Effects of Colonization, Geography and Environment on Genetic Divergence in the Intermediate Leaf-Nosed Bat, Hipposideros larvatus
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
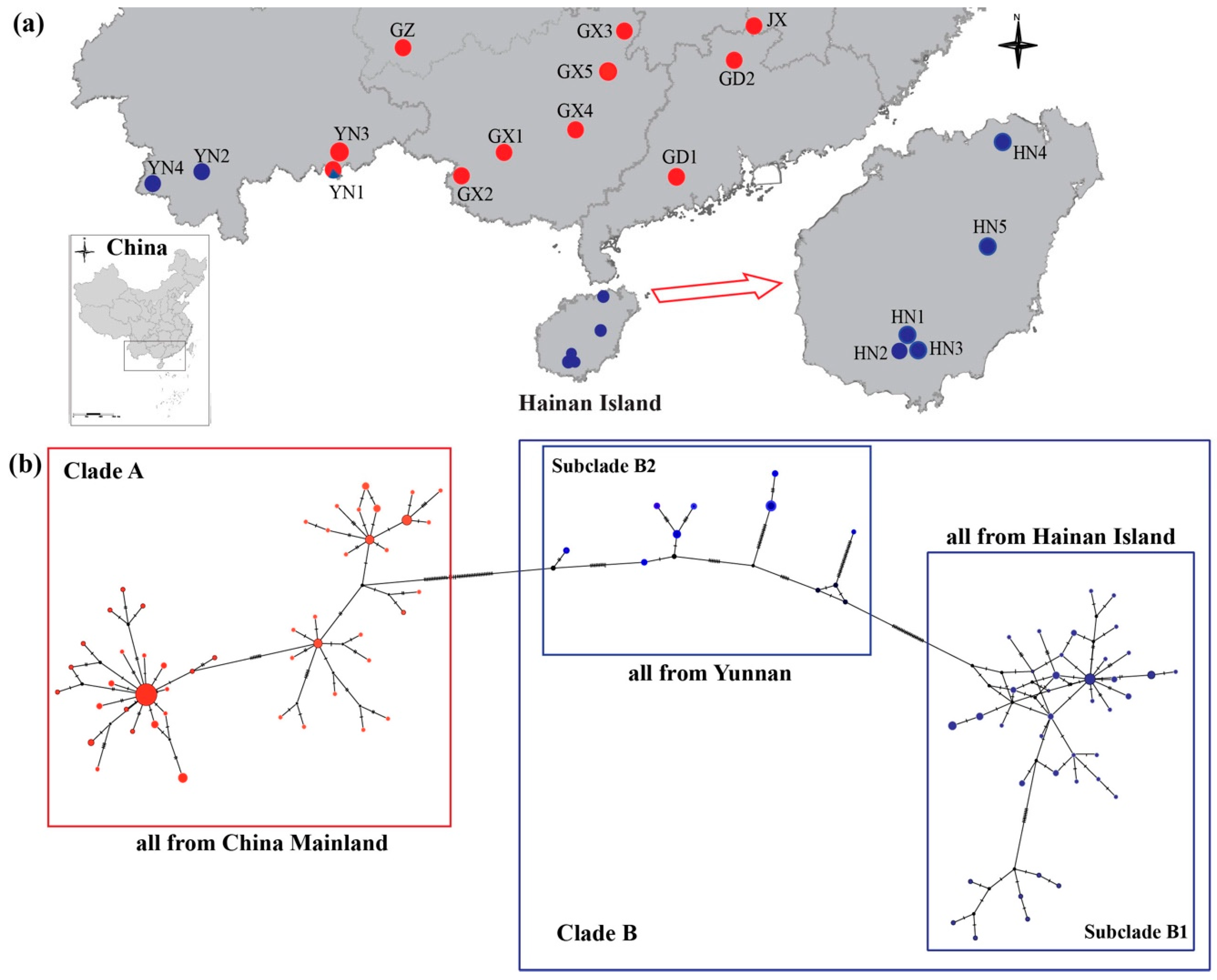
Sampling Collection
3. Genetic Data Collection
3.1. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
3.2. Genetic Analyses
3.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
3.4. Tests for IBD, IBA and IBC
4. Results
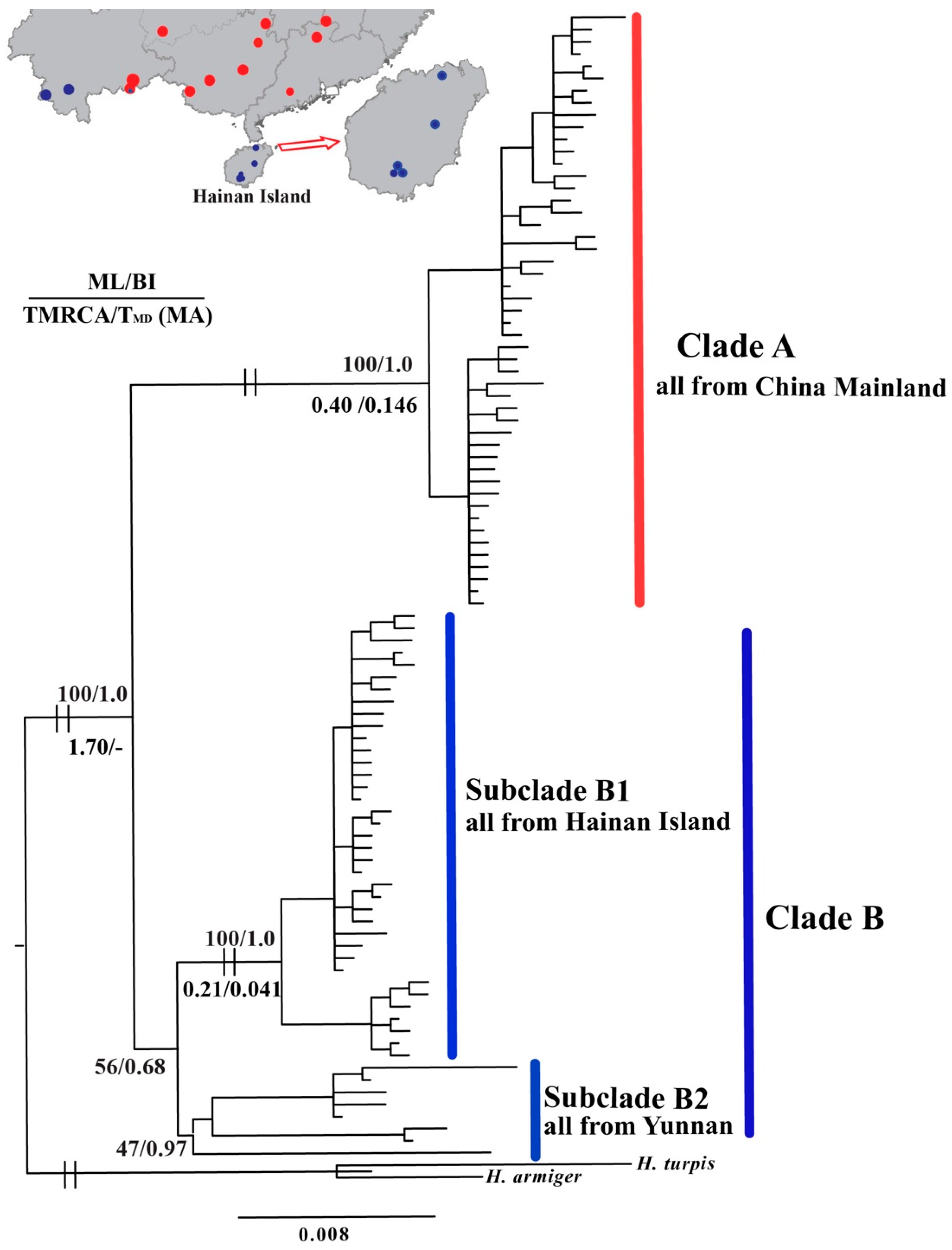
4.1. Mitochondrial Genetic Analyses
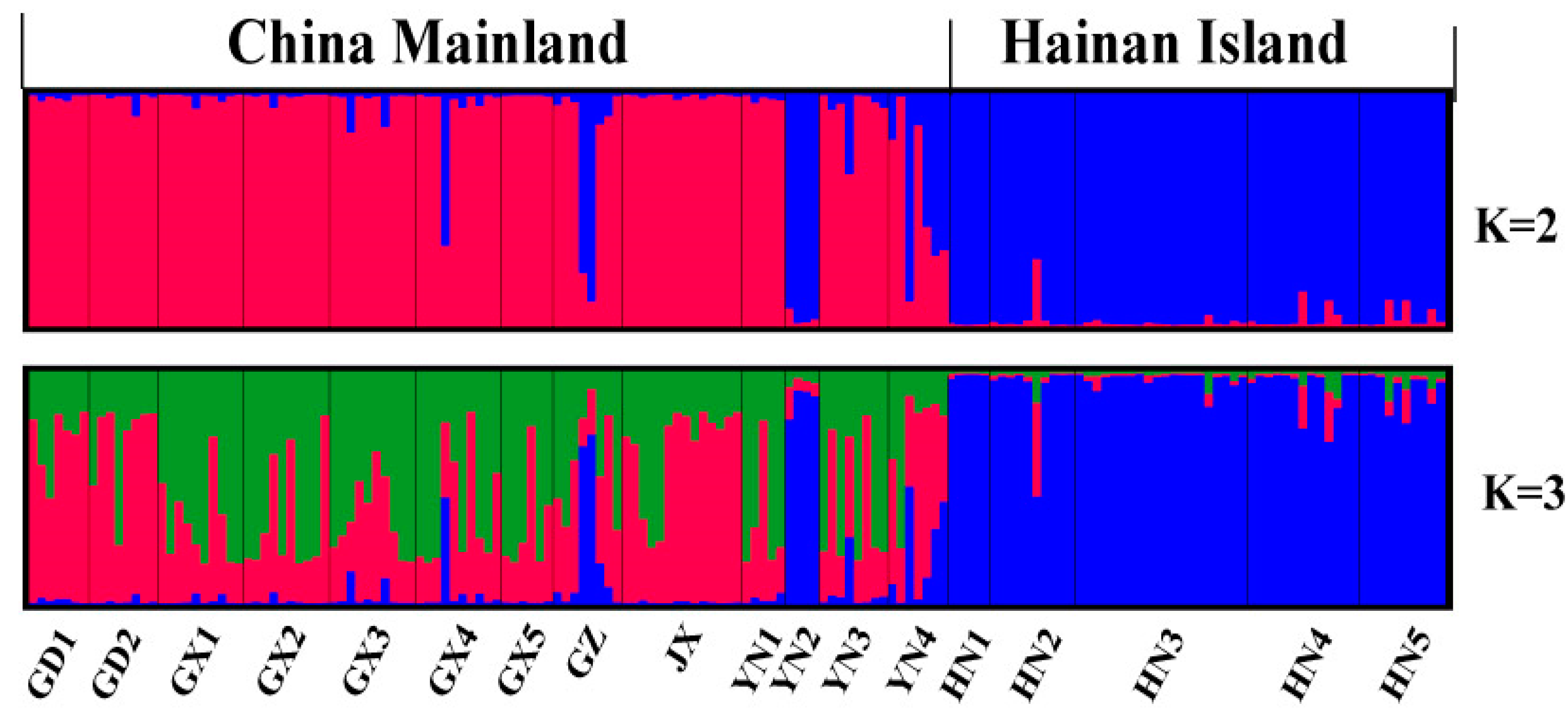
4.2. Microsatellite Genetic Analyses
4.3. Tests for IBD, IBA and IBC
5. Discussion
5.1. Phylogeographic History of H. Larvatus
5.2. Drives of Genetic Variation in H. Larvatus
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orsini, L.; Vanoverbeke, J.; Swillen, I.; Mergeay, J.; De Meester, L. Drivers of population genetic differentiation in the wild: Isolation by dispersal limitation, isolation by adaptation and isolation by colonization. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5983–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgin, L.G.; Illera, J.C.; Jorgensen, T.H.; Dawson, D.A.; Richardson, D.S. Genetic and phenotypic divergence in an island bird: Isolation by distance, by colonization or by adaptation? Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slatkin, M. Isolation by distance in equilibrium and nonequilibrium populations. Evolution 1993, 47, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. Isolation by distance. Genetics 1943, 28, 114–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DeWoody, J.; Trewin, H.; Taylor, G. Genetic and morphological differentiation in Populus nigra L.: Isolation by colonization or isolation by adaptation? Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 2641–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, L.; Mergeay, J.; Vanoverbeke, J.; De Meester, L. The role of selection in driving landscape genomic structure of the waterflea Daphnia magna. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, I.J.; Bradburd, G.S. Isolation by environment. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 5649–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradburd, G.S.; Ralph, P.L.; Coop, G.M. Disentangling the effects of geographic and ecological isolation on genetic differentiation. Evolution 2013, 67, 3258–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.P.; Quintela, M.; Laurila, A. Genetic divergence and isolation by thermal environment in geothermal populations of an aquatic invertebrate. J. Evol. Biol. 2016, 29, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sexton, J.P.; Hangartner, S.B.; Hoffmann, A.A. Genetic isolation by environment or distance: Which pattern of gene flow is most common? Evolution 2014, 68, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onn, C.K.; Brown, R.M. Elucidating the drivers of genetic differentiation in Malaysian torrent frogs (Anura: Ranidae: Amolops): A landscape genomics approach. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 190, 65–78. [Google Scholar]
- De Lafontaine, G.; Ducousso, A.; Lefevre, S.; Magnanou, E.; Petit, R.J. Stronger spatial genetic structure in recolonized areas than in refugia in the European beech. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 4397–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeau, S.; Meirmans, P.G.; Aitken, S.N.; Ritland, K.; Isabel, N. The challenge of separating signatures of local adaptation from those of isolation by distance and colonization history: The case of two white pines. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 8649–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, E. Animal Species and Evolution; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1963; pp. 516–555. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.H.; Wang, B.S.; Zhao, W.; Pan, J.; Mao, J.F.; Wang, X.R. Combining mitochondrial and nuclear genome analyses to dissect the effects of colonization, environment, and geography on population structure in Pinus tabuliformis. Evol. Appl. 2018, 11, 1931–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, N.B.; Cirranello, A.L. Bat Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Database. 2019. Available online: https://batnames.org (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Centeno-Cuadros, A.; Hulva, P.; Romportl, D.; Santoro, S.; Stribna, T.; Shohami, D.; Evin, A.; Tsoar, A.; Benda, P.; Horacek, I.; et al. Habitat use, but not gene flow, is influenced by human activities in two ecotypes of Egyptian fruit bat (Rousettus aegyptiacus). Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 6224–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, K.K.; Dai, W.T.; Jin, L.R.; Sun, K.P.; Feng, J. Evolutionary insights into Rhinolophus episcopus (Chiroptera, Rhinolophidae) in China: Isolation by distance, environment, or sensory system? J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2021, 59, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, P.J.; Harrison, D. Bats of the Indian Subcontinent; Harrison Zoological Museum: Sevenoaks, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, N.B. Order Chiroptera. In Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, 3rd ed.; Wilson, D.E., Reeders, D.M., Eds.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2005; Volume 1, pp. 312–529. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, A.Q.; Csorba, G.; Li, L.F.; Jiang, T.L.; Lu, G.J.; Thong, V.D.; Soisook, P.; Sun, K.P.; Feng, J. Phylogeography of Hipposideros armiger (Chiroptera: Hipposideridae) in the Oriental Region: The contribution of multiple Pleistocene glacial refugia and intrinsic factors to contemporary population genetic structure. J. Biogeogr. 2014, 41, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.Q.; Gong, X.Y.; Dong, K.; Zhou, D.Y.; He, S.Y. Phylogeography of Apis cerana populations on Hainan island and southern mainland China revealed by microsatellite polymorphism and mitochondrial DNA. Apidologie 2017, 48, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Luo, M.X.; Gao, R.H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.Z.; Li, Y.J.; Liao, P.C. Isolation-by-environment as a driver of genetic differentiation among populations of the only broad-leaved evergreen shrub Ammopiptanthus mongolicus in Asian temperate deserts. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger, D.N.; Conrad, O.; Bohner, J.; Kawohl, T.; Kreft, H.; Soria-Auza, R.W.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Linder, H.P.; Kessler, M. Data Descriptor: Climatologies at high resolution for the earth’s land surface areas. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger, D.N.; Conrad, O.; Böhner, J.; Kawohl, T.; Kreft, H.; Soria-Auza, R.W.; Zimmermann, N.E.; Linder, H.P.; Kessler, M. CHELSA climatologies at high resolution for the earth’s land surface areas (Version 1.1). World Data Cent. Clim. DKRZ. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; van Etten, J. Raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling. R Package Version 2.8-4. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster. (accessed on 3 November 2018).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, v. 2.3-5. 2016. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html (accessed on 9 April 2016).
- Irwin, D.M.; Kocher, T.D.; Wilson, A.C. Evolution of the cytochrome-B gene of mammals. J. Mol. Evol. 1991, 32, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocher, T.D.; Thomas, W.K.; Meyer, A.; Edwards, S.V.; Paabo, S.; Villablanca, F.X.; Wilson, A.C. Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals: Amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 6196–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, G.S.; Chapman, A.M. Length and sequence variation in evening bat d-loop mtdna. Genetics 1991, 128, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.P.; Kimball, R.T.; Liu, T.; Wei, X.W.; Jin, L.R.; Jiang, T.L.; Lin, A.Q.; Feng, J. The complex evolutionary history of big-eared horseshoe bats (Rhinolophus macrotis complex): Insights from genetic, morphological and acoustic data. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.T.; Hua, P.Y.; Lin, L.K.; Zhang, S.Y. Characterization of novel microsatellite loci in the great leaf-nosed bat, Hipposideros armiger and cross-amplification in other related species. Conserv. Genet. 2008, 9, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Hua, P.Y.; Zhang, J.P.; Rossiter, S.J.; Zhang, S.Y. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in Pratt’s Leaf-nosed Bat (Hipposideros pratti) and cross-species amplification in closely related taxa. Conserv. Genet. 2008, 9, 1341–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, F. GENEPOP’007: A complete re-implementation of the GENEPOP software for Windows and Linux. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oosterhout, C.; Hutchinson, W.F.; Wills, D.P.M.; Shipley, P. MICRO-CHECKER: Software for identifying and correcting genotyping errors in microsatellite data. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudet, J. FSTAT, a Program to Estimate and Test Gene Diversities and Fixation Indices (Version 2.9.4). 2001. Available online: https://www.scienceopen.com/document?vid=79097bb4-ec3c-47c3-94a1-47085d721e6b (accessed on 8 March 2021).
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: A new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabholz, B.; Glemin, S.; Galtier, N. Strong variations of mitochondrial mutation rate across mammals—The longevity hypothesis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, V.D.; Puechmaille, S.J.; Denzinger, A.; Bates, P.J.J.; Dietz, C.; Csorba, G.; Soisook, P.; Teeling, E.C.; Matsumura, S.; Furey, N.M.; et al. Systematics of the Hipposideros turpis complex and a description of a new subspecies from Vietnam. Mamm. Rev. 2012, 42, 166–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Xie, W.; Heled, J. Bayesian inference of species trees from multilocus data using* BEAST. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Suchard, M.; Xie, W.; Drummond, A. Tracer v. 1.6. 2014. Available online: http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk/Tracer (accessed on 10 March 2015).
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hohna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earl, D.A.; Vonholdt, B.M. STRUCTURE HARVESTER: A website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv. Genet. Resour. 2012, 4, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanno, G.; Regnaut, S.; Goudet, J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: A simulation study. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate—A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiewicz, T.M.; Fine, P.V.A. Evidence for ecological divergence across a mosaic of soil types in an Amazonian tropical tree: Protium subserratum (Burseraceae). Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 2543–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Heckel, G.; Liang, W.; Zhang, Y.Y. Phylogeography of Silver Pheasant (Lophura nycthemera L.) across China: Aggregate effects of refugia, introgression and riverine barriers. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 3376–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.G.; He, G.M.; Zhang, J.P.; Rossiter, S.J.; Zhang, S.Y. Lineage divergence and historical gene flow in the Chinese horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus sinicus). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Flanders, J.R.; Rossiter, S.J.; Miller-Butterworth, C.M.; Zhang, L.B.; Zhang, S.Y.Y. Phylogeography of the Japanese pipistrelle bat, Pipistrellus abramus, in China: The impact of ancient and recent events on population genetic structure. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2010, 99, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jing, C.R.; Liu, H.P. On the glacial and interglacial stages in Quaternary of China. J. Chengdu Univ. Tech. 1999, 26, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Chang, J.; Li, S.H.; Liu, Y.; Liang, W.; Zhou, F.; Yao, C.T.; Zhang, Z.W. Was the exposed continental shelf a long-distance colonization route in the ice age? The Southeast Asia origin of Hainan and Taiwan partridges. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 83, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.X.; Xu, Q.Q.; Shen, Y.P. The relationship between climate change and Quaternary glacial cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Review and speculation. Quat. Int. 2002, 97, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Glaciers and Related Environments in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 462–467. [Google Scholar]
- Mayr, E. Systematics and the Origin of Species, from the Viewpoint of a Zoologist; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Seeholzer, G.F.; Brumfield, R.T. Isolation by distance, not incipient ecological speciation, explains genetic differentiation in an Andean songbird (Aves: Furnariidae: Cranioleuca antisiensis, Line-cheeked Spinetail) despite near threefold body size change across an environmental gradient. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.F.M.; Diniz, J.A.F. Dispersal is more important than climate in structuring turtle communities across different biogeographical realms. J. Biogeogr. 2017, 44, 2109–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussy, C.; Hosken, D.J.; Mathews, F.; Smith, G.C.; Aegerter, J.N.; Bearhop, S. Migration and dispersal patterns of bats and their influence on genetic structure. Mamm. Rev. 2013, 43, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, H.; Armstrong, K.N.; Izawa, M.; Yokoyama, J.; Kawata, M. Genetic and acoustic population structuring in the Okinawa least horseshoe bat: Are intercolony acoustic differences maintained by vertical maternal transmission? Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 4978–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saether, S.A.; Fiske, P.; Kalas, J.A.; Kuresoo, A.; Luigujoe, L.; Piertney, S.B.; Sahlman, T.; Hoglund, J. Inferring local adaptation from Q(ST)-FST comparisons: Neutral genetic and quantitative trait variation in European populations of great snipe. J. Evol. Biol. 2007, 20, 1563–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangartner, S.; Laurila, A.; Rasanen, K. Adaptive divergence in moor frog (Rana Arvalis) populations along an acidification gradient: Inferences from Qst-Fst correlations. Evolution 2012, 66, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geue, J.C.; Vagasi, C.I.; Schweizer, M.; Pap, P.L.; Thomassen, H.A. Environmental selection is a main driver of divergence in house sparrows (Passer domesticus) in Romania and Bulgaria. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 7954–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, G.T.; Bugoni, L. Local adaptation drives population isolation in a tropical seabird. J. Biogeogr. 2018, 45, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, L.; Spanier, K.I.; De Meester, L. Genomic signature of natural and anthropogenic stress in wild populations of the waterflea Daphnia magna: Validation in space, time and experimental evolution. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2160–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, E.; Nason, J.D.; Machado, C.A.; Zheng, L.; Yu, H.; Kjellberg, F. Lack of genetic isolation by distance, similar genetic structuring but different demographic histories in a fig-pollinating wasp mutualism. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 5976–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancillotto, L.; Bosso, L.; Smeraldo, S.; Mori, E.; Mazza, G.; Herkt, M.; Galimberti, A.; Ramazzotti, F.; Russo, D. An African bat in Europe, Plecotus gaisleri: Biogeographic and ecological insights from molecular taxonomy and species distribution models. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 5785–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, A.; Spada, M.; Russo, D.; Mucedda, M.; Agnelli, P.; Crottini, A.; Ferri, E.; Martinoli, A.; Casiraghi, M. Integrated operational taxonomic units (IOTUs) in echolocating bats: A bridge between molecular and traditional taxonomy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Sun, K.P.; Csorba, G.; Zhang, K.K.; Feng, J. Species delimitation and evolutionary reconstruction within an integrative taxonomic framework: A case study on Rhinolophus macrotis complex (Chiroptera: Rhinolophidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 139, 106544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Abbrev. | Locality | N | cytb | CR | nSSR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hap | h | π (%) | Hap | h | π (%) | A | AR | Ho | He | |||
| GD1 | Yangchun, Guangdong Province | 7 | 2 | 0.286 | 0.025 | 4 | 0.714 | 0.242 | 6.83 | 4.972 | 0.643 | 0.811 |
| GD2 | Shaoguan, Guangdong Province | 8 | 2 | 0.429 | 0.038 | 5 | 0.893 | 0.325 | 6.50 | 4.701 | 0.500 | 0.821 |
| GX1 | Congzuo, Guangxi Province | 10 | 5 | 0.800 | 0.135 | 3 | 0.600 | 0.156 | 9 | 5.174 | 0.783 | 0.825 |
| GX2 | Longzhou, Guangxi Province | 10 | 5 | 0.667 | 0.244 | 6 | 0.844 | 0.753 | 8.17 | 5.091 | 0.717 | 0.827 |
| GX3 | Guilin, Guangxi Province | 10 | 7 | 0.867 | 0.17 | 7 | 0.911 | 0.452 | 7.33 | 4.634 | 0.767 | 0.812 |
| GX4 | Laibin, Guangxi Province | 10 | 3 | 0.378 | 0.228 | 4 | 0.711 | 0.683 | 8.5 | 5.271 | 0.800 | 0.860 |
| GX5 | Qiepu, Guangxi Province | 6 | 3 | 0.733 | 0.076 | 3 | 0.733 | 0.184 | 4.83 | 3.977 | 0.556 | 0.720 |
| GZ | Lipu, Guizhou Province | 8 | 2 | 0.250 | 0.088 | 3 | 0.464 | 0.106 | 7 | 4.619 | 0.688 | 0.783 |
| JX | Gaozhou, Jiangxi Province | 14 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 9.67 | 5.139 | 0.845 | 0.822 |
| YN1 | Hekou 1, Yunnan Province | 5 | 4 | 0.900 | 1.649 | 5 | 1.000 | 3.284 | 5.83 | 5.152 | 0.700 | 0.796 |
| YN2 | Simao, Yunnan Province | 4 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 2 | 0.500 | 0.317 | 3.67 | 3.667 | 0.708 | 0.708 |
| YN3 | Hekou 2, Yunnan Province | 8 | 3 | 0.464 | 0.066 | 6 | 0.893 | 0.409 | 8.5 | 5.38 | 0.625 | 0.799 |
| YN4 | Puer, Yunnan Province | 7 | 5 | 0.857 | 0.685 | 5 | 0.857 | 1.271 | 7 | 5.059 | 0.714 | 0.826 |
| HN1 | Baoting 1, Hainan Province | 5 | 3 | 0.700 | 0.105 | 5 | 1.000 | 0.508 | 4.83 | 4.396 | 0.533 | 0.785 |
| HN2 | Baoting 2, Hainan Province | 10 | 4 | 0.733 | 0.749 | 7 | 0.933 | 0.546 | 8.33 | 5.093 | 0.717 | 0.840 |
| HN3 | Baoting 3, Hainan Province | 20 | 9 | 0.753 | 0.119 | 9 | 0.847 | 0.452 | 11 | 5.318 | 0.683 | 0.867 |
| HN4 | Haikou, Hainan Province | 13 | 6 | 0.821 | 0.315 | 8 | 0.885 | 1.249 | 8.5 | 4.667 | 0.679 | 0.809 |
| HN5 | Tuncang, Hainan Province | 10 | 8 | 0.956 | 0.242 | 7 | 0.867 | 1.045 | 8.67 | 5.201 | 0.750 | 0.852 |
| Comparison | r | p |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Mantel Tests | ||
| Geneticssr, geography | 0.544 | 0.001 |
| Geneticssr, climate | 0.419 | 0.001 |
| Geneticmt, geography | 0.415 | 0.002 |
| Geneticmt, climate | 0.445 | 0.001 |
| Geneticssr, geneticmt | 0.518 | 0.001 |
| Partial Mantel Tests | ||
| Geneticssr, geography|climate | 0.449 | 0.001 |
| Geneticssr, climate|geography | 0.254 | 0.008 |
| Geneticmt, geography|climate | 0.284 | 0.021 |
| Geneticmt, climate|geography | 0.330 | 0.001 |
| Geneticssr, geneticmt|geography | 0.383 | 0.001 |
| Geneticssr, geneticmt|climate | 0.408 | 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Jin, L.; Sun, K.; Feng, J. Effects of Colonization, Geography and Environment on Genetic Divergence in the Intermediate Leaf-Nosed Bat, Hipposideros larvatus. Animals 2021, 11, 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030733
Meng X, Liu T, Zhang L, Jin L, Sun K, Feng J. Effects of Colonization, Geography and Environment on Genetic Divergence in the Intermediate Leaf-Nosed Bat, Hipposideros larvatus. Animals. 2021; 11(3):733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030733
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Xiangfeng, Tong Liu, Lin Zhang, Longru Jin, Keping Sun, and Jiang Feng. 2021. "Effects of Colonization, Geography and Environment on Genetic Divergence in the Intermediate Leaf-Nosed Bat, Hipposideros larvatus" Animals 11, no. 3: 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030733
APA StyleMeng, X., Liu, T., Zhang, L., Jin, L., Sun, K., & Feng, J. (2021). Effects of Colonization, Geography and Environment on Genetic Divergence in the Intermediate Leaf-Nosed Bat, Hipposideros larvatus. Animals, 11(3), 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030733





