Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium Isolated from Laying Hens, Table Eggs, and Humans with Respect to Antimicrobial Activity of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Salmonella spp. Isolation
2.3. Molecular Identification of Salmonella spp.
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
2.5. Biosynthesis and Characterization of AgNPs
2.6. Antimicrobial Activity of Biosynthesized AgNPs
2.7. Virulence and Resistance Genes Expression
2.7.1. Bacterial Counting
2.7.2. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR Analysis of Genes Expression
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Salmonella spp. Isolation and Identification
3.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
3.3. Virulence and Resistance Genes
3.4. Characterization of Biosynthesized AgNPs
3.5. Antimicrobial Activity of Biosynthesized AgNPs
3.6. Antivirulent and Antiresistant Activity of Biosynthesized AgNPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceyssens, P.J.; Mattheus, W.; Vanhoof, R.; Bertrand, S. Trends in serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility in Salmonella enterica isolates from humans in Belgium, 2009 to 2013. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, B.R.; Griffin, P.M.; Cole, D.; Walsh, K.A.; Chai, S.J. Outbreak-associated Salmonella enterica serotypes and food commodities, United States, 1998–2008. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Reu, K.; Grijspeerdt, K.; Messens, W.; Heyndrickx, M.; Uyttendaele, M.; Debevere, J.; Herman, L. Eggshell factors influencing eggshell penetration and whole egg contamination by different bacteria, including Salmonella enteritidis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 112, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Lai, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Shen, J.; Wu, C. Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella species isolated from pigs, ducks and chickens in Sichuan Province, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 163, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heider, L.C.; Funk, J.A.; Hoet, A.E.; Meiring, R.W.; Gebreyes, W.A.; Wittum, T.E. Identification of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica organisms with reduced susceptibility to ceftriaxone from fecal samples of cows in dairy herds. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2009, 70, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemfareji, O.I.; Thong, K.L. Comparative Virulotyping of Salmonella typhi and Salmonella enteritidis. Indian J. Microbiol. 2013, 53, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huehn, S.; La Ragione, R.M.; Anjum, M.; Saunders, M.; Woodward, M.J.; Bunge, C.; Helmuth, R.; Hauser, E.; Guerra, B.; Beutlich, J. Virulotyping and antimicrobial resistance typing of Salmonella enterica serovars relevant to human health in Europe. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugkar, H.; Rahman, H.; Dutta, P. Distribution of virulence genes in Salmonella serovars isolated from man & animals. Indian J. Med. Res. 2003, 117, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Fluit, A.C. Towards more virulent and antibiotic-resistant Salmonella? FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zishiri, O.T.; Mkhize, N.; Mukaratirwa, S. Prevalence of virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes in Salmonella spp. isolated from commercial chickens and human clinical isolates from South Africa and Brazil. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2016, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaalan, M.; Saleh, M.; El-Mahdy, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Recent progress in applications of nanoparticles in fish medicine: A review. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurunathan, S. Biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles enhance antibiotic activity against Gram-negative bacteria. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Korbekandi, H.; Mirmohammadi, S.V.; Zolfaghari, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Chemical, physical and biological methods. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- Khodashenas, B.; Ghorbani, H.R. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles with different shapes. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1823–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Gohary, F.A.; Abdel-Hafez, L.J.M.; Zakaria, A.I.; Shata, R.R.; Tahoun, A.; El-Mleeh, A.; Elfadl, E.A.A.; Elmahallawy, E.K. Enhanced Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Combined with Hydrogen Peroxide Against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens Isolated from Dairy Farms and Beef Slaughterhouses in Egypt. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3485–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A.; Grzenia, A.; Wierzbicki, M.; Strojny-Cieslak, B.; Kalińska, A.; Gołębiewski, M.; Radzikowski, D.; Sawosz, E.; Jaworski, S. Silver and copper nanoparticles inhibit biofilm formation by mastitis pathogens. Animals 2021, 11, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, M.C.; Jeong, S.J.; Kwon, Y.-K.; Jeong, O.-M.; Kang, M.-S.; Lee, Y.J. Prevalence and characteristics of Salmonella spp. isolated from commercial layer farms in Korea. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Brisbin, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, Q.; Yin, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sabour, P.; Sharif, S.; Gong, J. Selected lactic acid-producing bacterial isolates with the capacity to reduce Salmonella translocation and virulence gene expression in chickens. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFaddin, J. Biochemical Tests for Identification of Medical Bacteria; Lippicott Williams Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman, G. Kauffmann white scheme. J. Acta. Path. Microbiol. Sci. 1974, 61, 385. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, S.; Rodenbusch, C.; Cé, M.; Rocha, S.; Canal, C. Evaluation of selective and non-selective enrichment PCR procedures for Salmonella detection. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 36, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarmehr, J.; Salehi, T.Z.; Brujeni, G. Identification of Salmonella isolated from poultry by MPCR technique and evaluation of their hsp groEL gene diversity based on the PCR-RFLP analysis. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 1594–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Dan, X.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Development of a novel multiplex PCR assay for the identification of Salmonella enterica Typhimurium and Enteritidis. Food Control 2012, 27, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute). Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Test; Approved Standard; CLSI Document M02-A11; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of fecal contamination of foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colom, K.; Pérez, J.; Alonso, R.; Fernández-Aranguiz, A.; Lariño, E.; Cisterna, R. Simple and reliable multiplex PCR assay for detection of bla TEM, bla SHV and bla OXA–1 genes in Enterobacteriaceae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 223, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randall, L.; Cooles, S.; Osborn, M.; Piddock, L.; Woodward, M.J. Antibiotic resistance genes, integrons and multiple antibiotic resistance in thirty-five serotypes of Salmonella enterica isolated from humans and animals in the UK. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 53, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabarinath, A.; Tiwari, K.P.; Deallie, C.; Belot, G.; Vanpee, G.; Matthew, V.; Sharma, R.; Hariharan, H. Antimicrobial resistance and phylogenetic groups of commensal Escherichia Coli isolates from healthy pigs in Grenada. Webmed Cent. Vet. Med. 2011, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mottaghizadeh, F.; Haeili, M.; Darban-Sarokhalil, D. Molecular epidemiology and nitrofurantoin resistance determinants from nitrofurantoin non-susceptible Escherichia coli isolated from urinary tract infections. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 21, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabie, G.; El-Abedeen, A.Z.; Bakry, A.A. Biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using filamentous fungi. Nano Sci. Nano Technol. J. 2013, 7, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- El-Gazzar, N.S.; Rabie, G.H. Application of silver nanoparticles on Cephalosporium maydis in vitro and in vivo. Egypt. J. Microbiol. 2018, 53, 69–81. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR Protoc. A Guide Methods Appl. 1990, 18, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- DeAlba-Montero, I.; Guajardo-Pacheco, J.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Araujo-Martínez, R.; Loredo-Becerra, G.; Martínez-Castañón, G.-A.; Ruiz, F.; Compeán Jasso, M. Antimicrobial properties of copper nanoparticles and amino acid chelated copper nanoparticles produced by using a soya extract. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2017, 2017, 1064918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disc method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Arumugam, V.; Vasaviah, S.K. The MIC and MBC of silver nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis—A facultative anaerobe. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 285. [Google Scholar]
- Thatcher, F.S.; Clark, D.S. Micro-Organisms in Foods: Their Significance and Methods of Enumeration; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.S.; Reed, A.; Chen, F.; Stewart, C.N. Statistical analysis of real-time PCR data. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kruskal, J.B. Multidimensional scaling by optimizing goodness of fit to a nonmetric hypothesis. Psychometrika 1964, 29, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughini-Gras, L.; Enserink, R.; Friesema, I.; Heck, M.; van Duynhoven, Y.; van Pelt, W. Risk factors for human salmonellosis originating from pigs, cattle, broiler chickens and egg laying hens: A combined case-control and source attribution analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87933. [Google Scholar]
- Elkenany, R.; Elsayed, M.M.; Zakaria, A.I.; El-sayed, S.A.-E.-S.; Rizk, M.A. Antimicrobial resistance profiles and virulence genotyping of Salmonella enterica serovars recovered from broiler chickens and chicken carcasses in Egypt. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, R.; Fandiño, C.; Donado, P.; Guzmán, L.; Verjan, N. Characterization of Salmonella from commercial egg-laying hen farms in a central region of Colombia. Avian. Dis. 2015, 59, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, A.; Fernandez-No, I.; Miranda, J.; Vázquez, B.; Cepeda, A.; Franco, C. Prevalence, molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella serovars isolated from northwestern Spanish broiler flocks (2011–2015). Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.; Gharieb, R.M.; Mohamed, M.E.; Amin, M.A.; Mohamed, R.E. Bacteriological and molecular characterization of Salmonella species isolated from humans and chickens in Sharkia Governorate, Egypt. Zagazig Vet. J. 2017, 45, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharieb, R.M.; Tartor, Y.H.; Khedr, M.H. Non-Typhoidal Salmonella in poultry meat and diarrhoeic patients: Prevalence, antibiogram, virulotyping, molecular detection and sequencing of class I integrons in multidrug resistant strains. Gut Pathog. 2015, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zubair, A.I.; Al-Berfkani, M.I.; Issa, A.R. Prevalence of Salmonella species from poultry eggs of local stores in Duhok. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 2468–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, C.; Soriano, J.; Benítez, V.; Catalá-Gregori, P. Assessment of Salmonella spp. in feces, cloacal swabs, and eggs (eggshell and content separately) from a laying hen farm. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 1581–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, V.; Cranstoun, S.; Solomon, S. Relationship between shell structure and movement of Salmonella enteritidis across the eggshell wall. Br. Poult. Sci. 1992, 33, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, K.A.; Furian, T.Q.; Borsoi, A.; Moraes, H.L.; Salle, C.T.; Nascimento, V.P. Detection of virulence-associated genes in Salmonella Enteritidis isolates from chicken in South of Brazil. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2013, 33, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Yadav, A.; Tripathi, V.; Singh, R. Antimicrobial resistance profile of Salmonella present in poultry and poultry environment in north India. Food Control 2013, 33, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, L.A.; Dalsgaard, A.; Obiri-Danso, K.; Newman, M.; Barco, L.; Olsen, J.E. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella serovars isolated from poultry in Ghana. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 3288–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, K.; Uwiera, R.R.; Kalmokoff, M.L.; Brooks, S.P.; Inglis, G.D. Antimicrobial growth promoter use in livestock: A requirement to understand their modes of action to develop effective alternatives. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdeen, E.; Elmonir, W.; Suelam, I.; Mousa, W. Antibiogram and genetic diversity of Salmonella enterica with zoonotic potential isolated from morbid native chickens and pigeons in Egypt. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, M.S.; Zaki, R.S.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Abd El Hafez, M.S. Prevalence of Multidrug Resistance Non-Typhoidal Salmonellae Isolated from Layer Farms and Humans in Egypt. World Vet. J. 2019, 9, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Kumar, D.; Hussain, S.; Pathak, A.; Shukla, M.; Kumar, V.P.; Anisha, P.; Rautela, R.; Upadhyay, A.; Singh, S. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance and virulence genes characterization of nontyphoidal Salmonella isolated from retail chicken meat shops in Northern India. Food Control 2019, 102, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.; Guarddon, M.; Vázquez, B.; Fente, C.; Barros-Velázquez, J.; Cepeda, A.; Franco, C. Antimicrobial resistance in Enterobacteriaceae strains isolated from organic chicken, conventional chicken and conventional turkey meat: A comparative survey. Food Control 2008, 19, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, W.Q.; Thakur, S.; Berghaus, R.D.; Martin, M.P.; Gebreyes, W.A. Prevalence and distribution of Salmonella in organic and conventional broiler poultry farms. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, L.; Lan, R.; Zhang, X.; Cui, S.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, D. Prevalence of Salmonella isolates from chicken and pig slaughterhouses and emergence of ciprofloxacin and cefotaxime co-resistant S. enterica serovar Indiana in Henan, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Ye, C.; Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Chang, W. Prevalence and characteristics of Salmonella isolated from free-range chickens in Shandong Province, China. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8183931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lekshmi, M.; Ammini, P.; Kumar, S.; Varela, M.F. The food production environment and the development of antimicrobial resistance in human pathogens of animal origin. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Qu, D.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Cui, S.; Shi, Y.; Xi, M.; Sheng, M.; Zhi, S.; Meng, J. Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella serovars in retail meats of marketplace in Shaanxi, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 141, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thung, T.Y.; Radu, S.; Mahyudin, N.A.; Rukayadi, Y.; Zakaria, Z.; Mazlan, N.; Tan, B.H.; Lee, E.; Yeoh, S.L.; Chin, Y.Z. Prevalence, virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Salmonella serovars from retail beef in Selangor, Malaysia. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Sharkawy, H.; Tahoun, A.; El-Gohary, A.E.-G.A.; El-Abasy, M.; El-Khayat, F.; Gillespie, T.; Kitade, Y.; Hafez, H.M.; Neubauer, H.; El-Adawy, H. Epidemiological, molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from chicken farms in Egypt. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Shafi, S.; Al-Mohammadi, A.-R.; Osman, A.; Enan, G.; Abdel-Hameid, S.; Sitohy, M. Characterization and Antibacterial Activity of 7S and 11S Globulins Isolated from Cowpea Seed Protein. Molecules 2019, 24, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Gazzard, N.; Ismail, A. The potential use of Titanium, Silver and Selenium nanoparticles in controlling leaf blight of tomato caused by Alternaria alternata. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 27, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakkala, J.R.; Mata, R.; Sadras, S.R. Green synthesized nano silver: Synthesis, physicochemical profiling, antibacterial, anticancer activities and biological in vivo toxicity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 499, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaligram, N.S.; Bule, M.; Bhambure, R.; Singhal, R.S.; Singh, S.K.; Szakacs, G.; Pandey, A. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous extract from the compactin producing fungal strain. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavassin, E.D.; de Figueiredo, L.F.P.; Otoch, J.P.; Seckler, M.M.; de Oliveira, R.A.; Franco, F.F.; Marangoni, V.S.; Zucolotto, V.; Levin, A.S.S.; Costa, S.F. Comparison of methods to detect the in vitro activity of silver nanoparticles (AgNP) against multidrug resistant bacteria. J. Nanobiotechnology 2015, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.Y.; Rukayadi, Y.; Nor-Khaizura, M.-A.-R.; Kuan, C.H.; Chieng, B.W.; Nishibuchi, M.; Radu, S. In vitro antimicrobial activity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against selected gram-negative foodborne pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondi, I.; Siiman, O.; Matijević, E. Synthesis of CdSe nanoparticles in the presence of aminodextran as stabilizing and capping agent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanhaeian, A.; Ahmadi, F.S. Inhibitory effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticle on growth and virulence of E. coli. Zahedan J. Res. Med. Sci. 2018, 20, e10269. [Google Scholar]

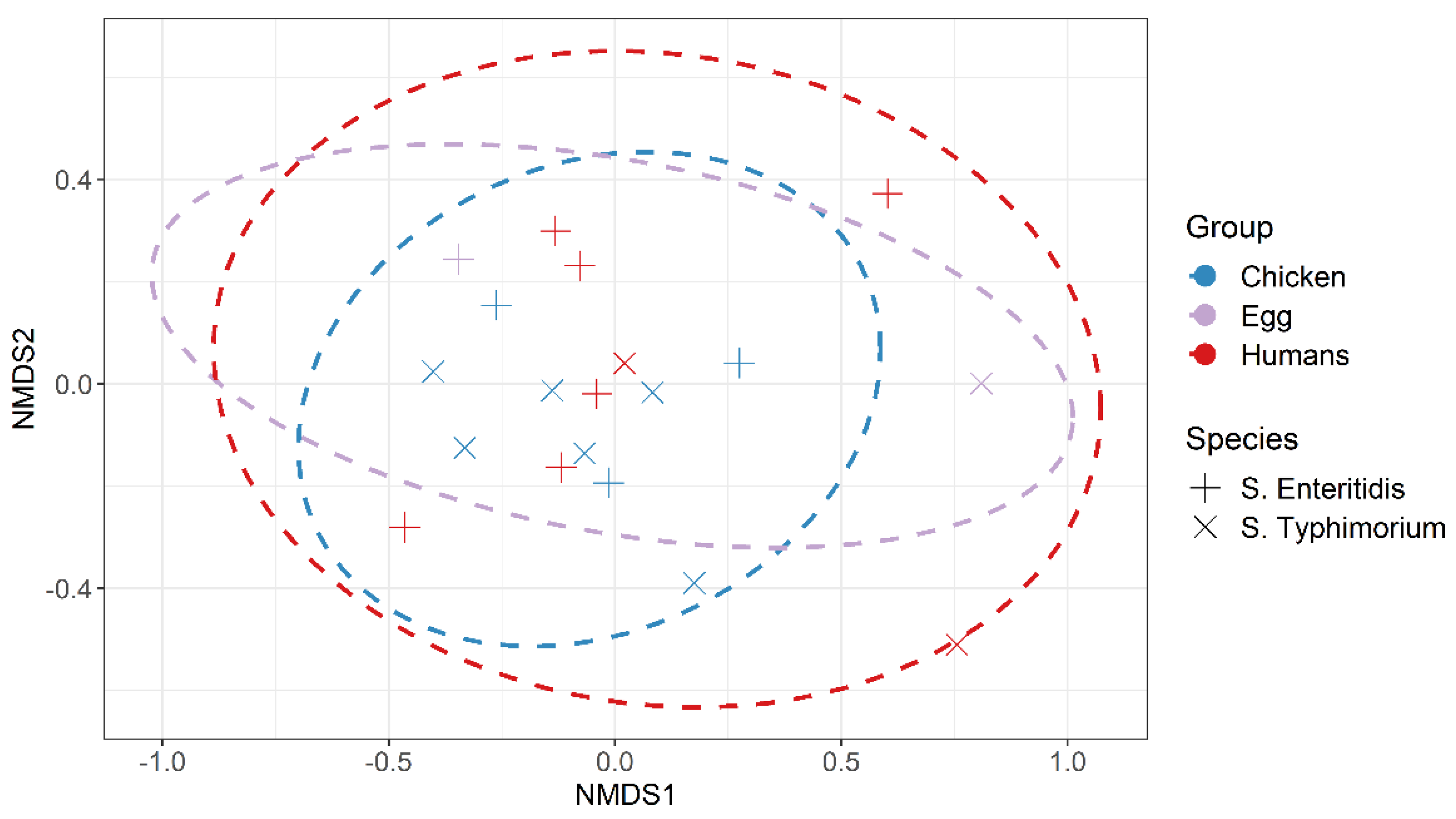


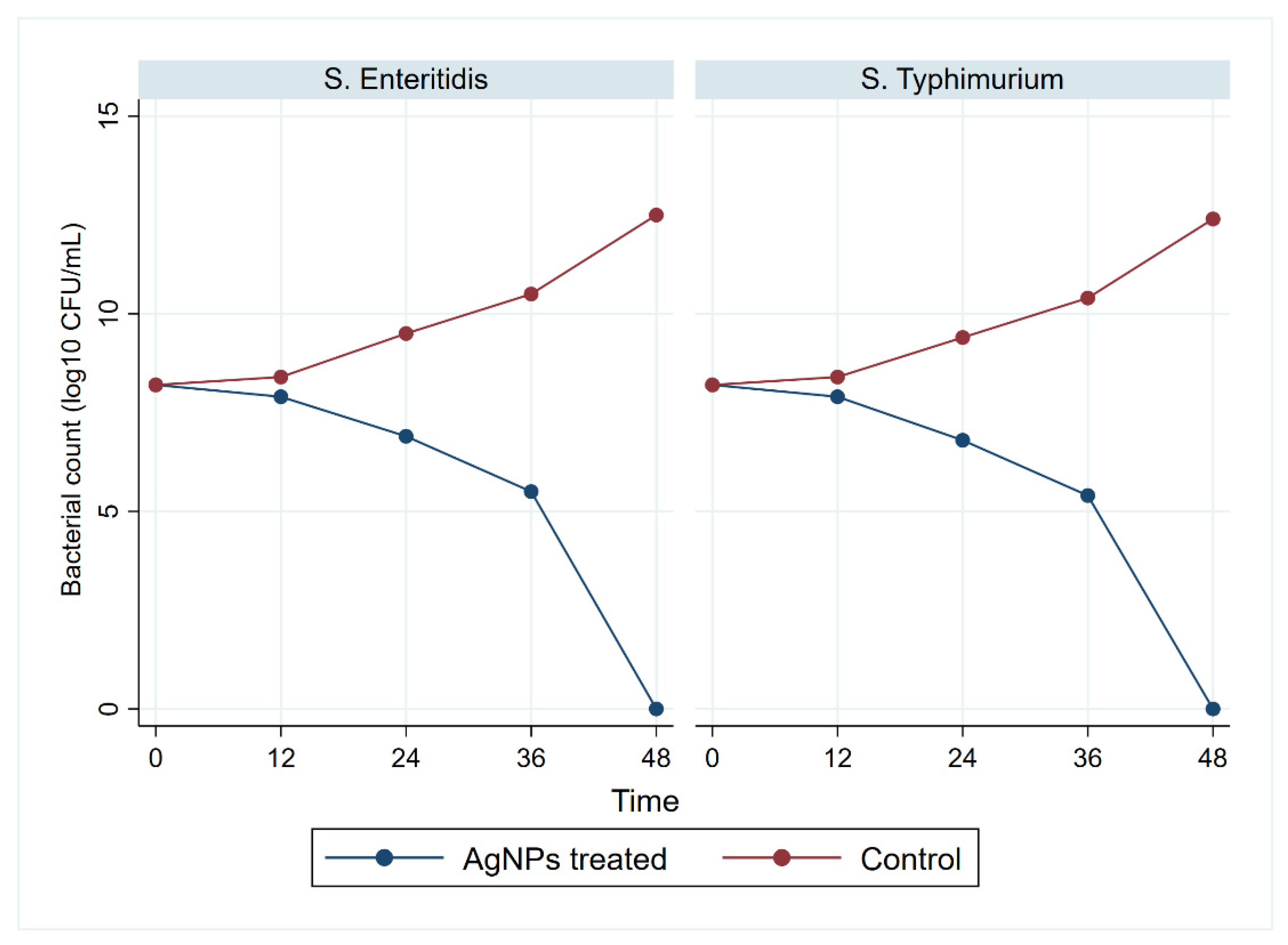
| Serotypes | Pathotypes | No. (%) of Isolates | Total (n = 431) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laying Hens (n = 166) | Table Eggs (n = 165) | Humans (n = 100) | |||
| S.enteritidis | D1; O:1, 9, 12; H:g, m:− | 12 (7.2) | 5 (3.0) | 8 (8.0) | 25 (5.8) |
| S.typhimurium | B; O:1, 4, 5, 12; H:i:1, 2 | 7 (4.2) | 1 (0.6) | 4 (4.0) | 12 (2.8) |
| S.kentukey | C3; O:8, 20; H:i:z6 | 5 (3.01) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (3.0) | 8 (1.9) |
| S.virchow | C1; O:6, 7, 14; H:r:1, 2 | 5 (3.01) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (2.0) | 7 (1.6) |
| S.tamale | C3; O:8, 20; H:Z29:e, n, Z15 | 4 (2.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.0) | 5 (1.2) |
| S.inganda | C1; O:6, 7; H:Z10:1, 5 | 4 (2.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.0) | 5 (1.2) |
| S.wingrove | C2; O:6, 8; H:c:1, 2 | 4(2.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.0) | 5 (1.2) |
| S.bargny | C3; O:8, 20; H:i:1, 5 | 4 (2.4) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.0) | 5 (1.2) |
| S.anatum | E1; O:3, 10; H:e, h:1, 6 | 4 (2.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (0.9) |
| S.tsavie | B; O:4,5; H:i:e, n, z15 | 3 (1.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (0.7) |
| S.larochell | C1; O:6, 7; H:e, h:1, 2 | 3 (1.8) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (0.7) |
| S.apeyeme | C3; O:8, 20; H:Z38:− | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.0) | 1 (0.2) |
| Total | 55 (33.1) | 6 (3.6) | 22 (22) | 83 (19.3) | |
| Antimicrobials Class | Antimicrobials | S. enteritidis Isolates (%) | S. typhimurium Isolates (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | I | S | R | I | S | ||
| Penicillin | Ampicillin (AMP) | 25 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 12 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Ampicillin/Sulbactam (SAM) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (16.0) | 21 (84.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (16.7) | 10 (83.3) | |
| Amoxicillin-Clavulanate (AMC) | 15 (60.0) | 0 (0.0) | 10 (40.0) | 6 (50.0) | 3 (25.0) | 3 (25.0) | |
| Cephalosporine | Cefataxime (CTX) | 9 (36.0) | 0 (0.0) | 16 (64.0) | 3 (25.0) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (75.0) |
| Carbapenems | Imipenem (IPM) | 11 (44.0) | 0 (0.0) | 14 (56.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (16.7) | 10 (83.3) |
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin (GEN) | 2 (8.0) | 0 (0.0) | 23 (92.0) | 2 (16.7) | 0 (0.0) | 10 (83.3) |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline (TET) | 22 (88.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (12.0) | 8 (66.7) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (33.3) |
| Quinolones | Ciprofloxacin (CIP) | 3 (12.0) | 6 (24.0) | 16 (64.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (25.0) | 9 (75.0) |
| Nalidixic acid (NAL) | 5 (20.0) | 2 (8.0) | 18 (72.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (8.3) | 11 (91.7) | |
| Sulphonamides | Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole (SXT) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (20.0) | 20 (80.0) | 1 (8.3) | 2 (16.7) | 9 (75.0) |
| Phenicols | Chloramphenicol (CHL) | 4 (16.0) | 3 (12.0) | 18 (72.0) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (25.0) | 9 (75.0) |
| Macrolides | Azithromycin (AZM) | 5 (20.0) | 0 (0.0) | 20 (80.0) | 4 (33.3) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (66.7) |
| Nitrofurans | Nitrofurantoin (NIT) | 20 (80.0) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (20.0) | 8 (66.7) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (33.3) |
| Carbapenem | Meropenem (MEM) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 25 (100) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 12 (100) |
| Source | No. of Isolates | Virulence Genes | Resistance Genes | No. of Ab | Resistance Patterns | MARIndex | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sopB | stn | pefA | spvC | hilA | blaTEM | tetA | tetB | nfsA | nfsB | |||||
| (I) S. enteritidis | ||||||||||||||
| Human | 2 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 8 | AMP, AMC, CTX, IPM, TET, CIP, NA, NIT | 0.57 |
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 8 | AMP, AMC, CTX, IPM, TET, CIP, NA, NIT | 0.57 |
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | 7 | AMP, AMC, CTX, IPM, TET, NA, NIT | 0.50 |
| Egg | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | 7 | AMP, AMC, CTX, IPM, TET, NA, NIT | 0.50 |
| Egg | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | 6 | AMP, AMC, CTX, IPM, TET, NIT | 0.43 |
| Human | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | 6 | AMP, AMC, CTX, IPM, TET, NIT | 0.43 |
| Egg | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 6 | AMP, CTX, IPM, TET, NAL, NIT | 0.43 |
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 6 | AMP, CTX, IPM, TET, NAL, NIT | 0.43 |
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | − | − | 5 | AMP, IPM, TET, AZM, NIT | 0.36 |
| Human | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | − | − | 5 | AMP, IPM, TET, AZM, NIT | 0.36 |
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 4 | AMP, AMC, TET, NIT | 0.29 |
| Egg | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 4 | AMP, AMC, TET, NIT | 0.29 |
| Human | 2 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 4 | AMP, AMC, TET, NIT | 0.29 |
| Egg | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 4 | AMP, TET, AZM, NIT | 0.29 |
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 4 | AMP, TET, AZM, NIT | 0.29 |
| Human | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 4 | AMP, TET, AZM, NIT | 0.29 |
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | + | 4 | AMP, AMC, IPM, GEN | 0.29 |
| Human | 1 | + | + | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | + | 4 | AMP, AMC, IPM, GEN | 0.29 |
| Chicken | 2 | + | + | − | − | + | + | − | − | + | + | 3 | AMP, AMC, NIT | 0.21 |
| Chicken | 3 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 2 | AMP, AMC | 0.14 |
| (II) S. typhimurium | ||||||||||||||
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | 7 | AMP, AMC, CTX, GEN, TET, AZM, NIT | 0.50 |
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | − | 6 | AMP, AMC, GEN, TET, AZM, NIT | 0.43 |
| Human | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 5 | AMP, AMC, TET, SXT, NIT | 0.36 |
| Chicken | 2 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 4 | AMP, CTX, TET, NIT | 0.29 |
| Human | 1 | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | 3 | AMP, TET, NIT | 0.21 |
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | 3 | AMP, TET, NIT | 0.21 |
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | − | − | + | + | 3 | AMP, AZM, NIT | 0.21 |
| Chicken | 1 | + | + | − | − | + | + | + | − | + | + | 3 | AMP, AMC, TET | 0.21 |
| Human | 1 | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | + | 2 | AMP, AMC | 0.14 |
| Egg | 1 | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | + | 2 | AMP, AMC | 0.14 |
| Human | 1 | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | + | + | 2 | AMP, AZM | 0.14 |
| Storage Time (Hours) | Virulence Genes Expression | Resistance Genes Expression | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SopB | stn | hilA | blaTEM | tetA | nfsA | |
| (I) S. enteritidis | ||||||
| 0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 |
| 6 | 0.71 ± 0.015 | 0.73 ± 0.025 | 0.69 ± 0.015 | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 0.78 ± 0.01 | 0.83 ± 0.006 |
| 12 | 0.45 ± 0.015 | 0.44 ± 0.015 | 0.41 ± 0.015 | 0.69 ± 0.01 | 0.61 ± 0.01 | 0.66 ± 0.015 |
| 24 | 0.11 ± 0.001 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.025 | 0.46 ± 0.01 | 0.42 ± 0.006 | 0.47 ± 0.006 |
| 36 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.16 ± 0.006 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.006 |
| (II) S. typhimurium | ||||||
| 0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 |
| 6 | 0.77 ± 0.02 | 0.79 ± 0.01 | 0.76 ± 0.01 | 0.92 ±0.015 | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 0.94 ± 0.015 |
| 12 | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 0.47 ± 0.025 | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 0.56 ± 0.01 | 0.79 ± 0.01 |
| 24 | 0.23 ± 0.025 | 0.26 ± 0.025 | 0.15 ± 0.025 | 0.59 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.015 | 0.57 ± 0.01 |
| 36 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.38 ± 0.015 | 0.18 ± 0.015 | 0.36 ± 0.015 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abou Elez, R.M.M.; Elsohaby, I.; El-Gazzar, N.; Tolba, H.M.N.; Abdelfatah, E.N.; Abdellatif, S.S.; Mesalam, A.A.; Tahoun, A.B.M.B. Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium Isolated from Laying Hens, Table Eggs, and Humans with Respect to Antimicrobial Activity of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles. Animals 2021, 11, 3554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123554
Abou Elez RMM, Elsohaby I, El-Gazzar N, Tolba HMN, Abdelfatah EN, Abdellatif SS, Mesalam AA, Tahoun ABMB. Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium Isolated from Laying Hens, Table Eggs, and Humans with Respect to Antimicrobial Activity of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles. Animals. 2021; 11(12):3554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123554
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbou Elez, Rasha M. M., Ibrahim Elsohaby, Nashwa El-Gazzar, Hala M. N. Tolba, Eman N. Abdelfatah, Samah S. Abdellatif, Ahmed Atef Mesalam, and Asmaa B. M. B. Tahoun. 2021. "Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium Isolated from Laying Hens, Table Eggs, and Humans with Respect to Antimicrobial Activity of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles" Animals 11, no. 12: 3554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123554
APA StyleAbou Elez, R. M. M., Elsohaby, I., El-Gazzar, N., Tolba, H. M. N., Abdelfatah, E. N., Abdellatif, S. S., Mesalam, A. A., & Tahoun, A. B. M. B. (2021). Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella enteritidis and Salmonella typhimurium Isolated from Laying Hens, Table Eggs, and Humans with Respect to Antimicrobial Activity of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles. Animals, 11(12), 3554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123554







