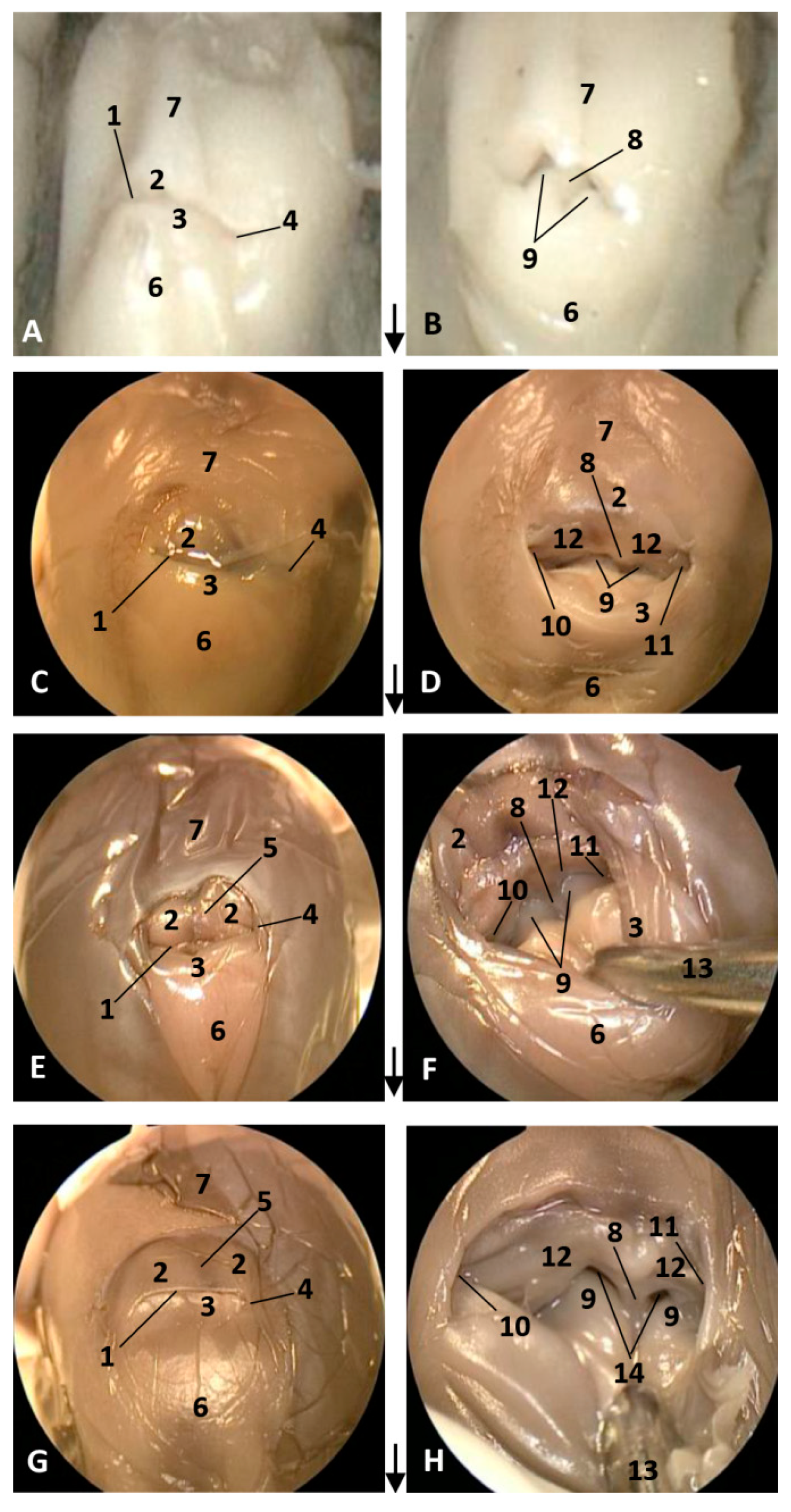
Figure 1.
Endoscopic images of the external nose and nasal cavity at the level of nasal vestibule. Images are oriented so that the left side of the head is to the right of the image and rostral is at the bottom (arrow). (A,B) 1.5 months, dde1; (C,D) 3.5 months, dde2; (E,F) 4 months, dde3; (G,H) 4.5 months, scop1. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Angulus naris; 5, Nasal groove; 6, Melon; 7, Forehead; 8, Nasal septum: membranous part; 9, Nasal plugs; 10. Vestibule: right diverticulum (vestibular sac); 11, Vestibule: left diverticulum (vestibular sac); 12, Vestibular folds; 13, Delicate hook; 14, Nasal cavity: respiratory part.
Figure 1.
Endoscopic images of the external nose and nasal cavity at the level of nasal vestibule. Images are oriented so that the left side of the head is to the right of the image and rostral is at the bottom (arrow). (A,B) 1.5 months, dde1; (C,D) 3.5 months, dde2; (E,F) 4 months, dde3; (G,H) 4.5 months, scop1. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Angulus naris; 5, Nasal groove; 6, Melon; 7, Forehead; 8, Nasal septum: membranous part; 9, Nasal plugs; 10. Vestibule: right diverticulum (vestibular sac); 11, Vestibule: left diverticulum (vestibular sac); 12, Vestibular folds; 13, Delicate hook; 14, Nasal cavity: respiratory part.
Figure 2.
Endoscopic images of the external nose and nasal cavity at level of the vestibule. Images are oriented so that the left side of the head is to the right of the image and rostral is at the bottom (arrow). Detail of monkey or phonic lips from now on (K,L,O). (A–D) 5 months, gma1; (E–H) 5.5 months, dde4; (I–L) 6 months, dde8; (M–P) 7 months, dde9. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Angulus naris; 5, Nasal groove; 6, Melon; 7, Forehead; 8, Nasal septum: membranous part; 9, Nasal plugs; 10. Vestibule: right diverticulum; 11, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 12, Vestibular folds; 13, Delicate hook; 14, Nasal cavity: respiratory part.
Figure 2.
Endoscopic images of the external nose and nasal cavity at level of the vestibule. Images are oriented so that the left side of the head is to the right of the image and rostral is at the bottom (arrow). Detail of monkey or phonic lips from now on (K,L,O). (A–D) 5 months, gma1; (E–H) 5.5 months, dde4; (I–L) 6 months, dde8; (M–P) 7 months, dde9. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Angulus naris; 5, Nasal groove; 6, Melon; 7, Forehead; 8, Nasal septum: membranous part; 9, Nasal plugs; 10. Vestibule: right diverticulum; 11, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 12, Vestibular folds; 13, Delicate hook; 14, Nasal cavity: respiratory part.
Figure 3.
Endoscopic images of the external nose and nasal cavity at the level of vestibule. Images are oriented so that the left side of the head is to the right of the image and rostral is at the bottom (arrow). (A–D) 7.5 months, dde10; (E–H) 8 months, dde11; (I–L) 8.5 months, dde12; (M–P) 9 months, dde13 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Angulus naris; 5, Nasal groove; 6, Melon; 7, Forehead; 8, Nasal septum: membranous part; 9, Nasal plugs; 10. Vestibule: right diverticulum; 11, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 12, Vestibular folds; 13, Delicate hook; 14, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 15, Diverticulum extension.
Figure 3.
Endoscopic images of the external nose and nasal cavity at the level of vestibule. Images are oriented so that the left side of the head is to the right of the image and rostral is at the bottom (arrow). (A–D) 7.5 months, dde10; (E–H) 8 months, dde11; (I–L) 8.5 months, dde12; (M–P) 9 months, dde13 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Angulus naris; 5, Nasal groove; 6, Melon; 7, Forehead; 8, Nasal septum: membranous part; 9, Nasal plugs; 10. Vestibule: right diverticulum; 11, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 12, Vestibular folds; 13, Delicate hook; 14, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 15, Diverticulum extension.
Figure 4.
Endoscopic images of the external nose and nasal cavity at the level of vestibule. Images are oriented so that the left side of the head is to the right of the image and rostral is at the bottom (arrow). (A–D) 10 months, dde14; (E–H) newborn, scoce1; (I–P) juvenile, scomu4. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Angulus naris; 5, Nasal groove; 6, Melon; 7, Forehead; 8, Nasal septum: membranous part; 9, Nasal plugs; 10. Vestibule: right diverticulum; 11, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 12, Vestibular folds; 13, Delicate hook, 14. Hyperkeratosis; 15, Striation marks.
Figure 4.
Endoscopic images of the external nose and nasal cavity at the level of vestibule. Images are oriented so that the left side of the head is to the right of the image and rostral is at the bottom (arrow). (A–D) 10 months, dde14; (E–H) newborn, scoce1; (I–P) juvenile, scomu4. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Angulus naris; 5, Nasal groove; 6, Melon; 7, Forehead; 8, Nasal septum: membranous part; 9, Nasal plugs; 10. Vestibule: right diverticulum; 11, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 12, Vestibular folds; 13, Delicate hook, 14. Hyperkeratosis; 15, Striation marks.
Figure 5.
Endoscopic images of the nasal cavity at the level of respiratory and olfactory parts. Arrows show the entry to the incisive recess (3) and to the nasopharynx (4) (A,B,H) Right nasal cavity, (C–G,I–L) Left nasal cavity, (A–C) 5.5 months, dde4; (D–F) 6 months, dde7. (G–I) 7 months, dde9; (J–L) Detailed images. 8.5 months, dde12. Walls indicate orientation. Vertical view. 1. Nasal plug; 2, Longitudinal folds; 3, Incisive recess (premaxillary sac); 4, Choanae; 5, Nasal septum: bony part; 6, Small vesicles; 7, Small fossae; 8, Caudal wall; 9, Rostral wall; 10, Right lateral wall; 11, Left lateral wall; 12, Medial wall.
Figure 5.
Endoscopic images of the nasal cavity at the level of respiratory and olfactory parts. Arrows show the entry to the incisive recess (3) and to the nasopharynx (4) (A,B,H) Right nasal cavity, (C–G,I–L) Left nasal cavity, (A–C) 5.5 months, dde4; (D–F) 6 months, dde7. (G–I) 7 months, dde9; (J–L) Detailed images. 8.5 months, dde12. Walls indicate orientation. Vertical view. 1. Nasal plug; 2, Longitudinal folds; 3, Incisive recess (premaxillary sac); 4, Choanae; 5, Nasal septum: bony part; 6, Small vesicles; 7, Small fossae; 8, Caudal wall; 9, Rostral wall; 10, Right lateral wall; 11, Left lateral wall; 12, Medial wall.
Figure 6.
Endoscopic images of the nasal cavity at the level of respiratory and olfactory parts. Arrows show the entry to the incisive recess (2) and to the nasopharynx (5) 9 months, dde13. (A–C,L) Left nasal cavity. (D–K) Right nasal cavity. (A–C) 9 months, dde13; (D–F) 10 months, dde14; (G–I) Hypertrophied longitudinal folds. Newborn, scoce1; (J–L) juvenile, scomu4. Walls indicate orientation. Vertical view. 1, Nasal plug; 2, Incisive recess; 3, Nasal folds; 4, Nasal septum: bony part. 5, Choanae; 6, Caudal wall; 7, Rostral wall; 8, Right lateral wall; 9, Left lateral wall; 10, Median wall.
Figure 6.
Endoscopic images of the nasal cavity at the level of respiratory and olfactory parts. Arrows show the entry to the incisive recess (2) and to the nasopharynx (5) 9 months, dde13. (A–C,L) Left nasal cavity. (D–K) Right nasal cavity. (A–C) 9 months, dde13; (D–F) 10 months, dde14; (G–I) Hypertrophied longitudinal folds. Newborn, scoce1; (J–L) juvenile, scomu4. Walls indicate orientation. Vertical view. 1, Nasal plug; 2, Incisive recess; 3, Nasal folds; 4, Nasal septum: bony part. 5, Choanae; 6, Caudal wall; 7, Rostral wall; 8, Right lateral wall; 9, Left lateral wall; 10, Median wall.
Figure 7.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the caudal to the top. MR coronal images (C,D) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and the caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted Spin echo (SE) sagittal plane, (D) T2-weighted Fast Recovery Fast Spin Echo (FrFSE) sagittal plane. (C,D) T1-weighted SE coronal plane. (C) Level 1. (D) Level 2. 1.5 months, dde1. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 5, Nasal septum: membranous part; 6, Nasal septum: bony part; 7. Nasal cavity: respiratory part.
Figure 7.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the caudal to the top. MR coronal images (C,D) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and the caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted Spin echo (SE) sagittal plane, (D) T2-weighted Fast Recovery Fast Spin Echo (FrFSE) sagittal plane. (C,D) T1-weighted SE coronal plane. (C) Level 1. (D) Level 2. 1.5 months, dde1. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 5, Nasal septum: membranous part; 6, Nasal septum: bony part; 7. Nasal cavity: respiratory part.
Figure 8.
MRI of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the dorsal to the top. MR coronal images (C,H) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and the caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane, (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C,E,G) T1-weighted SE coronal plane (D,F,H) T2-weighted FrFSe coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1, (E,F) Level 2, (G,H) Level 3. 4 months, dde3. 1. Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Nasal cavity: vestibule (left and right diverticula); 5, Nasal plugs; 6, Nasal septum: membranous part; 7, Nasal septum: bony part; 8, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 9, Choanae: 10, Nasal bone; 11, Frontal bone; 12, Presphenoid bone; 13, Basisphenoid bone; 14, Pterygoid bone; 15, Incisive bone (premaxilla); 16, Maxillary bone; 17, Vomer bone; 18, Ethmoidal mesenchyme.
Figure 8.
MRI of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the dorsal to the top. MR coronal images (C,H) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and the caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane, (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C,E,G) T1-weighted SE coronal plane (D,F,H) T2-weighted FrFSe coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1, (E,F) Level 2, (G,H) Level 3. 4 months, dde3. 1. Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Nasal cavity: vestibule (left and right diverticula); 5, Nasal plugs; 6, Nasal septum: membranous part; 7, Nasal septum: bony part; 8, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 9, Choanae: 10, Nasal bone; 11, Frontal bone; 12, Presphenoid bone; 13, Basisphenoid bone; 14, Pterygoid bone; 15, Incisive bone (premaxilla); 16, Maxillary bone; 17, Vomer bone; 18, Ethmoidal mesenchyme.
Figure 9.
Images of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that rostral is to the left and dorsal to the top. MRI coronal images (C–H) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and the caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane. (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C,E,G) T1-weighted SE coronal plane, (D,F,H) T2-weighted FrFSE coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1. (E,F) Level 2. (G,H) Level 3. 4.5 months, scop1. 1, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 2, Nasal plug; 3, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 4, Nasal septum: membranous part; 5, Nasal septum: bony part; 6, Choanae; 7, Melon; 8, Incisive bone; 9, Maxillary bone; 10, Vomer bone.
Figure 9.
Images of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that rostral is to the left and dorsal to the top. MRI coronal images (C–H) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and the caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane. (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C,E,G) T1-weighted SE coronal plane, (D,F,H) T2-weighted FrFSE coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1. (E,F) Level 2. (G,H) Level 3. 4.5 months, scop1. 1, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 2, Nasal plug; 3, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 4, Nasal septum: membranous part; 5, Nasal septum: bony part; 6, Choanae; 7, Melon; 8, Incisive bone; 9, Maxillary bone; 10, Vomer bone.
Figure 10.
Images of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the dorsal to the top. MR coronal images (C,D) are oriented so that rostral is to the bottom and caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane, (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C) T1-weighted SE coronal plane. (D) T2-weighted FrFSE coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1. 5 months, gma1. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Melon; 5, Nasal septum: membranous part; 6, Nasal plugs; 7, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 8, Vestibule: right diverticulum; 9, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 10, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 11, Nasal bone; 12, Frontal bone; 13, Presphenoid bone; 14, Ethmoid bone: perpendicular lamina; 15, Incisive bone; 16, Maxillary bone; 17, Vomer bone, 18, Pterygoid bone; 19, Vestibular folds.
Figure 10.
Images of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the dorsal to the top. MR coronal images (C,D) are oriented so that rostral is to the bottom and caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane, (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C) T1-weighted SE coronal plane. (D) T2-weighted FrFSE coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1. 5 months, gma1. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Melon; 5, Nasal septum: membranous part; 6, Nasal plugs; 7, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 8, Vestibule: right diverticulum; 9, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 10, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 11, Nasal bone; 12, Frontal bone; 13, Presphenoid bone; 14, Ethmoid bone: perpendicular lamina; 15, Incisive bone; 16, Maxillary bone; 17, Vomer bone, 18, Pterygoid bone; 19, Vestibular folds.
Figure 11.
Images of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the dorsal to the top. MR coronal images (C,H) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane, (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C,E,G) T1-weighted SE coronal plane. (D,F,H) T2-weighted FrFSE coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1. (E,F) Level 2. (G,H) Level 3. 6 months, dde7. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Melon; 5, Nasal septum: membranous part; 6, Nasal plugs; 7, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 8, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 9, Nasal cavity: incisive recess; 10, Choanae; 11, Nasal septum: bony part; 12, Mesorostral cartilage.
Figure 11.
Images of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the dorsal to the top. MR coronal images (C,H) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane, (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C,E,G) T1-weighted SE coronal plane. (D,F,H) T2-weighted FrFSE coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1. (E,F) Level 2. (G,H) Level 3. 6 months, dde7. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Melon; 5, Nasal septum: membranous part; 6, Nasal plugs; 7, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 8, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 9, Nasal cavity: incisive recess; 10, Choanae; 11, Nasal septum: bony part; 12, Mesorostral cartilage.
Figure 12.
Images of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the dorsal to the top. MR coronal images (C–H) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane, (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C,E,G) T1-weighted SE coronal plane. (D,F,H) T2-weighted FrFSE coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1. (E,F) Level 2. (G,H) Level 3. 7.5 months, dde10. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Melon; 5, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 6, Nasal plugs; 7, Nasal septum: membranous part; 8, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 9, Nasal septum: bony part; 10, Choanae; 11, Incisive bone; 12, Maxillary bone; 13, Presphenoid bone; 14. Vomer; 15, Ethmoid bone: perpendicular lamina; 16, Frontal bone; 17, Nasal bone.
Figure 12.
Images of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the dorsal to the top. MR coronal images (C–H) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane, (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C,E,G) T1-weighted SE coronal plane. (D,F,H) T2-weighted FrFSE coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1. (E,F) Level 2. (G,H) Level 3. 7.5 months, dde10. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Melon; 5, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 6, Nasal plugs; 7, Nasal septum: membranous part; 8, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 9, Nasal septum: bony part; 10, Choanae; 11, Incisive bone; 12, Maxillary bone; 13, Presphenoid bone; 14. Vomer; 15, Ethmoid bone: perpendicular lamina; 16, Frontal bone; 17, Nasal bone.
Figure 13.
Images of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the dorsal to the top. MR coronal images (C,H) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane, (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C,E,G) T1-weighted SE coronal plane. (D,F,H) T2-weighted FrFSE coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1. (E,F) Level 2. (G,H) Level 3. 10 months, dde14. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Melon; 5, Nasal septum: bony part; 6, Nasal plug; 7, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 8, Vestibule: nasal diverticulum; 9, Vestibule: nasal accessory diverticulum (nasofrontal sac); 10, Caudal vestibular muscles; 11, Rostral vestibular muscles; 12, Nasal plug muscles; 13, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 14, Nasal cavity: incisive recess; 15, Nasal bone; 16, Frontal bone; 17, Ethmoid bone: perpendicular lamina; 18, Incisive bone; 19, Maxillary bone; 20, Presphenoid bone; 21, Basisphenoid bone; 22, Pterygoid bone; 23, Vomer bone; 24, Mesorostral cartilage; 25, Choanae; 26, Pharyngeal muscles.
Figure 13.
Images of the external nose and nasal cavity. MR sagittal images (A,B) are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the dorsal to the top. MR coronal images (C,H) are oriented so that the rostral is to the bottom and caudal to the top. (A) T1-weighted SE sagittal plane, (B) T2-weighted FrFSE sagittal plane. (C,E,G) T1-weighted SE coronal plane. (D,F,H) T2-weighted FrFSE coronal plane. (C,D) Level 1. (E,F) Level 2. (G,H) Level 3. 10 months, dde14. 1, Rima naris; 2, Upper lip; 3, Lower lip; 4, Melon; 5, Nasal septum: bony part; 6, Nasal plug; 7, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 8, Vestibule: nasal diverticulum; 9, Vestibule: nasal accessory diverticulum (nasofrontal sac); 10, Caudal vestibular muscles; 11, Rostral vestibular muscles; 12, Nasal plug muscles; 13, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 14, Nasal cavity: incisive recess; 15, Nasal bone; 16, Frontal bone; 17, Ethmoid bone: perpendicular lamina; 18, Incisive bone; 19, Maxillary bone; 20, Presphenoid bone; 21, Basisphenoid bone; 22, Pterygoid bone; 23, Vomer bone; 24, Mesorostral cartilage; 25, Choanae; 26, Pharyngeal muscles.
![Animals 11 00441 g013]()
Figure 14.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and PET/SPEC/CT. 3.5 months, dde2. (A) Dorsal view. (B) Caudal view. (C) Dorsal view. (D) Ventral view. 1, Incisive bone; 2, Maxillary bone; 3, Nasal face of maxillary bone; 4, Vomer bone: groove; 5, Vomer bone: ventral crest; 6, Presphenoid bone: body; 7, Presphenoid bone: wings; 8, Basisphenoid bone: body; 9, Basisphenoid bone: wings; 10, Ethmoid bone; 11, Maxillary bone (nasal face): ossification nuclei; 12, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 13, Pterygoid bone; 14 Palatine bone; 15, Choanae; 16, Fontanelles.
Figure 14.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and PET/SPEC/CT. 3.5 months, dde2. (A) Dorsal view. (B) Caudal view. (C) Dorsal view. (D) Ventral view. 1, Incisive bone; 2, Maxillary bone; 3, Nasal face of maxillary bone; 4, Vomer bone: groove; 5, Vomer bone: ventral crest; 6, Presphenoid bone: body; 7, Presphenoid bone: wings; 8, Basisphenoid bone: body; 9, Basisphenoid bone: wings; 10, Ethmoid bone; 11, Maxillary bone (nasal face): ossification nuclei; 12, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 13, Pterygoid bone; 14 Palatine bone; 15, Choanae; 16, Fontanelles.
Figure 15.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and PET/SPEC/CT. 4.5 months, scop1. (A) Rostral view. (B) Caudal view. 1, Incisive bone; 2, Incisive bone: nasal process; 3, Maxillary bone: external face; 4, Maxillary bone: nasal face; 5, Frontal bone: external face; 6, Frontal bone: nasal face; 7, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 8, Temporal bone; 9, Nasal bone; 10, Basisphenoid bone: body; 11, Basisphenoid bone: wings; 12, Presphenoid bone: body; 13, Presphenoid bone: wings; 14, Ethmoid bone; 15, Vomer bone: groove; 16, Fontanelles; 17, Maxilloincisive fissure (bony naris opening).
Figure 15.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and PET/SPEC/CT. 4.5 months, scop1. (A) Rostral view. (B) Caudal view. 1, Incisive bone; 2, Incisive bone: nasal process; 3, Maxillary bone: external face; 4, Maxillary bone: nasal face; 5, Frontal bone: external face; 6, Frontal bone: nasal face; 7, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 8, Temporal bone; 9, Nasal bone; 10, Basisphenoid bone: body; 11, Basisphenoid bone: wings; 12, Presphenoid bone: body; 13, Presphenoid bone: wings; 14, Ethmoid bone; 15, Vomer bone: groove; 16, Fontanelles; 17, Maxilloincisive fissure (bony naris opening).
Figure 16.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and PET/SPEC/CT. 5.5 months, dde5. (A) Caudal view. (B) Ventrocaudal view. 1, Maxillary bone: nasal face; 2, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 3, Frontal bone: wall projections; 4, Vomer bone: groove; 5, Vomer: ventral crest; 6, Presphenoid bone: body; 7, Presphenoid bone: wings; 8, Ethmoid bone: crista galli; 9, Palatine bone; 10, Pterygoid bone; 11, Fontanelles; 12, Maxilloincisive fissure (bony naris opening).
Figure 16.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and PET/SPEC/CT. 5.5 months, dde5. (A) Caudal view. (B) Ventrocaudal view. 1, Maxillary bone: nasal face; 2, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 3, Frontal bone: wall projections; 4, Vomer bone: groove; 5, Vomer: ventral crest; 6, Presphenoid bone: body; 7, Presphenoid bone: wings; 8, Ethmoid bone: crista galli; 9, Palatine bone; 10, Pterygoid bone; 11, Fontanelles; 12, Maxilloincisive fissure (bony naris opening).
Figure 17.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and PET/SPEC/CT. 5.8 months, dde6. (A) Dorsal view. (B) Caudal view. 1, Incisive bone: external face; 2, Maxillary bone: external nasal face; 3, Maxillary bone: nasal face; 4, Nasal bone; 5, Frontal bone: external face; 6, Frontal bone: nasal faces; 7, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 8, Frontal bone: wall projections; 9, Vomer bone: groove; 10, Presphenoid bone: body; 11, Presphenoid bone: wings; 12, Ethmoid bone; 12, Fontanelles; 13, Maxilloincisive fissure (bony naris opening).
Figure 17.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and PET/SPEC/CT. 5.8 months, dde6. (A) Dorsal view. (B) Caudal view. 1, Incisive bone: external face; 2, Maxillary bone: external nasal face; 3, Maxillary bone: nasal face; 4, Nasal bone; 5, Frontal bone: external face; 6, Frontal bone: nasal faces; 7, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 8, Frontal bone: wall projections; 9, Vomer bone: groove; 10, Presphenoid bone: body; 11, Presphenoid bone: wings; 12, Ethmoid bone; 12, Fontanelles; 13, Maxilloincisive fissure (bony naris opening).
Figure 18.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and CT. 9 months, dde13. (A) Dorsal view. (B) Caudal view. 1, Incisive bone; 2, Maxillary bone: external nasal face; 3, Pterygoid bone; 4, Frontal bone: external face; 5, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 6, Frontal bone: wall projections; 7, Vomer bone: groove; 8, Basisphenoid bone; 9, Presphenoid bone; 10, Ethmoid bone: crista galli; 11, Fontanelles; 12, Maxilloincisive fissure (bony naris opening); 13, Nasal cavities.
Figure 18.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and CT. 9 months, dde13. (A) Dorsal view. (B) Caudal view. 1, Incisive bone; 2, Maxillary bone: external nasal face; 3, Pterygoid bone; 4, Frontal bone: external face; 5, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 6, Frontal bone: wall projections; 7, Vomer bone: groove; 8, Basisphenoid bone; 9, Presphenoid bone; 10, Ethmoid bone: crista galli; 11, Fontanelles; 12, Maxilloincisive fissure (bony naris opening); 13, Nasal cavities.
Figure 19.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and CT. 10 months, dde14. (A) Caudal view. (B) Ventrocaudal view. 1, Maxillary bone: nasal face (rostral nasal wall); 2, Maxillary bone: lateral nasal projections; 3, Ethmoid bone; 4, Ethmoid bone: ossification area (lamina cribosa); 5, Presphenoid bone: body; 6, Presphenoid bone: wings; 7, Basisphenoid bone: body; 8, Basisphenoid bone: wings; 9, Frontal bone: external face; 10, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 11, Vomer bone: groove; 12, Vomer bone: wings; 13, Vomer bone: ventral crest; 14, Interparietal bone; 15, Basisphenoid bone: pterygoid crest; 16, Palatine bone; 17, Pterygoid bone; 18, Choanae; 19, Fontanelles.
Figure 19.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and CT. 10 months, dde14. (A) Caudal view. (B) Ventrocaudal view. 1, Maxillary bone: nasal face (rostral nasal wall); 2, Maxillary bone: lateral nasal projections; 3, Ethmoid bone; 4, Ethmoid bone: ossification area (lamina cribosa); 5, Presphenoid bone: body; 6, Presphenoid bone: wings; 7, Basisphenoid bone: body; 8, Basisphenoid bone: wings; 9, Frontal bone: external face; 10, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 11, Vomer bone: groove; 12, Vomer bone: wings; 13, Vomer bone: ventral crest; 14, Interparietal bone; 15, Basisphenoid bone: pterygoid crest; 16, Palatine bone; 17, Pterygoid bone; 18, Choanae; 19, Fontanelles.
Figure 20.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and CT. newborn, scomu1. (A) Dorsal view. (B) Frontal view. (C,D) Caudal view. 1, Incisive bone; 2, Maxillary bone: external face; 3, Maxillary bone: nasal face; 4, Ethmoid bone: ossification nuclei (lamina cribosa); 5, Frontal bone: external face; 6, Frontal bone: nasal face; 7, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 8, Nasal bone; 9, Interparietal bone; 10, Presphenoid bone: body; 11, Presphenoid bone: wings; 12, Ethmoid bone: crista galli; 13, Ethmoid bone: lamina perpendicular; 14, Fontanelles; 15, Maxilloincisive fissure (bony naris opening); 16, Left nasal cavity; 16, Right nasal cavity.
Figure 20.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and CT. newborn, scomu1. (A) Dorsal view. (B) Frontal view. (C,D) Caudal view. 1, Incisive bone; 2, Maxillary bone: external face; 3, Maxillary bone: nasal face; 4, Ethmoid bone: ossification nuclei (lamina cribosa); 5, Frontal bone: external face; 6, Frontal bone: nasal face; 7, Frontal bone: cerebral face; 8, Nasal bone; 9, Interparietal bone; 10, Presphenoid bone: body; 11, Presphenoid bone: wings; 12, Ethmoid bone: crista galli; 13, Ethmoid bone: lamina perpendicular; 14, Fontanelles; 15, Maxilloincisive fissure (bony naris opening); 16, Left nasal cavity; 16, Right nasal cavity.
Figure 21.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and CT. newborn, scomu1. (A) Level sections. Dorsal view; (B) Level 1 (L1), Rostral view; (C) Level 2 (L2), Caudal view; (D) Level 3 (L3), Ventrocaudal view. 1, Incisive bone; 2, Maxillary bone; 3, Frontal bone; 4, Ethmoid bone; 5, Ethmoid bone: perpendicular lamina; 6, Ethmoidal fossa: lamina cribosa; 7, Vomer bone: ventral crest; 8, Vomer bone: wings; 9, Presphenoid bone: wings; 10, Palatine bone; 11, Pterygoid bone; 12, Mandibles; 13, Basisphenoid bone: body; 14, Basisphenoid bone: wings; 15, Basisphenoid bone: pterygoid crest.
Figure 21.
3D reconstruction images of bony nasal cavity using AMIRA and CT. newborn, scomu1. (A) Level sections. Dorsal view; (B) Level 1 (L1), Rostral view; (C) Level 2 (L2), Caudal view; (D) Level 3 (L3), Ventrocaudal view. 1, Incisive bone; 2, Maxillary bone; 3, Frontal bone; 4, Ethmoid bone; 5, Ethmoid bone: perpendicular lamina; 6, Ethmoidal fossa: lamina cribosa; 7, Vomer bone: ventral crest; 8, Vomer bone: wings; 9, Presphenoid bone: wings; 10, Palatine bone; 11, Pterygoid bone; 12, Mandibles; 13, Basisphenoid bone: body; 14, Basisphenoid bone: wings; 15, Basisphenoid bone: pterygoid crest.
Figure 22.
Amira 3D reconstructions of nasal cavity spaces after injecting silicone. Hiperattenuated CT images and air spaces were used to obtain the internal endocast. (A) Right rostral aspect. 3.5 months, dde2. (B) Right lateral aspect. 4.5 months, scop1. (C) Left rostral aspect. 5 months, gma1. (D) Left lateral aspect. 5.8 months, dde6. (E) Left lateral aspect. 10 months, dde14. (F) Left rostral aspect. Adult, scomu5. 1, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 2, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 3, Vestibule: right diverticulum; 4, Vestibule: left accessory diverticulum; 5, Nasal cavity: right respiratory part; 6, Nasal cavity: left respiratory part; 7, Nasal cavity: right incisive recess; 8, Nasal cavity: left incisive recess; 9, Choanae.
Figure 22.
Amira 3D reconstructions of nasal cavity spaces after injecting silicone. Hiperattenuated CT images and air spaces were used to obtain the internal endocast. (A) Right rostral aspect. 3.5 months, dde2. (B) Right lateral aspect. 4.5 months, scop1. (C) Left rostral aspect. 5 months, gma1. (D) Left lateral aspect. 5.8 months, dde6. (E) Left lateral aspect. 10 months, dde14. (F) Left rostral aspect. Adult, scomu5. 1, Nasal cavity: vestibule; 2, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 3, Vestibule: right diverticulum; 4, Vestibule: left accessory diverticulum; 5, Nasal cavity: right respiratory part; 6, Nasal cavity: left respiratory part; 7, Nasal cavity: right incisive recess; 8, Nasal cavity: left incisive recess; 9, Choanae.
Figure 23.
(A,B) Sagittal sections of nasal cavity. Sagittal sections images are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the caudal to the right. (A) Level sections (L1–L6), Fresh section, juvenile, scomu3. (B) Fixed section, adult, scomu6. 1, Nasal cavity: vestibule (line) and (arrow) accessory nasal diverticulum; 2, Upper lip and vestibular fold muscles; 3, Vestibular fold; 4, Nasal plug; 5, Nasal plug and lower lip muscles; 6, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 7, Nasal cavity: incisive recess; 8, Choanae; 9, Aditus laryngis; 10, Pterygopalatine recess: pharyngeal recess of pterygoid and palatine bones; 11, Palatopharyngeal muscles (sectioned); 12, Melon; 13, Nasal bone; 14, Frontal bone; 15, Ethmoid bone; 16, Presphenoid bone; 17, Basisphenoid bone; 18, Incisive bone; 19, Maxillary bone; 20, Mesorostral cartilage; 21, Palatine bone; 22, Pterygoid bone; 23, Vomer bone; 24, Interparietal bone; 25, Hypophysis; 26, Oral cavity; 27, Tongue; 28, “Monkey or phonic lips”.
Figure 23.
(A,B) Sagittal sections of nasal cavity. Sagittal sections images are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the caudal to the right. (A) Level sections (L1–L6), Fresh section, juvenile, scomu3. (B) Fixed section, adult, scomu6. 1, Nasal cavity: vestibule (line) and (arrow) accessory nasal diverticulum; 2, Upper lip and vestibular fold muscles; 3, Vestibular fold; 4, Nasal plug; 5, Nasal plug and lower lip muscles; 6, Nasal cavity: respiratory part; 7, Nasal cavity: incisive recess; 8, Choanae; 9, Aditus laryngis; 10, Pterygopalatine recess: pharyngeal recess of pterygoid and palatine bones; 11, Palatopharyngeal muscles (sectioned); 12, Melon; 13, Nasal bone; 14, Frontal bone; 15, Ethmoid bone; 16, Presphenoid bone; 17, Basisphenoid bone; 18, Incisive bone; 19, Maxillary bone; 20, Mesorostral cartilage; 21, Palatine bone; 22, Pterygoid bone; 23, Vomer bone; 24, Interparietal bone; 25, Hypophysis; 26, Oral cavity; 27, Tongue; 28, “Monkey or phonic lips”.
Figure 24.
Coronal sections of nasal cavity. Coronal sections images are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the caudal to the right. (A,B) Level 1 and 2. Nasal cavity: vestibule. (C–F) Levels 3 to 6. Nasal cavity: respiratory and olfactory parts. Newborn, scomu2. 1, Vestibule: right diverticulum; 2, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 3, Vestibular folds; 4, External nose muscles; 5, Nasal plugs; 6, Nasal plug muscles and connective tissue; 7, Melon; 8, Melon muscles; 9, Nasal cavity: respiratory part (nasal mucosae); 10, Nasal cavity: incisive recess; 11, Choanae; 12, Pharyngeal muscles; 13, Nasal septum: membranous part; 14, Nasal septum: bony part (vomer); 15, Mesorostral cartilage; 16, Frontal bone; 17, Nasal bone; 18, Incisive and maxillary bones; 19, Ethmoid bone.
Figure 24.
Coronal sections of nasal cavity. Coronal sections images are oriented so that the rostral is to the left and the caudal to the right. (A,B) Level 1 and 2. Nasal cavity: vestibule. (C–F) Levels 3 to 6. Nasal cavity: respiratory and olfactory parts. Newborn, scomu2. 1, Vestibule: right diverticulum; 2, Vestibule: left diverticulum; 3, Vestibular folds; 4, External nose muscles; 5, Nasal plugs; 6, Nasal plug muscles and connective tissue; 7, Melon; 8, Melon muscles; 9, Nasal cavity: respiratory part (nasal mucosae); 10, Nasal cavity: incisive recess; 11, Choanae; 12, Pharyngeal muscles; 13, Nasal septum: membranous part; 14, Nasal septum: bony part (vomer); 15, Mesorostral cartilage; 16, Frontal bone; 17, Nasal bone; 18, Incisive and maxillary bones; 19, Ethmoid bone.
Figure 25.
Dissection of nasal cavity. (A,B) Head is oriented so that the rostral side of the head is to the right up corner and caudal is to the left down corner. (C,D) Head is oriented so that the rostral to the left and the caudal to the right. scoce1. (A) Right nasal cavity: vestibule. Clogged right nasal cavity (hyperkeratosis). (B) Nasal cavity: vestibule after removed melon skin. (C,D) Nasal plug opened and closed. Newborn, scoce1. 1, Nasal cavity: right diverticulum; 2, Nasal cavity: left diverticulum; 3, Nasal cavity: accessory diverticulum opened; 4, Accessory diverticulum opened and mucosa partly removed; 5, Right nasal plug clogged; 6, Left nasal plug normal but hypertrophied; 7, Left nasal plug closed; 8, Left nasal plug opened; 9, Right nasal cavity: respiratory part; 10, Left nasal cavity: respiratory part; 11, Nasal septum: bony part (lamina perpendicular ethmoid bone); 12, Frontal bones.
Figure 25.
Dissection of nasal cavity. (A,B) Head is oriented so that the rostral side of the head is to the right up corner and caudal is to the left down corner. (C,D) Head is oriented so that the rostral to the left and the caudal to the right. scoce1. (A) Right nasal cavity: vestibule. Clogged right nasal cavity (hyperkeratosis). (B) Nasal cavity: vestibule after removed melon skin. (C,D) Nasal plug opened and closed. Newborn, scoce1. 1, Nasal cavity: right diverticulum; 2, Nasal cavity: left diverticulum; 3, Nasal cavity: accessory diverticulum opened; 4, Accessory diverticulum opened and mucosa partly removed; 5, Right nasal plug clogged; 6, Left nasal plug normal but hypertrophied; 7, Left nasal plug closed; 8, Left nasal plug opened; 9, Right nasal cavity: respiratory part; 10, Left nasal cavity: respiratory part; 11, Nasal septum: bony part (lamina perpendicular ethmoid bone); 12, Frontal bones.
Figure 26.
Dissection of nasal cavity: vestibule. Detailed images of a nasal diverticulum. Adult, scomu5. (A) Nasal cavity: vestibule. Right diverticulum dilated. Right lateral aspect. (B) Nasal cavity: vestibule. Right diverticulum partially sectioned. Rostral view. (C) Right diverticulum opened. Rostral view. (D) Right diverticulum opened. Caudal view. (E) Right diverticulum border displaced dorsally. Caudal view. 1, Nasal cavity: right diverticulum (dilated); 2, Right diverticulum: mucosa; 3, Nasal plug; 4, Accessory diverticulum.
Figure 26.
Dissection of nasal cavity: vestibule. Detailed images of a nasal diverticulum. Adult, scomu5. (A) Nasal cavity: vestibule. Right diverticulum dilated. Right lateral aspect. (B) Nasal cavity: vestibule. Right diverticulum partially sectioned. Rostral view. (C) Right diverticulum opened. Rostral view. (D) Right diverticulum opened. Caudal view. (E) Right diverticulum border displaced dorsally. Caudal view. 1, Nasal cavity: right diverticulum (dilated); 2, Right diverticulum: mucosa; 3, Nasal plug; 4, Accessory diverticulum.
Figure 27.
Dissection of nasal cavity: vestibule and respiratory part. (A,D) Head is oriented so that the rostral side of the head is to the top and caudal is at the bottom. Adult, scomu7. (A) Right nasal cavity: vestibule open. (B) Right nasal cavity: nasal plug displaced rostrally. (C) Right nasal cavity: nasal plug displaced rostrally and vestibular fold caudally. (D) Right nasal plug has been removed and left is observed closed. 1, Nasal cavity: right diverticulum; 2, Accessory diverticulum opened; 3, Right nasal plug; 4, Vestibular fold; 5, Left nasal cavity: left nasal plug; 6, Right nasal cavity: respiratory part.
Figure 27.
Dissection of nasal cavity: vestibule and respiratory part. (A,D) Head is oriented so that the rostral side of the head is to the top and caudal is at the bottom. Adult, scomu7. (A) Right nasal cavity: vestibule open. (B) Right nasal cavity: nasal plug displaced rostrally. (C) Right nasal cavity: nasal plug displaced rostrally and vestibular fold caudally. (D) Right nasal plug has been removed and left is observed closed. 1, Nasal cavity: right diverticulum; 2, Accessory diverticulum opened; 3, Right nasal plug; 4, Vestibular fold; 5, Left nasal cavity: left nasal plug; 6, Right nasal cavity: respiratory part.
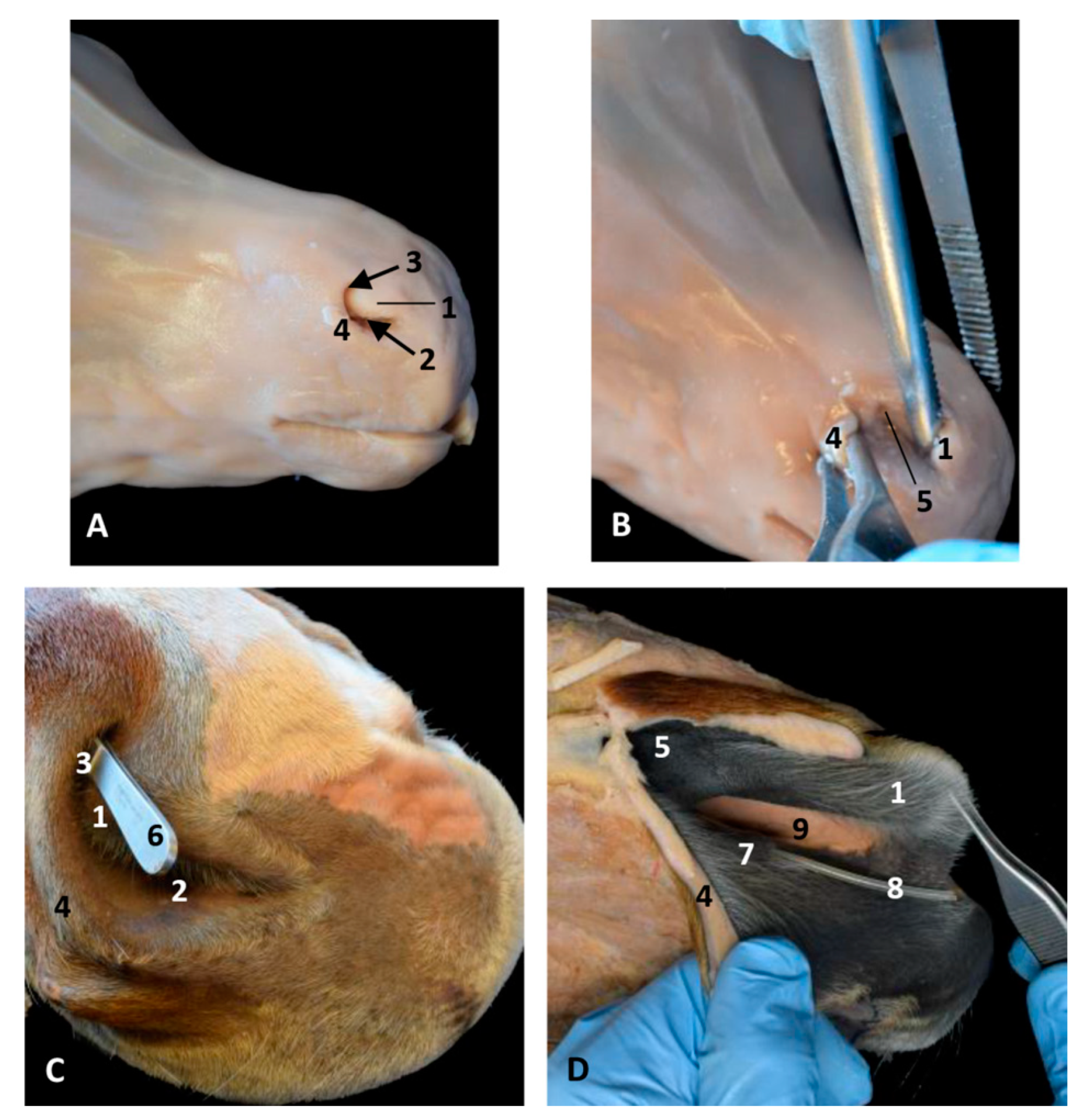
Figure 28.
Nose dissections at right nasal vestibule level in a foal fetus (A,B) and two adult horses. (C,D). (B) Wing of the nostril has been retracted laterally to observe the nasal diverticulum. (C) Forceps are inside the nasal diverticulum. (D) The nose has been dissected to observe pigmentation differences between mucosa of the vestibule and the respiratory part of the nasal cavity. (A–D) Right lateral view. 1, Alar fold; 2, Nostril; 3, False nostril; 4, Wing of the nostril; 5, Nasal diverticulum; 6, Forceps; 7, Nasal vestibule: mucosa; 8, Nasolacrimal orifice (plastic tube); 9, Nasal cavity: respiratory part.
Figure 28.
Nose dissections at right nasal vestibule level in a foal fetus (A,B) and two adult horses. (C,D). (B) Wing of the nostril has been retracted laterally to observe the nasal diverticulum. (C) Forceps are inside the nasal diverticulum. (D) The nose has been dissected to observe pigmentation differences between mucosa of the vestibule and the respiratory part of the nasal cavity. (A–D) Right lateral view. 1, Alar fold; 2, Nostril; 3, False nostril; 4, Wing of the nostril; 5, Nasal diverticulum; 6, Forceps; 7, Nasal vestibule: mucosa; 8, Nasolacrimal orifice (plastic tube); 9, Nasal cavity: respiratory part.
Figure 29.
Histological study of nasal mucosa: vestibule, respiratory and olfactory parts. H-E staining technique. Adult, scomu6. (A) Left diverticulum, 10×. (B) Vestibular fold, 10×. (C) Nasal plug, 10×. (D) Respiratory part, 10×. (E) Olfactory part, 20×. (F) Incisive recess, 20×. 1, Epithelium: stratified squamous keratinized and pigmented; 2, Papillary layer; 3, Connective tissue base; 4, Cartilage; 5, Striated muscular base; 6, Vessels.
Figure 29.
Histological study of nasal mucosa: vestibule, respiratory and olfactory parts. H-E staining technique. Adult, scomu6. (A) Left diverticulum, 10×. (B) Vestibular fold, 10×. (C) Nasal plug, 10×. (D) Respiratory part, 10×. (E) Olfactory part, 20×. (F) Incisive recess, 20×. 1, Epithelium: stratified squamous keratinized and pigmented; 2, Papillary layer; 3, Connective tissue base; 4, Cartilage; 5, Striated muscular base; 6, Vessels.
Figure 30.
Histological study of nasal mucosa: vestibule, respiratory and olfactory parts. H_E stain technique. Adult Ecal4 (A) Nasal vestibule 10×. (B) Alar fold 40×. (C) Respiratory part. 40×. (D) Olfactory part. 20×. 1, Epithelium: stratatified squamous keratinized and pigmented; 2, Papillary stratum; 3, hair; 4, Fat tissue; 5, Connective tissue base; 6, Cartilage; 7, Respiratory epithelium.
Figure 30.
Histological study of nasal mucosa: vestibule, respiratory and olfactory parts. H_E stain technique. Adult Ecal4 (A) Nasal vestibule 10×. (B) Alar fold 40×. (C) Respiratory part. 40×. (D) Olfactory part. 20×. 1, Epithelium: stratatified squamous keratinized and pigmented; 2, Papillary stratum; 3, hair; 4, Fat tissue; 5, Connective tissue base; 6, Cartilage; 7, Respiratory epithelium.
Table 1.
Specimens of dolphin used in this study.
Table 1.
Specimens of dolphin used in this study.
| Study Code | Species, Sex [29,39,40] | Anatomical, Surgical/Imaging Diagnostic and 3D Reconstruction Techniques |
|---|
| dde1 | Delphinus delphis L., male fetus | Endoscopy, MRI |
| dde2 | Delphinus delphis L., male fetus | Endoscopy, MRI, PET/SPEC/CT, AMIRA®, silicone injection |
| dde3 | Delphinus delphis L., female fetus | Endoscopy, MRI |
| scop1 | Stenella coeruleoalba M., female fetus | Endoscopy, MRI, PET/SPECT/CT, AMIRA®, silicone injection |
| gma1 | Globicephala melas T., male fetus | Endoscopy, MRI, PET/SPEC/CT |
| dde4 | Delphinus delphis L., male fetus | Endoscopy |
| dde5 | Delphinus delphis L., female fetus | Endoscopy, MRI, PET/SPEC/CT, AMIRA® |
| dde6 | Delphinus delphis L., female fetus | Endoscopy, PET/SPEC/CT, AMIRA®, silicone injection |
| dde7 | Delphinus delphis L., male fetus | Endoscopy, MRI |
| dde8 | Delphinus delphis L., female fetus | Endoscopy |
| dde9 | Delphinus delphis L., male fetus | Endoscopy, MRI, CT, AMIRA®, silicone injection |
| dde10 | Delphinus delphis L., female fetus | Endoscopy, MRI |
| dde11 | Delphinus delphis L., male fetus | Endoscopy, MRI |
| dde12 | Delphinus delphis L., male fetus | Endoscopy, MRI |
| dde13 | Delphinus delphis L., female fetus | Endoscopy, MRI, CT, AMIRA®, silicone injection |
| dde14 | Delphinus delphis L., female fetus | Endoscopy, MRI, CT, AMIRA®, silicone injection |
| scoce1 | Stenella coeruleoalba M., male newborn | Endoscopy,
Head dissection, Anatomopathological study |
| scomu1 | Stenella coeruleoalba M., female newborn | CT, AMIRA®, silicone injection |
| scomu2 | Stenella coeruleoalba M., male newborn | Head coronal section |
| scomu3 | Stenella coeruleoalba M., male juvenile | Head sagittal section |
| scomu4 | Stenella coeruleoalba M., Male juvenile | Endoscopy |
| scomu5 | Stenella coeruleoalba M., female adult | Head dissection, vascular latex injection |
| scomu6 | Stenella coeruleoalba M., female adult | Head sagittal section, histological analysis |
| scomu7 | Stenella coeruleoalba M., female adult | Head dissection |
| scomu8 | Stenella coeruleoalba M., female adult | CT, AMIRA®, silicone injection |
| ecal1 | Equus caballus L., male, fetus | Head dissection |
| ecal2 | Equus caballus L., adult | Head dissection |
| ecal3 | Equus caballus L., adult | Head section |
| ecal4 | Equus caballus L., adult | Head section |