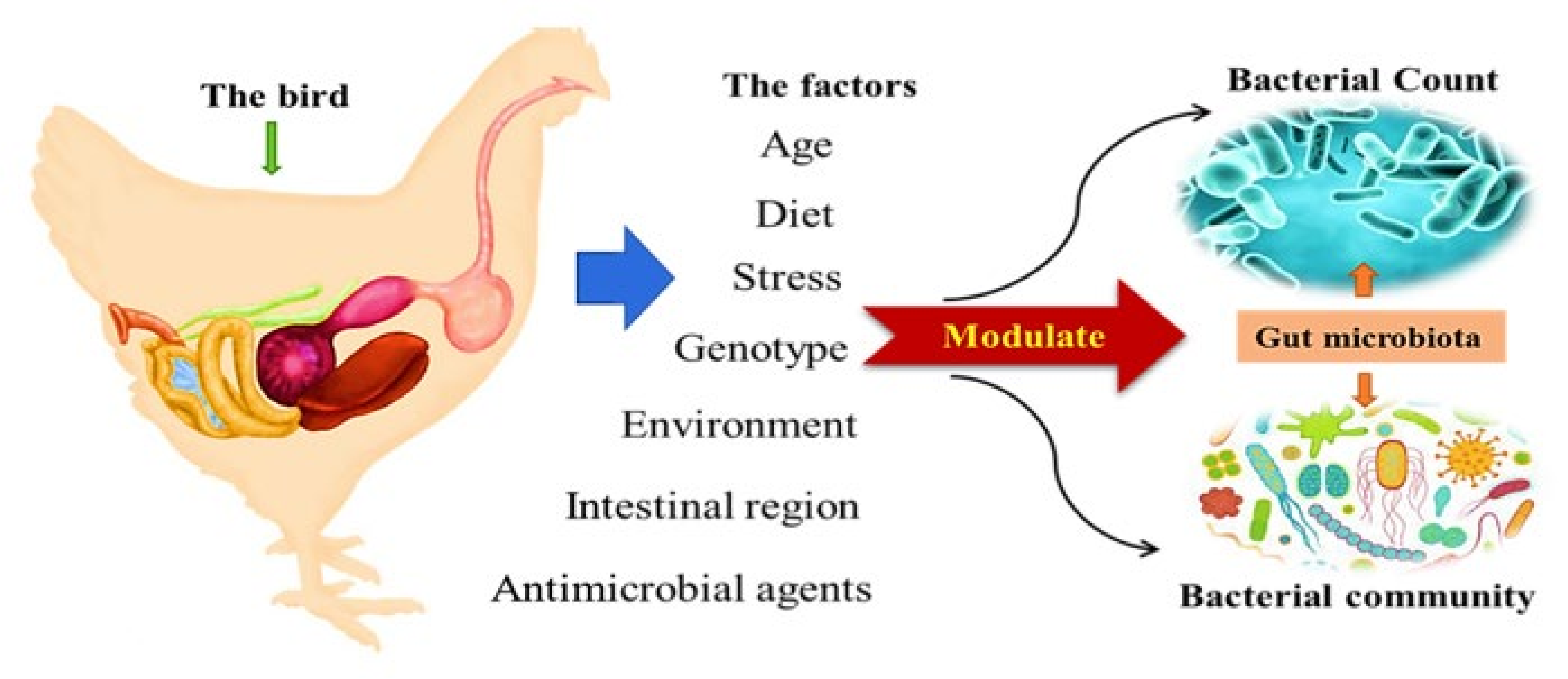
2. Modulation of Gut Microbiota
3. In Ovo Technique as a Novel Tool for Early-Life Programming
4. Basics of In Ovo Technique
5. Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Immune Homeostasis
6. Gut Microbiota and Growth Performance
7. Gut Microbiota and Immune Responses
8. Gut Microbiota and Cecal SCFA Concentration
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E.; Shehata, A.M.; Mohamed, N.G.; Elbaz, A.M.; Ibrahim, N.S. Synergistic effect of Spirulina platensis and selenium nanoparticles on growth performance, serum metabolites, immune responses, and antioxidant capacity of heat-stressed broiler chickens. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uni, Z.; Yadgary, L.; Yair, R. Nutritional limitations during poultry embryonic development. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2012, 21, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Romanini, C.E.; Exadaktylos, V.; Bahr, C.; Berckmans, D.; Bergoug, H.; Eterradossi, N.; Roulston, N.; Verhelst, R.; McGonnell, I.M.; et al. Embryonic development and the physiological factors that coordinate hatching in domestic chickens. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shira, E.B.; Sklan, D.; Friedman, A. Impaired immune responses in broiler hatchling hindgut following delayed access to feed. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2005, 105, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Hodgins, D.C.; Lammers, A.; Alkie, T.N.; Sharif, S. Effects of early feeding and dietary interventions on development of lymphoid organs and immune competence in neonatal chickens: A review. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2018, 201, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, E.T. Nutrition of the Developing Embryo and Hatchling1. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, G.A.; Richardson, E.; Clark, J.; Keshri, J.; Drechsler, Y.; Berrang, M.E.; Meinersmann, R.J.; Cox, N.A.; Oakley, B.B. Broiler chickens and early life programming: Microbiome transplant-induced cecal community dynamics and phenotypic effects. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.; Singh, A.K.; Yadav, S.; Berrocoso, J.F.D.; Mishra, B. Early Nutrition Programming (in ovo and Post-hatch Feeding) as a Strategy to Modulate Gut Health of Poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, L.A. Possibilities of early life programming in broiler chickens via intestinal microbiota modulation. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, G. Essential fatty acids and early life programming in meat-type birds. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2011, 67, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, J.; Dai, R.; Yang, L.; He, C.; Xu, K.; Liu, S.; Zhao, W.; Xiao, L.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Inheritance and establishment of gut microbiota in chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kers, J.G.; Velkers, F.C.; Fischer, E.A.J.; Hermes, G.D.A.; Stegeman, J.A.; Smidt, H. Host and environmental factors affecting the intestinal microbiota in chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shang, Y.; Kumar, S.; Oakley, B.; Kim, W.K. Chicken gut microbiota: Importance and detection technology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Moneim, A.E.-M.E.; El-Wardany, I.; Abu-Taleb, A.M.; Wakwak, M.M.; Ebeid, T.A.; Saleh, A.A. Assessment of in ovo administration of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Bifidobacterium longum on performance, ileal histomorphometry, blood hematological, and biochemical parameters of broilers. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensollen, T.; Iyer, S.S.; Kasper, D.L.; Blumberg, R.S. How colonization by microbiota in early life shapes the immune system. Science 2016, 352, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roto, S.M.; Kwon, Y.M.; Ricke, S.C. Applications of In Ovo Technique for the Optimal Development of the Gastrointestinal Tract and the Potential Influence on the Establishment of Its Microbiome in Poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uni, Z.; Tako, E.; Gal-Garber, O.; Sklan, D. Morphological, molecular, and functional changes in the chicken small intestine of the late-term embryo. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunislawska, A.; Herosimczyk, A.; Lepczynski, A.; Slama, P.; Slawinska, A.; Bednarczyk, M.; Siwek, M. Molecular Response in Intestinal and Immune Tissues to In Ovo Administration of Inulin and the Combination of Inulin and Lactobacillus lactis Subsp. cremoris. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hino, S.; Takemura, N.; Sonoyama, K.; Morita, A.; Kawagishi, H.; Aoe, S.; Morita, T. Small intestinal goblet cell proliferation induced by ingestion of soluble and insoluble dietary fiber is characterized by an increase in sialylated mucins in rats. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pender, C.M.; Kim, S.; Potter, T.D.; Ritzi, M.M.; Young, M.; Dalloul, R.A. In ovo supplementation of probiotics and its effects on performance and immune-related gene expression in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arreguin-Nava, M.A.; Graham, B.D.; Adhikari, B.; Agnello, M.; Selby, C.M.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Vuong, C.N.; Solis-Cruz, B.; Hernandez-Patlan, D.; Latorre, J.D.; et al. Evaluation of in ovo Bacillus spp. based probiotic administration on horizontal transmission of virulent Escherichia coli in neonatal broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 6483–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E.; Elbaz, A.M.; Khidr, R.E.-S.; Badri, F.B. Effect of in ovo inoculation of Bifidobacterium spp. on growth performance, thyroid activity, ileum histomorphometry, and microbial enumeration of broilers. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 12, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.P.; Paswan, V.K.; Alolofi, A.M.A.; Abdelrazeq, A.M.; Rathaur, A. Dietary Supplementation of Mannan-Oligosaccharide on Carcass Traits and Physico-Chemical Attributes of Meat of Broiler Chickens. Int. J. Livest. Res. 2019, 9, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Shafi, M.E.; Alghamdi, W.Y.; Abdelnour, S.A.; Shehata, A.M.; Noreldin, A.E.; Ashour, E.A.; Swelum, A.A.; Al-Sagan, A.A.; Alkhateeb, M.; et al. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Meal as a Promising Feed Ingredient for Poultry: A Comprehensive Review. Agriculture 2020, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E.; Shehata, A.M.; Khidr, R.E.; Paswan, V.K.; Ibrahim, N.S.; El-Ghoul, A.A.; Aldhumri, S.A.; Gabr, S.A.; Mesalam, N.M.; Elbaz, A.M.; et al. Nutritional manipulation to combat heat stress in poultry—A comprehensive review. J. Therm. Biol. 2021, 98, 102915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, Y.A.; Alagawany, M.M.; Farag, M.R.; Alkhatib, F.M.; Khafaga, A.F.; Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E.; Asiry, K.A.; Mesalam, N.M.; Shafi, M.E.; Al-Harthi, M.A. Phytogenic products and phytochemicals as a candidate strategy to improve tolerance to coronavirus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 573159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Shehata, A.M.; Arif, M.; Paswan, V.K.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Khafaga, A.F.; Elbestawy, A.R. Approaches to prevent and control Campylobacter spp. colonization in broiler chickens: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 4989–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naiel, M.A.E.; Shehata, A.M.; Negm, S.S.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Amer, M.S.; Khafaga, A.F.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Allam, A.A. The new aspects of using some safe feed additives on alleviated imidacloprid toxicity in farmed fish: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 250–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.E.; Shehata, A.M.; Alzahrani, S.O.; Shafi, M.E.; Mesalam, N.M.; Taha, A.E.; Swelum, A.A.; Arif, M.; Fayyaz, M.; Abd El-Hack, M.E. The role of polyphenols in poultry nutrition. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 1851–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Shehata, A.M.; Saad, A.M.; Aldhumri, S.A.; Ouda, S.M.; Mesalam, N.M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Spirulina platensis extracts and biogenic selenium nanoparticles against selected pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kholy, M.S.; Ibrahim, Z.A.E.-G.; El-Mekkawy, M.M.; Alagawany, M. Influence of in ovo administration of some water-soluble vitamins on hatchability traits, growth, carcass traits and blood chemistry of Japanese quails. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2019, 19, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeed, M.; Babazadeh, D.; Naveed, M.; Alagawany, M.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Arain, M.A.; Tiwari, R.; Sachan, S.; Karthik, K.; Dhama, K. In ovo delivery of various biological supplements, vaccines and drugs in poultry: Current knowledge. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 3727–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fakhrany, H.H.; Ibrahim, Z.A.; Ashour, E.A.; Alagawany, M. Efficacy of in ovo delivered resveratrol (Trans 3, 4, 5-trihydroxystilbene) on growth, carcass weights, and blood metabolites of broiler chicks. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fakhrany, H.H.; Ibrahim, Z.A.; Ashour, E.A.; Osman, A.; Alagawany, M. Effects of in ovo injection of Astragalus kahericus polysaccharide on early growth, carcass weights and blood metabolites in broiler chickens. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lu, L.; Liao, X.; Zhang, L.; Lin, X.; Luo, X.; Ma, Q. Effect of in ovo zinc injection on the embryonic development and epigenetics-related indices of zinc-deprived broiler breeder eggs. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 185, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorska, M.; Siwek, M.; Slawinska, A.; Dunislawska, A. miRNA Profiling in the Chicken Liver under the Influence of Early Microbiota Stimulation with Probiotic, Prebiotic, and Synbiotic. Genes 2021, 12, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, G.R. Fibre and effects on probiotics (the prebiotic concept). Clin. Nutr. Suppl. 2004, 1, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Shafi, M.E.; Alshahrani, O.A.; Saghir, S.A.M.; Al-wajeeh, A.S.; Al-shargi, O.Y.A.; Taha, A.E.; Mesalam, N.M.; Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E. Prebiotics can restrict Salmonella populations in poultry: A review. Anim. Biotechnol. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Shafi, M.E.; Qattan, S.Y.A.; Batiha, G.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; Abdel-Moneim, A.E.; Alagawany, M. Probiotics in poultry feed: A comprehensive review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 1835–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, R.; Tang, L.; Gong, L.; Li, W. Effects of probiotics Lactobacillus plantarum 16 and Paenibacillus polymyxa 10 on intestinal barrier function, antioxidative capacity, apoptosis, immune response, and biochemical parameters in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5028–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemi, F.T.; Ding, J.; Zhou, H.; Xu, K.; He, C.; Han, C.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, H.; Yang, K.; Gu, C.; et al. Dynamic distribution of gut microbiota during embryonic development in chicken. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5079–5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Li, Q.; Lan, F.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Yan, Y.; Wu, G.; Yang, N.; Sun, C. Microbiota continuum along the chicken oviduct and its association with host genetics and egg formation. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, A.A.; Batal, A.B.; Lee, M.D. Effect of in ovo administration of an adult-derived microbiota on establishment of the intestinal microbiome in chickens. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 77, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellman-Labadie, O.; Picman, J.; Hincke, M.T. Avian antimicrobial proteins: Structure, distribution and activity. Worlds. Poult. Sci. J. 2007, 63, 421–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-L.; Cheng, Y.-S. A novel minisequencing single-nucleotide polymorphism marker of the lysozyme gene detects high hatchability of Tsaiya ducks (Anas platyrhynchos). Theriogenology 2014, 82, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; La, T.-M.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, I.-S.; Song, C.-S.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-B.; Lee, S.-W. Characterization of microbial communities in the chicken oviduct and the origin of chicken embryo gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Lei, F.; Zhu, L.; Li, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Gao, G.F.; Zhu, B.; Wang, X. Exposure of different bacterial inocula to newborn chicken affects gut microbiota development and ileum gene expression. ISME J. 2010, 4, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denbow, D.M. Gastrointestinal anatomy and physiology. In Sturkie’s Avian Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 337–366. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, D.E. The anatomy of the avian digestive tract as related to feed utilization. Poult. Sci. 1982, 61, 1225–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancabelli, L.; Ferrario, C.; Milani, C.; Mangifesta, M.; Turroni, F.; Duranti, S.; Lugli, G.A.; Viappiani, A.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; van Sinderen, D. Insights into the biodiversity of the gut microbiota of broiler chickens. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4727–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roto, S.M.; Rubinelli, P.M.; Ricke, S.C. An introduction to the avian gut microbiota and the effects of yeast-based prebiotic-type compounds as potential feed additives. Front. Vet. Sci. 2015, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayaraman, S.; Das, P.P.; Saini, P.C.; Roy, B.; Chatterjee, P.N. Use of Bacillus Subtilis PB6 as a potential antibiotic growth promoter replacement in improving performance of broiler birds. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2614–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A.; Cooper, C.; Thornburg, K.L. Effect of in utero and early-life conditions on adult health and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schokker, D.; Veninga, G.; Vastenhouw, S.A.; Bossers, A.; de Bree, F.M.; Kaal-Lansbergen, L.M.T.E.; Rebel, J.M.J.; Smits, M.A. Early life microbial colonization of the gut and intestinal development differ between genetically divergent broiler lines. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, D.; Yu, Z. Intestinal microbiome of poultry and its interaction with host and diet. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wielen, P.W.J.J.; Keuzenkamp, D.A.; Lipman, L.J.A.; Knapen, F.; Biesterveld, S. Spatial and Temporal Variation of the Intestinal Bacterial Community in Commercially Raised Broiler Chickens During Growth. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 44, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogut, M.H.; Lee, A.; Santin, E. Microbiome and pathogen interaction with the immune system. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1906–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenner, C.; Hitch, T.C.A.; Riedel, T.; Wortmann, E.; Tiede, S.; Buhl, E.M.; Abt, B.; Neuhaus, K.; Velge, P.; Overmann, J. Early-Life Immune System Maturation in Chickens Using a Synthetic Community of Cultured Gut Bacteria. Msystems 2021, 6, e01300–e01320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Eijk, J.A.J.; Rodenburg, T.B.; de Vries, H.; Kjaer, J.B.; Smidt, H.; Naguib, M.; Kemp, B.; Lammers, A. Early-life microbiota transplantation affects behavioural responses, serotonin and immune characteristics in chicken lines divergently selected on feather pecking. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gaboriaud, P.; Sadrin, G.; Guitton, E.; Fort, G.; Niepceron, A.; Lallier, N.; Rossignol, C.; Larcher, T.; Sausset, A.; Guabiraba, R. The absence of gut microbiota alters the development of the apicomplexan parasite Eimeria tenella. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Guo, Y. Dietary fiber and chicken microbiome interaction: Where will it lead to? Anim. Nutr. 2020, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J Tejeda, O.; K Kim, W. Role of Dietary Fiber in Poultry Nutrition. Animals 2021, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinttilä, T.; Apajalahti, J. Intestinal microbiota and metabolites—Implications for broiler chicken health and performance. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2013, 22, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheravii, S.K.; Morgan, N.K.; Swick, R.A.; Choct, M.; Wu, S.-B. Roles of dietary fibre and ingredient particle size in broiler nutrition. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2018, 74, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Moore, R.J.; Stanley, D.; Chousalkar, K.K. The gut microbiota of laying hens and its manipulation with prebiotics and probiotics to enhance gut health and food safety. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00600–e00620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rychlik, I. Composition and function of chicken gut microbiota. Animals 2020, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Classen, H.L.; Apajalahti, J.; Svihus, B.; Choct, M. The role of the crop in poultry production. Worlds. Poult. Sci. J. 2016, 72, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.H.; Song, W.; Lee, S.H.; Lillehoj, H.S. Differential gene expression profiles of β-defensins in the crop, intestine, and spleen using a necrotic enteritis model in 2 commercial broiler chicken lines. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierończyk, B.; Rawski, M.; Długosz, J.; Świątkiewicz, S.; Józefiak, D. Avian crop function—A review. Ann. Anim. Sci 2016, 16, 653–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeller, E.; Schollenberger, M.; Kühn, I.; Rodehutscord, M. Dietary effects on inositol phosphate breakdown in the crop of broilers. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 70, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Vahjen, W.; Dadi, T.; Saliu, E.-M.; Boroojeni, F.G.; Zentek, J. Synergistic Effects of Probiotics and Phytobiotics on the Intestinal Microbiota in Young Broiler Chicken. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuller, R. The chicken gut microflora and probiotic supplements. J. Poult. Sci. 2001, 38, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, X.; Shao, Y.; Sun, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Luo, X.; Lu, L. The relationship among gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, and intestinal morphology of growing and healthy broilers. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5883–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, H.; Kamikado, K.; Aoki, R.; Suganuma, N.; Nishijima, T.; Nakatani, A.; Kimura, I. Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis GCL2505 modulates host energy metabolism via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukunaga, T.; Sasaki, M.; Araki, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Yasuoka, T.; Tsujikawa, T.; Fujiyama, Y.; Bamba, T. Effects of the soluble fibre pectin on intestinal cell proliferation, fecal short chain fatty acid production and microbial population. Digestion 2003, 67, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Blay, G.; Blottière, H.M.; Ferrier, L.; Le Foll, E.; Bonnet, C.; Galmiche, J.-P.; Cherbut, C. Short-chain fatty acids induce cytoskeletal and extracellular protein modifications associated with modulation of proliferation on primary culture of rat intestinal smooth muscle cells. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2000, 45, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuki, T.; Pédron, T.; Regnault, B.; Mulet, C.; Hara, T.; Sansonetti, P.J. Epithelial cell proliferation arrest induced by lactate and acetate from Lactobacillus casei and Bifidobacterium breve. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, K.Y.C.; Cosgrove, L.; Lockett, T.; Head, R.; Topping, D.L. A review of the potential mechanisms for the lowering of colorectal oncogenesis by butyrate. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nepelska, M.; Cultrone, A.; Beguet-Crespel, F.; Le Roux, K.; Dore, J.; Arulampalam, V.; Blottière, H.M. Butyrate produced by commensal bacteria potentiates phorbol esters induced AP-1 response in human intestinal epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uni, Z.; Smirnov, A.; Sklan, D. Pre- and posthatch development of goblet cells in the broiler small intestine: Effect of delayed access to feed. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilburn, M.S.; Loeffler, S. Early intestinal growth and development in poultry. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyra, A.; Uni, Z.; Sklan, D. Enterocyte dynamics and mucosal development in the posthatch chick. Poult. Sci. 2001, 80, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Li, Z.; Mahmood, T.; Liu, D.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Y. The association between microbial community and ileal gene expression on intestinal wall thickness alterations in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1847–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutsko, S.L.; Meizlisch, K.; Wick, M.; Lilburn, M.S. Early intestinal development and mucin transcription in the young poult with probiotic and mannan oligosaccharide prebiotic supplementation. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forder, R.E.A.; Nattrass, G.S.; Geier, M.S.; Hughes, R.J.; Hynd, P.I. Quantitative analyses of genes associated with mucin synthesis of broiler chickens with induced necrotic enteritis. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacMillan, J.L.; Vicaretti, S.D.; Noyovitz, B.; Xing, X.; Low, K.E.; Inglis, G.D.; Zaytsoff, S.J.M.; Boraston, A.B.; Smith, S.P.; Uwiera, R.R.E. Structural analysis of broiler chicken small intestinal mucin O-glycan modification by Clostridium perfringens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5074–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Jha, R. Strategies to modulate the intestinal microbiota and their effects on nutrient utilization, performance, and health of poultry. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheled-Shoval, S.L.; Gamage, N.S.W.; Amit-Romach, E.; Forder, R.; Marshal, J.; Van Kessel, A.; Uni, Z. Differences in intestinal mucin dynamics between germ-free and conventionally reared chickens after mannan-oligosaccharide supplementation. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandori, H.; Hirayama, K.; Takeda, M.; Doi, K. Histochemical, lectin-histochemical and morphometrical characteristics of intestinal goblet cells of germfree and conventional mice. Exp. Anim. 1996, 45, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szentkuti, L.; Riedesel, H.; Enss, M.-L.; Gaertner, K.; Von Engelhardt, W. Pre-epithelial mucus layer in the colon of conventional and germ-free rats. Histochem. J. 1990, 22, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forder, R.E.A.; Howarth, G.S.; Tivey, D.R.; Hughes, R.J. Bacterial modulation of small intestinal goblet cells and mucin composition during early posthatch development of poultry. Poult. Sci. 2007, 86, 2396–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Shira, E.; Friedman, A. Development and adaptations of innate immunity in the gastrointestinal tract of the newly hatched chick. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegorzewska, M.M.; Glowacki, R.W.P.; Hsieh, S.A.; Donermeyer, D.L.; Hickey, C.A.; Horvath, S.C.; Martens, E.C.; Stappenbeck, T.S.; Allen, P.M. Diet modulates colonic T cell responses by regulating the expression of a Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron antigen. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewole, D.; Akinyemi, F. Gut Microbiota Dynamics, Growth Performance, and Gut Morphology in Broiler Chickens Fed Diets Varying in Energy Density with or without Bacitracin Methylene Disalicylate (BMD). Microorganisms 2021, 9, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontinha, F.; Magalhães, R.; Moutinho, S.; Santos, R.; Campos, P.; Serra, C.R.; Aires, T.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Peres, H. Effect of dietary poultry meal and oil on growth, digestive capacity, and gut microbiota of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) juveniles. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, S.M.; Al-Ajeeli, M.; Bailey, C.A.; Athrey, G. The role of housing environment and dietary protein source on the gut microbiota of chicken. Animals 2019, 9, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, R.; Mishra, P.; Jha, R. In ovo feeding as a tool for improving performance and gut health of poultry: A Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 754246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwek, M.; Slawinska, A.; Stadnicka, K.; Bogucka, J.; Dunislawska, A.; Bednarczyk, M. Prebiotics and synbiotics - in ovo delivery for improved lifespan condition in chicken. BMC Vet Res. 2018, 14, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faseleh Jahromi, M.; Shokryazdan, P.; Idrus, Z.; Ebrahimi, R.; Liang, J.B. In Ovo and dietary administration of oligosaccharides extracted from palm kernel cake influence general health of pre-and neonatal broiler chicks. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angwech, H.; Tavaniello, S.; Ongwech, A.; Kaaya, A.N.; Maiorano, G. Efficacy of In Ovo Delivered Prebiotics on Growth Performance, Meat Quality and Gut Health of Kuroiler Chickens in the Face of a Natural Coccidiosis Challenge. Animals 2019, 9, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricks, C.A.; Avakian, A.; Bryan, T.; Gildersleeve, R.; Haddad, E.; Ilich, R.; King, S.; Murray, L.; Phelps, P.; Poston, R. In ovo vaccination technology. Adv. Vet. Med. 1999, 41, 495–515. [Google Scholar]
- Bublot, M.; Sharma, J. Vaccination against Marek’s disease. In Marek’s Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 168–185. [Google Scholar]
- Salary, J.; Sahebi-Ala, F.; Kalantar, M.; Matin, H.R.H. In ovo injection of vitamin E on post-hatch immunological parameters and broiler chicken performance. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, S616–S619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhanja, S.K.; Mandal, A.B.; Majumdar, S.; Mehra, M.; Goel, A. Effect of in ovo injection of vitamins on the chick weight and post-hatch growth performance in broiler chickens. Indian J. Poult. Sci. 2012, 47, 306–310. [Google Scholar]
- Bhanja, S.K.; Mandal, A.B.; Johri, T.S. Standardization of injection site, needle length, embryonic age and concentration of amino acids for in ovo injection in broiler breeder eggs. Indian J. Poult. Sci. 2004, 39, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Bhanja, S.K.; Mandal, A.B.; Goswami, T.K. Effect of in ovo injection of amino acids on growth, immune response, development of digestive organs and carcass yields of broiler. Indian J. Poult. Sci. 2004, 39, 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Meaney, M.J.; Szyf, M.; Seckl, J.R. Epigenetic mechanisms of perinatal programming of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function and health. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babenko, O.; Kovalchuk, I.; Metz, G.A.S. Stress-induced perinatal and transgenerational epigenetic programming of brain development and mental health. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 48, 70–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanima, M.M.A.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Othman, S.I.; Taha, A.E.; Allam, A.A.; Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E. Impact of different rearing systems on growth, carcass traits, oxidative stress biomarkers and humoral immunity of broilers exposed to heat stress. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 3070–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehata, A.M.; Saadeldin, I.M.; Tukur, H.A.; Habashy, W.S. Modulation of Heat-Shock Proteins Mediates Chicken Cell Survival against Thermal Stress. Animals 2020, 10, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczypka, M.; Suszko-Pawłowska, A.; Kuczkowski, M.; Gorczykowski, M.; Lis, M.; Kowalczyk, A.; Łukaszewicz, E.; Poradowski, D.; Zbyryt, I.; Bednarczyk, M.; et al. Effects of Selected Prebiotics or Synbiotics Administered in ovo on Lymphocyte Subsets in Bursa of the Fabricius, Thymus, and Spleen in Non-Immunized and Immunized Chicken Broilers. Animals 2021, 11, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefaniak, T.; Madej, J.P.; Graczyk, S.; Siwek, M.; Łukaszewicz, E.; Kowalczyk, A.; Sieńczyk, M.; Maiorano, G.; Bednarczyk, M. Impact of Prebiotics and Synbiotics Administered in ovo on the Immune Response against Experimental Antigens in Chicken Broilers. Animals 2020, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madej, J.P.; Stefaniak, T.; Bednarczyk, M. Effect of in ovo-delivered prebiotics and synbiotics on lymphoid-organs’ morphology in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slawinska, A.; Plowiec, A.; Siwek, M.; Jaroszewski, M.; Bednarczyk, M. Long-term transcriptomic effects of prebiotics and synbiotics delivered in ovo in broiler chickens. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Oliveira, J.E.; van der Hoeven-Hangoor, E.; van de Linde, I.B.; Montijn, R.C.; van der Vossen, J.M.B.M. In ovo inoculation of chicken embryos with probiotic bacteria and its effect on posthatch Salmonella susceptibility. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGruder, B.M.; Zhai, W.; Keralapurath, M.M.; Bennett, L.W.; Gerard, P.D.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of in ovo injection of electrolyte solutions on the pre-and posthatch physiological characteristics of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, W.; Rowe, D.E.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of commercial in ovo injection of carbohydrates on broiler embryogenesis. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankowiakowska, A.; Bogucka, J.; Sobolewska, A.; Tavaniello, S.; Maiorano, G.; Bednarczyk, M. Effects of in ovo injection of prebiotics and synbiotics on the productive performance and microstructural features of the superficial pectoral muscle in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5157–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarczyk, M.; Stadnicka, K.; Kozłowska, I.; Abiuso, C.; Tavaniello, S.; Dankowiakowska, A.; Sławińska, A.; Maiorano, G. Influence of different prebiotics and mode of their administration on broiler chicken performance. Animal 2016, 10, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sławińska, A.; Siwek, M.; Żylińska, J.; Bardowski, J.; Brzezińska, J.; Gulewicz, K.A.; Nowak, M.; Urbanowski, M.; Płowiec, A.; Bednarczyk, M. Influence of synbiotics delivered in ovo on immune organs development and structure. Folia Biol. 2014, 62, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sławinska, A.; Siwek, M.Z.; Bednarczyk, M.F. Effects of synbiotics injected in ovo on regulation of immune-related gene expression in adult chickens. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 75, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, A.T.; Vinolo, M.A.R. Regulation of immune cell function by short chain fatty acids and their impact on arthritis. In Bioactive Food as Dietary Interventions for Arthritis and Related Inflammatory Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- Brisbin, J.T.; Gong, J.; Sharif, S. Interactions between commensal bacteria and the gut-associated immune system of the chicken. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2008, 9, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaspers, B.; Bondl, H.; Göbel, T.W.F. Transfer of IgA from albumen into the yolk sac during embryonic development in the chicken. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A 1996, 43, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamal, K.R.; Burgess, S.C.; Pevzner, I.Y.; Erf, G.F. Maternal Antibody Transfer from Dams to Their Egg Yolks, Egg Whites, and Chicks in Meat Lines of Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2006, 85, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Si, W.; Barbe, F.; Chevaux, E.; Sienkiewicz, O.; Zhao, X. Effects of novel probiotic strains of Bacillus pumilus and Bacillus subtilis on production, gut health, and immunity of broiler chickens raised under suboptimal conditions. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.K.; Gu, M.J.; Ko, K.H.; Bae, S.; Kim, G.; Jin, G.-D.; Kim, E.B.; Kong, Y.-Y.; Park, T.S.; Park, B.-C.; et al. Regulation of CD4+CD8−CD25+ and CD4+CD8+CD25+ T cells by gut microbiota in chicken. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, K.D. Diversity and function of the avian gut microbiota. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2012, 182, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadde, U.D.; Oh, S.; Lee, Y.; Davis, E.; Zimmerman, N.; Rehberger, T.; Lillehoj, H.S. Dietary Bacillus subtilis-based direct-fed microbials alleviate LPS-induced intestinal immunological stress and improve intestinal barrier gene expression in commercial broiler chickens. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 114, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madej, J.P.; Skonieczna, J.; Siwek, M.; Kowalczyk, A.; Łukaszewicz, E.; Slawinska, A. Genotype-dependent development of cellular and humoral immunity in the spleen and cecal tonsils of chickens stimulated in ovo with bioactive compounds. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 4343–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefaniak, T.; Madej, J.P.; Graczyk, S.; Siwek, M.; Łukaszewicz, E.; Kowalczyk, A.; Sieńczyk, M.; Bednarczyk, M. Selected prebiotics and synbiotics administered in ovo can modify innate immunity in chicken broilers. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusawa, Y.; Obata, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Endo, T.A.; Nakato, G.; Takahashi, D.; Nakanishi, Y.; Uetake, C.; Kato, K.; Kato, T. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 2013, 504, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; Van Der Veeken, J.; Deroos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Cai, K.; Mishra, R.; Jha, R. In ovo supplementation of chitooligosaccharide and chlorella polysaccharide affects cecal microbial community, metabolic pathways, and fermentation metabolites in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 4776–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremaroli, V.; Bäckhed, F. Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 2012, 489, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, E.; Tremaroli, V.; Lee, Y.S.; Koren, O.; Nookaew, I.; Fricker, A.; Nielsen, J.; Ley, R.E.; Bäckhed, F. Analysis of gut microbial regulation of host gene expression along the length of the gut and regulation of gut microbial ecology through MyD88. Gut 2012, 61, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Kinoshita, M.; Harada, K.; Mizutani, M.; Masahata, K.; Kayama, H.; Takeda, K. Commensal bacteria-dependent indole production enhances epithelial barrier function in the colon. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80604. [Google Scholar]
- Dunislawska, A.; Slawinska, A.; Bednarczyk, M.; Siwek, M. Transcriptome modulation by in ovo delivered Lactobacillus synbiotics in a range of chicken tissues. Gene 2019, 698, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, E.; Dunislawska, A.; Siwek, M.; Zampiga, M.; Sirri, F.; Meluzzi, A.; Tavaniello, S.; Maiorano, G.; Slawinska, A. Splenic Gene Expression Signatures in Slow-Growing Chickens Stimulated in Ovo with Galactooligosaccharides and Challenged with Heat. Animals 2020, 10, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramlucken, U.; Ramchuran, S.O.; Moonsamy, G.; Lalloo, R.; Thantsha, M.S.; van Rensburg, C.J. A novel Bacillus based multi-strain probiotic improves growth performance and intestinal properties of Clostridium perfringens challenged broilers. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Deng, X.; Deng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, N. Probiotic Lactobacilli Improved Growth Performance and Attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium Infection Via Jak/Stat Signaling in Broilers. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gong, L.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, L.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zou, P.; Yu, D.; Li, W. Probiotic Paenibacillus polymyxa 10 and Lactobacillus plantarum 16 enhance growth performance of broilers by improving the intestinal health. Anim. Nutr. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaz, A.M.; Ibrahim, N.S.; Shehata, A.M.; Mohamed, N.G.; Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E. Impact of multi-strain probiotic, citric acid, garlic powder or their combinations on performance, ileal histomorphometry, microbial enumeration and humoral immunity of broiler chickens. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiorano, G.; Sobolewska, A.; Cianciullo, D.; Walasik, K.; Elminowska-Wenda, G.; Sławińska, A.; Tavaniello, S.; Żylińska, J.; Bardowski, J.; Bednarczyk, M. Influence of in ovo prebiotic and synbiotic administration on meat quality of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2963–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majidi-Mosleh, A.; Sadeghi, A.A.; Mousavi, S.N.; Chamani, M.; Zarei, A. Ileal MUC2 gene expression and microbial population, but not growth performance and immune response, are influenced by in ovo injection of probiotics in broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2017, 58, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunislawska, A.; Slawinska, A.; Stadnicka, K.; Bednarczyk, M.; Gulewicz, P.; Jozefiak, D.; Siwek, M. Synbiotics for broiler chickens—in vitro design and evaluation of the influence on host and selected microbiota populations following in ovo delivery. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168587. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, C.N.; McDaniel, C.D.; Wamsley, K.G.S.; Kiess, A.S. The potential for inoculating Lactobacillus animalis and Enterococcus faecium alone or in combination using commercial in ovo technology without negatively impacting hatch and post-hatch performance. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 7050–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolewska, A.; Elminowska-Wenda, G.; Bogucka, J.; Dankowiakowska, A.; Kułakowska, A.; Szczerba, A.; Stadnicka, K.; Szpinda, M.; Bednarczyk, M. The influence of in ovo injection with the prebiotic DiNovo® on the development of histomorphological parameters of the duodenum, body mass and productivity in large-scale poultry production conditions. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pacifici, S.; Song, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Glahn, R.P.; Kolba, N.; Tako, E. Intra amniotic administration of raffinose and stachyose affects the intestinal brush border functionality and alters gut microflora populations. Nutrients 2017, 9, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruszynska-Oszmalek, E.; Kolodziejski, P.A.; Stadnicka, K.; Sassek, M.; Chalupka, D.; Kuston, B.; Nogowski, L.; Mackowiak, P.; Maiorano, G.; Jankowski, J.; et al. In ovo injection of prebiotics and synbiotics affects the digestive potency of the pancreas in growing chickens. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladokun, S.; Koehler, A.; MacIsaac, J.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M.; Adewole, D.I. Bacillus subtilis delivery route: Effect on growth performance, intestinal morphology, cecal short-chain fatty acid concentration, and cecal microbiota in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płowiec, A.; Sławińska, A.; Siwek, M.Z.; Bednarczyk, M.F. Effect of in ovo administration of inulin and Lactococcus lactis on immune-related gene expression in broiler chickens. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2015, 76, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogut, M.H. The effect of microbiome modulation on the intestinal health of poultry. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2019, 250, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Carrasco, J.M.; Casanova, N.A.; Fernández Miyakawa, M.E. Microbiota, gut health and chicken productivity: What is the connection? Microorganisms 2019, 7, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kogut, M.H. The gut microbiota and host innate immunity: Regulators of host metabolism and metabolic diseases in poultry? J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2013, 22, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaluenga, C.M.; Wardeńska, M.; Pilarski, R.; Bednarczyk, M.; Gulewicz, K. Utilization of the chicken embryo model for assessment of biological activity of different oligosaccharides. Folia Biol. 2004, 52, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pilarski, R.; Bednarczyk, M.; Lisowski, M.; Rutkowski, A.; Bernacki, Z.; Wardeńska, M.; Gulewicz, K. Assessment of the effect of α-galactosides injected during embryogenesis on selected chicken traits. Folia Biol. 2005, 53, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tzortzis, G.; Goulas, A.K.; Gibson, G.R. Synthesis of prebiotic galactooligosaccharides using whole cells of a novel strain, Bifidobacterium bifidum NCIMB 41171. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 68, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Bioactive Compound | Description and Dose | Site and Time of Injection | Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synbiotic (S) | S1. (Lactobacillus salivarius 105 cfu + 2 mg galactooligosaccharides (GOS))/egg S2. (Lactobacillus plantarum 105 cfu + 2 mg raffinose)/egg | Amnion on day 18 of incubation | S1 activated mostly genes involved in immune processes | [138] |
| Prebiotic and synbiotic | Probiotic (1.76 mg inulin/egg). Synbiotic (1.76 mg of inulin + 1000 CFU Lactobacillus lactis subsp. lactis IBB2955)/egg | Air cell on day 12 of incubation | Prebiotic or synbiotic had a powerful effect on gene expression in the spleen and cecal tonsils of broiler chickens. The effect of synbiotic was greater than those of the prebiotic. | [18] |
| Prebiotic | Oligosaccharides extracted from palm kernel cake (20 mg/egg). | Air cell on day 12 of incubation | In ovo injection of prebiotics increased IgG production and antioxidant capacity in serum and liver of prenatal chicks. | |
| Prebiotics and synbiotics | Inulin (1.76 mg), trans-galactooligosaccharides (0.528 mg), (1.76 mg inulin + 1000 cfu L. lactis ssp. lactis), and (0.528 mg trans-galactooligosaccharides + 1000 cfu L. lactis ssp. cremoris) | Air cell on day 12 of incubation | The authors concluded that in ovo administration with synbiotic (inulin and Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis was the most effective stimulator to the immune system | [111] |
| Prebiotics | Galactooligosaccharides (3.5 mg/egg) | Air cell on day 12 of incubation | Galactooligosaccharides administered in ovo down-regulated the expression of immune-related genes that were activated by heat stress. | [139] |
| Probiotics | 2 × 108 cfu of Bifidobacterium bifidum, B. animalis, B. longum, or B. infantis | Yolk sac, on day 17 of incubation | The in ovo injection of Bifidobacterium improved the immune responses of broiler chickens and increased immunoglobulin levels (IgG, IgM, IgA, and total Igs) in the serum of the broilers. | [13] |
| Bioactive Compound | Description and Dose | Site and Time of Injection | Findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probiotics alone or in combination | 1. Marek’s Disease (HVT) vaccination as a control group. 2. L. animalis (∼106 cfu/50 μL). 3. E. faecium (∼106 cfu/50 μL). 4. L. animalis + E. faecium (∼106 cfu & ∼106 cfu/50 μL each). | Amnion on day 18 of incubation | The length, weight, and pH of gastrointestinal tissue were affected by in ovo probiotic, resulting in increased FCR from days 7 to 14. | [147] |
| Synbiotic (S) | S1. (Lactobacillus salivarius 105 cfu + 2 mg galactooligosaccharides (GOS))/egg S2. (Lactobacillus plantarum 105 cfu + 2 mg raffinose)/egg | Amnion on day 18 of incubation | S2 up-regulated expression of genes involved in metabolic pathways | [138] |
| Prebiotic | Extract of Laminaria species of seaweed 0.88 mg/egg. | Air cell on day 12 of incubation | On day 42 of age, there was no significant effect of prebiotic injection on the growth performance of broiler chickens. In ovo treatment showed a significant increase in villi width and crypt depth on d 21 of age. Prebiotics injected in ovo impaired villus height, width, and surface area in the duodenum compared to the control group. | [148] |
| Prebiotics | Stachyose (1. 5% and 2. 10%/mL) Raffinose (3. 5% and 4. 10%/mL) | Amnion on day 17 of incubation | There was a significant increase in the relative expression of brush border membrane functioning proteins and villus surface area, as well as a reduction in the relative expression of Fe-related proteins in birds treated with probiotics. Probiotics significantly lowered the relative abundance of harmful bacteria while enhanced that of probiotics. Fe bioavailability, brush border membrane function, and gut microbiota were all positively influenced. | [149] |
| Prebiotic | Trans-galactooligosaccharides 3.5 mg/egg | Air cell on day 12 of incubation | Prebiotics improved growth performance and carcass weight of chickens at six weeks of age. Prebiotics reduced severity of intestinal lesions and oocyst excretion induced by natural infection with Eimeria. | [100] |
| Prebiotics and synbiotics | Inulin (1.76 mg), trans-galactooligosaccharides (0.528 mg), (1.76 mg inulin + 1000 cfu L. lactis ssp. lactis), and (0.528 mg trans-galactooligosaccharides + 1000 cfu L. lactis ssp. cremoris) | Air cell on day 12 of incubation | No significant effects of probiotics and synbiotics were observed on FCR. However, trans-galactooligosaccharides and inulin + Ls lactis subsp. lactis significantly increased final body weight of treated chickens. | [150] |
| Probiotic | Bacillus subtilis fermentation extract 10 × 106 cfu/egg | Amnion on day 18.5 of incubation | In ovo administration of the probiotic improved intestinal morphology without impairing hatch performance or gut homeostasis. | [151] |
| Probiotic | Bacillus spp. base probiotic 107 cfu | Amnion on day 18 of incubation | Probiotics administered in ovo decreased the severity of virulent E. coli horizontal transmission and infection in broiler chickens during the hatching period. | [21] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shehata, A.M.; Paswan, V.K.; Attia, Y.A.; Abdel-Moneim, A.-M.E.; Abougabal, M.S.; Sharaf, M.; Elmazoudy, R.; Alghafari, W.T.; Osman, M.A.; Farag, M.R.; et al. Managing Gut Microbiota through In Ovo Nutrition Influences Early-Life Programming in Broiler Chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123491
Shehata AM, Paswan VK, Attia YA, Abdel-Moneim A-ME, Abougabal MS, Sharaf M, Elmazoudy R, Alghafari WT, Osman MA, Farag MR, et al. Managing Gut Microbiota through In Ovo Nutrition Influences Early-Life Programming in Broiler Chickens. Animals. 2021; 11(12):3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123491
Chicago/Turabian StyleShehata, Abdelrazeq M., Vinod K. Paswan, Youssef A. Attia, Abdel-Moneim Eid Abdel-Moneim, Mohammed Sh. Abougabal, Mohamed Sharaf, Reda Elmazoudy, Wejdan T. Alghafari, Mohamed A. Osman, Mayada R. Farag, and et al. 2021. "Managing Gut Microbiota through In Ovo Nutrition Influences Early-Life Programming in Broiler Chickens" Animals 11, no. 12: 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123491
APA StyleShehata, A. M., Paswan, V. K., Attia, Y. A., Abdel-Moneim, A.-M. E., Abougabal, M. S., Sharaf, M., Elmazoudy, R., Alghafari, W. T., Osman, M. A., Farag, M. R., & Alagawany, M. (2021). Managing Gut Microbiota through In Ovo Nutrition Influences Early-Life Programming in Broiler Chickens. Animals, 11(12), 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123491










